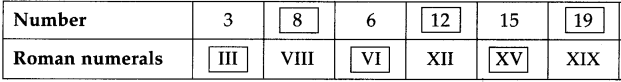
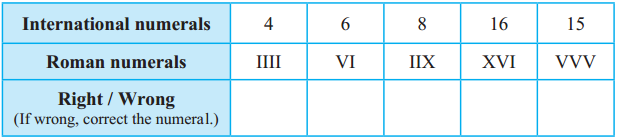
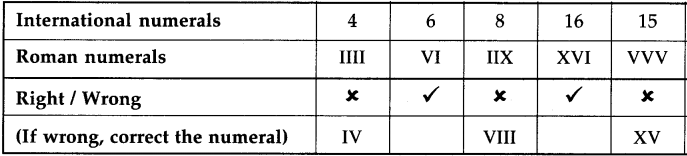
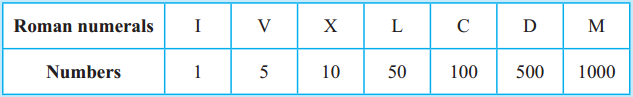
Introduction to Partnership and Partnership Final Accounts 12th BK Commerce Chapter 1 Solutions Maharashtra Board
Balbharti Maharashtra State Board 12th Commerce Book Keeping & Accountancy Solutions Chapter 1 Introduction to Partnership and Partnership Final Accounts Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
Class 12 Commerce BK Chapter 1 Exercise Solutions
I. Objective Questions:
A. Select the most appropriate alternatives from the following and rewrite the sentences:
Question 1.
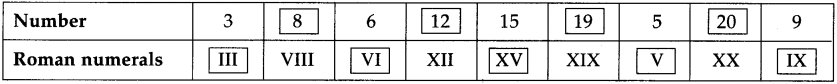
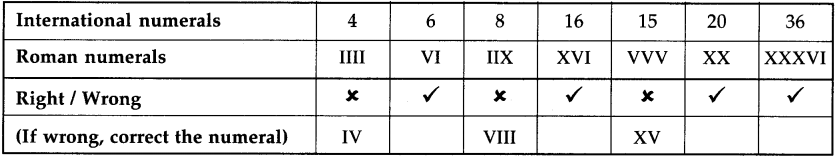
When there is no partnership agreement between partners, the division of profits takes place in ____________ ratio.
(a) equal
(b) capital ratio
(c) initial contribution
(d) experience and tenure of partners
Answer:
(a) equal
Question 2.
To find out Net Profit or Net Loss of the business ____________ Account is prepared.
(a) Trading
(b) Capital
(c) Current
(d) Profit & Loss
Answer:
(d) Profit & Loss

Question 3.
A ____________ is an Intangible Asset.
(a) Goodwill
(b) Stock
(c) Cash
(d) Furniture
Answer:
(a) Goodwill
Question 4.
In the absence of an agreement, interest on a loan advanced by the partner to the firm is allowed at the rate of ____________
(a) 5%
(b) 6%
(c) 10%
(d) 9%
Answer:
(b) 6%
Question 5.
Liability of partners in a partnership business is ____________
(a) limited
(b) unlimited
(c) limited and unlimited
(d) none of the above
Answer:
(b) unlimited
Question 6.
The Indian Partnership Act is in force since ____________
(a) 1932
(b) 1881
(c) 1956
(d) 1984
Answer:
(a) 1932

Question 7.
Maximum number of Partners in a firm are ____________ according to Companies Act, 2013.
(a) 10
(b) 25
(c) 20
(d) 50
Answer:
(d) 50
B. Write the word/phrase/term, which can substitute each of the following statements.
Question 1.
Persons who form the partnership firm.
Answer:
Partners
Question 2.
Amount of cash or goods withdrawn by partners from the business from time to time.
Answer:
Drawings
Question 3.
An association of two or more persons according to Indian Partnership Act 1932.
Answer:
Partnership firm
Question 4.
Act under which partnership firms are regulated.
Answer:
Indian Partnership Act
Question 5.
Process of entering the name of the partnership firm in the register of the Registrar.
Answer:
Registration
Question 6.
Partnership agreement in written form.
Answer:
Partnership Deed

Question 7.
Under this method capital, balances of partners remain constant.
Answer:
Fixed Capital Method
Question 8.
Proportion in which partners share profit.
Answer:
Profit-Sharing Ratio
Question 9.
Such a capital method in which only Capital Account is maintained for each partner.
Answer:
Fluctuating Capital Method
Question 10.
The account to which all adjustments are made when capital is fixed.
Answer:
Current Account
Question 11.
Expenses that are paid before they are due.
Answer:
Prepaid expenses
Question 12.
The accounts are prepared at the end of each accounting year.
Answer:
Final Accounts
Question 13.
An asset that can be converted into cash easily.
Answer:
Current Assets or Liquid Assets
Question 14.
Order in which fixed assets are recorded first in the Balance Sheet.
Answer:
Order of liquidation

Question 15.
The account in which selling expenses of the business are recorded.
Answer:
Profit and Loss Account
Question 16.
Debit balance of Trading Account.
Answer:
Gross loss
Question 17.
The credit balance of Profit and Loss Account.
Answer:
Net profit
C. State whether the following statements are True or False with reasons:
Question 1.
A partnership firm is a Non-Trading concern.
Answer:
This statement is False.
The main aim of a partnership firm Is to earn maximum profit. The partnership is a trading concern. It undertakes either manufacturing or distributive activities with the sole aim of earning profit and distribute that profit among the partners in a specific ratio. It is never formed for charitable purposes.
Question 2.
A profit and Loss Account is a Real Account.
Answer:
This statement is False.
Account of expenses, losses, gains, and incomes is called a Nominal account. The profit and Loss Account contains all indirect expenses and indirect incomes of the firm. Therefore, a Profit and Loss Account is a Nominal Account and not a real account.
Question 3.
Carriage inward is carriage on purchase.
Answer:
This statement is True.
Total transport expenses incurred on bringing the goods from market to the place of business is called the carriage. When goods are purchased, the carriage is supposed to be borne by the firm. It is known as carriage inward. It means carriage paid on purchase.

Question 4.
Adjustments are recorded in Partners Current Account in Fixed Capital Method.
Answer:
This statement is True.
In Fixed Capital Method, as the name suggests capital balances (opening and closing) are generally remain fixed. Under this method, adjustments are not to be recorded in Capital Account. All adjustments are recorded in a separate account called Partners’ Current Accounts.
Question 5.
Prepaid expenses are treated as liabilities.
Answer:
This statement is False.
Prepaid expenses are expenses that are paid before they are due. Therefore, they are considered an asset of the business organization.
Question 6.
If the partnership deed is silent, partners share profits and losses in proportion to their capital.
Answer:
This statement is False.
As per the provisions made under the Indian Partnership Act 1932, when a partnership deed is silent about profit and loss sharing ratio, partners are supposed to share profits and losses in equal proportion, and not in their capital ratio.
Question 7.
Balance Sheet is an Account.
Answer:
This statement is False.
A financial statement showing all assets and liabilities is called a Balance sheet. It is not an account. It is a position statement that shows various assets owned by the firm and various liabilities owned by it. On the left-hand side, all liabilities are listed and on the right-hand side, all assets are recorded.
Question 8.
Wages paid for the installation of machinery is a Revenue expenditure.
Answer:
This statement is False.
Wages paid for the installation of machinery is a capital expenditure and therefore it is added to the cost of machinery. It is generally, paid once in a life of an asset. It is a long-term and capital expenditure.
Question 9.
Income received in advance is a liability.
Answer:
This statement is True.
When Income in respect to next year, it received in the current year, it is known as income received in advance. So, in next year firm will not be able to receive that amount and therefore it is considered as a liability for the current year.
Question 10.
R.D.D. is created on Creditors.
Answer:
This statement is Raise.
R.D.D. stands for Reserve for Doubtful Debts. It is created on the value of debtors. Such provision is made against profit and loss accounts. In the future, if the loss is incurred on account of bad debts, such an amount is used to run the business.

