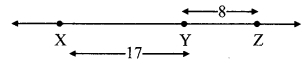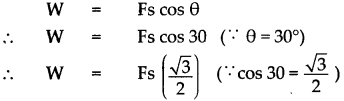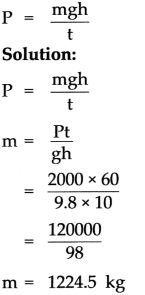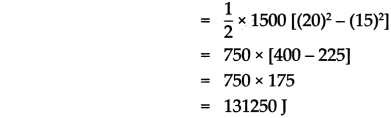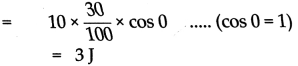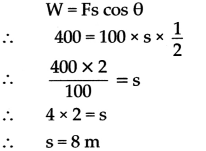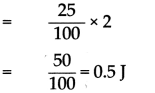Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 9 Science Solutions Chapter 2 Work and Energy Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Std 9 Science Chapter 2 Work and Energy Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Class 9 Science Chapter 2 Work and Energy Question Answer Maharashtra Board
1. Write detailed answers?
a. Explain the difference between potential energy and kinetic energy.
Answer:
| Kinetic Energy |
Potential Energy |
| (i) Kinetic energy is the energy possessed by the body due to its motion. |
(i) Potential energy is the energy possessed by the body because of its shape or position. |
| (ii) K.E = 1/2 mv2 |
(ii) P.E = mgh |
| (iii) e.g., flowing water, such as when falling from a waterfall. |
(iii) e.g., water at the top of a waterfall, before the drop. |
b. Derive the formula for the kinetic energy of an object of mass m, moving with velocity v.
Answer:
Suppose a stationary object of mass ‘m’ moves because of an applied force. Let ‘u’ be its initial velocity (here u = 0). Let the applied force be ‘F’. This generates an acceleration a in the object, and after time T, the velocity of the object becomes equal to ‘v’. The displacement during this time is s. The work done on the object is
W = F x s ……………….. (1)
Using Newton’s 2nd law of motion,
F = ma ……………….. (2)
Using Newton’s 2nd equation of motion
\(s=u t+\frac{1}{2} a t^{2}\)
However, as initial velocity is zero, u = 0


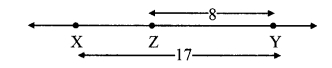
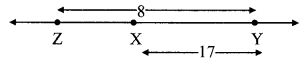
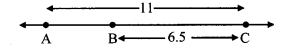
c. Prove that the kinetic energy of a freely falling object on reaching the ground is nothing but the transformation of its initial potential energy.
Answer:
Let us look at the kinetic and potential energies of an object of mass (m), falling freely from height (h), when the object is at different heights.
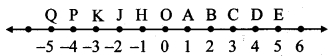
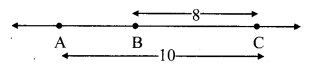
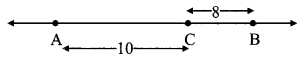
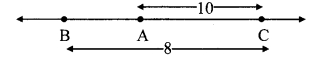
As shown in the figure, the point A is at a height (h) from the ground. Let the point B be at a distance V, vertically below A. Let the point C be on the ground directly below A and B. Let us calculate the energies of the object at A, B and C.
(1) Let the velocity of the object be vB when it reaches point B, having fallen through a distance x.
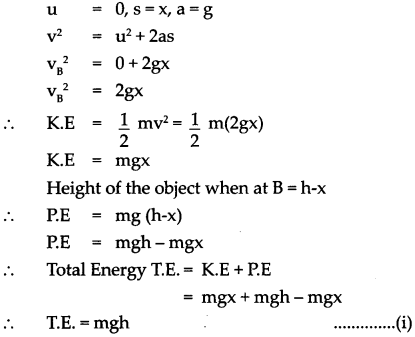
(2) When the object is stationary at A, its initial velocity is u = 0
∴ K.E = 1/2 mass x velocity2
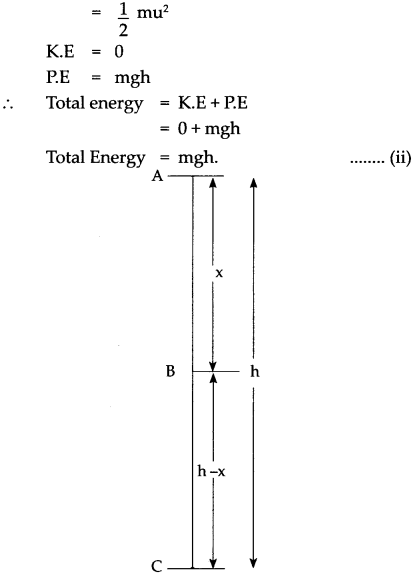

(3) Let the velocity of the object be vc when it reaches the ground, near point C.

