Class 6 Hindi Chapter 1 Upyog Hamare Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 6 Hindi Solutions Sulabhbharati Chapter 1 उपयोग हमारे Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Std 6 Hindi Chapter 1 Upyog Hamare Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Hindi Sulabhbharti Class 6 Solutions Chapter 1 उपयोग हमारे Textbook Questions and Answers
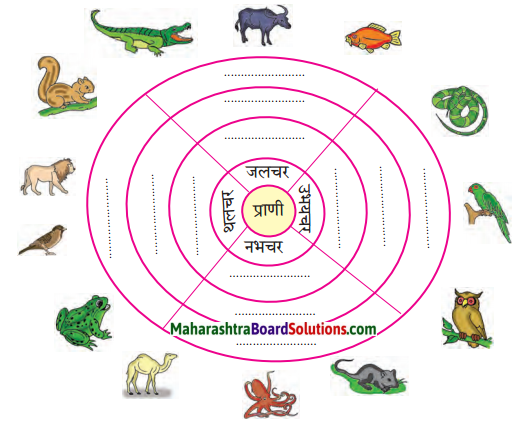
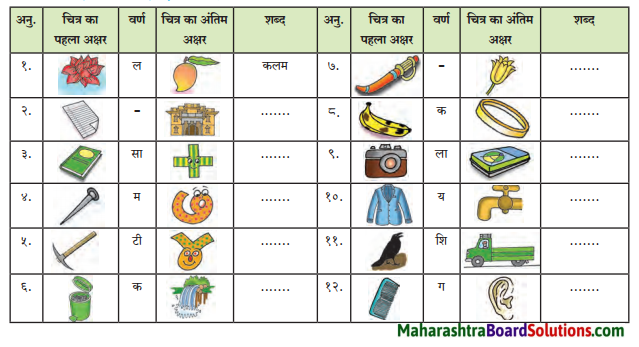
चित्रो का परिचय: चित्र का निरीक्षण करो और बताओ।
डाकघर:

विद्यार्थियों से चित्रों का निरीक्षण कराकर उनको प्रश्न पूछने के लिए कहें । बड़ों की सहायता से उन्हें डाकघर में जाकर टिकट खरीदने तथा बैंक में बाल-बचत खाता खुलवाने और परिचित डाकिए, बैंक कर्मचारी, नर्स, हवलदार से बातचीत करने की सूचना दें।
![]()
Answer:
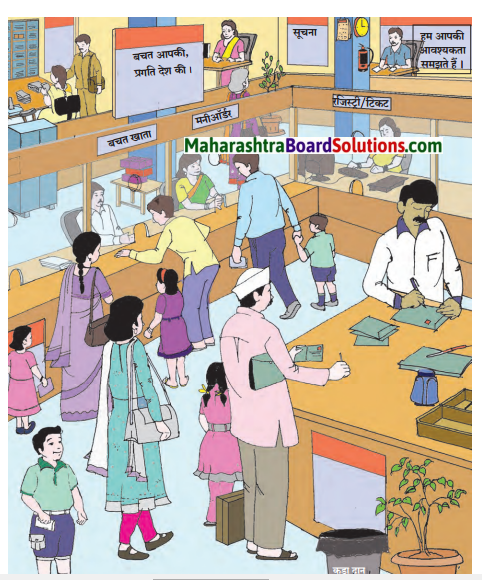
प्रस्तुत चित्र डाकघर का है। डाकघर भारत-सरकार का सबसे पुराना व बड़ा उपक्रम है। चित्र में डाकघर के अलग-अलग हिस्सों में होने वाले काम के बारे में बताया गया है। लोग अपना पत्र और मनी ऑर्डर भेजने के लिए कतार में खड़े हैं। पोस्टमैन पत्रों पर कुछ लिख रहे हैं। एक व्यक्ति बचत खाता-काउन्टर पर डाक कर्मचारी से कुछ पूछताछ कर रहा है। दूसरा व्यक्ति मनी ऑर्डर-काउन्टर पर बैठी डाक-कर्मचारी से कुछ जानकारी प्राप्त कर रहा है। डाकघर में सूचना-फलक लगा हुआ है। डाकघर के अन्य कर्मचारी भी अपने काम में व्यस्त हैं। हम आपकी आवश्यकता समझते हैं।’ इस सुविचार के माध्यम से ग्राहकों में अपनेपन का भाव पैदा करने का प्रयास किया गया है। छोटे बच्चे अपने माता-पिता के साथ डाकघर में आए हैं और सभी चीज़ों का निरीक्षण कर रहे हैं। गमले के पास कूड़ेदान रखा गया है। ‘बचत आपकी, प्रगति देश की।’ इस सुंदर पंक्ति द्वारा लोगों में देश की प्रगति की भावना भी जागृत करने का प्रयत्न किया गया है। प्रगति के आज के दौर में हमारी सरकार डाकघरों का महत्त्व बरकरार रखने के लिए बैंकों की तर्ज पर उनका पुनर्गठन कर रही है।
बैंक:

उपरोक्त स्थानों की कार्य प्रक्रिया संबंधी जानकारी देकर चर्चा करें । प्रत्यक्ष जाकर विद्यार्थियों को वहाँ की सूचना पढ़ने के लिए कहें । उनसे अपने गाँव/शहर के महत्त्वपूर्ण स्थानों के दूरध्वनि क्रमांकों की सूची बनवाएँ और सहायता लेने की सूचना दें।
