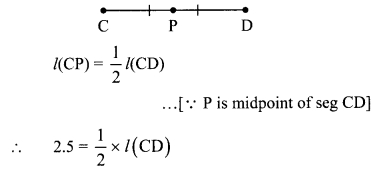
Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 9 Maths Solutions covers the Problem Set 1 Geometry 9th Class Maths Part 2 Answers Solutions Chapter 1 Basic Concepts in Geometry.
9th Standard Maths 2 Problem Set 1 Chapter 1 Basic Concepts in Geometry Textbook Answers Maharashtra Board
Class 9 Maths Part 2 Problem Set 1 Chapter 1 Basic Concepts in Geometry Questions With Answers Maharashtra Board
Question 1.
Select the correct alternative answer for the questions given below.
i. How many midpoints does a segment have ?
(A) only one
(B) two
(C) three
(D) many
Answer:
(A) only one
ii. How many points are there in the intersection of two distinct lines ?
(A) infinite
(B) two
(C) one
(D) not a single
Answer:
(C) one
iii. How many lines are determined by three distinct points?
(A) two
(B) three
(C) one or three
(D) six
Answer:
(C) one or three
iv. Find d(A, B), if co-ordinates of A and B are – 2 and 5 respectively.
(A) -2
(B) 5
(C) 7
(D) 3
Answer:
Since, 5 > -2
∴ d(A, B) = 5 – (-2) = 5+2 = 7
(C) 7
v. If P – Q – R and d(P, Q) = 2, d(P, R) = 10, then find d(Q, R).
(A) 12
(B) 8
(C) √96
(D) 20
Answer:
d(P, R) = d(P, Q) + d(Q, R)
∴ 10 = 2 + d(Q, R)
∴ d(Q, R) = 8
(B) 8
Question 2.
On a number line, co-ordinates of P, Q, R are 3,-5 and 6 respectively. State with reason whether the following statements are true or false.
i. d(p, Q) + d(Q, R) = d(P, R)
ii. d(P, R) + d(R, Q) = d(P, Q)
iii. d(R, P) + d(P, Q) = d(R, Q)
iv. d(P, Q) – d(P, R) = d(Q, R)
Solution:
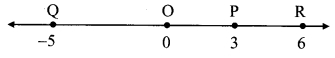
Co-ordinate of the point P is 3.
Co-ordinate of the point Q is -5.
Since, 3 > -5
d(P, Q) = 3 – (-5) = 3 + 5
∴ d(P,Q) = 8
Co-ordinate of the point Q is -5.
Co-ordinate of the point R is 6.
Since, 6 > -5
d(Q, R) = 6 – (-5) = 6 + 5
∴ d(Q, R) = 11
Co-ordinate of the point P is 3.
Co-ordinate of the point R is 6.
Since, 6 > 3
d(P, R) = 6 – 3
∴ d(P, R) = 3
i. d(P, Q) + d(Q, R) = 8 + 11
= 19 …(i)
d(P, R) = 3 …(ii)
∴ d(P, Q) + d(Q, R) ≠ d(P, R) … [From (i) and (ii)]
∴ The given statement is false.
ii. d(P, R) + d(R, Q) = 3 + 11
d(P,Q) = 8 …(ii)
∴ d(P, R) + d(R, Q) + d(P, Q) …[From (i) and (ii)]
∴ The given statement is false.
iii. d(R, P) + d(P, Q) = 3 + 8
= 11 …(i)
d(R, Q) =11 . -(ii)
∴ d(R,P) + d(P,Q) = d(R,Q) ….[From (i) and (ii)]
∴ The given statement is true.
iv. d(P, Q) – d(P, R) = 8 – 3
= 5 …(i)
d(Q,R) = 11 ..(h)
∴ d(P, Q) – d(P, R) ≠ d(Q, R) …[From (i) and (ii)]
∴ The given statement is false.
Question 3.
Co-ordinates of some pairs of points are given below. Hence find the distance between each pair.
i. 3,6
ii. -9, -1
iii. A, 5
iv. 0,-2
v. x + 3, x – 3
vi. -25, -47
vii. 80, -85
Solution:
i. Co-ordinate of first point is 3.
Co-ordinate of second point is 6.
Since, 6 > 3
∴ Distance between the points = 6 – 3 = 3
ii. Co-ordinate of first point is -9.
Co-ordinate of second point is -1.