Question 11.
Depreciation is not calculated on Current Assets.
Answer:
This statement is True.
Current Assets mean liquid assets having no fixed tenure therefore depreciation cannot be calculated on it. Depreciation is calculated and charged on fixed assets for their use, wear and tear, etc.
Question 12.
Goodwill is an intangible asset.
Answer:
This statement is True.
Goodwill is a reputation of business computed in terms of money. Reputation can be experienced but can’t be seen or felt. Therefore, Goodwill is an intangible asset.
Question 13.
Indirect expenses are debited to Trading Account.
Answer:
This statement is Raise.
Indirect expenses mean expenses that are not directly related to the production of goods and services. Therefore, indirect expenses cannot be debited to Trading Account. All indirect expenses are debited to the Profit and Loss Account.
Question 14.
A bank loan is a current liability.
Answer:
This statement is Raise.
A loan usually taken for the period of more than 1 year say 5 years from the bank is called Bank Loan. It is a long term loan. It is not repaid within 1 year but paid in installments over a number of years. It might be paid in lumpsum at the expiry of the term.
Question 15.
Net profit is the debit balance of Profit and Loss Account.
Answer:
This statement is Raise.
In a Profit and Loss Account, when the credit side total i.e. a total of incomes is more than the debit side total, i.e. expenses it is known as a credit balance. When incomes exceed expenses there is profit. Therefore credit balance of the Profit and Loss Account indicates net profit.
D. Find an odd one.
Question 1.
Wages, Salary, Royalty, Import Duty
Answer:
Salary
Question 2.
Postage, Stationery, Advertising, Purchases
Answer:
Purchases
Question 3.
Capital, Bills Receivable, Reserve fund, Bank overdraft
Answer:
Bills Receivable
Question 4.
Building, Machinery, Furniture, Bills Payable
Answer:
Bill Payable

Question 5.
Discount received, Dividend received, Interest received, Depreciation
Answer:
Depreciation
E. Complete the sentences.
Question 1.
Partners share profits & losses in ____________ ratio in the absence of partnership deed.
Answer:
equal
Question 2.
Registration of partnership is ____________ in India.
Answer:
optional
Question 3.
Partnership business must be ____________
Answer:
lawful
Question 4.
Liabilities of partners in partnership firm is ____________
Answer:
unlimited
Question 5.
The balance of the Drawings Account of a partner is transferred to his ____________ account under the Fixed Capital Method.
Answer:
Current
Question 6.
The interest on capital of a partner is debited to ____________ account.
Answer:
Profit and Loss

Question 7.
Partners are ____________ liable for the debts of the firm.
Answer:
joint & several
Question 8.
Partnership Deed is an ____________ of Partnership.
Answer:
Article
Question 9.
The withdrawal by the partner for personal use from the firm is ____________ to his account.
Answer:
debited
Question 10.
Commission payable to partner is ____________ to the firm.
Answer:
liability/outstanding expense
Question 11.
When partners adopt Fixed Capital Method then they have to operate ____________ Account.
Answer:
Partner’s Current
Question 12.
If the partners Current Account shows ____________ balance it is shown to the Liability side of the Balance Sheet.
Answer:
credit
Question 13.
The expenses paid for trading purpose are known as ____________ expenses.
Answer:
trade
Question 14.
Cash receipts which are recurring in nature are called as ____________ Receipts.
Answer:
Revenue
Question 15.
Return outward are deducted from ____________
Answer:
purchase

Question 16.
Expenses which are paid before due date are called as ____________
Answer:
Prepaid Expenses
Question 17.
Assets which are held in the business for a long period are called ____________
Answer:
Fixed Assets
Question 18.
Trading Account is prepared on the basis of ____________ expenses.
Answer:
direct
Question 19.
When commission is allowed to any partner, it is ____________ of the business.
Answer:
expenditure
Question 20.
When goods are distributed as free samples, it is treated as ____________ of the business.
Answer:
advertisement expense
F. Answer in one sentence only:
Question 1.
What is Fluctuating Capital?
Answer:
When capital balances of the partners go on changing every year due to transactions of partners with the firm, it is known as Fluctuating Capital.
Question 2.
Why is Partnership Deed necessary?
Answer:
Partnership Deed is necessary to prevent disputes or misunderstandings among the partners in the future.

Question 3.
If the Partnership Deed is silent, in which ratio, the partners will share the profit or loss?
Answer:
If the Partnership Deed is silent, partners will share profits and losses in equal ratio.
Question 4.
What is the Fixed Capital Method?
Answer:
Fixed Capital Method is one in which capital balances of the partners remain the same at the end of every financial year unless any amount of additional capital is introduced or part of the capital is withdrawn by the partner from the business.
Question 5.
How many partners are required to form a partnership firm?
Answer:
Minimum two persons are required to form a partnership firm.
Question 6.
What is Partnership Deed?
Answer:
A partnership deed is a written agreement duly stamped and signed document containing the terms and conditions of the partnership.
Question 7.
What are the objectives of the Partnership Firm?
Answer:
To earn a maximum profit is the main objective of the partnership firm.
Question 8.
What rate of interest is allowed on a partner’s loan in the absence of an agreement?
Answer:
6 % is the rate of interest to be allowed on a partner’s loan in the absence of an agreement.
Question 9.
What is the minimum number of partners in a partnership firm according to the Indian Partnership Act 1932?
Answer:
Minimum two persons are required a number of partners in a partnership firm according to Indian Partnership Act 1932.
Question 10.
What is the liability of a partner?
Answer:
The liability of a partner (except minor partner) is unlimited.
Question 11.
In the absence of Partnership Deed, what is the rate of interest on a loan advanced by the partner to the firm is allowed?
Answer:
In the absence of Partnership Deed, 6% is the rate of interest on a loan advanced by the partner to the firm.

Question 12.
What do you mean by pre-received income?
Answer:
Income that is received by the partnership firm before it is due is called pre-received income.
Question 13.
What is the effect of the adjustment of provision for discount on debtors in the final accounts of partnership?
Answer:
The effects of the adjustment of provision for discount on debtors in the final accounts of partnership are as follows:
Debit Profit and Loss A/c and deduct the amount of provision for discount on debtors from the number of debtors.
Question 14.
When are the Partners Current Account is opened?
Answer:
When Fixed Capital Method is adopted by the firm, Partners’s Current Account is opened.
Question 15.
As per which principle of accounting, closing stock is valued at cost price or at market price whichever is less?
Answer:
As per the Conservatism principle of accounting, the closing stock is valued at cost price or at market price whichever is less.
Question 16.
What is the provision of the Indian Partnership Act with regard to Interest on Capital?
Answer:
As per the provision of the Indian Partnership Act, Interest in Capital is not to be allowed.
Question 17.
Why is the Balance Sheet prepared?
Answer:
The Balance Sheet is prepared to know the financial position of the business in the form of its assets and liabilities on a particular date.
Question 18.
Why wages paid for the installation of machinery are not shown in Trading Account?
Answer:
Wages paid for the installation of machinery is a capital expenditure and it is not to be recorded in Trading Account.
Question 19.
What do you mean by indirect incomes?
Answer:
All incomes other than direct incomes are called indirect incomes.
[e.g. Interest received on investments, Incomes like discount, commission, dividend, rent, etc. received].

Question 20.
Why partners capital is treated as a long-term liability of business?
Answer:
Partner’s Capital is not refunded during the existence of the partnership firm unless the partner is retired or expired.
G. Do you agree/disagree with the following statements:
Question 1.
When Partnership Deed is silent, partners share profits of the firm according to capital ratio.
Answer:
Disagree
Question 2.
The current Account always shows a debit balance.
Answer:
Disagree
Question 3.
It is compulsory to have a partnership agreement in writing.
Answer:
Disagree
Question 4.
Partnership Firm is a trading concern.
Answer:
Agree
Question 5.
Interest in the capital is an expenditure for the partnership firm.
Answer:
Agree
Question 6.
A partnership is an association of two or more persons.
Answer:
Agree

Question 7.
Partners are entitled to get a Salary or Commission.
Answer:
Disagree
Question 8.
The balance of the Capital Account remains constant under Fixed Capital Method.
Answer:
Agree
Question 9.
The Indian Partnership Act came into existence in the year 1945.
Answer:
Disagree
Question 10.
Profit and Loss Account reflects the true financial position.
Answer:
Disagree
Question 11.
The amount borrowed by a partner from his business will be debited to the Current Account.
Answer:
Agree
Question 12.
Sold but undispatched goods must be part of the valuation of closing stock.
Answer:
Disagree
Question 13.
Carriage inward is a selling and distribution overhead.
Answer:
Disagree

Question 14.
Gross profit is an operating profit.
Answer:
Disagree
Question 15.
All financial expenditures are debited to the Profit and Loss Account.
Answer:
Agree
Question 16.
Free distribution of goods is debited to Trading Account.
Answer:
Disagree
H. Calculate the following:
Question 1.
Undervaluation of closing stock by 10%, closing stock was ₹ 30,000. Find out the value of the closing stock.
Solution:
Undervaluation of closing stock by 10 %
Revised value = \(\frac{\text { Book value }}{100-\% \text { of undervaluation }} \times 100\)
= \(\frac{30,000}{100-10} \times 100\)
= ₹ 33,333.
∴ Value of closing stock = ₹ 33,333.
Question 2.
Calculate 12.5% P.A. depreciation on Furniture:
(a) on ₹ 220,000 for 1 year
(b) on ₹ 10,000 for 6 months
Solution:
Depreciation = Amount of asset × Period × %
(a) Depreciation on furniture = 220,000 × 1 × \(\frac{12.5}{100}\) = ₹ 27,500
∴ Deprecation on furniture for 1 year = ₹ 27,500
(b) Depreciation on furniture = 10,000 × \(\frac{6}{12} \times \frac{12.5}{100}\) = ₹ 625
∴ Depreciation on furniture for 6 months = ₹ 625
Question 3.
The insurance premium is paid for the year ending on 1st September 2019 amounted to ₹ 1500. Calculate prepaid insurance assuming that the year-end is 31st March 2019.
Solution:
From 31st March to 1st September, 5 months period prepaid insurance amount we have to find.
An insurance premium paid for the 12 months = ₹ 1500
∴ for 5 months period it is 1500 × \(\frac{5}{12}\) = ₹ 625
Thus, prepaid insurance premium amount = ₹ 625.

