Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Marathi Yuvakbharati 12th Digest Chapter 1 वेगवशता Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
12th Marathi Chapter 1 Exercise Question Answer Maharashtra Board
वेगवशता 12 वी मराठी स्वाध्याय प्रश्नांची उत्तरे
12th Marathi Guide Chapter 1 वेगवशता Textbook Questions and Answers
कृती
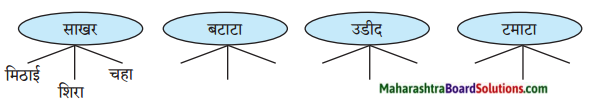
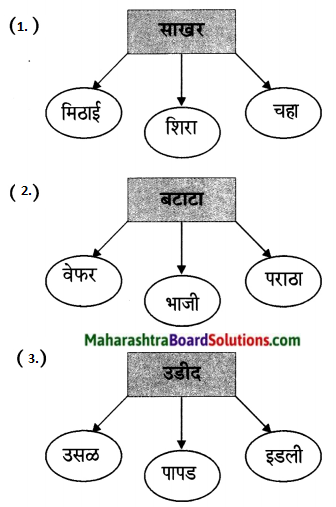
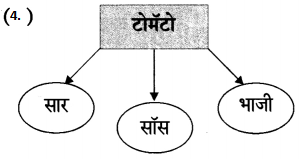
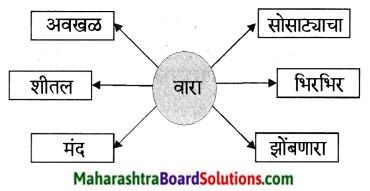
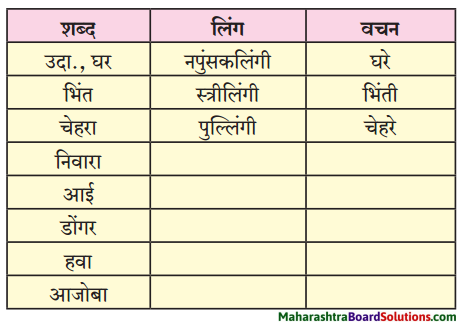
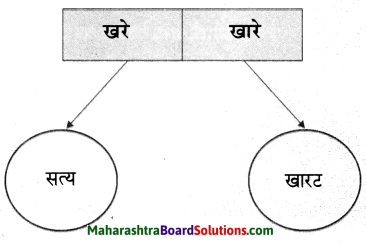
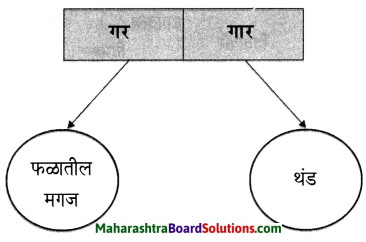
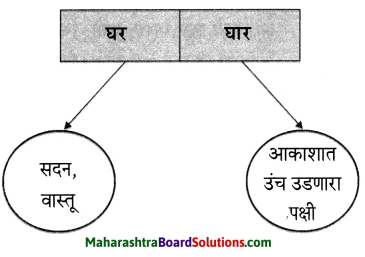
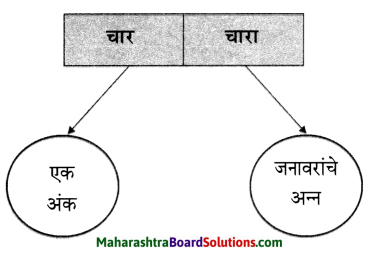
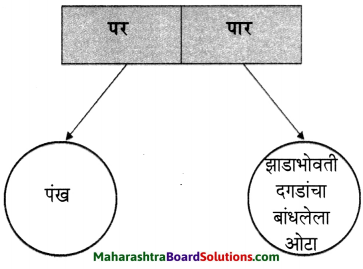
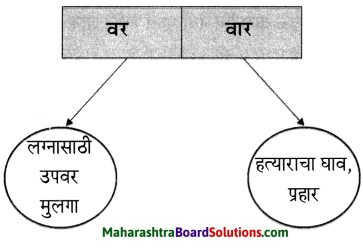
1. अ. पाठाच्या आधारे खालील चौकटी पूर्ण करा.
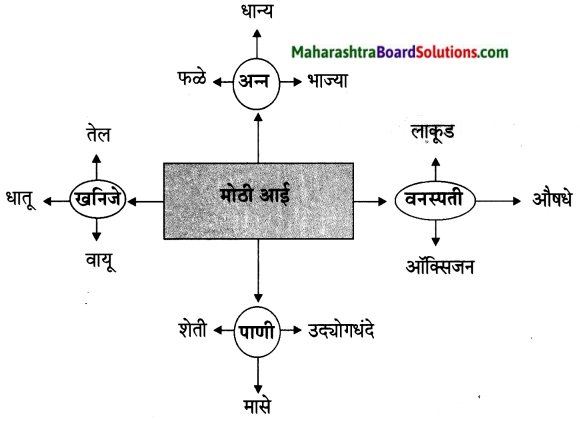
प्रश्न 1. अ
पाठाच्या आधारे खालील चौकटी पूर्ण करा.