![]()
Answer:
प्रस्तुत चित्र बैंक का है। प्रतिदिन के कार्य का चित्रण इसमें किया गया है। छोटे बच्चे अपने माता-पिता के साथ बैंक में आए हैं। बैंक में आए कई ग्राहक अपना कार्य कर रहे हैं। एक महिला पूछताछ-काउन्टर पर बैठे बैंक कर्मचारी से कुछ बातचीत कर रही है। दूसरी महिला बचत खाता काउन्टर पर अपना कार्य करने के लिए खड़ी है। कुछ ग्राहक कैशिअर के पास से अपने रुपये लेने के लिए कतार में खड़े हैं। एक महिला कैशिअर काउन्टर पर रुपये जमा कर रही है। कुछ ग्राहक अपने कार्य की प्रतीक्षा में बैठे हैं। एक ग्राहक शाखा प्रबंधक (मैनेजर) के कक्ष में बैठकर कुछ वार्तालाप कर रहा है। बंदूकधारी सुरक्षा कर्मचारी बैंक की सुरक्षा के लिए खड़ा है। अन्य ग्राहक अपने काम में व्यस्त दिखाई दे रहे हैं। बैंक की ओर से ग्राहकों को सूचना देने के लिए सूचना फलक लगा हुआ है।
Hindi Sulabhbharti Class 6 Solutions Chapter 1 उपयोग हमारे Additional Important Questions and Answers
निम्नलिखित शब्दों में से उचित शब्द चुनकर रिक्त स्थानों की पूर्ति कीजिए:
(प्रगति, सूचना, टिकट, कूड़ेदान)
Question 1.
डाकघर में लोगों और कर्मचारियों को सूचित करने के लिए ………………… फलक लगाया जाता है।
Answer:
सूचना
Question 2.
हमें कचरा ……………….. में फेंकना चाहिए।
Answer:
कूड़ेदान
Question 3.
हमारे बचत करने से देश की …………………. होगी।
Answer:
प्रगति
Question 4.
पत्र पर ……………… लगाकर हम उसे डाकघर में देते है।
Answer:
टिकट प्रश्न
![]()
निम्नलिखित वाक्य सही हैं या गलत लिखिए:
Question 1.
डाकघर में हम पैसे जमा कर सकते हैं।
Answer:
सही
Question 2.
हमें कचरा गमले में फेंकना चाहिए।
Answer:
गलत
Question 3.
बच्चे डाकघर में खेल रहे हैं।
Answer:
गलत
Question 4.
मेज पर पत्र बिखरे पड़े हैं।
Answer:
सही
Question 5.
बचत खाता काउंटर पर महिला कर्मचारी बैठी है।
Answer:
गलत
![]()
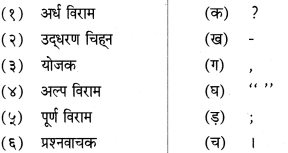
निम्नलिखित चित्रों के साथ सही जोड़ियाँ मिलाइए:

Answer:
१ – घ
२ – ग
३ – ड़
४ – क
५ – ख
निम्नलिखित प्रश्नों के उत्तर एक-एक वाक्य में लिखिए:
Question 1.
डाकघर में हम क्यों जाते हैं?
Answer:
हम डाकघर में पत्र डालने, लाने अथवा मनी ऑर्डर तथा रजिस्ट्री करने जाते हैं।
Question 2.