Question 4.
Find out Gross Profit/Gross Loss: Purchases ₹ 30,000, Sales ₹ 15,000, Carriage inward ₹ 2400, Opening stock ₹ 10,000, Purchase return ₹ 1000, Closing stock ₹ 36,000.
Solution:
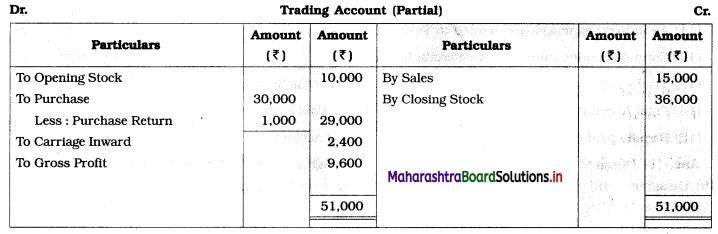
Question 5.
A borrowed loan from Bank of Maharashtra ₹ 2,00,000 on 1st October 2019 @15 % p.a. Calculate interest on a bank loan for the year 2019 – 20 assuming that the financial year ends on 31st March, every year.
Solution:
From 1st October to 31st March, 6 months period interest on loan is to be calculated.
Interest (I) = \(\frac{\text { PRN }}{100}\)
∴ Interest on loan = 2,00,000 × \(\frac{15}{100} \times \frac{6}{12}\) = ₹ 15,000
∴ Interest on loan on ₹ 2,00,000 for 6 months = ₹ 15,000
Practical Problems
Question 1.
Amitbhai and Narendrabhai are in Partnership Sharing Profits and Losses equally. From the following Trial Balance and Adjustments given below, you are required to prepare the Trading and Profit and Loss Account for the year ended 31st March 2019 and Balance Sheet as of that date.
Trial Balance as of 31st March 2019
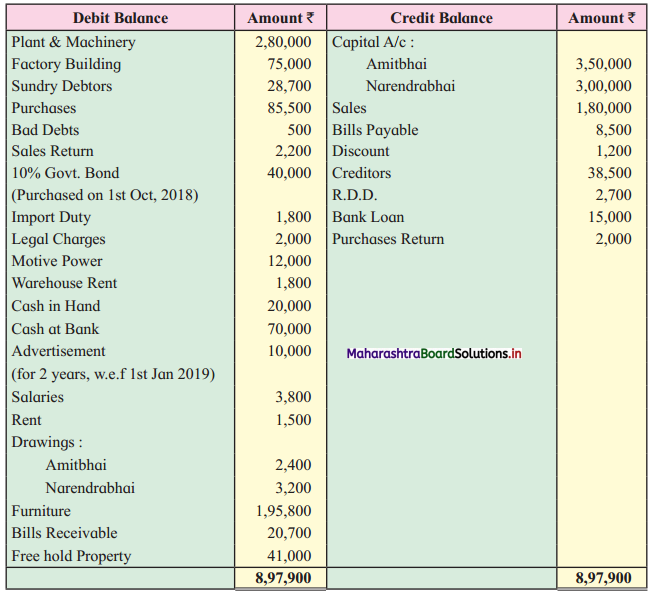
Adjustments:
1. Stock on hand on 31st March 2019 was valued at ₹ 43,000.
2. Uninsured goods worth ₹ 8,000 were stolen.
3. Create R.D.D. at 2 % on sundry debtors.
4. Mr. Patil, our customer becomes insolvent and could not pay his debts of ₹ 500.
5. Outstanding Expenses – Rent ₹ 800 and salaries ₹ 300.
6. Depreciate Factory Building by ₹ 2,500 and Furniture by ₹ 1,800.
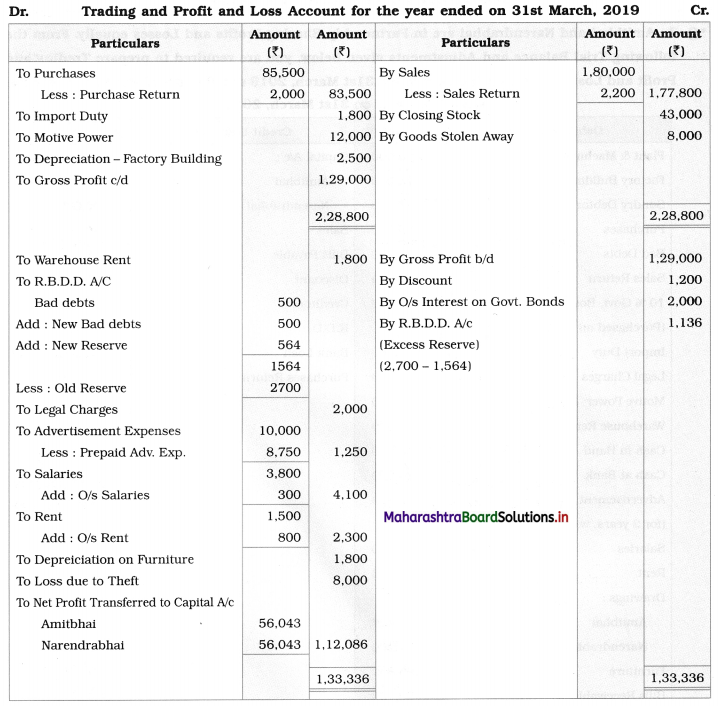
Solution:
In the books of Amitbhai and Narendrabhai
Balance Sheet as of 31st March 2019
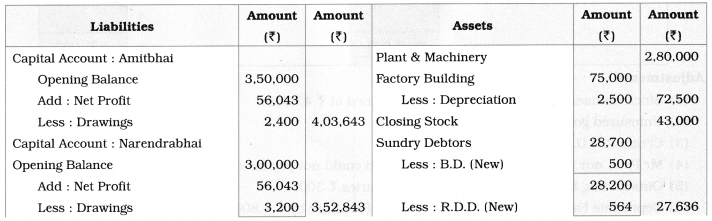
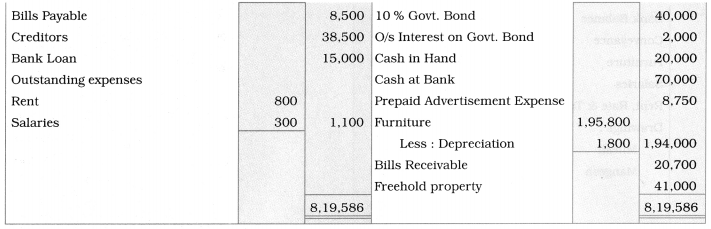
Notes:
1. Import duty, Motive power, and Depreciation on Factory building are recorded in the Trading A/c.
2. 10% govt, the bond is an investment. It was purchased on 1 – 10 – 2018.
∴ Interest is calculated for six months.
Interest on Govt. Bond = \(\frac{40,000}{1} \times \frac{6}{12} \times \frac{10}{100}\) = ₹ 2,000
3. Adv. exp. paid for 2 years from 01 – 01 – 2019. Upto 31 – 3 – 2019, 3 months adv. exp. is written off to Profit and Loss A/c. It is calculated as below:
= 10,000 × \(\frac{3}{24}\) = ₹ 1,250
∴ Prepaid adv. exp. = 10,000 – 1,250 = ₹ 8,750