From equations (i) and (iii) we see that the total potential energy of the object at its initial position is the same as the kinetic energy at the ground.
d. Determine the amount of work done when an object is displaced at an angle of 300 with respect to the direction of the applied force.
Answer:
When an object is displaced by displacement ‘s’ and by applying force ‘F’ at an ’angle’ 30°. work done can be given as
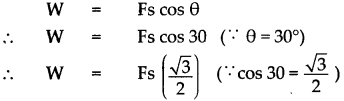
e. If an object has 0 momenta, does it have kinetic energy? Explain your answer.
Answer:
- No, it does not have kinetic energy if it does not have momentum.
- Momentum is the product of mass and velocity. If it is zero, it implies that v = 0 (since mass can never be zero).
- Now K.E = ~ mv2, So if v = 0 then K.E also will be zero.
- Thus, if an object has no momentum then it cannot possess kinetic energy.
f. Why is the work done on an object moving with uniform circular motion zero?
Answer:
- In uniform circular motion, the force acting on an object is along the radius of the circle.
- Its displacement is along the tangent to the circle. Thus, they are perpendicular to each other.
Hence θ = 90° and cos 90 = θ
∴ W = Fs cos θ = 0

2. Choose one or more correct alternatives.
a. For work to be performed, energy must be ….
(i) transferred from one place to another
(ii) concentrated
(iii) transformed from one type to another
(iv) destroyed
b. Joule is the unit of …
(i) force
(ii) work
(iii) power
(iv) energy
c. Which of the forces involved in dragging a heavy object on a smooth, horizontal surface, have the same magnitude?
(i) the horizontal applied force
(ii) gravitational force
(iii) reaction force in vertical direction
(iv) force of friction
d. Power is a measure of the …….
(i) the rapidity with which work is done
(ii) amount of energy required to perform the work
(iii) The slowness with which work is performed
(iv) length of time
e. While dragging or lifting an object, negative work is done by
(i) the applied force
(ii) gravitational force
(iii) frictional force
(iv) reaction force
3. Rewrite the following sentences using a proper alternative.
a. The potential energy of your body is least when you are …..
(i) sitting on a chair
(ii) sitting on the ground
(iii) sleeping on the ground
(iv) standing on the ground
Answer:
(iii) sleeping on the ground
b. The total energy of an object falling freely towards the ground …
(i) decreases
(ii) remains unchanged
(iii) increases
(iv) increases in the beginning and then decreases
Answer:
(iii) increases

c. If we increase the velocity of a car moving on a flat surface to four times its original speed, its potential energy ….
(i) will be twice its original energy
(ii) will not change
(iii) will be 4 times its original energy
(iv) will be 16 times its original energy.
Answer:
(ii) will not change
d. The work done on an object does not depend on ….
(i) displacement
(ii) applied force
(iii) initial velocity of the object
(iv) the angle between force and displacement.
Answer:
(iii) initial velocity of the object
4. Study the following activity and answer the questions.
1. Take two aluminium channels of different lengths.
2. Place the lower ends of the channels on the floor and hold their upper ends at the same height.
3. Now take two balls of the same size and weight and release them from the top end of the channels. They will roll down and cover the same distance.
Questions
1. At the moment of releasing the balls, which energy do the balls have?
2. As the balls roll down which energy is converted into which other form of energy?
3. Why do the balls cover the same distance on rolling down?
4. What is the form of the eventual total energy of the balls?
5. Which law related to energy does the above activity demonstrate? Explain.
Answer:
1. At the moment of releasing the ball they possess Potential energy as they are at a height above the ground.
2. As the balls roll down, the Potential energy is converted into Kinetic energy since they are now in motion.
3. Since they have been released from the same height, they will cover the same distance.
4. The eventual form of the total energy of the balls is “Mechanical Energy” i.e, a combination of Potential energy and Kinetic energy
5. The above activity demonstrates the “Law of Conservation of Energy”
5. Solve the following examples.
a. An electric pump has 2 kW power. How much water will the pump lift every minute to a height of 10 m? (Ans : 1224.5 kg)
Answer:
Given:
Power (P) = 2 kW = 2000 W
Height (h) = 10 m
Time (t) = 1 min = 60 s
Acceleration due to gravity (g) = 9.8 m/s2
To Find:
Mass of water (m)= ?
Formula:
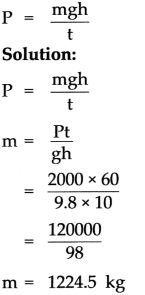
Water lifted by the pump is 1224.5 kg

b. If the energy of a ball falling from a height of 10 metres is reduced by 40%, how high will it rebound? (Ans : 6 m)
Answer:
Given: Initial height (h1) = 10m
Let Initial (P.E1) = 100
Final (P.E2) = 100 – 40
= 60
To Find:
Final height (h2) = ?
Formula:
P.E. = mgh
Solution:

The ball will rebound by 6 m.
d. The velocity of a car increase from 54 km/hr to 72 km/hr. How much is the work done if the mass of the car is 1500 kg? (Ans. : 131250 J)
Answer:

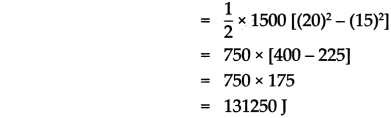
Work done to increase the velocity = 131250 J
e. Ravi applied a force of 10 N and moved a book 30 cm in the direction of the force. How much was the work done by Ravi? (Ans: 3 J)
Answer:
Given:
Force (F) = 10 N
θ = 0°, (Since force and displacement are in same direction)
Displacement (s) = 30 cm = 30/100 m
To Find:
Work (W) = ?
Formula:
W = Fs cos θ
Solution:
W = Fs cos θ
Solution:
The work done by Ravi is 3J
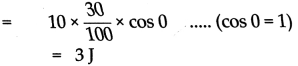
Numericals For Practice

Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Laws of Motion Intext Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What are different types of forces? Give examples.
Answer:
Forces are of two types.
- Contact force e.g.: Mechanical force, frictional force, muscular force
- Non-contact force e.g.: gravitational force, magnetic force, electrostatic force
Question 2.
Monashee wants to displace a wooden block from point A to point B along the surface of a table as shown. She has used force F for the purpose.