उत्तर :

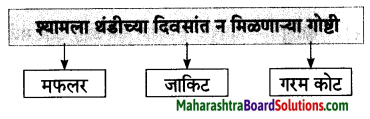
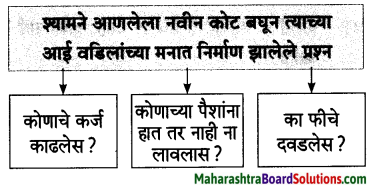
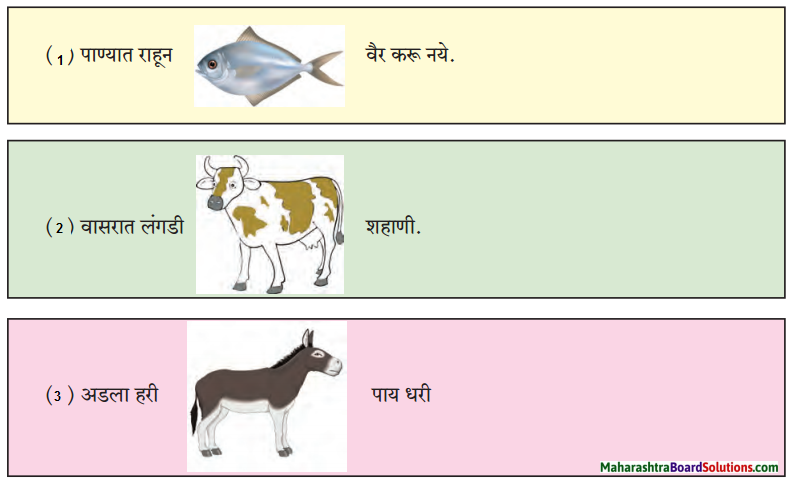
आ. कृती करा.
प्रश्न 1. आ.
कृती करा

उत्तर :



इ. कारणे शोधा व लिहा.
प्रश्न 1.
अमेरिकेतील माणसांचे जीवन वेगवान असते, कारण ………………. .
उत्तर :
अमेरिकेतील माणसांचे जीवन वेगवान असते; कारण वेगवेगळ्या ठिकाणांमधील अंतर खूपच असते आणि दरडोई वाहन उपलब्ध असते
![]()
प्रश्न 2.
लेखकांच्या मते, गरजेच्या वेळी वाहनांचा वापर करायला हवा; कारण ………………… .
उत्तर :
लेखकांच्या मते, गरजेच्या वेळी वाहनांचा वापर करायला हवा; कारण रस्त्यावर अडचणी निर्माण होणार नाहीत.
2. अ. योग्य पर्याय निवडून उत्तर लिहा.
प्रश्न 1.
जीवन अर्थ पूर्ण होईल, जर ………………….
अ. वाहन कामापुरतेच वापरले तर.
आ. वाहन आवश्यक कामासाठी वापरले तर
इ. वाहनाचा वेग आटोक्यात ठेवला तर.
ई. वरील तिन्ही गोष्टींचा अवलंब केला तर.
उत्तर :
ई. वरील तिन्ही गोष्टींचा अवलंब केला तर.
प्रश्न 2.
निसर्गविरोधी वर्तन नसणे, म्हणजे……………..
अ. स्वत:ला वाहनाशी सतत जखडून ठेवणे.
आ. वाहनाचा अतिवेग अंगीकारणे.
इ. तातडीचा भाग म्हणून कधीतरी वाहन वापरणे.
ई. गरज नसताना वाहन वापरणे.
उत्तर :
इ. तातडीचा भाग म्हणून कधीतरी वाहन वापरणे.
![]()
आ. वाहन वापरातील फरक स्पष्ट करा.
प्रश्न 1.

उत्तर :
| अमेरिका | भारत |
| घरोघर, दरडोई वाहन उपलब्ध असते. | अंतरे कमी आहेत. |
| रस्ते रुंद, सरळ, निर्विघ्न व एकमार्गी | माणसे खूप आहेत. |
| कामांची वेगवेगळी ठिकाणे किमान शंभर मैल अंतरावर असतात. | कामे फारशी नसतात. |
| दूरदूरची ठिकाणे गाठण्यासाठी वेगाचा आश्रय घ्यावा लागतो. | महानगरे रेल्वेने जोडलेली आहेत. |
3. खालील वाक्यांचा अर्थ सोदाहरण स्पष्ट करा.
प्रश्न अ.
यथाप्रमाण गती ही गरज आहे ; पण अप्रमाण, अवास्तव आणि अनावश्यक गती ही एक विकृती आहे.
उत्तर :
योग्य त्या प्रमाणात, आवश्यक त्या प्रमाणात वाहन वापरणे ही माणसाची गरज आहे. योग्य त्या प्रमाणात वाहन न वापरणे, अव्यवहार्य रितीने वापरणे आणि गरज नसताना वापरणे हे अनैसर्गिक आहे.
प्रश्न आ.
आरंभी माणसे वाहनांवर स्वार होतात. मग वाहने माणसांवर स्वार होतात.
उत्तर :
सुरुवातीला लोक गाडी जपून चालवतात. थोड्या काळासाठीच जपून चालवतात. मात्र हळूहळू त्यांना गाडीची चटक लागते. मग ते गरज असतानाच नव्हे, तर केवळ मौजमजा करण्यासाठीसुद्धा गाडीचा वापर करतात. हळूहळू त्यांना गाडीशिवाय कुठे जाताही येत नाही. पूर्णपणे ते गाडीवरच अवलंबून राहतात. हे सिगारेटच्या व्यसनासारखेच आहे.
सुरुवातीला फक्त एकदाच, मग फक्त एकच. असे करता करता दिवसाला एक पाकीट कधी होते हे कळतच नाही. नंतर नंतर सिगारेट मिळाली नाही तर त्या व्यक्तीचे मनःस्वास्थ्यच नाहीसे होते. सिगारेटशिवाय ती राहू शकत नाही. ती व्यक्ती सिगारेटचा गुलाम होऊन जाते. तद्वतच माणसेही गाड्यांचे गुलाम होतात. त्यांच्या वापराबाबत माणसांना कोणतेही तारतम्य राहत नाही.