Question 2.
From the following Trial Balance of M/s Mitesh and Mangesh, you are required to prepare Trading and Profit and Loss Account for the year ended 31st March 2019 and Balance Sheet as of that date.
Trial Balance as of 31st March 2019
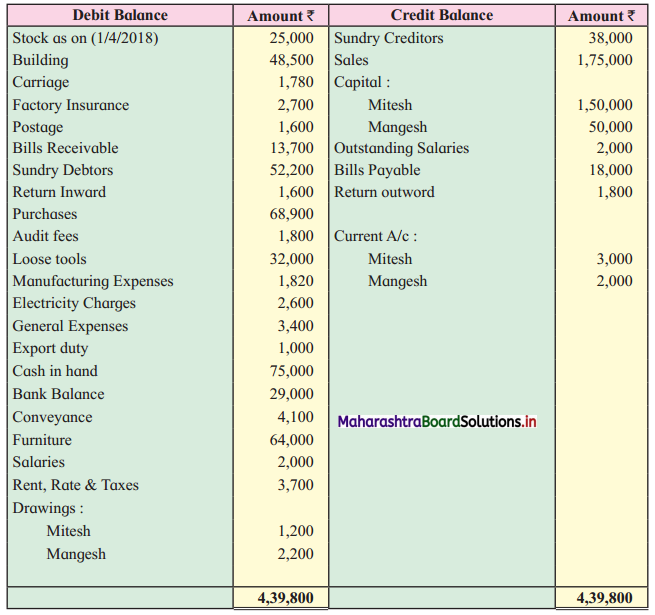
Adjustments:
1. Mitesh and Mangesh are sharing profit and losses in the ratio 3 : 1.
2. Partners are entitled to get commission @ 1% each on gross profit.
3. The closing stock is valued at ₹ 23,700.
4. Outstanding Expenses – Audit fees ₹ 400; Carriage ₹ 600.
5. Building is valued at ₹ 46,500.
6. Furniture is depreciated by 5%.
7. Provide interest on partner’s capital at 2.5% p.a.
8. Goods of ₹ 900 were taken by Mangesh for his personal use.
9. Write off ₹ 1,000 as Bad debts and maintain R.D.D. at 3 % on Sundry Debtors.
Solution:
In the books of M/s Mitesh and Mangesh
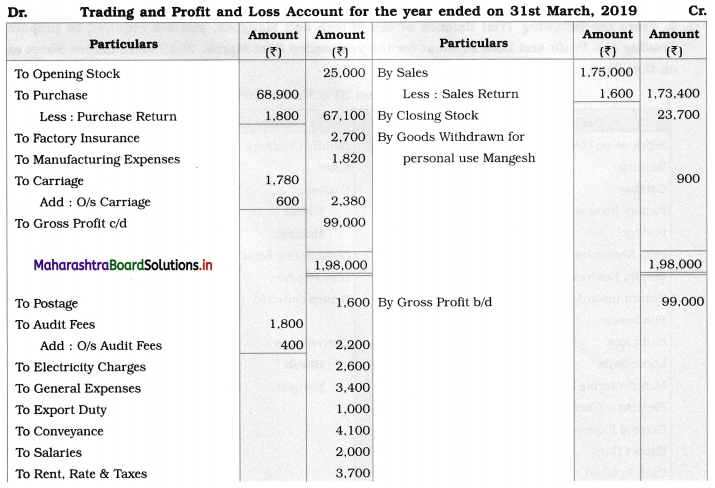
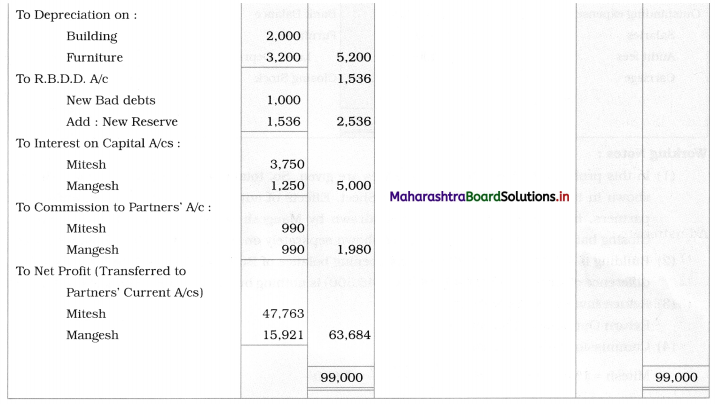
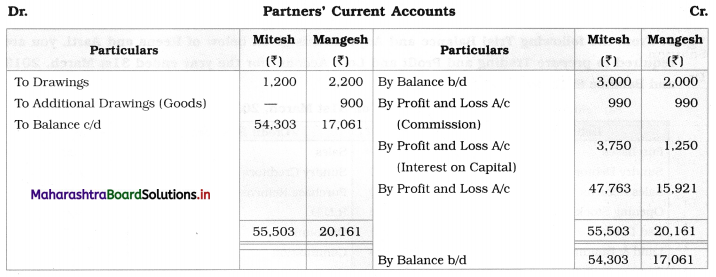
Balance Sheet as of 31st March 2019
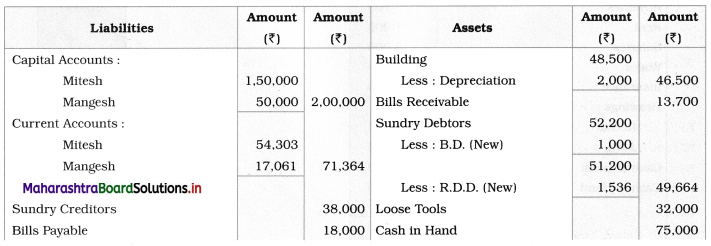
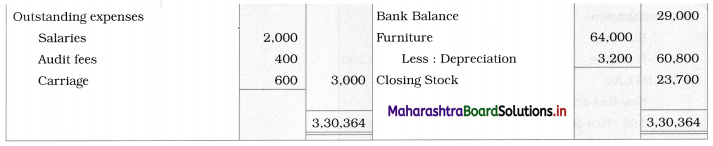
Working Notes:
1. In this problem, Current Account balances are given. So, the total amount of fixed capital is directly shown in the Liabilities side of the Balance Sheet. Effects of adjustments related to commission to partners, interest on capital, goods are withdrawn by Mangesh are given in the Current Account. Closing balances of the Current Account are shown separately on the Liability side of the Balance Sheet.
2. Building is valued at ₹ 46,500 whereas the opening balance of Building given is ₹ 48,500. Therefore, a difference of the amount of ₹ 2,000 (48,500 – 46,500) is nothing but Depreciation charged on Building.
3. Return Inward ⇒ Sales Return
Return Outward ⇒ Purchase Return
4. Commission payable to partners:
Mitesh = 1% on Gross Profit = \(\frac{1}{100} \times \frac{99,000}{1}\) = ₹ 990/-
Mangesh = 1% on Gross Profit = \(\frac{1}{100}\) × 99,000 = ₹ 990/-
Question 3.
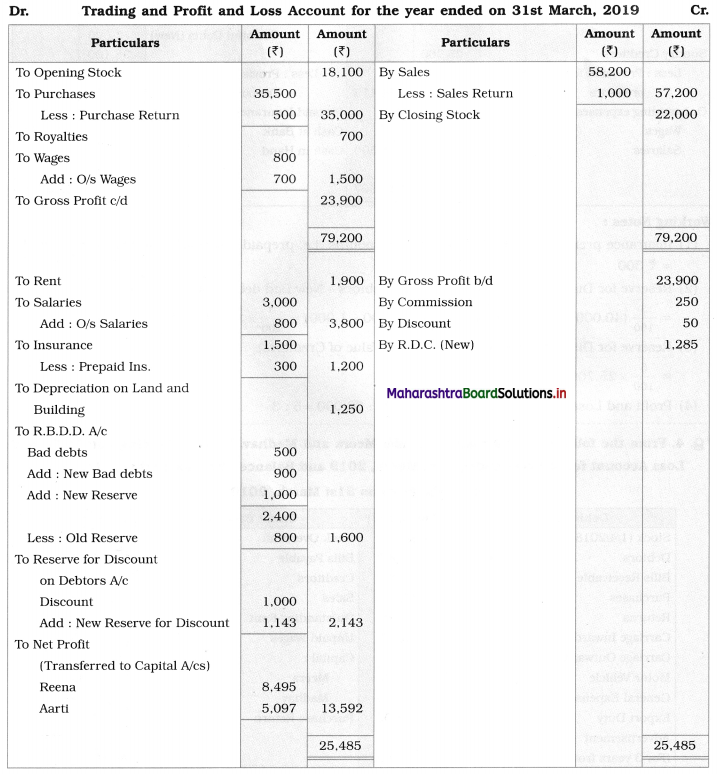
From the following Trial Balance and Adjustments given below of Reena and Aarti, you are required to prepare Trading and Profit and Loss Account for the year ended 31st March 2019 and Balance Sheet as of that date.
Trial Balance as of 31st March 2019
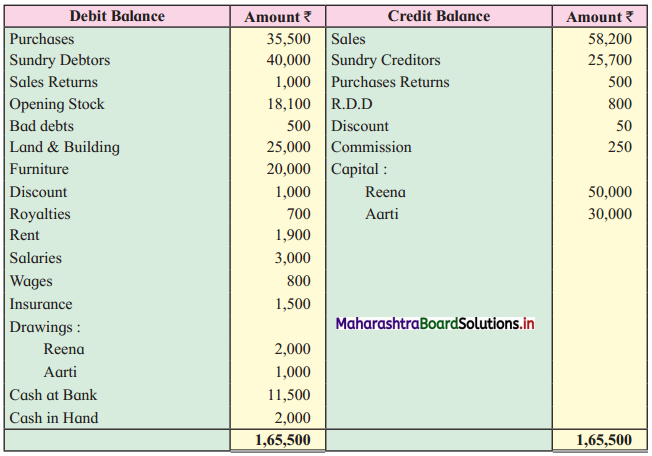
Adjustments:
1. Closing stock valued at ₹ 22,000.
2. Write off ₹ 900 for bad & doubtful debts and create a provision for reserve for doubtful debts ₹ 1,000.
3. Create a provision for discount on debtors @ 3 % and on creditors @ 5%.
4. Outstanding Expenses – Wages ₹ 700 and Salaries ₹ 800.
5. Insurance is paid for 15 months, w.e.f. 1st April 2018.
6. Depreciate land and building @ 5%.
7. Reena & Aarti are sharing Profits & Losses in their Capital Ratio.
Solution:
In the books of Reena and Aarti
Balance Sheet as of 31st March 2019
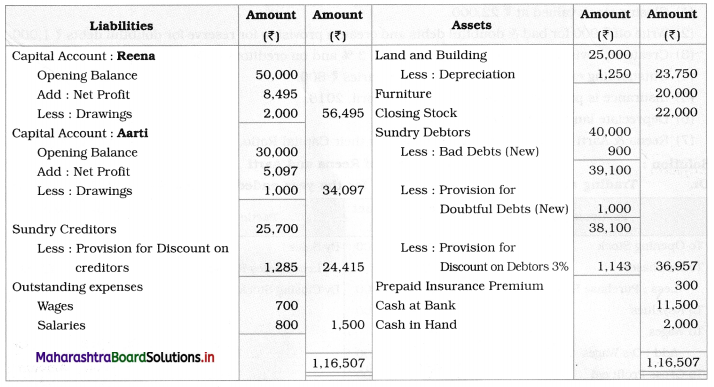
Working Notes:
1. Insurance premium ₹ 1,500 is paid for 15 months, i.e. prepaid insurance premium for 3 months = ₹ 300.
2. Reserve for Discount on Debtors = 3% on (Debtors – New Bad debts – New Reserve)
= \(\frac{3}{100}\) × (40,000 – 900 – 1,000)
= \(\frac{3}{100}\) × (40,000 – 1,900)
= \(\frac{3}{100}\) × 38,100
= ₹ 1,143
3. Reserve for Discount on Creditors = 5% on (Value of Creditors)
= \(\frac{5}{100}\) × 25,700
= ₹ 1,285
4. Profit and Loss ratio = Capital ratio = 50,000 : 30,000 = 5 : 3

Question 4.
From the following Trial Balance of M/s Meera and Madhav. Prepare Trading and Profit and Loss Account for the year ended 31st March 2019 and Balance Sheet as on that date.
Trial Balance as of 31st March, 2019
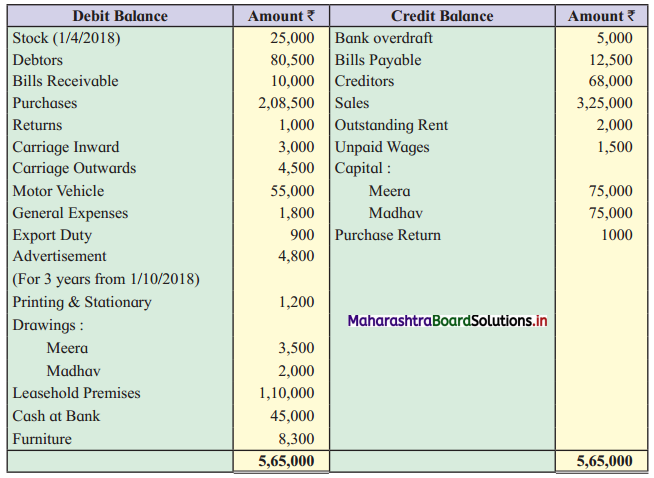
Adjustments:
1. Closing stock is valued at ₹ 32,000.
2. Provide provision for doubtful debts ₹ 2,000.
3. Create a reserve for a discount on debtors @ 3%.
4. Value of leasehold premises on 31st March 2019 ₹ 1,00,000.
5. Outstanding Expenses: Printing & stationery ₹ 500.
Solution:
In the books of M/s Meera and Madhav
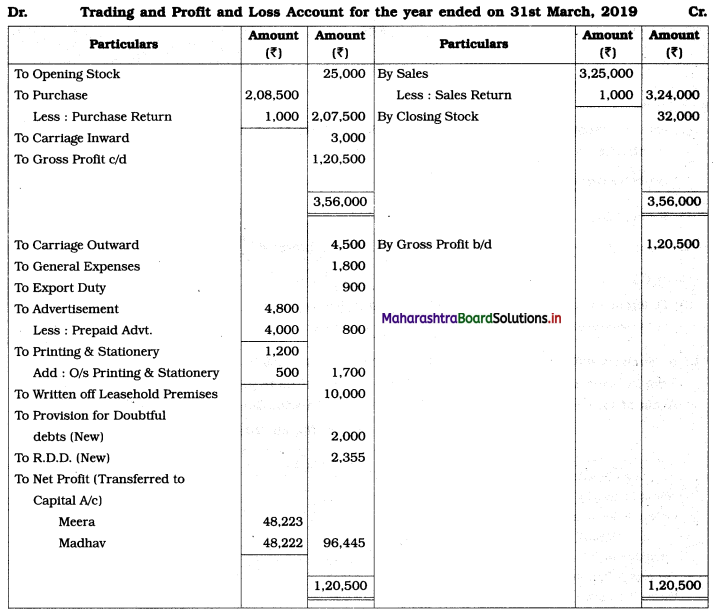
Balance Sheet as of 31st March 2019
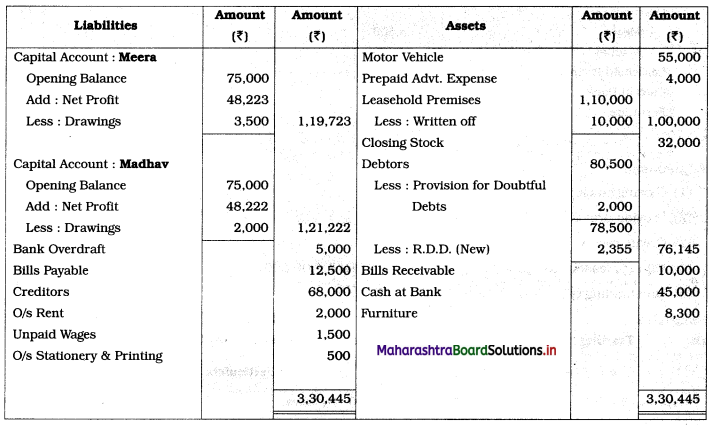
Working Notes:
1. Advertisement expenses written off to Profit and Loss account during the year 2018-19 for six months i.e. from 1/10/18 to 31/03/19.
Advertisement expenses W/off = (Advertisement bill paid) × \(\frac{1}{3} \times \frac{6}{12}\)
= 4,800 × \(\frac{1}{3} \times \frac{6}{12}\)
= ₹ 800.
Prepaid advertisement = 4,800 – 800 = ₹ 4,000.
2. Reserve for Discount on Debtors = 3% (Balance in debtors)
= \(\frac{3}{100}\) × (80,500 – 2,000)
= \(\frac{3}{100}\) × 78,500
= ₹ 2,355.
3. Difference between the opening balance (₹ 1,10,000) and the closing balance (₹ 1,00,000) for leasehold premises is to be considered as written off on leasehold premises.
Question 5.
Sucheta & Gayatri are partners sharing Profit and Losses in the ratio 3 : 2. From the following Trial Balance and additional information, you are required to prepare Trading and Profit and Loss Account for the year ended 31st March 2019 and Balance Sheet as of that date.
Trial Balance as of 31st March 2019
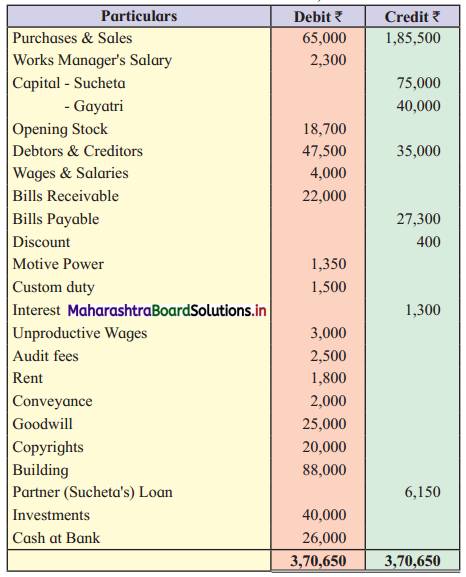
Adjustments:
1. Stock on 31st March 2019 was valued at ₹ 19,700.
2. Goods costing ₹ 3,000 distributed as a free sample.
3. Motive power includes ₹ 500 paid for deposit of Power Meter.
4. Depreciate building @ 5 %.
5. Write off ₹ 2000 for bad debts and maintain R.D.D. at 3% on debtors.
6. Bills receivable included dishonored of Bill of ₹ 4,000.
Solution:
In the books of Sucheta and Gayatri
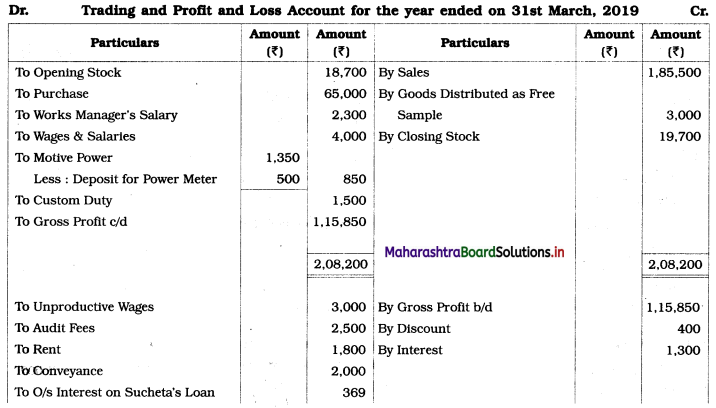
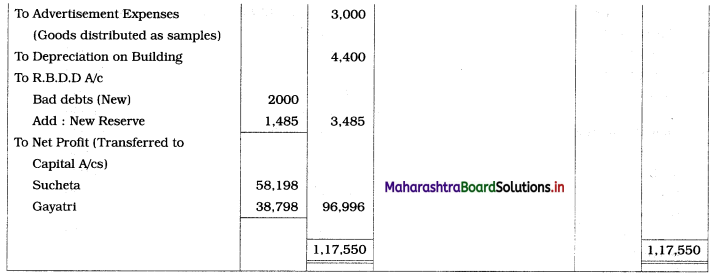
Balance Sheet as of 31st March, 2019
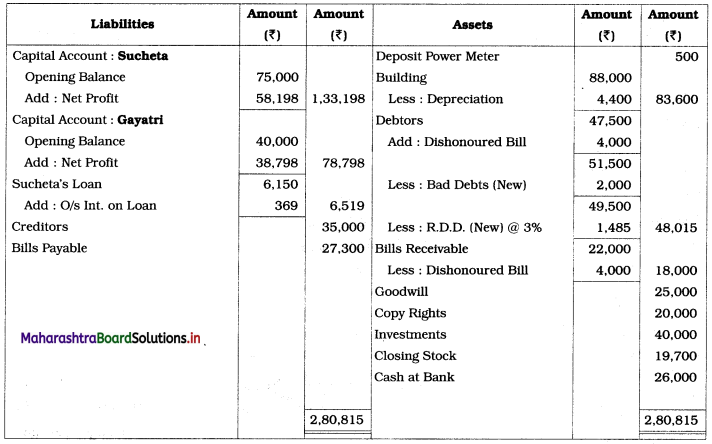
Working Notes:
1. Rate of interest on the partner’s loan is not mentioned, therefore interest on the loan is calculated at 6% p.a.
∴ Interest on Sucheta’s Loan = 6,150 × 1 × \(\frac{6}{100}\) = ₹ 369
2. Add dishonored bill amount to debtors amount and then calculate B.D. and R.D.D.
3. Subtract dishonored bill amount from bills receivable amount.

