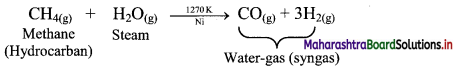
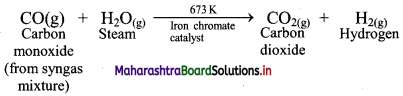
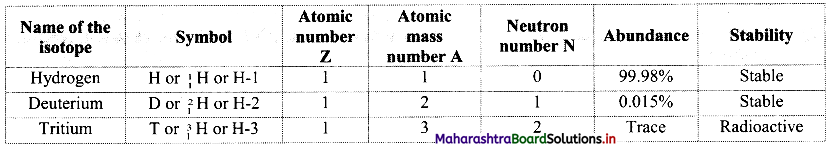
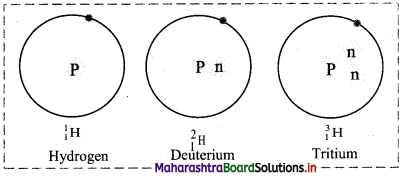
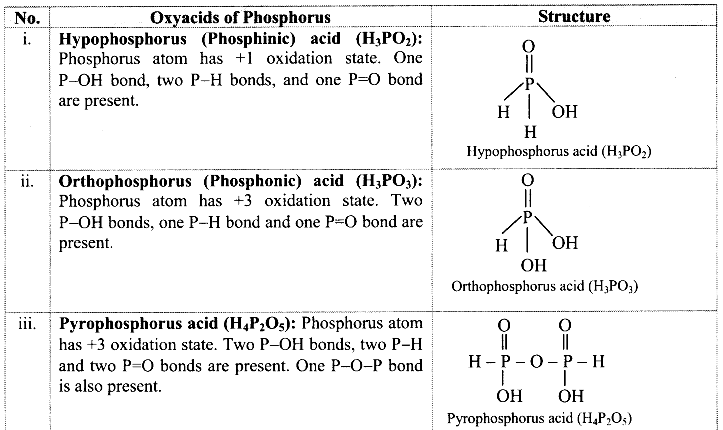
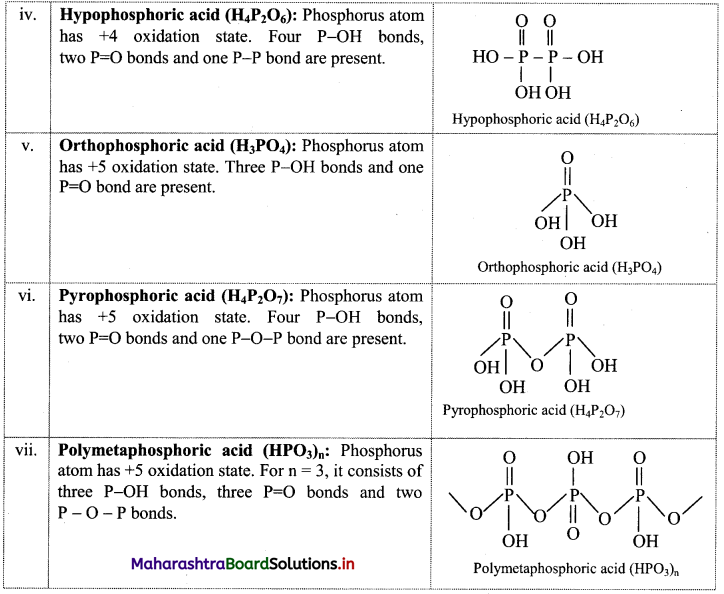
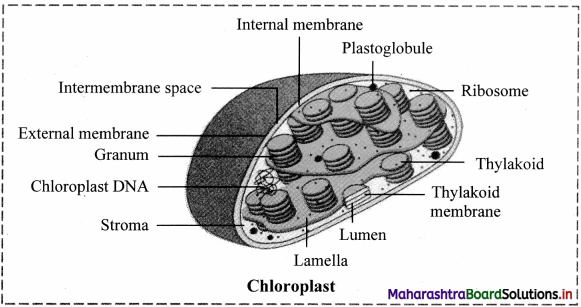
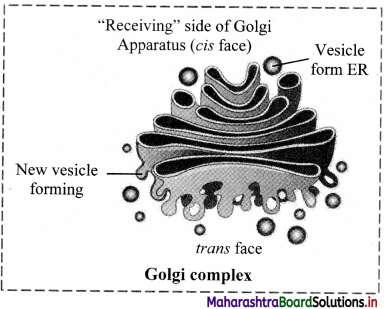
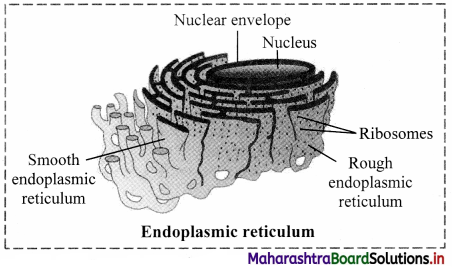
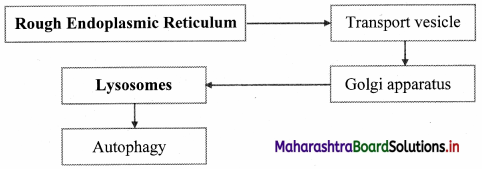
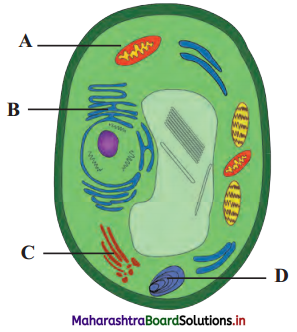
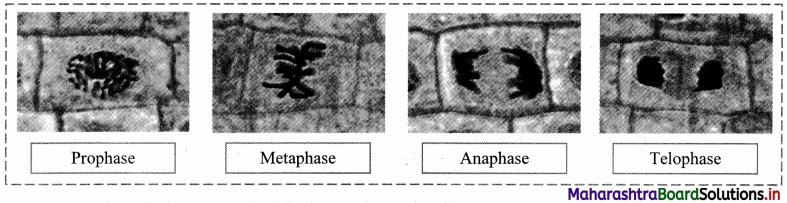
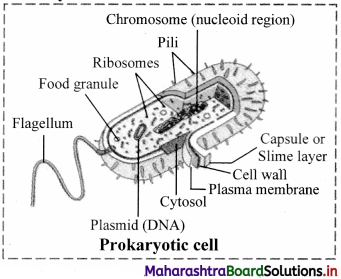
Balbharti Maharashtra State Board 11th Biology Textbook Solutions Chapter 2 Systematics of Living Organisms Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
Systematics of Living Organisms Class 11 Exercise Question Answers Solutions Maharashtra Board
Class 11 Biology Chapter 2 Exercise Solutions Maharashtra Board
Biology Class 11 Chapter 2 Exercise Solutions
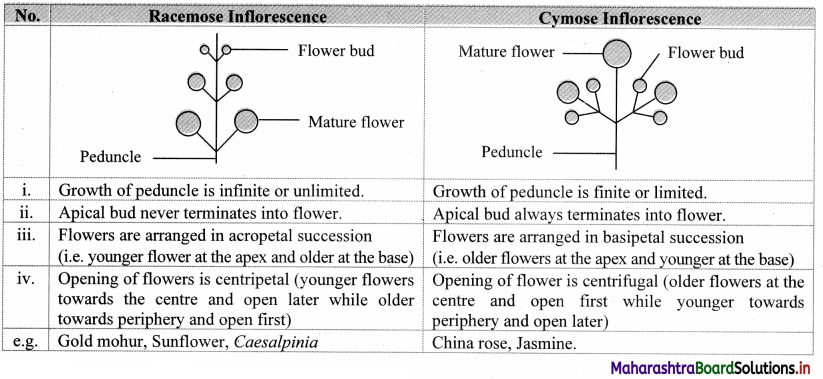
1. Choose correct option.
Question (A)
Which of the following shows single stranded RNA and lacks protein coat?
(a) Bacteriophage
(b) Plant virus
(c) Viroid
(d) Animal virus
Answer:
(c) Viroid
![]()
Question (B)
Causative agent of red tide is ________ .
(a) Dinoflagellate
(b) Euglenoid
(c) Chrysophyte
(d) Lichen
Answer:
(A) Dinoflagellate
Question (C)
Select odd one out for Heterotrophic bacteria.
(a) Nitrogen fixing bacteria
(b) Lactobacilli
(c) Methanogens
(d) Cyanobacteria
Answer:
(c) Methanogens or (d) Cyanobacteria
Question (D)
Paramoecium: Ciliated Protist :: Plasmodium: _______ .
(a) Amoeboid protozoan
(b) Ciliophora
(c) Flagellate protozoan
(d) Sporozoan
Answer:
(d) Sporozoan
![]()
2. Answer the following
Question (A)
What are the salient features of Monera?
Answer:
Salient features of Kingdom Monera:
- Size: The organisms included in this kingdom are microscopic, unicellular and prokaryotic.
- Occurrence: These are omnipresent. They are found in all types of environment which are not generally inhabited by other living beings.
- Nucleus: These organisms do not have well-defined nucleus. DNA exists as a simple double-stranded circular single chromosome called as nucleoid. Apart from the nucleoid they often show presence of extrachromosomal DNA which is small circular called plasmids.
- Cell wall: Cell wall is made up of peptidoglycan (also called murein) which is a polymer of sugars and amino acids.
