Std 12 Geography Chapter 6 Question Answer Tertiary Economic Activities Maharashtra Board
Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 12 Geography Solutions Chapter 6 Tertiary Economic Activities Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
Class 12 Geography Chapter 6 Tertiary Economic Activities Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Geography Class 12 Chapter 6 Question Answer Maharashtra Board
1. Complete the Chain
Question 1.
| A |
B |
C |
| (1) Matheran |
(1) Tea |
(1) Communication |
| (2) GPS |
(2) the Atlantic Ocean |
(2) Tertiary Activity |
| (3) Sri Lanka |
(3) Satellite |
(3) Export |
| (4) Panama Canal |
(4) Tourism |
(4) the Pacific Ocean |
Answer:
| A |
B |
C |
| (1) Matheran |
(1) Tourism |
(1) Tertiary Activity |
| (2) GPS |
(2) Satellite |
(2) Communication |
| (3) Sri Lanka |
(3) Tea |
(3) Export |
| (4) Panama Canal |
(4) Atlantic Ocean |
(4) Pacific Ocean |

2. Choose the correct option.
Question 1.
Tertiary activities include
(a) Use of natural resources
(b) Finished product
(c) Raw material
(d) Transportation
Answer:
(d) Transportation
Question 2.
Natural ports
(a) Kochi
(b) JNPT
(c) Delhi International Terminal
(d) Nagpur Cargo Hub (MIHAN)
Answer:
(a) Kochi
Question 3.
Trans-Australian Railway connects
(a) Perth – Sydney
(b) Perth – Vladivostok
(c) Sydney – Vancouver
(d) Vancouver – Vladivostok
Answer:
(b) Perth – Vladivostok
3. Give geographical reasons.
Question 1.
Tertiary activities include both services and exchapge.
Answer:
- Transportation, communication, trade and commerce are the main tertiary activities.
- Road, rail and airways are the important modes of transportation, which help in exchange of goods and services. Therefore, it is a service activity.
- Transportation provides facilities for the movement of goods from areas of surplus to areas of scarcity produced in primary and secondary activities.
- Credit facilities, banking facilities, marketing are also tertiary activities, they provide services to people.
- Postal services, shopkeepers, vegetable sellers, fruit sellers, etc., are also included in service activities.
Question 2.
The proportion of airways as means of transportation is increasing.
Answer:
- Air transport is an important enabler to achieve economic growth and development.
- In the global world, there is exchange of goods between countries. Therefore, there is more use of air transport to carry perishable, valuable and light goods from surplus areas to scarcity areas.
- It facilitates integration into global economy and provides vital connectivity on a national, regional and international scale.
- Nowadays tourism is the fastest growing industry; air transport is more used for international tourism.
- Therefore, the proportion of airways as means of transportation is increasing.

Question 3.
Geographical diversity is responsible for trade to occur.
Answer:
- The geographical diversity is the set of physical, human and cultural elements differentiated from each other that converge in the relatively small geographic space that is part of the same zone, region or country.
- If you take into consideration natural regions of the world, each region is different from another.
- The natural resource available in one country will be different from the ones available in different regions.
- There is variation in climate, soil, minerals, forest, relief, water supply etc.
- Depending upon the availability of geographical factors, there is specialisation of certain economic activities in certain areas and there is trade from surplus areas to scarcity areas. For example, in one region, plenty of oil is available while in another region no oil reserves are available.
- This variation in distribution of oil will be responsible for the development of trade between oil rich and oil poor countries.
- Thus, geographical diversity is responsible for trade to occur.
4. Write short notes on.
Question 1.
Importance of satellite as means of communication.
Answer:
- A communications satellite is an artificial satellite that relays and amplifies radio telecommunication signals via. transponder.
- Communications satellites are used for television, telephone, radio, internet and military applications.
- The information about physical and human factors is obtained from satellite communication.
- Satellite communication is used in remote islands, in some countries and continents where landline telecommunication is rare or not available.
- As television becomes the main market, its demand for satellite communication becomes very important.
- Satellites are also used for internet communication, military communications, etc.
- Thus, importance of satellite as means of communication is increasing.
Question 2.
Role of transportation in trade.
Answer:
- Transport support trade and industry in carrying raw material to the place of production and distribution of finished products for consumption.
- Transport means to make goods available to consumers.
- Transport makes possible movement of goods from one place to another with great ease and speed.
- Trade means exchange of goods and services. In trade there is movement of goods from surplus areas to scarcity areas. The movement of goods is possible only because of transport.
- In other words, without the help of transport development of trade is not possible.
- Thus, transport plays an important role in economic development and globalisation of trade.
Question 3.
Tourism and GDP.
Answer:
- Tourism is vital for the success of many economies around the world.
- Tourism boosts the revenue of the economy, creates thousands of jobs and develops the infrastructures of the country.
- It also creates jobs in agriculture, communication, health and educational sectors.
- The government that depends on tourism, invests a lot in the infrastructure of the country. They construct new roads and highways, develop parks, improve public places, and set up airports, etc.
- With augmenting facilities, more and more tourists are attracted in such countries, thus, there is boosting of the GDP.
5. Differentiate between.
Question 1.
Secondary Economic Activities and Tertiary Economic Activities
Answer:
| Secondary Economic Activities |
Tertiary Economic Activities |
| (i) Secondary activities are concerned with activities adding value to already existing products from primary activities. |
(i) Tertiary activities are concerned with providing services rather than providing material goods. |
| (ii) Development of secondary activities depends upon the production of resources in primary activities. |
(ii) Development of tertiary activities depends upon the development of secondary activities. |
| (iii) Manufacturing and construction are important secondary activities. |
(iii) Trade, transport communication, banking, insurance, etc., are tertiary activities. |
| (iv) Secondary activities produce goods and commodities. |
(iv) Tertiary activities help reach these goods and commodities to the consumers. |
| (v) Secondary activities may be away from the market and settlement. |
(v) Tertiary activities are always near the market and settlement. |