(a) Has all the energy she spent been used to produce an acceleration in the block?
(b) Which forces have been overcome using that energy?
Answer:
(a) Only part of the energy applied by Minakshee is used in accelerating the block.
(b) Force of friction has been overcome using the energy.
Question 3.
Mention the type of energy used in the following examples.
(i) Stretched rubber string.
(ii) Fast-moving car.
(iii) The whistling of a cooker due to steam.
(iv) A fan running on electricity.
(v) Drawing out pieces of iron from garbage, using a magnet.
(vi) Breaking of a glass window pane because of a loud noise.
(vii) The drackers exploded in Diwali.
Answer:
(i) Potential energy
(ii) Kinetic energy
(iii) Sound energy
(iv) Electrical energy
(v) Magnetic energy
(vi) Sound energy
(vii) Sound energy, light energy and heat energy

Question 4.
Study the pictures given below and answer the questions:
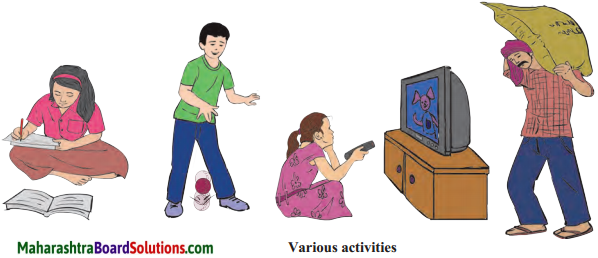
(a) In which of the pictures above has work been done?
(b) From scientific point of view, when do we say that no work was done?
Answer:
(a) Girl studying : No work done
Boy playing with ball: Work is done
Girl watching T.V.: No work done Person lifting sack of grains : Work is done
(b) No work is said to be done when force is applied but there is no displacement.
Question 5.
Make two pendulums of the same length with the help of thread and two nuts. Tie another thread in the horizontal position.
Tie the two pendulums to the horizontal thread in such a way that they will not hit each other while swinging. Now swing one of the pendulums and observe. What do you see?
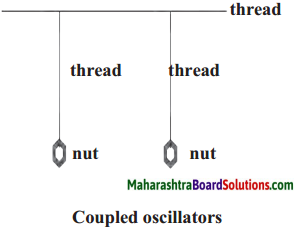
Answer:
You will see that as the speed of oscillation of the pendulum slowly decreases, the second pendulum which was initially stationary, begins to swing. Thus, one pendulum transfers its energy to the other.
Question 6.
Ajay and Atul have been asked to determine the potential energy of a ball of mass m kept on a table as shown in the figure. What answers will they get? Will they be different? What do you conclude from this?
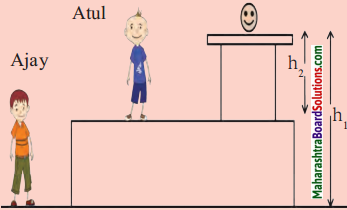
Answer:
- According to Ajay P.E1 = mgh1 and according to Atul P.E2 = mgh2.
- Yes, the answer will be different as the two heights are different.
- Potential energy is relative.

Question 7.
Discuss the directions of force and of displacement in each of the following cases.
(i) Pushing a stalled vehicle.
(ii) Catching the ball which your friend has thrown towards you.
(iii) Tying a stone to one end of a string and swinging it round and round by the other end of the string.
(iv) Walking up and down a staircase; climbing a tree.
(v) Stopping a moving car by applying brakes.
Answer:
(i) Force and displacement are in the same direction.
(ii) Force and displacement are in the opposite direction.
(iii) Force and displacement are perpendicular to each other.
(iv) Force and displacement are in the opposite direction.
(v) Force and displacement are in the opposite direction.
Question 8.
(A) An arrow is released from a stretched bow.
(B) Water kept at a high flows through a pipe into the tap below.
(C) A compressed spring is released.
(a) Which words describe the state of the object in the above examples?
(b) Where did the energy required to cause the motion of the objects come from?
(c) If the obj ects were not brought in those states, would they have moved?
Answer:
(a) Words such as stretched bow, water kept at a height and compressed spring describe the state of the objects.
(b) The energy required for the objects came from its specific state or motion in the form of potential energy.
(c) No, if the objects were not brought in those states, they would have not moved.
Question 9.
Study the activity and answer the following questions.
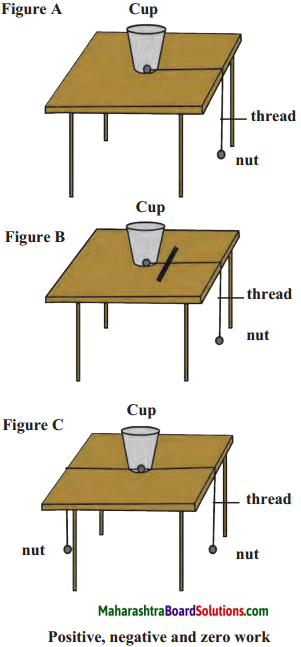
(a) Figure A – Why does the cup get pulled?
(b) Figure B – What is the relation between the displacement of the cup and the force applied through the ruler?
(c) In Figure C-Why doesn’t the cup get displaced?
(d) What is the type of work done in figures A, B and C?
(e) In the three actions above, what is the relationship between the applied force and the displacement?
Answer:
(a) The cup gets pulled as the force of the nut and the displacement of the cup is in the same direction.
(b) The displacement of the cup and the force applied through the ruler is in the opposite direction.
(c) Tire cup does not get displaced as two equal forces are working in opposite directions.
(d) The work done in figure A is positive, figure B is negative and in figure C is zero.
(e) In figure A the applied force and the displacement is in the same direction, in figure B the applied force and the displacement is in the opposite direction and in figure C the applied force and displacement is perpendicular to each other.