![]()
प्रश्न इ.
उगाच भावविवश होऊन वेगवश होऊ नये.
उत्तर :
वाहन हे सोयीसाठी असते. ते साधन आहे. आपला वेळ व आपले श्रम वाहनामुळे वाचतात. आपली कामे भराभर होतात. वाहनाचे हे स्थान ओळखले पाहिजे. यापलीकडे आपल्या भावना गुंतवू नयेत. वाऱ्यासोबत त्याच्या वेगाने धावू लागलो तर काही क्षण आनंद मिळतो. उत्साह, उल्हास शरीरात सळसळतो. म्हणजे आपल्या भावना उचंबळून येतात. या भावनांवर आपण आरूढ झालो, तर आपला वाहनावर ताबा राहत नाही आणि अपघातांची शक्यता निर्माण होते.
आपल्या वाहनाला धडकेल का, आपल्याला जिथे वळायचे आहे तिथे वळता येईल का, त्या वेळी बाकीच्या वाहनांची स्थिती कशी असेल, त्यांच्यापैकी कोणीही स्वत:ची दिशा बदलण्याचा संभव आहे का इत्यादी अनेक बाबींचा विचार काही क्षणांत करावा लागतो. त्या अनुषंगाने सतत विचार करीत राहावे लागते. वाहन आणि वाहनाची गती यांखेरीज अन्य कोणतेही विचार मनात आणता येत नाहीत.
एकाच विचाराला जखडले गेल्यामुळे डोळ्यांवर, शरीरावर व मनावर विलक्षण ताण येतो. अपघाताची भीती मनात सावलीसारखी वावरत असते. तासन्तास तणावाखाली राहावे लागल्याने मनावर विपरीत परिणाम होतात. वाहनाचा वेग जास्त असल्यामुळे अगदी बारीकशा खड्ड्यानेसुद्धा वाहनाला हादरे बसतात. सांधे दुखतात. ते कमकुवत होतात. अशा प्रकारे वाढता वेग म्हणजे ताण, हे समीकरण तयार होते.
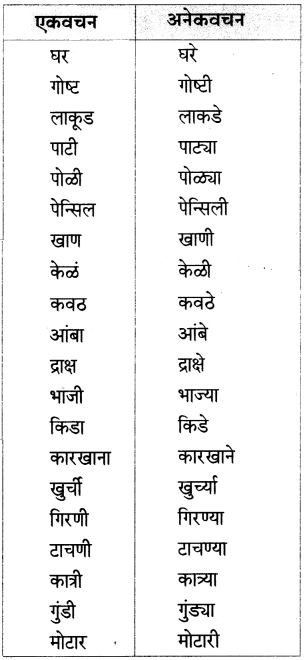
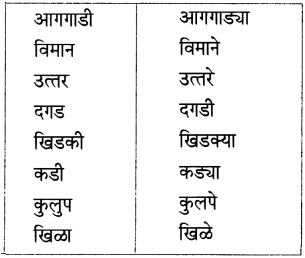
4. व्याकरण.
अ. समानार्थी शब्द लिहा.
प्रश्न अ.
समानार्थी शब्द लिहा.
- निकड –
- उचित –
- उसंत –
- व्यग्न –
उत्तर :
- निकड – गरज
- उचित – योग्य
- उसंत – सवड
- व्यग्र – गर्क
![]()
आ. खालील सामासिक शब्दांचा विग्रह करून समास ओळखा.
प्रश्न आ.
खालील सामासिक शब्दांचा विग्रह करून समास ओळखा.
- ताणतणाव –
- दरडोई –
- यथाप्रमाण –
- जीवनशैली –
उत्तर :
- ताणतणाव – ताण, तणाव वगैरे → समाहार व्वंद्व
- दरडोई – प्रत्येक डोईला → अव्ययीभाव
- यथाप्रमाण – प्रमाणाप्रमाणे → अव्ययीभाव
- जीवनशैली – जीवनाची शैली → विभक्ती तत्पुरुष
इ. कंसातील सूचनेनुसार वाक्यरूपांतर करा.
प्रश्न इ.
कंसातील सूचनेनुसार वाक्यरूपांतर करा.
- आजच्या जीवनात विलक्षण वेगवानता आढळते. (उद्गारार्थी करा.)
- आपल्याकडे कामाच्या ठिकाणाची अंतरे कमी आहेत. (नकारार्थी करा.)
- निसर्गरम्य स्थान किंवा मंदिर पाहण्यासाठी ही माणसे का जात नाहीत? (विधानार्थी करा.)
उत्तर :
- किती विलक्षण वेगवानता आढळते आजच्या जीवनात!
- आपल्याकडे कामाच्या ठिकाणांची अंतरे जास्त नाहीत.
- माणसांनी निसर्गरम्य स्थान किंवा मंदिर पाहण्यासाठी जायला हरकत नाही.
![]()
5. स्वमत.
प्रश्न अ.
‘वाहनांच्या अतिवापराने शरीर व्यापारात अडथळे निर्माण होतात’, तुमचे मत सोदाहरण स्पष्ट करा.
उत्तर :
अलीकडच्या काळात जीवन विलक्षण गतिमान झाले आहे. एकाच माणसाला अनेक कामे पार पाडावी लागतात. तीसुद्धा कमी अवधीत. कामांशी संबंधित ठिकाणी अनेक माणसांना अनेक ठिकाणी गाठावे लागते. मोठमोठी अंतरे कापावी लागतात. चालत जाऊन ही कामे करता येणे शक्य नसते. साहजिकच वाहनांचा उपयोग अपरिहार्य ठरतो.
फक्त एका-दोघांना किंवा फक्त काहीजणांनाच वाहन वापरावे लागते असे नाही. सामान्य माणसांनाही वाहन वापरणे गरजेचे होऊन बसले आहे. सतत वाहन वापरण्याचे दुष्परिणाम खूप होतात. आपण चालत चालत जाऊन कामे करतो, तेव्हा शरीराच्या सर्व प्रकारच्या हालचाली होतात. इकडे-तिकडे वळणे, खाली वाकणे, वर पाहणे, मागे पाहणे, हात वर-खाली करणे, पाय दुमडून बसणे.
पाय लांब करून बसणे, उकिडवे बसणे अशा कितीतरी लहान लहान कृतींतून शारीरिक हालचाली घडत असतात. या हालचालींमुळे शरीराच्या सगळ्याच स्नायूंना आणि सांध्यांना भरपूर व्यायाम मिळतो. शरीर लवचीक बनते. आपण या हालचाली सहजगत्या, एका लयीत करू शकतो. एक सुंदर, नैसर्गिक लय शरीराला लाभते. मात्र, सतत वाहनांचा उपयोग करावा लागल्यामुळे हालचालींना आपण मुकतो.
शरीराला लवचिकता प्राप्त होत नाही. शरीराच्या अनेक व्याधींना सुरुवात होते. दुःखे, कटकटी भोगाव्या लागतात. पैसा, वेळ खर्च होतो. दैनंदिन जीवन विस्कळीत होते. जगण्यातला आनंद नाहीसा होतो. म्हणजे आपल्या शरीर व्यापारात अनेक अडथळे निर्माण होतात.
![]()
प्रश्न आ.
‘वाढता वेग म्हणजे ताण’, याविषयी तुमचे मत सविस्तर लिहा.
उत्तर :
माणसे वाहनात बसली की ते दृश्य पाहण्यासारखे असते. सर्वजण उल्हसित मन:स्थितीत असतात. सगळ्यांच्या बोलण्याच्या कोलाहलामुळे वातावरणात आनंद भरून जातो. वाहनचालकाला हळूहळू सुरसुरी येते. तो हळूहळू वेग वाढवू लागतो. सर्वजण उत्तेजित होतात. गाडीचा वेग वाढतच जातो. मागे पडत जाणाऱ्या वाहनांकडे सगळेजण विजयी मुद्रेने पाहू लागतात.
चालक हळूहळू बेभान होतो. अन्य गाडीवाले सामान्य आहेत, कमकुवत आहेत, आपण सम्राट आहोत, अशी भावना मनातून उसळी घेऊ लागते. अशा मन:स्थितीत माणूस विवेक गमावतो. गाडी सुरक्षितपणे चालवण्यासाठी ही मन:स्थिती अनुकूल नसते. गाडी सुरक्षितपणे चालवण्यासाठी चित्त एकवटून वाहनावर केंद्रित करावे लागते. हात आणि पाय यांच्या हालचाली अचूक जुळवून घेण्यासाठी सतत मनाची तयारी ठेवावी लागते.
क्लच, ब्रेक, अक्सलरेटर, यांच्याकडे बारीक लक्ष ठेवावे लागते. त्याच वेळी पाठीमागून व बाजूने येणारी वाहने आणि आपण यांच्यात सुरक्षित अंतर ठेवण्याचा कसोशीने प्रयत्न करावा लागतो. अन्य एखादे वाहन मध्येच आडवे येईल का, आपल्या वाहनाला धडकेल का, आपल्याला जिथे वळायचे आहे तिथे वळता येईल का, त्या वेळी बाकीच्या वाहनांची स्थिती कशी असेल, त्यांच्यापैकी कोणीही स्वत:ची दिशा बदलण्याचा संभव आहे का इत्यादी अनेक बाबींचा विचार काही क्षणांत करावा लागतो.
त्या अनुषंगाने सतत विचार करीत राहावे लागते. वाहन आणि वाहनाची गती यांखेरीज अन्य कोणतेही विचार मनात आणता येत नाहीत. एकाच विचाराला जखडले गेल्यामुळे डोळ्यांवर, शरीरावर व मनावर विलक्षण ताण येतो. अपघाताची भीती मनात सावलीसारखी वावरत असते. तासन्तास तणावाखाली राहावे लागल्याने मनावर विपरीत परिणाम होतात. वाहनाचा वेग जास्त असल्यामुळे अगदी बारीकशा खड्ड्यानेसुद्धा वाहनाला हादरे बसतात. सांधे दुखतात. ते कमकुवत होतात. अशा प्रकारे वाढता वेग म्हणजे ताण, हे समीकरण तयार होते.
![]()
प्रश्न इ.
‘वाहन हे वेळ वाचवण्यासाठी असते. ते वेळ घालवण्यासाठी नसते’, हे विधान तुमच्या शब्दांत स्पष्ट करा.
उत्तर :
खरे तर प्राचीन काळापासून वाहन निर्माण करणे, हे माणसाचे स्वप्न होते. त्याच्या मनात खोलवर रुजलेले हे स्वप्न प्राचीन कथांमधून, देवदेवतांच्या कथांमधून सतत व्यक्त होत राहिले आहे. माणसाच्या मनातल्या या प्रबळ प्रेरणेतूनच वाहनाची निर्मिती झाली आहे. वेळ आणि श्रम वाचवणे हाच वाहनाच्या निर्मितीमागील हेतू आहे. अलीकडच्या काळात जीवनाचा वेग प्रचंड वाढला आहे. वेळ थोडा असतो. कामे भरपूर असतात. कामाची ठिकाणेसुद्धा दूर दूर असतात. अनेक ठिकाणी जावे लागते.
अनेक माणसांना भेटावे लागते. म्हणूनच वाहनांची निर्मिती झाली आहे. वाहनांमुळे माणसाची प्रचंड प्रगती झाली आहे. त्यामुळे वाहनाला माणसाच्या जीवनात फार मोठे स्थान मिळालेले आहे. अशी ही अत्यंत महत्त्वाची वस्तू आपल्याकडे असावी, असे सगळ्यांना वाटू लागते. माणसे धडपडून वाहने प्राप्त करतात. प्रतिष्ठा मिळवतात. पण वेळ व श्रम वाचवणे हा उद्देश मात्र त्यांच्या मनातून केव्हाच दूर होतो. वाहन हे साधन आहे.
ते आपला वेळ वाचवते यात शंकाच नाही. परंतु काहीही केले तरी किमान वेळ हा लागतोच. शून्य वेळामध्ये आपण कुठेही पोहोचू शकत नाही. वाहन ही अखेरीस एक वस्तू आहे. वस्तूला तिच्या मर्यादा असतात. हे लक्षात न घेता आपण जास्तीत जास्त वेग वाढवून कमीत कमी वेळात पोहोचण्याचा हव्यास बाळगतो. अतिवेगामुळे आपलेच नुकसान होते. अनेक शारीरिक व्याधी आपल्याला जडतात. शारीरिक क्षमता उणावते. जगण्यातला आनंद कमी होतो. हे सर्व आपण सतत लक्षात ठेवले पाहिजे.
पण हे कोणीही लक्षात घेत नाही. केवळ हौसेसाठी, गंमत-जंमत करण्यासाठी, आपल्याकडे गाडी आहे, ऐश्वर्य आहे हे दाखवण्यासाठी लोक गाडीचा उपयोग करतात. हळूहळू गाडीचे गुलाम बनतात. गाडी हे एक साधन आहे, हे आपण सतत लक्षात ठेवले पाहिजे.
![]()
प्रश्न ई.
‘वाहनाची अतिगती ही विकृती आहे’, स्पष्ट करा.
उत्तर :
वाहनाची अतिगती ही विकृती आहे, हे विधान शंभर टक्के सत्य आहे. हे विधान मला पूर्णपणे मान्य आहे. विकृती म्हणजे जे सहज नाही, नैसर्गिक नाही ते. कल्पना करा. आपल्याला चॉकलेट खूप आवडते. सर्व जगात असे किती जण आहेत, जे सकाळी, दुपारी, संध्याकाळी व रात्री आवडते म्हणून फक्त चॉकलेटच खातात? समजा एखादयाला पांढरा रंग खूप आवडतो, म्हणून तो घरातल्या सर्व माणसांना फक्त पांढऱ्या रंगाचेच कपडे घेतो. घराला पांढरा रंग देतो. अंथरुणे-पांघरुणे पांढरी, खिडक्यांचे पडदे पांढरे, भांडीकुंडी, फर्निचर पांढऱ्या रंगाचे. हे असे करणारा जगामध्ये.
एक तरी माणूस असेल का? सर्वजण पायांनी चालतात. उलटे होऊन हातांवर तोल सावरत प्रयत्नपूर्वक चालता येऊ शकते. पण अशा त-हेने नियमितपणे जाणारा एक तरी माणूस सापडेल का? जे सहज आहे, नैसर्गिक आहे तेच साधारणपणे माणूस करतो. तीच खरे तर प्रकृती असते. याच्या विरुद्ध वागणे म्हणजे विकृती होय. रोजच्या जेवणात वरण-भात आणि भाजी-पोळी असणे, घरात विविध रंगसंगती योजणे, पायांनी चालणे हे सर्व सहज, नैसर्गिक आहे.
सर्व माणसे तसेच वागतात. हाच न्याय वाहनांनासुद्धा लागू पडतो. मर्यादित वेगाने वाहन चालवत, अपघाताची शक्यता निर्माण होऊ न देता, सुरक्षितपणे, वेळेत पोहोचणे हा वाहनाने प्रवास करण्याचा हेतू असतो. हा हेतू आपण अतिवेगाचा हव्यास बाळगला नाही तरच यशस्वी होतो. म्हणून अतिवेग ही विकृती होय, हेच खरे.
6. अभिव्यक्ती.
प्रश्न अ.
रस्त्यावरील वाहतूक कोंडीत सापडल्यावर तुमची भूमिका काय असेल ते लिहा.
उत्तर :
सध्या वाहनांची प्रचंड गर्दी झाली आहे. रस्ते मात्र पूर्वीएवढेच आहेत. रस्त्यांची संख्या पूर्वीइतकीच आणि त्यांची लांबी-रुंदीसुद्धा पूर्वीइतकीच. गाड्यांची संख्या मात्र प्रचंड वाढली आहे. कमी वेळात पोहोचण्याच्या इच्छेने वाहन खरेदी केले जाते खरे; पण वाहतूक कोंडीतच तासन्तास वाया जातात. या परिस्थितीमुळे मनाचा संताप होतो. वाहन आपल्या मालकीचे असते. पण रस्ता.
आपल्या मालकीचा नसतो. मग वाहतूक कोंडीच्या ठिकाणी प्रचंड गदारोळ माजतो. प्रत्येकजण स्वत:ची गाडी वाटेल तशी पुढे दामटत राहतो. सर्व गाड्या एकमेकांच्या वाटा अडवून उभ्या राहतात. कोणीही पुढे जाऊ शकत नाही की मागे परतू शकत नाही. गाड्यांचे हॉर्न कर्कश आवाजात मोठमोठ्याने कोकलत असतात. काही जणांची भांडणे सुरू होतात. पोलीस हतबल होतात.
अशा प्रसंगात मी सापडलो तर? सर्वप्रथम हे लक्षात घेईन की परिस्थिती माझ्या नियंत्रणात नाही. मी पूर्णपणे शांत राहीन. मनाची चिडचिड होऊ देणार नाही. अस्वस्थ होणार नाही. हॉर्न तर मुळीच वाजवणार नाही. मध्ये मध्ये घुसून पुढे जाण्याचा प्रयत्न करणार नाही. तसे करणाऱ्यांना समजावून सांगण्याचा प्रयत्न करीन. कारण अशा पद्धतीने कोणीही पुढे जाऊ शकत नाही.
उलट अडचणींमध्ये भर पडण्याची शक्यता जास्त. आपण स्वतः पुढे होऊन रहदारीचे नियंत्रण करू लागलो तर लोक आपले ऐकणार नाहीत. पण आणखी एका दोघांशी बोलून दोघे-तिघे जण तिथल्या पोलीस काकांना भेटू. आमची मदत करण्याची इच्छा बोलून दाखवू. त्यांच्याशी चर्चा करून काय काय करायचे ते ठरवून घेऊ. कामांची आपापसांत वाटणी करून घेऊ आणि पोलीस काकांच्या मार्गदर्शनाखाली वाहतूक नियंत्रण सुरू करू.
![]()
प्रश्न आ.
वाहन चालवत असताना कोणती काळजी घ्यावी, ते तुमच्या शब्दांत लिहा.
उत्तर :
गाडी चालवताना काळजी घेतली आणि वाहतुकीचे नियम काटेकोरपणे पाळले तर प्रवास सुखाचा, सुरक्षित आणि कमीत कमी वेळेत पूर्ण होतो.
गाडी चालवायला बसण्यापूर्वीची पूर्वतयारी :
- प्रत्येक वेळी गाडी चालवायला बसण्यापूर्वी वाहन चालवण्याचा परवाना (ड्रायव्हिंग लायसन्स), अन्य आवश्यक कागदपत्रे (विमा, पीयुसी इत्यादी) घेतल्याची खात्री करून घ्यावी.
- टायरमधील हवा आणि गाडीतील इंधन पुरेपूर असल्याची खात्री करावी.
- गाडीतील प्रवाशांना वाहतुकीच्या सामान्य नियमांची कल्पना दयावी. आणीबाणीच्या प्रसंगी काय करावे त्याची माहिती दयावी.
प्रत्यक्ष गाडी चालवताना घ्यायची काळजी :
- गाडीवर पूर्ण लक्ष ठेवावे.
- गाडीतील प्रवाशांच्या गप्पांत सामील होऊ नये.
- गाडीचा वेग पन्नास-साठ किलोमीटरच्या पलीकडे जाऊ देऊ नये; कारण आपल्याकडील रस्ते अजूनही साठ किलोमीटरपेक्षा जास्त वेगाने जाण्यास योग्य बनवलेले नाहीत.
- जास्त वेगामुळे सतत हादरे बसतात आणि सर्वांनाच त्रास होतो. शारीरिक व्याधी जडतात. म्हणून जास्त वेगाचा मोह टाळावा.
- गाडीतील प्रवाशांना गप्पा मारण्यास बंदी घालता येत नाही. तरीही गप्पांच्या ओघात अचानक मोठ्याने ओरडणे किंवा हास्यस्फोटक विनोद करणे या गोष्टी टाळण्याच्या सूचना दयाव्यात.
- स्वत:ची लेन सोडून जाऊ नये.
- लेन बदलताना, वळण घेताना, रस्ता बदलताना खूप आधीपासून तयारी करावी. योग्य ते सिग्नल दयावेत.
- वाटेत जागोजागी लावलेल्या वाहतुकीच्या सूचनांचे काटेकोर पालन करावे.
- गाडीत धूम्रपान, मद्यपान करू नये. गाडी चालकाने तर मुळीच करू नये.
अशा प्रकारे काळजी घेतल्यास आपला प्रवास सुखाचा होतो.
![]()
उपक्रम :
‘वाहतूक नियंत्रण पोलीस कर्मचारी’ यांची अभिरूप मुलाखत तुमच्या वर्गमित्राच्या/मैत्रिणीच्या मदतीने वर्गात सादर करा.
तोंडी परीक्षा :
‘वाहतूक सुरक्षेची गरज’ या विषयावर पाच मिनिटांचे भाषण दया.
Marathi Yuvakbharati 12th Digest Chapter 1 वेगवशता Additional Important Questions and Answers
प्रश्न. पुढील उतारा वाचा आणि दिलेल्या सूचनांनुसार कृती करा :
कृती 1 : (आकलन)
योग्य पर्याय निवडून उत्तर लिहा.
प्रश्न 1.
1. वाहनाचा वेग अनिवार झाला, तर …….
2. शरीर-मनावरील ताण नाहीसे होतात.
3. शरीरभर आनंदाची स्पंदने निर्माण होतात.
4. आरोग्याची हानी होते.
5. एकाच जागी तासन्तास जखडून बसण्याचे शारीरिक कौशल्य अवगत होते.
उत्तर :
4. आरोग्याची हानी होते.
पुढील वाक्यांचा अर्थ सोदाहरण स्पष्ट करा :
प्रश्न 1.
जीवन हे दशदिशांना विभागले आहे.