- Membrane-bound cell organelles: Membrane-bound cell organelles like mitochondria, chloroplast, endoplasmic reticulum are absent. Ribosomes are present, which are smaller in size (70S) than in eukaryotic cells.
- Nutrition: Majority are heterotrophic, parasitic or saprophytic in nutrition. Few are autotrophic that can be either photoautotrophs or chemoautotrophs.
- Reproduction: The mode of reproduction is asexual or with the help of binary fission or budding. Very rarely, sexual reproduction occurs by conjugation method.
- Examples:
Archaebacteria: e.g. Methanobacillus, Thiobacillus, etc.
Eubacteria: e.g. Chlorobium, Chromatium, and Cyanobacteria e.g. Nostoc, Azotobacter, etc.
Question (B)
What will be the shape of a bacillus and coccus type of bacteria?
Answer:
The shape of bacillus type of bacteria is rod-shaped and coccus is spherical.
Question (C)
Why is binomial nomenclature important?
Answer:
Binomial nomenclature is important because:
- The binomials are simple, meaningful and precise.
- They are standard since they do not change from place to place.
- These names avoid confusion and uncertainty created by local or vernacular names. The organisms are known by the same name throughout the world.
- The binomials are easy to understand and remember.
- It indicates phylogeny (evolutionary history) of organisms.
- It helps to understand inter-relationship between organisms.
![]()
3. Write short notes
Question (A)
Write a note on useful and harmful bacteria.
Answer:
(i) Useful bacteria:
Most of the bacteria act as a decomposer. They breakdown large molecules in simple molecules or minerals. Examples of some useful bacteria:
Lactobacillus’. It helps in curdling of milk.
Azotobacter. It helps to fix nitrogen for plants.
Streptomyces: It is used in antibiotic production such as streptomycin.
Methanogens: These are used for production of methane (biogas) gas from dung.
Pseudomonas spp. and Alcanovorax borkumensis: These bacteria have the ability to destroy the pyridines and other chemicals. Hence, used to clear the oil spills.
(ii)Harmful bacteria:
This includes disease causing bacteria. They cause various diseases like typhoid, cholera, tuberculosis, tetanus, etc. Examples of some harmful bacteria:
Salmonella typhi: It is a causative organism of typhoid.
Vibrio cholerae: It causes cholera.
Mycobacterium tuberculosis’. It causes tuberculosis.