Question 2.
Quaternary Activities and Quinary Activities
Answer:
| Quaternary Activities |
Quinary Activities |
| (i) Quaternary activities refer to those activities where the task is to think, research and develop ideas. |
(i) Quinary activities involve work related to administration. |
| (ii) Confined to research, training and education. |
(ii) Confined to the highest-level decision taking and policy making. |
| (iii) Software developers, statisticians, hospital staff, teachers, financial planners tax consultants, people working in theatres, etc., comes under quaternary activities. |
(iii) Senior business executives, government officials, scientists, judges, etc., comes under quinary activities. |
Question 3.
Waterways and Airways
Answer:
| Waterways |
Airways |
| (i) Development of water transport needs courted area with broken coastlines. |
(i) Development of airways needs favourable climate, advance technology and plain land for airports. |
| (ii) This is the cheapest mode of transport. |
(ii) This is an expensive mode of transport. |
| (iii) Heavy and bulky goods are transported, e.g., minerals, oil, coal, machinery, etc. |
(iii) Light, perishable and expensive goods are transported, e.g., electronic goods, gold, silver, fish, dairy products, etc. |
| (iv) Slow mode of transportation. |
(iv) Fast mode of transportation. |
| (v) More used for goods transport than passengers’ transport |
(v) More used for passengers’ transport than for goods transport. |
6. Answer in Detail
Question 1.
Explain the factors affecting trade between two countries.
Answer:
Trade refers to transfer of goods or services from one person to another or from one country to another. Factors which affect the trade are natural resources, climate, population, culture, economic cost, specialization, etc.
Natural resources : Distribution of natural resources is uneven. The natural resources available in one country differs from another. Because of this uneven distribution of resource, there is trade between resources surplus and resource deficit.
Climate : Climate mainly affects the plants and animals in a region. In the areas of different climate, there are different types of plants and animals. Example, in the tropical countries like Sri Lanka whose major export is tea or Malaysia and Indonesia, whose major export is rubber. This occurs naturally because of favourable climate for growing tea and rubber plants in these countries.
Population : Population size, distribution and density are different in different countries. This leads to difference in production and consumption and hence trade occurs.
Standard of living can also determine the demand for various goods and services. The country with less population depends more on trade because fewer human resources is engaged in production of goods.
Culture : Some countries are known for their specific art and craft, based on their culture, specific production of goods which have worldwide market, for e.g., Kashmiri shawls or Iranian carpets.
Economic Cost : Cost of production is the major factor in the process of production. It is cheaper to import certain goods than producing it in the country itself. For example, it is cheaper to import tea from India and Sri Lanka than producing it in England.
Specialisation : Due extremely favourable factors of production, some countries have specialisation for certain goods and they have name and fame in the world market, so they develop export trade. For example, watches of Switzerland or electronic goods of Japan or tender beef of Argentina.
Government Policy: Government policy about export or import affects trade. For example, Government may increase import duties of some goods, to encourage people to buy domestic goods. Thus, import trade of those goods goes down.

Question 2.
Development of transportation is dependent on geographical factors. Explain.
Answer:
- Various geographical factors affect the development of transport.
- Relief, climate and location are the three most important factors that affect the development of transportation.
- It is easier to build roadways and railways in plain areas.
- Dense forests, hilly and mountainous regions affect the construction of roads and railways, in Africa and South America.
- Coastal location with broken coast lines is favourable for development of ports and harbours.
- For the development of airways; favourable climate and plain region for construction of airports are essential.
- Foggy and smoggy weather and high peaks will be obstacles for the development of air transport.
Question 3.
Why is transportation system important in the development of any nation?
Answer:
- Transportation plays important role in rapid economic growth of a nation.
- The introduction of railways has been historically the most important and powerful single factor in the process of economic development of industrial nations of the world like USA, France, Germany, Japan, etc.
- The significance of transportation in economic activity is found in its effects on both human wants and satisfaction of wants through production and distribution of goods.
- Transportation increases the quality and variety of consumer goods, thereby stimulating the demand and development of trade and economy of the nation.
- Transport provides various employment opportunities and boosts up the economy of the country. For example, many people got employment in construction work of Metro rail track.
Question 4.
Tertiary activities are expanding day-by-day. Explain the statement.
Answer:
- Tertiary activities act as the link between primary and secondary activities.
- These activities are mostly in the form of services.
- Tertiary activities include transport and communication, trade, loading and unloading of goods, banking, insurance, marketing, export, etc.
- Providing public services like hospital, education, research and development, administration, etc., are also included in tertiary activities.
- With increasing industrialisation population growth and trade, number of people working in banking, insurance, tax consultants, software developers, teachers, etc., went on expanding day by day.
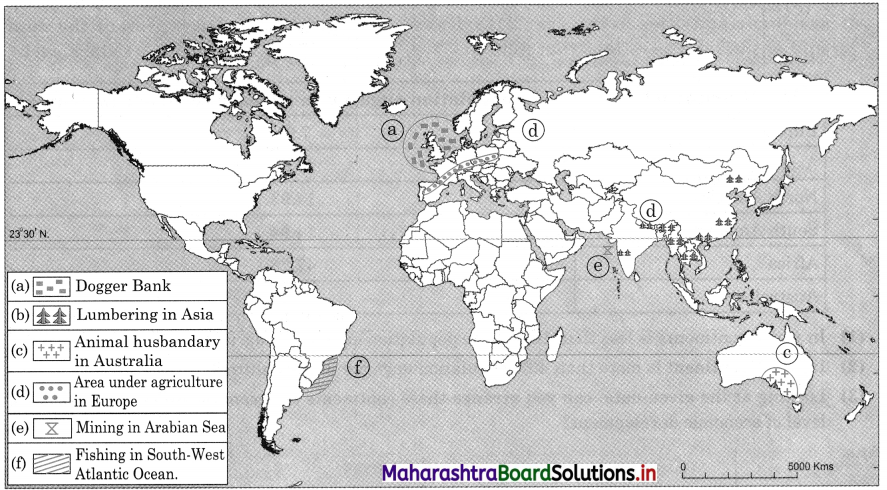
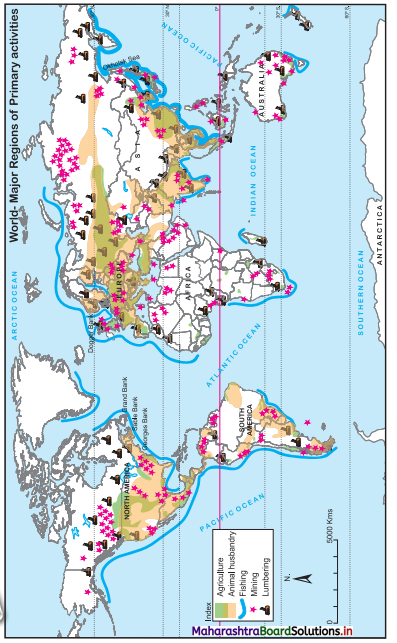
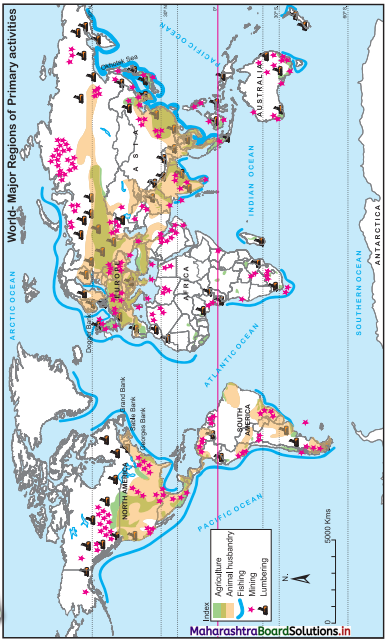
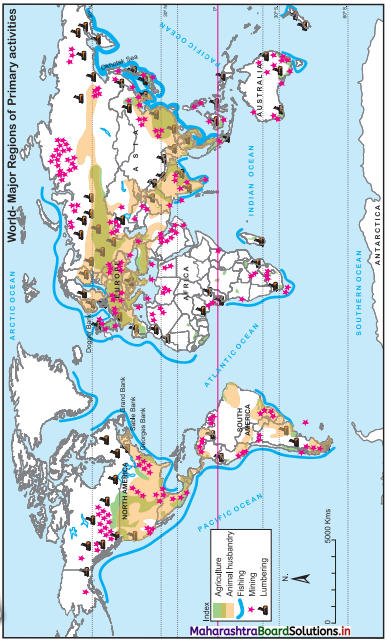
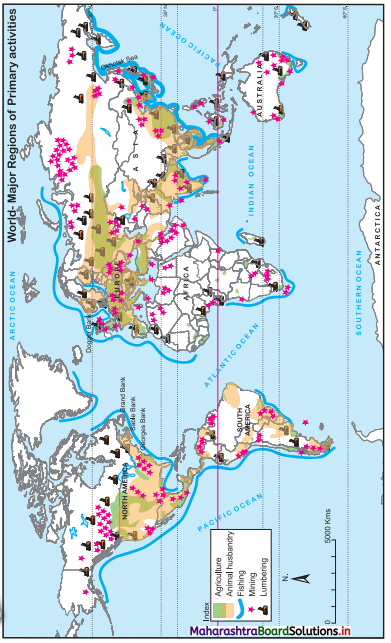
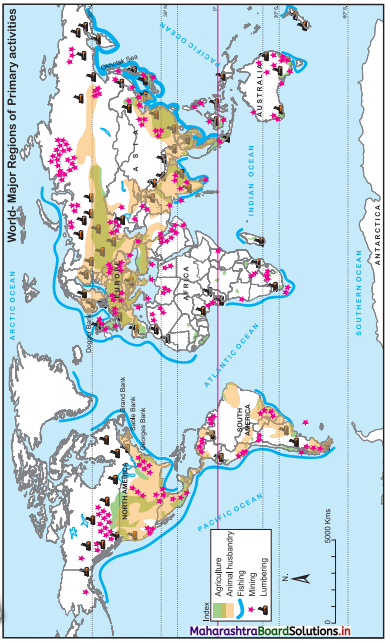
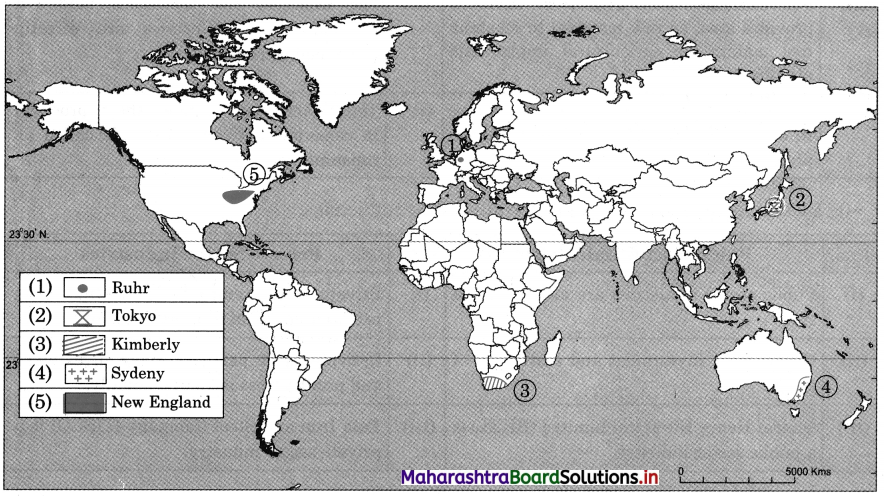
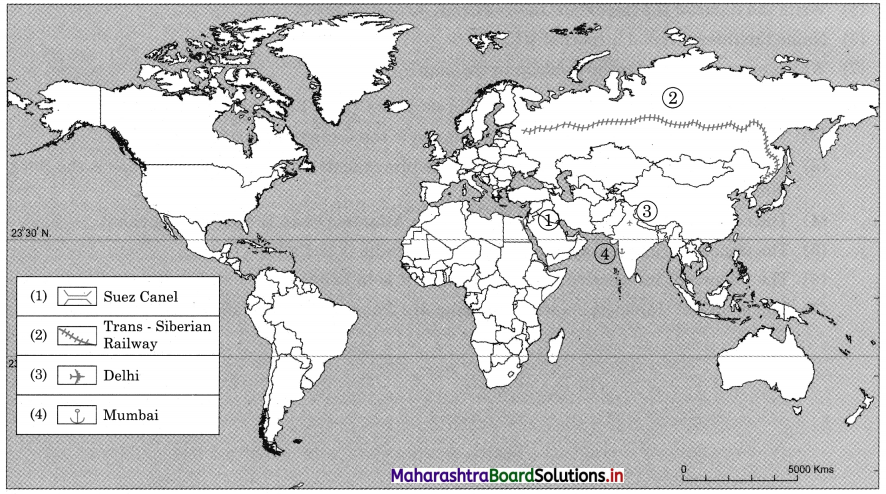
7. On an outline map of the world, show the following with the help of suitable index
(1) A canal bringing radical changes in sea transport.
(2) Railway connecting two continents.
(3) An international airport in India.
(4) An important port in India.
Answer:

8. Read the given passage and answer the following questions
Careful planning and implementation is necessary for economic development of any country. In the tourism sector the need for planned development is of great importance. It involves many industries working together in a complex way and needs special attention. Planning basically tries to allot limited resources between various competitors with a view to maximize output, income and employment and to make sure different sectors have fair growth. Tourism planning is a process through which the set goals can be achieved and the various choices linked to tourism development can be addressed. It is a long term and constant process of preparing, upgrading and improving a destination for tourist.
Communities are the basic elements of tourism. It mainly depends upon the level of acceptance shown by local communities. In the process of planning their involvement is essential. The development of tourism creates impact on mainly environment, socio-culture and economy of the host community at any destination. These impacts produce both negative as well as positive impacts. Planning is necessary to reduce the negative impact and boost the positive impact for sustainable development of a destination.
Question 1.
Why does the tourism sector need planning?
Answer:
Plan development in the tourist sector is of great importance, since it involves many industries working together in a complex and hence special attention.
Planning will help to allot limited resources between various competitors with view to maximise output, income and-employment.
Question 2.
What is the importance of communities in planning?
Answer:
- In the process of planning communities are basic elements of tourism.
- It mainly depends upon level of acceptance shown by local communities.
- In the process of planning their involvement is necessary and therefore, community planning is necessary.
Question 3.
Explain any two benefits of planning.
Answer:
Planning reduces the negative impact and boosts the positive impact for sustainable development of a destination.
Question 4.
What factors affect the economy of the host community?
Answer:
The development of tourism creates impact on mainly environment socio-culture and economy and economy of host community at any destination.
Question 5.
Why planning is a long-term task?
Answer:
Planning is a long-term task because planning is a constant process of preparing, upgrading and improving a destination for tourists.