उत्तर :
आधुनिक काळात खूप प्रगती झाल्यामुळे माणसे पूर्वीच्या काळापेक्षा कमी वेळात जास्त कामे करतात. त्यामुळे कामांची ठिकाणे अनेक असतात. ही ठिकाणे दूर दूर पसरलेली असतात.
![]()
प्रश्न 2.
अंतरावरच्या गोष्टींशी जवळीक साधण्यासाठी दूरवर जावे लागते.
उत्तर :
अमेरिकेसारख्या देशामध्ये राहण्याची ठिकाणे, नोकरीव्यवसायाची ठिकाणे, अन्य कामाची ठिकाणे ही सर्व दूर दूर अंतरावर असतात. ही अंतरे पार करण्यासाठी खूप प्रवास करावा लागतो. भारतातील अनेक व्यक्तींची मुले अमेरिकेसारख्या दूरदूरच्या देशांमध्ये राहतात. ही सर्व माणसे एकमेकांना नियमितपणे व सहजपणे भेटू शकत नाहीत. साहजिकच अंतरामुळे त्यांच्यात दुरावा निर्माण होतो.
शकत नाही. गाड्यांचे हॉर्न कर्कश आवाजात मोठमोठ्याने कोकलत असतात. काही जणांची भांडणे सुरू होतात. पोलीस हतबल होतात. अशा प्रसंगात मी सापडलो तर? सर्वप्रथम हे लक्षात घेईन की परिस्थिती माझ्या नियंत्रणात नाही. मी पूर्णपणे शांत राहीन. मनाची चिडचिड होऊ देणार नाही. अस्वस्थ होणार नाही. हॉर्न तर मुळीच वाजवणार नाही.
मध्ये मध्ये घुसून पुढे जाण्याचा प्रयत्न करणार नाही. तसे करणाऱ्यांना समजावून सांगण्याचा प्रयत्न करीन. कारण अशा पद्धतीने कोणीही पुढे जाऊ शकत नाही. उलट अडचणींमध्ये भर पडण्याची शक्यता जास्त. आपण स्वतः पुढे होऊन रहदारीचे नियंत्रण करू लागलो तर लोक आपले ऐकणार नाहीत. पण आणखी एका दोघांशी बोलून दोघे-तिघे जण तिथल्या पोलीस काकांना भेटू. आमची मदत करण्याची इच्छा बोलून दाखवू. त्यांच्याशी चर्चा करून काय काय करायचे ते ठरवून घेऊ. कामांची आपापसांत वाटणी करून घेऊ आणि पोलीस काकांच्या मार्गदर्शनाखाली वाहतूक नियंत्रण सुरू करू.
![]()
प्रश्न 3.
रस्त्याने कोणी चालण्याऐवजी पळू लागला तर त्याचे कौतुक करावे का?
उत्तर :
रस्त्याने कोणीही चालण्याऐवजी पळू लागला, तर कोणीही कौतुक करणार नाही. रस्ते, वाटा या चालण्यासाठी असतात. माणसे सर्वसाधारणपणे जशा कृती करतात, जशी वागतात, तशी वागली तर लोकांना बरे वाटते. वेगळी वागली, तर काहीतरी विचित्र घडत आहे, असे वाटू लागते.
लिहा :
प्रश्न 1.
- घरोघर व दरडोई वाहन उपलब्ध असलेला देश : ………….
- वेगामुळे बेभान होणारी : ………….
- अमेरिकन जीवनशैली ज्यांनी पत्करू नये ते : ………….
- गाड्यांनी एकमेकांना जोडली जाणारी : ………….
- वाहनांमुळे वाचतात : ………….
- माणसांवर स्वार होणारी : ………….
उत्तर :
- अमेरिका
- माणसे
- भारतीय
- महानगरे
- वेळ, श्रम
- वाहने.
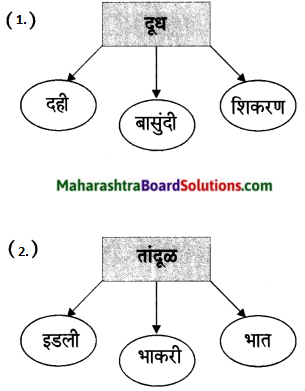
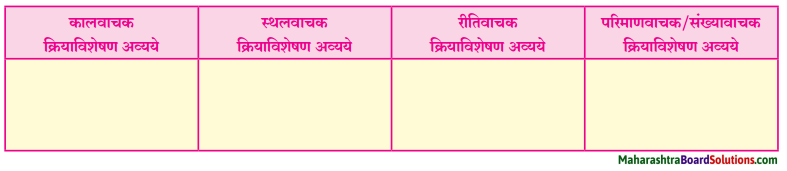
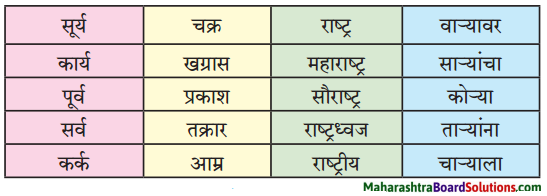
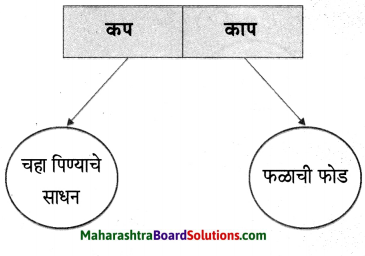
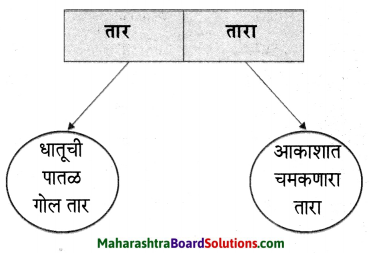
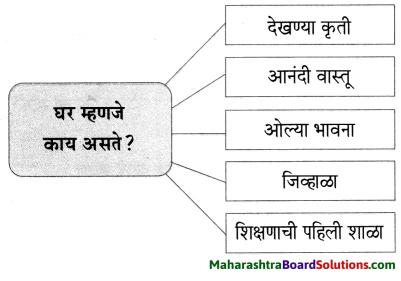
कृती करा :
प्रश्न 1.

