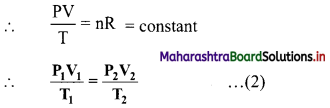Balbharti Maharashtra State Board 11th Biology Textbook Solutions Chapter 6 Biomolecules Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
Biomolecules Class 11 Exercise Question Answers Solutions Maharashtra Board
Class 11 Biology Chapter 6 Exercise Solutions Maharashtra Board
Biology Class 11 Chapter 6 Exercise Solutions
1. Choose correct option
Question (A)
Sugar, amino acids and nucleotides unite to their respective subunits to form ________
(a) bioelements
(b) micromolecules
(c) macromolecules
(d) all of these
Answer:
(c) macromolecules

Question (B)
Glycosidic bond is found in __________ .
(a) Disaccharide
(b) Nucleosides
(c) Polysaccharide
(d) all of these
Answer:
(d) all of these
Question (C)
Amino acids in a polypeptide are joined by _______ bond.
(a) Disulphide
(b) glycosidic
(c) hydrogen bond
(d) none of these
Answer:
(d) none of these
Question (D)
Lipids associated with cell membrane are _________ .
(a) Sphingomyelin
(b) Isoprenoids
(c) Phospholipids
(d) Cholesterol
Answer:
(c) Phospholipids
Question (E)
Linoleic, Linolenic and ________ acids are referred as essential fatty acids since they cannot be synthesized by the body and hence must be included in daily diet.
(a) Arachidonic
(b) Oleic
(c) Steric
(d) Palmitic
Answer:
(a) Arachidonic

Question (F)
Hemoglobin is a type of ________ protein, which plays indispensable part in respiration.
(a) simple
(b) derived
(c) conjugated
(d) complex
Answer:
(c) conjugated
Question (G)
When inorganic ions or metallo-organic molecules bind to apoenzyme, they together form
(a) isoenzyme
(b) holoenzyme
(c) denatured enzyme
(d) none of these
Answer:
(b) holoenzyme
Question (H)
In enzyme kinetics, Km = Vmax/2. If Km value is lower, it indicates _______
(a) Enzyme has less affinity for substrate
(b) Enzyme has higher affinity towards substrate
(c) There will be no product formation
(d) All active sites of enzyme are saturated
Answer:
(b) Enzyme has higher affinity towards substrate
2. Solve the following questions
Question (A)
Observe the following figures and write the differences between them.
Answer:
| Saturated fats |
Unsaturated fats |
| 1. They contain single chain of carbon atoms with single bonds. |
They contain chain of carbon atoms with one or more double bonds. |
| 2. They are solid at room temperature. |
They are liquid at room temperature. |
| 3. They increase blood cholesterol level by depositing it in the inner wall of arteries. |
They lower the blood cholesterol level and have many health benefits. |
| 4. They do not get spoiled. |
They get spoiled easily. |
| 5. Saturated fats are obtained from animal fats, palm oil, etc. |
Unsaturated fatty acids are obtained from plant and vegetable oil, etc. |

3. Answer the following questions
Question (A)
What are building blocks of life?
Answer:
Life is composed of four main building blocks: Carbohydrates, proteins, lipids and nucleic acids.
Question (B)
Explain the peptide bond.
Answer:
1. The covalent bond that links the two amino acids is called a peptide bond.
2. Peptide bond is formed by condensation reaction.
Question (C)
How many types of polysaccharides you know?
Answer:
There are two types of polysaccharides:
1. Homopolysaccharides: It contains same type of monosaccharides. E.g. Starch, glycogen, cellulose.
2. Heteropolysaccharides: It contains two or more different monosaccharides. E.g. Hyaluronic acid, heparin, hemicellulose.
Question (D)
Enlist the significance of carbohydrates.
Answer:
Significances of carbohydrates are as follows:
- Carbohydrates provide energy for metabolism.
- Glucose is the main substrate for ATP synthesis.
- Lactose, a disaccharide present in the milk provides energy to babies.