Question 10.
From the following activities find out whether work is positive, negative or zero. Give reasons for your answers.
(a) A boy is swimming in a pond.
(b) A coolie is standing with a load on his head.
(c) Stopping a moving car by applying brakes.
(d) Catching the ball which you friend has thrown towards you.
Answer:
(a) A boy is swimming in a pond: The work done is positive because the direction of applied force and displacement are the same.
(b) A coolie is standing with a load on his head: The work done is zero because the applied force does not cause any displacement.
(c) Stopping a moving car by applying brakes: The work done is negative because the fore applied by the brakes acts in a direction opposite to the direction of motion of car.
(d) Catching the ball which you friend has thrown towards you : Negative work because the force required to stop the ball, acts opposite to the displacement of the ball.
Question 11.
(a) Can your father climb stairs as fast as you can?
(b) Will you fill the overhead water tank with the help of a bucket or an electrical motor?
(c) Suppose Raj ashree, Yash and Ranjeet have to reach the top of a small hill. Raj ashree went by car. Yash went cycling while Ranjeet went walking. If all of them choose the same path, who will reach first and who will reach last? (Think before you answer.
Answer:
(a) No, father takes more time to climb stairs.
(b) Overhead water tank can be filled with the help of one electric motor rather than filling it with bucket.
(c) Raj ashree will reach first, followed by Yash and Ranjeet will reach last because car moves faster than a cycle and a person walking.
Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Laws of Motion Additional Important Questions and Answers
1. Choose and write the correct option:
Question 1.
Forces are of …………………… types.
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 5
Answer:
(a) 2

Question 2.
Example of Contact force is ………………….. .
(a) Gravitational Force
(b) Magnetic Force
(c) Electrostatic Force
(d) Muscular Force
Answer:
(d) Muscular Force
Question 3.
Example of Non-contact force is ………………….. .
(a) Mechanical Force
(b) Frictional Force
(c) Muscular Force
(d) Electrostatic Force
Answer:
(d) Electrostatic force
Question 4.
Work is said to be done on a body when a …………………… is applied on object causes displacement of the object.
(a) Direction
(b) Area
(c) Volume
(d) Force
Answer:
(d) force
Question 5.
W = ………………. .
(a) mgh
(b) mdh
(c) mv2
(d) mfe
Answer:
(a) mgh

Question 6.
The energy stored in the dry cell is in of ………………. energy.
(a) Light
(b) Chemical
(c) Solar
(d) Kinetic
Answer:
(b) chemical
Question 7.
The work done is zero if there is no ……………… .
(a) Direction
(b) Displacement
(c) Mass
(d) Angle
Answer:
(b) displacement
Question 8.
Flowing water has ………………. energy.
(a) Potential
(b) Chemical
(c) Solar
(d) Kinetic
Answer:
(d) kinetic
Question 9.
By stretching the rubber strings of a we store ………………. energy in it.
(a) Potential
(b) Chemical
(c) Electric
(d) Kinetic
Answer:
(a) potential

Question 10.
………………. is the unit of force.
(a) Both B and C
(b) Newton
(c) Dyne
(d) Volts
Answer:
(a) Both B and C
Question 11.
For a freely falling body, kinetic energy is ………………. at the ground level.
(a) Maximum
(b) Minimum
(c) Neutral
(d) Reversed
Answer:
(a) Maximum
Question 12.
Energy can neither be ………………. nor ……………… .
(a) Destroyed
(b) Created
(c) Saved
(d) Both A and B
Answer:
(d) Both A and B
Question 13.
Work and …………………… have the same unit.
(a) Energy
(b) Electricity
(c) Force
(d) Both B and C
Answer:
(a) Energy

Question 14.
S.I. unit of energy is ………………….. .
(a) Joule
(b) Ergs
(c) m/s2
(d) Both A and B
Answer:
(a) Joule
Question 15.
Work is the product of ………………….. .
(a) force and distance
(b) displacement and velocity
(c) kinetic and potential energy
(d) force and displacement
Answer:
(d) force and displacement
Question 16.
S.I. unit of work is ………………….. .
(a) dyne
(b) newton-meter or erg
(c) N/m2 or joule
(d) newton-meter or joule
Answer:
(d) newton-meter or joule
Question 17.
…………………… is the capacity to do work.
(a) Energy
(b) Force
(c) Power
(d) Momentum
Answer:
(a) Energy
Question 18.
Kinetic energy of a body (KE) = ………………….. .
(a) mv2
(b) 1/2 mv2
(c) mgh
(d) Fs
Answer:
(b) 1/2 mv2