Class 12 Geography Chapter 6 Tertiary Economic Activities Intext Questions and Answers
Think about it.
Read the following comprehension and answer the questions that follow:
There are three friends from different back-grounds. They decided to become entrepreneurs after graduating from the same college. Rohit is a farmer’s son. He pursued his bachelor degree in the Arts faculty. He was thinking of continuing his father’s profession but at a different level. He wanted to grow export-quality agricultural products in his two acres of farmland.
Sejal is the daughter of a businessman. They produce and sell bakery products on a wholesale basis. She has passed her degree in Science. She wants to become an entrepreneur in Fast Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG) products. Asif is a son of a small hotel owner. He has passed his graduation in Event Management. He wants to start his own company of Event Management.
After graduating with good grades, they decided to help each other and begin their careers. Rohit, Sejal and Asif tried to find out information about haw to start their businesses. They tried to get maximum information regarding their businesses. They wanted to plan, organise and then establish their start¬ups. During this period, they found information regarding their businesses.
Rohit found out that he will have to do major changes in his farmland to grow export-quality products like lily, orchid flowers and fruits like kiwis, dragon fruits, etc. He will have to maintain moisture and temperature in the air. He will also need to use special fertilizers to maintain the soil’s pH value.
He also came to know that he has to take help of the Agricultural officer from the same Taluka. More importantly, he has to take out a licence to establish a business. He also got to know that he will need an account which can be used for foreign transactions. He also got information from where, he would get saplings for the export-quality products. He came to know that, these flowers are in great demand in Gulf countries and they give high returns too. As these countries are within the reach of an hour or two by air, the flowers can remain fresh and retain their quality. He also decided to visit few vendors from these countries to directly setup his business.
Sejal realised that toothpaste is a product which is required daily by the people. Since her background was from Science, she decided to derive an advanced formula which will be good for dental health. She also took help from a cousin brother from the Pharmaceutical industry.
She came to know that she needed the following things to set up the industrial unit:
- Machinery and labour force to work in the plant.
- Land for setting up the plant.
- NOC from competent authorities before taking the product to the market.
- Other licenses like NOC from fire service department.
- Industries that will give tubes to fill ready toothpaste and cartons to wrap the product.
- Appoint an advertising agency to promote the product.
She was reluctant for this start-up since it required land and a large capital investment. But she felt relieved that due to the Government’s Start-up schemes, she can get subsidised loan. Her father helped her solve her land problem. He had a small piece of land near her town which was sufficient for this purpose. He arranged for other basic amenities like water, electricity, etc. which are required for an industry. He leased out that plot to Sejal.
Asif realised that he mainly needed services and labour for his start-up, which he can arrange by hiring them from various agencies like caterers, florists, hall owners, band players, sound systems, etc. He also understood how to take permission from various competent authorities to arrange various events. He realised that it will be good if he opens up an office to start his business in the market. To advertise his start up, he got a brochure designed and printed visiting cards for marketing his services.
After planning for a year, all the friends started their entrepreneurship in their respective businesses. As their businesses have been established as per their likings; they are enjoying their work. Their businesses are now their passions.
Question 1.
What do you understand by the term competent authorities?
Answer:
A competent authority is a person or organization that has the legally delegated or invested authority, capacity or power to perform a designated function.

Question 2.
In which types of economic activities are the children in the story engaged?
Answer:
Children in the story are engaged in the following economic activities:
- Rohit – primary activity
- Sejal – tertiary activity
- Asif – tertiary activity
Question 3.
While being occupied in their type of economic activity, which other activities they interact with?
Answer:
Rohit, Sejal and Asif interacted with the following activities for the development of their activities. Agriculture officer, vendors, pharmacist, competent authorities, service department, advertising agency, caterers, florists, hall owners, band players, sound system provider, brochure designer, etc.
Question 4.
Classify all the economic activities you come across in the passage.
Answer:
All economic activities we came across are basically tertiary economic activities. However, we can divide these tertiary economic activities in two groups
(i) Quaternary economic activities : Advertising agency, caterers, florists, hall owners, band players, sound system provider and brochure designer, etc.
(ii) Quinary economic activities : Agriculture officer, pharmacists, competent authority, fire service department, etc.
Use your brain power!
Question 1.
Do tertiary activities involve only services? (Textbook Page No. 56)
Answer:
Yes, tertiary activities involve only services to businessmen and people.
Question 2.
Can there be products in tertiary activities? (Textbook Page No. 56)
Answer:
There cannot be products in tertiary activities; they only provide services for distribution of primary and secondary products to consumers.
Question 3.
Given below are the countries which are least dependent on tourism. Locate these countries on a map. Explain the geographical factors which are responsible for non¬development of tourism in these countries. (Textbook Page No. 62)
| Country |
Contribution of Tourism to GDP (%) (2018) |
| Democratic Republic of the Congo |
0.66 |
| Papua New Guinea |
0.66 |
| Uzbekistan |
0.93 |
| Moldova |
0.96 |
| Gabon |
1.02 |
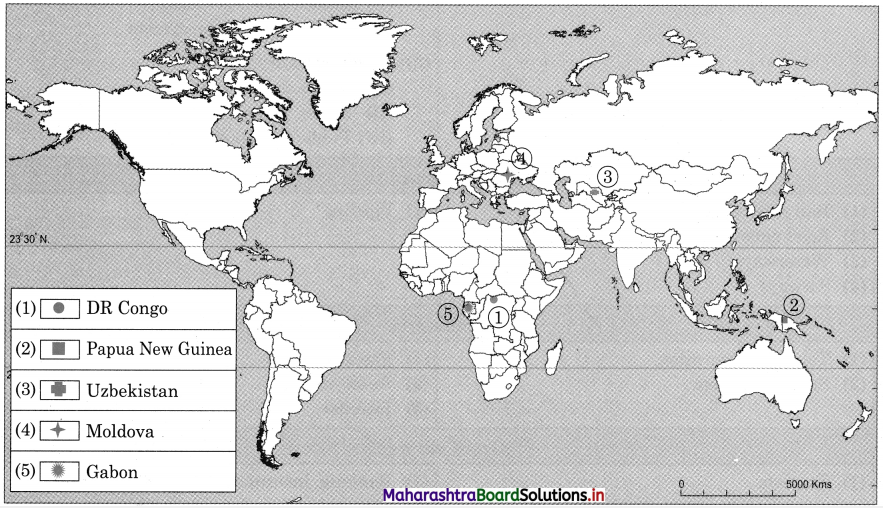
Tourism is not developed in these countries because of unfavourable physical factors such as climate, relief, location, dense forest, etc.
In Gabon, Papua New Guinea and in Democratic Republic of the Congo, there is equatorial type of climate, dense forest growth, wet land areas, so there are problems in development of transport facilities and infrastructure. Most of the areas in the country are inaccessible.
The countries of Moldova and Uzbekistan are landlocked countries, there is extreme climate, rainfall is very limited. Due to extreme climate tourists are not interested to visit these countries.

Question 4.
Are maps a means of communication? (Textbook Page No. 63)
Answer:
Yes, maps are means of communication because they provide a lot of information.
Can you tell?
Question 1.
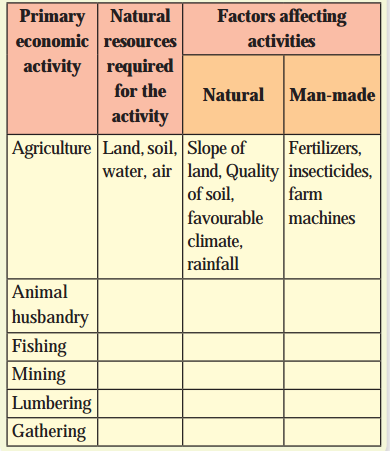
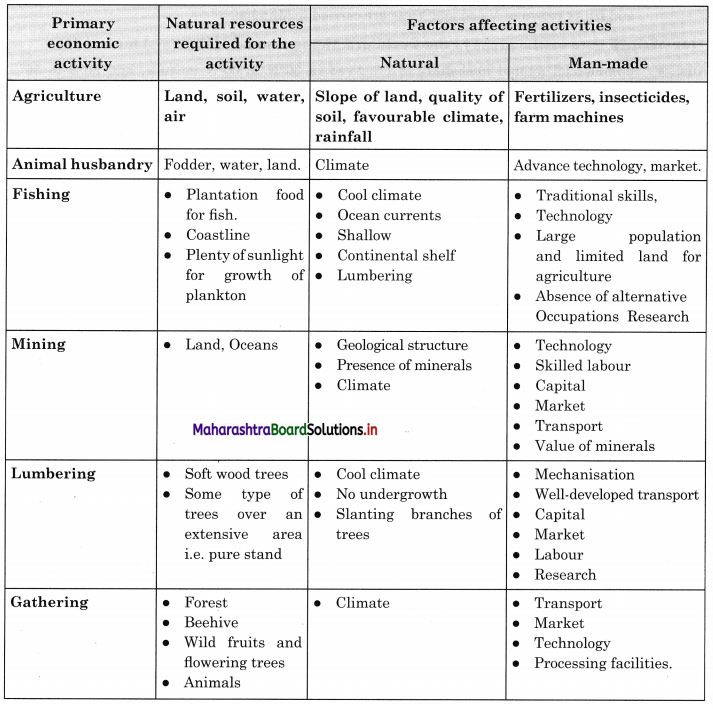
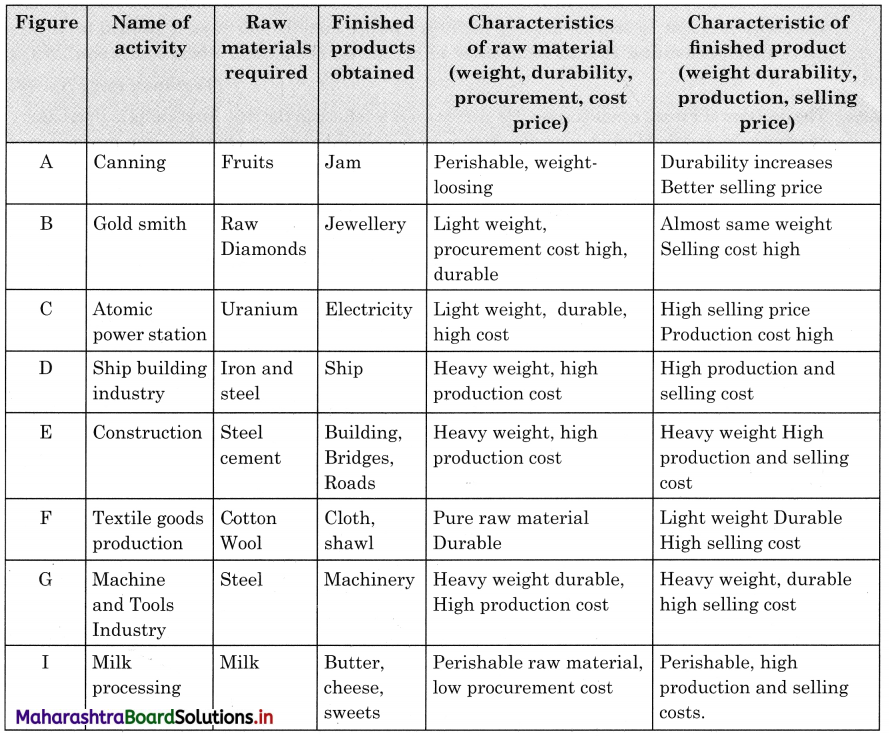
In many economic activities included in tertiary occupations are enlisted. Classify the following economic activities in the following two categories:
- Activities dependent on geographical factors.
- Activities not dependent on geographical factors. (Textbook Page No. 56)
Answer:
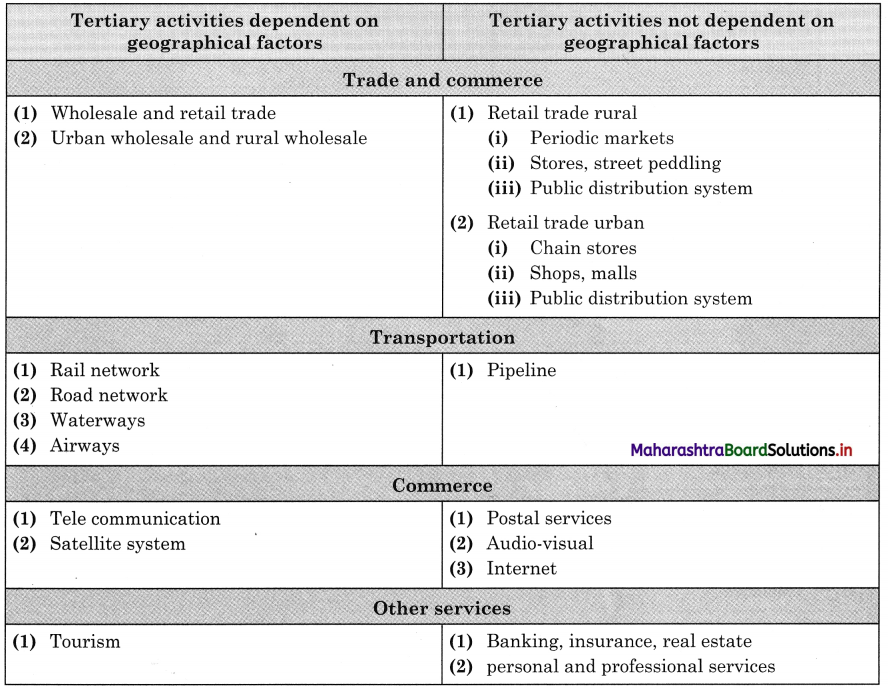
Question 2.
Make a list of things you use in your daily life. (Textbook Page No. 57)
Answer:
(i) Divide the activities through which they have been obtained into primary, secondary and tertiary. For example, salt is obtained from primary activity.
(ii) Does your list contain any products which have been derived by using either of the activities?
Answer:
| Primary Activities |
Secondary Activities |
Tertiary Activities |
| Rice |
Idli |
Newspaper |
| Wheat |
Bread |
TV program |
| Potato |
Potato chips |
Internet |
| Tomato |
Tomato ketchup |
Landline |
| Sugarcane |
Jaggery |
Banking services |
| Chili |
Chili powder |
Mobile services |
| Onion |
Mixer |
Hospitals |
| Pulses |
Washing machine |
Theatres |
|
Fans |
|
(ii) All above products are received from primary, secondary and tertiary activities.
Question 3.
Can intelligence or physical efforts be imported or exported? (Textbook Page No. 61)
Answer:
Yes, intelligence or physical efforts can be imported or exported in the form of intelligent people or skilled people. For example, Saudi Arabia invited many engineers to construct the roads, bridges, flyovers, etc., in their country, therefore there was development of infrastructure in their country.

Question 4.
(i) What are the lists of items mentioned in timeline related to?
(ii) Which means you are aware of?
(iii) Which means do you actually use?
(iv) Which of these are now outdated?
(v) What could be reasons for them getting outdated?
(vi) Can you add more to the list? (Textbook Page No. 62)
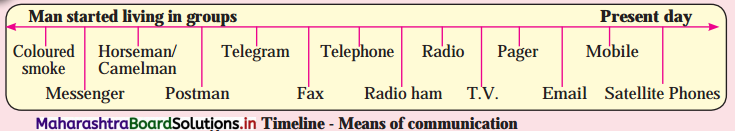
Answer:
(i) In the list means of communication are mentioned.
(ii) We are aware of a postman, telegram, telephone, fax, radio, pager, email, mobile, satellite phones.
(iii) We use telephone, radio, mobile, email, satellite phones.
(iv) Coloured smoke, messenger, horsemen/camel man are outdated means of communication
(v) Coloured smoke, messenger, horsemen/camel man are outdated means of communication because of limited speed. They can be operated in limited area and difficult to use as against modern communication system.
(vi) The Internet banking, email, WhatsApp, NEFT, RTGS, etc., are the other means of communication.
Question 5.
Which practicals of geography for Class 11 and Class 12 have you carried out with the help of satellites? (Textbook Page No. 63)
Answer:
Topographical maps of survey of India.
Make friends with maps!
Look at the map in Fig. 6.2 and answer the following questions : (Textbook Page No. 57)
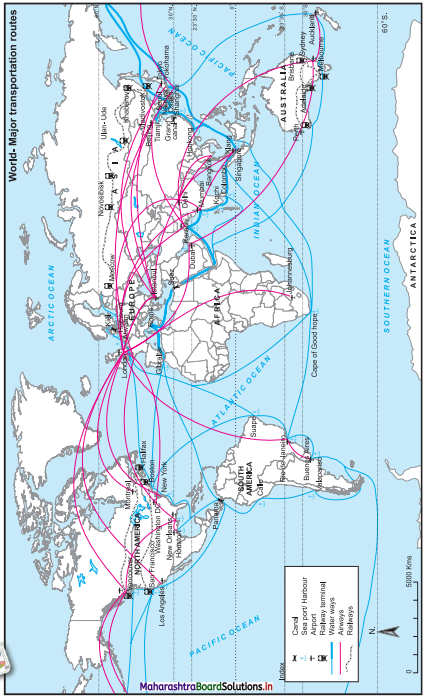
Question 1.
Which means of transportation are shown in the map?
Answer:
Waterways, airways and railways are shown in the map.
Question 2.
Between which continents do you see an overall higher flow of transportation?
Answer:
High flow of transportation is seen between North America and Europe.

Question 3.
Which canals can you see in their waterways? What can be the purpose?
Answer:
We see two canals in waterways: Suez Canal and Panama Canal.
The purpose of construction of Suez Canal is to avoid the long route along Cape of Good Hope in Africa. This canal reduced the distance of travel by thousands of kilometres between Europe and Asia.
The purpose of construction of Panama Canal is to avoid the long distance route between Eastern coastline and Western coastline of North America. This canal provided a short cut to connect two coastlines.
Question 4.
Which two major cities in India are connected internationally through airways?
Answer:
The two major cities in India connected internationally through airways are Delhi and Mumbai.
Question 5.
Which two continents show lesser use of air routes?
Answer:
Africa and South America show lesser use of air routes.
Question 6.
Which two continents show lesser use of rail routes? Why?
Answer:
The continents of Africa and South America have lesser use of rail route because in both the continents physical factors like climate and relief are not favourable for development of rail route. Due to the mountains, hills, dense forest and desert in these areas, the construction and maintenance of the railway line is difficult and expensive.
Question 7.
Which rail route connects two continents?
Answer:
The Trans-Siberian Railway connects two continents i.e., Asia and Europe.
Question 8.
Why do you see a concentration of transportation routes in the southern part of Australia as opposed to northern parts in all the continents?
Answer:
Compared to the northern part of Australia, southern part is having levelled land, equable climate, urbanisation and industrialisation. Therefore, concentration of transport routes is more in the southern part of Australia.
Question 9.
Which continents do not have continuous internal rail routes? Why?
Answer:
South America and Africa do not have continuous internal rail routes because some areas in these continents are densely forested and extensive areas are covered by deserts and mountains.

Try this
Question 1.
Consider the following conditions a, b, and c and answer the questions that follow
(a) There are two countries ‘A’ and ‘B’. ‘A’ produces 500 tonnes of wheat by employing 200 labourers. ‘B’ produces 1,000 tonnes of wheat by employing 300 labourers.
(b) Country ‘C’ produces 300 kg of tea and ‘D’ produces 500 kg of coffee. ‘C’ does not produce coffee and ‘D’ does not produce tea.
(c) Country ‘E’ has expertise in water engineering and agriculture. Country ‘F’ has expertise in metro-making. (Textbook Page No. 59)
(i) Will the trade take place between A and B in condition (a)?
Answer:
No, trade of wheat will not take place in between A and B because both are producing wheat.
Question 2.
Will trade take place between C and D in condition (b)?
Answer:
Yes, trade will take place between C and D in condition (b) because C country produces tea and D country produces coffee. Since they produce different products – tea and coffee, they will exchange their products through trade.
Question 3.
If trade occurs between A and B in condition (a), what does it tell you about the conditions of countries in term of their economy?
Answer:
Firstly, both countries are producing wheat and therefore, if their production of wheat is sufficient for their population, trade will not take place.
Secondly, per capita production of wheat in country A is less than country B. As a result, the cost of production of wheat in country A is more than B country.
Under the above conditions if country B is ready to export wheat to country A, country A will get wheat from B at the lower cost than the production cost in their country and trade in wheat will take place and both countries will be economically benefited and can improve their economy.

Question 4.
If trade occurs between C and D in (b), what does it tell you about the climate of the countries?
Answer:
Country C produces tea and country D produces coffee. So country C can export tea to country D and country D can export coffee to country C and trade will take place between C and D depending upon market for tea and coffee in respective countries.
As far as climate is concerned in both countries there must be tropical climate because cultivation of tea as well as coffee needs same type of climate conditions. Since both crops requires same climate, both can produce tea and coffee too and avoid trade or one can specialize in tea cultivation and another in coffee cultivation and develop trade.
Question 5.
Considering that trade occurs between two countries in condition (c), what does it tell you about the human resources of the countries?
Answer:
Country E has developed technology in water engineering and agriculture. While F has developed technology in construction of the metro. This shows that both countries are technologically advanced and hence their human resources are very rich.
Question 6.
Make a list of factors which affect the trade between any two countries.
Answer:
The various factors which affect the trade area are as follows:
- Difference in natural resources
- Climate
- Population
- Culture
- Economic cost
- Specialisation
- Government policy
Question 7.
The graph shows trade carried from 1980 to 2010 through sea transport. Interpret the graph in your own words. (Textbook Page No. 61)
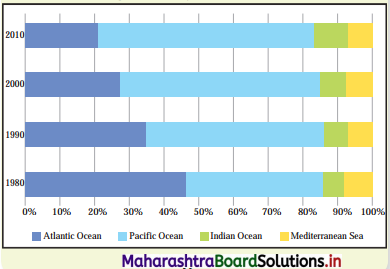
Answer:
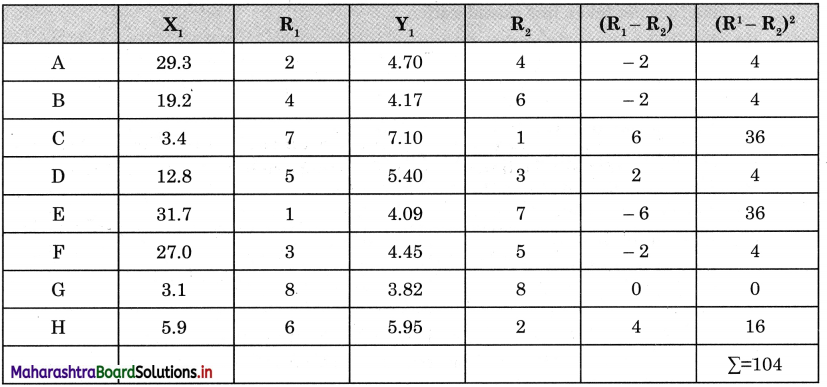
Between 1980 and 2010 transportation in the Atlantic Ocean declined by almost 50%, whereas sea transport in the Pacific Ocean has increased considerably. There is slight growth in the sea transport in Indian Ocean. There is no change in sea transport in Mediterranean Sea during the same period.

Question 8.
See the following two tables and answer the questions given below:
What do the tables shows?
Are the countries in the table same?
Locate them on the world map.
Can you tell, why contribution of tourism is high in these countries in terms of GDP and employment?
Write a concluding paragraph on factors affecting tourism as an occupation in a country. (Textbook Page No. 61)
| TABLE 1: Direct Contribution of Travel and Tourism to GDP of some regions (%) (2018) |
| Maldives |
38.92 |
| British Virgin Islands |
32.96 |
| Macao |
28.01 |
| Aruba |
27.64 |
| Seychelles |
25.73 |
| TABLE 2 : People engaged in tourism in some regions (%) (2018) |
| Aruba |
29.91 |
| St. Lucia |
27.29 |
| The Bahamas |
26.49 |
| Macao |
26.48 |
| Seychelles |
25.35 |
Answer:
(i) Table 1 shows direct contribution of travel and tourism to GDP of some regions in (%) 2018. Table 2 shows people engaged in tourism in some regions in (%) in 2018.
(ii) Countries shown in the table are island countries.
(iii) 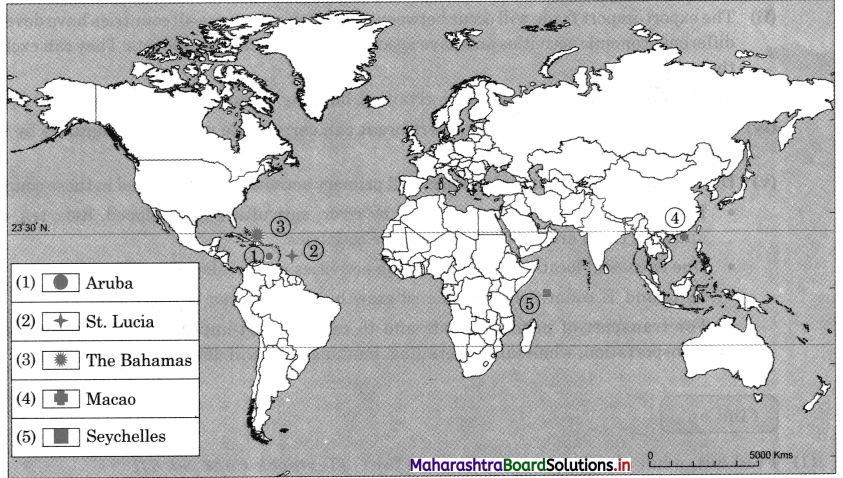
(iv) These are island countries having beautiful beaches and scenery. They provide coastal water sports as well as sea adventure sports facilities to tourists. Naturally large numbers of tourists are attracted and therefore, the contribution of tourists in these countries in terms of GDP and employment is very high.
(v) Today, tourism is one of the fastest growing economic activities in the world. Beautiful natural scenery attracts a large number of tourists. Waterfalls, glaciers, beautiful beaches attract large number of tourists.
Apart from good climate and beautiful scenery, the development of tourism also depends upon the availability of certain amenities for tourists. The tourist centres must be easily accessible. Air transports have revolutionized travel. Roads and railways are other modes of transportation which make tourist places accessible.
Places of tourist interest must provide good accommodation facilities. Five star hotels, ordinary hotels, guest houses, holiday camps, etc., are essential for the overnight stay of tourists.

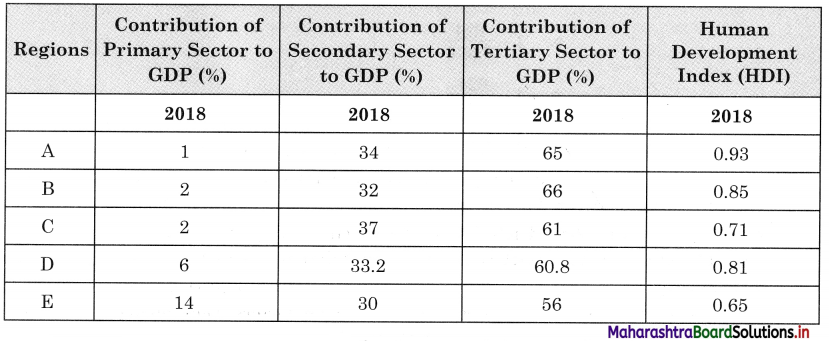
Question 9.
In Fig. 6.6, five hypothetical countries and some information about their conditions are given. Study them carefully and answer the following questions:
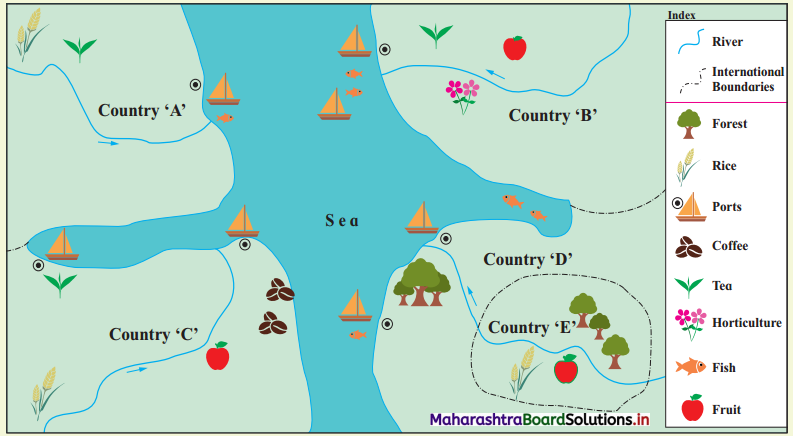
(i) Considering the natural resources available in these countries, which activities will flourish here? (Textbook Page No. 63)
(ii) Between which countries will export-import of goods occur? (Textbook Page No. 63)
(iii) Which tertiary activities will take place here? (Textbook Page No. 64)
(iv) Considering the location of E country, how will it carry out trade with other countries? (Textbook Page No. 64)
(v) Write in your own words the effect of geographical factors on human economic activities in these countries. (Textbook Page No. 64)
Answer:
(i) Agriculture, fishing, trade, lumbering activities will flourish.
(ii) The export-import trade will occur between all countries because all countries have developed different economic activities and have specialisation of different products. They can exchange the goods.
(iii) Transportation, trade, wholesaling, retailing, banking, financial institutes, etc., will develop.
(iv) ‘E’ country is an island country, therefore it can carry trade with other countries by water transport.
(v) Due to availability of natural resources all primary activities are developed in these countries.
- Due to fertile soil, and water supply by river, agriculture is developed. Rice, tea, coffee and fruit crops are grown in most of the countries.
- Due to coastal location, trade & fishing activities are developed in all countries.
- In ‘D’ and ‘E’ countries, due to forest growth lumbering can be developed.
- For transport of primary goods and to carry export-import, tertiary activities like transportation, wholesaling, retailing, banking, etc., will develop.

Find out
Question 1.
Find out, what are these places famous for (Textbook Page No. 61)
(i) Coorg, Yusmarg, Saputara, Ladghar, Milan, Marina beach, Istanbul.
(ii) What is the main economic activity carried here?
(iii) Is there any relationship between their location (geographical) and their economic activities?
Answer:
(i) All places mentioned are places of tourist interest. Coorg, Yusmarg, Saputara are hill stations, Ladghar and Marina are beaches, Milan is world famous fashion centre and Istanbul is a major city and cultural centre in Turkey.
(ii) Main economic activity is tourism at all places.
(iii) Yes, there is relationship between their location and their economic activities. For e.g., Marina and Ladghar are beaches, Coorg and Saputara are hill stations.
Give it a try
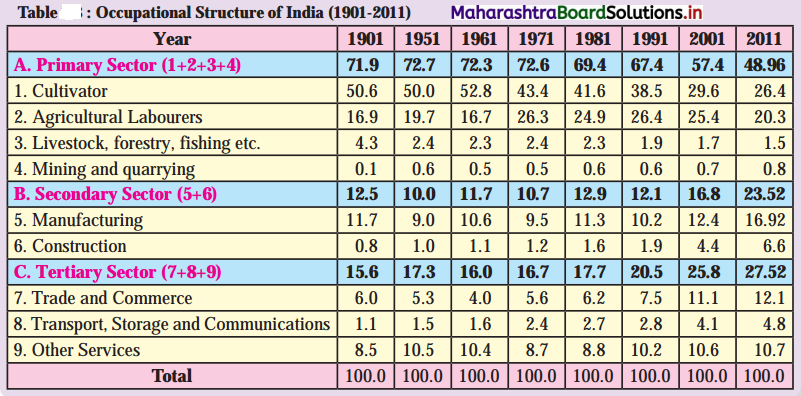
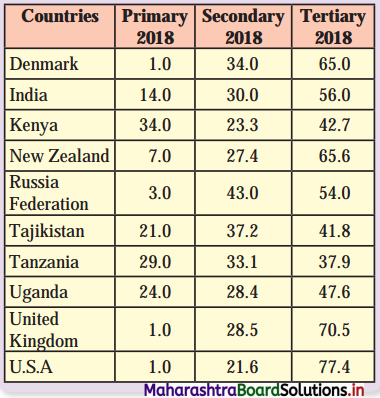
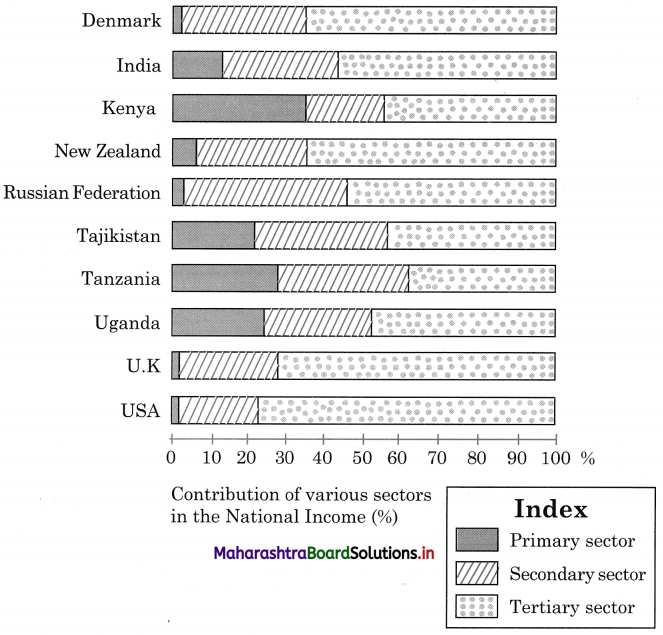
Question 1.
Draw a suitable graph for the information given in table 6.1. and write a paragraph interpreting the data. (Textbook Page No. 63)
Answer:
Interpretation of the data and graph.
The data and graph shows contribution of primary, secondary and tertiary sectors in the national income in the year 2018.
We can divide these ten countries, on the basis of persons engaged in primary activities, as less than 5% workers engaged in primary activity and more than 50% workers engaged in tertiary activities.
There are four countries – Denmark, Russia, United Kingdom and USA, where less than 5% workers are engaged in primary activities and there are six countries – Denmark, Russia, United Kingdom, USA and India, where more than 50% workers are engaged in tertiary activities.
In all ten countries, number of workers engaged in secondary activities are in the range of 20% to 30%, except Russia where 43% workers are engaged in secondary activities.
From the above discussion we can draw the conclusion that Kenya, Uganda, Tajikistan, Tanzania are developing countries and Denmark, Russia, USA, United Kingdom, New Zealand are the developed countries.
Class 12 Geography Solutions Digest
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()