- Polysaccharide serves as a structural component of cell membrane, cell wall and reserved food as starch and glycogen.
Question (E)
What is reducing sugar?
Answer:
1. A sugar that serves as a reducing agent due to presence of free aldehyde or ketone group is called a reducing sugar.
2. These sugars reduce the Benedict’s reagent (Cu2+ to Cu+) since they are capable of transferring hydrogens (electrons) to other compounds, a process called reduction.
3. All monosaccharides are reducing sugars.

Question (F)
Enlist the examples of simple proteins and their significance.
Answer:
Examples of simple proteins are: E.g.: Albumins and histones.
Significance:
1. Albumin:
a. % It is the main protein in the blood.
b. It maintains the pressure in the blood vessels.
c. It helps in transportation of substances like hormone and drugs in the body.
2. Histones:
a. It is the chief protein of chromatin.
b. They are involved in packaging of DNA into structural units called nucleosomes.
Question (G)
Describe the secondary structure of protein with examples.
Answer:
- There are two types of secondary structure of protein: a-helix and P-pleated sheets.
- The polypeptide chain is arranged in a spiral helix. These spiral helices are of two types: a-helix (right handed) and P-helix (left handed).
- This spiral configuration is held together by hydrogen bonds.
- The sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide chain determines the location of its bend or fold and the position of formation of hydrogen bonds between different portions of the chain or between different chains. Thus, peptide chains form an a-helix structure.
- Example of a-helix structure is keratin.
- In some proteins two or more peptide chains are linked together by intermolecular hydrogen bonds. Such structures are called P-pleated sheets.
- Example of P-pleated sheet is silk fibres.
- Due to formation of hydrogen bonds peptide chains assume a secondary structure.
Question (H)
Explain the induced fit model for mode of enzyme action.
Answer:
1. The induced fit model shows that enzymes are flexible structures in which the active site continually reshapes by its interactions with the substrate until the time the substrate is completely bound to it. It is also the point at which the final form and shape of the enzyme is determined.
2. Three-Dimensional conformation:
a. All enzymes have specific 3-dimensional conformation.
b. They have one or more active sites to which substrate (reactant) combines.
c. The points of active site where the substrate joins with the enzyme is called substrate binding site.
Question (I)
What is RNA? Enlist types of RNA.
Answer:
1. RNA stands for Ribonucleic Acid. It is a long single stranded polynucleotide chain which helps in protein synthesis, functions as a messenger and translates messages coded in DNA into protein.
2. There are three types of RNA:
mRNA (messenger RNA), rRNA (ribosomal RNA) and tRNA (transfer RNA)
Question (J)
Describe the concept of metabolic pool.
Answer:
1. Metabolic pool is the reservoir of biomolecules in the cell on which enzymes can act to produce useful products as per the need of the cell.
2. The concept of metabolic pool is significant in cell biology because it allows one type of molecule to change into another type E.g. Carbohydrates can be converted to fats and vice-versa.

Question (K)
How do secondary metabolites useful for mankind?
Answer:
1. Drugs developed from secondary metabolites have been used to treat infectious diseases, cancer, hypertension and inflammation.
2. Morphine, the first alkaloid isolated from Papaver somniferum is used as pain reliver and cough suppressant.
3. Secondary metabolites like alkaloids, nicotine, cocaine and the terpenes, cannabinol are widely used for recreation and stimulation.
4. Flavours of secondary metabolites improve our food preferences.
5. Tannins are added to wines and chocolate for improving astringency.
6. Since most secondary metabolites have antibiotic property, they are also used as food preservatives.
7. Glucosinolates is a secondary metabolite which is naturally present in cabbage imparts a characteristic flavour and aroma because of nitrogen and sulphur-containing chemicals. It also offers protection to these plants from many pests.