Question 19.
Potential energy of a body is given by (P.E.) = ………………….. .
(a) Fs
(b) mgh
(c) ma
(d) mv2
Answer:
(b) mgh
Question 20.
1 hp = ………………….. .
(a) 476 watts
(b) 746 watts
(c) 674 watts
(d) 764 watts
Answer:
(b) 746 watts
Question 21.
…………………… is the commercial unit of power.
(a) kilowatt second
(b) dyne
(c) kilowatt
(d) erg
Answer:
(c) kilowatt
Question 22.
1 kWh = …………………… joules.
(a) 3.6 x 103
(b) 3.6 x 106
(c) 6.3 x 106
(d) 6.3 x 103
Answer:
(b) 3.6 x 106

Based on Practicals
Question 23.
The work done by a force is said to be …………………… when the applied force does not produce displacement.
(a) positive
(b) negative
(c) zero
(d) none of these
Answer:
(c) zero
Question 24.
When some unstable atoms break up, they release a tremendous amount of …………………… energy.
(a) chemical
(b) potential
(c) nuclear
(d) mechanical
Answer:
(c) nuclear.
Name the following:
Question 1.
Unit of energy used for commercial purpose.
Answer:
Kilowatt-hour kW h is the unit of energy used for commercial purpose.
Question 2.
Unit used in industry to measure power.
Answer:
Horse power (hp) is the unit used in industry to express power.
Question 3.
SI unit of energy.
Answer:
SI unit of energy is Joule (J).
Question 4.
Two types of mechanical energy.
Answer:
Potential energy and kinetic energy are the two types of mechanical energy.

Question 5.
An example where force acting on an object does not do any work.
Answer:
In a simple pendulum, the gravitational force acting on the bob does not do any work as there is no displacement in the direction of force.
Question 6.
The relationship between 1 joule and 1 erg.
Answer:
1 joule = 107 erg.
Question 7.
Various forms of energy
Answer:
The various forms of energy are mechanical, heat, light, sound, electro-magnetic, chemical, nuclear and solar.
State whether the following statements are true or false:
(1) The potential energy of a body of mass 1 kg kept at height 1 m is 1 J.
(2) Water stored at some height has potential energy.
(3) Unit of power is joule.
(4) Mechanical energy can be converted into electrical energy.
(5) Work is a vector quantity.
(6) Power is a scalar quantity.
(7) The kilowatt hour is the unit of energy.
(8) The CGS unit of energy is dyne.
(9) The SI unit of work is newton.
(10) Kinetic energy has formula – mv2
Answer:
(1) False
(2) True
(3) False
(4) True
(5) False
(6) True
(7) True
(8) False
(9) False
(10) True

Find the odd man out.
Question 1.
Work, Energy, Power, Force.
Answer:
Force.
Question 2.
A stretched spring, A body placed in at some height, A bullet fired from gun.
Answer:
A bullet fired from gun.
Question 3.
A stretched spring, A rock rolling downhill, A bullet fired from gun.
Answer:
A stretched spring.
Write the formula of the following.
Question 1.
Kinetic energy
Answer:
\(\frac{1}{2}\)mv2
Question 2.
Potential energy
Answer:
mgh
Question 3.
Work
Answer:
Fs or Fs cosθ
Question 4.
Force
Answer:
ma

Question 5.
Power
Answer:
\(\frac{w}{1}\)
One line answer.
Question 1.
(i) When is work done said to be zero?
Answer:
Work done is zero when force acting on the body and its displacement are perpendicular to each other.
(ii) Which quantities are measured in ergs?
Answer:
Work and energy are measured in ergs.
(iii) What is the relationship between newton, meter and joule?
Answer:
1 joule = 1 newton x 1 meter
(iv) What is energy?
Answer:
The ability of a body to do work is called energy.
(v) Give 4 examples of energy
Answer:
Solar, wind, mechanical and heat.
(vi) Which device converts electrical energy into heat?
Answer:
Electric water heater (Geyser) converts electrical energy into heat.
(vii) What is the relationship between second, horsepower and joule?
Answer:
1 horse power = \(\frac{746 \text { joules }}{1 \text { second }\)
Question 2.
Find whether work is positive, negative or zero.

(a) Person moving along circle from A to B.
Answer:
Work done is positive as direction of applied force and displacement are the same.
(b) Person completing one circle and returns to position A.
Answer:
Work done is zero because there is no displacement for the person.
(c) Person pushing a car in the forward direction.
Ans,
Work done is positive as the motion of car is in the direction of the applied force.
(d) A car coming downhill even after pushing it in the opposite uphill direction.
Ans,
Work done is negative as the motion of car is in opposite direction of the applied force.
(e) Motion of the clock pendulum.
Answer:
work done is zero as there is no displacement of the pendulum and it comes back to its original position.
Give Scientific reasons:
Question 1.
A moving ball hits a stationary ball and displaces it.
Answer:
- The moving ball has certain energy.
- When it hits the stationary ball, the energy is transferred to the stationary ball, because of which it moves.
- Hence, a moving ball hits a stationary ball and displaces it.