Clostridium tetani: It causes tetanus.
Clostridium spp.: It causes food poisoning.
Many forms of mycoplasma are pathogenic.
Agrobacterium , Erwinia, etc are the pathogenic bacteria causing plant diseases.
Animals and pets also suffer from bacterial infections caused by Brucella, Pastrurella, etc.
Question (B)
Write short note on five kingdom system.
Answer:
Five kingdom system of classification was proposed by R.H. Whittaker in 1969. This system shows the phylogenetic relationship between the organisms.
The five kingdoms are:
- Kingdom Monera
- Kingdom Protista
- Kingdom Plantae
- Kingdom Fungi
- Kingdom Animalia
Question (C)
Write short note on useful fungi.
Answer:
Economic importances of fungi are as follows:
1. Role of fungi in medicine:
(a) Antibiotic penicillin is obtained from Penicillium.
(b) Drugs like cyclosporine, immunosuppressant drugs, precursors of steroid hormones, etc are isolated from fungi.
2. Role of fungi in industries:
(a) Yeast is used in bread making. It causes dough to rise and make the bread light and spongy. It is also used in breweries or wine making industries. Sugars present in grapes are fermented by using yeast. This results in production of alcohol which is used for making wine.
(b) Lichen is a symbiotic association of algae and fungi are used in preparation of litmus paper which is used as acid-base indicator.
3. Role of fungi in food:
(a) Fungi like mushrooms are consumed as a food. These are rich source of protein.
(b) Fungi genus Penicillium helps in ripening of cheese.
4. Role of fungi as biocontrol agents:
(a) Fungi help to control growth of weeds.
(b) Pathogenic fungi like Fusarium sp., Phytophthorapalmivora, Alternaria crassa, etc act as mycoherbicides.
![]()
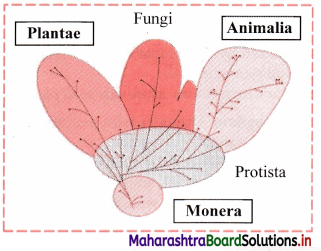
Question 4.
Complete tree diagram in detail.
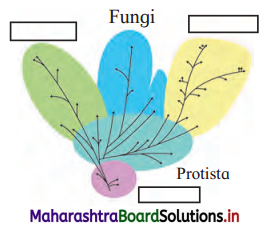
Answer:
5. Draw neat labelled diagrams
Question (A)
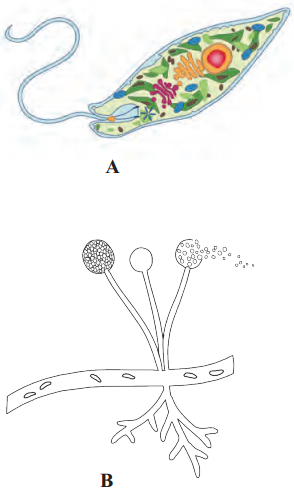
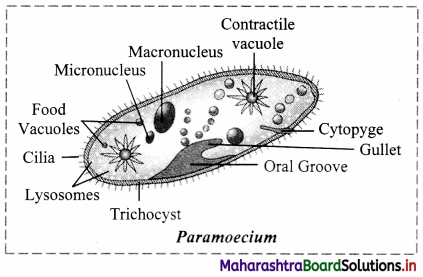
Draw neat and labelled diagram of Paramoecium.
Answer:
Characteristics:
- It belongs to kingdom Protista. It is further classified as animal like protist.
- It lacks cell wall.
- It shows heterotrophic and holozoic nutrition.
- It is a ciliated protozoan where locomotion is due to cilia.
- It has gullet (a cavity) which opens on the cell surface.
Quesiton (B)
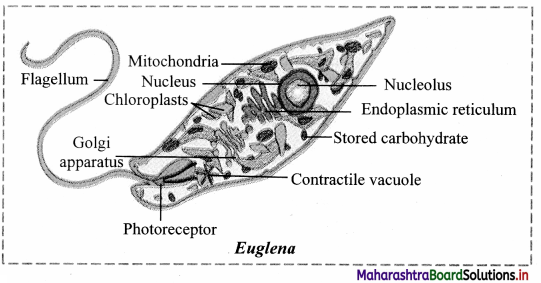
Draw neat and labelled diagram of Euglena.
Answer:
Characteristics:
It belongs to kingdom Protista. It is further classified into euglenoids.
1. Dinoflagellates:
- They are aquatic (mostly marine) and autotrophic (photosynthetic).
- They have wide range of photosynthetic pigments which can be yellow, green, brown, blue and red.
- The cell wall is made up of cellulosic stiff plates.
- A pair of flagella is present, hence they are motile.
- They are responsible for famous ‘red tide’. E.g. Gonyaulax. It makes sea appear red.
2. Euglenoids:
- They lack cell wall but have a tough covering of proteinaceous pellicle.
- Pellicle covering provides flexibility and contractibility to Euglena.
- They possess two flagella, one short and other long.
- They behave as heterotrophs in absence of light but possess pigments, similar to that of higher plants, for photosynthesis.
![]()
Question (C)
Draw a neat labelled diagram of TMV.
Answer:
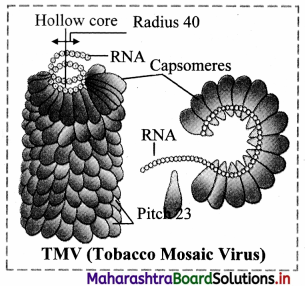
Question 6.
Complete chart and explain in your word.
Answer:
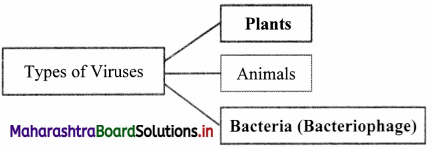
Depending upon the host, viruses are classified into three types as:
1. Plant virus
2. Animal virus
3. Bacterial virus (Bacteriophage)
1. Plant virus:
(a) Generally, they are rod shaped or cylindrical with helical symmetry.
(b) Majority of plant viruses have RNA as their genetic material. (Exception: Cauliflower Mosaic Virus has double stranded DNA as genetic material)
(c) Plant viruses cause disease in plants, e.g. Tobacco Mosaic Virus (TMV).
2. Animal virus:
(a) Generally, they are polyhedral in shape with radial symmetry.
(b) They have either DNA or RNA as genetic material.
(c) It causes disease to majority of animals including human beings, e.g. Influenza virus.
3. Bacteriophage:
(a) They have tadpole-like shape.
(b) They infect bacteria and hence are called as bacteriophage.
(c) Bacteriophages were discovered by Twort.
(d) Bacteriophages have double stranded DNA as the genetic material.
(e) Its body consists of head, collar and tail.
![]()
Question 7.
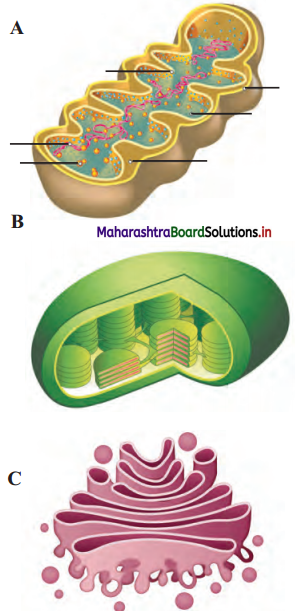
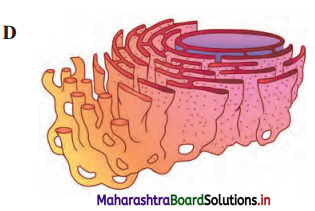
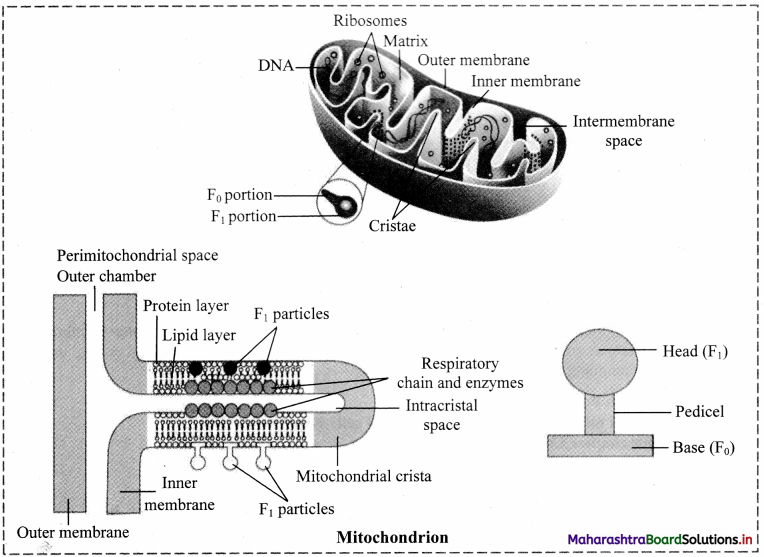
Identify the following diagram, label it and write detail information in your words.
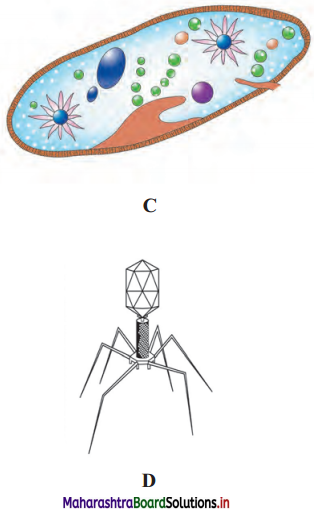
Answer:
The given figure represents Bacteriophage.
A.
B.
c.
D.
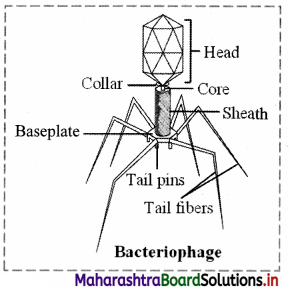
E.
F.
![]()
Question 8.
The scientific name of sunflower is given below. Identify the correctly written name.
(A) Helianthus annus
(B) Helianthus Annus
(C) Helianthus annuus L.
(D) Helianthus annuus l.
Answer:
The correctly written scientific name of sunflower is Helianthus annuus L.
Question 9.
Match the following.
| Kingdom | Examples |
| 1. Monera | a. Riccia |
| 2. Protista | b. Cyanobacteria |
| 3. Plantae | c. Rhizopus |
| 4. Fungi | d. Diatoms |
Answer:
| Kingdom | Examples |
| 1. Monera | b. Cyanobacteria |
| 2. Protista | d. Diatoms |
| 3. Plantae | a. Riccia |
| 4. Fungi | c. Rhizopus |
Question 10.
Complete the following.
1. Plant-like Protista – [ ]
2. [ ] – Entamoeba
Practical /Project:
Question 1.
Make a group of students. Observe living organisms in your school/college campus and try to write their characters with respect to habit, habitat, mode of nutrition, growth- determinate or indeterminate, type of reproduction – vegetative reproduction, asexual reproduction, sexual reproduction. With the help of similarity and dissimilarity, try to classify organisms into different categories. Similar work should implement for animal group.
Answer:
The common living organisms observed near school/college are:
1. Plants
Habit: Herb, shrub, tree, etc.
Habitat: Terrestrial or aquatic
Mode of nutrition: Autotrophic
Growth: Indeterminate
Types of reproduction: Vegetative, asexual and sexual reproduction.
2. Animal e.g. dog, cats, cow, etc.
Habitat: Terrestrial
Mode of nutrition: Heterotrophs
Growth: Determinate
Types of reproduction: Only sexual reproduction
3. Birds e.g. Crow, sparrow, etc.
Habitat: Aviary (shows diverse habitat)
Mode of nutrition: Heterotrophs Growth: Determinate
Types of reproduction: Only sexual reproduction
[Note: Students are expected to collect more information about characteristics of living organisms and classify them into different categories]
![]()
Question 2.
Find out types of lichens and its economic importance.
Answer:
Types of lichens are:
1. Based on fungal components:
(a) Ascolichens:
In this category, the fungal partner belongs to Ascomycetes group of fungi.
(b) Basidiolichens:
Here, the fungal partner belongs to Basidiomycetes group of fungi.
(c) Deuterolichens:
In this category, the fungal partner belongs to Deuteromycetes group of fungi.
2. Based on their forms:
(a) Crustose lichen:
These lichens show crust-like growth.
These lichens grow on rocks and bark of the trees,
e. g. Graphis, Lecanora, Haematomma, etc.
(b) Foliose lichen:
These lichens grow on trees in the hilly regions.
The thallus is like a dry forked leaf,
e. g. Parmelia, Collema, Peltigera
(c) Fruticose lichen:
These lichens are seen on the branches of trees hanging down.
They are cylindrical, well branched and pendulous, with hair-like outgrowths,
e. g. Usnea, Cladonia, Alectoria, etc.
3. Economic importance of lichens:
(a) Lichen as food and fodder:
Many species of lichens are used as food by animals including man. Lichens contain a substance lichenin which is similar to carbohydrate making them edible. Parmelia is used in curry powder in India. Lichens like Cladonia, Citraria, Evernia, Parmelia are used as fodder as they form a favourite food for reindeers and cattles.
(b) Lichens in medicine:
Lichens contain usnic acid due to which they are used in medicines. Usnea and Cladonia species are used as an antibiotic against Gram positive bacteria.
Species like Lobaria, Citraria are useful in respiratory disease like T.B., Peltigera is useful in hydrophobia, Parmelia is used in treatment of epilepsy, whereas Usnea is used in urinary disease. Some lichens are also used in medicine due to their anticarcinogenic property.
(c) Industrial use of lichens:
1. Lichens are used in various dyes for colouring fabrics.
2. Species like Rocella and Lasallia are used in preparation of litmus paper which is acid-base indicator.
3. In Sweden and Russia, lichens are used for production of alcohol.
4. Orcein is a biological stain obtained from Orchrolechia androgyna and O. tortaria.
5. Some lichens are also used in tanning process in leather industry.
6. Evernia and Ramalina are the sources of essential oils which are used in preparation of soaps and other cosmetics.
(d) Other uses of lichens:
1. Lichens are used in cosmetics.
2. Some lichens like Everniaprunastri also known as oakmoss is used in making perfumes.
3. Lichen is also used as a preservative for beer.
11th Biology Digest Chapter 2 Systematics of Living Organisms Intext Questions and Answers
Can you tell? (Textbook Page No. 7)
Enlist uses of taxonomy?
Answer:
Uses of taxonomy are as follows:
- It is used to assign each organism an appropriate place in a systematic framework of classification.
- It is used to group animals and plants by their characteristics and relationships.
- It is used to classify organisms based upon their similarities and differences.
- It is used for nomenclature of an organism. Assigning a name to an organism is essential for its identification without confusion throughout the scientific world.
- It is used to serve as an instrument for identification of an organisms. A newly isolated organism can be placed to its nearest relative or can be identified as a new organism with unknown characteristics.
- It becomes easier to understand the evolutionary trends in different groups of organisms.
![]()
Can you tell? (Textbook Page No. 7)
Which characters of organisms are visible characters?
Answer:
The visible characters of organisms include habit, colour, mode of respiration, growth, reproduction, etc.
Can you tell? (Textbook Page No. 7)
What is evolution?
Answer:
- It is believed that the life originated on earth in its very simple form.
- Constant struggle of the early living beings gave rise to more and more perfect forms of life.
- This struggle and progress are evolution which led to formation of diverse life forms.
Can you tell? (Textbook Page No. 7)
What is DNA barcoding?
Answer:
DNA barcoding is a new method for identification of any species based on its DNA sequence, which is obtained from a tiny tissue sample of the organism under study.
Can you tell? (Textbook Page No. 7)
Name the recent approaches in taxonomy.
Answer:
The recent approaches in taxonomy includes:
- Morphological Approach
- Embryological Approach
- Ecological Approach
- Behavioral Approach / Ethological Approach
- Genetical Approach / Cytological Approach
- Biochemical Approch
- Numerical Taxonomy
![]()
Can you tell? (Textbook Page No. 9)
Make a flow chart showing taxonomic hierarchy.
Answer:
Kingdom → Sub-kingdom → Division / Phylum → Class → Cohort / Order → Family Genus → Species
Do Yourself (Textbook Page No. 16)
Complete the table (given on textbook Page No.16) through collecting information about sunflower, tiger with characteristic features.
