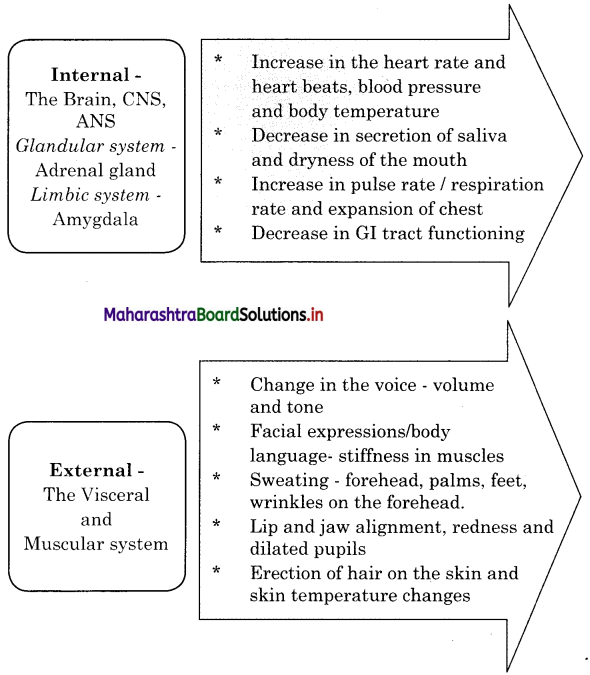
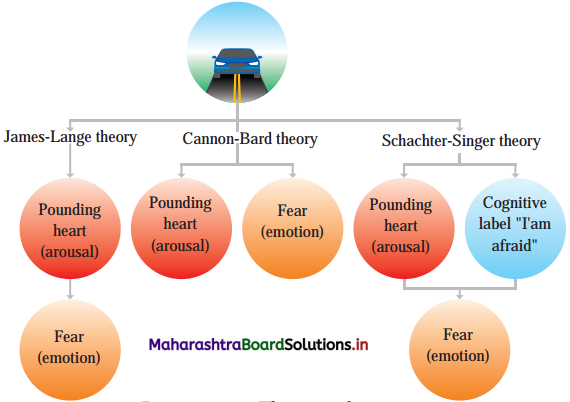
Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 12 Psychology Important Questions Chapter 8 Positive Psychology Important Questions and Answers.
Maharashtra State Board 12th Psychology Important Questions Chapter 8 Positive Psychology
Choose the correct option and complete the following statements.
Question 1.
Life …………….. indicates a life full of stress and anxiety.
(a) below zero
(b) at zero
(c) above zero
Answer:
(a) below zero
Question 2.
………………. refers to the ability to handle adverse situations effectively.
(a) Coping
(b) Competence
(c) Confidence
Answer:
(b) Competence
![]()
Question 3.
……………….. helps us to focus on the ‘Here and Now’ effectively.
(a) Mindfulness
(b) Mindlessness
(c) Optimism
Answer:
(a) Mindfulness
Question 4.
………………. is the key to most successful relationships.
(a) Resilience
(b) Mindfulness
(c) Empathy
Answer:
(c) Empathy
Match the pairs.
Question 1.
| Group A | Group B |
| (1) Seligman | (a) Broaden and Build theory |
| (2) Fredrickson | (b) empathy |
| (3) Masten | (c) mindfulness |
| (4) Baron-Cohen | (d) resilience |
| (e) optimism |
Answer:
| Group A | Group B |
| (1) Seligman | (e) optimism |
| (2) Fredrickson | (a) Broaden and Build theory |
| (3) Masten | (d) resilience |
| (4) Baron-Cohen | (b) empathy |
![]()
State whether the following statements are true or false.
Question 1.
Negative events easily attract our attention compared to positive ones.
Answer:
True
Question 2.
Positive psychology focuses on life at and below zero.
Answer:
False
Question 3.
A positive frame of mind effectively builds our social and psychological resources.
Answer:
True
Question 4.
There are subjective differences in the experience of happiness.
Answer:
True
Question 5.
We must always choose very easy goals so we can feel happiness.
Answer:
False
Question 6.