Question 2.
Flowing water from some height can rotate turbine.
Answer:
- Flowing water has certain energy.
- When it hits the turbine, energy is transferred to the turbine, because of which it rotates.
- Hence, flowing water from some height can rotate a turbine.
Question 3.
A stretched rubber band when released regains its original length.
Answer:
- When we stretch a rubber band we give energy to it.
- This energy is stored in it.
- Hence, when we release it, it regains its original length.
Question 4.
Wind can move the blades of a windmill.
Answer:
- Wind has certain energy.
- When it hits the windmill energy is transferred to the windmill because of which it moves.
- Hence, wind can move the blades of a wind mill.
Question 5.
An exploding firecracker lights up as well as makes a sound.
Answer:
- The exploding firecracker converts the chemical energy stored in it into light and sound respectively.
- Here, energy is converted from one type to another.
- Hence, an exploding firecracker lights as well as makes a sound.
Question 6.
Work done on an artificial satellite by gravity is zero while moving around the earth.
Answer:
- When the artificial satellite moves around the earth in a circular orbit, gravitation force acts on it.
- The gravitational force acting on the satellite and its displacement are perpendicular to each other. i.e. 0 = 90°
- For 0 = 90°, work done is zero. [ v cos 90 = 0)
- Hence, work done on an artificial satellite by gravity is zero while moving around the earth.

Difference between :
Question 1.
Work and Power:
Answer:
| Work |
Power |
(i) Work is the product of force and displacement.
(ii) Work is given by the formula : W = Fs
(iii) MKS unit – joule, CGS unit-erg |
(i) Power is the rate of doing work.
(ii) Power is given by the formula : \(\mathrm{P}=\frac{\mathrm{W}}{\mathrm{t}}\)
(iii) MKS unit – joule/sec, CGS unit – erg/sec |
Question 2.
Work and Energy:
Answer:
| Work |
Energy |
(i) It is the product of the magnitude of the force acting on the body and the displacement of the body in the direction of the force.
(ii) It is the effect of energy. |
(i) It is the capacity to do work.
(ii) It is the cause of work. |
Solve the following:
Type – A
Formula:
W = Fs cosθ
If force and displacement are in same direction, then θ = 0°, and cos θ = 1
If force and displacement are in opposite direction, then θ = 180°, and cos θ = -1
If force and displacement are perpendiculars, then θ = 90°, and cos θ = 0
Question 1.
Pravin has applied a force of 100 N on an object, at an angle of 60° to the horizontal. The object gets displaced in the horizontal direction and 400 J work is done. What is the displacement of the object? (cos 600 =12)
To Find:
Displacement (s) = ?
Formula:
W = Fs cos θ
Solution:
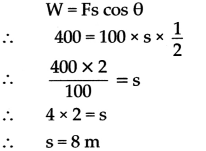
The object will be displaced through 8 m.

Question 2.
A force of 50 N acts on an object and displaces it by 2 m. If the force acts at an angle of 60° to the direction of its displacement, find the work done.
Answer:
50 J
Question 3.
Raj applied a force of 20 N and moved a book 40 cm in the direction of the force. How much was the work done by Raj?
Answer:
8J
Type -B
Formula:
1) W = K.E = 1/2 mv2
2) W = P.E = mgh
• W = P.E, W = K.E
1 km/hr =
\(\frac{1000}{3600} \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}=\frac{5}{18} \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}\)
Question 4.
A stone having a mass of 250 gm is falling from a height. How much kinetic energy does it have at the moment when its velocity is 2 m/s?
Answer:

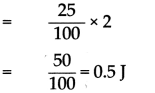
The kinetic energy of the stone is 0.5 J

Question 5.
500 kg water is stored in the overhead tank of a 10 m high building. Calculate the amount of potential energy stored in the water.
Answer:
Given:
Mass (m) = 500 kg
Height (h) = 10 m
Acceleration due to gravity (g) = 9.8 m/s2
To Find:
Potential energy (P.E) = ?
Formula:
P.E = mgh
Solution:
P.E = mgh
= 500 x 9.8 x 10
= 500 x 98
= 49000J
The P.E of the stored water is 49000 J
Question 6.
Calculate the work done to take an object of mass 20 kg to a height of 10 m. (g = 9.8 m/s2)
Answer:
Given:
Mass (m) = 20 kg
Acceleration due to gravity (g) = -9.8 m/s2
Displacement (s) = (h) = 10 m.
To Find:
Work done (W) = ?
Formula:
(i) W = P.E = mgh
Solution:
W = mgh
= 20 x (-9.8) x 10
= -1960J
The work done to take an object of mass 20 kg to a height of 10 m is -1960 J.