(i) Sunflower:
| Category | Taxon | Characteristics |
| Kingdom | Plantae | Autotrophic, photosynthetic, cell wall present. |
| Sub-kingdom | Phanerogamae | Seed producing plants, reproductive structures are visible. |
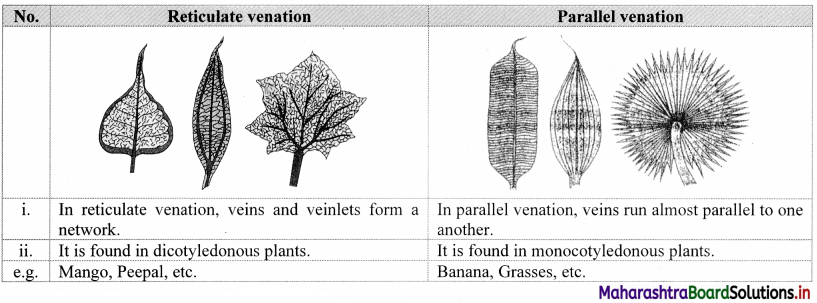
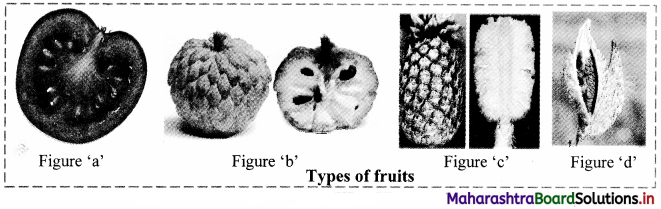
| Division | Angiospermae | Seeds are enclosed within the fruit. |
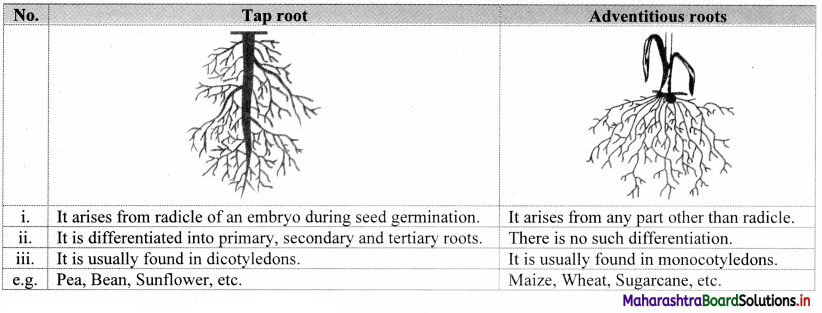
| Class | Dicotyledonae | Two cotyledons, tap root system, reticulate venation, pentamerous symmetry of flower, vascular bundle open. |
| Order | Asterales | Capitulum inflorescence, showing ray florets and disc florets. |
| Family | Asteraceae | Aster family |
| Genus | Helianthus | – |
| Species | annuus | – |
(ii) Tiger:
| Category | Taxon | Characteristics |
| Kingdom | Animalia | Multicellular eukaryotes, cell wall absent, heterotrophic nutrition. |
| Phylum | Chordata | Notochord present |
| Class | Mammalia | Presence of mammary gland |
| Order | Carnivora | Carnivorous in nature |
| Family | Felidae | Cat-like mammals |
| Genus | Panthera | Large cats |
| Species | tigris | – |
Can you tell? (Textbook Page No. 9)
Why horse and ass are considered to be two different species or animals?
Answer:
1. Species is a group of organisms that can interbreed under natural conditions to produce fertile offsprings.
2. Horse and ass (donkey) are considered to be two different species or animals, because they cannot interbreed under natural condition to produce fertile offspring.
![]()
Internet my friend: (Textbook Page No. 9)
(i) Collect the information about most recent system of classification of living organisms and Kingdom System of Classification, e.g. Search for APG system of classification for Plants.
Answer:
[Note: Students are expected to collect more information about most recent system of classification of living organisms and Kingdom System of Classification from internet on their own.]
(ii) Collect the information about classification systems for all types of organisms.
Answer:
[Note: Students are expected to collect more information about classification systems for all types of organisms from internet on their own.]
Can you recall? (Textbook Page No. 6)
What is Five Kingdom system of classification?
Answer:
Five kingdom system of classification was proposed by R.H. Whittaker in 1969. This system shows the phylogenetic relationship between the organisms.
The five kingdoms are:
- Kingdom Monera
- Kingdom Protista
- Kingdom Plantae
- Kingdom Fungi
- Kingdom Animalia
Can you tell (Textbook Page No. 14)
Classify fungi into their types.
Answer:
Fungi are classified into four types on the basis of their structure, mode of spore formation and fruiting bodies as follows:
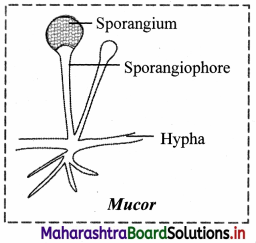
1. Phycomycetes:
Members of this class are commonly called as algal fungi.
These are consisting of aseptate coenocytic hyphae.
They grow well in moist and damp places on decaying organic matter as well as in aquatic habitats or as parasites on plants.
e.g. Mucor, Rhizopus (bread mold), Albugo (parasitic fungus on mustard).
2. Ascomycetes:
These are commonly called as sac fungi.
These are multicellular. Rarely they are unicellular (e.g. Yeast).
Hyphae are branched and septate.
They can be decomposers, parasites or coprophilous (grow on dung).
Some varieties of this class are consumed as delicacies such as morels and truffles.
Neurospora is useful in genetic and biochemical assays.
e.g. Aspergillus, Penicillium, Neurospora, Claviceps, Saccharomyces (unicellular ascomycetes).
3. Basidiomycetes:
These are commonly called as club fungi.
They have branched septate hyphae.
e.g. Agaricus (mushrooms), Ganoderma (bracket fungi), Ustilago (smuts), Puccinia (rusts), etc.
4. Deuteromycetes:
It is a group of fungi which are known to reproduce only asexually.
They are commonly called imperfect fungi.
They are mainly decomposers, while few are parasitic, e.g. Alternaria.
![]()
Can you tell? (Textbook Page No. 14)
Write a note on economic importance of fungi.
Answer:
Economic importances of fungi are as follows:
1. Role of fungi in medicine:
(a) Antibiotic penicillin is obtained from Penicillium.
(b) Drugs like cyclosporine, immunosuppressant drugs, precursors of steroid hormones, etc are isolated from fungi.
2. Role of fungi in industries:
(a) Yeast is used in bread making. It causes dough to rise and make the bread light and spongy. It is also used in breweries or wine making industries. Sugars present in grapes are fermented by using yeast. This results in production of alcohol which is used for making wine.
(b) Lichen is a symbiotic association of algae and fungi are used in preparation of litmus paper which is used as acid-base indicator.
3. Role of fungi in food:
(a) Fungi like mushrooms are consumed as a food. These are rich source of protein.