डाकघर के चित्र में कितने विभाग दिखाये गए हैं और कौन से?
Answer:
डाकघर के चित्र में तीन विभाग दिखाये गए है।
- बचत खाता
- मनी ऑर्डर
- रजिस्ट्री/टिकट
![]()
Question 3.
डाकघर के फलक पर कौन-सा सुंदर वाक्य लिखा है?
Answer:
डाकघर के फलक पर ‘बचत आपकी, प्रगति देश की’ यह सुंदर वाक्य लिखा है।
Question 4.
छोटे बच्चे किसके साथ डाकघर में आए है?
Answer:
छोटे बच्चे अपने माता – पिता के साथ डाकघर में आए है।
Question 5.
‘हम आपकी आवश्यकता समझते हैं।’ इस वाक्य से आप क्या समझते हैं?
Answer:
इस वाक्य से हम यह समझते है कि आपका समय और आपका कार्य हमारे लिए महत्त्वपूर्ण है।
निम्नलिखित शब्दों में से उचित शब्द चुनकर रिक्त स्थानों की पूर्ति कीजिए:
(ग्राहक, पूछताछ, बंदूक, बचत, छड़ी)
Question 1.
महिला . …………… कर रही है।
Answer:
पूछताछ
Question 2.
दूसरी महिला ……………… खाता काउन्टर के पास खड़ी है।
Answer:
बचत
Question 3.
सुरक्षा कर्मचारी के पास ……………… है।
Answer:
बंदूक
![]()
Question 4.
मैनेजर ……………….. से बातचीत कर रहा है।
Answer:
ग्राहक
Question 5.
बूढ़े ग्राहक के हाथ में ………………….
Answer:
छड़ी
निम्नलिखित बाक्य सही हैं या गलत लिखिए:
Question 1.
बैंक में कैशिअर पैसे का लेन-देन एवं हिसाब का काम देखता है।
Answer:
सही
Question 2.
बैंक में हमें पत्र मिलता है।
Answer:
गलत
Question 3.
मैनेजर का काम लोगों की रक्षा करना होता है।
Answer:
गलत
Question 4.
आज-कल बैंक का अधिकतर काम संगणक पर होता है।
Answer:
सही
![]()
Question 5.
बैंक से हमें कर्ज मिलता है।
Answer:
सही
निम्नलिखित बैंक व पोस्ट से संबंधित शब्दों को अलग अलग करके लिखिए:
(पूछताछ, बचत खाता, कैशिअर, डाकिया, मैनेजर, डाक अधिकारी, रजिस्ट्री, चालू खाता, पत्र, धनादेश, मनी ऑर्डर)
Answer:
पोस्ट ऑफिस:
- डाकिया
- बचत खाता
- डाक अधिकारी
- रजिस्ट्री
- पत्र
- मनी ऑर्डर
बैंक:
- बचत खाता
- कैशिअर
- चालू खाता
- धनादेश
- पूछताछ
![]()
निम्नलिखित प्रश्नों के उत्तर एक-एक वाक्य में लिखिए:
Question 1.
बैंक में खजांची क्या कार्य करते हैं?
Answer:
बैंक में खजांची रुपये लेन-देन का एवं उसका हिसाब रखने का कार्य करते हैं।
Question 2.
बैंक में पूछताछ-कक्ष क्यों होता है?
Answer:
बैंक में आने वाले ग्राहकों की समस्याओं का निवारण करने के लिए बैंक में पूछताछ-कक्ष होता है।
Question 3.
बैंक में सुरक्षा कर्मचारी क्यों तैनात किए जाते हैं?
Answer:
बैंक में आने-जाने वाले ग्राहकों एवं बैंक के मालमत्ते की रक्षा करने के लिए बैंक में सुरक्षा कर्मचारी तैनात किए जाते हैं।
Question 4.
बैंकों की आवश्यकता क्यों होती है?
उत्तर :
हमारी धन-संपत्ति को सुरक्षित रखने के लिए हमें बैंकों की आवश्यकता होती है।
Question 5.
बैंक के मुख्य अधिकारी को क्या कहते हैं?
Answer:
बैंक के मुख्य अधिकारी को शाखा प्रबंधक कहते हैं।
![]()
Question 6.
साधारण या आम जनता बैंक में किस प्रकार का खाता खोलती है?
Answer:
साधारण या आम जनता बैंक में बचत खाता खोलती है।
Hindi Sulabhbharati 6th Standard Digest Guide दूसरी इकाई