Question 7.
A body of 0.5 kg thrown upwards reaches a maximum height of 5 m. Calculate the work done by the force of gravity during this vertical displacement.
Answer:
Given:
Mass (m) = 0.5 kg
Acceleration due to gravity (g) = -9.8 m/s2
Displacement (s) = 5 m.
To Find:
Work done (W) = ?
Formula:
W = P.E = mgh
Solution:
W = mgh
= 0.5 x (-9.8) x 5
= -24.5 J
The work done by the force of gravity is -24.5 joule.
Question 8.
1 kg mass has a kinetic energy of 2 joule. Calculate its velocity.
Answer:
Given:
Mass (m) = 1 kg
Kinetic Energy (K.E) = 2 J
To Find:
Velocity (v) = ?
Formula:

The velocity is 2 m/s

Question 9.
A rocket of mass 100 tonnes is propelled with a vertical velocity 1 km/s. Calculate kinetic energy.
Answer:

The kinetic energy of the rocket is 5 x 1010 J
Type – C
Formula:
\(\text { 1) Power }=\frac{\text { work }}{\text { time }}=\frac{\text { mgh }}{t}\)

Power should be expressed in kW
Time should be expressed in hours
1 k Wh = 1 unit
Question 10.
Swaralee takes 20 s to carry a bag weighing 20 kg to a height of 5 m. How much power has she used?
Given:
Mass (m) = 20 kg
Height (h) = 5 m
Time (t) = 20s
Acceleration due to gravity (g) = 9.8 m/s2
To Find:
Power (P) = ?
Formula:
\(\mathrm{P}=\frac{\mathrm{mgh}}{\mathrm{t}}\)
Solution:
\(\begin{aligned}
P &=\frac{m g h}{t} \\
&=20 \times 9.8 \times \frac{5}{20} \\
&=9.8 \times 5
\end{aligned}\)
= 49 W
Power used by Swaralee is 49 W

Write notes on the following:
Question 1.
Derive the expression for potential energy.
Answer:
(i) To carry an object of mass ‘m’ to a height ‘h’ above the earth’s surface, a force equal to ‘mg’ has to be used against the direction of the gravitational force.
(ii) The amount of work done can be calculated as follows:
Work = force x displacement
∴ W = mg x h
∴ W = mgh
(iii) The amount of potential energy stored in the object because of its displacement.
PE = mgh (W = P.E)
(iv) Displacement to height h causes energy equal to mgh to be stored in the object.
Question 2.
When can you say that the work done is either positive, negative or zero?
Answer:
- When the force and the displacement are in the same direction, the work done by the force is positive.
- When the force and displacement are in the opposite directions, the work done by the force is negative.
- When the applied force does not cause any displacement or when the force and the displacement are perpendicular to each other, the work done by the force is zero.
Question 3.
Explain the relation between, the commercial and SI unit of energy.
Answer:
The commercial unit of energy is a kilowatt-hour (kWh) while the SI unit of energy is the joule. Their relation is
1 kWh = 1kW x 1hr
= 1000 Wx 3600 s
= 3600000J
(Watt x Sec = Joule)
1 kWh = 3.6 x 106 J.
Question 4.
How is work calculated if the direction of force and the displacement are inclined to each other?
Answer:
If the direction of force and the displacement are inclined to each other then, we must convert the applied force into the force acting along the direction of displacement.

If θ is angle between force and displacement, then force (F1) in direction of displacement is
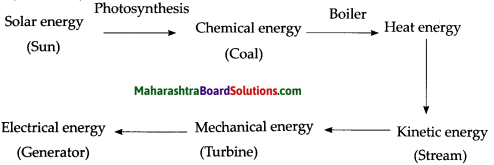
Complete the flow chart.
Question 1.
Transformation of energy
Answer:
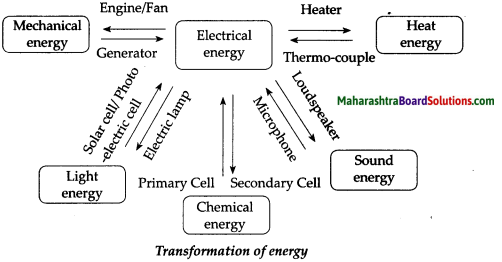

Question 2.
Transformation of energy
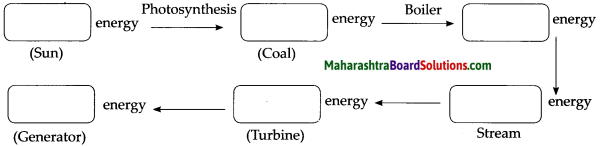
Answer:
Write effects of the following with examples.
Question 1.
Force
Answer:
- A force can move a stationary object. The force of engine makes a stationery car to move.
- A force can stop a moving object. The force of brakes can stop a moving car.
- A force can change the speed of a moving object. When a hockey player hits a moving ball, the speed of ball increases.
- A force can change the direction of a moving object. In the game of carrom ,when we take a rebound then the direction of striker changes because the edge of the carrom board exerts a force on the strike.
- A force can change the shape and size of an object. The shape of kneaded wet clay changes when a potter converts it into pots of different shapes and sizes because the p otter applies force on the kneaded wet clay.
Give two examples in each of the following cases:
Question 1.
Potential energy
Answer:
- Water stored in a dam
- A compressed spring
Question 2.
Kinetic energy
Answer:
- Water flowing
- Bullet fired from a gun
Question 3.
Chemical energy
Answer:
- Chemical in cell
- Explosive mixture of a bomb

Question 4.
Zero work done
Answer:
- A stone tied to a string and whirled in a circular path
- Motion of the earth and other planets moving around the sun
Question 5.
Negative work done
Answer:
- A cyclist applies brakes to his bicycle, but the bicycle still covers some distance.
- When a body is made to slide on a rough surface, the work done by the frictional force.
Question 6.
Positive work done
Answer:
(i) A boy moving from the ground floor to the first floor.
(ii) A fruit falling down from the tree.
= 0.5 hr x 30 days
= 15 hrs
To Find:
Energy consumed = ?

The units of energy consumed in the month of April by the iron is 18 units.
Question 7.
A 25 W electric bulb is used for 10 hours every day. How much electricity does it consume each day?
Answer:
Given:
Power (P) = 25 W
25/1000 kW
Time (E) = 10 hrs
To Find:
Electric energy consumed = ?
Formula:
Electric energy consumed = power x time
Solutions:
Electric energy consumed = power x time
= 25/1000 x 10
= 0.25 kWh
The electric bulb consumes 0.25 kWh of electricity each day.

Question 8.
If a TV of rating 100W is operated for 6 hrs per day, find the amount of energy consumed in any leap year?
Answer:

= 2196 hrs.
To Find:
Electric energy consumed
Formula:
Electric energy consumed = power x time
Solution:
Electric energy consumed = power x time
= 0.1 x 2196
= 219.6 kWh
The amount of energy consumed is 219.6 kWh
Complete the paragraph.
Question 1.
………….. is the measure of energy transfer when a force (F) moves an object through a ………….. (d). So when ………….. is done, energy has been transferred from one energy store to another, and so: energy transferred = ………….. done. Energy transferred and work done are both measured in ………….. (J)
Answer:
Work is the measure of energy transfer when a force (F) moves an object through a distance (d). So when work is done, energy has been transferred from one energy store to another, and so: energy transferred = work done. Energy transferred and work done are both measured in joules (J).
Question 2.
………….. energy and ………….. done are the same thing as much as ………….. energy and work done are the same thing. Potential energy is a state of the system, a way of ………….. energy as of virtue of its configuration or motion, while ………….. done in most cases is a way of channeling this energy from one body to another.
Answer:
Potential energy and work done are the same thing as much as kinetic energy and work done are the same thing. Potential energy is a state of the system, a way of storing energy as of virtue of its configuration or motion, while work done in most cases is a way of channeling this energy from one body to another.

Question 3.
In physics, ………….. is the rate of doing work or, i.e., the amount of energy transferred or converted per unit time. In the International System of Units, the unit of power is the ………….. equal to one ………….. per second.
Power is a ………….. quantity that requires both a change in the physical system and a specified time interval in which the change occurs. But more ………….. is needed when the work is done in a shorter amount of time.
Answer:
In physics, power is the rate of doing work or, i.e., the amount of energy transferred or converted per unit time. In the International System of Units, the unit of power is the watt. equal to one joule per second.
Power is a scalar quantity that requires both a change in the physical system and a specified time interval in which the change occurs. But more power is needed when the work is done in a shorter amount of time.
Activity-based questions
Answer in detail:
Question 1.
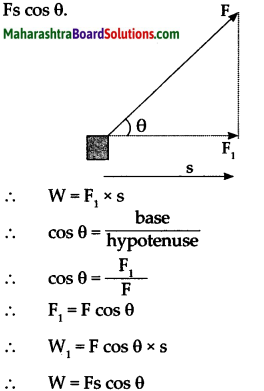
State the expression for work done when displacement and force makes an angle θ OR State the expression for work done when force is applied making an angle θ with the horizontal force.
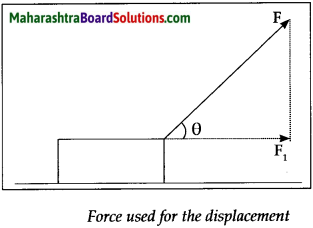
Answer:
Let ‘F’ be the applied force and Fj be its component in the direction of displacement. Let ’S’ be the displacement.
The amount of work done is given by W = F1s ……………………………………… (1)
The force ‘F’ is applied in the direction of the string.
Let ‘θ’ be the angle that the string makes with the horizontal. We can determine the component ‘F1‘, of this force F, which acts in the horizontal direction by means of trigonometry.
\(\begin{aligned}
\cos \theta=\frac{\text { base }}{\text { hypotenuse }} \\
\therefore \quad \cos \theta=\frac{\mathrm{F}_{1}}{\mathrm{~F}} \\
\therefore \quad \mathrm{F}_{1}=\mathrm{F} & \cos \theta
\end{aligned}\)
Substituting the value of F1 in equation 1
Thus, the work done by F1 is
W cos θ s
∴ W = Fscosθ

Question 2.
When a body is dropped on the ground from some height its P.E is converted into K.E but when it strikes the ground and it stops, what happens to the K.E?
Answer:
When a body is dropped on the ground, its K.E appears in the form of:
- Heat (collision between the body and the ground).
- Sound (collision of the body with the ground).
- The potential energy of change in state of the body and the ground.
- Kinetic energy is also utilized to do work i.e., the ball bounces to a certain height and moves to a certain distance vertically and horizontally till Kinetic energy becomes zero.
- The process in which the kinetic energy of a freely falling body is lost in an unproductive chain of energy is called the dissipation of energy.
Question 3.
Explain the statement “Potential Energy is relative”.
Answer:
- The potential energy of an object is determined and calculated according to a height of the object with respect to the observer.
- So, the person staying on 6th floor more potential energy than those staying on the 3rd floor.
- But, the person on the 6th floor will have lesser potential energy than on the 8th floor. Hence potential energy is relative.
9th Std Science Questions And Answers: