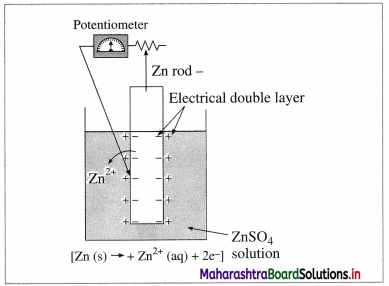
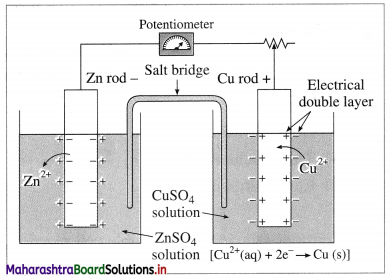
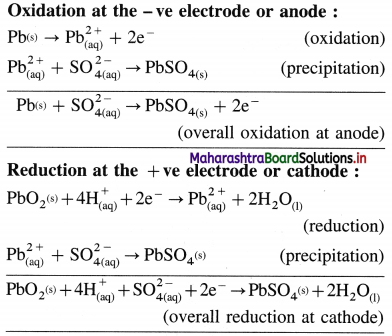
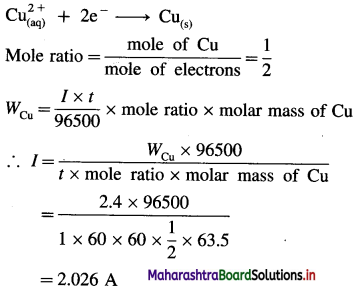
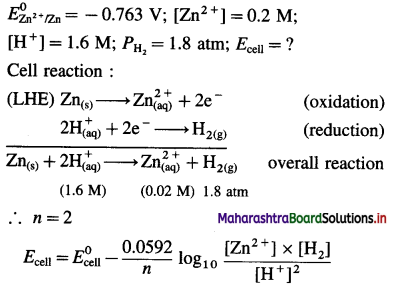
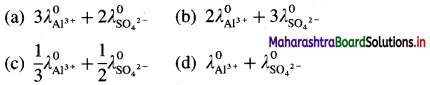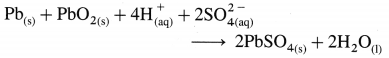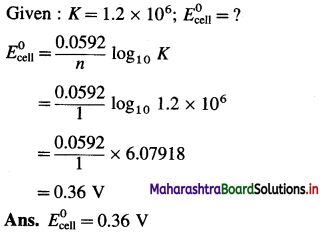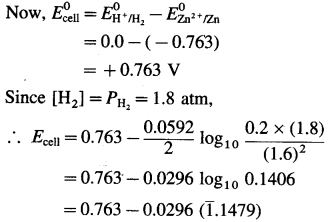Balbharti Maharashtra State Board 12th Chemistry Textbook Solutions Chapter 15 Introduction to Polymer Chemistry Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
Introduction to Polymer Chemistry Class 12 Exercise Question Answers Solutions Maharashtra Board
Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 15 Exercise Solutions Maharashtra Board
Chemistry Class 12 Chapter 15 Exercise Solutions
1. Choose the correct option from the given alternatives.
Question i.
Nylon fibers are …………………………………..
A. Semisynthetic fibres
B. Polyamide fibres
C. Polyester fibres
D. Cellulose fibres
Answer:
B. polyamide fibres
![]()
Question ii.
Which of the following is naturally occurring polymer?
A. Telfon
B. Polyethylene
C. PVC
D. Protein
Answer:
D. Protein
Question iii.
Silk is a kind of …………………………………. fibre
A. Semisynthetic
B. Synthetic
C. Animal
D. Vegetable
Answer:
C. an animal
Question iv.
Dacron is another name of …………………………………. .
A. Nylon 6
B. Orlon
C. Novolac
D. Terylene
Answer:
D. Terylene
Question v.
Which of the following is made up of polyamides?
A. Dacron
B. Rayon
C. Nylon
D. Jute
Answer:
C. Nylon
Question vi.
The number of carbon atoms present in the ring of ε – caprolactam is
A. Five
B. Two
C. Seven
D. Six
Answer:
D. Six
Question vii.
Terylene is …………………………………. .
A. Polyamide fibre
B. Polyester fibre
C. Vegetable fibre
D. Protein fibre
Answer:
B. Polyester fibre
Question viii.
PET is formed by …………………………………. .
A. Addition
B. Condensation
C. Alkylation
D. Hydration
Answer:
D. Hydration
Question ix.
Chemically pure cotton is …………………………………. .
A. Acetate rayon
B. Viscose rayon
C. Cellulose nitrate
D. Cellulose
Answer:
D. Cellulose
![]()
Question x.
Teflon is chemically inert, due to presence of …………………………………. .
A. C-H bond
B. C-F bond
C. H- bond
D. C=C bond
Answer:
A. C-H bond
2. Answer the following in one sentence each.
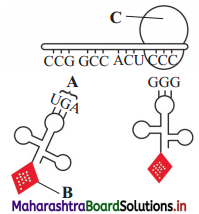
Question i.
Identify ‘A’ and ‘B’ in the following reaction …………………………………. .
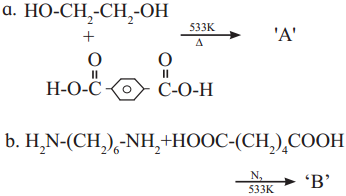
Answer:
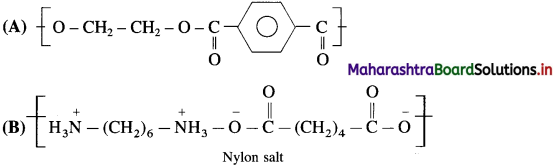
Question ii.
Complete the following statements
a. Caprolactam is used to prepare …………………………………. .
b. Novolak is a copolymer of …………………………………. and …………………………………. .
c. Terylene is ………………………………….. polymer of terephthalic acid and ethylene glycol.
d. Benzoyl peroxide used in addtion polymerisation acts as …………………………………. .
e. Polyethene consists of polymerised …………………………………. .
Answer:
a. Nylon-6
b. Phenol, formaldehyde
c. polyester
d. initiator (catalyst)
e. linear or branched-chain
Question iii.
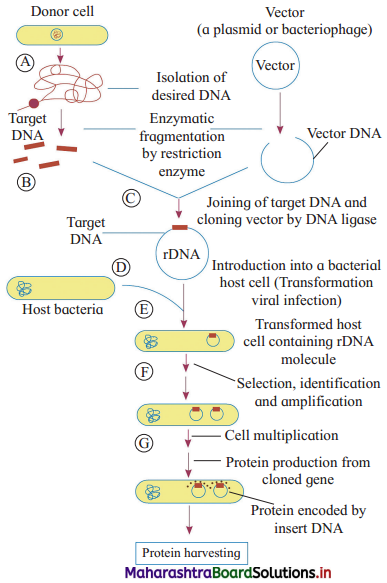
Draw the flow chart diagram to show the classification of polymers based on type of polymerisation.
Answer:
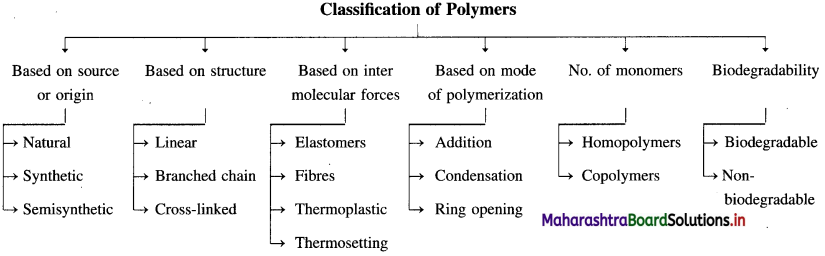
Question iv.
Write examples of Addition polymers and condensation polymers.
Answer:
Addition polymers : Polyvinyl chloride, polythene
Condensation polymers : Bakelite, terylene, Nylon-66
Question v.
Name some chain-growth polymers.
Answer:
Chain growth polymers : Polythene, polyacrylonitrile and polyvinyl chloride.
![]()
Question vi.
Define the terms :
1) Monomer
2) Vulcanisation
3) Synthetic fibres
Answer:
1. Monomer is a small and simple molecule and has a capacity to form two chemical bonds with other monomers. Examples : Ethene, Propylene.
2. The process by which a network of cross-links is introduced into an elastomer is called vulcanisation or it can also be defined as the process of heating natural rubber with sulphur to increase the tensile strength, toughness and elasticity of natural rubber is known as vulcanization of rubber.
3. The man-made fibres prepared by polymerization of one monomer or copolymerization of two or more monomers are called synthetic fibres.
Question vii.
What type of intermolecular force leads to high-density polymer?
Answer:
High density polymers have low degree of branching along the hydrocarbon chain. The molecules are closely packed together during crystallization. This closer packing means that the van der Waals attraction between the chains are greater and so the plastic (high density polymer) is stronger and has a melting point.
Question viii.
Give one example each of copolymer and homopolymer.
Answer:
Homopolymer : PVC, Nylon-6
Copolymer : Terylene, Buna-S
Question ix.
Identify Thermoplastic and Thermosetting Plastics from the following …………………………………. .
1. PET
2. Urea-formaldehyde resin
3. Polythene
4. Phenol formaldehyde
Answer:
Thermoplastic plastics : PET, Polythene
Thermosetting plastics : Urea formaldehyde resin, Phenol formaldehyde
3. Answer the following.
Question i.
Write the names of classes of polymers formed according to intermolecular forces and describe briefly their structural characteristics.
Answer:
Molecular forces bind the polymer chains either by hydrogen bonds or Vander Waal’s forces. These forces are called intermolecular forces. On the basis of magnitude of intcrmolccular forces, polymers are further classified as ebstomers, fibres, thermoplastic polymers. thermosetting polymers.
(1) Elastomers: Weak van der Waals type of intermolecular forces of attraction between the polymer chains are observed in cbstomcrs. When polymer is stretched, the polymer chain stretches and when the strain is relieved the chain returns to its odginal position, Thus, polymer shows elasticity and is called elastomers. Elastomers, the elastic polymers, have weak van der Waals type of intermolecular forces which permit the polymer to be stretched. Lilastorners are soft and stretchy and used in making rubber bands. E.g.. neoprene, vulcanized rubber, buna.S, buna-N.
(2) Fibres : It consists of strong intermolecular forces of’ attraction due to hydrogen bonding and strong dipole-dipole forces. These polymers possess high tensile strength. Due to these strong intermolecular forces the fibres are crystalline in nature. They are used in textile industries, strung tyres. etc.. e.g., nylon, terylene.
(3) Thermoplastic polymers: These polymer possess moderately strong intermolecular forces of attraction between those of elastomers and fibres. These polymers arc called thermoplastic because they become soft on heating and hard on cooling. They are either linear or branched chain polymers. They can be remoulded and recycled. E.g. polyethenc, PVC, polystyrene.
(4) Thermosetting polymers: These polymers are cross linked or branched molecules and are rigid polymers. During their formation they have property of being shaped on heating. but they get hardened while hot. Once hardened these become infusible, cannot be softened by heating and therefore, cannot be remoulded and recycled.
This shows extensive cross linking by covalent bonds formed in the moulds during hardening/setting process while hot. E.g. Bakelite, urea formaldehyde resin.
![]()
Question ii.
Write reactions of formation of :
a. Nylon 6
b. Terylene
Answer:
Terylene is polyester fibre formed by the polymerization of terephthalic acid and ethylene glycol.
Terylene is obtained by condensation polymerization of ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid in presence of catalyst zinc acetate and antimony trioxide at high temperature.
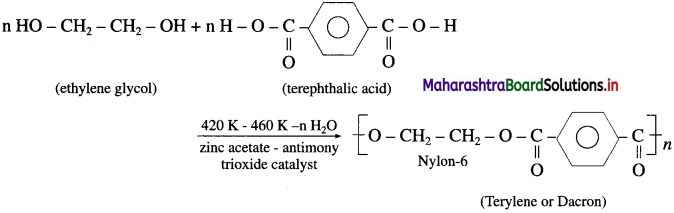
Properties :
- Terylene has relatively high melting point (265 °C)
- It is resistant to chemicals and water.
Uses :
- It is used for making wrinkle free fabrics by blending with cotton (terycot) and wool (terywool), and also as glass reinforcing materials in safety helmets.
- PET is the most common thermoplastic which is another trade name of the polyester polyethylenetereph- thalate.
- It is used for making many articles like bottles, jams, packaging containers.
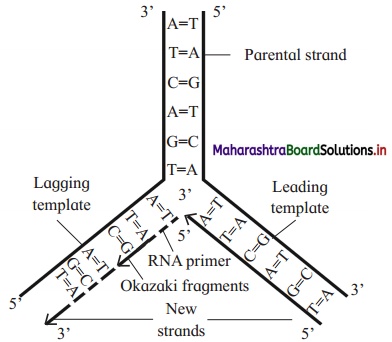
Question iii.
Write the structure of natural rubber and neoprene rubber along with the name and structure of thier monomers.
Answer:
Question iv.
Name the polymer type in which the following linkage is present.
Answer:
The 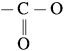 linkage is present in terylene or dacron polymer.
linkage is present in terylene or dacron polymer.
Question v.
Write the structural formula of the following synthetic rubbers :
a. SBR rubber
b. Buna-N rubber
c. Neoprene rubber
Answer:
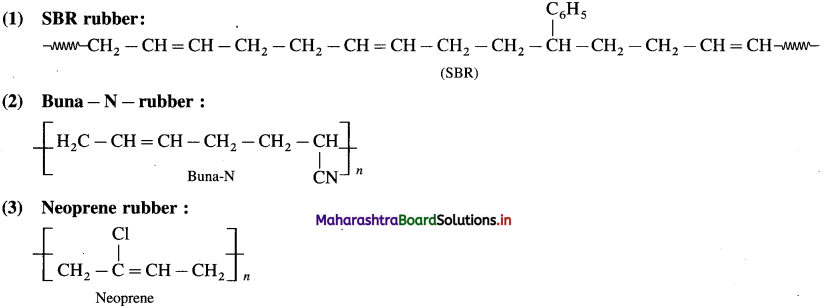
![]()
Question vi.
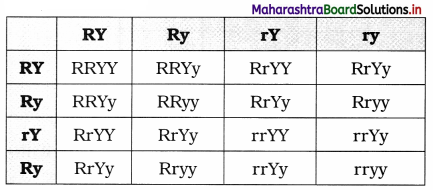
Match the following pairs :
Name of polymer – Monomer
1. Teflon – a. CH2 = CH2
2. PVC – b. CF2 = CF2
3. Polyester – c. CH2 = CHCl
4. Polythene – d. C6H5OH and HCHO
5. Bakelite – e. Dicarboxylic acid and polyhydoxyglycol
Answer:
- Teflon – CF2 = CF2
- PVC – CH2 = CHCI
- Polyester-Dicarboxylic acid and polyhydoxyglycol
- Polythene – CH2 = CH2
- Bakelite – C6H5OH and HCHO
Question vii.
Draw the structures of polymers formed from the following monomers
1. Adipic acid + Hexamethylenediamine
2. e – Aminocaproic acid + Glycine
Answer:
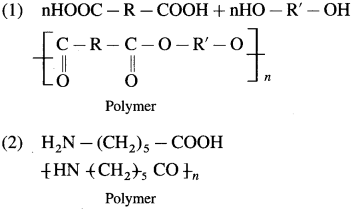
Question viii.
Name and draw the structure of the repeating unit in natural rubber.
Answer:
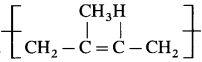 Repeating unit of natural rubber (Basic unit : isoprene)
Repeating unit of natural rubber (Basic unit : isoprene)
Question ix.
Classify the following polymers as natural and synthetic polymers
a. Cellulose
b. Polystyrene
c. Terylene
d. Starch
e. Protein
f. Silicones
g. Orlon (Polyacrylonitrile)
h. Phenol-formaldehyde resins
Answer:
| Natural Polymers | 1. Cellulose 4. Starch 5. Protein |
| Synthetic Polymers | 2. Polystyrene 3. Terylene 6. Silicones 7. Orion (Polyacrylonitrile) 8. phenol-formaldehyde resin |
Question x.
What are synthetic resins? Name some natural and synthetic resins.
Answer:
Synthetic resins are artificially synthesised high molecular weight polymers. They are the basic raw material of plastic. The main properties of plastic depend on the synthetic resin it is made from.
Examples of natural resins : Rosin, Damar, Copal, Sandarac, Amber, Manila
Examples of synthetic resins : Polyester resin, Phenolic resin, Alkyl resin, Polycarbonate resin, Polyamide resin, Polyurethane resin, silicone resin, Epoxy resin, Acrylic resin.
![]()
Question xi.
Distinguish between thermosetting and thermoplastic resins. Write example of both the classes.
Answer:
| Thermosetting resin | Thermoplastic resin |
| (1) They harden when heated. Once hardened it no longer melts. | (1) They soften when heated and harden again when cooled. |
| (2) They cannot be re-shaped. | (2) They can be reshaped |
| (3) They are strong, hard. | (3) They are weak, soft. |
| (4) Thermosetting resin show cross-linking. Examples : Melamine resin Epoxy resins, Bake-lite. |
(4) Thermoplastic molecules do not cross link, hence are flexible. Examples : Polythene, polypropylene, nylon, polyester. |
Question xii.
Write name and formula of raw material from which bakelite is made.
Answer:
The raw material or monomers used to prepare bakelite are o-hydroxymethyl phenol 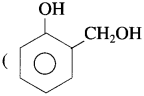 and formaldehyde (HCHO)
and formaldehyde (HCHO)
4. Attempt the following :
Question i.
Identify condensation polymers and addition polymers from the following.
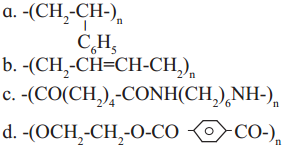
Answer:

Question ii.
Write the chemical reactions involved in the manufacture of Nylon 6, 6
Answer:
Nylon-6, 6 is a linear polyamide polymer formed by the condensation polymerisation reaction. The monomers used in the preparation of Nylon-6, 6 are :
(1) Adipic acid : HOOC-(CH2)4-COOH
(2) Hexamethylene diamine : H2N-(CH2)6-NH2
When equimolar aqueous solutions of adipic acid and hexamethylene diamine are mixed and heated, there is neutralization to form a nylon salt. During polymerisation at 553 k nylon salt loses a water molecule to form nylon 6, 6 polymer. Both monomers (hexamethylene diamine and adipic acid) contain six carbon atoms each, hence the polymer is termed as Nylon-6,6.
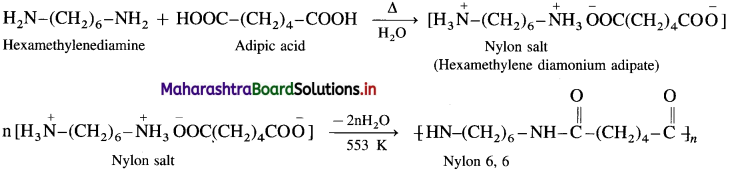
Properties and uses : Nylon 6,6 is high molecular mass (12000 – 50000 u) linear condensation polymer. It possesses high tensile strength. It does not soak in water. It is used for making sheets, bristles for brushes, surgical sutures, textile fabrics, etc.
![]()
Question iii.
Explain the vulcanisation of rubber. Which vulcanizing agents are used for the following synthetic rubber.
a. Neoprene
b. Buna-N
Answer:
The process by which a network of cross links is introduced into an elastomer is called vulcanization.
Vulcanization enhances the properties of natural rubber like tensile strength, stiffness, elasticity, toughness etc. Sulphur forms cross links between polyisoprene chains which results in improved properties of rubber.
- For neoprene vulcanizing agent is MgO.
- For Buna-N vulcanizing agent is sulphur.
Question iv.
Write reactions involved in the formation of …………………………………. .
1) Teflon
2) Bakelite
Answer:
The monomers phenol and formaldehyde undergo polymerisation in the presence of alkali or acid as catalyst.
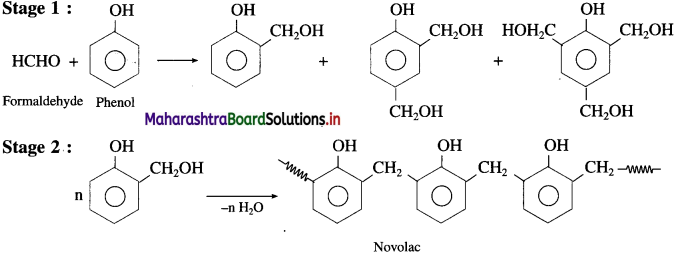
Phenol reacts with formaldehyde to form ortho or p-hydroxy methyl phenols, which further reacts with phenol to form a linear polymer called Novolac. It is used in paints.
In the third stage, various articles are shaped from novolac by putting it in appropriate moulds and heating at high temperature (138 °C to 176 °C) and at high pressure forms rigid polymeric material called bakelite. Bakelite is insoluble and infusible and has high tensile strength.
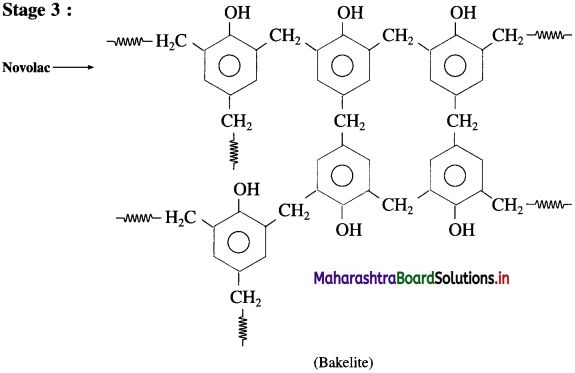
Bakelite is used in making articles like telephone instrument, kitchenware, electric insulators frying pans, etc.
2. Teflon is polytetrafluoroethylene. The monomer used in preparation of teflon is tetrafluoroethylene, (CF2 = CF2) which is a gas at room temperature. Tetrafluoroethylene is polymerized by using free radical initiators such as hydrogen peroxide or ammonium persulphate at high pressure.

Properties:
- Telflon is tough, chemically inert and resistant to heat and attack by corrosive reagents.
- C – F bond is very difficult to break and remains unaffected by corrosive alkali, organic solvents.
Uses : Telflon is used in making non-stick cookware, oil seals, gaskets, etc.
![]()
Question v.
What is meant by LDP and HDP? Mention the basic difference between the same with suitable examples.
Answer:
- LDP is low density polyethylene and HDP is high density polyethylene.
- LDP is a branched polymer with low density due to chains are loosely held and HDP is a linear polymer with density due to close packing.
- HDP is much stiffer than LDP and has high tensile strength and hardness.
LDP is mainly used in preparation of pipes for agriculture, irrigation and domestic water line connections. HDP is used in manufacture of toys and other household articles like bucket, bottles, etc.
Question vi.
Write preparation, properties and uses of Teflon.
Answer:
Teflon is polytetrafluoroethylene. The monomer used in preparation of teflon is tetrafluoroethylene, (CF2 = CF2) which is a gas at room temperature. Tetrafluoroethylene is polymerized by using free radical initiators such as hydrogen peroxide or ammonium persulphate at high pressure.

Properties:
- Telflon is tough, chemically inert and resistant to heat and attack by corrosive reagents.
- C – F bond is very difficult to break and remains unaffected by corrosive alkali, organic solvents.
Uses : Telflon is used in making non-stick cookware, oil seals, gaskets, etc.
Question vii.
Classify the following polymers as straight-chain, branched-chain and cross-linked polymers.
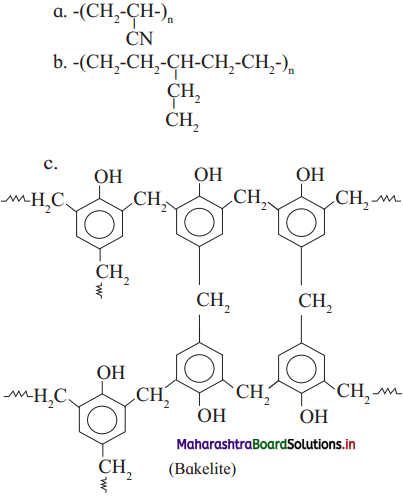
Answer:

![]()
5. Answer the following.
Question i.
How is polythene manufactured? Give their properties and uses.
Answer:
LDP means low density polyethylene. LDP is obtained by polymerization of ethylene under high pressure (1000 – 2000 atm) and temperature (350 – 570 K) in presence of traces of O2 or peroxide as initiator.
The mechanism of this reaction involves free radical addition and H-atom abstraction. The latter results in branching. As a result the chains are loosely held and the polymer has low density.
Properties of LDP :
- LDP films are extremely flexible, but tough chemically inert and moisture resistant.
- It is poor conductor of electricity with melting point 110 °C.
Uses of LDP :
- LDP is mainly used in preparation of pipes for agriculture, irrigation, domestic water line connections as well as insulation to electric cables.
- It is also used in submarine cable insulation.
- It is used in producing extruded films, sheets, mainly for packaging and household uses like in preparation of squeeze bottles, attractive containers, etc.
HDP means high density polyethylene. It is a linear polymer with high density due to close packing.
HDP is obtained by polymerization of ethene in presence of Zieglar-Natta catalyst which is a combination of triethyl aluminium with titanium tetrachloride at a temperature of 333K to 343K and a pressure of 6-7 atm.
Properties of HDP :
- HDP is crystalline, melting point in the range of 144 – 150 °C.
- It is much stiffer than LDP and has high tensile strength and hardness.
- It is more resistant to chemicals than LDP.
Uses of HDP :
- HDP is used in manufacture of toys and other household articles like buckets, dustbins, bottles, pipes, etc.
- It is used to prepare laboratory wares and other objects where high tensile strength and stiffness is required.
Question ii.
Is synthetic rubber better than natural rubber? If so, in what respect?
Answer:
Yes. Synthetic rubber is more resistant to abrasion than natural rubber and is also superior in resistance to heat and the effects of aging (lasts longer). Many types of synthetic rubber are flame-resistant, so they can be used in insulation for electrical devices.
It also remains flexible at low temperatures and is resistant to grease and oil. It is resistant to heat, light and certain chemicals.
Question iii.
Write main specialities of Buna-S, Neoprene rubber?
Answer:
Buna-S is an elastomer and it is copolymer of styrene with butadiene. Its trade name is SBR. Buna-S is superior to natural rubber, because of its mechanical strength and abrasion resistance. It is used in tyre industry. It is vulcanized with sulphur. Neoprene is a synthetic rubber and it is a condensation polymer of chloroprene (2-chloro-l, 3-butadiene). Vulcanization of neoprene takes place in presence of MgO. It is resistant to petroleum, vegetable oils. Neoprene is used in making hose pipes for transport of gasoline and making gaskets.
![]()
Question iv.
Write the structure of isoprene and the polymer obtained from it.
Answer:

Question v.
Explain in detail the free radical mechanism involved during the preparation of the addition polymer.
Answer:
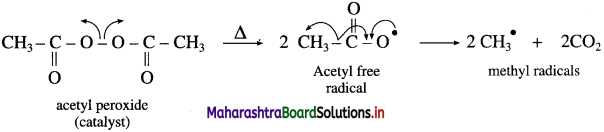
Polymerisation of ethylene is carried out at high temperature and at high pressure in presence of small amount of acetyl peroxide as initiator.
(1) Formation of free radicals : The first step involves clevage of acetyl peroxide to form two carboxy radicals. These carboxy radicals immediately undergo decarboxylation to give methyl initiator free radicals.
(2) Chain initiating step : The methyl radical thus formed adds to ethylene to form a new larger free radical.
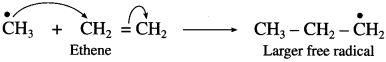
(3) Chain propagation step : The larger free radical formed in the chain initiating step reacts with another molecule of ethene to form another big size free radicals and chain grows. This is called chain propagation step.

The chain reaction continues till thousands of ethylene molecules are added.
(4) Chain terminating step : The continuous chain reaction can be terminated by the combination of free radicals to form polyethene.
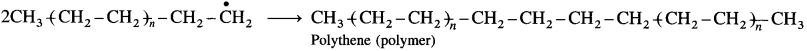
Activity :
i. Collect the information of the process like extrusion and moulding in Textile Industries.
ii. Make a list of polymers used to make the following articles
a. Photographic film
b. Frames of spectacles
c. Fountain pens
d. Moulded plastic chains
e. Terywool or Terycot fabric
iii. Prepare a report on factors responsible for degradation of polymers giving suitable example.
iv. Search and make a chart/note on silicones with reference to monomers, structure, properties and uses.
v. Collect the information and data about Rubber industry, plastic industry and synthetic fibre (rayon) industries running in India.
![]()
12th Chemistry Digest Chapter 15 Introduction to Polymer Chemistry Intext Questions and Answers
Use your brain power! (Textbook Page No 323)
Question 1.
Differentiate between natural and synthetic polymers.
Answer:
| Natural polymers | Synthetic polymers |
| (1) The polymers are obtained either from plants or animals. | (1) The man made fibres prepared by polymerization of monomer or copolymerization of two or more monomers. |
| (2) They are further divided into two types : (i) plant polymers (ii) Animal polymers.Examples: Cotton, linen, latex |
(2) They are further divided into three subtypes : (i) fibres (ii) synthetic rubbers (iii) plastics.Examples : Nylon, terylene Buna-S |
Use your brain power! (Textbook Page No 325)
Question 1.
What is the type of polymerization in the following examples?

Answer:
(i) Addition polymerization
(ii) Condensation polymerization
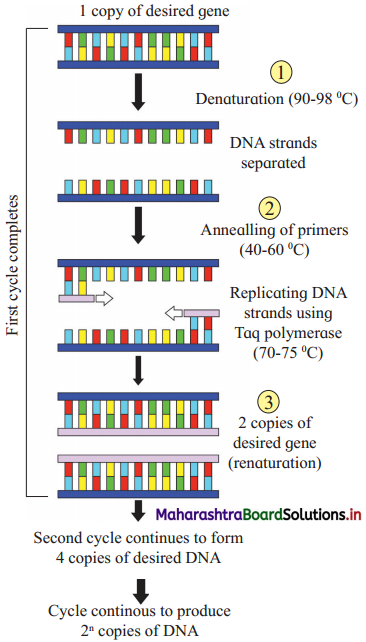
Problem 15.1 : (Textbook Page No 326)
Question 1.
Refer to the following table listing for different polymers formed from respective monomers. Identify from the list whether it is copolymer or homopolymer.
| Monomer | Polymers |
| Ethylene | Polyethene |
| Vinyl chloride | Polyvinyl chloride |
| Isobutylene | Polyisobutylene |
| Acrylonitrile | Polyacrylonitrile |
| Caprolactam | Nylon 6 |
| Hexamethylene diammonium adipate | Nylon 6, 6 |
| Butadiene + styrene | Buna-S |
Solution :
In each of first five cases, there is only one monomer which gives corresponding homopolymer. In the sixth case hexamethylene diamine reacts with adipic acid to form the salt hexamethylene diammonium adipate which undergoes condensation to form Nylon 6, 6. Hence nylon 6, 6 is homopolymer. The polymer Buna-S is formed by polymerization of the monomers butadiene and styrene in presence of each other. The repeating units corresponding to the monomers butadiene and styrene are randomly arranged in the polymer. Hence Buna-S is copolymer.
![]()
Use your brain power! (Textbook Page No 328)
Question 1.
(1) From the cis-polyisoprene structure of natural rubber explain the low strength of van der Waals forces in it.
(2) Explain how the vulcanization of natural rubber improves its elasticity. (Hint : consider the intermolecular links.)
Answer:
(1) (i) Natural rubber is cis-polyisoprene. It is obtained by polymerization of isoprene units at 1, 4 positions. In rubber molecule, double bonds are located between C2 and C3 of each isoprene unit. These cis-double bonds do not allow the polymer chain to come closer. Therefore, only weak vander Waals’ forces are present. Since the chains are not linear, they can be stretched just like springs and exhibit elastic properties.
(ii) Cis-1, 4 polyisoprene (Natural rubber), due to this cis configuration about the double bonds, has the adjacent chain that do not fit together well (there is no close packing of adjacent chains). The only force that interact is the weak or low strength of van der Waals’ forces.
(iii) Cis-polyisoprene has a coiled structure in which the various polymer chains are held together by weak van der Waals’ forces.
(2) (i) Vulcanization of rubber is a process of improvement of the rubber elasticity and strength by heating it in the presence of sulphur, which results in three dimensional cross-linking of the chain rubber molecules (polyisoprene) bonded to each other by sulphur atoms.
(ii) Vulcanisation makes rubber more elastic and more stiffer. On vulcanisation, sulphur forms cross links at the reactive sites of double bonds and thus rubber get stiffened.
(iii) The improved properties of vulcanised rubber are (i) high elasticity (ii) low water absorption tendency,
(iii) resistance to oxidation.
Use your brain power! (Textbook Page No 334)
Question 1.
Write structural formulae of styrene and polybutadiene.
Answer:

(1) Classify the following polymers as addition or condensation.
(i) PVC (ii) Polyamides
(iii) Polystyrene
(iv) Polycarbonates
(v) Novolac
Answer:
Addition polymers: PVC, Polystyrene
(ondensatlon polymers: Polyamides. Polycarbonates, Novolac
Question 2.
Completed the following table :
Answer:
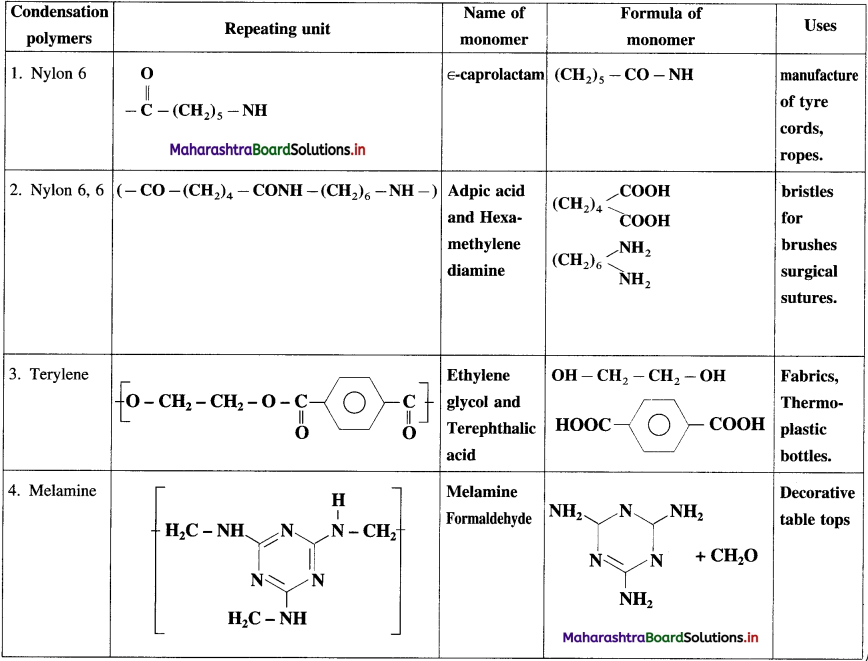
![]()
Use your brain power! (Textbook Page No 335)
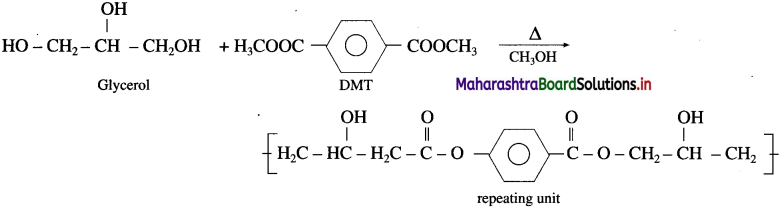
(1) Represent the copolymerization reaction between glycine and e aminocaproic acid to form the copolymer nylon 2-nylon 6.
(2) What is the origin of the numbers 2 and 6 in the name of this polymer?
Answer:
(1) It is a copolymer and has polyamide linkages. The monomers glycine and e-amino caproic acid undergo condensation polymerisation to form nylon-2-nylon-6.
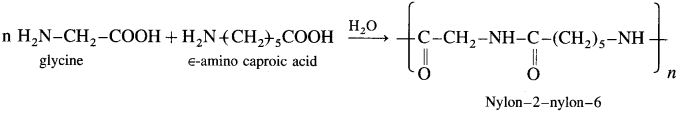
Nylon-2-nylon-6 is used in orthopaedic devices and implants.
(2) Monomer glycine contains two carbon atoms and e amino caproic acid contains six carbon atoms, hence the polymer is termed as nylon-2-nylon-6.
12th Std Chemistry Questions And Answers:
- Coordination Compounds Class 12 Chemistry Questions And Answers
- Halogen Derivatives Class 12 Chemistry Questions And Answers
- Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Class 12 Chemistry Questions And Answers
- Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Class 12 Chemistry Questions And Answers
- Amines Class 12 Chemistry Questions And Answers
- Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Questions And Answers
- Introduction to Polymer Chemistry Class 12 Chemistry Questions And Answers
- Green Chemistry and Nanochemistry Class 12 Chemistry Questions And Answers