Since, -1 > -9
∴ Distance between the points = -1 – (-9) = -1+9 = 8
iii. Co-ordinate of first point is -4.
Co-ordinate of second point is 5.
Since, 5 > -4
∴ Distance between the points = 5 – (-4)
= 5 + 4 = 9
iv. Co-ordinate of first point is 0.
Co-ordinate of second point is -2. Since,
0 > – 2
∴ Distance between the points = 0 – (-2)
= 0 + 2
= 2
v. Co-ordinate of first point is x + 3.
Co-ordinate of second point is x – 3.
Since, x + 3 > x – 3
∴ Distance between the points = x + 3 – (x – 3)
= x + 3 – x + 3 = 3 + 3
= 6
vi. Co-ordinate of first point is -25.
Co-ordinate of second point is -47.
Since, -25 > -47
∴ Distance between the points = -25 – (-47)
= -25 + 47
= 22
vii. Co-ordinate of first point is 80.
Co-ordinate of second point is -85.
Since, 80 > -85
∴ Distance between the points = 80 – (-85)
= 80 + 85
= 165
Question 4.
Co-ordinate of point P on a number line is – 7. Find the co-ordinates of points on the number line which are at a distance of 8 units from point P.
Solution:
Let point Q be at a distance of 8 units from P and on left side of P
Let point R be at a distance of 8 units from P and on right side of P.
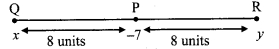
i. Let the co-ordinate of point Q be x.
Co-ordinate of point P is -7.
Since, point Q is to the left of point P.
∴ -7 > x
∴ d(P, Q) = -7 -x
∴8 = -7 – x
∴ x = – 7 – 8
∴x = -15
ii. Let the co-ordinate of point R be y.
Co-ordinate of point P is -7.
Since, point R is to the right of point P.
∴ y > -7
∴ d(P, R) = 7- (-7)
∴ 8 = y + 7
∴ 8 – 7 = 7
∴ y = 1
∴ The co-ordinates of the points at a distance of 8 units from P are -15 and 1.
Question 5.
Answer the following questions.
i. If A – B – C and d(A, C) = 17, d(B, C) = 6.5, then d (A, B) = ?
ii. If P – Q – R and d(P, Q) = 3.4, d(Q, R) = 5.7, then d(P, R) = ?
Solution:
i. Given, (A, C) = 17, d(B, C) = 6.5
d(A, C) = d(A, B) + d(B, C) …[A – B – C]
∴ 17 = d(A, B) + 6.5
∴ d(A,B)= 17 – 6.5
∴ d(A, B) = 10.5
ii. Given, d(P, Q) = 3.4, d(Q, R) = 5.7
d(P,R) = d(P,Q) + d(Q,R) …[P – Q – R]
= 34 + 5.7
∴ d(P, R) = 9.1
Question 6.
Co-ordinate of point A on a number line is 1. What are the co-ordinates of points on the number line which are at a distance of 7 units from A ?
Solution:
Let point C be at a distance of 7 units from A and on left side of A
Let point B be at a distance of 7 units from A and on right side of A.
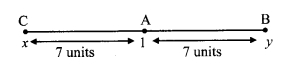
i. Let the co-ordinate of point C be x.
Co-ordinate of point A is 1.
Since, point C is to the left of point A.
∴ 1 > x
∴ d(A, C) = 1 – x
∴ 7 = 1 -x
∴x = 1 – 7
∴ x = – 6
ii. Let the co-ordinate of point B be y.
Co-ordinate of point A is 1.
Since, point B is to the right of point A.
∴y > 1
∴ d(A, B) = 7 – 1
∴ 7 = y – 1
∴ 7 + 1 = 7
∴ 7 = 8
∴ The co-ordinates of the points at a distance of 7 units from A are -6 and 8.
Question 7.
Write the following statements in conditional form.
i. Every rhombus is a square.
ii. Annies in a linear pair are supplementary.
iii. A triangle is a figure formed by three segments
iv. A number having only two divisors is called a prime number.
Solution:
i If a quadrilateral is a rhombus, then it is a square.
ii. If iwo angles are in a linear pair, then they are supplementary.
iii. If a figure is a triangle, then it is formed by three segments.
iv. If a number has only two divisors, then it is a prime number.
Question 8.
Write the converse of each of the following statements.
i. If the sum of measures of angles in a figure is 180°, then the figure is a triangle.
ii If the sum of measures of two angles is 90°, thfcn they are eomplement of each other.
iii. If the corresponding angles formed by a transversal of two lines are congruent, then the two lines are parallel.
iv. If the sum of the digits of a number is divisible by 3, then the number is divisible by 3.
Answer:
i. If a figure is a triangle, then the sum of the measures of its angles is 180°.
ii. if two angles are eomplement of each other, then sum of their measures is 90°,
iii. If two lines are parallel, then the corresponding angles formed by a transversal of two lines are congruent.
iv. If a number is divisible by 3, then the sum of its digits is also divisible by 3.
Question 9.
Write the antecedent (given part) and the consequent (part to be proved) in the following statements.
i. If all sides of a triangle are congruent, then its all angles are congruent.
ii. The diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other.
Answer:
i. If all sides of a triangle are congruent, then its all angles are congruent.
Antecedent (Given): All the sides of the triangle are congruent.
Consequent (To prove): All the angles are congruent.
ii. The diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other.
Conditional statement: “If a quadrilateral is a parallelogram then its diagonals bisect each other.
Antecedent (Given): Quadrilateral is a parallelogram.
Consequent (To prove): Its diagonals bisect each other.
Question 10.
Draw a labelled figure showing information in each of the following statements and write the antecedent and the consequent.
i. Two equilateral triangles are similar.
ii. If angles in a linear pair are congruent, then each of them is a right angle.
iii. If the altitudes drawn on two sides of a triangle are congruent, then these two sides are congruent.
Answer:
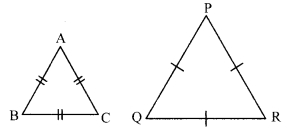
i. Two equilateral triangles are similar.
Conditional statement: “If two triangles are equilateral, then they are similar.
Antecedent (Given): Two triangles are equailateral.
i.e. ∆ABC and ∆PQR are equilatral triangle.
Consequent (To prove): Triangles are similar
i.e. ∆ABC ∼ ∆PQR
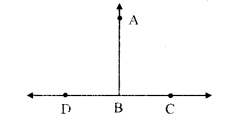
ii. If angles in a linear pair are congruent, then each of them is a right angle.
Antecedent (Given): Angles in a linear pair are congrunent.
∠ABC and ∠ABD are angles in a linear pair i.e. ∠ABC = ∠ABD
Consequent (To prove): Each angle is a right angle.
i.e. ∠ABC – ∠ABD = 90°
iii. If the altitudes drawn on two sides of a triangle are congruent, then these two sides are congruent.
Antecedent (Given): Altitude drawn on two sides of triangle are congrunent.
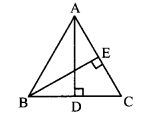
In ∆ABC, AD ⊥ BC . and BE ⊥ AC. seg AD ≅ seg BE
Consequent (To prove): Two sides are congruent.
side BC ≅ side AC A
Maharashtra Board Class 9 Maths Chapter 1 Basic Concepts in Geometry Problem Set 1 Intext Questions and Activities
Question 1.
Points A, B, C are given below. Check, with a stretched thread, whether the three points are collinear or not. If they are collinear, write which one of them is between the other two. (Textbook pg. no. 4)
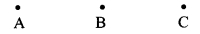
Answer:
Point B is between the points A and C.
Question 2.
Given below are four points P, Q, R, and S. Check which three of them are collinear and which three are non collinear. In the case of three collinear points, state which of them is between the other two. (Textbook pg. no. 4)

Answer:
Points P, R and S are collinear.
Point R is between the points P and S.
Question 3.
Students are asked to stand in a line for mass drill. How will you check whether the students standing are in a line or not ? (Textbook pg. no. 4)
Answer:
If one stands in front of the line and observes only the first student standing in the line, then all the students standing in that line are collinear i.e., standing in the same line. We can use this property of collinearity to check whether the students are standing in the same line or not.
Question 4.
How had you verified that light rays travel in a straight line? Recall an experiment in science which you have done in a previous standard. (Textbook pg. no. 4)
Answer:
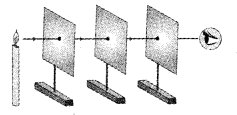
The flame of the candle can be seen only when the pin holes in all cardboards are in the same straight line. We can use the set up shown in the figure above to verify that light rays travels in a straight line.
Class 9 Maths Digest