उत्तर :

प्रश्न 2.


उत्तर :


प्रश्न 3.

उत्तर :

रिकाम्या चौकटी भरा :
प्रश्न 1.

उत्तर :

रिकाम्या जागा भरा :
प्रश्न 1.
वाई, सातारा अशा गावी वाहनाचा उपयोग होऊ शकतो, जर …
i. ………………….
ii. …………………
उत्तर :
वाई, सातारा अशा गावी वाहनाचा उपयोग होऊ शकतो, जर …
i. तातडीने शेतमळ्यावर जाण्याची वेळ आली.
ii. आपण गावाबाहेर राहत असू.
प्रश्न 2.
इतरांशी मानसिक स्पर्धा करण्यासाठी किंवा आपल्या ऐश्वर्याचे प्रदर्शन घडवण्यासाठी माणसे …..
उत्तर :
इतरांशी मानसिक स्पर्धा करण्यासाठी किंवा आपल्या ऐश्वर्याचे प्रदर्शन घडवण्यासाठी माणसे गरज नसताना कर्ज काढून वाहने खरेदी करतात.
![]()
सूचनेप्रमाणे उत्तरे लिहा :
प्रश्न 1.
वाहनाचा वेग बेताचा हवा, असे लेखक सांगतात त्यामागील कारण लिहा.
उत्तर :
वाहनाचा वेग बेताचा हवा, असे लेखक सांगतात, त्यामागील कारण अतिघाई किंवा अतिवेग यांत कोणतेही औचित्य नसते.
प्रश्न 2.
अपघात होण्याची दोन कारणे लिहा.
उत्तर :
- वेग वाढल्यामुळे वाहनावरचा ताबा सुटणे आणि
- पुढच्या वाहनाला मागे टाकून पुढे जाण्याचा हव्यास या दोन कारणांनी अपघात होतात.
वाक्ये पूर्ण करा :
प्रश्न 1.
- जर वाहनाचा वेग वाढला, तर …………..
- पुढचे वाहन मागे टाकून पुढे जाण्याचा जर हव्यास बाळगला, तर …………
- रात्री भरधाव वेगाने प्रवास करू नये; कारण ………….
उत्तर :
- जर वाहनाचा वेग वाढला, तर त्यावरचा ताबा कमी होतो.
- पुढचे वाहन मागे टाकून पुढे जाण्याचा जर हव्यास बाळगला, तर अपघात होतो.
- रात्री भरधाव वेगाने प्रवास करू नये; कारण झटपट पार पडलीच पाहिजेत अशी महत्त्वाची कामे दरवेळी नसतात.
व्याकरण :
वाक्यप्रकार:
वाक्यांच्या आशयावरून वाक्यप्रकार ओळखा :
प्रश्न 1.
- वेग हे गतीचे रूप आहे. → [ ]
- जीवनाची ही टोके सांधणार कशी? → [ ]
- बापरे! किती हा जीवघेणा वेग! → [ ]
उत्तर :
- विधानार्थी वाक्य
- प्रश्नार्थी वाक्य
- उद्गारार्थी वाक्य
![]()
प्रश्न 2.
क्रियापदाच्या रूपांवरून वाक्यप्रकार ओळखा :
- गतीला जेव्हा दिशा असते, तेव्हाच ती प्रगती या संज्ञेला पात्र ठरते. → [ ]
- सुसाट गतीला आवरा. → [ ]
- कामापुरते व कामासाठी वाहन काढावे. → [ ]
- वाहनांच्या वेगाची चिंता वाटते. → [ ]
उत्तर :
- संकेतार्थी वाक्य
- आज्ञार्थी वाक्य
- विध्यर्थी वाक्य
- स्वार्थी वाक्य
प्रयोग ओळखा :
प्रश्न 1.
- अचानक वेग वाढतो. → [ ]
- माणसाने वाहन चालविले. → [ ]
- माणसाने वेगाला आवरावे. → [ ]
उत्तर :
- कर्तरी प्रयोग
- कर्मणी प्रयोग
- भावे प्रयोग
अलंकार :
पुढील अलंकार ओळखा :
प्रश्न 1.
आईसारखे दैवत आईच होय!
उत्तर :
अनन्वय अलंकार
![]()
शब्दार्थ :
- प्रगती – जीवनाचा स्तर, दर्जा उंचावणे.
- अगतिक – असहाय, केविलवाणे.
- अवखळ – खट्याळ, उपद्रवी.
- उरकणे – आटोपणे.
- यथाप्रमाण – आवश्यक तेवढे.
- त्वरा – घाई, जलदगती.
- कृतकृत्य – धन्य, यशस्वी.
- अनिवार – अतिशय.
- भावविवश – हळवा, भावनाप्रधान.
- यथासांग – (यथा + स + अंग) आवश्यक त्या सर्व बाजूंनी.
वाक्प्रचार व त्याचा अर्थ :
यथासांग पार पाडणे – सर्व बाजू पूर्ण करून पार पाडणे.
Marathi Yuvakbharati 12th Digest Pdf भाग-१