4. Solve the following questions
Question (A)
Complete the following chart.
| Protein |
Physiological role |
| Collagen |
(i) |
| (ii) |
Responsible for muscle contraction |
| Immunoglobulin |
(iii) |
| (iv) |
Significant in Respiration |
| Fibrinogen |
(v) |
Answer:
| Protein |
Physiological role |
| 1. Collagen |
Provides strength and plays structural role |
| 2. Myosin & Actin |
Responsible for muscle contraction |
| 3. Immunoglobulin |
Protects the body from infection |
| 4. Haemoglobin |
Significant in Respiration |
| 5. Fibrinogen |
Responsible for normal clotting of blood. |

Question (B)
Answer the following with reference
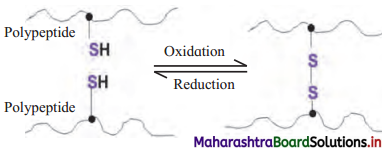
i. Name the type of bond formed between two polypeptides.
ii. Which amino acid is involved in the formation of such bond?
iii. Amongst I, II, III and IV structural level of protein, which level of structure includes such bond? Answer:
i. Disulfide bond.
ii. Cysteine
iii. Tertiary structure.
[Note: Quaternary structure of protein also have disulfide bond, for stabilization of protein structure.!
Question (C)
Match the following items given in column I and II.
| Column I |
Column 11 |
| 1. RNA |
(a) Induced fit model |
| 2. Yam plant |
(b) Flax seeds |
| 3. Koshland |
(c) Hydrolase |
| 4. Omega – 3 – fatty acid |
(d) Uracil |
| 5. Sucrase |
(e) Anti-fertility pills |
Answer:
| Column I |
Column 11 |
| 1. RNA |
(d) Uracil |
| 2. Yam plant |
(e) Anti-fertility pills |
| 3. Koshland |
(a) Induced fit model |
| 4. Omega – 3 – fatty acid |
(b) Flax seeds |
| 5. Sucrase |
(c) Hydrolase |

5. Long answer questions
Question (A)
What are biomolecules? Explain the building blocks of life.
Answer:
Biomolecules are essential substances produced by our body which are necessary for life.
The building blocks of life are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids.
1. Carbohydrates:
a. Carbohydrates are biomolecules made from carbon, hydrogen and oxygen.
b. The general formula of carbohydrates is (CH20) n.
c. They contain hydrogen and oxygen in the same ratio as in water (2:1).
d. Carbohydrates can be broken down to release energy.
e. Based on sugar units, carbohydrates are classified into three types: Monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides.
2. Lipids:
a. These are group of substances with greasy consistency with long hydrocarbon chain containing carbon, hydrogen and oxygen.
b. In lipids hydrogen to oxygen ration is greater than 2:1.
c. Lipid is a broader term used for fatty acids and their derivatives.
d. They are soluble in organic solvents (non-polar solvents).
e. Fatty acids are organic acids which are composed of hydrocarbon chain ending in carboxyl group (COOH) ….
f. These are divided into: Saturated fatty acids and unsaturated fatty acids.
g. Fatty acids are basic molecules which form different kinds of lipids.
h. Lipids are classified into three types:
Simple lipids, Compound lipids, Derived lipids.
3. Proteins:
a. Proteins are large molecules containing amino acid units ranging from 100 to 3000.
b. They have higher molecular weight.
c. In proteins, amino acids are linked together by peptide bonds which join the carboxyl group of one amino acid residue to the amino group of another residue.
d. A protein molecule consists of one or more polypeptide chains.
e. Proteins contain any or all twenty naturally occurring amino acid types.
f. Proteins have different structures like primary structure, secondary structure, tertiary structure and quaternary structure.
g. Proteins are classified into three types:
Simple proteins: Simple proteins on hydrolysis yield only amino acids. E.g. Histones and albumins. Conjugated proteins: It consists of a simple protein united with some non-protein substance. E.g. Haemoglobin.
Derived proteins: These proteins are not found in nature as such but are derived from native protein molecules on hydrolysis. E.g. Metaproteins, peptones.