(b) Fungi genus Penicillium helps in ripening of cheese.
4. Role of fungi as biocontrol agents:
(a) Fungi help to control growth of weeds.
(b) Pathogenic fungi like Fusarium sp., Phytophthorapalmivora, Alternaria crassa, etc act as mycoherbicides.
Can you tell? (Textbook Page No. 14)
Why are fungi considered as heterotrophic organisms?
Answer:
In fungi, chloroplast is absent, thus they cannot synthesize their own food by photosynthesis. Fungi decompose the organic matter by breaking down with the help of enzymes from which they absorb nutrients. Thus, exhibiting heterotrophic mode of nutrition.
![]()
Can you tell? (Textbook Page No. 14)
What are coenocytic hyphae?
Answer:
1. In filamentous fungi, body consists of mycelium which is formed by a network of hyphae.
2. When these hyphae are non-septate, multinucleated, they are known as coenocytic hyphae.
Can you tell? (Textbook Page No. 14)
(i) How are fungi different from plants?
Answer:
Fungi are different from plants because:
(a) They lack chloroplast hence, do not perform photosynthesis and are heterotrophic in nutrition. Whereas plants are autotrophic and prepare their own food by photosynthesis.
(b) They are separated from Plantae based on their saprophytic mode of nutrition.
(c) Fungi are decomposers of ecosystem whereas plants are producers of ecosystem.
(d) In fungi, cell wall is made up of fungal cellulose or chitin. Whereas in plants, cell wall is made up of cellulose and pectic compounds.
(ii) Have you seen any diseased plant in your farm?
Answer:
Yes, I have seen some diseased plants in our farm.
There are different pathogens like fungi, bacteria, viruses that cause diseases in plants.
The common plant diseases are:
(a) Leaf rust disease: It is caused by fungus Puccinia triticina. It is the most common rust disease of wheat.
(b) Blight disease in rice: It is caused by harmful bacteria Xanthomonas oryzae. It causes wilting of seedlings and yellowing and drying of leaves.
(c) Early blight of potato: It is caused by fungi Alternaria solani. It causes ‘bulls eye’ patterned leaf spots and tuber blight on potato.
(d) Crown gall disease: It is caused by Agrobacterium tumefaciens. This pathogen infects the plant and forms rough surfaced galls on stem and roots.
[Students are expected to write their observations about diseased plants found informs]
![]()
Can you tell? (Textbook Page No. 14)
Complete the following table:
Answer:
| Plantae | Animalia |
| 1. Autotrophic mode of nutrition. | Heterotrophic mode of nutrition. |
| 2. They do not show locomotion. | They show locomotion. |
| 3. Cell wall is present. | Cell wall is absent. |
| 4. Chloroplast present. | Chloroplast absent. |
| 5. They do not possess nervous system. | They possess well developed nervous system, i |
| 6. Reproduction can be both sexual and asexual. | Mainly shows sexual reproduction. |
Can you tell? (Textbook Page No. 15)
Why are viruses called infectious nucleoproteins?
Answer:
1. Viruses are acellular, highly infectious and ultramicroscopic.
2. Viruses possess their own genetic material in the form of either DNA or RNA, but never both. The genetic material in viruses is covered by a protein coat (capsid), hence called nucleoprotein.
3. They do not show any activity outside the body of host but once they enter their specific host cell, they start multiplying within the living host cells.
4. Viruses lack their own metabolic machinery, they make use of the cellular machinery of the host i.e. ribosome for the synthesis of protein during their reproduction and therefore, they cause severe infection. Thus, they are called infectious nucleoproteins.
Can you tell? (Textbook Page No. 15)
Describe genetic material in plant and animal viruses as well as in bacteriophages.
Answer:
The genetic material in different viruses is as given below:
1. Plant virus: (b) Majority of plant viruses have RNA as their genetic material. (Exception: Cauliflower Mosaic Virus has double-stranded DNA as genetic material)
2. Animal virus: (b) They have either DNA or RNA as genetic material.
3. Bacteriophage: (d) Bacteriophages have double-stranded DNA as the genetic material.
![]()
Can you tell? (Textbook Page No. 15)
Differentiate between viruses and viroids.
Answer:
| Viruses | Viroids |
| 1. They have high molecular weight. | They have low molecular weight. |
| 2. They are larger in size. | They are smaller in size. |
| 3. They can infect plant, animals and bacteria. | They mainly infect plants. |
| 4. The genetic material can be ss-RNA, ds-RNA or DNA. | The genetic material is single stranded circular RNA. |
| 5. Protein coat is present. | Protein coat is absent. |
| 6. mosaic disease is a plant disease caused by viruses. | Tomato chloric dwarf is a plant disease caused by viroids. |
Internet my friend. (Textbook Page No. 15)
In modern medicine, certain infectious neurological diseases were found to be transmitted by abnormally folded proteins. These proteins are called prions. The word prion comes from ‘proteinaceous infectious particle’, e.g. mad cow disease in cattle, Jacob’s disease in human.
Find more information about prions.
Answer:
Prions:
1. A prion is a misfolded form of a protein generally present in brain cells.
2. When the prion gets into a cell containing the normal form of the protein, the prion somehow converts normal protein molecules to the misfolded prion versions.
3. Several prions then aggregate into a complex that can convert other normal proteins to prions.
4. Prions can be transmitted through blood, surgical instruments and contaminated food.
5. Diseases caused by prions are Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy in cattles, Kuru and Creutzfeldt – Jakob disease in humans.
