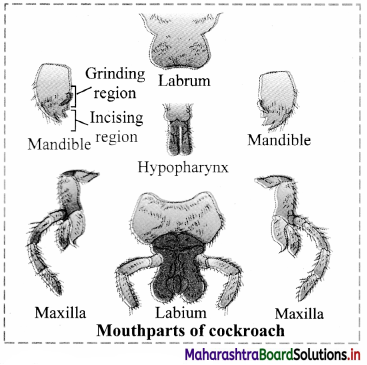
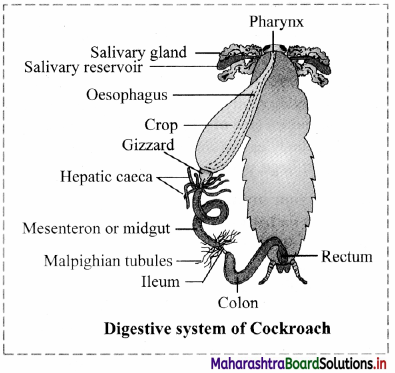
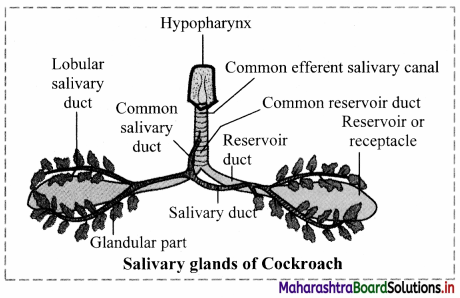
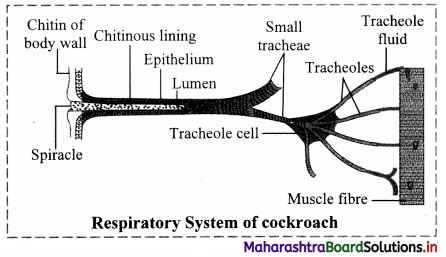
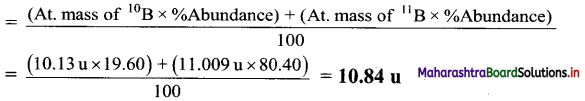Balbharti Maharashtra State Board 11th Chemistry Textbook Solutions Chapter 4 Structure of Atom Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
Structure of Atom Class 11 Exercise Question Answers Solutions Maharashtra Board
Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 4 Exercise Solutions Maharashtra Board
Chemistry Class 11 Chapter 4 Exercise Solutions
1. Choose correct option.
Question A.
The energy difference between the shells goes on ……….. when moved away from the nucleus.
a. Increasing
b. decreasing
c. equalizing
d. static
Answer:
b. decreasing
Question B.
The value of Plank’s constant is
a. 6.626× 10-34 Js
b. 6.023× 10-24 Js
c. 1.667 × 10-28 Js
d. 6.626× 10-28 Js
Answer:
a. 6.626× 10-34 Js
Question C.
p-orbitals are ……. in shape.
a. spherical
b. dumb bell
c. double dumb bell
d. diagonal
Answer:
b. dumbbell
Question D.
“No two electrons in the same atoms can have identical set of four quantum numbers”. This statement is known as
a. Pauli’s exclusion principle
b. Hund’s rule
c. Aufbau rule
d. Heisenberg uncertainty principle
Answer:
a. Pauli’s exclusion principle
Question E.
Principal Quantum number describes
a. shape of orbital
b. size of the orbital
c. spin of electron
d. orientation of in the orbital electron cloud
Answer:
b. size of the orbital
![]()
2. Make the pairs:
| A | B | ||
| a. | Neutrons | i. | six electrons |
| b. | p-orbital | ii. | -1.6 × 10-19 C |
| c. | charge on electron | iii. | Ultraviolet region |
| d. | Lyman series | iv. | Chadwick |
Answer:
a – iv,
b – i,
c – ii,
d – iii
3. Complete the following information about the isotopes in the chart given below :
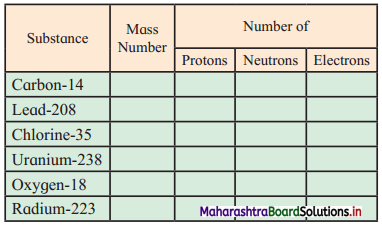
(Hint: Refer to Periodic Table if required)
Answer:
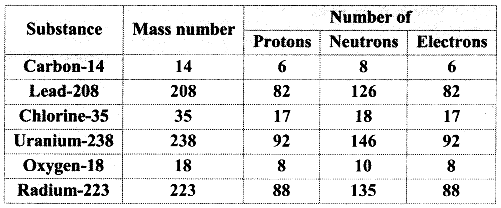
![]()
4. Match the following :

Answer:
a – iv,
b – iii,
c – ii,
d – i
5. Answer in one sentence :
Question A.
If an element ‘X’ has mass number 11 and it has 6 neutrons, then write its representation.
Answer:
The representation of the given element is \({ }_{5}^{11} \mathrm{X}\).
Question B.
Name the element that shows simplest emission spectrum.
Answer:
The element that shows simplest emission spectrum is hydrogen.
Question C.
State Heisenberg uncertainty principle.
Answer:
Heisenberg uncertainty principle states that “It is impossible to determine simultaneously, the exact position and exact momentum (or velocity) of an electron”.
Question D.
Give the names of quantum numbers.
Answer:
The four quantum numbers are: principal quantum number (n), azimuthal or subsidiary quantum number (l), magnetic quantum number (ml) and electron spin quantum number (ms).
![]()
Question E.
Identify from the following the isoelectronic species:
Ne, O2-, Na+ OR Ar, Cl2-, K+
Answer:
Atoms and ions having the same number of electrons are isoelectronic.
| Species | No. of electrons |
| Ne | 10 |
| O2- | 8 + 2 = 10 |
| Na+ | 11 – 1 = 10 |
| Ar | 18 |
| Cl2- | 17 + 2 = 19 |
| K+ | 19 – 1 = 18 |
Hence, Ne, O2-, Na+ are isoelectronic species.
6. Answer the following questions.
Question A.
Differentiate between Isotopes and Isobars.
Answer:
| No. | Isotopes | Isobars |
| i. | Isotopes are atoms of same element. | Isobars are atoms of different elements. |
| ii. | They have same atomic number but different atomic mass number. | They have same atomic mass number but different atomic numbers. |
| iii. | They have same number of protons but different number of neutrons. | They have different number of protons and neutrons. |
| iv. | They have same number of electrons. | They have different number of electrons. |
| V. | They occupy same position in the modem periodic table. | They occupy different positions in the modem periodic table. |
| vi. | They have similar chemical properties. | They have different chemical properties. |
| e.g. | \({ }_{6}^{12} \mathrm{C}\) and \({ }_{6}^{14} \mathrm{C}\) | \({ }_{6}^{14} \mathrm{C}\) and \({ }_{7}^{14} \mathrm{~N}\) |
Question B.
Define the terms:
i. Isotones
ii. Isoelectronic species
iii. Electronic configuration
Answer:
i. Isotones: Isotones are defined as the atoms of different elements having same number of neutrons in their nuclei. e.g. \({ }_{5}^{11} \mathrm{B}\) and \({ }_{6}^{12} \mathrm{C}\) having 6 neutrons each are isotones.
ii. Isoelectronic species:
soelectronic species are defined as atoms and ions having the same number of electrons.
e. g. Ar, Ca2+ and K+ containing 18 electrons each.
iii. Electronic configuration:
Electronic configuration of an atom is defined as the distribution of its electrons in orbitals.
![]()
Question C.
State and explain Pauli’s exclusion principle.
Answer:
Pauli’s exclusion principle:
i. Statement: “No two electrons in an atom can have the same set of four quantum numbers”. OR “Only two electrons can occupy the same orbital and they must have opposite spins. ”
ii. The capacity of an orbital to accommodate electrons is decided by Pauli’s exclusion principle.
iii. According to this principle, for an electron belonging to the same orbital, the spin quantum number must be different since the other three quantum numbers are the same.
iv. The spin quantum number can have two values: +\(\frac {1}{2}\) and –\(\frac {1}{2}\).
v. Example, consider helium (He) atom with electronic configuration 1 s2.
For the two electrons in Is orbital, the four quantum numbers are as follows:
Electron number Quantum number Set of values of quantum numbers
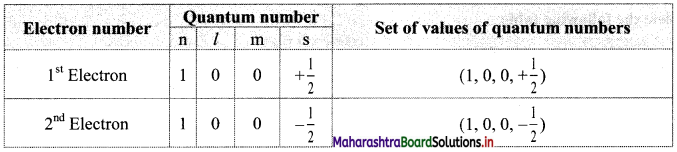
Thus, in an atom, any two electrons can have the same three quantum numbers, but the fourth quantum number must be different.
vi. This leads to the conclusion that an orbital can accommodate maximum of two electrons and if it has two electrons, they must have opposite spin.
Question D.
State Hund’s rule of maximum multiplicity with suitable example.
Answer:
Hund’s rule of maximum multiplicity:
i. Statement: “Pairing of electrons in the orbitals belonging to the same subshell does not occur unless each orbital belonging to that subshell has got one electron each.”
ii. Example, according to Hund’s rule, each of the three-degenerate p-orbitals must get one electron of parallel spin before any one of them receives the second electron of opposite spin. Therefore, the configuration of four electrons occupying p-orbitals is represented as
![]()
iii. As a result of Hund’s rule, the atom with fully filled and half-filled set of degenerate orbitals has extra stability.
Question E.
Write the drawbacks of Rutherford’s model of an atom.
Answer:
Drawbacks of Rutherford’s model of an atom:
i. Rutherford’s model of an atom resembles the solar system with the nucleus playing the role of the massive sun and the electrons are lighter planets. Thus, according to this model, electrons having negative charge revolve in various orbits around the nucleus. However, the electrons revolving about the nucleus in fixed orbits pose a problem. Such orbital motion is an accelerated motion accompanied by a continuous change in the velocity of electron as noticed from the continuously changing direction. According to Maxwell’s theory of electromagnetic radiation, accelerated charged particles would emit electromagnetic radiation. Hence, an electron revolving around the nucleus should continuously emit radiation and lose equivalent energy. As a result, the orbit would shrink continuously and the electron would come closer to the nucleus by following a spiral path. It would ultimately fall into the nucleus. Thus, Rutherford’s model has an intrinsic instability of atom. However, real atoms are stable.
ii. Rutherford’s model of an atom does not describe the distribution of electrons around the nucleus and their energies.
Question F.
Write postulates of Bohr’s Theory of hydrogen atom.
Answer:
Postulates of Bohr’s theory of hydrogen atom:
i. The electron in the hydrogen atom can move around the nucleus in one of the many possible circular paths of fixed radius and energy. These paths are called orbits, stationary states or allowed energy states. These orbits are arranged concentrically around the nucleus in an increasing order of energy.
ii. The energy of an electron in the orbit does not change with time. However, the electron will move from a lower stationary state to a higher stationary state if and when the required amount of energy is absorbed by the electron. Energy is emitted when electron moves from a higher stationary state to a lower stationary state. The energy change does not take place in a continuous manner.
iii. The frequency of radiation absorbed or emitted when transition occurs between two stationary states that differ in energy by ΔE is given by the following expression:
ν = \(\frac{\Delta E}{h}=\frac{E_{2}-E_{1}}{h}\) ………….(1)
Where E1 and E2 are the energies of the lower and higher allowed energy states respectively. This expression is commonly known as Bohr’s frequency rule.
iv. The angular momeñtum of an electron in a given stationary state can be expressed as mvr = n × h/2π
where, n 1,2, 3
Thus, an electron can move only in those orbits for which its angular momentum is integral multiple of h/2π.
Thus, only certain fixed orbits are allowed.
![]()
Question G.
Mention demerits of Bohr’s Atomic model.
Answer:
Demerits of Bohr’s atomic model:
- Bohr’s atomic model (theory) failed to account for finer details of the atomic spectrum of hydrogen as observed in sophisticated spectroscopic experiments.
- Bohr’s atomic model (theory) was unable to explain the spectrum of atoms other than hydrogen.
- Bohr’s atomic model (theory) could not explain the splitting of spectral lines in the presence of a magnetic field (Zeeman effect) or electric field (Stark effect).
- Bohr’s atomic model (theory) failed to explain the ability of atoms to form molecules by chemical bonds.
Question H.
State the order of filling atomic orbitals following Aufbau principle.
Answer:
Aufbau principle:
i. Aufbau principle gives the sequence in which various orbitals are filled with electrons.
ii. In the ground state of an atom, the orbitals are filled with electrons based on increasing order of energies of orbitals, Pauli’s exclusion principle and Hund’s rule of maximum multiplicity.
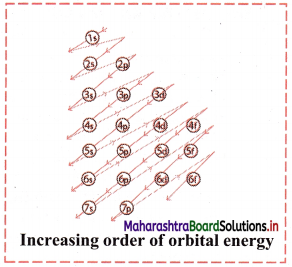
iii. Increasing order of energies of orbitals:
- Orbitals are filled in order of increasing value of (n + l)
- In cases where the two orbitals have same value of (n + l), the orbital with lower value of n is filled first.
iv. The increasing order of energy of different orbitals in a multi-electron atom is:
1s < 2s < 2p < 3s < 3p < 4s < 3d < 4p < 5s < 4d < 5p < 6s < 4f < 5d < 6p < 7s and so on.
Question I.
Explain the anomalous behavior of copper and chromium.
Answer:
i. Copper:
- Copper (Cu) has atomic number 29.
- Its expected electronic configuration is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d9.
- The 3d orbital is neither half-filled nor fully filled. Hence, it has less stability.
- Due to interelectronic repulsion forces, one 4s electron enters into 3d orbital. This makes 3d orbital completely filled and 4s orbital half-filled which gives extra stability and the electronic configuration of Cu becomes, 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s1 3d10.
ii. Chromium:
- Chromium (Cr) has atomic number 24.
- Its expected electronic configuration is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s23d4.
- The 3d orbital is less stable as it is not half-filled.
- Due to inter electronic repulsion forces, one 4s electron enters into 3d orbital. This makes 4s and 3d orbitals half-filled which gives extra stability and the electronic configuration of Cr becomes, 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s1 3d5.
Question J.
Write orbital notations for electrons in orbitals with the following quantum numbers.
a. n = 2, l =1
b. n = 4, l = 2
c. n = 3, l = 2
Answer:
i. 2p
ii. 4d
iii. 3d
![]()
Question K.
Write electronic configurations of Fe, Fe2+, Fe3+
Answer:
| Species | Orbital notation |
| Fe | 1s2 2s2 2p63s2 3p6 4s2 3d6 OR [Ar] 4s2 3d6 |
| Fe2+ | Is2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d6 OR [Ar] 3d6 |
| Fe3+ | 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d5 OR [Ar] 3d5 |
Question L.
Write condensed orbital notation of electonic configuration of the following elements:
a. Lithium (Z = 3)
b. Carbon (Z=6)
c. Oxygen (Z = 8)
d. Silicon (Z = 14)
e. Chlorine (Z = 17)
f. Calcium (Z = 20)
Answer:
| No. | Element | Condensed orbital notation |
| i. | Lithium (Z = 3) | [He] 2s1 |
| ii. | Carbon (Z = 6) | [He] 2s2 2p2 |
| iii. | Oxygen (Z = 8) | [He] 2s2 2p4 |
| iv. | Silicon (Z = 14) | [Ne] 3s2 3p2 |
| v. | Chlorine (Z = 17) | [Ne] 3s2 3p5 |
| vi. | Calcium (Z = 20) | [Ar] 4s2 |
Question M.
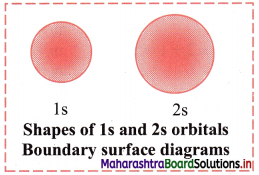
Draw shapes of 2s and 2p orbitals.
Answer:
2s orbital:
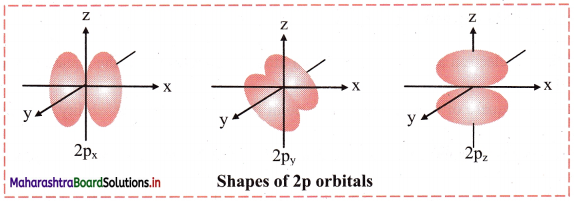
2p orbital:
Question N.
Explain in brief, the significance of azimuthal quantum number.
Answer:
Azimuthal quantum number (l):
- Azimuthal quantum number is also known as subsidiary quantum number and is represented by letter l.
- It represents the subshell to which the electron belongs. It also defines the shape of the orbital that is occupied by the electron.
- Its value depends upon the value of principal quantum number ‘n’. It can have only positive values between 0 and (n – 1).
- Atomic orbitals with the same value of ‘n’ but different values of ‘l’ constitute a subshell belonging to the shell for the given ‘n’ The azimuthal quantum number gives the number of subshells in a principal shell. The subshells have l to be 0, 1, 2,3 … which are represented by symbols s, p, d, f, … respectively.

![]()
Question O.
If n = 3, what are the quantum number l and ml?
Answer:
: For a given n, l = 0 to (n – 1) and for given l, ml = -l……, 0…….. + l
Therefore, the possible values of l and ml for n = 3 are:
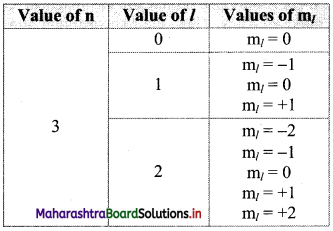
Question P.
The electronic configuration of oxygen is written as 1s2 2s2 2px2 2py1 2pz1 and not as 1s2 2s2 2px2 2py2 2pz0. Explain.
Answer:
- According to Hund’s rule of maximum multiplicity “Pairing of electrons in the orbitals belonging to the same subshell does not occur unless each orbital belonging to that subshell has got one electron each.”
- Oxygen has 8 electrons. The first two electrons will pair up in the Is orbital, the next two electrons will pair up in the 2s orbital and this leaves 4 electrons, which must be placed in the 2p orbitals.
- Each of the three degenerate p-orbitals must get one electron of parallel spin before any one of them receives the second electron of opposite spin. Therefore, two p orbitals have one electron each and one p-orbital will have two electrons.
Thus, the electronic configuration of oxygen is written as 1s2 2s2 2px2 2py1 2pz1 and not as 1s2 2s2 2px2 2py2 2pz0.
Question Q.
Write note on ‘Principal Quantum number.
Answer:
Principal quantum number (n):
i. Principal quantum number indicates the principal shell or main energy level to which the electron belongs.
ii. It is denoted by ‘n’ and is a positive integer with values 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, ….
iii. A set of atomic orbitals with given value of ‘n’ constitutes a single shell. These shells are also represented by the letters K, L, M, N, etc.
iv. With increase of ‘n’, the number of allowed orbitals in that shell increases and is given by n2.
v. The allowed orbitals in the first four shells are given below:
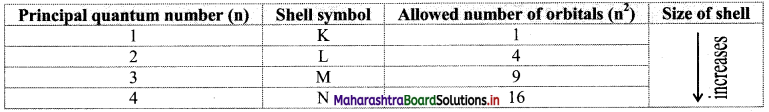
vi. As the value of ‘n’ increases, the distance of the shell from the nucleus increases and the size of the shell increases. Its energy also goes on increasing.
Question R.
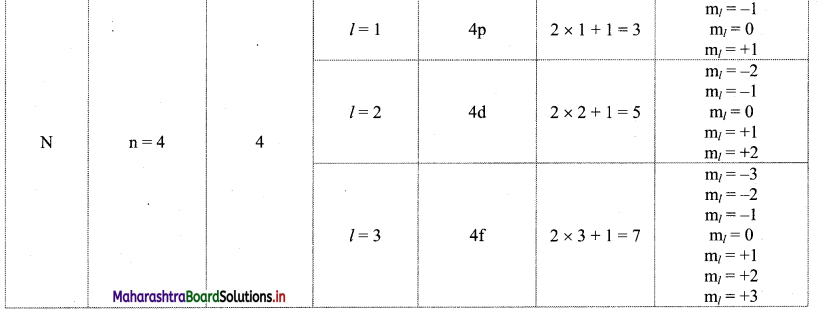
Using concept of quantum numbers, calculate the maximum numbers of electrons present in the ‘M’ shell. Give their distribution in shells, subshells and orbitals.
Answer:
i. Each main shell contains a maximum of 2n2 electrons.
For ‘M’ shell, n = 3.
Therefore, the maximum numbers of electrons present in the ‘M’ shell = 2 × (3)2 = 18.
ii. The distribution of these electrons in shells, subshells and orbitals can be given as follows:
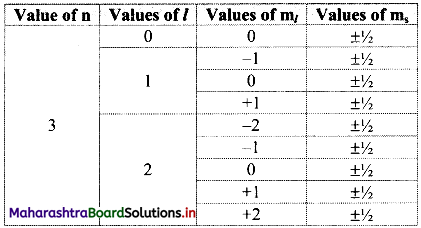
Note: Orbital distribution in the first four shells:
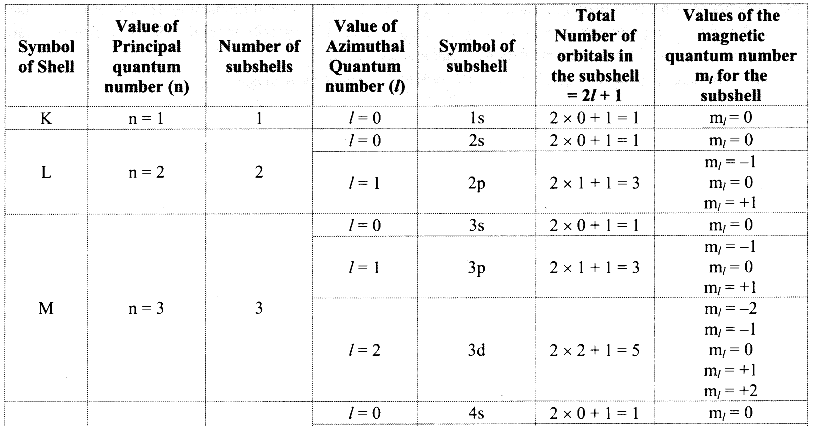
Question S.
Indicate the number of unpaired electrons in :
a. Si (Z = 14)
b. Cr (Z = 24)
Answer:
i. . Si (Z = 14): 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p2
Orbital diagram:
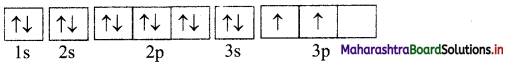
Number of unpaired electrons = 2
ii. Cr (Z = 24): 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s1 3d5
Orbital diagram:

Number of unpaired electrons = 6
Question T.
An atom of an element contains 29 electrons and 35 neutrons. Deduce-
a. the number of protons
b. the electronic configuration of that element.
Answer:
a. In an atom, number of protons is equal to number of electrons.
The given atom contains 29 electrons.
∴ Number of protons = 29
b. The electronic configuration of an atom of an element containing 29 electrons is:
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s1 3d10
[Note: Given element is copper (Cu) with Z = 29]
![]()
11th Chemistry Digest Chapter 4 Structure of Atom Intext Questions and Answers
Can you recall? (Textbook Page No. 35)
Question i.
What is the smallest unit of matter?
Answer:
The smallest unit of matter is atom.
Question ii.
What is the difference between molecules of an element and those of a compound?
Answer:
The molecules of an element are made of atoms of same element while the molecules of a compound are made of atoms of different elements.
Question iii.
Does an atom have any internal structure or is it indivisible?
Answer:
Yes, an atom has internal structure. Different subatomic particles such as protons, electrons and neutrons constitute an atom. So, it is divisible.
Question iv.
Which particle was identified by J. J. Thomson in the cathode ray tube experiment?
Answer:
Electron was identified by J.J. Thomson in the cathode ray tube experiment.
Question v.
Which part of an atom was discovered by Ernest Rutherford from the experiment of scattering of α-particles by gold foil?
Answer:
Nucleus of an atom was discovered by Ernest Rutherford from the experiment of scattering of α-particles by gold foil.
![]()
Just Think (Textbook Page No. 41)
Question 1.
What does the negative sign of electron energy convey?
Answer:
Negative sign for the energy of an electron in any orbit in a hydrogen atom indicates that the energy of the electron in the atom is lower than the energy of a free electron at rest. A free electron at rest is an electron that is infinitely far away from the nucleus and is assigned the energy value of zero.
As the electron gets close to the nucleus, value of ‘n’ decreases and En becomes large in absolute value and more negative. The negative sign corresponds to attractive forces between electron and nucleus.
Internet my friend (Textbook Page No. 44)
Question 1.
Collect information about structure of atom.
Answer:
Students can use links given below as reference and collect information about structure of atom on their own.
https://www.livescience.com/65427-fundamental-elementary-particles.html http://www.chemistryexplained.com/Ar-Bo/Atomic-Structure.html
https://www.thoughtco.com/basic-model-of-the-atom-603799
11th Std Chemistry Questions And Answers:
- Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry Class 11 Chemistry Questions And Answers
- Introduction to Analytical Chemistry Class 11 Chemistry Questions And Answers
- Basic Analytical Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Questions And Answers
- Structure of Atom Class 11 Chemistry Questions And Answers
- Chemical Bonding Class 11 Chemistry Questions And Answers
- Redox Reactions Class 11 Chemistry Questions And Answers
- Modern Periodic Table Class 11 Chemistry Questions And Answers
- Elements of Group 1 and 2 Class 11 Chemistry Questions And Answers