4. Nucleic Acids:
a. Nucleic acids are macromolecules composed of many small units or monomers called nucleotides.
b. Each nucleotide is formed of three components i.e. pentose sugar, a nitrogen base and a phosphate (phosphoric acid).
c. When sugar combine with nitrogenous base it forms nucleoside. Nucleotides can be called as nucleoside phosphate.
d. There are two types of nucleic acids, i.e. DNA and RNA.
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) is a genetic material of a cell. It is double stranded helix. Each strand of helix is made up of deoxyribose nucleotides.
RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) is a single stranded structure having fewer nucleotides as compared to DNA. The strands may be straight or variously folded upon itself. It is made up of nucleotides.

Question (B)
Explain the classes of carbohydrates with examples.
Answer:
Based on number of sugar units, carbohydrates are classified into three types namely, monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides.
1. Monosaccharides:
a. Monosaccharides are the simplest sugars having crystalline structure, sweet taste and soluble in water.
b. They cannot be further hydrolyzed into smaller molecules.
c. They are the building blocks or monomers of complex carbohydrates.
d. They have the general molecular formula (CH20)n, where n can be 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7.
e. They can be classified as triose, tetrose, pentose, etc.
f. Monosaccharides containing the aldehyde (-CHO) group are classified as aldoses e.g. glucose, xylose, and those with a ketone(-C=0) group are classified as ketoses. E.g. ribulose, fructose.
2. Disaccharides:
a. Disaccharide is formed when two monosaccharide react by condensation reaction releasing a water molecule. This process requires energy.
b. A glycosidic bond forms and holds the two monosaccharide units together.
c. Sucrose, lactose and maltose are examples of disaccharides.
d. Sucrose is a nonreducing sugar since it lacks free aldehyde or ketone group.
e. Lactose and maltose are reducing sugars.
f. Lactose also exists in beta form, which is made from P-galactose and p-glucose.
g. Disaccharides are soluble in water, but they are too big to pass through the cell membrane by diffusion.
3. Polysaccharides:
a. Monosaccharides can undergo a series of condensation reactions, adding one unit after the other to the chain till a very large molecule (polysaccharide) is formed. This is called polymerization.
b. Polysaccharides are broken down by hydrolysis into monosaccharides.
c. The properties of a polysaccharide molecule depends on its length, branching, folding and coiling.
d. Examples: Starch, glycogen, cellulose.
Question (C)
Describe the types of lipids and mention their biological significance.
Answer:
Lipids are classified into three main types:
1. Simple lipids:
a. These are esters of fatty acids with various alcohols. Fats and waxes are simple lipids.
b. Fats are esters of fatty acids with glycerol (CH2OH-CHOH-CH2OH).
c. Triglycerides are three molecules of fatty acids and one molecule of glycerol.
d. Unsaturated fats are liquid at room temperature and are called oils. Unsaturated fatty acids are hydrogenated to produce fats e.g. Vanaspati ghee.
Biological significance:
a. Fats are a nutritional source with high calorific value and they act as reserved food materials.
b. In plants, fat is stored in seeds to nourish embryo during germination.
c. In animals, fat is stored in the adipocytes of the adipose tissue.
d. Fats deposited in subcutaneous tissue act as an insulator and minimize loss of body heat.
e. Fats deposited around the internal organs act as cushions to absorb mechanical shocks.
f. Wax is another example of simple lipid. They are esters of long chain fatty acids with long chain alcohols.
g. They are found in the blood, gonads and sebaceous glands of the skin.
h. Waxes are not as readily hydrolyzed as fats.
i. They are solid at ordinary temperature.
j. Waxes form water insoluble coating on hair and skin in animals, waxes form an outer coating on stems, leaves and fruits.
2. Compound lipids:
a. These are ester of fatty acids containing other groups like phosphate (Phospholipids), sugar (glycolipids), etc.
b. They contain a molecule of glycerol, two molecules of fatty acids and a phosphate group or simple sugar.
c. Some phospholipids such as lecithin also have a nitrogenous compound attached to the phosphate group.
