Balbharti Maharashtra State Board 12th Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 6 Chemical Kinetics Important Questions and Answers.
Maharashtra State Board 12th Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 6 Chemical Kinetics
Question 1.
What is chemical kinetics?
Answer:
Chemical kinetics is a branch of physical chemistry which involves the study of the rates and mechanisms of chemical reactions and the influence of various factors like temperature, pressure, catalyst, etc., on the rates of reactions.
![]()
Question 2.
What is the importance of chemical kinetics?
Answer:
- It deals with the study of the rates and mechanism of reactions.
- The effect of temperature on the reaction rates can be studied.
- The influence of catalysts can be studied.
- The conditions for altering the rates and mechanisms of chemical reactions can be predicted.
- Thermodynamic parameters like energy, enthalpy changes, Δ5, ΔG of the reactions can be calculated.
Question 3.
How are reactions classified according to their rates? Give one example of each.
Answer:
According to the rates of the reactions, they can be classified as :
(1) Fast reactions,
(2) Very slow reactions,
(3) Moderately slow reactions.
(1) Fitst actions : In this, reactants react almost instantaneously, e.g., neutralisation reaction between H+ and OH-, forming water.
\(\mathrm{H}_{(\mathrm{xa})}^{+}+\mathrm{OH}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{-} \rightarrow \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{0 \mathrm{D}}\)
(2) Very slow reactions : In this, the reactants react extremely slow, so that there is no appreciable change in the concentrations of the reactants over a long period of time. E.g., reaction of silica with mineral acids, rusting of iron, etc.
(3) Moderately slow reactions : In this, the reactants react moderately slow with a measurable velocity, e.g., the hydrolysis of the esters.
\(\begin{aligned}
\mathrm{CH}_{3} \mathrm{COOC}_{2} \mathrm{H}_{5}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O} \stackrel{\mathrm{H}^{+}}{\longrightarrow} \mathrm{CH}_{3} \mathrm{COOH} \\
&+\mathrm{C}_{2} \mathrm{H}_{5} \mathrm{OH}
\end{aligned}\)
Question 4.
Define rate of a reaction.
Answer:
Definition : The rate of a chemical reaction is defined as the change in the concentration of the reactants or products per unit time.
![]()
It is often expressed in mol dm-3s-1.
Question 5.
Explain the following :
(A) Rate of the reaction in terms of the concentration of the reactants.
(B) Rate of reaction in terms of the concentration of the products.
Answer:
(A) Rate of the reaction in terms of the concentration of the reactants :
If c1 and c2 are the concentrations of the reactant A at time t1 and t2 respectively, then, the change in concentration, Δc = c2 – c1
Since c2 < c1, the term Δc is negative often written as – Δc.
The time interval is, Δt – t2 – t1
If Δ [A] is the change in concentration of A, then A[A] = C2 – C1
∴ Rate of the reaction = \(\mathrm{A}=\frac{-\Delta[\mathrm{A}]}{\Delta t}\)
∴ Rate of the reaction = \(\frac{-\Delta c}{\Delta t}\)
(B) Rate of the reaction in terms of the concentration of the products :
If x1 and x2 are the concentrations of the product B at time t1 and t2 respectively, then the change in concentration, Δx = x2 – x1.
∴ x2 > x1, the term Δx is positive.
The time interval is, Δt = t2 – t1
If Δ B is the change in concentration of product B, then Δ[B] = x2 – x1 = Δx
∴ Rate of formation of \(\mathrm{B}=+\frac{\Delta[\mathrm{B}]}{\Delta t}\)
∴ Rate of the reaction \(=\frac{\Delta x}{\Delta t}\)
![]()
Question 6.
What are the units of rate of a chemical reaction?
Answer:

∴ The unit of the rate of a chemical reaction : mol L-1 3t-1 or mol dm-3s-1 (According to IUPAC, the rate of a chemical reaction should be expressed in mol m-3s-1 [SI unit]).
Question 7.
Mention the factors that affect the rate of a chemical reaction.
Answer:
The rate of a chemical reaction depends on the following factors :
- Nature of the reactants.
- The concentration of the reactants. In case of a gaseous reaction the rate depends on the pressures of the reactants.
- Temperature of the reaction.
- The presence of a catalyst and its nature.
Question 8.
Explain the term Average rate of a reaction.
Answer:
In chemical kinetics the rate of a reaction is measured in terms of the changes in the concentrations of the reactants or the products per unit time. Average rate of a chemical reaction : It is expressed as a finite change in concentration (- Δc) of the reactant divided by the time interval (Δt) for the change in concentration.
Consider a reaction,
A → B
The rate of a reaction, \(R=\frac{-\Delta[\mathrm{A}]}{\Delta t}=\frac{-\Delta c}{\Delta t}=\frac{c_{2}-c_{1}}{t_{2}-t_{1}}\)
![]()

∴ Average rate \(=\frac{-\Delta[\mathrm{A}]}{\Delta t}\) (in mol dm-3s-1)
Δc is negative, since the concentrartion of the reactant decreases with the time.
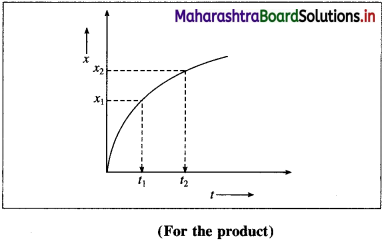
The rate of a reaction is also measured in terms of a finite change in the concentration (Δx) of the product divided by the time interval (Δt), for the change.
For the reaction,

Question 9.
Explain the term Instantaneous rate of a reaction.
Answer:
Instantaneous rate of a reaction : It is defined as a rate of a reaction at a specific instant during a course of the reaction.
If the average reaction rate is calculated over shorter and shorter intervals (making Δt very small) then instantaneous rate is obtained.
In case of reactant A, the instantaneous rate is represented as, \(R=\frac{-d[\mathrm{~A}]}{d t}\) and in case of product B, it is represented as \(R=\frac{+d[B]}{d t}\)
![]()
Question 10.
Define :
(a) Average rate of reaction.
(b) Instantaneous rate of reaction.
Answer:
(a) Average rate of a chemical reaction : It is expressed as a finite change in concentration (- Δc) of the reactant divided by the time interval (Δt) for the change in concentration.
∴ Average rate, \(R=\frac{-\Delta c}{\Delta t}\)
(b) Instantaneous rate of reaction : It is defined as a rate of a reaction at a specific instant during a course of the reaction.
Instantaneous rate \(=\frac{-d c}{d t}\)
Question 11.
Represent the average rates of the following reaction. N2(g) + 3H2(g) → 2NH3(g).
Answer:
For the reation,

This is because the rate of consumption of H2 is thrice the rate of consumption of N2 while the rate of formation of NH3 will be twice the rate of consumption of N2.
Question 12.
Express the rate of a reaction in terms of change in concentration of each constituent in the following reaction : aA+bB → cC+ dD
Answer:
The rate of a reaction may be expressed in terms of decrease in the concentration of the reactants or in-crease in the concentration of the product per unit time,
∴ For the given reaction, aA T bB → cC +dD

Question 13.
For a hypothetical reaction, A + 2B → products, the concentration of A and B at different intervals of time are given in the following table. Find the rates of the reaction in terms of concentration changes in A and B.
The equilibrium concentration of A and B at different time intervals :
| Time t/minute | [A]/mol L-1 | [B]/ml L-1 |
| 0 | 1.000 | 2.000 |
| 10 | 0.534 | 1.068 |
| 20 | 0.342 | 0.360 |
| 30 | 0.180 | 0.360 |
Answer:
Rate of a reaction = \(\frac{-\Delta[\mathrm{A}]}{\Delta t}=-\frac{1}{2} \frac{\Delta[\mathrm{B}]}{\Delta t}\)
(1) Over time interval from O to 10 minutes

(Note that the rate of a reaction in terms of changes in concentration of any reactant or product at the given time remains the same.)
![]()
(2) Over the time interval from 10 to 20 minutes,

Question 14.
Show that the rate of reaction is the same whether expressed in terms of the rate of consumption of any reactant or of the formation of any product.
2N2O5(g) → 4NO2(g) + O2(g)
The concentrations of reactants and products at different time intervals are given in the following table :
Concentrations of various species at different times for the reaction N2O5(g) → 4NO2(g) + O2(g) :
| Time/s | [N2O5]/M | [NO2]/M | [O2]/M |
| 0 | 0.0300 | 0 | 0 |
| 200 | 0.0213 | 0.0174 | 0.00435 |
| 400 | 0.0152 | 0.0296 | 0.00740 |
| 600 | 0.0108 | 0.0384 | 0.00960 |
Answer:
The rate of the reaction can be expressed in terms of rate of consumption of reactants or rate of formation of products.

Consider concentrations at time t1 = 200 seconds and t2 = 400 seconds

The constant values of rate of reaction proves that the rate of the reaction may be measured in terms of concentration changes of reactants or products per unit time.
![]()
Question 15.
Define Rate law (or differential rate law).
Answer:
Rate law (or differential rate law) : It is defined as an experimentally determined mathematical equation which expresses the rate of a chemical reaction in terms of molar concentrations of the reactants which influence the rate of the reaction. For example, for a reaction, A + B → Products By rate law, Rate = R = k[A] x [B] where k is a rate constant and [Al and [B] are molar concentrations of the reactants A and B respectively.
Question 16.
Give examples of rate law with illustrations.
Answer:
Consider following examples :
(i) H2(g) + I2(g) → 2HI(g)
R = k[H2] [I2]
(ii) 2H2O2(g) → 2H2O(I) + O2(g)
Experimentally it is observed that the rate of the reaction is proportional to the concentration of H2O2.
∴ R = k [H2O2]
(iii) NO2(g) + CO(g) → NO(g) + CO2(g)
Experimentally it is observed that rate of the reaction does not depend on the concentration of CO but it is proportional to [NO2]2.
∴ R = k[NO2]2
Question 17.
What are the applications of the rate law?
Answer:
- The rate of any reaction at the given concentration can be measured by knowing the rate law and the rate constant.
- The concentration of the reactants or the products at any instant during the progress of a reaction can be estimated with the help of rate law and the rate constant.
- The mechanisms of simple or complex chemical reactions can be predicted and studied.
Question 18.
Define the rate constant. What are the factors which influence the rate constant of a chemical reaction?
Answer:
(A) Rate constant : The rate constant of a chemical reaction is defined as the rate of the chemical reaction when the concentration (or active masses) of each reactant has unit value, i.e., 1 mol dm-3 in the case of solution and the pressure is 1 atm in case of gases, e.g., for a reaction, A → products, Rate R = k[A].
If [A] = 1 mol dm-3, then k = R.
(B) The rate constant of a reaction depends on the following factors:
- Nature of the reactants.
- Temperature of the reaction. As the temperature increases, the velocity constant (rate constant) increases.
- The conditions of the reactions like the presence of the catalyst, solvent, pH, etc.
- It does not depend on the concentration of the reactants. But if one or more substances are in excess concentration, then the order of the reaction is independent of them.
Question 19.
What are the characteristics of rate constant?
Answer:
The characteristics of rate constant are as follows :
- The rate constant depends upon the nature of the reaction.
- Higher the value of the rate constant, faster is the reaction.
- Lower the value of the rate constant, slower is the reaction.
- By increasing the temperature, the magnitude of the rate constant increases.
- For the given reaction, the rate constant has higher value in the presence of a catalyst than in the absence of the catalyst.
- The reactions having lower activation energy have higher values for rate constants.
Solved Examples 6.2 – 6.3.2
Question 20.
Solve the following :
(1) Write the rate expressions for the following reactions in terms of rate of consumption of the reactants and the rate of formation of the products.
(i) 2NO(g) + O2(g) → 2NO2(g)
(ii) H2(g) + I2(g) → 2HI(g)
Solution :
(i) Given : 2NO(g) + O2(g) → 2NO2(g)
Rate of consumption of NO at time \(t=\frac{-d[\mathrm{NO}]}{d t}\)
Rate of consumption of O2 at time \(t=\frac{-d\left[\mathrm{O}_{2}\right]}{d t}\)
Rate of formation of NO2 at time \(t=\frac{d\left[\mathrm{NO}_{2}\right]}{d t}\)
Rate of the reaction \(=-\frac{1}{2} \frac{d[\mathrm{NO}]}{d t}=\frac{-d\left[\mathrm{O}_{2}\right]}{d t}\)
\(=\frac{1}{2} \frac{d\left[\mathrm{NO}_{2}\right]}{d t}\)
(ii) Given : H2(g) + I2(g) → 2HI(g)
Rate of consumption of H2 at time \(t=\frac{-d\left[\mathrm{H}_{2}\right]}{d t}\)
Rate of consumption of I2 at time \(t=\frac{-d\left[\mathrm{I}_{2}\right]}{d t}\)
Rate of formation of HI at time \(t=\frac{d[\mathrm{HI}]}{d t}\)
∴ Rate of reaction at any time t \(=-\frac{d\left[\mathrm{H}_{2}\right]}{d t}=-\frac{d\left[\mathrm{I}_{2}\right]}{d t}=\frac{1}{2} \frac{d[\mathrm{HI}]}{d t}\)
![]()
(2) The gas-phase reaction between NO and Br2 is represented by the equation. 2NO(g) + Br2(g) → 2NOBr(g)
(a) Write the expressions for the rate of consumption of reactants and formation of products.
(b) Write the expression for the rate of overall reaction in terms of rates of consumption of reactants and formation of products.
Solution :
Given : 2NO(g) + Br2(g) → 2NOBr(g)
(a) Rate of consumption of NO at time t \(=-\frac{d[\mathrm{NO}]}{d t}\)
Rate of consumption of Br2 at time t \(=\frac{-d\left[\mathrm{Br}_{2}\right]}{d t}\)
Rate of formation of NOBr at time \(t=\frac{d[\mathrm{NOBr}]}{d t}\)
(b) Rate of reaction \(=-\frac{1}{2} \frac{d[\mathrm{NO}]}{d t}=\frac{-d\left[\mathrm{Br}_{2}\right]}{d t}\)
\(=\frac{1}{2} \frac{d[\mathrm{NOBr}]}{d t}\)
(3) The decomposition of N2Os is represented by the equation
2N2O5(g) → 4NO2(g) + O2(g)
(a) How is the rate of formation of NO2 related to the rate of formation of O2?
(b) How is the rate of formation of O2 related to the rate of consumption of N2O5?
Solution :
Given : 2N2O5(g) → 4NO2(g) + O2(g)
(a) Rate of formation of NO2 at time \(t=\frac{d\left[\mathrm{NO}_{2}\right]}{d t}\)
Rate of formation of O2 at time \(t=\frac{d\left[\mathrm{O}_{2}\right]}{d t}\)
They are related to each other through rate of reaction.
∴ Rate of reaction \(=\frac{1}{4} \frac{d\left[\mathrm{NO}_{2}\right]}{d t}=\frac{d\left[\mathrm{O}_{2}\right]}{d t}\)
(b) Rate of consumption of N2O5 at time t \(=-\frac{d\left[\mathrm{~N}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{5}\right]}{d t}\)
Rate of reaction \(=-\frac{1}{2} \frac{d\left[\mathrm{~N}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{5}\right]}{d t}=\frac{d\left[\mathrm{O}_{2}\right]}{d t}\)
In general,
Rate of reaction \(=-\frac{1}{2} \frac{d\left[\mathrm{~N}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{5}\right]}{d t}=\frac{1}{4} \frac{d\left[\mathrm{NO}_{2}\right]}{d t}=\frac{d\left[\mathrm{O}_{2}\right]}{d t}\)
(4) Nitric oxide reacts with H2 according to the reaction. 2NO(g) + 2H2(g) → N2(g) + 2H2O(g)
What is the relationship among \(\frac{d[\mathrm{NO}]}{d t}=\frac{d\left[\mathrm{H}_{2}\right]}{d t}=\frac{d\left[\mathrm{~N}_{2}\right]}{d t} \text { and } \frac{d\left[\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}\right]}{d t} ?\)
Solution :
Given : 2NO(g) + 2H2(g) → N2(g) + 2H2O(g)
The relationship among the rate of consumption of the reactants and the rate of formation of products is as follows :
Rate of reaction :
\(R=-\frac{1}{2} \frac{d[\mathrm{NO}]}{d t}=-\frac{1}{2} \frac{d\left[\mathrm{H}_{2}\right]}{d t}=\frac{d\left[\mathrm{~N}_{2}\right]}{d t}=\frac{1}{2} \frac{d\left[\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}\right]}{d t}\)
(5) The rate of decomposition of N2Os was studied in liquid bromine,
2N2O5(g) → 4NO2(g) + O2(g)
If at a certain time, the rate of disappearance of N2O5 is 0.015 Ms-1 find the rates of formation of NO2 and O2. What is the rate of the reaction at this instant?
Solution :
Given : 2N2O5(g) → 4NO2(g) + O2(g)
Rate of disappearance of N2O5 = 0.015 M s-1
Rate of formation of NO2 =?
Rate of formation of O2 =?
Rate of reaction = ?
Rate of disappearance of \(\mathrm{N}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{5}=\frac{-d\left[\mathrm{~N}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{5}\right]}{d t}\)
= 0.015 M s-1
Since 4 moles of NO2 are formed from 2 moles of N2O5 Rate of formation of NO2
Answer:
Rate of formation of NO2 = 0.03 Ms-1
Rate of formation of O2 = 0.0075 M s-1
Rate of reaction = 0.0075 Ms-1.
(6) In the reaction, PCl5(g) → PCl3(g) + CI2(g), at a particular moment, the rate of disappearance of PCl5 is 0.015 Ms-1. What are the rates of formation of PCI3 and Cl2?
Solution :
Given : PCl5(g) → PCl3(g) + Cl2(g)
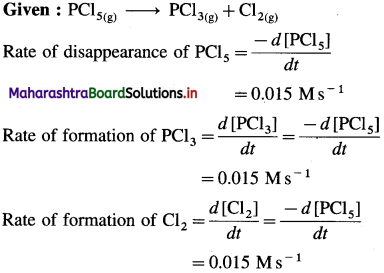

Answer:
Rate of formation of PCl3 = 0.015 Ms-1
Rate of formation of Cl2 = 0.015 Ms-1
![]()
(7) In the reaction, 2N3O5(g) → 4NO2(g) + O2(g), at a certain time, the rate of formation of NO2 is 0. 04 Ms-1. Find the rate of consumption of N2O5, rate of formation of O2 and the rate of the reaction.
Solution :
Given : 2N2O5(g) → 4NO2(g) + O2(g)
Rate of formation of NO2 = \(\frac{d\left[\mathrm{NO}_{2}\right]}{d t}\) = 0.04 Ms-1
From the reaction, rate of consumption of N2O5 is half the rate of formation of NO2 since when 2 moles of N2O5 are consumed, 4 moles of NO2 are formed.
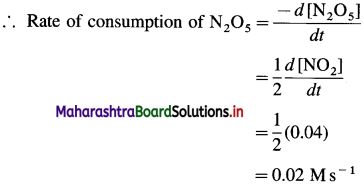
Rate of formation of O2 is one-fourth rate of formation of NO2.

Answer:
(i) Rate of consumption of N2O5
(ii) Rate of formation of O2 = 0.01 Ms-1
(iii) Rate of reaction = 0.01 Ms-1
(8) Consider the reaction 2A + B → 2C. Suppose that at a particular moment during the reaction, rate of disappearance of A is 0.076 M/s,
(a) What is the rate of formation of C?
(b) What is the rate of consumption of B?
(c) What is the rate of the reaction?
Solution :
Given : 2A + B → 2C
Rate of disappearance of A = 0.076 Ms-1
(a) Rate of formation of C =?
(b) Rate of consumption of B =?
(c) Rate of reaction = ?

Answer:
(a) Rate of formation of C = 0.076 Ms-1
(b) Rate of consumption of B = 0.038 M s-1
(c) Rate of reaction = 0.038 Ms-1
![]()
(9) Consider the reation \(\mathbf{3 I}_{(\mathbf{a q})}^{-}+\mathbf{S}_{2} \mathbf{O}_{8(u q)}^{2-} \longrightarrow \mathbf{I}_{3(\mathrm{aq})}^{-}+2 \mathrm{SO}_{4}^{2-}\) At a particular time t, \(t, \frac{d\left[\mathrm{SO}_{4}^{2-}\right]}{d t}=2.2 \times 10^{-2} \mathrm{M} / \mathrm{s}\) What are the values of \(\text { (a) }-\frac{d\left[\mathrm{I}^{-}\right]}{d t}\) \(-\frac{d\left[\mathrm{~S}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{8}^{2-}\right]}{d t}\) \(\text { (c) } \frac{d\left[\mathbf{I}_{3}^{-}\right]}{d t}\) at the same time?
Solution :
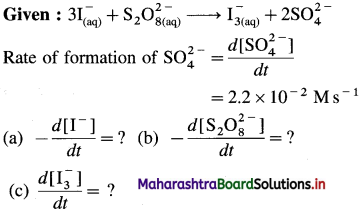
(a) Rate of consumption of \(\mathrm{I}^{-}=-\frac{d\left[\mathrm{I}^{-}\right]}{d t}\)
When 2 moIes of \(\mathrm{SO}_{4}^{2-}\) are formed, 3 moves of I– are consumed in the same time.
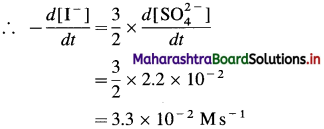
(b) In the formation of 2 moles of \(\mathrm{SO}_{4}^{2-}\), 1 mole of \(\mathrm{S}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{8}^{2-}\) is consumed in the same time.

Answer:

(10) Ammonia and oxygen react at high temperature as :
4NH3(g) + 5O2(g) → 4NO(g) + 6H2O(g)
In an experiment, rate of formation of NO(g) is 3.6 x 10-3 mol L-1s-1.
Calculate-
(a) Rate of disappearance of ammonia
(b) Rate of formation of water.
Solution :

Answer:
(a) Rate of disappearance of NH3
= 3.6 x 10-3 mol L-1s-1
(b) Rate of formation of H2O
= 5.4 x 10-3 mol L-1s-1
![]()
(11) The rate law for the reaction
C2H4Br2 + 3I– → C2H4 + 2Br– +I–3 is Rate = k [C2H4Br2][I–]. The rate of the reac-tion is found to be 1.1 x 10-4 M/s when the concentrations of C2H4Br2 and I–– are 0.12M and 0.18 M respectively. Calculate the rate constant of the reaction.
Solution :
Given : C2H4Br2 + 3I– → C2H4 + 2Br– +I–3
By rate law, Rate of reaction = R = k x [C2H4Br2][I–]
R = 1.1 x 10-4 Ms-1
[C2H4Br2] = 0.12 M; [I–] =0.18 M
Rate constant = k =?
R = k x [C2H4Br2] x [I–]

Answer:
Rate constant = k = 5.1 x 10-3 M-1s-1
(12) For a reaction, 2A + B → C, the rate law is, rate =k x [A]2 x [B]. If the rate constant of the reaction is 3.74 x 10-2M-2s-1, calculate the rate of the reaction when the concentrations of A, B and C are 0.108 M, 0.132 M and 0.124 M respectively.
Solution :
Given : Rate constant of the reaction = k
= 3.74 x 10-2M-2s-1
[A] =0.108 M, [B] = 0.132M, [C] = 0.124 M
Rate of the reaction = R = ?
By rate law,
R = k [A]2 x [B] = (0.108)2 x 0.132 = 1.54 x 10-3 Ms-1
(Concentration of C need not be considered since it is a product.)
Answer:
Rate of reaction = 1.54 x10-3 Ms-1
(13) For a reaction, A + B → C, if the concentration of A doubles, the rate of the reaction doubles. While if the concentration of B doubles the rate of the reaction increases by four fold. Write rate law. .
Solution :
Let x moles of A react with y moles of B. xA + yB → C
To write rate law, it is necessary to find x and y values.
(i) Initial rate \(=R_{1}=k[\mathrm{~A}]_{1}^{x}[\mathrm{~B}]_{1}^{y}\)
Final rate R2 is doubled when the concentration of A is doubled, i.e., R2 = 2R1 when final concentration,
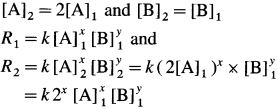
(It is assumed that the concentration of B remains same.)

(ii) Initial rate \(=R_{1}=k[\mathrm{~A}]_{1}^{x}[\mathrm{~B}]^{y}\)
If the concentration of B is doubled keeping of A constant, rate becomes four times, i.e.,
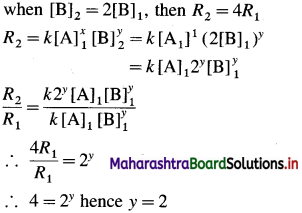
Hence the rate law is represented by an expression.
Rate = k[A] [B]2
Answer:
Rate law is. Rate = k [A] [B]2
![]()
(14) For the reaction, A2 + B + C → AC + AB, it is found that tripling the concentration of A2 triples the rate, doubling the concentration of C doubles the rate and doubling the concentration of B has no effect,
(a) What is the rate law?
(b) Why the change in concentration of B has no effect?
Solution :
Given : A2 + B + C → AC + AB
(a) The rate law may be represented as,
Rate = k [A2]x [B]y [C]z
Let [A]1, [B]1 and [C]1 represent initial concentration and [A]2, [B]2 and [C]2 represent final concentrations, and let R1 and R2 be initial and final rates of the reaction when the concentrations are changed.
(i) If [A]2 = 3[A]1, R2 = 3R1

If the concentrations of B and C remain constant, then
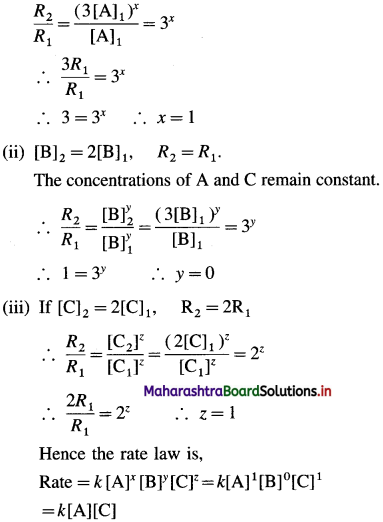
(b) In the rate determining step, B may not be involved as the reactant, hence rate is independent of changes in concentration of B. (OR B may be in large excess as compared to the concentrations of A and C.)
Answer:
(a) Rate law : Rate = k [A] [C]
Question 21.
Define and explain the term order of a chemical reaction.
Answer:
Order of a chemical reaction : The order of a chemical reaction is defined as the number of molecules (or atoms) whose concentrations influence the rate of the chemical reaction.
OR
The order of a chemical reaction is defined as the sum of the powers (or exponents) to which the concentration terms of the reactants are raised in the rate law expression for the given reaction.
Explanation :
Consider a reaction,
n1A + n2B → Products
where n1 moles of A react with n2 moles of B.
The rate of this reaction can be expressed by the rate law equation as,
R = k [A]n1 [B]n2
where k is the rate constant of the reaction, hence, the order of the reaction is n – n1 + n2, (observed, experimentally).
If n = 1, the reaction is called the first order reaction, if n = 2, it is called the second order reaction, etc.
If n = 0, it is called the zero order reaction, e.g., photochemical reaction of H2(g) and Cl2(g).
Question 22.
What are the features (or key points) of order of a reaction?
Answer:
The features of order of reaction are as follows :
- It represents the number of atoms, ions or molecules whose concentrations influence the rate of the reaction.
- It is not related to the stoichiometric equation of the reaction, hence it cannot be predicted from stoichiometric balanced equation.
- It is experimentally determined quantity.
- It is defined only in terms of the concentrations of the reactants and not of products.
- It may have values which are integers, fractional or zero.
- Higher values are rare. Reactions of first and second order are in large number. Third order reactions are very few like,
2NO(g) + Cl2(g) → 2NOCl(g).
![]()
Solved Examples 6.3.3
Question 23.
Solve the following :
(1) From the rate expressions for the following reactions, determine their order :
(a) 2N2O5(g) → 4NO2(g) + O2(g) : Rate = k [N2O5]
(b) CHCl3(g) + Cl2(g) → CCl4(g) + HCl(g) : Rate = k [CHL3] [Cl2]1/2
(c) C2H5Cl(g) → C2H4(g) + HCl(g): Rate = k [C2H5Cl]
(d) 2NO2(g) + F2(g) → 2NO2F(g) → : Rate = k (NO2] [F2]
Solution :
(a) 2N2O5(g) → 4NO2(g) + O2(g)
The rate law expression given for the reaction is Rate = k x [N2O5]
Hence the reaction is of first order.
(b) CHCl3(g) + Cl2(g) → CCl4(g) + HCl(g)
The given rate law expression is, R = k [CHCl3] x [Cl2]1/2 Here the order of a reaction is one with respect to CHCl3(g) and half with respect to Cl2(g). Therefore the overall order of the reaction is 1 + 1/2 = 1.5.
(c) C2H5Cl(g) → C2H4(g) + HCl(g)
The given rate law expression is, Rate = k [C2H5Cl]
Hence the reaction has order equal to one.
(d) 2NO2(g) + F2(g) → 2NO2F(g)
The given rate law expression for the reaction is Rate = k [NO2] x [F2]
Hence the reaction is first order with respect to NO2 and first order with respect to F2. The overall order of the reaction is, n = nNO2 + nF1 = 1 + 1 = 2.
(2) Determine the order of following reactions from their rate expressions :
(a) 2H2O2 → 2H2O + O2 Rate = k [H2O2]
(b) NO2 + CO → NO + CO2 Rate = k [NO2]2
(c) 2NO + O2 → 2NO2 Rate = k [NO]2 x [O2]
(d) CHCl3(g) + Cl2(g) → CCl4(g) + HCl(g)
Rate = k [CHCl3] [Cl2]
Solution :
(a) For the reaction,
2H2O2 → 2H2O + O2
Since the rate law expression given is,
Rate = k [H2O2]
Hence the reaction is of first order.
(b) For the reaction,
NO2 + CO → NO + CO2
Since the rate law given is Rate = k [NO2]2, the reaction is second order with respect to NO2 and zero order with respect to CO. Hence the net order of the reaction is, n = nNO2 + nco = 2 + 0 = 2
(c) For the reaction,
2NO + O2 → 2NO2
Since the rate law expression given is, Rate = k [NO]2 x [O2] the reaction is second order with respect to NO and first order with respect to O2. Hence the overall order of reaction is n = nNO2 + no2 = 2 + 1 = 3.
(d) For the reaction, by rate law,
Rate = k [CHCl3] x [Cl2] reaction is first order with respect to CHCl3 and first order with respect to Cl2. Hence the overall order is, n = ncHcl3 + ncl2 = 1 + 1 = 2.
(3) Write the rate law expressions for the following reactions:
(1) 2N2O5(g) → 4NO2 + O2; order of the reaction is 1.
(2) CH3CHO → CH4 + CO; order of the reaction Is 3/2.
Solution :
(1) For the given reaction, order is one hence the rate law expression is, Rate = k [N2O5].
(2) For the given reaction, order is 3/2, hence the rate law expression is Rate = k x [CH2CHO]3/2.
(4) The reaction \(\mathbf{H}_{2} \mathbf{O}_{2(\mathbf{a q})}+3 \mathbf{I}_{(\mathbf{a q})}^{-}+2 \mathbf{H}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{+} \longrightarrow 2 \mathbf{H}_{2} \mathbf{O}_{(0)}+\mathbf{I}_{3(a q)}^{-}\) is first order in H2O2 and I–, zero order in H+. Write the rate law.
Solution:
Given :
\(\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{2(\mathrm{~g})}+3 \mathrm{I}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{-}+2 \mathrm{H}^{+}{ }_{(\mathrm{aq})} \longrightarrow 2 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{(\mathrm{i})}+\mathrm{I}_{3(\mathrm{aq})}^{-}\)
Since the reaction is first order in H2O2 and F and zero order in H+, the expression for rate law will be,
Rate =k [H2O2]1 [I–]1 [H+]0
∴ Rate = k [H2O2] [I–]
Answer:
Rate = k [H2O2] [I–]
![]()
(5) The rate law for the gas-phase reaction
2NO(g) + O2(g) → 2NO2(g) is rate = k [NO2]2 [O2]. What is the order of the reaction with respect to each of the reactants and what is the overall order of the reaction?
Solution :
Given : 2NO(g) + O2(g) → 2NO2(g)
Rate = k [NO]2[O2]
Order of the reaction with respect to NO = nNo = 2
Order with respect to O2 = nO2 = 1
Overall order of the reaction = n = nNO + nO2
= 2 + 1
= 3
Answer:
Order with respect to NO = 2
Order with respect to O2 = 1
Overall order = 3
(6) What is the order for the following reactions?
(a) 2NO2(g) + F2(g) → 2NO2F(g), rate = k [NO2][F2]
(b) CHCl3(g) + Cl2(g) → CCl4(g) + HCl(g), rate = k[CHCl3][Cl2]1/2
Solution :
(a) Given : 2NO2(g) + F2(g) → 2NO2F
Rate = k [NO2][F2]
Hence the reaction is first order with respect to NO2 and first order with respect to F2
∴ Order of reaction = nNO2 + nF2 = 1 + 1 = 2
(b) Given :
CHCl3(g) + Cl2(g) → CCl4(g) + HCl(g),
Rate = k [ CHCl3] [Cl2]1/2
Hence the reaction is first order in CHCl3 and half order in Cl2.
∴ Order of reaction
= nCHCl3 + nCl2 = 1 + \(\frac{1}{2}\) = \(\frac{3}{2}\)
Answer:
(a) Order of the reaction = 2
(b) The order of the reaction = \(\frac{3}{2}\)
(7) Write the rate law for the following reactions :
(a) A reaction that is zero order in A and second order in B.
(b) A reaction that is second order in NO and first order in Br2.
Solution :
(a) Given : A + B → Products
The reaction is zero order in A and second order in B. Hence the rate law is represented as, Rate = k [A]O[B]2
Rate = k[B]2
(b) Given : 2NO(g) + Br2(g) → 2NOBr(g)
The reaction is second order in NO and first in Br2. Hence the rate law is,
∴ Rate = k [NO]2[Br2]
Answer: (a) Rate law : Rate = k[B]2
(b) Rate law : Rate = k [NO]2[Br2]
(8) The reaction A + B → Products, is first order in each of the reactants, (a) Write the rate law.
(b) How does the reaction rate change if the concentration of B is decreased by a factor 3?
(c) What is the change in the rate if the concentration of each reactant is tripled? (d) What is the change in the rate, if the concentration of A is doubled and that of B is halved?
Solution :
(a) The reaction is first order in A and B. Hence the equation for rate law is,
Rate = k [A] [B]
(b) Before changing the concentration of B, Initial rate = R1 – k [A]1 [B]1
After change in concentration of B,
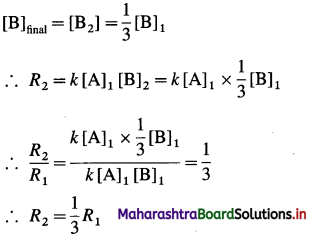
Hence the rate of the reaction will be decreased by a factor 3.
![]()
(c) When the concentration of each reactant is tripled, then the final concentrations will be, [A]2 = 3[A]1 and [B]2 = 3[B1]
∴ R2 = k x 3[A]1 x 3 [B]1
∴ R2 = k x 3[A]1 x 3 [B]1

Hence the rate of the reaction will be increased by 9 times.
(d) When the concentration A is doubled and that of B is halved then the final concentrations will be,

Rate of the reaction will remain unchanged.
Answer:
(a) Rate law is, Rate = k [A] [B],
(b) Rate is decreased by a factor 3,
(c) Rate is increased by 9 times,
(d) Rate remains unchanged.
(9) Consider the reaction A2 + B → products. If the concentration of A2 and B are halved, the rate of the reaction decreases by a factor of 8. If the concentration of A2 is increased by a factor of 2.5, the rate increases by the factor of 2.5. What is the order of the reaction? Write the rate law.
Solution :
Given : A2 + B → Products
(i) When concentration of A2 and B are halved :
[A2]2(final) = 1/2 [A2]1(final) and [B]2 = 1/2 [B]1 then, R2(final) = 1/8R1(intial).
(ii) When concentration of A2 is increased by the factor 2.5,
[A2]2 = 2.5 [A2]1 (concentration of B is same) then, R2 = 2.5 R1
Now let the reaction be, XA2 + yB → Products
From data in (ii),
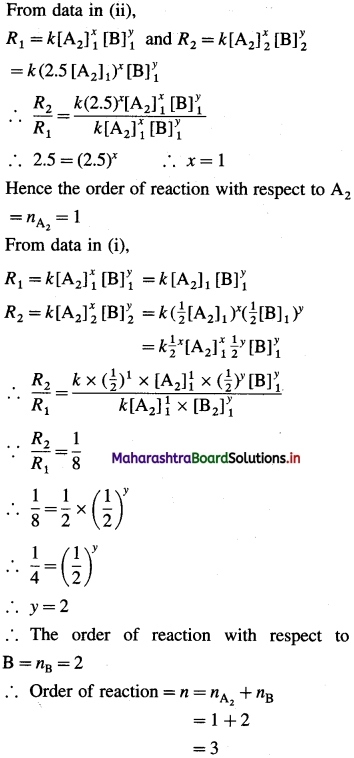
Hence the reaction is of third order. The rate law can be represented as,
Rate = k [A2] [B]2
Answer:
(i) Order of the reaction = 3
(ii) Rate law : Rate = k [A2] [B]3
![]()
(10) Consider the reaction C + D → Products. The rate of the reaction increases by a factor of 4 when the concentration of C is doubled. The rate of the reaction is tripled when concentration of D is tripled. What is the order of the reaction? Write the rate law.
Solution :
Given : C + D → Products OR xC + yD → Products
(i) When the concentration of C is doubled, the rate of the reaction increases by 4.
[C]2(final) = 2[C]1(initial) then R2(final) = 4R1(initial)
(In this, the concentration of D is assumed to be constant.)

Hence, the reaction is second order in C.
∴ nC = 2
(ii) When the concentration of D is tripled, rate is tripled. The concentration of C is assumed to be constant.

Rate law : Rate = A[C]2[D]
Answer:
(i) Order of the reaction = 3
(ii) Rate law : Rate = A[C]2[D]
(11) The reaction F2(g) + 2ClO2(g) → 2FClO2(g) is first order in each of the reactants. The rate of the reaction is 4.88 x 10-4 M/s when [F2] = 0.015 M and [ClO2]= 0.025 M. Calculate the rate constant of the reaction.
Solution :
Given :
F2(g) + 2ClO2(g) → 2FClO2(g)
Order of reaction in F2 = nF2 = 1
Order of reaction in CIO2 = nClO2 = 1
Rate = R = 4.88 x 10-4 Ms-1
[F2] = 0.015 M; [ClO2] = 0.025 M
Rate = k = ?
By rate law,

Answer:
Rate constant = 1 = 1.3 M-2s-1
(12) The reaction 2H2(g) + 2NO(g) → 2H2O(g) + N2(g) is first order in H2 and second order in NO. The rate constant of the reaction at a certain temperature is 0.42M-2s-1. Calculate the rate when [H2] = 0.015 M and [NO] = 0.025 M.
Solution :
Given : 2H2(g) + 2NO(g) → 2H2O(g) + N2(g)
Order of reaction in H2 = nH1 = 1
Order of reaction in NO = nNO = 2
Rate constant = k = 0.42 M-2s-1
[H2] = 0.015 M; [NO] = 0.025 M
Rate of reaction = R = ?
By rate law,
Rate = R = k [H2] [NO]2
= 0.42 x 0.015 x (0.025)2 M-2s-1 M M
= 3.94 x 10-6 Ms-1
Answer:
Rate of reaction = R = 3.94 x 10-6 Ms-1
![]()
(13) Find the order of following reactions whose rate laws are expressed as follows. CA and CB are the concentrations of reactants A and B respectively :

Solution :
Given :
(1) For, – \(\frac{d c}{d t}\) = k x \(\mathrm{C}_{A}^{0}\) the order of the reaction, n = 0. Hence it is a zero order reaction.
(2) For, – \(\frac{d c}{d t}\) = k x \(\mathrm{C}_{A}^{3 / 2}\), the overall order of the reaction is 3/2.
(3) For, –\(\frac{d c}{d t}\) = k x \(\mathrm{C}_{A}^{1 / 2} \mathrm{C}_{B}^{2}\), the reaction has order 1/2 with respect to A and 2 with respect to B.
∴ n = nA + nB = \(\frac{1}{2}\) + 2 = \(\frac{5}{2}\).
Hence the (overall) order of the reaction is \(\frac{5}{2}\).
(4) For, \(-\frac{d c}{d t}=k \mathrm{C}_{A}^{5 / 2} \times \mathrm{C}_{B}^{0}\)
The reaction has order \(\frac{5}{2}\) with respect to A and zero with respect to B.
∴ n = nA + nB = \(\frac{5}{2}\) + 0 = \(\frac{5}{2}\)
Hence the order of the reaction is \(\frac{5}{2}\).
(5) For, \(-\frac{d c}{d t}=k \times \mathrm{C}_{A}^{1 / 3} \times \mathrm{C}_{B}^{2 / 3}\). The reaction has order \(\frac{1}{3}\) with respect to A and \(\frac{2}{3}\) with respect to B.
∴ n = nA + nB = \(\frac{1}{3}\) + \(\frac{2}{3}\) = 1
Hence the order of the reaction is 1.
(14) The rate of a reaction, 2A + B → Products is 3.78 x 10-4 M s-1 when the concentrations of A and B are 0.3 M each. If the rate constant of the reaction is 4.2 x 10-3s-1 find the order of the reaction.
Solution :
Given : 2A + B → Products
Rate = R = 3.78 x 10-4Ms-1
[A] = [B] = 0.3 M
Rate constant = 1 = 4.2 x 10-3 s-1
Let the order of the reaction in A be x and in B be y.
Then, by rate law,
Rate = R = k [A]x [B]y 3.78 x 10-4
= 4.2 x 10-3(0.3)x(0.3)y
= 4.2 x 10-3 (0.3)x+y
∴ \(\frac{3.78 \times 10^{-4}}{4.2 \times 10^{-3}}\) = (0.3)x+y
0.09 = (0.3)x+y
(0.3)2 = (0.3)x+y .
∴ x + y = 2
Hence the order of overall reaction is 2.
Answer:
The order of the reaction is 2.
(15) The rate of the reaction, A → Products is 1.25 x 10-2 M/s when concentration of A is 0. 45 M. Determine the rate constant if the reaction is
(a) first order in A
(b) second order in A.
Solution :
Given : A → Products
Rate = R = 1.25 x 10-2 M/s
[A] = 0.45 M
(a) Rate constant, k = ? if order is one.
For first order, rate law is, R = k [A]
∴ \(k=\frac{R}{[\mathrm{~A}]}=\frac{1.25 \times 10^{-2}}{0.45}\)
= 2.78 x 10-2s-1
(b) Rate constant, k =? if order is two. For second order, rate law is, R = k [A]2
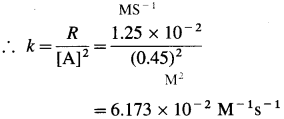
Answer:
(a) Rate constant, k = 2.78 x 10-2
(b) Rate constant, k = 6.173 x 10-2
![]()
Question 24.
Define and explain the term elementary reaction.
Answer:
Many reactions take place in a series of steps. Such reactions are called complex reactions. Each step taking place in a complex reaction is called an elementary reaction. This shows that a complex reaction is broken down in a series of elementary chemical reactions.
By adding all the elementary steps of a complex reaction we get the overall reaction.
The mechanism of a reaction is decided from the sequence of the elementary steps that are added to give overall reaction.
Elementary reaction : It is defined as the reaction which takes place in a single step and cannot be divided further into simpler chemical reactions.
The order and molecularity of the elementary reaction are same.
Some reactions take place in one step and cannot be broken down into simpler reactions. For example,
C2H5I(g) → C2H4(g) + HI(g)
O3(g) → O2(g) + O(g)
Question 25.
Define and explain the term molecularity of a reaction. Give examples.
OR
Define the molecularity of a chemical reaction.
Answer:
Molecularity : The molecularity of an elementary reaction is defined as the number of molecules (or atoms or ions) which take part in a chemical reaction.
Explanation :
- The molecularity of a reaction is always integral.
- It cannot be determined experimentally.
- The minimum value of the molecularity is one.
- It cannot have fractional or zero values.
- The reactions are classified according to the molecularity as follows :
(a) Unimolecular reaction (OR First order reaction) : In this only one molecule takes part in the reaction, e.g., N2O5(g) → 2NO2(g) + \(\frac{1}{2}\)O2(g)
The rate law expression for this reaction is, Rate = k [N2O5]. Hence it is unimolecular and first order.
Other unimolecular reactions are,
O3(g) → O2(g) + O(g)
C2H5I(g) → C2H2(g) + HI(g)
(B) Bimolecular reaction In this two molecules take part in the reaction,
e.g., 2HI(g) → H2(g) + I2(g)
O3(g) + O(g) → 2O2(g)
2NO2(g) → 2NO(g) + O2(g)
(c) Trimolecular reaction: In this three molecules take part in the reaction.
e.g., 2NO(g) + O2(g) → 2NO2(g)
The higher molecularity is rare since the prob ability of simultaneous collisions between more molecules is very low.
Question 26.
Explain order and molecularity of elementary reactions.
Answer:
(1) The order and molecularity of elementary reaction are same.
(2) Consider second order bimolecular reaction,
2NO2(g) → 2NO(g) + O2.
(3) The rate of the reaction is given by, Rate = k [NO2]2
(4) Similarly consider unimolecular first order reaction,
C2H5I(g) → C2H4(g) + HI(g)
Rate = k [C2H5I]
![]()
Question 27.
Define and explain the term rate-determining step.
Answer:
(1) Many chemical reactions take place in a series of elementary steps. Among many steps of the reaction, one of the steps is the slowest step compared to other steps.
Rate determining step : The slowest step in the reaction mechanism which involves many steps is called the rate-determining step.
(2) Example :
Consider decomposition of gaseous NO2Cl.
2NO2Cl(g) → 2NO2(g) + Cl2(g)
This reaction takes place in two steps :
Step I : \(\mathrm{NO}_{2} \mathrm{Cl}_{(g)} \stackrel{k_{1}}{\longrightarrow} \mathrm{NO}_{2(\mathrm{~g})}+\mathrm{Cl}_{(\mathrm{g})}\) (slow, unimolecular)
Step II: \(\mathrm{NO}_{2} \mathrm{Cl}_{(g)} \stackrel{k_{2}}{\longrightarrow} \mathrm{NO}_{2(\mathrm{~g})}+\mathrm{Cl}_{(\mathrm{g})}\) (fast, bimolecular)
2NO2CI(g) → 2NO2(g) + CI2(g) (overall reaction)
Among two steps, first step being slower represents rate-determining step. The rate law can be represented as, Rate = k1 [NO2CI]
Hence, the reaction is first order.
In this Cl(g) is formed as a reaction intermediate.
Question 28.
What are the features of rate-determining step?
Answer:
Features of rate-determining step :
- The overall reaction can never occur faster than its rate-determining step.
- The rate-determining step can occur anywhere in the reaction mechanism and depends on nature of reactants, conditions of the reaction, etc.
- The rate law of a rate-determining step can directly be obtained from its stoichiometric equation.
- The rate law of a rate-determining step can directly be obtained from its stoichiometric equation.
Question 29.
What is reaction intermediate? Explain with an example.
Answer:
Reaction intermediate : The additional species other than the reactants or products formed in the mechanism during progress of the reaction is called reaction intermediate.
Features of reaction intermediate :
- The reaction intermediate appears in the reaction mechanism but does not appear in the overall reaction or in the products.
- It is always formed in one step and consumed in the subsequent step in the mechanism.
- Its concentration is very small and cannot be determined easily.
- Rate of the reaction is independent of concentration of this intermediate.
- The life period of the reaction intermediate is extremely small, hence cannot be isolated.
- The composition of the reaction intermediate, decides the mechanism of the reaction.
- Consider decomposition of gaseous NO2Cl. 2NO2Cl(g) → 2NO2(g) + Cl2(g)
This reaction takes place in two steps :
Step I : \(\mathrm{NO}_{2} \mathrm{Cl}_{(\mathrm{g})} \stackrel{k_{1}}{\longrightarrow} \mathrm{NO}_{2(\mathrm{~g})}+\mathrm{Cl}_{(\mathrm{g})}\) (slow, unimolecular)
Step II : \(\mathrm{NO}_{2} \mathrm{Cl}_{(\mathrm{g})}+\mathrm{Cl}_{(\mathrm{g})} \stackrel{k_{2}}{\longrightarrow} \mathrm{NO}_{2(\mathrm{~g})}+\mathrm{Cl}_{2(\mathrm{~g})}\) (fast, bimolecular)
2NO2Cl(g) → 2NO2(g) + Cl2(g) (overall reaction)
Cl formed in Step I is removed in Step II, Hence Cl is a reaction intermediate.
Question 30.
Identify the molecularity and write the rate law for each of the following elementary reactions :
(a) NO(g) + O3(g) → NO3(g) + O(g)
(b) H2I(g) + I(g) → 2HI(g)
(c) CI(g) + Cl(g) + N2(g) → N2(g)
Answer:
NO(g) + O3(g) → NO3(g) + O(g) Molecularity is 2.
Rate law : Rate = k [NO] x [O3]
(b) H2I(g) + I(g) → 2HI(g) Molecularity is 2.
Rate law : Rate = k [H2I] x [I]
(c) Cl(g) + Cl(g) + N2(g) →Cl2(g) + N2(g) Molecularity is 3.
Rate law : Rate = k [Cl]2
![]()
Question 31.
Write molecularity of the following reaction:
2NO(g) + O2(g) → 2NO2(g).
Answer:
For the reaction, 2NO(g) + O2(g) → 2NO2(g) Molecularity = 3.
Question 32.
How Is reaction intermediate predicted in the reaction?
Answer:
(1) When a reaction takes place in more than one steps, then a substance produced in one step is removed in the next step is called reaction intermediate.
(2) For example,
(I) NO(g) + O3(g) → NO3(g) + O(g)
(ii) NO3(g) + O(g) → NO2(g) + O(g)
In the reaction. NO3 and O are reaction intermediates.
Question 33.
A certain reaction occurs in the following steps :
(i) Cl(g) + O3(g) → ClO(g) + O2(g)
(ii) ClO(g) + O(g) → Cl(g) + O2(g)
(a) Write the chemical equation for overall reaction.
(b) Identify the reaction intermediate.
(c) Identify the catalyst.
(d) What is the molecularity of each step?
Answer:
Step I : Cl(g) + O3(g) → ClO(g) + O2(g)
Step II : ClO(g) + O(g) → Cl(g) + O2(g)
(a) Overall reaction is obtained by adding both the reactions.
O3(g) + O(g) → 2O2(g)
(b) Reaction intermediate is ClO(g) which is formed in the first step and removed in the second step.
(c) Cl(g) acts as a catalyst. It is an example of homo-geneous catalysis in which catalyst Cl(g) forms an intermediate ClO(g) and again is released in the second step.
(d) Since both the steps involve two reactants each, both the steps are bimolecular.
Question 34.
The rate law for the reaction 2H2(g) + 2NO(g) → N2(g) + 2H2O(g) is given by rate = k [H2] [NO]2.
The reaction occurs in the following two steps :
(i) H2(g) + 2NO(g) → N2O(g) + H2O(g)
(ii) N2O(g) + H2(g) → N2(g) + H2O(g)
What is the role of N2O in the mechanism? What is the molecularity of each of the elementary steps?
Answer:
N2O is a reaction intermediate which is formed in the first step and removed in the second step. Molecularity of the elementary steps :
(a) First step – Termolecular.
(b) Second step-Bimolecular.
Question 35.
What is the rate law for the reaction,
NO2(g) + CO(g) → NO(g) + CO2(g)
The reaction occurs in the following steps :
NO2 + NO2 → NO3 + NO (slow)
NO3 + CO → NO2 + CO2 (fast)
What is the role of NO3?
Answer:
Overall reaction :
NO2(g) + CO(g) → NO(g) + CO2(g)
Step-I NO2 + NO2 → NO3 + NO (slow) (slow)
Step-II NO3 + CO → NO2 + CO2 (fast)
(A) From first rate determining slow step, rate law is, Rate = k[NO2]2
(B) Role of NO3 : In the reaction, NO3 is the reaction intermediate which is formed in first step and removed in the second step.
![]()
Question 36.
The rate law for the reaction 2NO(g) + Cl2(g) → 2NOCl(g) is given by rate = k[NO][Cl2]. The reaction occurs in the following steps :
(i) NO(g) + Cl2(g) → NOCl2(g)
(ii) NOCl2(g) + NO(g) → 2NOCl(g)
(a) Is NOCl2 a catalyst or reaction intermedi-ate? Why?
(b) Identify the rate determining step.
Answer:
(a) NOCl2 is a reaction intermediate since it is formed in the first step and removed in the second step. It is not a catalyst since it was not present in the first step or on reactant side nor in the second step on product side.
(b) Since rate law is, Rate = k[NO][Cl2], and the sub-stances NO and Cl2 are present in the first step as reactants, it is the slow and rate-determining step.
Question 37.
The rate law for the reaction 2H2(g) + 2NO(g) → N2(g) + 2H2O(g) is given by rate = k[H2][NO]2. The reaction occurs in the following steps :
(i) H2 + 2NO → N2O + H2O
(ii) N2O + H2 → N2 + H2O
What is the role of N2O in the mechanism? Identify the slow step.
Answer:
(a) N2O is the reaction intermediate since it is formed in the first step and removed in the second step.
(b) By rate law, Rate = k [H2][NO]2. Since the first step involves the substances H2 and NO, it is the slow and rate-determining step.
Question 38.
What are integrated rate laws?
Answer:
Integrated rate laws : The equations which are obtained by integrating the differential rate laws (expressions) and which provide direct relationship between the concentrations of the reactants and time are called integrated rate laws.
For example, integrated rate law for first order reaction is represented as,
\(k=\frac{2.303}{t} \log _{10} \frac{[\text { Reactant }]_{\text {final }}}{[\text { Reactant }]_{\text {initial }}}\)
Question 39.
Derive the expression for integrated rate law (equation) for the first-order reaction.
Answer:
Consider the following first-order reaction, A → B The rate of the chemical reaction is given by the rate law expression as, Rate, R = k [A] where [A] is the concentration of the reactant A and k is the velocity constant or specific rate of the reaction.
The instantaneous rate is given by,

If [A0] is the initial concentration of the reactant and [A]t at time t, then by integrating the above equation,

This is the integrated rate equation for the first order reaction. This is also called integrated rate law.
Question 40.
How is the integrated rate equation for the first order reaction represented by considering the concentration of the product?
Answer: The
integrated rate equation for the first order reaction can be represented as,
\(k=\frac{2.303}{t} \log _{10} \frac{[\mathrm{A}]_{0}}{[\mathrm{~A}]_{t}}\) where [A]0 is the initial concentration of the reactant (at time, 1 = 0) and [A]t is that at time t. Consider the reaction, A → B

If a is the initial concentration of the reactant A and x is the concentration of the product B after time t, then

![]()
Question 41.
Explain the exponential rate law expression for the first order reaction.
Answer:
The integrated rate equation for the first order reaction can be represented as,
\(k=\frac{1}{t} \log _{\mathrm{e}} \frac{[\mathrm{A}]_{0}}{[\mathrm{~A}]_{t}}\)
where k is a rate constant, [A]0 and [A]t are initial and final concentrations of the reactant after time t.
∴ k = \(-\frac{1}{t} \log _{\mathrm{e}} \frac{[\mathrm{A}]_{t}}{[\mathrm{~A}]_{0}}\)
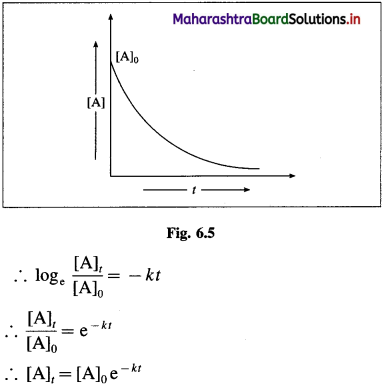
where [A]0 and [A]t are the concentrations of the reactant when t = 0 and t = t respectively.
Thus, the concentration of the reactant decreases exponentially with time and the time required to complete the first order reaction will be infinity.
Another feature of the exponential behaviour is the time required to complete a definite fraction of the reaction is always constant. Therefore, the first order reactions are also described in terms of the half-life of the reaction ™.
Question 42.
What are the units of rate constant of first order reaction?
Answer:
The units of rate constant (k) for the first order reaction is per time (or s-1).
Question 43.
Give three examples of first order reaction.
Answer:
The examples of first order reaction are :
(1) Decomposition of H2O2 :
2H2O2(I) → 2H2O(1) + O2(g) Rate = k[H2O2]
(2) Decomposition of N2Os :
2N2O5(g) → 4NO2(g) + O2(g) Rate = k[N2O5]
(3) Isomerisation of cyclopropane to propene :
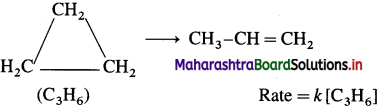
Question 44.
Write a note on a zero order reaction.
OR
What is a zero order reaction? Explain.
Answer:
(1) Definition : Zero order reaction : A reaction in which the rate of the reaction does not depend on the concentration of any reactant taking part in the reaction is called zero order reaction.
(2) Explanation : For example, consider photochemical reaction between H2 and Cl2 gases.
![]()
In this the rate of the reaction remains constant throughout the progress of the reaction, even if the concentrations of the reactants decrease with time, until the reactant has reacted entirely.
Hence, by the rate law,
R = k [H2]° [Cl2]° = k (constant).
Question 45.
Derive the expression for integrated rate law for zero-order reaction A → Products.
Answer:
Consider a zero order reaction, A → Products
The rate of the reaction is, Rate \(=\frac{-d[\mathrm{~A}]}{d t}\)
By rate law,
Rate = k x [A]0 = k
∴ – d[A] = k x dt
If [A]0 is the initial concentration of the reactant A at t = 0 and [A]t is the concentration of A present after time t, then by integrating above equation,
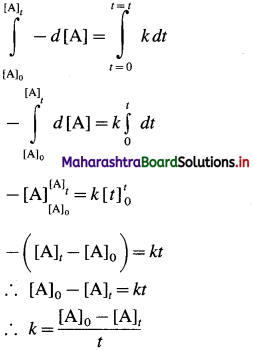
This is the integrated rate law expression for rate constant for zero order reaction.
∴ k x t = [A]0 – [A]t
∴ [A]t = – kt + A0
![]()
Question 46.
How would you obtain the unit of the velocity constant k for (i) the first order reaction (ii) the zero order reaction?
Answer:
(i) For a first order reaction :
Consider the reaction,
A → B
The rate (R) of the reaction will be, R = k [A] = kc, where [A] is concentration in mol dm-3
Hence, the SI unit of velocity constant for the first order reaction is second-1.
(ii) For a zero order reaction :
The rate of reaction is R = k [A]0 = k
Hence, the velocity constant k has the unit of the rate of the reaction, i.e., mol dm-3 s-1.
Question 47.
Obtain an expression for half-life period of zero order reaction.
Answer:
The rate law expression for zero order reaction is, [A]t = – kt + [A]0
where [A]0 and [A]t are the concentrations of the reactant at time, t = 0 and after time t respectively, Half-life period, t1/2 is the time when the concentration reduces from [A]0 to [A]0/2. i.e., at t = t1/2, [A]t = [A]0/2.

Hence for a zero-order reaction, the half-life period is directly proportional to the initial concentration of the reactant.
Question 48.
Give the examples of zero order reactions.
Answer:
Zero order reactions are not common. They take place under special conditions. They are hetero-geneous catalysed reactions generally involving metals as catalysts.
(1) Decomposition NH3 on Pt surface :
![]()
(2) Decomposition of N2O to N2 and O2 on Pt :
![]()
(3) Decomposition of PH3 on hot tungsten catalyst at high pressure.
Question 49.
Decomposition of NH3(g) on platinum surface at high temperature is a zero order reaction. Explain.
Answer:
- The decomposition of NH3(g) on platinum surface is represented as,
2NH3(g) \(\frac{1130 \mathrm{~K}}{\mathrm{Pt}}\) N2(g) + 3H2(g) - Since it is a heterogeneous catalysed reaction, NH3 gaseous molecules at high pressure are adsorbed on the metal surface covering the surface area.
- The number of NH3 molecules adsorbed is small compared to NH3 molecules in the gaseous phase.
- Only the molecules adsorbed on the surface get decomposed. Hence rate of the decomposition becomes independent of the concentration (pressure) of NH3. Therefore the decomposition reaction is zero order.
Question 50.
The catalysed decomposition of nitrous oxide (N2O) to nitrogen and oxygen is a zero order reaction. Explain.
Answer:
- The decomposition of N2O(g) on platinum can be represented as, \(2 \mathrm{~N}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{(\mathrm{g})} \stackrel{\mathrm{Pt}}{\longrightarrow} 2 \mathrm{~N}_{2(\mathrm{~g})}+\mathrm{O}_{2(\mathrm{~g})}\)
- Since it is heterogeneously catalysed reaction, N2O gaseous molecules are adsorbed on the metal surface covering the surface area.
- The number of N2O molecules adsorbed is small compared to N2O molecules in the gaseous phase.
- Only the molecules adsorbed on the metal surface get decomposed. Hence rate of decomposition becomes independent of the concentration (pressure) of N2O. Therefore the decomposition of N2O is a zero order reaction.
![]()
Question 51.
Inversion of cane sugar (sucrose) is a pseudo-first-order reaction. Explain.
OR
The reaction,

Can it be of pseudo-first-order type?
Answer:
The inversion of cane sugar (sucrose) is an acid catalysed hydrolysis reaction which can be represented as,
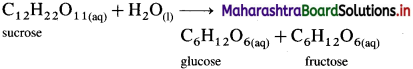
This is a bimolecular reaction. Hence, the true rate law for the reaction should be, Rate = k[C12H22O11] [H2O]. This shows that the reaction should be second order.
Since water (H2O) is in large excess, its concentration remains constant and the rate depends only upon the concentration of cane sugar.
∴ Rate = k[C12H22O11]
Therefore the second order true rate law becomes first order rate law. Hence the inversion of cane sugar is a pseudo first order reaction.
Solved Examples 6.4-6.5
Question 52.
Solve the following :
(1) For the reaction 2A + B → products, find the rate law from the following data :
| [A]/M | [B]/M | rate/Ms-1 |
| 0.3 | 0.05 | 0.15 |
| 0.6 | 0.05 | 0.30 |
| 0.6 | 0.2 | 1.20 |
Solution:
In steps (i) and (ii), the concentration of A is doubled but the concentration of B remains constant. Since the rate is doubled the rate is proportional to the concentration of A or R α [A] and hence with respect to A order of the reaction is 1 or nA = 1.
In steps (ii) and (iii), the concentration of A is kept constant but the concentration of B is increased 4 times and rate of the reaction is increased 4 times. Hence the rate of reaction is proportional to concentration of B, R α [B] and hence with respect of B, order is 1 or nB = 1. Hence rate law will be, Rate = k [A] x [B].
(2) In a first order reaction A → product, 80 % of the given sample of compound decomposes in 40 min. What is the half life period of the reaction ?
Solution :

Answer:
Half life period = 17.22 min
(3) The reaction A + B → products is first order in each of the reactants.
(a) How does the rate of reaction change if the concentration of A is increased by factor 3?
(b) What is the change in the rate of reaction if the concentration of A is halved and concentration of B is doubled?
Solution :

Hence the rate remains the same.
Answer:
(a) The rate increases by factor 3.
(b) The rate remains the same.
![]()
(4) Half-life period of a first order reaction is 41.09 min. Calculate rate constant in per second.
Solution :
Given : Half-life period = t1/2
= 41.09 min = 41.09 x 60 s
= 2.465 x 103s
Rate constant = k = ?
For a first order reaction,
\(\begin{aligned}
k &=\frac{0.693}{t_{1 / 2}} \\
&=\frac{0.693}{2.465 \times 10^{3}}
\end{aligned}\)
= 2.81 x 10-4 s-1
Answer:
Rate constant = k = 2.81 x 10-4 s-1
(5) A first order reaction takes 15 minutes to complete 25%. How much will it take to complete 65 %?
Solution:
(i) Given : For 25% completion, t1 = 15 min.
For 35 % completion, t2 = ?

Answer:
Time required to complete 65 % reaction = 547 min
(6) Gaseous A2 dissociates as, A2(g) → 2A(g). Initial pressure of A2 is 0.8 atm. After 20 minutes the pressure is 1.1 atm. Calculate rate constant and half-life period for the reaction.
Solution :
Given : [A]0 = Initial pressure = P0 = 0.8 atm
Final pressure = Total pressure = PT = 1.1 atm
Rate constant = k = ?
Half life period = t1/2 = ?
A2(g) → 2A(g)
P0 – x 2x
Pressure of A2 = Pt = P0 – x
Total pressure of the mixture,
PT = P0 – x + 2x = P0 + x
∴ x = PT – P0
∴ Pt = P0 – X = P0 – (PT – P0) – 2P0 – PT
\(k=\frac{2.303}{t} \log _{10} \frac{[\mathrm{A}]_{0}}{[\mathrm{~A}]_{t}}\)
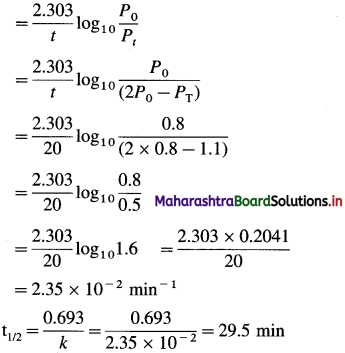
Answer:
Rate constant = k = 2.35 x 10-2 min-1
Half-life period = t1/2 = 29.5 min
![]()
(7) The decomposition of N2O5(g) at 320 K according to the following equation follows first order reaction :
N2O5(g) → 2NO2(g) + \(\frac{1}{2}\)O2(g)
The initial concentration of N2O5(g) is 1-24 x 10-2 mol. L-1 and after 60 minutes,
0.20 x 10-2 mol. L-1. Calculate the rate constant of the reaction at 320 K.
Solution :
Given :
Initial concentration

(8) From the following data for the liquid phase reaction A → B, determine the order of reaction and calculate its rate constant:
| t/s | 0 | 600 | 1200 | 1800 |
| [A]/Mol L-1 | 0.624 | 0.446 | 0.318 | 0.226 |
Solution:

Answer:
Rate constant = k = 5.618 x 10-4 s-1
(9) The concentration of a reactant in a first-order reaction A → products, varies with time as follows :
| t/min | 0 | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 |
| [AJ/M | 0.0800 | 0.0536 | 0.0359 | 0.0241 | 0.0161 |
Show that the reaction is first order.
Solution :
Given : A → Products
[A]0 = 0.08 M

Since all the values of rate constant using first order rate law equation come constant, the reaction is of first order.
Answer:
Order of the reaction is one.
![]()
(10) In a first order reaction x → y, 40% of the given sample of compound remains unreacted in 45 minutes. Calculate rate constant of the reaction.
Solution :

Answer:
k = 0.02036 min-1
(11) If the half-life period of a zero order reaction with initial concentration 0.1 M is 21.3 min, what will be the half-life when the concentration is 0.3 M?
Solution :
Given : Reaction is zero order. t1/2 = 21.3, when
initial concentration = [A]1 x = 0.1 M t1/2 = 2 when
initial concentration = [A]2 = 0.3 M
For zero order reaction, t1/2 = \(\frac{[\mathrm{A}]_{0}}{2 k}\)
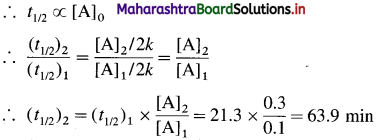
Answer:
Half life period = 63.9 min
(12) Consider the reaction 2A + 2B → 2C + D.
From the following data, calculate the order and rate constant of the reaction.
| [A]0/M | [B]0/M | r0/Ms_1 |
| 0.488 | 0.160 | 0.24 |
| 0.244 | 0.160 | 0.06 |
| 0.244 | 0.320 | 0.12 |
Write the rate law of the reaction.
Solution :
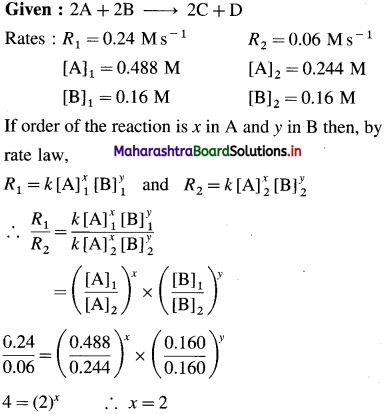
Hence the reaction is 2nd order in A.
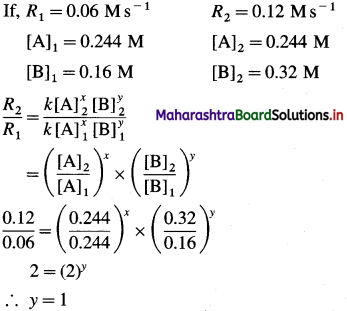
Hence the reaction is first order in B.
The order of overall reaction = n = nA + nB = 2 + 1 = 3
By rate law,
Rate = R = k[A]2[B]
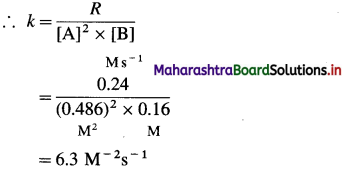
Answer:
(i) Order of reaction = 3
(ii) Rate constant = k = 63M-2s-1
(iii) Rate law : Rate = k [A]2 [B]
![]()
(20) In acidic solution, sucrose is converted to a mixture of glucose and fructose in pseudo first order reaction. It has been found that the con-centration of sucrose decreased from 20 mmol L-1 to 8 mmol L-1 in 38 minutes. What is the half-life of the reaction?
Solution :
Given :
Initial concentration = [A]0 = [sucrose]0
= 20 mmol L-1
= 20 x 10-3 mol L-1
Final concentration = [A]t = [sucrose]t
= 8 mmol L-1
= 8 x 10-3 mol L-3
time = t = 38 min
Half-life period = t1/2 =?
For first order reaction,

Answer:
Half-life period = t1/2 = 28.74 min
(21) The half-life of a first order reaction is 1.7 hours. How long will it take for 20 % of the reactant to disappear?
Solution :
Given : Half-life period = t1/2 = 1.7 hrs.


Answer:
Time required for 20% reaction = 32.86 min
(22) The gaseous reaction A2 → 2A is first order in A2. After 12.3 minutes, 65% of A2 remains undecomposed. How long will it take to decompose 90% of A2? What is the half-life of the reaction?
Solution :
Given : A2 → 2A
t1 = 12.3 min
[A]0 = 100, [A], = 65
t2 = ? for 90 % decomposition Half-life period = t1/2 = ?

Answer:
(i) Time required for 90% reaction = 65.8 min
(ii) Half-life periods = t1/2 = 19.8 min
![]()
(23) Sucrose decomposes in acid solution to give glucose and fructose according to the first-order rate law. The half-life of the rection is 3 hours. Calculate the fraction of sucrose which will remain after 8 hours.
Solution :
Given : Half-life period = t1/2 = 3 hrs
Time = t = 8 hrs

Answer:
Fraction of sucrose left = 0.1576
(24) The rate constant of a first order reaction is 6.8 x 10-4 s-1. If the initial concentration of the reactant is 0.04 M, what is its molarity after 20 minutes? How long will it take for 25% of the reactant to react?
Solution :
Given : Rate constant = k = 6.8 x 10-4s-1
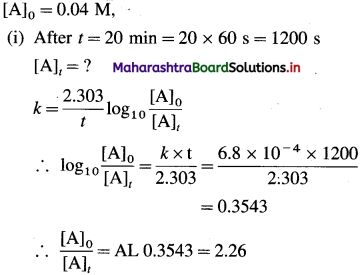

Answer:
(i) Molarity of reactant after 20 min = 0.0177 M
(ii) Time for 25 % of the reaction = 7.05 min
![]()
(25) The rate constant of a certain first-order reaction is 3.12 x 10-3 min-1,
(a) How many minutes does it take for the reactant concentration to drop to 0.02 M if the initial concentration of the reactant is 0.045 M?
(b) What is the molarity of the reactant after 1.5 hr?
Solution :
Given : Rate constant = k = 3.12 x 10-3 min-1

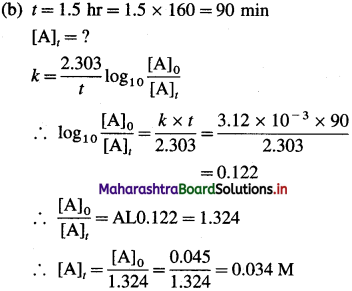
Answer:
(i) Time required to drop the concentration to 0.02 M = 260 min
(ii) Molarity after 1.5 hr = 0.034 M
(26) From the following data for the decomposition of azoisopropane,
(CH32)2 CHN = NCH(CH3)2 → N2 + C6H14 estimate the rate of the reaction when total pressure is 0.75 stm.
| Time/s | Total pressure/atm |
| 0 | 0.65 |
| 200 | 1.0 |
Solution :
Given :
(CH3)2CHN = NCH(CH3)2(g) → N2(g) + C6H14(g)
At time t P0 – x x x
At t = 0, [A]0 = P0 = 0.65 atm
At t = 200 s,
Total pressure = PT = 0.75 atm, Rate =?
From the reaction,


Answer:
Rate of the reaction = 2.13 x 10-3 atm s-1
![]()
(27) The rate constant for a zero order reaction is 0.04 Ms-1. Calculate the half-life period of the reaction, when the initial concentration of the reactant is 0.01 M.
Solution :
Given : Order of the reaction = 0
Rate constant = k = 0.04 Ms-1
Concentration = [A]0 = 0.01 M
Half-life period = t1/2 =?
For zero order reaction,
\(t_{1 / 2}=\frac{[\mathrm{A}]_{0}}{2 k}=\frac{0.01}{0.04}=0.25 \mathrm{~s}\)
Answer:
Half-life period = t1/2 = 0.25 s
(28) A flask contains a mixture of A and B. Both the compounds decompose by first order kinetics. The half-lives are 60 min for A and 15 min for B. If the initial concentrations of A and B are equal, how long will it take for the concentration of A to be three times that of B?
Solution :
Given :
For A : tm = 60 min For B : t1/2 = 15 min
Let initial concentrations of
[A]0 = [B]0 = M mol dm-3
After time t, let the concentrations be, [B]t = x, then [A]t = 3x

Answer:
After 31.8 min, concentration of A will be three time that of B. ‘
Question 53.
Obtain Arrhenius equation from collision theory of bimolecular reactions.
Answer:
Consider a bimolecular reaction,
A – B + C → A + B – C
(i) Collisions of reactant molecules : The basic
requirement for a reaction to occur is reacting species A – B and C must come together and collide. The rate of reaction will depend on the rate and frequency of collisions between them. As the i concentration and temperature increase, rate of collisions increases, hence the rate of reaction increases. But the rate of reaction is low as com-pared to the rate of collisions.
(ii) Energy of activation : For fruitful collisions, the colliding molecules must possess a certain amount of energy called activation energy Ea. Due to collisions between A – B and C, there is a change in electron distribution about three nuclei namely A, B and C so that old A – B bond is weakened while new bond is partially formed between B and C, and results in the formation of an activated complex or a transition state.

Therefore transition state always has higher energy than reactants or products. Due to high energy, activated complex is unstable, short lived and decomposes into the products.
To form activated complex, the reactant mol-ecules have to climb the potential energy barrier i. e., activation energy level, hence molecular collision energy of colliding molecules must be high so that reactant molecules form activated complex and further decompose into products.
The fraction (f) of molecules at temperature T having activation energy Ea is given by f = e-Ea/RT.
If P represents the probability of Z collisions with proper orientation then,
Reaction rate = P x Z x e-Ea/RT,
Hence the rate constant k of the reaction may be represented as, k = A x e-Ea/RT where A is called frequency factor or pre-exponential factor and ΔH is the enthalpy change of the reaction. This equation is called Arrhenius equation.
![]()
Question 54.
Define :
(i) Transition state or activated complex.
Answer:
Transition state or activated complex : The configuration of atoms formed from reactant molecules and which is at the peak of barrier in energy profile diagram having maximum potential energy compared to reactants and products is called transition state or activated complex.
Question 55.
If a gaseous reaction has activation energy 75k J mol-1 at 298 K, find the fraction of successful collisions.
Answer:
Activation energy = Ea = 75 kJ mol-1 = 75000 mol-1; Temperature = T = 298 K The fraction (f) of successful collisions between the molecules with an energy equal to Ea is given by,


This shows that only 7 collisions out of 1014 collisions are sufficiently energetic to convert reactants into products.
Question 56.
Draw energy profile diagram and show
(i) Activated complex
(ii) Energy of activation for forward reaction
(iii) Energy of activation for backward reaction
(iv) Heat of reaction.
Answer:
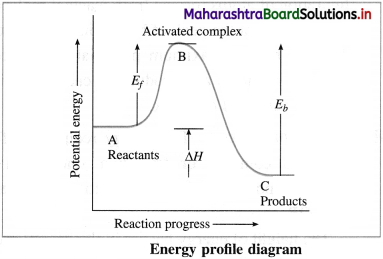
(i) B → Activated complex
(ii) Ef → Energy of activation for forward reaction
(iii) Eb → Energy of activation for backward reaction
(iv) ΔH → Heat of reaction.
Question 57.
Obtain Arrhenius equation, k = A x e-Ea/RT
Answer:
(i) From experimental observations of variation in rate constants with temperature, Arrhenius developed a mathematical equation between reaction rate constant (k), activation energy (Ea) and temperature T.
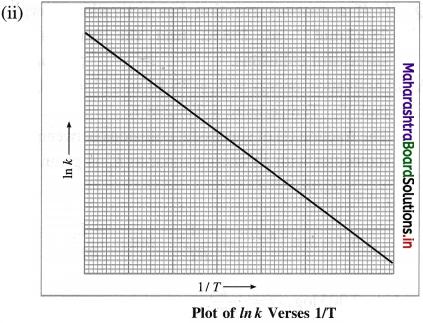
When a graph of Ink is plotted against reciprocal of temperature (1/T) a straight line with a negative slope is obtained. This is described by a mathematical equation as,

![]()
where k is a rate constant, R is the gas constant, E.a is activation energy, T is absolute temperature and the parameter A is called frequency factor or preexponential factor. This is Arrhenius equation.
Question 58.
What is a frequency factor or pre-exponential factor?
Answer:
In Arrhenius equation, k=A x e-Ea/RT the factor A is called frequency factor and since it is a coefficient of exponential expression, e~Ea/RT it is also called a pre-exponential factor.
In the above equation k is a rate constant at temperature T, Ea is the energy of activation and R is a gas constant.
A is related to frequency of collisions (Z) or rate of collisions. It is represented as, A = P x Z where P is the probability of collisions with proper orientations and Z is the frequency of collisions of reacting molecules.
The units of A are same as that of k.
Question 59.
Obtain a relation, \(\log _{10} \frac{k_{2}}{k_{1}}=\frac{E_{\mathrm{a}}\left(T_{2}-T_{1}\right)}{2.303 R \times T_{1} \times T_{2}}\),
OR
Obtain a relation showing variation in rate constant with temperature.
Answer:
By arrhenius equation, the rate constant k of the reaction at a temperature T is represented as, k = A x e-Ea/RT where A is a frequency factor, R is a gas constant and Ed is the energy of activation.
By taking logarithm to the base e, we get,

If kt and k2 are the rate constants at temperatures T1 and T2 respectively, then

By measuring the rate constants k1 and k2 at two different temperatures T1 and T2, the energy of activation Ea of the reaction can be obtained.
Question 60.
How is the energy of activation determined from rate constants at two different temperatures?
Answer:
For the given reaction, rate constants k1 and k2 are measured at two different temperatures T1 and T2 respectively. Then \(\log _{10} \frac{k_{2}}{k_{1}}=\frac{E_{\mathrm{a}}\left(T_{2}-T_{1}\right)}{2.303 R \times T_{1} \times T_{2}}\) where Ea is the energy of activation.
Hence by substituting appropriate values, energy of activation Ea for the reaction is determined.
Question 61.
Obtain a relation, \(\frac{k_{2}}{k_{1}}=\frac{\left(t_{1 / 2}\right)_{2}}{\left(t_{1 / 2}\right)_{1}}\), where k1 and k2 are rate constants while (t1/2)1 and (t1/2)2 are halflife periods of the first order reaction at temperatures T1 and T2 respectively. Write the relation for activation energy.
Answer:
The rate constant k and half-life period t1/2 are related as
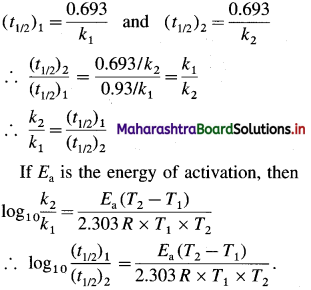
Question 62.
How does a catalyst differ from reaction intermediate?
Answer:
- A catalyst accelerates the rate of reaction, while reaction intermediate has no effect on the rate of the reaction.
- The catalyst is always present at the start of the reaction whereas reaction intermediate is produced during the mechanism of the reaction.
- A catalyst is consumed in one of the steps of mechanism and regenerated in a subsequent step while the reaction intermediate is formed in one step and consumed in subsequent step.
- The catalyst is stable but the reaction intermediate is unstable and short lived.
![]()
Question 63.
How is lowering of activation energy in the presence of a catalyst obtained?
Answer:
- In the presence of a catalyst, activation energy of a reaction is lowered, hence rate and rate constant increase.
- If ΔEa is lowering of activation energy, while k1 and k2 are the rate constants of the reaction in the absence and presence of the catalyst respectively then,
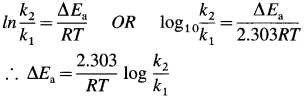
Question 64.
The rate constant of a reaction of 400 K is 1.35 x 102s-1. When a nickel catalyst is used, the rate constant of the reaction becomes 3.8 x 102s-1. Find activation energy. If the initial activation energy is 20 KJ, what will be activation energy in the presence of the catalyst?
Answer:
In the presence of a catalyst, the activation energy is lowered and rate constant is increased.

The decrease activation energy of the reaction in the presence of a catalyst will be Ea = 20 – 3.446 = 16.554 kJ.
Solved Examples 6.6-6.7
Question 65.
Solve the following :
(1) Calculate activation energy for a reaction of which rate constant becomes four times when temperature changes from 30 °C to 50 °C. (Given : R = 8.314 K-1mol-1)
Solution :
Given : k2 = 4k1
T1 = 273 + 30 = 303 K
T2 = 273 + 50 = 323 K
Activation energy = Ea =?
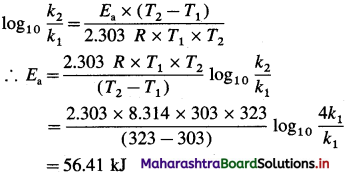
Answer:
Activation energy = Ea = 56.41 kJ
(2) The rate constant of a first order reaction are 0.58 s-1 at 313 K and 0.045 s-1 at 293 K. What is the energy of activation for the reaction?
Solution :

Answer:
Energy of activation = Ea = 97.46 kJ mol-1
![]()
(3) The energy of activation for a first order reaction is 104 kJ mol-1. The rate constant at 25°C is 3.7 x 10-5s-1. What is the rate constant at 30 °C?
Solution :
Given : Energy of activation = Ea = 104 kJ mol-1 = 104 x 103 mol-1
Initial rate constant – k1= 3.7 x 10-5 s-1
Initial temperature = T1 = 273 + 25 = 298 K
Final temperature = T2 = 273 + 30 = 303 K
Final rate constant = k2 =?
![]()
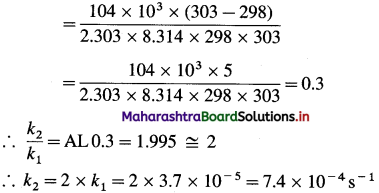
Answer:
Rate constant at 30 0C = 7.4 x 10-4 s-1
(4) What is the activation energy for a reaction whose rate constant doubles when temperature changes from 30 °C to 40 °C?
Solution :
Given :
Initial rate constant = k1
and final rate constant = k2; \(\frac{k_{2}}{k_{1}}\) = 2
Initial temperature = T1 = 273 + 30 = 303 K
Final temperature = T2 = 273 + 40 = 313 K
Energy of activation = Ea = ?
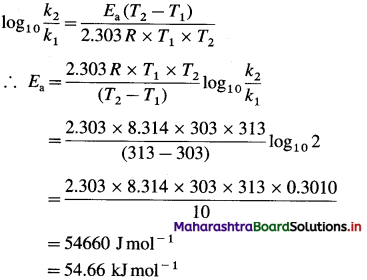
Answer:
Activation energy = Ea = 54.66 kj mol-1
(5) The activation energy for a certain reaction is 334.4 kj mol-1. How many times larger is the rate constant at 610 K than the rate constant at 600 K?
Solution :
Given :
Activating energy = Ea = 334.4 kJ mol-1
= 334.4 x 103 J mol-1
Initial temperature = T1 = 600 K
Final temperature = T2 = 610 K

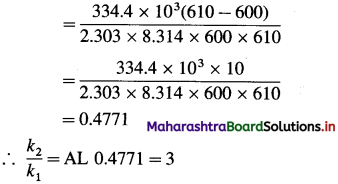
Answer:
Rate constant increase three time.
![]()
(6) The rate of a reaction at 600 K is 7.5 x 105 times the rate of the same reaction at 400 K. Calculate the energy of activation for the reaction. (Hint: The ratio of rates is equal to the ratio of rate constants.)
Solution :
Given : \(\frac{R_{2}}{R_{1}}\) = 7.5 x 105.
From the hint, \(\frac{R_{2}}{R_{1}}=\frac{k_{2}}{k_{1}}\) = 7.5 x 10s
Initial temperature = T1 = 400 K
Final temperature = T2 = 600 K
Energy of activation = Ea = ?

Answer:
Activation energy = Ea = 135 kj mol-1
(7) The rate constant of a first order reaction at 25 °C is 0.24 s’. If the energy of activation of the reaction is 88 kJmol-1, at what temperature would this reaction have rate constant of 4 x 10-2s-1?
Solution :
Given : k2 =0.24s-1; k2 =4 x 10-2s-1 T1 = 273 + 25 = 298 K
Energy of activation = Ea
= 88 kJ mol-1 = 88000 J mol-1
T2 = ?
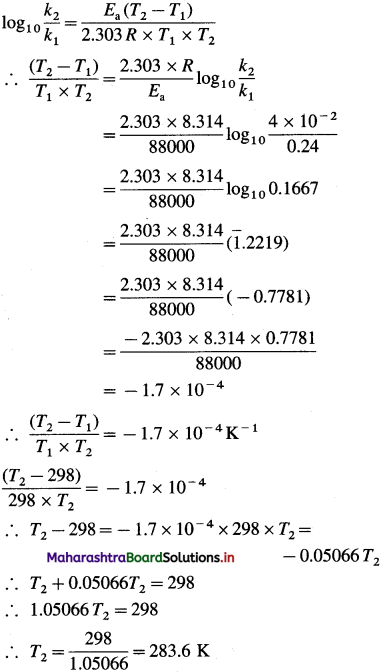
Answer:
Temperature = 283.6 K
(8) The half-life of a first order reaction is 900 min at 820 K. Estimate its half-life at 720 K if the energy of activation ot the reaction is 250 kJ mol-1 (1.464 x 105 mm).
Solution:
Given: Initial half-life period = (t1/2)1 = 900 min
Energy of activation = 250 kJ mol-1
= 250 x 103 kJ mol-1
Initial temperature = T1 = 820 K
Final temperature = T2 = 720 K
Final half-life period = (t1/2)2 = ?

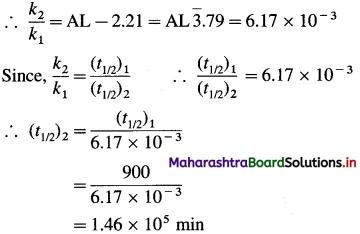
Answer:
Half-life period = 1.46 x 105 min
![]()
(9) The rate of a gaseous reaction is 6.08 x 10-2 Ms-1 at 50°C. What will be its rate at 60°C? Energy of activation of the reaction is 18.26 kj mol-1. (R = 8.314k-1 mol-1)
Solution :
Given : Initial rate = R1 = 6.08 x 10″2Ms-1
Energy of activation = Ea = 18.26 kJmol-1 = 18260 mol-1
Initial temperature = T1 = 273 + 50 = 323 K
Final temperature = T2 = 273 + 60 = 333 K
Final rate of the reaction = R2 = ?

Answer:
Rate of reaction at 37°C = 7.46 x 10-2 Ms-1
(10) A first order gas-phase reaction has an energy of activation of 240 kj mol-1. If the frequency factor of the reaction is 1.6 x 1013 s-1, calculate its rate constant at 600 K.
Solution :
Given : Energy of activation = Ea = 240 kJ mol-1 = 240 x 103 mol-1
Frequency factor = A = 1.6x 1013 s-1
Temperature = T= 600 K
Rate constant = k = ?
By Arrhenius equation,

Answeer:
Rate constant = k = 2.01 x 10-8 s-1
(11) In the Arrhenius equation for a first order reaction, the values of ‘A’ and ‘Ea’ are 4 x 1013 sec-1 and 98.6 kJ mol-1 respectively. At what temperature will its half-life period be 10 minutes? [R = 8.314 JK-1 mol-2]
Solution :
Given

= 311.3 K
Answer:
Temperature = T = 311.3 K
![]()
(12) The frequency factor for a second-order reaction is 4.83 x 1012M-1s-1 at 27°C. If the rate constant of the reaction is 1.37 x 10-3M-1s-1, find the energy of activation.
Solution :
Given : Frequency factor = A
= 4.83 x 1012 M-1s-1
Rate constant = k= 1.37 x 10-3 M-1s-1
Temperature = T = 273 + 27 = 300 K
Energy of activation = Ea = ?
By Arrhenius equation,
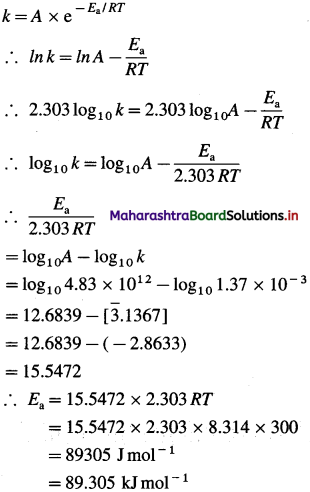
Answer:
Energy of activation = Ea = 89.305 kJ mol–1
(13) Rate constants (k) for a reaction were measured at different temperatures. When log10ft was plotted against 1/T, the slope of the graph was 3.28 x 103. Calculate the energy of activation.
Solution :
Given : Slope of a graph = 3.28 x 103
Activation energy = Ea = ?
From Arrhenius equation, k = A x e-Ea/RT
\(\log _{10} k=\frac{-E_{\mathrm{a}}}{2.303 R} \times \frac{1}{T}+\log _{10} A\)
The graph is a straight line with slope equal to Ea/2.303R
∴ \(\frac{E_{\mathrm{a}}}{2.303 R}\) = 3.28 x 103
∴ Ea = 2.303/? x 3.28 x 103
= 2.303 x 8.314 x 3.28 x 103
= 62.8 x 103 mol-1
= 62.8 kJ mol-1
Answer:
Activation energy = Ea = 62.8 kj mol-1
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 66.
Select and write the most appropriate answer from the given alternatives for each subquestion :
1. The rate of a reaction is expressed in the units
(a) L mol-1t-1
(b) mol dm-3 t-1
(c) Ms
(d) M-1s-1
Answer:
(b) mol dm-3 t-1
2. For a gaseous reaction the unit of rate of reaction is
(a) L atm s-1
(b) atm mol-1s-1
(c) atm s-1
(d) mol s
Answer:
(c) atm s-1
![]()
3. In the reaction A 4- 3B → 2C, the rate of formation of C is
(a) the same as rate of consumption of A
(b) the same as the rate of consumption of B
(c) twice the rate of consumption of A
(d) 3/2 times the rate of consumption of B
Answer:
(c) twice the rate of consumption of A
4. The units of rate of a reaction and rate constant are same for a reaction of order.
(a) zero
(b) one
(c) two
(d) fractional
Answer:
(a) zero
5. During the progress of a reaction, the rate constant of a reaction
(a) increases
(b) decreases
(c) remains unchanged
(d) first increases and then decreases
Answer:
(a) increases
6. For the reaction, 2A → 3C, the reaction rate is equal to
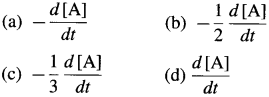
Answer:
(c)
7. For the reaction, 2X + 3Y → 4Z, reaction may be represented as
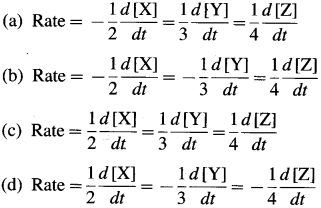
Answer:
(b)
8. For the reaction 2N2O5(g) → 4NO2(g) + O2(g) liquid bromine, which of the following rate equation is ‘incorrect’?
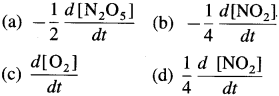
Answer:
(b)
9. The rate of reaction for certain reaction is expressed as :
![]()
The reaction is
(a) 3A → 2B + C
(b) 2B → 3A + C
(c) 2B+C → 3A
(d) 3A + 2B → C
Answer:
(c) 2B+C → 3A
10. Order of a reaction is
(a) number of molecules reacting in a reaction
(b) the number of molecules whose concentration changes during a reaction
(c) the number of molecules of reactants whose concentration determine the rate
(d) increase in number of molecules of products
Answer:
(c) the number of molecules of reactants whose concentration determine the rate
11. The unit of rate constant for zero order reaction is
(a) t-1
(b) mol dm-3 t-1
(c) mol-1 dm3 t-1
(d) mol-2 dm6 t-1
Answer:
(b) mol dm-3 t-1
![]()
12. A → B is a first order reaction with rate 6.6 x 10-5 ms-1. When [A] is 0.6 m, rate constant of the reaction is-
(a) 1.1 x 10-5 s-1
(b) 1.1 x 10-4 s-1
(c) 9 x 10-5 s-1
(d) 9 x 10-4 s-1
Answer:
(b) 1.1 x 10-4 s-1
13. For a first order reaction, when the rate of a reaction is plotted against concentration of the reactant, then the graph obtained is
(a) a curve
(b) a straight line with negative slope
(c) a straight line with a positive slope
(d) a straight line with positive intercept
Answer:
(c) a straight line with a positive slope
14. For a chemical reaction, A → products, the rate of reaction doubles when the concentration of ‘A’ is increased by a factor of 4, the order of reaction is
(a) 2
(b) 0.5
(c) 4
(d) 1
Answer:
(b) 0.5
15. The order of reaction between equimolar mixture of H2 and Cl2 in the presence of sunlight is
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) 2
(d) 3
Answer:
(a) 0
16. Molecularity of reaction can be
(a) zero
(b) integral
(c) fractional
(d) negative
Answer:
(b) integral
17. The reaction,
CH3COOC2H5 + H2O \(\stackrel{\mathrm{H}^{+}}{\longrightarrow}\) CH3COOH + C2H5OH is of
(a) zero order
(b) first order
(c) second order
(d) pseudo first order reaction
Answer:
(d) pseudo first order reaction
18. A reaction is first order with respect to reactant A and second order with respect to reactant B. The rate law for the reaction is given by
(a) rate = k[A][B]2
(b) rate = [A][B]2
(c) rate = k [A]2[B]
(d) rate = k[A]0[B]2
Answer:
(a) rate = k[A][B]2
19. Molecularity of an elementary reaction
(a) may be zero
(b) is always integral
(c) may be semi-integral
(d) may be integral, fractional or zero.
Answer:
(b) is always integral
20. The unit of rate constant for first order reaction is
(a) min-2
(b) s
(c) s-1
(d) min
Answer:
(c) s-1
![]()
21. The integrated rate equation for first order reaction A → products is given by

Answer:
(b)
22. Time required to complete 90% of the first order reaction is

Answer:
(a)
23. The rate constant of a first order reaction is given by
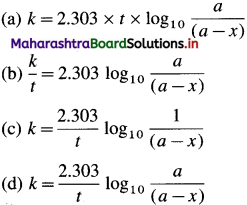
Answer:
(d)
24. The half-life of a first order reaction is 30 min and the initial concentration of the reactant is 0.1M. If the initial concentration of reactant is doubled, then the half-life of the reaction will be
(a) 1800s
(c) 15 min
(b) 60 min
(d) 900s
Answer:
(a) 1800s
25. The rate constant for a first order reaction is loos the time required for completion of 50% of reaction is-
(a) 0.0693 milliseconds
(b) 0.693 milliseconds
(c) 6.93 milliseconds
(d) 69.3 milliseconds
Answer:
(c) 6.93 milliseconds
26. The slope of the straight line obtained by plotting rate versus concentration of reactant for a first order reaction is
(a) – k
(b) – k/2.303
(c) k/2.303
(d) k
Answer:
(d) k
27. If C0 and C are the concentrations of a reactant initially and after time t then, for a first order reaction
(a) C = C0ekr
(b) C0 = 1/C e-kr
(c) C = C0e-kr
(d) CO = C ekr
Answer:
(b) C0 = 1/C e-kr
![]()
28. A graph corresponding to a first order reaction is

Answer:
(b)
29. For two first order reactions, A → products and B → products, k1 and k2 are the rate constants. The fIrst reaction (A) is slower than the second reaction (B). The graphical observation corresponding to this observation will be
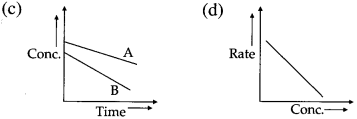
Answer:
(b)
30. Half-life (t1/2) of first order reaction is
(a) dependent of concentration
(b) independent of concentration
(c) dependent of time
(d) dependent of molecularity
Answer:
(b) independent of concentration
31. For a first order reaction, the half-life period is

Answer:
(c)
32. When half-life period of a zero order reaction is plotted against concentration of the reactant at constant temperature, the graph obtained is
(a) a curve
(b) a straight line with a positive slope
(c) a straight line with a negative slope
(d) an exponential graph
Answer:
(b) a straight line with a positive slope
![]()
33. The rate of a reaction between A and B is R = k [A]n x [B]m On doubling the concentration of A and halving the concentration of B, the ratio of the new rate to the earlier rate of the reaction will be
(a) m + n
(b) n – m
(c) 2(n-m)
(d) \(\frac{1}{{ }_{2} n+m}\)
Answer:
(c) 2(n-m)
34. Consider the reaction

(a) 0,052 M/s
(b) 0.114 M/s
(c) 0.026 M/s
(d) -0.026 M/s
Answer:
(c)
35. The rate of the first order reaction A → products is 0.01 M/s, when reactant concentration is 0.2 M. The rate constant for the reaction will be
(a) 0.05 s-1
(b) 0.05 min-1
(c) 0.1 s-1
(d) 0.01 s-1
Answer:
(a) 0.05 s-1
36. The rate constant of a reaction
(a) decreases with increasing Ea
(b) decreases with decreasing Ea
(c) is independent of Ea
(d) decreases with increasing temperature
Answer:
(a) decreases with increasing Ea
37. The slope of a graph In [A]t versus t for a first order reaction is -2.5 x 10-3s-1. The rate constant for the reaction will be
(a) 5.76 x 10-3s-1
(b) 1.086 x 10-3s-1
(c) -2.5 x 10-3s-1
(d) 2.5 x 10-3s-1
Answer:
(d) 2.5 x 10-3s-1
38. For the reaction, Cl2 + 2I– → 2CI– + I2, the initial concentration of I– was 0.2 mol L– and the concentration after 20 minutes was 0.18 mol L-1. Then the rate of formation of I2 in mol L– min-1 will be
(a) 1 x 10-3
(b) 5 x 10-4
(c) 1 x 10-4
(d) 2 x 10-3
Answer:
(b) 5 x 10-4
39. A catalyst increases the rate of the reaction by
(a) increasing Ea
(b) increasing T
(c) decreasing Ea
(d) decreasing T
Answer:
(c) decreasing Ea
40. The Arrhenius equation is
(a) A = ke-Ea/RT
(b) A/k = e-Ea/RT
(c) k = AeEa/RT
(d) k = Aee-RT/Ea
Answer:
(b) A/k = e-Ea/RT
![]()
41. The Arrhenius equation is
(a) k = Ae-RT/Ea
(b) A = ke–Ea/RT
(c) k = Ae-RT/Ea
(d) A = keEa/RT
Answer:
(d) A = keEa/RT
42. When the initial concentration of the reactant is doubled, the half-life period of the reaction is also doubled. Hence the order of the reaction is
(a) one
(b) two
(c) fraction
(d) zero
Answer:
(d) zero
43. If k1 and k2 are the rate constants of the given reaction in the presence and absence of the catalyst, then
(a) k1 = k2
(b) k1 > k2
(c) k1 < k2
(d) k1 > k2
Answer:
(b) k1 > k2
44. If the ratio of rate constants at two temperatures for the given reaction is 2.5, the ratio of corresponding half-life periods is
(a) 2.5
(b) 4
(c) 5
(d) 0.4
Answer:
(d) 0.4
45. For a zero order reaction, if Co is the initial concentration, then the half life period will be
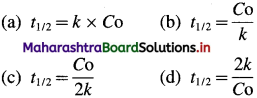
Answer:
(c)
46. The order of nuclear disintegration reaction is
(a) zero
(b) one
(c) two
(d) fraction
Answer:
(b) one
47. The unit of rate constant for zero order reaction is
(a) mol L-2 s-1
(b) mol-1Ls-1
(c) mol2L-2s-1
(d) mol L-1 s-1
Answer:
(d) mol L-1 s-1
48. When a graph of log10k is plotted against 1 /T, the slope of the line is,

Answer:
(d)
49. The slope of a graph obtained by plotting half-life period and initial concentration of the reactant in zero order reaction is
\((a) \frac{2.303}{k}
(b) \frac{1}{k}
(c) \frac{1}{2 k}
(d) \frac{k}{2.303}\)
Answer:
(c)
![]()
50. When a graph of log, 0k against 1/T is plotted, for reaction, a graph with slope equal to 1 x 103 is obtained. Hence the activation energy is
(a) 8.314 x 103 Jmor-1
(b) 3.61 kJ mol-1
(c) 4.85 x 103 Jmol-1
(d) 19.1 kJ mol-1
Answer:
(d) 19.1 kJ mol-1
51. The correct expression for activation energy is,

Answer:
(c)
52. In the reaction, 2A(g) → B(g), the initial pressure of A is 2.5 atm. After 10 minutes the pressure becomes 2.2 atm. Hence the pressure of A is
(a) 1.2 atm
(b) 1.9 atm
(c) 2.3 atm
(d) 0.3 atm
Answer:
(b) 1.9 atm
53. The half-life period of zero order reaction A → product is given by –

Answer:
(c)





 .
.































 ethyl-N-methylethanamine since compound X is tertiary amine. It reacts with one mole of CH3I to give a quaternary ammonium salt.
ethyl-N-methylethanamine since compound X is tertiary amine. It reacts with one mole of CH3I to give a quaternary ammonium salt.



































































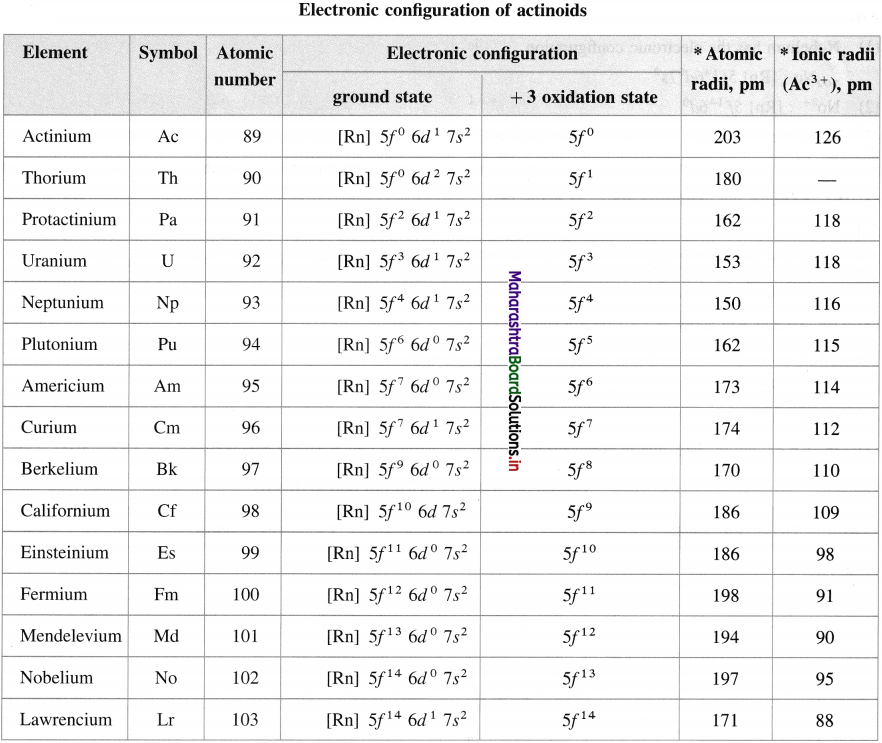

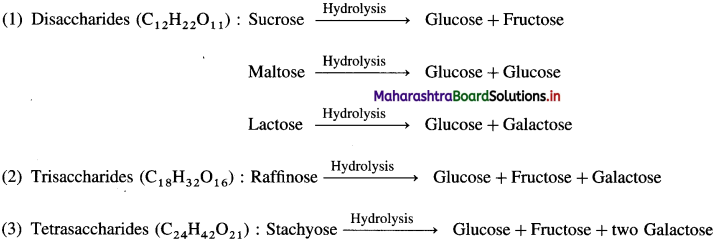
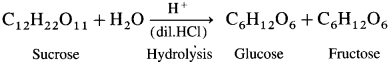

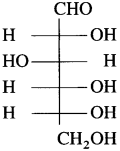



 (where R is an alkyl group or aryl group).
(where R is an alkyl group or aryl group).