Most pessimists perceive difficulties as challenges/ opportunities.
Answer:
False
![]()
Question 7.
Empathy and sympathy are synonymous.
Answer:
Question 8.
Brain damage can diminish a person’s ability to empathize.
Answer:
True
Answer the following in one sentence each.
Question 1.
What does positive psychology focus on?
Answer:
Positive psychology focuses on building of character strengths such as courage, happiness and perseverance rather than on anxiety, conflict and avoidance.
Question 2.
What does ‘life below zero’ indicate?
Answer:
‘Life below zero’ indicates a life that is full of problems, stress, diseases, etc.
Question 3.
How does an optimist view challenges and difficulties?
Answer:
Optimists have a positive approach towards challenges and difficulties and hence view them as opportunities to progress and become strong.
Question 4.
What does mindlessness mean?
Answer:
Mindlessness means performing a task with less concentration and awareness mainly because we are absorbed in our own thoughts, worries, etc.
![]()
Question 5.
What is psychological resilience?
Answer:
Psychological resilience refers to developing coping strategies that enable one to adapt to uncertainty, challenges and adversity and to move on without prolonged negative consequences.
Explain the concepts in 25 – 30 words each.
Question 1.
Broaden and Build theory.
Answer:
The ‘Broaden and Build theory of positive emotions’ by Barbara Fredrickson explains that when we experience positive emotions, we have more positive thoughts and also indulge in positive behaviours. Experiencing a positive emotion leads to broadening the number of actions that we can think of performing. This will increase and strengthen our psychological and social resources to lead a fulfilling life.
Question 2.
Life above zero.
Answer:
Traditional psychology focused on life at and below zero. Zero is the line that divides illness from health. Hence, life below zero indicates a life that is full of problems, stress, diseases, etc. Positive psychology emphasizes the study of life above zero. Life above zero covers a large area of positive aspects of behaviour such as mindfulness, resilience, happiness, hope, trust and empathy.
Question 3.
Mindfulness meditation
Answer:
Mindfulness means a moment-by-moment awareness of our bodily sensations, thoughts and feelings. In Buddhist philosophy, mindfulness practice is a form of meditation. Mindfulness meditation helps in developing a non-reactive state of mind which is the foundation of a peaceful mind. This helps to reduce anxiety, frustration, etc., and enhances mental well-being.
![]()
Answer the following questions in 35 – 40 words each.
Question 1.
Why is positive psychology considered significant today?
Answer:
Positive psychology is a newly emerging branch of psychology. Martin Seligman officially introduced Positive Psychology as a subfield of psychology. It is the science of happiness, human strength and growth.
Negative events tend to be intense and hence easily attract our attention, e.g., outburst of anger by a person will be quickly noticed. Positive psychology believes that a person can prevent and overcome many psychological problems by adopting a positive approach. Therefore, today, positive psychology is important. Positive psychology is concerned with the “good life” and the factors that contribute the most to a fulfilling, happy life. It can help increase self esteem, improve relationships and greater chances of success.
Question 2.
What are the characteristics of optimists?
Answer:
Optimism is a mental attitude that includes feelings of hopefulness. It is a belief that the future will be positive and favourable and that negative events are merely setbacks that are temporary and can be overcome.
The characteristics of optimists are-
- they try to choose the best options available
- they tend to be high on self confidence
- they face difficulties positively as they view them as a challenge for a person to become strong
- they are hopeful about the future and do not generalize present failure to future events.
Question 3.
How can empathy be nurtured?
Answer:
Empathy is the capacity to understand and feel what another person is experiencing from within their frame of reference i.e. capacity to place oneself in another’s position. According to Simon Baron-Cohen there are three components of emotions viz. cognitive empathy emotional reactivity and social skills.
Empathy builds a sense of security and trust. It is closely related to emotional intelligence and is a key to successful relationships. Empathy can be nurtured by employing methods like-
- increase social interactions
- connecting through similarities
- understanding one’s own feelings
- challenge your self
- cultivate a sense of curiosity
- widen the social contact circle.
![]()
Write short notes on the following in 50 – 60 words each.
Question 1.
Components of empathy
Answer:
Empathy is the capacity to understand and feel what another person is experiencing from within their frame of reference, i.e., capacity to place oneself in another’s position.
According to Simon Baron-Cohen, there are three components of empathy viz. cognitive empathy emotional reactivity and social skills.
- Cognitive empathy – This is called perspective taking, i.e., knowing how the other thinks and feels. Cognitive empathy responds to a problem using brainpower.
- Emotional reactivity – We feel the emotions as intensely as the other person. It involves connecting intimately with another person to form a strong bonds.
- Social skills – It involves being moved to help the person using our emotional person to form a strong bonds.
Answer the following questions in 80 – 100 words each.
Question 1.
Types of resilience
Points:
(i) Physical resilience
(ii) Psychological resilience
(iii) Emotional resilience
(iv) Community resilience
Answer:
According to the American Psychological Association, resilience is the process of adapting well in the face of adversity, trauma, tragedy, threats or significant sources of stress such as family, health, etc. It is the act of ‘bouncing back’ inspite of barriers or set backs.
There are three ways in which people face adverse situations viz.
- consider oneself as a ‘victim’ and hence indulge in self pity or anger
- get overwhelmed by negative emotions like fear, anxiety, etc., which makes them vulnerable to physiological and psychological collapse
- become upset about the disruption and experience a sense of loss, pain, grief, etc.
However, they understand that setbacks are a part of life. Hence, they work through these feelings in ways that foster strength and growth. Sometimes, they may emerge stronger than they were prior to the setback. Such persons are called Resilient individuals. The four types of resilience are-
(i) Physical resilience – It is the body’s ability to adapt to challenges, maintain stamina, and quickly recover when faced with illness, injury or other physical demands.
(ii) Psychological resilience – It is developing coping strategies that enable one to adapt to uncertainty, challenges and adversity and to move on without prolonged negative consequence. The person can remain calm and focused during stressful situations.
![]()
(iii) Emotional resilience – It refers to the ability to manage one’s emotions by adequately using one’s resources to cope with adversity and stress. It is the ability to understand what one is feeling and why?
(iv) Community resilience – It is the ability of groups of people to respond to and recover from adverse situations such as natural disasters, epidemics, war, economic hardships and other challenges to their community. This is mainly due to strong connections or bonds that community members have with each other.
Question 2.
Empathy
Points:
(i) Meaning
(ii) Components
(iii) Nurturing empathy
Answer:
(i) Meaning – Empathy is the capacity to understand and feel what another person is experiencing from within their frame of reference, i.e., capacity to place oneself in another’s position. Empathy builds a sense of security and trust. It is closely related to emotional intelligence. It supports social corrections required for communication and shared activities. Empathy is considered the key to successful relationships. Research indicates that there is a neurological foundation of empathy. A broad range of brain areas spanning the sensory motor area, insula and cingulate cortex together form a neural network for empathy processing.
(ii) Components-
- Cognitive empathy – This is called perspective taking, i.e., knowing how the other thinks and feels. Cognitive empathy responds to a problem using brainpower.
- Emotional reactivity – We feel the emotions as intensely as the other person. It involves connecting intimately with another person to form a strong bonds.
- Social skills – It involves being moved to help the person using our emotional intelligence. One should not become overwhelmed by sadness or trying to ‘fix’ things.
![]()
(iii) Nurturing empathy-
A world with empathetic persons will be nurturing and supportive. The methods to nurture empathy are-
- Increase social interactions – Especially with people who need help in order to understand their perspectives and motives.
- Connecting through similarities with others, e.g., those having same hobbies/ work/ goals, etc.
- Understanding what you are feeling – Those who are able to accurately judge their own motives, can empathize better.
- Challenge yourself – Tasks that are challenging lead to the person struggling to achieve a goal. This lead to humility which enables empathy.
- Cultivate a sense of curiosity – This leads to open-mindedness and a better understanding of those around us.
- Widen our social circle – Contact with people of different races, cultures, viewpoints helps to increase empathy towards them at a neurological level.