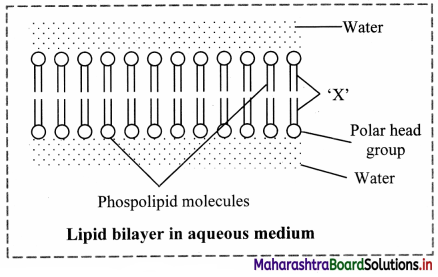
d. Phospholipids have both hydrophilic polar groups (phosphate and nitrogenous group) and hydrophobic non-polar groups (hydrocarbon chains of fatty acids).
e. Glycolipids contain glycerol, fatty acids, simple sugars such as galactose. They are also called cerebrosides.
Biological significance:
a. Phospholipids contribute in the formation of cell membrane.
b. Large amounts of glycolipids are found in the brain white matter and myelin sheath.
3. Derived Lipids:
a. They are composed of fused hydrocarbon rings (steroid nucleus) and a long hydrocarbon side chain.
b. One of the most common sterols is cholesterol.
Biological significance:
a. It is widely distributed in all cells of the animal body, but particularly in nervous tissue.
b. Cholesterol exists either free or as cholesterol ester.
c. Adrenocorticoids, sex hormones (progesterone, testosterone) and vitamin D are synthesized from cholesterol.
d. Cholesterol is not found in plants.
e. Sterols exist as phytosterols in plants.
f. Yam Plant (Dioscorea) produces a steroid compound called diosgenin. It is used in the manufacture of antifertility pills, i.e. birth control pills.

Question (D)
Explain the chemical nature, structure and role of phospholipids in biological membrane.
Answer:
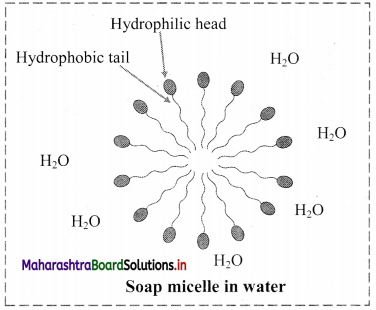
Chemical nature: Phospholipids are amphiphilic in nature. As they have hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tail.
Structure: It contains an alcohol, two fatty acid chains and a phosphate group.
Role: Phospholipids forms the membranes around the cells and cellular organelles. They form a lipid bilayer membrane. The phospholipids are arranged tail to tail. It serves as a barrier against movement of any ions or polar compounds into and out of the cell.
Question (E)
Describe classes of proteins with their importance.
Answer:
On the basis of structure, proteins are classified into three categories:
1. Simple proteins:
a. Simple proteins on hydrolysis yield only amino acids.
b. These are soluble in one or more solvents.
c. Simple proteins may be soluble in water.
d. Histones of nucleoproteins are soluble in water.
e. Globular molecules of histones are not coagulated by heat.
f. Albumins are also soluble in water but they get coagulated on heating.
g. Albumins are widely distributed e.g. egg albumin, serum albumin and legumelin of pulses are albumins.
Importance: They are involved in structural components; they also act as a storage kind of protein.
Some are associated with nucleic acids in nucleoproteins of cell.
2. Conjugated proteins:
a. Conjugated proteins consist of a simple protein united with some non-protein substance.
b. The non-protein group is called prosthetic group e.g. haemoglobin.
c. Globin is the protein and the iron containing pigment haem is the prosthetic group.
d. Similarly, nucleoproteins have nucleic acids.
e. Proteins are classified as glycoproteins and mucoproteins.
f. Mucoproteins are carbohydrate-protein complexes e.g. mucin of saliva and heparin of blood.
g. Lipoproteins are lipid-protein complexes e.g. conjugate protein found in brain, plasma membrane, milk etc. Importance: They are involved in structural components of cell membranes and organelles.
They also act as a transporter.
Some conjugated proteins are important in electron transport chain in respiration.
3. Derived proteins:
a. These proteins are not found in nature as such.
b. These proteins are derived from native protein molecules on hydrolysis.
c. Metaproteins, peptones are derived proteins.