Question 6.
Archana and Prerana are partners, sharing Profits and Losses in the ratio 2 : 1 with the help of the following Trial Balance and Adjustments given below. You are required to prepare a Trading and Profit and Loss Account for the year ended 31st March 2019 and a Balance Sheet as of that date.
Trial Balance as of 31st March, 2019
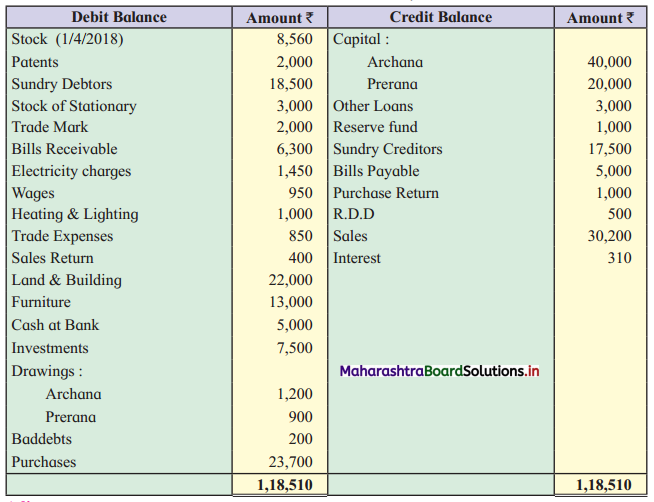
Adjustments:
1. Stock on 31st March 2019 is valued at Cost Price ₹ 12,000 and Market Price ₹ 17,000.
2. Our customer Mr. Shekhar failed to pay his dues of ₹ 800.
3. 1/8th of Patents are to be written off.
4. A part of Furniture ₹ 5,000 is purchased on 1st Oct. 2018.
5. Depreciation on Land & Building 10% and on Furniture 5%.
6. Outstanding Expenses Wages ₹ 300 and Electricity Charges ₹ 200.
7. Allow Interest on Capital 3%.
Solution:
In the books of Archana and Prema
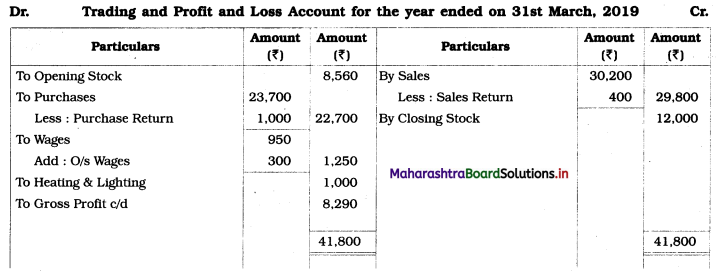
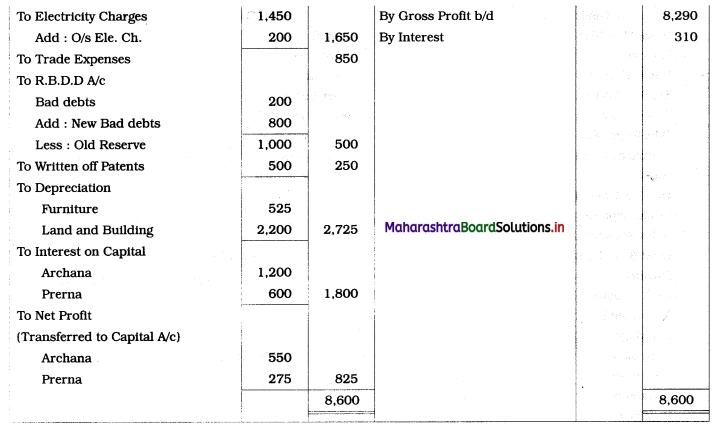
Balance Sheet as of 31st March 2019
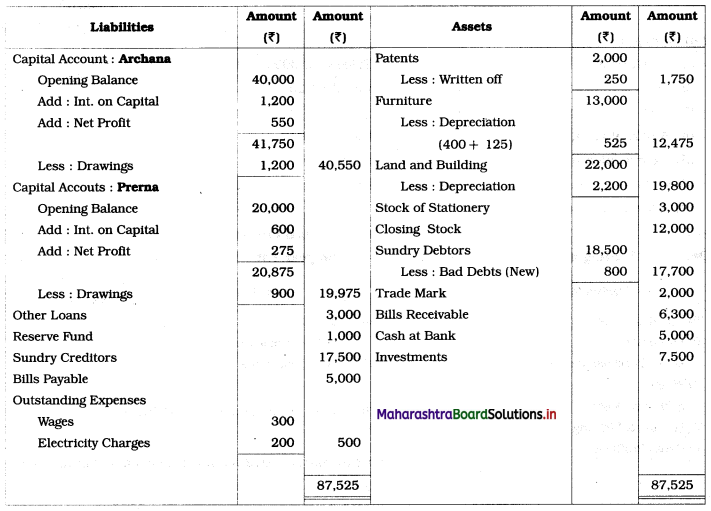
Working Notes:
1. Stationery stock is an asset.
2. Depreciation of furniture:
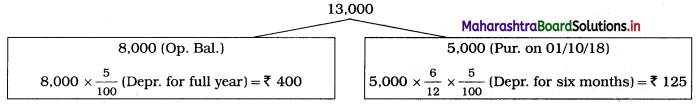
∴ Total Depreciation = 400 + 125 = ₹ 525
3. \(\frac{1}{8}\) patents to be written off = 2,000 × \(\frac{1}{8}\) = ₹ 250.
4. As no other expenses are given, Trade Expense is recorded in Profit and Loss Account.
Question 7.
Satish and Pramod are partners. Prepare Trading Account and Profit and Loss Account for the year 31st March 2019. You have to find out Gross Profit and Net Profit only.
Trial Balance as of 31st March 2019
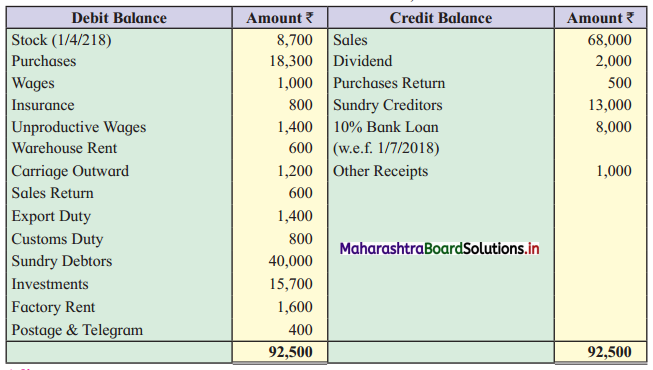
Adjustments:
1. The Closing stock is valued at ₹ 15,400.
2. Outstanding wages ₹ 500.
3. Create provision for Bad debts ₹ 800 and maintain R.D.D. 3 % on Sundry Debtors.
4. Goods of ₹ 1,800 distributed as a free sample.
5. Goods of ₹ 2,000 were sold and delivered on 31st March 2019 but no entry is passed in the Books of Account.
Solution:
In the books of Satish and Pramod
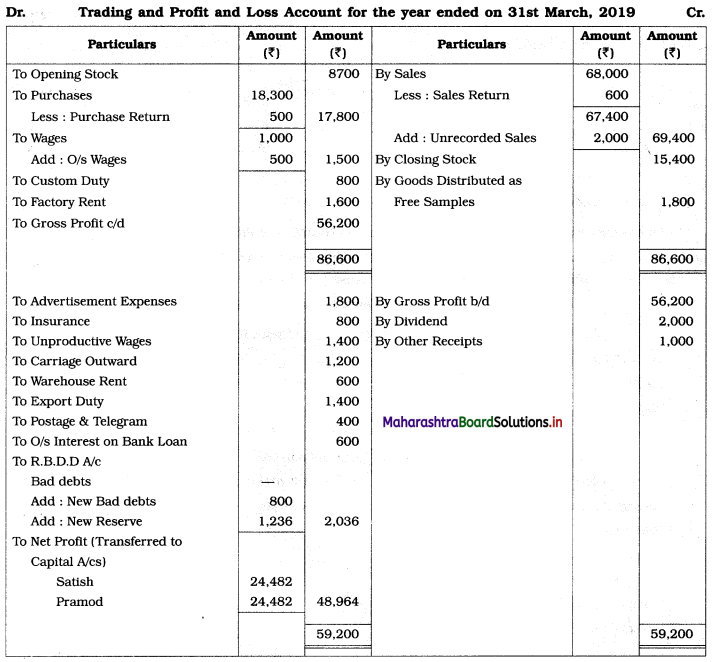
Working Notes :
1. Here only gross profit and net profit is to find out. Therefore, the Balance Sheet is not prepared.
2. Interest on a 10% bank loan is calculated for 9 months (From 1/7/2018 to 31/3/2019)
I = \(\frac{\mathrm{PRN}}{100}\) = 8,000 × \(\frac{10}{100} \times \frac{9}{12}\) = ₹ 600
3. Goods distributed as free samples is an advertisement expense for business.
4. Sundry Debtors = 40,000
Add: Unrecorded Sales = 2,000
Less: Provision for Bad Debts = 800
Total = 41,200
Less: R.D.D. (New) (3% of 41,200 = 1,236) = 39,964

Question 8.
Nana and Nani are partners in a Partnership Firm sharing Profits and Losses equally. You are required to give effects of Adjustments in Profit & Loss A/c and Balance Sheet with the help of the following information.
Trial Balance as of 31st March 2019
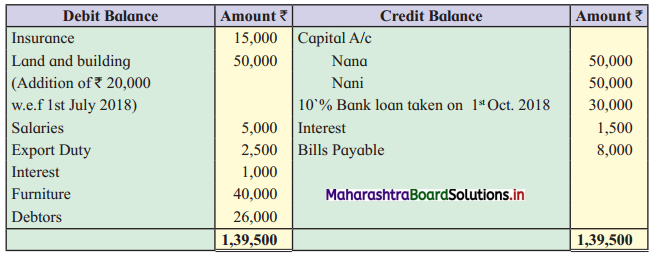
Adjustments:
1. Gross profit amounted to ₹ 34,500.
2. Insurance paid for 15 months w.e.f. 1-4-2018.
3. Depreciate Land and Building at 10 % p.a. and Furniture at 5% p.a.
4. Write off ₹ 1,000 for Bad debts and maintain R.D.D. at 5 % on Sundry debtors.
5. Closing stock is valued at ₹ 34,500.
Solution:
In the books of Nana and Nani
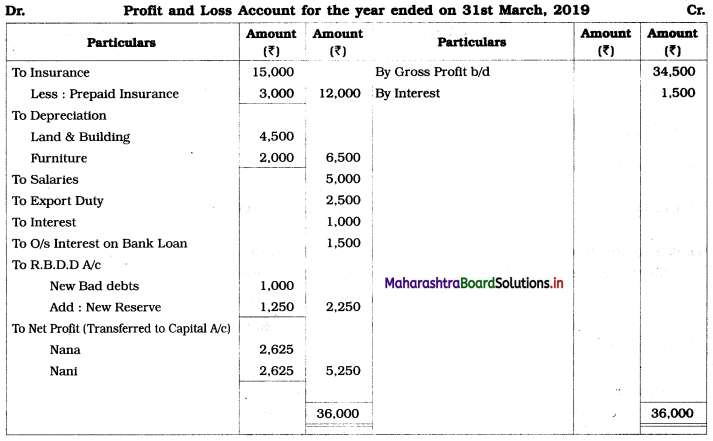
Balance Sheet as of 31st March 2019
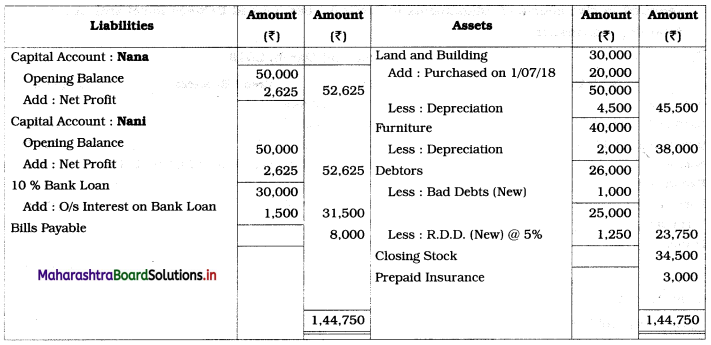
Working Notes:
1. Here, the Profit and Loss Account and Balance Sheet are to be prepared. Therefore, Trading Account is not prepared. Gross profit (given) is recorded on the Credit side of the Profit and Loss Account.
2. Land and Building
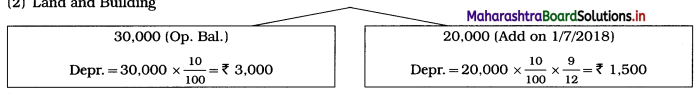
Total Depreciation = ₹ 4,500
3. Interest on 10% bank loan is calculated for 6 months. (From 1/10/2018 to 31/3/2019)
I = \(\frac{\text { PRN }}{100}\)
= 30,000 × \(\frac{10}{100} \times \frac{6}{12}\)
= ₹ 1,500
4. Prepaid insurance = \(\frac{3}{15}\) × (Insurance Amount)
= \(\frac{3}{15}\) × 15,000
= ₹ 3,000
5. RDD = 5% on (Debtors – New Bad debts)
= \(\frac{5}{100}\) × (26,000 – 1,000)
= \(\frac{5}{100}\) × 25,000
= ₹ 1,250
Question 9.
Sun and Moon are partners in a Partnership Firm sharing Profits and Losses equally. You are required to give effects of Adjustments with the help of the following information:
Trial Balance as of 31st March 2019
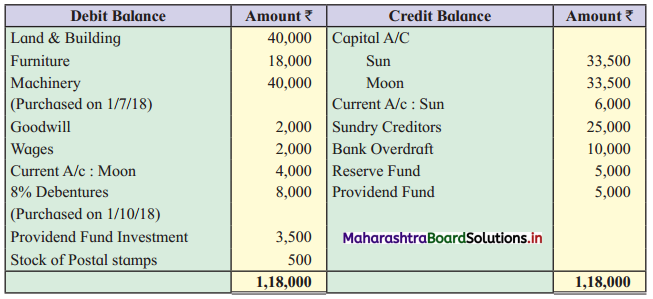
Adjustments:
1. Partners are entitled to get a salary of ₹ 6,000 p.a. in addition to their profit & loss sharing.
2. Depreciation on Land & Building, Furniture and Machinery @ 10%, 5% and 3% respectively.
3. Interest in Capital 5% p.a.
4. Closing stock ₹ 60,743.
5. Wages included ₹ 1,000 as advance is given to workers.
6. Interest due but not paid ₹ 800.
7. Total net profit amounted to ₹ 38,113.
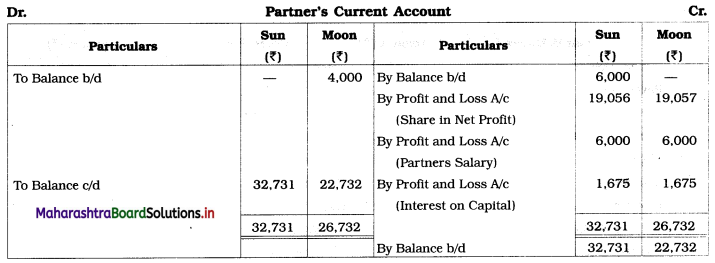
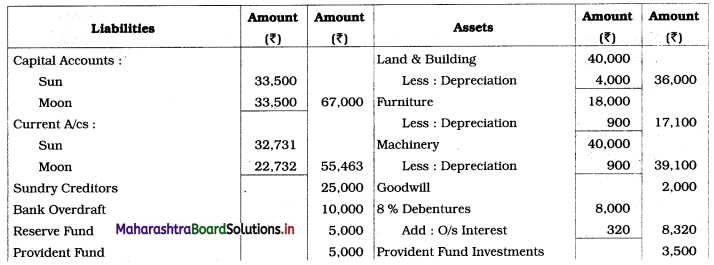
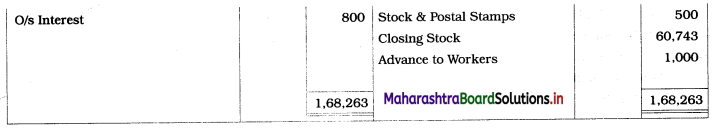
You are required to prepare the Balance Sheet and Partners Current A/c only.
Solution:
In the books of Sun and Moon
Balance Sheet as of 31st March 2019
Working Notes:
1. Depreciation on machinery is calculated for 9 months. (i.e. from 1/7/18 to 31/3/19)
Depreciation = 40,000 × \(\frac{3}{100} \times \frac{9}{12}\) = ₹ 900
2. Interest on 8% debentures, calculated for 6 months. (i.e. from 1/10/18 to 31/3/19)
I = \(\frac{\text { PRN }}{100}\)
= 8,000 × \(\frac{8}{100} \times \frac{6}{12}\)
= ₹ 320
3. Advance given to workers (by firm) ₹ 1,000 is an asset for the firm, so, it is shown on the Assets side.
4. Interest due but not paid is a liability for the firm, so, it is shown on the Liabilities side.

Question 10.
Kshipra and Manisha are partners sharing Profit and Losses in their Capital ratio. You are required to prepare Trading Account and Profit and Loss Account for the year ended 31st March 2019 and a Balance Sheet as of that date.
Trial Balance as of 31st March 2019
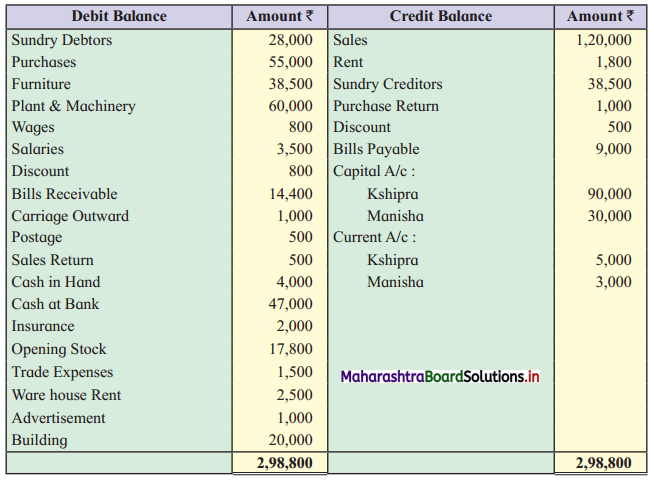
Adjustments:
1. Stock on 31st March 2019 was at ₹ 37,000.
2. Sales include the sale of machinery of ₹ 2,000, which is sold on 1st April 2018.
3. Depreciation on fixed assets @ 5%
4. Each partner is entitled to get a commission at 1% of Gross profit and interest on Capital 5% p.a.
5. Outstanding Expenses wages ₹ 200 & Salaries ₹ 500.
6. Create provision for Doubtful debts @ 3% on Sundry debtors.
Solution:
In the books of Kshipra and Manisha
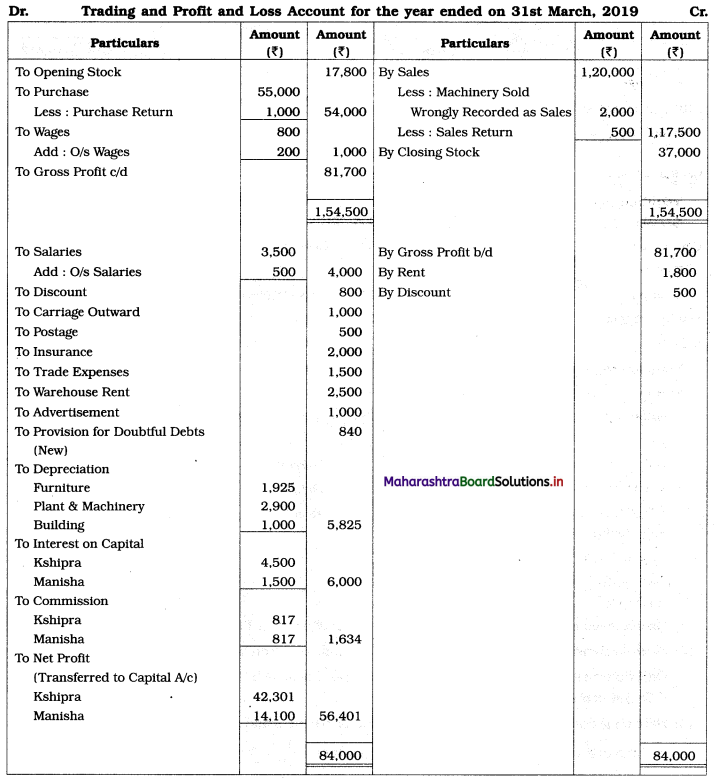
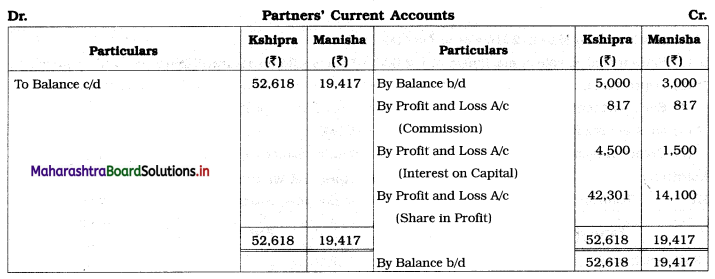
Balance Sheet as of 31st March 2019
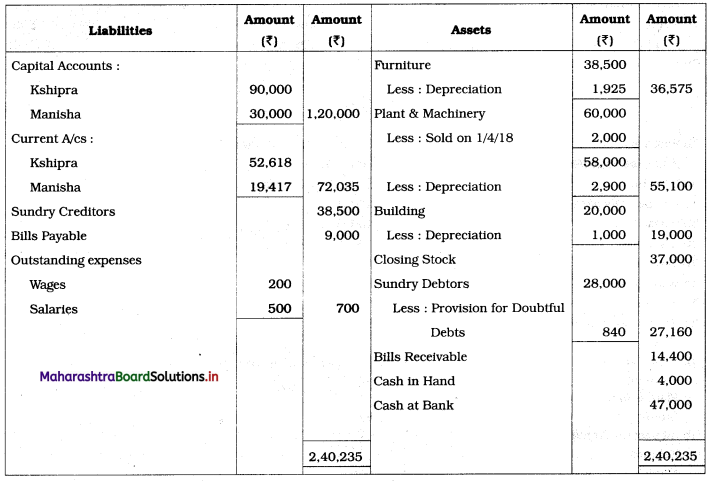
Working Notes:
1. Depreciation on fixed assets means depreciation on Furniture, Plant & Machinery, and Building.
2. Sales includes the sale of Machinery of ₹ 2,000 is subtracted from sales and from Plant & Machinery.
On balance amount of Plant & Machinery ₹ 58,000, calculate 5 % depreciation i.e. 60,000 – 2,000 = ₹ 58,000 × 5% = ₹ 2,900
3. Here on gross profit calculate 1% commission for partners and record it to Profit and Loss A/c and in Current A/cs. Commission payable to each partner = \(\frac{1}{100}\) × Gross profit
= \(\frac{1}{100}\) × 81,700
= ₹ 817.
Class 12 Commerce BK Textbook Solutions Digest
![]()
![]()
![]()

![]()


![]()
![]()
![]()

![]()