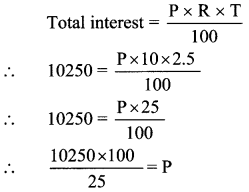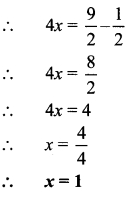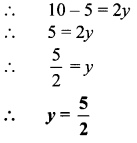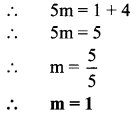Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 7 Maths Solutions covers the 7th Std Maths Practice Set 41 Answers Solutions Chapter 10 Bank and Simple Interest.
Bank and Simple Interest Class 7 Maths Chapter 10 Practice Set 41 Solutions Maharashtra Board
Std 7 Maths Practice Set 41 Solutions Answers
Question 1.
If the interest on Rs 1700 is Rs 340 for 2 years, the rate of interest must be__.
(A) 12%
(B) 15%
(C) 4%
(D) 10%
Solution:
(D) 10%
Hint:
∴ \(\text { Total interest }=\frac{P \times R \times T}{100}\)
∴ \(340=\frac{1700 \times R \times 2}{100}\)
∴ R = 10%
Question 2.
If the interest on Rs 3000 is Rs 600 at a certain rate for a certain number of years, what would the interest be on Rs 1500 under the same conditions?
(A) Rs 300
(B) Rs 1000
(C) Rs 700
(D) Rs 500
Solution:
(A) Rs 300
Hint:
The interest on Rs 3000 at certain rate of interest is Rs 600.
Let us suppose the interest on Rs 1500 at the same rate is x.
∴ \(\frac{600}{3000}=\frac{x}{1500}\)
∴ x = Rs 300
Question 3.
Javed deposited Rs 12000 at 9 p.c.p.a in a bank for some years, and withdrew his interest every year. At the end of the period, he had received altogether Rs 17,400. For how many years had he deposited his money?
Solution:
Here, P = Rs 12000, R = 9 p.c.p.a and amount = Rs 17400
Amount = Principal + Interest
∴17400 = 12000 + Interest
∴Interest = 17400 – 12000 = Rs 5400
∴ \(\text { Total interest }=\frac{P \times R \times T}{100}\)
\(5400=\frac{12000 \times 9 \times \mathrm{T}}{100}\)
∴ \(\frac{5400 \times 100}{12000 \times 9}=\mathrm{T}\)
∴ T = 5 years
∴ Javed had deposited the amount for 5 years.
Question 4.
Lataben borrowed some money from a bank at a rate of 10 p.c.p.a interest for \(2\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) years to start a cottage industry. If she paid Rs 10250 as total interest, how much money had she borrowed?
Solution:
Here, R = 10 p.c.p.a, T = 2.5 years, I = Rs 10250
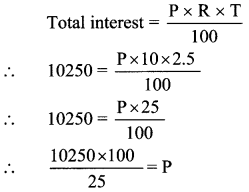
∴ P = Rs 41000
∴ Lataben had borrowed an amount of Rs 41000 from the bank.
Question 5.
Fill in the blanks in the table.
|
Principal |
Rate of interest (p.c.p.a.) |
Time |
Interest |
Amount |
| i. |
Rs 4200 |
7% |
3 years |
|
|
| ii. |
|
6% |
4 years |
Rs 1200 |
|
| iii. |
Rs 8000 |
5% |
|
Rs 800 |
|
| iv. |
|
5% |
|
Rs 6000 |
Rs 18000 |
| v. |
|
\(2\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) % 2 |
5 years |
Rs 2400 |
|
Solution:
i. \(\text { Total interest }=\frac{P \times R \times T}{100}\)
= \(\frac{4200 \times 7 \times 3}{100}\)
= Rs 882
Amount = Principal + interest
= 4200 + 882
= Rs 5082
ii. \(\text { Total interest }=\frac{P \times R \times T}{100}\)
∴ \(1200=\frac{\mathrm{P} \times 6 \times 4}{100}\)
∴ \(\frac{1200 \times 100}{6 \times 4}=\mathrm{P}\)
∴ P = Rs 5000
Amount = Principal + interest
= 5000 + 1200
= Rs 6200
iii. \(\text { Total interest }=\frac{P \times R \times T}{100}\)
∴ \(800=\frac{8000 \times 5 \times \mathrm{T}}{100}\)
∴ \(\frac{800 \times 100}{8000 \times 5}=\mathrm{T}\)
∴ T = 2 years
Amount = Principal + interest
= 8000 + 800
= Rs 8800
iv. Amount = Principal + interest
∴ 18000 = Principal + 6000
∴ Principal = Rs 12000
\(\text { Total interest }=\frac{P \times R \times T}{100}\)
∴ \(6000=\frac{12000 \times 5 \times \mathrm{T}}{100}\)
∴ \(\frac{6000 \times 100}{12000 \times 5}=\mathrm{T}\)
∴ T = 10 years
v. R = \(2\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) % = 2.5 %
∴ \(\text { Total interest }=\frac{P \times R \times T}{100}\)
∴ \(2400=\frac{\mathrm{P} \times 2.5 \times 5}{100}\)
∴ \(2400=\frac{P \times 25 \times 5}{100 \times 10}\)
∴ \(\frac{2400 \times 10 \times 100}{25 \times 5}=P\)
∴ P = Rs 19200
Amount = Principal + interest
= 19200 + 2400
= Rs 21600
|
Principal |
Rate of interest (p.c.p.a.) |
Time |
Interest |
Amount |
| i. |
Rs 4200 |
7% |
3 years |
Rs 882 |
Rs 5082 |
| ii. |
Rs 5000 |
6% |
4 years |
Rs 1200 |
Rs 6200 |
| iii. |
Rs 8000 |
5% |
2 years |
Rs 800 |
Rs 8800 |
| iv. |
Rs 12000 |
5% |
10 years |
Rs 6000 |
Rs 18000 |
| v. |
Rs 19200 |
\(2\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) % 2 |
5 years |
Rs 2400 |
Rs 21600 |
Maharashtra Board Class 7 Maths Chapter 10 Banks and Simple Interest Practice Set 41 Intext Questions and Activities
Question 1.
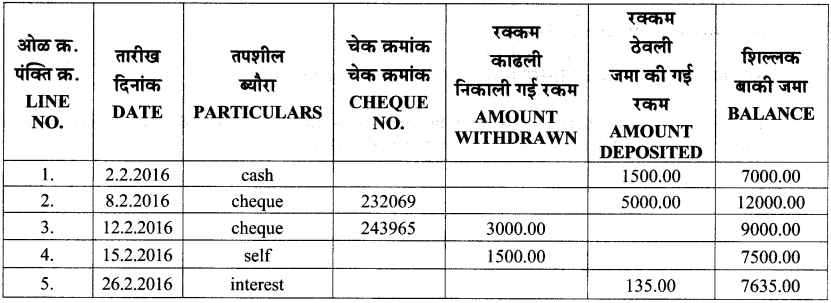
Ask an adult in your house to show you a passbook and explain the entries made in it. (Textbook pg. no. 70)
Solution:
(Students should attempt the above activities with the help of their parent / teacher.)
Question 2.
Visit different banks and find out the rates of the interest they give for different types of accounts. (Textbook pg. no. 74)
Solution:
(Students should attempt the above activities with the help of their parent / teacher.)
Question 3.
With the help of your teachers, start a Savings Bank in your school and open an account in it to save up some money. (Textbook pg. no. 74)
Solution:
(Students should attempt the above activities with the help of their parent / teacher.)
Std 7 Maths Digest