[Note: Students are expected to search for more information about Prions on internet]
11th Std Biology Questions And Answers:
- Living World Class 11 Biology Questions And Answers
- Systematics of Living Organisms Class 11 Biology Questions And Answers
- Kingdom Plantae Class 11 Biology Questions And Answers
- Kingdom Animalia Class 11 Biology Questions And Answers
- Cell Structure and Organization Class 11 Biology Questions And Answers
- Biomolecules Class 11 Biology Questions And Answers
- Cell Division Class 11 Biology Questions And Answers
- Plant Tissues and Anatomy Class 11 Biology Questions And Answers





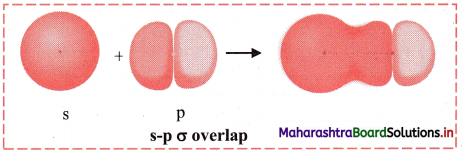
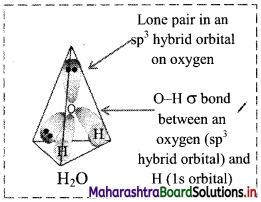
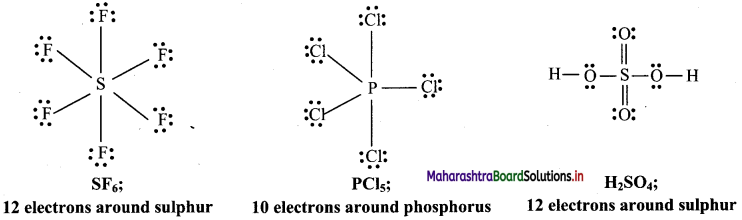
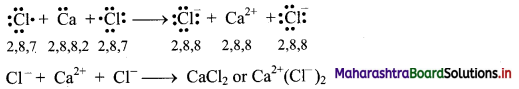
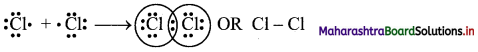
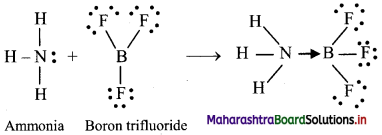
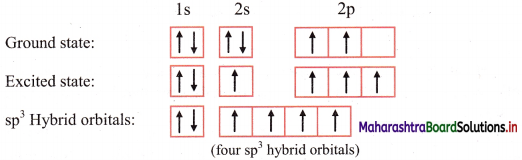
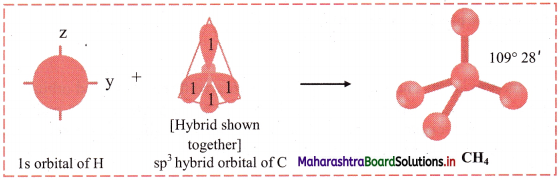
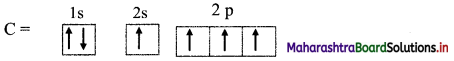
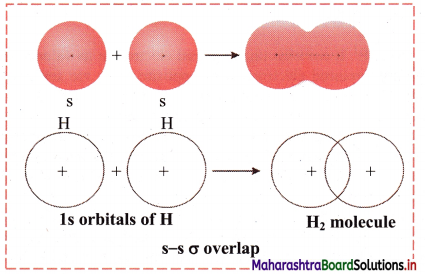
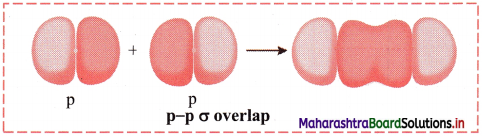
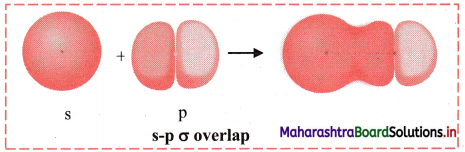
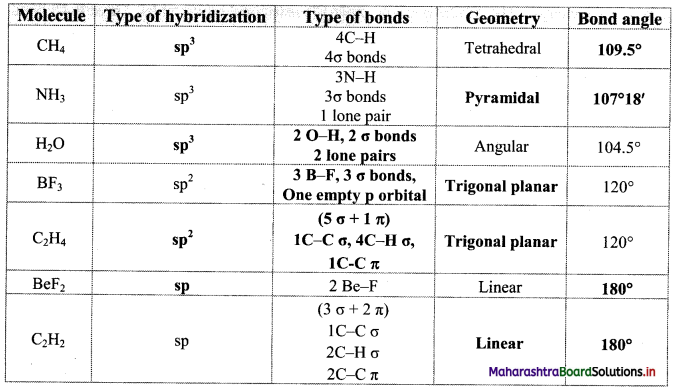
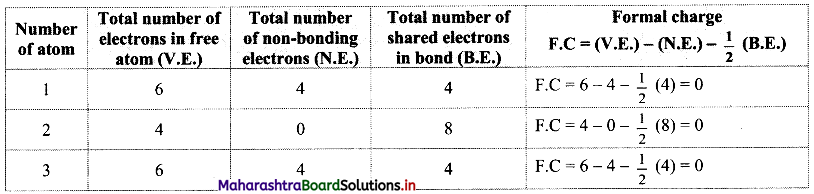
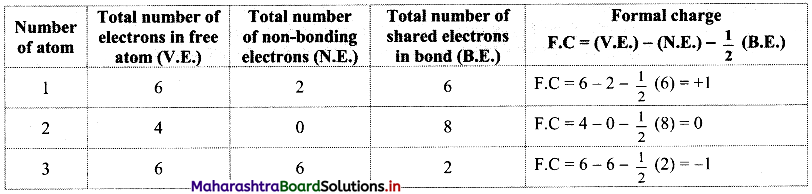
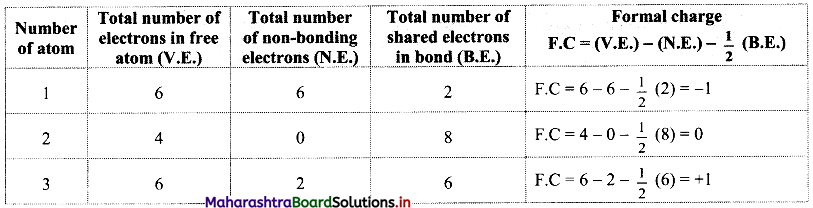


 Answer:
Answer: