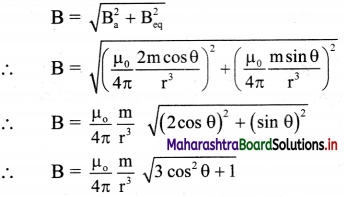
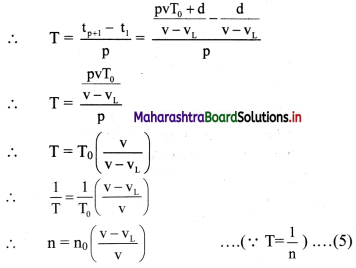
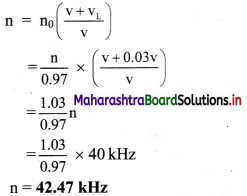
Balbharti Maharashtra State Board 11th Physics Important Questions Chapter 11 Electric Current Through Conductors Important Questions and Answers.
Maharashtra State Board 11th Physics Important Questions Chapter 11 Electric Current Through Conductors
Question 1.
Define current. State its formula and SI unit.
Answer:
- Current is defined as the rate of flow of electric charge.
- Formula: I = \(\frac {q}{t}\)
- SI unit: ampere (A)
Question 2.
Derive an expression for a current generated due to flow of charged particles
Answer:
i. Consider an imaginary gas of both negatively and positively charged particles moving randomly in various directions across a plane P.
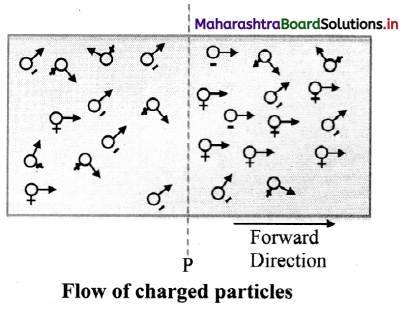
ii. In a time interval t, let the amount of positive charge flowing in the forward direction be q+ and the amount of negative charge flowing in the forward direction be q–. Thus, the net charge flowing in the forward direction is q = q+ – q–

iii. Let I be the current varying with time. Let ∆q be the amount of net charge flowing across the plane P from time t to t + At, i.e. during the time interval ∆t.
iv. Then the current is given by
I(t) = \(\lim _{\Delta t \rightarrow 0} \frac{\Delta \mathrm{q}}{\Delta \mathrm{t}}\)
Flere, the current is expressed as the limit of the ratio (∆q/∆t) as ∆t tends to zero.
Question 3.
Match the amount of current generated A given in column – II with the sources given in column -I.
| Column I |
Column II |
| 1. Lightening |
a. Few amperes |
| 2. House hold circuits |
b. 10000 A |
|
c. Order of µA |
Answer:
| Column I |
Column II |
| 1. Lightening |
b. 10000 A |
| 2. House hold circuits |
a. Few amperes |
Question 4.
Which are the most common units of current used in semiconductor devices?
Answer:
- milliampere (mA)
- microampere (µA)
- nanoampere (nA)
Question 5.
Six ampere current flows through a bulb. Find the number of electrons that should flow through the bulb in a time of 4 hrs.
Answer:
Given: I = 6 A, t = 4 hrs = 4 × 60 × 60 s
To find: Number of electrons (N)
Formula: I = \(\frac {q}{t}\) = \(\frac {Ne}{t}\)
Calculation: As we know, e = 1.6 × 10-19 C
From formula,
N = \(\frac {It}{e}\) = \(\frac {6×4×60×60}{1.6×10^{-19}}\) 6x4x60x60 = 5.4 × 1023
Question 6.
Explain flow of current in different conductor.
Answer:
- A current can be generated by positively or negatively charged particles.
- In an electrolyte, both positively and negatively charged particles take part in the conduction.
- In a metal, the free electrons are responsible for conduction. These electrons flow and generate a net current under the action of an applied electric field.
- As long as a steady field exists, the electrons continue to flow in the form of a steady current.
- Such steady electric fields are generated by cells and batteries.
Question 7.
State the sign convention used to show the flow of electric current in a circuit.
Answer:
The direction of the current in a circuit is drawn in the direction in which positively charged particles would move, even if the current is constituted by the negatively charged particles, (electrons), which move in the direction opposite to that the electric field.
Question 8.
Explain the concept of drift velocity with neat diagrams.
Answer:
i. When no current flows through a copper rod, the free electrons move in random motion. Therefore, there is no net motion of these electrons in any direction.
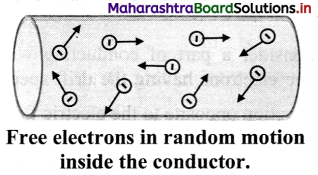
ii. If an electric field is applied along the length of the copper rod, a current is set up in the rod. The electrons inside rod still move randomly, but tend to ‘drift’ in a particular direction.
iii. Their direction is opposite to that of the applied electric field.
iv. The electrons under the action of the applied electric field drift with a drift speed vd.
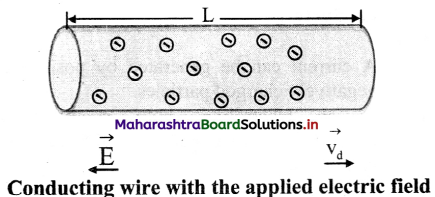
Question 9.
What is current density? State its SI unit.
Answer:
i. Current density at a point in a conductor is the amount of current flowing per unit area of the conductor.
Current density, J = \(\frac {I}{A}\)
where, I = Current
A = Area of cross-section
ii. SI unit: A/m²
Question 10.
A metallic wire of diameter 0.02 m contains 10 free electrons per cubic metre. Find the drift velocity for free electrons, having an electric current of 100 amperes flowing through the wire.
(Given: charge on electron = 1.6 × 10-19C)
Answer:
Given: e = 1.6 × 10-19 C, n = 1028 electrons/m³,
D = 0.02 m, r = D/2 = 0.01 m,
I = 100 A
To find: Drift velocity (vd)
Formula: vd = \(\frac {I}{nAe}\)
Calculation: From formula,
vd = \(\frac {I}{nπr^2e}\)
∴ vd = \(\frac {100}{10^{28}×3.142×10^{-4}×1.6×10^{-19}}\)
= \(\frac {10^{-3}}{3.142×1.6}\)
= 1.989 × 10-4 m/s
Question 11.
A copper wire of radius 0.6 mm carries a current of 1 A. Assuming the current to be uniformly distributed over a cross sectional area, find the magnitude of current density. Answer:
Given: r = 0.6 mm = 0.6 × 10-3 m, I = 1 A
To find: Current density (J)
Formula: J = \(\frac {I}{A}\)
Calculation: From formula,
J = \(\frac {1}{3.142×(0.6)^2×10^{-6}}\)
= 0.884 × 106 A/m²
Question 12.
A metal wire of radius 0.4 mm carries a current of 2 A. Find the magnitude of current density if the current is assumed to be uniformly distributed over a cross sectional area.
Answer:
Given: r = 0.4 mm = 0.4 × 10-3 m, I = 2 A
To find: Current density (J)
Formula: J = \(\frac {I}{A}\)
Calculation: From formula,
J = \(\frac {2}{3.142×(0.4)^2×10^{-6}}\)
= 3.978 × 106 A/m²
Question 13.
State and explain ohm’s law.
Answer:
Statement: The current I through a conductor is directly proportional to the potential difference V applied across its two ends provided the physical state of the conductor is unchanged.
Explanation:
According to ohm’s law,
I ∝ V
∴ V = IR or R = \(\frac {V}{I}\)
where, R is proportionality constant and is called the resistance of the conductor.

Question 14.
Draw a graph showing the I-V curve for a good conductor and ideal conductor.
Answer:
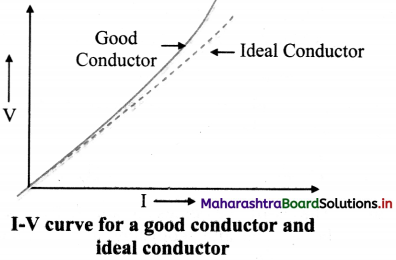
Question 15.
Define one ohm.
Answer:
If potential difference of 1 volt across a conductor produces a current of 1 ampere through it, then the resistance of the conductor is one ohm.
Question 16.
Define conductance. State its SI unit.
Answer:
- Reciprocal of resistance is called conductance.
C = \(\frac {I}{R}\)
- S.I unit statement or Ω-1
Question 17.
Explain the concept of electrical conduction in a conductor.
Answer:
- Electrical conduction in a conductor is due to mobile charge carriers (electrons).
- These conduction electrons are free to move inside the volume of the conductor.
- During their random motion, electrons collide with the ion cores within the conductor. Assuming that electrons do not collide with each other these random motions average out to zero.
- On application of an electric field E, the motion of the electron is a combination of the random motion of electrons due to collisions and that due to the electric field \(\vec{E}\).
- The electrons drift under the action of the field \(\vec{E}\) and move in a direction opposite to the direction of the field \(\vec{E}\). In this way electrons in a conductor conduct electricity.
Question 18.
Derive expression for electric field when an electron of mass m is subjected to an electric field (E).
Answer:
i. Consider an electron of mass m subjected to an electric field E. The force experienced by the electron will be \(\vec{F}\) = e\(\vec{E}\).
ii. The acceleration experienced by the electron will then be
\(\vec{a}\) = \(\frac {e\vec{E}}{m}\) …………. (1)
iii. The drift velocities attained by electrons before and after collisions are not related to each other.
iv. After the collision, the electron will move in random direction, but will still drift in the direction opposite to \(\vec{E}\).
v. Let τ be the average time between two successive collisions.
vi. Thus, at any given instant of time, the average drift speed of the electron will be,
vd = a τ = \(\frac {eEτ}{m}\) ………………(From 1)
vd = \(\frac {eEτ}{m}\) = \(\frac {J}{ne}\) ……………(2) [∵ vd = \(\frac {J}{ne}\)]
vii. Electric field is given by,
E = (\(\frac {m}{e^2nτ}\))J ………… (from 2)
= ρJ = [∵ ρ = \(\frac {m}{ne^2τ}\)]
where, ρ is resistivity of the material.
Question 19.
A Flashlight uses two 1.5 V batteries to provide a steady current of 0.5 A in the filament. Determine the resistance of the glowing filament.
Answer:
Given: For each battery, V1 = V2 = 1.5 volt,
I = 0.5 A
To find: Resistance (R)
Formula: V = IR
Calculation: Total voltage, V = V1 + V2 = 3 volt
From formula,
R = \(\frac {V}{I}\) = \(\frac {3}{0.5}\) = 6.0 Ω
Question 20.
State an expression for resistance of non-ohmic devices and draw I-V curve for such devices.
Answer:
i. Resistance (R) of a non-ohmic device at a particular value of the potential difference V is given by,
R = \(\lim _{\Delta I \rightarrow 0} \frac{\Delta V}{\Delta I}=\frac{d V}{d I}\)
where, ∆V = potential difference between the
two values of potential V – \(\frac {∆V}{2}\) to V + \(\frac {∆V}{2}\),
and ∆I = corresponding change in the current.
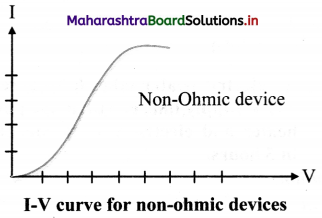
Question 21.
Derive an expression for decrease in potential energy when a charge flows through an external resistance in a circuit.
Answer:
i. Consider a resistor AB connected to a cell in a circuit with current flowing from A to B.
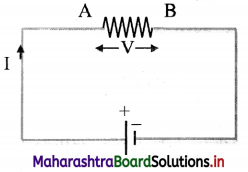
ii. The cell maintains a potential difference V between the two terminals of the resistor, higher potential at A and lower at B.
iii. Let Q be the charge flowing in time ∆t through the resistor from A to B.
iv. The potential difference V between the two points A and B, is equal to the amount of work (W) done to carry a unit positive charge from A to B.
∴ V = \(\frac {W}{Q}\)
v. The cell provides this energy through the charge Q, to the resistor AB where the work is performed.
vi. When the charge Q flows from the higher potential point A to the lower potential point B, there is decrease in its potential energy by an amount
∆U = QV = I∆tV
where I is current due to the charge Q flowing in time ∆t.
Question 22.
Prove that power dissipated across a resistor is responsible for heating up the resistor. Give an example for it.
OR
Derive an expression for the power dissipated across a resistor in terms of its resistance R.
Answer:
i. When a charge Q flows from the higher potential point to the lower potential point, its potential energy decreases by an amount,
∆U = QV = I∆tV
where I is current due to the charge Q flowing in time ∆t.
ii. By the principle of conservation of energy, this energy is converted into some other form of energy.
iii. In the limit as ∆t → 0, \(\frac {dU}{dt}\) = IV
Here, \(\frac {dU}{dt}\) is power, the rate of transfer of energy ans is given by p = \(\frac {dU}{dt}\) = IV
Hence, power is transferred by the cell to the resistor or any other device in place of the resistor, such as a motor, a rechargeable battery etc.
iv. Due to the presence of an electric field, the free electrons move across a resistor and their kinetic energy increases as they move.
v. When these electrons collide with the ion cores, the energy gained by them is shared among the ion cores. Consequently, vibrations of the ions increase, resulting in heating up of the resistor.
vi. Thus, some amount of energy is dissipated in the form of heat in a resistor.
vii. The energy dissipated per unit time is actually the power dissipated which is given by,
P = \(\frac {V^2}{R}\) = I²R
Hence, it is the power dissipation across a resistor which is responsible for heating it up.
viii. For example, the filament of an electric bulb heats upto incandescence, radiating out heat and light.
Question 23.
Calculate the current flowing through a heater rated at 2 kW when connected to a 300 V d. c. supply.
Answer:
Given: P = 2 kW = 2000 W, V = 300 V
To find: Current (I)
Formula: P = IV
Calculation: From formula,
I = \(\frac {P}{V}\) = \(\frac {2000}{300}\) = 6.67 A
Question 24.
An electric heater takes 6 A current from a 230 V supply line, calculate the power of the heater and electric energy consumed by it in 5 hours.
Answer:
Given: I = 6 A, V = 230 V, t = 5 hours
To find: Power (P), Energy consumed
Formulae: i. P = IV
ii. Energy consumed = power × time
Calculation: From formula (i),
P = 6 × 230
= 1380 W = 1.38 kW
From formula (ii),
Energy consumed = 1.38 × 5 = 6.9 kWh
= 6.9 units

Question 25.
When supplied a voltage of 220 V, an electric heater takes 6 A current. Calculate the power of heater and electric energy consumed by its in 2 hours?
Answer:
Given: I = 6 A, V = 220 volt, t = 2 hour
To find: i. Power of heater (P)
ii. Electric energy consumed (E)
Formulae: i. P = IV
ii. Electric energy consumed
= Power × time
Calculation: From formula (i),
P = 6 × 220 = 1320 W = 1.32 kW
From formula (ii),
Electric energy consumed
= 1.32 × 2 = 2.64 kWh = 2.64 units
Question 26.
Explain the colour code system for resistors with an example.
Answer:
i. In colour code system, resistors has 4 bands on it.
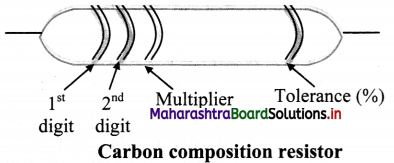
ii. In the four band resistor, the colour code of the first two bands indicate two numbers and third band often called decimal multiplier.
iii. The fourth band separated by a space from the three value bands, indicates tolerance of the resistor.
iv. Following table represents the colour code of carbon resistor.
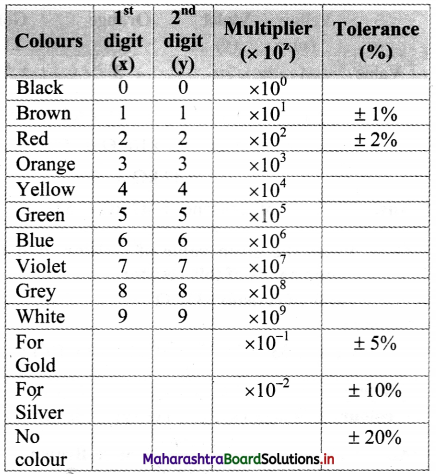
v. Example:
Let the colours of the rings of a resistor starting from one end be brown, red and orange and gold at the other end. To determine resistance of resistor we have,
x = 1, y = 2, z = 3 (From colour code table)
∴ Resistance = xy × 10z Ω ± tolerance
= 12 × 10³ Ω ± 5%
= 12 kΩ ± 5%
[Note: To remember the colours in order learn the Mnemonics: B.B. ROY of Great Britain had Very Good Wife]
Question 27.
Explain the concept of rheostat.
Answer:
- A rheostat is an adjustable resistor used in applications that require adjustment of current or resistance in an electric circuit.
- The rheostat can be used to adjust potential difference between two points in a circuit, change the intensity of lights and control the speed of motors, etc.
- Its resistive element can be a metal wire or a ribbon, carbon films or a conducting liquid, depending upon the application.
- In hi-fi equipment, rheostats are used for volume control.
Question 28.
Explain series combination of resistors.
Answer:
i. In series combination, resistors are connected in single electrical path. Hence, the same electric current flows through each resistor in a series combination.
ii. Whereas, in series combination, the supply voltage between two resistors R1 and R2 is divided into V1 and V2 respectively.
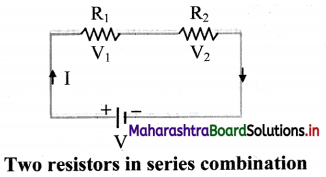
iii. According to Ohm’s law,
R1 = \(\frac {V_1}{I}\), R2 = \(\frac {v_2}{I}\)
Total Voltage, V = V1 + V2
= I(R1 + R2)
∴ V = I Rs
Thus, the equivalent resistance of the series circuit is, Rs = R1 + R2
iv. When a number of resistors are connected in series, the equivalent resistance is equal to the sum of individual resistances.
For ‘n’ number of resistors,
Rs = R1 + R2 + R2 + ………….. + Rn = \(\sum_{i=1}^{i=n} R_{i}\)
Question 29.
Explain parallel combination of resistors.
Answer:
i. In parallel combination, the resistors are connected in such a way that the same voltage is applied across each resistor.
ii. A number of resistors are said to be connected in parallel if all of them are connected between the same two electrical points each having individual path.
iii. In parallel combination, the total current I is divided into I, and I2 as shown in the circuit diagram.
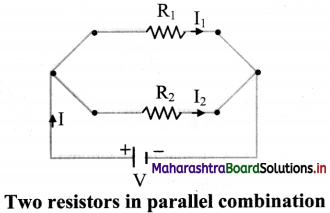
iv. Since voltage V across them remains the same,
I = I1 + I2
where I1 is current flowing through R1 and I2 is current flowing through R2.
v. When Ohm’s law is applied to R1,
V = I1R1
i.e. I1 = \(\frac {V}{R_1}\) ………(1)
When Ohm’s law applied to R2,
V = I2R2
i.e., I2 = \(\frac {V}{R_2}\) …………(2)
vi. Total current is given by,
I = I1 + I2
∴ I = \(\frac {V}{R_1}\) + \(\frac {V}{R_2}\) ………[From (1) and (2)]
Since, I = \(\frac {V}{R_p}\)
∴ \(\frac {V}{R_p}\) = \(\frac {V}{R_1}\) + \(\frac {V}{R_2}\)
∴ \(\frac {1}{R_p}\) = \(\frac {1}{R_1}\) + \(\frac {1}{R_2}\)
Where, Rp is the equivalent resistance in parallel combination.
vii. If ‘n’ number of resistors R1, R2, R3, ………….. Rn are connected in parallel, the equivalent resistance of the combination is given by
\(\frac {1}{R_p}\) = \(\frac {1}{R_1}\) + \(\frac {1}{R_2}\) + \(\frac {1}{R_3}\) ……….. + \(\frac {1}{R_n}\) = \(\sum_{i=1}^{\mathrm{i}=\mathrm{n}} \frac{1}{\mathrm{R}}\)
Thus, when a number of resistors are connected in parallel, the reciprocal of the equivalent resistance is equal to the sum of the reciprocals of individual resistances.
Question 30.
Colour code of resistor is Yellow-Violet- Orange-Gold. Find its value.
Answer:
|
Yellow (x) |
Violet (y) |
Orange (z) |
Gold (T%) |
| Value |
4 |
7 |
3 |
± 5 |
Value of resistance: xy × 10z Ω ± tolerance
∴ Value of resistance = 47 × 10³ Ω ± 5%
= 47 kΩ ± 5%

Question 31.
From the given value of resistor, find the colour bands of this resistor.
Value of resistor: 330 Ω
Answer:
Value = 330 Ω = 33 × 101 Ω = xy × 10z Ω
| Value |
3 |
3 |
1 |
| Colour |
Orange (x) |
Orange (y) |
Broen(z) |
ii. Given: Green – Blue – Red – Gold
Question 32.
Evaluate resistance for the following colour-coded resistors:
i. Yellow – Violet – Black – Silver
ii. Green – Blue – Red – Gold
ill. Brown – Black – Orange – Gold
Answer:
i. Given: Yellow – Violet – Black – Silver
To find: Value of resistance
Formula: Value of resistance
= (xy × 10z ± T%)Ω
| Colour |
Yellow (x) |
Violet (y) |
Black (z) |
Sliver (T%) |
| Code |
4 |
7 |
0 |
±10 |
Hence x = 4, y = 7, z = 0, T = 10%
Value of resistance = (xy ×10z ± T%) Ω
= (47 × 10° ± 10%) Ω
Value of resistance = 47 Ω ± 10%
To find: Value of resistance
Formula: Value of resistance
= (xy × 10z ± T%) Ω
Calculation:
| Colour |
Green (x) |
Blue (y) |
Red (z) |
Gold (T%) |
| Code |
5 |
6 |
2 |
±5 |
Hence x = 5, y = 6, z = 2, T = 5%
Value of resistance = (xy × 10z ± T%) Q
= 56 × 102 Ω ± 5%
= 5.6 k Ω ± 5%
iii. Given: Brown – Black – Orange – Gold
To find: Value of the resistance
Formula: Value of the resistance
= (xy × 10z ± T%) Ω
Calculation:
| Colour |
Brown (x) |
Black (y) |
Orange (z) |
Gold (T%) |
| Code |
1 |
0 |
3 |
±5 |
Hence x = 1, y = 0, z = 3, T = 5%
Value of resistance = (xy × 10z ± T%) Ω
= 10 × 10³ Ω ± 5%
= 10 kΩ ± 5%
Question 33.
Calculate
i. total resistance and
ii. total current in the following circuit.
R1 = 3 Ω, R2 = 6 Ω, R3 = 5 Ω, V = 14 V
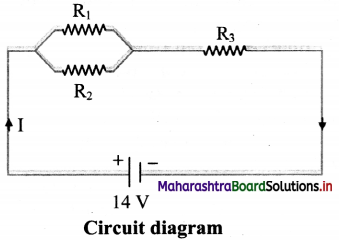
Answer:
i. R1 and R2 are connected in parallel. This combination (Rp) is connected in series with R3.
∴ Total resistance, RT = Rp + R3
Rp = \(\frac {R_1R_2}{R_1+R_2}\) = \(\frac {3×6}{3+6}\) = 2 Ω
∴ RT = 2+ 5 = 7 Ω
ii. Total current: I = \(\frac {V}{R_T}\) = \(\frac {14}{7}\) = 2 A
Question 34.
State the factors affecting resistance of a conductor.
Answer:
Factors affecting resistance of a conductor:
- Length of conductor
- Area of cross-section
- Nature of material
Question 35.
Derive expression for specific resistance of a material.
Answer:
At a particular temperature, the resistance (R) of a conductor of uniform cross section is
i. directly proportional to its length (l),
i.e., R ∝ l ……….. (1)
ii. inversely proportional to its area of cross section (A),
R ∝ \(\frac {1}{A}\) ……….. (1)
From equations (1) and (2),
R = ρ\(\frac {l}{A}\)
where ρ is a constant of proportionality and it is called specific resistance or resistivity of the material of the conductor at a given temperature.
iii. Thus, resistivity is given by,
ρ = \(\frac {RA}{l}\)
Question 36.
State SI unit of resistivity.
Answer:
SI unit of resistivity is ohm-metre (Ω m).
Question 37.
What is conductivity? State its SI unit.
Answer:
i. Reciprocal of resistivity is called as conductivity of a material.
Formula: σ = \(\frac {1}{ρ}\)
ii. SI unit: (\(\frac {1}{ohm m}\)) or siemens/metre
Question 38.
Explain the similarities between R = \(\frac {V}{I}\) and ρ = \(\frac {E}{J}\)
Answer:
- Resistivity (ρ) is a property of a material, while the resistance (R) refers to a particular object.
- The electric field \(\vec{E}\) at a point is specified in a material with the potential difference across the resistance and the current density \(\vec{J}\) in a material is specified instead of current I in the resistor.
- For an isotropic material, resistivity is given by ρ = \(\frac {E}{J}\)
For a particular resistor, the resistance R given by, R = \(\frac {V}{I}\)
Question 39.
State expression for current density in terms of conductivity.
Answer:
Current density, \(\vec{J}\) = \(\frac {1}{ρ}\) \(\vec{E}\) = σ \(\vec{E}\)
where, ρ = resistivity of the material
E = electric field intensity
σ = conductivity of the material
Question 40.
Calculate the resistance per metre, at room temperature, of a constantan (alloy) wire of diameter 1.25 mm. The resistivity of constantan at room temperature is 5.0 × 10-7 Ωm.
Answer:
Given: ρ = 5.0 × 10-7 Ω m, d = 1.25 × 10-3 m,
∴ r = 0.625 × 10-3 m
To find: Resistance per metre (\(\frac {R}{l}\))
Formula: ρ = \(\frac {RA}{l}\)
Calculation:
From formula,
\(\frac{\mathrm{R}}{l}=\frac{\rho}{\mathrm{A}}=\frac{\rho}{\pi \mathrm{r}^{2}}\)
= \(\frac{5 \times 10^{-7}}{3.142 \times\left(0.625 \times 10^{-3}\right)^{2}}\)
= \(\frac{5}{3.142 \times 0.625^{2}} \times 10^{-1}\)
= { antilog [log 5 – log 3.142 -2 log 0.625]} × 10-1
= {antilog [ 0.6990 – 0.4972 -2(1.7959)]} × 10-1
= {antilog [0.2018- 1.5918]} × 10-1
= {antilog [0.6100]} × 10-1
= 4.074 × 10-1
∴ \(\frac {R}{l}\) ≈ 0.41 Ω m-1
Question 41.
A negligibly small current is passed through a wire of length 15 m and uniform cross-section 6 × 10-7 m², and its resistance is measured to be 5 Ω. What is the resistivity of the material at the temperature of the experiment?
Answer:
Given: l = 15 m, A = 6.0 × 10-7 m², R = 5 Ω
To find: Resistivity (ρ)
Formula: ρ = \(\frac {RA}{l}\)
Calculation: From formula,
ρ = \(\frac {5×6×10^{-7}}{15}\)
∴ ρ = 2 × 10-7 Ω m
Question 42.
A constantan wire of length 50 cm and 0.4 mm diameter is used in making a resistor. If the resistivity of constantan is 5 × 10-7m, calculate the value of the resistor.
Answer:
Given: l = 50 cm = 0.5 m,
d = 0.4 mm = 0.4 × 10-3 m,
r = 0.2 × 10-3 m, p = 5 × 10-7 Ωm
To Find: Value of resistor (R)
Formula: ρ = \(\frac {RA}{l}\)
Calculation: from formula,
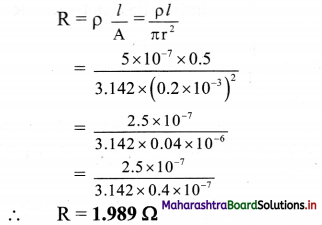
Question 43.
The resistivity of nichrome is 10-6 Ωm. What length of a uniform wire of this material and of 0.2 mm diameter will have a resistance of 200 ohm?
Answer:
Given: ρ = 10-6 Ω m, d = 0.2 mm,
∴ r = 0.1 mm = 0.1 × 10-3 m, R = 200 Ω
To find: Length (l)
Formula: R = \(\frac {ρl}{A}\) = \(\frac {ρl}{πr^2}\)
Calculation: From formula,
l = \(\frac {πr^2}{ρ}\)
∴ l = \(\frac{200 \times 3.142 \times\left(0.1 \times 10^{-3}\right)^{2}}{10^{-6}}\) = 6 284 m

Question 44.
A wire of circular cross-section and 30 ohm resistance is uniformly stretched until its new length is three times its original length. Find its resistance.
Answer:
Given: R1 = 30 ohm,
l1 = original length, A1 = original area,
l2 = new length, A2 = new area
l2= 3l1
To find: Resistance (R2)
Formula: R= ρ\(\frac {l}{A}\)
Calculation: From formula,

The volume of wire remains the same in two cases, we have

Question 45.
Define temperature coefficient of resistivity. State its SI unit.
Answer:
i. The temperature coefficient of resistivity is defined as the increase in resistance per unit original resistance at the chosen reference temperature, per degree rise in temperature.
α = \(\frac{\rho-\rho_{0}}{\rho_{0}\left(T-T_{0}\right)}\)
= \(\frac{\mathrm{R}-\mathrm{R}_{0}}{\mathrm{R}_{0}\left(\mathrm{~T}-\mathrm{T}_{0}\right)}\)
For small difference in temperatures,
α = \(\frac {1}{R_0}\) \(\frac {dR}{dT}\)
ii. SI unit: °C-1 (per degree Celsius) or K-1 (per kelvin).
Question 46.
Give expressions for variation of resistivity and resistance with temperature. Represent graphically the temperature dependence of resistivity of copper.
Answer:
i. Resistivity is given by,
ρ = ρ0 [1 + α (T – T0)] where,
T0 = chosen reference temperature
ρ0 = resistivity at the chosen temperature
α = temperature coefficient of resistivity
T = final temperature
ii. Resistance is given by,
R = R0 [1+ α (T – T0)]
Where,
T0 = chosen reference temperature
R0 = resistance at the chosen temperature
α = temperature coefficient of resistance
T = final temperature
iii. For example, for copper, the temperature dependence of resistivity can be plotted as shown:
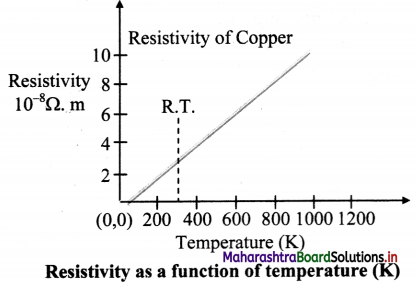
Question 47.
What is super conductivity?
Answer:
- The resistivity of a metal decreases as the temperature decreases.
- In case of some metals and metal alloys, the resistivity suddenly drops to zero at a particular temperature (Tc), this temperature is called critical temperature.
- Super conductivity is the phenomenon where resistivity of a material becomes zero at particular temperature.
- For example, mercury loses its resistance completely to zero at 4.2 K.
Question 48.
A piece of platinum wire has resistance of 2.5 Ω at 0 °C. If its temperature coefficient of resistance is 4 × 10-3/°C. Find the resistance of the wire at 80 °C.
Answer:
Given: R0 = 2.5 Ω
α = 4 × 10-3/°C = 0.004/°C
T = 80 °C
To find: Resistance at 80 °C (RT)
Formula: RT = R0(l + α T)
Calculation: From formula,
RT = 2.5 [1+ (0.004 × 80)]
= 2.5(1 + 0.32)
RT = 2.5 × 1.32
RT = 3.3 Ω
Question 49.
The resistance of a tungsten filament at 150 °C is 133 ohm. What will be its resistance at 500 °C? The temperature coefficient of resistance of tungsten is 0.0045 per °C.
Answer:
Given: Let resistance at 150 °C be R1 and resistance at 500 °C be R2
Thus,
R1= 133 Ω, α = 0.0045 °C-1
To find: Resistance (R2)
Formula: RT = R0 (1 + α∆T)
Calculation:
From formula,
R1 = R0 (1 + α × 150)
∴ 133 = R0(1 + 0.0045 × 150) ……….(i)
R2 = R0 (1 + α × 500)
∴ R2 = R0(1 + 0.0045 × 500) ………(ii)
Dividing equation (ii) by (i), we get
\(\frac{\mathrm{R}_{2}}{133}=\frac{1+(0.0045 \times 500)}{1+(0.0045 \times 150)}=\frac{3.25}{1.675}\)
∴ R2 = \(\frac {3.25}{1.675}\) × 133 = 258 Ω
Question 50.
A silver wire has resistance of 2.1 Ω at 27.5 °C. If temperature coefficient of silver is 3.94 × 10-3/°C, find the silver wire resistance at 100 °C.
Answer:
Given: R1 = 2.1 Ω, T1 = 27.5 °C,
α = 3.94 × 10-3/°C, T2 = 100 °C
To find: Resistance (R2)
Formula: RT = Ro (1 + αT)
Calculation:
From the formula,
R1 = R0(1 + α × 27.5) ……….. (i)
R2 = R0(l + α × 100) ………….. (ii)
Dividing equation (i) by (ii), we get,
\(\frac{\mathrm{R}_{1}}{\mathrm{R}_{2}}=\frac{1+\left(3.94 \times 10^{-3} \times 27.5\right)}{1+\left(3.94 \times 10^{-3} \times 100\right)}\)
\(\frac{\mathrm{R}_{1}}{\mathrm{R}_{2}}=\frac{1.10835}{1.394}\) = 0.795
∴ R2 = \(\frac{\mathrm{R}_{1}}{0.795}=\frac{2.1}{0.795}\) = 2.641 Ω
Question 51.
At what temperature would the resistance of a copper conductor be double its resistance at 0 °C?
(a for copper = 3.9 × 10-3/°C)
Answer:
Given: Let the resistance of the conductor at 0°C be R0
R1 = R0 at T1 = 0°C
R2 = 2R0 at T2 = T
To find: Final temperature (T)
Formula: α = \(\frac {R_2-R_1}{R_1(T_2-T_1)}\)
Calculation: From formula,
α = \(\frac {2R_0-R_0}{R_1(T_2-T_1)}\) = \(\frac {1}{T}\)
∴ T = \(\frac {1}{α}\) = \(\frac {1}{3.9×10^{-3}}\) ≈ 256 °C
Question 52.
A conductor has resistance of 15 Ω at 10 °C and 18 Ω at 400 °C. Find the temperature coefficient of resistance of the material.
Answer:
Given: R1 = 15 Ω, T1 = 10 °C, R2 = 18 Ω,
T2 = 400 °C
To find: Temperature coefficient of resistance (α)
Formula: RT = R0 (1 + αT)
Calculation:
From formula,
R1 = R0 (1 + α × 10) ……..(i)
R2 = R0 (1 + α × 400) …….(ii)
Dividing equation (i) by (ii), we get,
\(\frac{\mathrm{R}_{1}}{\mathrm{R}_{2}}=\frac{1+(\alpha \times 10)}{1+(\alpha \times 400)}\)
∴ \(\frac{15}{18}=\frac{1+10 \alpha}{1+400 \alpha}\)
∴ 18 + 180 α = 15 + 6000 α
∴ 5820 α = 3
∴ α = \(\frac {3}{5820}\) = 5.155 × 10-4/°C
Question 53.
Write short note on e.m.f. devices.
Answer:
- When charges flow through a conductor, a potential difference get established between the two ends of the conductor.
- For a steady flow of charges, this potential difference is required to be maintained across the two ends of the conductor.
- There is a device that does so by doing work on the charges, thereby maintaining the potential difference. Such a device is called an emf device and it provides the emf E.
- The charges move in the conductor due to the energy provided by the emf device. This energy is supplied by the e.m.f. device on account of its work done.
- Power cells, batteries, Solar cells, fuel cells, and even generators, are some examples of emf devices.

Question 54.
Explain working of a circuit when connected to emf device.
Answer:
i. A circuit is formed with connecting an emf device and a resistor R. Flere, the emf device keeps the positive terminal (+) at a higher electric potential than the negative terminal (-)
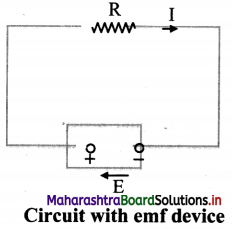
ii. The emf is represented by an arrow from the negative terminal to the positive terminal.
iii. When the circuit is open, there is no net flow of charge carriers within the device.
iv. When connected in a circuit, the positive charge carriers move towards the positive terminal which acts as cathode inside the emf device.
v. Thus, the positive charge carriers move from the region of lower potential energy, to the region of higher potential energy.
vi. Consider a charge dq flowing through the cross section of the circuit in time dt.
vii. Since, same amount of charge dq flows throughout the circuit, including the emf device. Hence, the device must do work dW on the charge dq, so that the charge enters the negative terminal (low potential terminal) and leaves the positive terminal (higher potential terminal).
viii. Therefore, e.m.f. of the emf device is,
E = \(\frac {dW}{dq}\)
The SI unit of emf is joule/coulomb (J/C).
Question 55.
What is an ideal e.m.f. device?
Answer:
- In an ideal e.m.f. device, there is no internal resistance to the motion of charge carriers.
- The emf of the device is then equal to the potential difference across the two terminals of the device.
Question 56.
What is a real e.m.f. device?
Answer:
- In a real emf device, there is an internal resistance to the motion of charge carriers.
- If such a device is not connected in a circuit, there is no current through it.
Question 57.
Derive an expression for current flowing through a circuit when an external resistance is connected to a real e.m.f. device.
Answer:
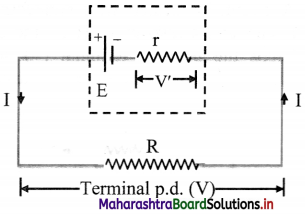
i. If a current (I) flows through an emf device, there is an internal resistance (r) and the emf (E) differs from the potential difference across its two terminals (V).
V = E – Ir ……… (1)
ii. The negative sign is due to the fact that the current I flows through the emf device from the negative terminal to the positive terminal.
iii. By the application of Ohm’s law,
V = IR …….(2)
From equations (1) and (2),
IR = E – Ir
∴ \(\frac {E}{R+r}\)
Question 58.
Explain the conditions for maximum current.
Answer:
- Current in a circuit is given by, I = \(\frac {E}{R+r}\)
- Maximum current can be drawn from the emf device, only when R = 0, i.e.
Imax = \(\frac {E}{R}\)
- Imax is the maximum allowed current from an emf device (or a cell) which decides the maximum current rating of a cell or a battery.
Question 59.
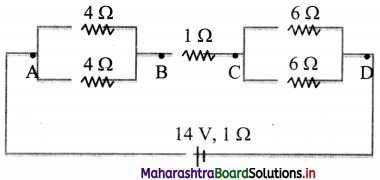
A network of resistors is connected to a 14 V battery with internal resistance 1 Q as shown in the circuit diagram.
i. Calculate the equivalent resistance,
ii. Current in each resistor,
iii. Voltage drops VAB, VBC and VDC.
Answer:
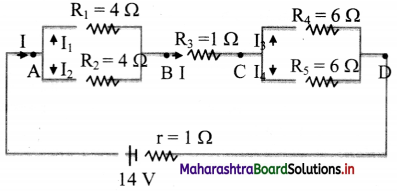
For equivalent resistance (Req):
RAB is given as,
\(\frac{1}{\mathrm{R}_{\mathrm{AB}}}=\frac{1}{\mathrm{R}_{1}}+\frac{1}{\mathrm{R}_{2}}=\frac{1}{4}+\frac{1}{4}=\frac{2}{4}\)
∴ RAB = 2 Ω
RBC = R3 = 1 Ω
Also, RCD is given as,
\(\frac{1}{\mathrm{R}_{\mathrm{CD}}}=\frac{1}{\mathrm{R}_{4}}+\frac{1}{\mathrm{R}_{5}}=\frac{1}{6}+\frac{1}{6}=\frac{2}{6}\)
∴ RCD = 3 Ω
∴ Req = RAB + RBC + RCD
= 2 + 1 + 3 = 6Ω
ii. Current through each resistor:
Total current, I = \(\frac{\mathrm{E}}{\mathrm{R}_{\mathrm{eq}}+\mathrm{r}}\) = \(\frac {14}{6+1}\) = 2 A
Across AB, as, R1 = R2
V1 = V2
∴I1 × 4 = I2 × 4
∴ I1 = I2
But, I1 + I2 = I
∴ 2I1 = I
∴ I1 = I2 =1 A ….(∵I = 2 A)
Similarly, as R4 = R5
I3 = I4 = 1 A
Current through resistor BC is same as I.
∴ IBC = 2 A
iii. Voltage drops across AB, BC and CD:
VAB = IRAB = 2 × 2 = 4 V
VBC = IRBC = 2 × 1 = 2 V
VCD = IRCD = 2 × 3 = 6 V
Question 60.
i. Three resistors 2 Ω, 4 Ω and 5 Ω are combined in parallel. What is the total resistance of the combination?
ii. If the combination is connected to a battery of e.m.f. 20 V and negligible internal resistance, determine the current through each resistor and the total current drawn from the battery.
Answer:
Given: R1 = 2Ω, R2 = 4 Ω, R3 = 5 Ω,
V = 20 V
To Find: i. Total resistance (R)
ii. Current through each resistor (I1, I2, I3 respectively)
iii. Total current (I)
Formulae:
i. \(\frac{1}{\mathrm{R}}=\frac{1}{\mathrm{R}_{1}}+\frac{1}{\mathrm{R}_{2}}+\frac{1}{\mathrm{R}_{3}}\)
ii. V = IR
iii. Total current, I = I1 +I2 + I3
Calculation
From formula (i):
\(\frac{1}{R}=\frac{1}{2}+\frac{1}{4}+\frac{1}{5}=\frac{19}{20}\)
∴ R = \(\frac {20}{19}\) Ω
From formula (ii):
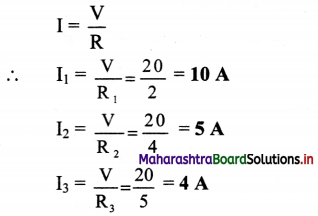
From formula (iii):
I = 10 + 5 + 4
∴ I = 19 A
Question 61.
i. Three resistors 1 Ω, 2 Ω and 3 Ω are combined in series. What is the total resistance of the combination?
ii. If the combination is connected to a battery of e.m.f. 12 V and negligible internal resistance, obtain the potential drop across each resistor.
Answer:
Given: R1 = 1Ω, R2 = 2 Ω, R3 = 3 Ω,
V = 12 V
To Find: i. Total resistance (R)
ii. P.D Across R1, R2, R3 (V1, V2, V3 respectively)
Formulae:
i. Rs = R1 + R2 + R3
ii. V = IR
Calculation
From formula (i):
Rs = l + 2 + 3 = 6 Ω
From formula (ii),
1 = \(\frac {V}{R}\) = \(\frac {12}{6}\) = 2A
∴ V1 = IR1 = 2 × 1 = 2 V
∴ V2 = IR2 = 2 × 2 = 4 V
∴ V3 = IR3 = 2 × 3 = 6 V

Question 62.
A voltmeter is connected across a battery of emf 12 V and internal resistance of 10 Ω. If the voltmeter resistance is 230 Ω, what reading will be shown by the voltmeter? Answer:
Given: E = 12 volt, r = 10 Ω, R = 230 Ω
To find: Reading shown by voltmeter (V)
Formula: i. I = \(\frac {E}{R+r}\)
ii. V = E – Ir
Calculation
From formula (i),
I = \(\frac{12}{230+10}=\frac{12}{240}=\frac{1}{20} \mathrm{~A}\)
From formula (ii),
V= 12 – \(\frac {1}{20}\) × 10 = 12 – 0.5
= 11.5 volt
Question 63.
A battery of e.m.f. 10 V and internal resistance 3 Ω is connected to a resistor. If the current in the circuit is 0.5 A, what is the resistance of the resistor? What is the terminal voltage of the battery when the circuit is closed?
Answer:
Given: E = 10 V, r = 3 Ω, I = 0.5 A
To find: i. Resistance of resistor (R)
ii. Terminal voltage of battery (V)
Formula: I = \(\frac {E}{R+r}\)
Calculation: From formula, R = \(\frac {E}{I}\) – r
∴ R = \(\frac {10}{0.5}\)– 3 = 17 Ω
∴ V = IR = 0.5 × 17 = 8.5 volt
Question 64.
How many cells each of 1.5 V/500 mA rating would be required in series-parallel combination to provide 1500 mA at 3 V?
Answer:
21 = ………… = 1.5 V (given)
I1 = I2 = …………… = 500 mA (given)
1500 mA at 3 V is required.
To determine required number of cells:
For series V = V1 + V2 + ………….., and current remains same.
For parallel I = I1 + I2 + ………, and voltage remains same.
To achieve battery output of 3V, the cells should be connected in series.
If n are the number of cells connected in series, then
V = V1 + V2 + …………. + Vn
∴ V = nV1
∴ 3 = n × 1.5
∴ n = 2 cells in series
The series combination of two cells in series will give a current 500 mA.
To achieve output of 1500 mA, the number of batteries (n) connected in parallel, each one having output 3V is,
I = I1 + I2 + ………. + In
∴ I = nI1
∴ 1500 = n × 500
∴ n = 3 batteries each of two cells
∴ No of cells required are 2 × 3 = 6 .
∴ Number of cells = 6
The six cells must be connected as shown

Question 65.
Explain the concept of series combination of cells.
Answer:
i. In a series combination, cells are connected in single electrical path, such that the positive terminal of one cell is connected to the negative terminal of the next cell, and so on.
ii. The terminal voltage of batteiy/cell is equal to the sum of voltages of individual cells in series. Example: Given figure shows two 1.5 V cells connected in series. This combination provides total voltage,
V = 1.5 V + 1.5 V = 3 V.
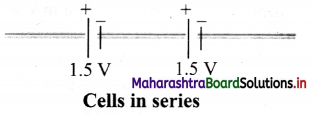
iii. The equivalent emf of n number of cells in series combination is the algebraic sum of their individual emf.
\(\sum_{i} \mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{i}}\) = E1 + E2 + E2+ …….. + En
iv. The equivalent internal resistance of n cells in a series combination is the sum of their individual internal resistance.
\(\sum_{i} \mathrm{r}_{\mathrm{i}}\) = r1 + r2 + r3 + ……… + rn
Question 66.
State advantages of cells in series.
Answer:
- The cells connected in series produce a larger resultant voltage.
- Cells which are damaged can be easily identified, hence can be easily replaced.
Question 67.
Explain combination of cells in parallel. Ans:
Answer:
i. Consider two cells which are connected in parallel. Here, positive terminals of all the cells are connected together and the negative terminals of all the cells are connected together.
ii. In parallel connection, the current is divided among the branches i.e. I1 and I2 as shown in figure.
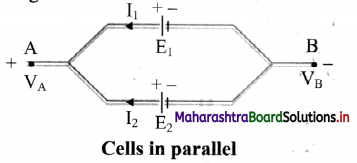
iii. Consider points A and B having potentials VA and VB, respectively.
iv. For the first cell the potential difference across its terminals is, V = VA – VB = E1 – I1 r1
∴ I1 = \(\frac {E_1V}{r_1}\) ………. (1)
v. Point A and B are connected exactly similarly to the second cell.
Hence, considering the second cell,
V = VA – VB = E2 – I2r2
∴ I2 = \(\frac {E_2V}{r_2}\) ………. (2)
vi. Since, I = I1 + I2 ………….. (3)
Combining equations (1), (2) and (3),
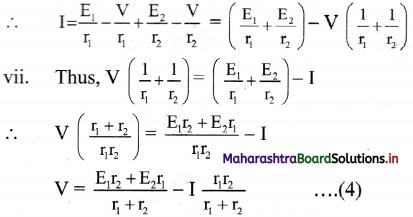
viii. If we replace the cells by a single cell connected between points A and B with the emf Eeq and the internal resistance req then,
V = Eeq– Ireq
From equations (4) and (5),
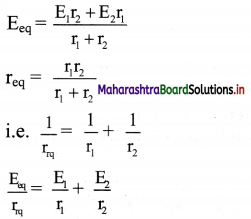
ix. For n number of cells connected in parallel with emf E1, E2, E3, ………….., En and internal resistance r1, r2, r3, …………, rn
\(\frac{1}{\mathrm{r}_{\mathrm{rq}}}=\frac{1}{\mathrm{r}_{1}}+\frac{1}{\mathrm{r}_{2}}+\frac{1}{\mathrm{r}_{3}}+\ldots \ldots \ldots+\frac{1}{\mathrm{r}_{\mathrm{n}}}\)
and \(\frac{\mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{eq}}}{\mathrm{r}_{\mathrm{rq}}}=\frac{\mathrm{E}_{1}}{\mathrm{r}_{1}}+\frac{\mathrm{E}_{2}}{\mathrm{r}_{2}}+\ldots \ldots \ldots+\frac{\mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{n}}}{\mathrm{r}_{\mathrm{n}}}\)
Question 68.
State advantages and disadvantages of cells in parallel.
Answer:
Advantages:
For cells connected in parallel in a circuit, the circuit will not break open even if a cell gets damaged or open.
Disadvantages:
The voltage developed by the cells in parallel connection cannot be increased by increasing number of cells present in circuit.
Question 69.
State the basic categories of electrical cells.
Answer:
Electrical cells can be divided into several categories like primary cell, secondary cell, fuel cell, etc.
Question 70.
Write short note on primary cell.
Answer:
- A primary cell cannot be charged again. It can be used only once.
- Dry cells, alkaline cells are different examples of primary cells.
- Primary cells are low cost and can be used easily. But these are not suitable for heavy loads.

Question 71.
Write short note on secondary cell.
Answer:
- The secondary cells are rechargeable and can be reused.
- The chemical reaction in a secondary cell is reversible.
- Lead acid cell and fuel cell are some examples of secondary cells.
- Lead acid battery is used widely in vehicles and other applications which require high load currents.
- Solar cells are secondary cells that convert solar energy into electrical energy.
Question 72.
Write short note on fuel cells vehicles.
Answer:
- Fuel cells vehicles (FCVs) are electric vehicles that use fuel cells instead of lead acid batteries to power the vehicles.
- Hydrogen is used as a fuel in fuel cells. The by product after its burning is water.
- This is important in terms of reducing emission of greenhouse gases produced by traditional gasoline fuelled vehicles.
- The hydrogen fuel cell vehicles are thus more environment friendly.
Question 73.
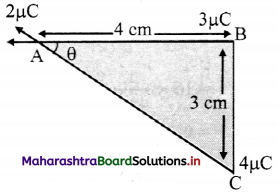
What can be concluded from the following observations on a resistor made up of certain material? Calculate the power drawn in each case.
| Case |
Current (A) |
Voltage (V) |
| A |
0.2 |
1.6 |
| B |
0.4 |
3.2 |
| C |
0.6 |
4.8 |
| d |
0.8 |
6.4 |
Answer:
i. As the ratio of voltage and current different readings are same, hence ohm’s is valid i.e., V = IR.
ii. Electric power is given by, P = IV
∴ (a) P1 = 0.2 × 1.6 = 0.32 watt
(b) P2 = 0.4 × 3.2 = 1.28 watt
(c) P3 = 0.6 × 4.8 = 2.88 watt
(d) P4 = 0.8 × 6.4 = 5.12 watt
Question 74.
Answer the following questions from the circuit given below. [S1, S2, S3, S4, S5 ⇒ Switches]. Calculate the current (I) flowing in the following cases:
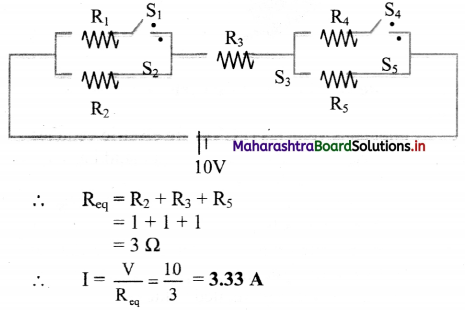
i. S1, S4 → open; S2, S3, S5 → closed.
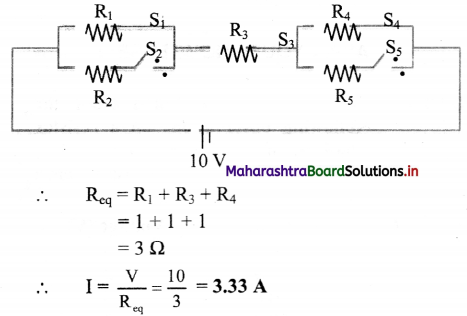
ii. S2, S5 → open; S1, S3, S4 → closed.
iii. S3 → open; S1, S2, S4, S5 → closed.
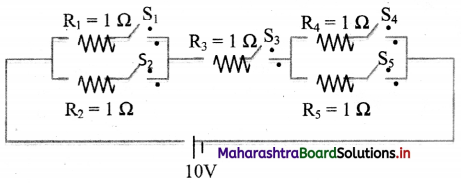
Answer:
i. Here, the circuit can be represented as,
ii. Here, the circuit can be represented as,
iii. Here, the circuit can be represented as,
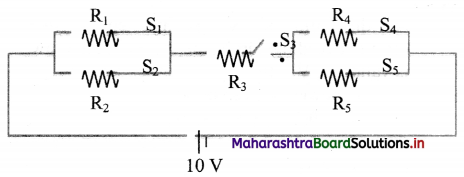
∴ As switch S3 is open, no current will flow in the circuit.
Question 75.
An electric circuit with a carton resistor and an electric bulb (60 watt, 300 Ω) are connected in series with a 230 V source.
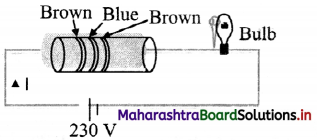
i. Calculate the current flowing through the circuit.
ii. If the electric bulb of 60 watt is replaced by an electric bulb (80 watt, 300 Ω), will it glow? Justify your answer.
Answer:
Resistance of carbon resistor (R1)
= 16 × 10 Ω = 160 Ω ….(using colour code)
Resistance of bulb (R2) = 300 Ω
∴ Current through the circuit = \(\frac{V}{R_{1}+R_{2}}\)
∴ I = \(\frac{230}{(160+300)}=\frac{230}{460}\) = 0.5 A
ii. Power drawn through electric bulb
= I²R2 = (0.5)² × 300 = 75 watt
Hence, if the bulb is replaced by 80 watt bulb, it will not glow.
Question 76.
From the graph given below, which of the two temperatures is higher for a metallic wire? Justify your answer.
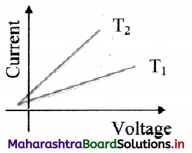
Answer:
As R = \(\frac {V}{I}\)
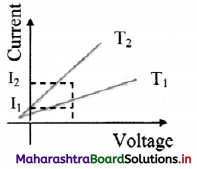
For constant V,
I2 > I1
∴ R1 > R2
Now, for metallic wire,
R ∝ T
∴ T1 > T2
T1 is greater than T2.
Question 77.
If n identical cells, each of emf E and internal resistance r, are connected in series, write an expression for the terminal p.d. of the combination and hence show that this is nearly n times that of a single cell.
Answer:
i. Let n identical cells, each of emf E and internal resistance r, be connected in series. Let the current supplied by this combination to an external resistance R be I.
ii. The equivalent emf of the combination,
Eeq = E + E + …….. (n times) = nE
iii. The equivalent internal resistance of the combination,
req= r + r + … (n times)
= nr
iv. The terminal p.d. of the combination is
V = Eeq – Ireq = nE – Inr = n (E – Ir)
∴ V = n × terminal p.d. of a single cell
Thus, the terminal p.d. of the series combination is n times that of a single cell.

Question 78.
If n identical cells, each of emf E and internal resistance r, are connected in parallel, derive an expression for the current supplied by this combination to external resistance R. Prove that the combination supplies current almost n times the current supplied by a single cell, when the external resistance R is much smaller than the internal resistance of the parallel combination of the cells.
Answer:
i. Consider n identical cells, each of emf E and internal resistance r, connected in parallel.
ii. Let the current supplied by the combination to the external resistance R be I.
In this case, the equivalent emf of the combination is E.
iii. The equivalent internal resistance r’ of the combination is,
\(\frac{1}{\mathrm{r}^{\prime}}=\frac{1}{\mathrm{r}}+\frac{1}{\mathrm{r}}\) + …………. (n terms)
∴ \(\frac{1}{\mathrm{r}^{\prime}}=\frac{\mathrm{n}}{\mathrm{r}} \Rightarrow \mathrm{r}^{\prime} \frac{\mathrm{n}}{\mathrm{r}}\)
iv. But V = IR is the terminal p.d. across each cell.
v. Hence, the current supplied by each cell,
I = \(\frac {E-V}{r}\)
vi. This gives the current supplied by the combination to the external resistance as
I = \(\frac {E-V}{r}\) + \(\frac {E-V}{r}\) + …….. (n terms) = n(\(\frac {E-V}{r}\))
Thus, current I = n × current supplied by a single cell
This proves that, the current supplied by the combination is n times the current supplied by a single cell.
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
The drift velocity of the free electrons in a conductor is independent of
(A) length of the conductor.
(B) cross-sectional area of conductor.
(C) current.
(D) electric charge.
Answer:
(A) length of the conductor.
Question 2.
The direction of drift velocity in a conductor is
(A) opposite to that of applied electric field.
(B) opposite to the flow of positive charge.
(C) in the direction of the flow of electrons,
(D) all of these.
Answer:
(D) all of these.
Question 3.
The drift velocity of free electrons in a conductor is vd, when the current is flowing in it. If both the radius and current are doubled, the drift velocity will be
(A) \(\frac {v_d}{8}\)
(B) \(\frac {v_d}{4}\)
(C) \(\frac {v_d}{2}\)
(D) vd
Answer:
(C) \(\frac {v_d}{2}\)
Question 4.
The drift velocity vd of electrons varies with electric field strength E as
(A) vd ∝ E
(B) vd ∝ \(\frac {1}{E}\)
(C) vd ∝ E1/2
(D) vd × E\(\frac {1}{1/2}\)
Answer:
(A) vd ∝ E
Question 5.
When a current I is set up in a wire of radius r, the drift speed is vd. If the same current is set up through a wire of radius 2r, then the drift speed will be
(A) vd/4
(B) vd/2
(C) 2vd
(D) 4vd
Answer:
(A) vd/4
Question 6.
When potential difference is applied across an electrolyte, then Ohm’s law is obeyed at
(A) zero potential
(B) very low potential
(C) negative potential
(D) high potential.
Answer:
(D) high potential.
Question 7.
A current of 1.6 A is passed through an electric lamp for half a minute. If the charge on the electron is 1.6 × 10-19 C, the number of electrons passing through it is
(A) 1 × 1019
(B) 1.5 × 1020
(C) 3 × 1019
(D) 3 × 1020
Answer:
(D) 3 × 1020
Question 8.
The SI unit of the emf of a cell is
(A) V/m
(B) V/C
(C) J/C
(D) C/J
Answer:
(C) J/C
Question 9.
The unit of specific resistance is
(A) Ω m-1
(B) Ω-1 m-1
(C) Ω m
(D) Ω m-2
Answer:
(C) Ω m

Question 10.
If the length of a conductor is halved, then its conductivity will be
(A) doubled
(B) halved
(C) quadrupled
(D) unchanged
Answer:
(D) unchanged
Question 11.
The resistance of a metal conductor increases with temperature due to
(A) change in current carriers.
(B) change in the dimensions of the conductor.
(C) increase in the number of collisions among the current carriers.
(D) increase in the rate of collisions between the current carriers and the vibrating atoms of the conductor.
Answer:
(D) increase in the rate of collisions between the current carriers and the vibrating atoms of the conductor.
Question 12.
The resistivity of Nichrome is 10-6 Ω-m. The wire of this material has radius of 0.1 mm with resistance 100 Ω, then the length will be
(A) 3.142 m
(B) 0.3142 m
(C) 3.142 cm
(D) 31.42 m
Answer:
(A) 3.142 m
Question 13.
Given a current carrying wire of non-uniform cross-section. Which of the following is constant throughout the length of the wire?
(A) Current, electric field and drift speed
(B) Drift speed only
(C) Current and drift speed
(D) Current only
Answer:
(D) Current only
Question 14.
A cell of emf E and internal resistance r is connected across an external resistance R (R >> r). The p.d. across R is A 1
(A) \(\frac {E}{R+r}\)
(B) E(I – \(\frac {r}{R}\))
(C) E(I + \(\frac {r}{R}\))
(D) E (R + r)
Answer:
(B) E(I – \(\frac {r}{R}\))
Question 15.
The e.m.f. of a cell of negligible internal resistance is 2 V. It is connected to the series combination of 2 Ω, 3 Ω and 5 Ω resistances. The potential difference across 3 Ω resistance will be
(A) 0.6 V
(B) 10 V
(C) 3 V
(D) 6 V
Answer:
(A) 0.6 V
Question 16.
A P.D. of 20 V is applied across a conductance of 8 mho. The current in the conductor is
(A) 2.5 A
(B) 28 A
(C) 160 A
(D) 45 A
Answer:
(C) 160 A
Question 17.
If an increase in length of copper wire is 0.5% due to stretching, the percentage increase in its resistance will be
(A) 0.1%
(B) 0.2%
(C) 1 %
(D) 2 %
Answer:
(C) 1 %
Question 18.
If a certain piece of copper is to be shaped into a conductor of minimum resistance, its length (L) and cross-sectional area A shall be respectively
(A) L/3 and 4 A
(B) L/2 and 2 A
(C) 2L and A2
(D) L and A
Answer:
(A) L/3 and 4 A
Question 19.
A given resistor has the following colour scheme of the various strips on it: Brown, black, green and silver. Its value in ohm is
(A) 1.0 × 104 ± 10%
(B) 1.0 × 105 ± 10%
(C) 1.0 × 106 + 10%
(D) 1.0 × 107 ± 10%
Answer:
(C) 1.0 × 106 + 10%
Question 20.
A given carbon resistor has the following colour code of the various strips: Orange, red, yellow and gold. The value of resistance in ohm is
(A) 32 × 104 ± 5%
(B) 32 × 104 ± 10%
(C) 23 × 105 ± 5%
(D) 23 × 105 ± 10%
Answer:
(A) 32 × 104 ± 5%
Question 21.
A typical thermistor can easily measure a change in temperature of the order of
(A) 10-3 °C
(B) 10-2 °C
(C) 10² °C
(D) 10³ °C
Answer:
(A) 10-3 °C
Question 22.
Thermistors are usually prepared from
(A) non-metals
(B) metals
(C) oxides of non-metals
(D) oxides of metals
Answer:
(D) oxides of metals

Question 23.
On increasing the temperature of a conductor, its resistance increases because
(A) relaxation time decreases.
(B) mass of the electron increases.
(C) electron density decreases.
(D) all of the above.
Answer:
(A) relaxation time decreases.
Question 24.
Which of the following is used for the formation of thermistor?
(A) copper oxide
(B) nickel oxide
(C) iron oxide
(D) all of the above
Answer:
(D) all of the above
Question 25.
Emf of a cell is 2.2 volt. When resistance R = 5 Ω is connected in series, potential drop across the cell becomes 1.8 volt. Value of internal resistance of the cell is
(A) 10/9 Ω
(B) 7/12 Ω
(C) 9/10 Ω
(D) 12/7 Ω
Answer:
(A) 10/9 Ω
Question 26.
A strip of copper, another of germanium are cooled from room temperature to 80 K. The resistance of
(A) copper strip decreases germanium decreases. and that of
(B) copper strip decreases germanium increases. and that of
(C) Both the strip increases.
(D) copper strip increases germanium decreases. and that of
Answer:
(B) copper strip decreases germanium increases. and that of
Question 27.
The terminal voltage of a cell of emf E on short circuiting will be
(A) E
(B) \(\frac {E}{2}\)
(C) 2E
(D) zero
Answer:
(D) zero
Question 28.
If a battery of emf 2 V with internal resistance one ohm is connected to an external circuit of resistance R across it, then the terminal p.d. becomes 1.5 V. The value of R is
(A) 1 Ω
(B) 1.5 Ω
(C) 2 Ω
(D) 3 Ω
Answer:
(D) 3 Ω
Question 29.
A hall is used 5 hours a day for 25 days in a month. It has 6 lamps of 100 W each and 4 fans of 150 W. The total energy consumed for the month is
(A) 1500 kWh
(B) 150 kWh
(C) 15 kWh
(D) 1.5 kWh
Answer:
(B) 150 kWh
Question 30.
The internal resistance of a cell of emf 2 V is 0.1 Ω. It is connected to a resistance of 3.9 Ω. The voltage across the cell will be
(A) 0.5 V
(B) 1.5 V
(C) 1.95 V
(D) 2 V
Answer:
(C) 1.95 V
Question 31.
The emf of a cell is 12 V. When it sends a current of 1 A through an external resistance, the p.d. across the terminals reduces to 10 V. The internal resistance of the cell is
(A) 0.1 Ω
(B) 0.5 Ω
(C) 1 Ω
(D) 2 Ω
Answer:
(D) 2 Ω
Question 32.
Three resistors, 8 Ω, 4 Ω and 10 Ω connected in parallel as shown in figure, the equivalent resistance is

(A) \(\frac {19}{40}\) Ω
(B) \(\frac {40}{19}\) Ω
(C) \(\frac {80}{19}\) Ω
(D) \(\frac {34}{23}\) Ω
Answer:
(B) \(\frac {40}{19}\) Ω
Question 33.
A potential difference of 20 V is applied across the ends of a coil. The amount of heat generated in it is 800 cal/s. The value of resistance of the coil will be
(A) 12 Ω
(B) 1.2 Ω
(C) 0.12 Ω
(D) 0.012 Ω
Answer:
(C) 0.12 Ω
Question 34.
In a series combination of cells, the effective internal resistance will
(A) remain the same.
(B) decrease.
(C) increase.
(D) be half that of the 1st cell.
Answer:
(C) increase.

Question 35.
The terminal voltage across a cell is more than its e.m.f., if another cell of
(A) higher e.m.f. is connected parallel to it.
(B) less e.m.f. is connected parallel to it.
(C) less e.m.f. is connected in series with it.
(D) higher e.m.f. is connected in series with it.
Answer:
(A) higher e.m.f. is connected parallel to it.
Question 36.
A 100 W, 200 V bulb is connected to a 160 volt supply. The actual’ power consumption would be
(A) 64 W
(B) 125 W
(C) 100 W
(D) 80 W
Answer:
(A) 64 W