Importance: They act as a precursor for many molecules which are essential for life.
Question (F)
What are enzymes? How are they classified? Mention example of each class.
Answer:
1. Enzymes are biological macromolecules which act as a catalyst and accelerates the reaction in the body.
2. Enzymes are classified into six classes:
a. Oxidoreductases: These enzymes catalyze oxidation and reduction reactions by the transfer of hydrogen and/or oxygen, e.g. alcohol dehydrogenase
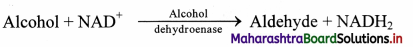
b. Transferases: These enzymes catalyse the transfer of certain groups between two molecules, e.g. glucokinase
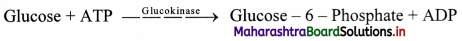
c. Hydrolases: These enzymes catalyse hydrolytic reactions. This class includes amylases, proteases, lipases etc. e.g. Sucrase

d. Lyases: These enzymes are involved in elimination reactions resulting in the removal of a group of atoms from substrate molecule to leave a double bond. It includes aldolases, decarboxylases, and dehydratases, e.g. fumarate hydratase.
e. Isomerases: These enzymes catalyze structural rearrangements within a molecule. Their nomenclature is based on the type of isomerism. Thus, these enzymes are identified as racemases, epimerases, isomerases, mutases, e.g. xylose isomerase.
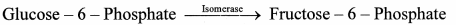
f. Ligases or Synthetases: These are the enzymes which catalyze the covalent linkage of the molecules utilizing the energy obtained from hydrolysis of an energy-rich compound like ATP, GTP e.g. glutathione synthetase, Pyruvate carboxylase.


Question (G)
Explain the properties of enzyme? Describe the models for enzyme actions.
Answer:
1. Proteinaceous Nature:
All enzymes are basically made up of protein.
2. Three-Dimensional conformation:
a. All enzymes have specific 3-dimensional conformation.
b. They have one or more active sites to which substrate (reactant) combines.
c. The points of active site where the substrate joins with the enzyme is called substrate binding site.
3. Catalytic property:
a. Enzymes are like inorganic catalysts and influence the speed of biochemical reactions but themselves remain unchanged.
b. After completion of the reaction and release of the product they remain active to catalyze again.
c. A small quantity of enzymes can catalyze the transformation of a very large quantity of the substrate
into an end product.
d. For example, sucrase can hydrolyze 100000 times of sucrose as compared with its own weight.
4. Specificity of action:
a. The ability of an enzyme to catalyze one specific reaction and essentially no other is perhaps its most significant property. Each enzyme acts upon a specific substrate or a specific group of substrates.
b. Enzymes are very sensitive to temperature and pH.
c. Each enzyme exhibits its highest activity at a specific pH i.e. optimum pH.
d. Any increase or decrease in pH causes decline in enzyme activity e.g. enzyme pepsin (secreted in stomach)shows highest activity at an optimum pH of 2 (acidic)
5. Temperature:
a. Enzymes are destroyed at higher temperature of 60-70°C or below, they are not destroyed but become inactive.
b. This inactive state is temporary and the enzyme can become active at suitable temperature.
c. Most of the enzymes work at an optimum temperature between 20°C and 35°C.
There are two types of models:
1. Lock and Key model:
a. Lock and Key model was first postulated in 1894 by Emil Fischer.
b. This model explains the specific action of an enzyme with a single substrate.
c. In this model, lock is the enzyme and key is the substrate.
d. The correctly sized key (substrate) fits into the key hole (active site) of the lock (enzyme).
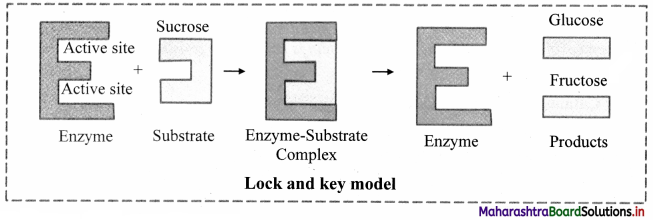
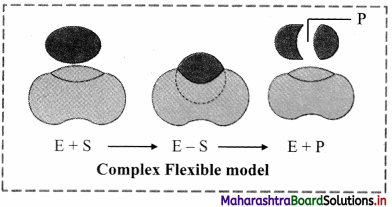
2. Induced Fit model (Flexible Model):
a. Induced Fit model was first proposed in 1959 by Koshland.
b. This model states that approach of a substrate induces a conformational change in the enzyme.
c. It is the more accepted model to understand mode of action of enzyme.
d. The induced fit model shows that enzymes are rather flexible structures in which the active site continually reshapes by its interactions with the substrate until the time the substrate is completely bound to it.
e. It is also the point at which the final form and shape of the enzyme is determined.
[Note: Temperature is a factor affecting enzyme activity and not a property of enzyme.]

Question (H)
Describe the factors affecting enzyme action.
Answer:
The factors affecting the enzyme activity are as follows:
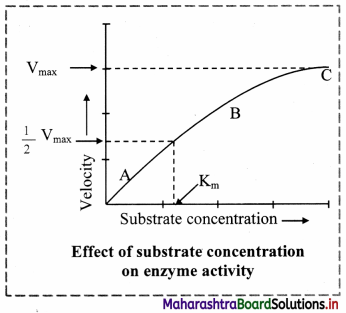
1. Concentration of substrate:
a. Increase in the substrate concentration gradually increases the velocity of enzyme activity within the limited range of substrate levels.
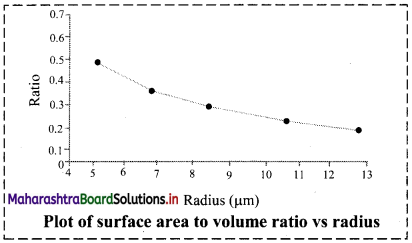
b. A rectangular hyperbola is obtained when velocity is plotted against the substrate concentration.
c. Three distinct phases (A, B and C) of the reaction are observed in the graph.
Where V = Measured velocity, Vmax = Maximum velocity, S = Substrate concentration,
Km = Michaelis-Menten constant.
d. Km or the Michaelis-Menten constant is defined as the substrate concentration (expressed in moles/lit) to produce half of maximum velocity in an enzyme catalyzed reaction.
e. It indicates that half of the enzyme molecules (i.e. 50%) are bound with the substrate molecules when the substrate concentration equals the Km value.
f. Km value is a constant and a characteristic feature of a given enzyme.
g. It is a representative for measuring the strength of ES complex.
h. A low Km value indicates a strong affinity between enzyme and substrate, whereas a high Km value reflects a weak affinity between them.
1. For majority of enzymes, the Km values are in the range of 10-5 to 10-2 moles.
2. Enzyme Concentration:
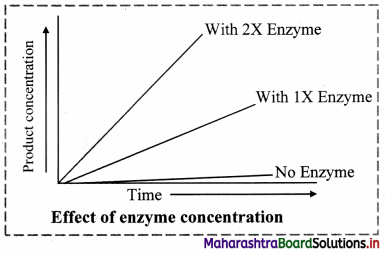
a. The rate of an enzymatic reaction is directly proportional to the concentration of the substrate.
b. The rate of reaction is also directly proportional to the square root of the concentration of enzymes.
c. It means that the rate of reaction also increases with the increasing concentration of enzyme and the rate of reaction can also decrease by decreasing the concentration of enzyme.
3. Temperature:
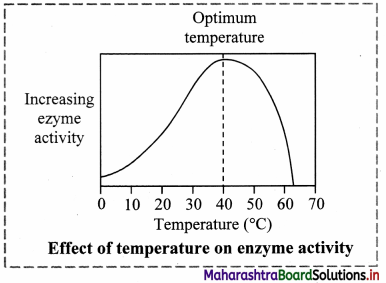
a. The temperature at which the enzymes show maximum activity is called Optimum temperature.
b. The rate of chemical reaction is increased by a rise in temperature but this is true only over a limited range of temperature.
c. Enzymes rapidly denature at temperature above 40°C.
d. The activity of enzymes is reduced at low temperature.
e. The enzymatic reaction occurs best at or around 37°C which is the average normal body temperature in homeotherms.
4. Effect of pH:
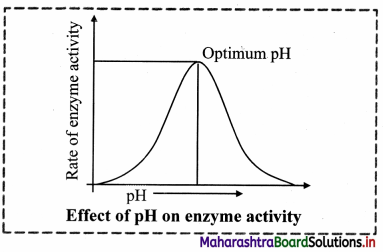
a. The pH at which an enzyme catalyzes the reaction at the maximum rate is known as optimum pH.
b. The enzyme cannot perform its function beyond the range of its pH value.
5. Other substances:
a. The enzyme action is also increased or decreased in the presence of some other substances such as co-enzymes, activators and inhibitors.
b. Most of the enzymes are combination of a co-enzyme and an apo-enzyme.
c. Activators are the inorganic substances which increase the enzyme activity.
d. Inhibitor is the substance which reduces the enzyme activity.

Question (I)
What are the types of RNA? Mention the role of each class of RNA.
Answer:
There are three types of cellular RNAs:
1. messenger RNA (mRNA),
2. ribosomal RNA (rRNA),
3. transfer RNA (tRNA). ‘
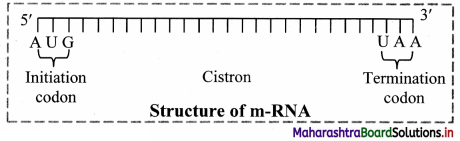
1. Messenger RNA (mRNA):
a. It is a linear polynucleotide.
b. It accounts 3% of cellular RNA.
c. Its molecular weight is several million. , d. mRNA molecule carrying information to form a complete polypeptide chain is called cistron.
e. Size of mRNA is related to the size of message it contains.
f. Synthesis of mRNA begins at 5’ end of DNA strand and terminates at 3’ end.
Role of messenger RNA:
It carries genetic information from DNA to ribosomes, which are the sites of protein synthesis.
2. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA):
a. rRNA was discovered by Kurland in 1960.
b. It forms 50-60% part of ribosomes.
c. It accounts 80-90% of the cellular RNA.
d. It is synthesized in nucleus.
e. It gets coiled at various places due to intrachain complementary base pairing.
Role of ribosomal RNA: It provides proper binding site for m-RNA during protein synthesis.
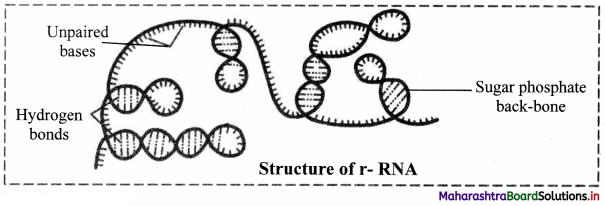
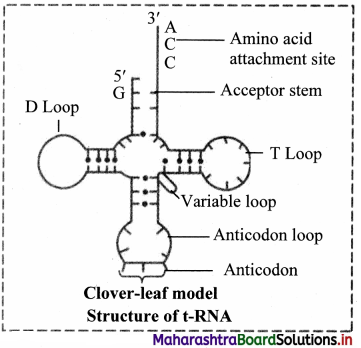
3. Transfer RNA (tRNA):
a. These molecules are much smaller consisting of 70-80 nucleotides.
b. Due to presence of complementary base pairing at various places, it is shaped like clover-leaf.
c. Each tRNA can pick up particular amino acid.
d. Following four parts can be recognized on tRNA
1. DHU arm (Dihydroxyuracil loop/ amino acid recognition site
2. Amino acid binding site
3. Anticodon loop / codon recognition site
4. Ribosome recognition site.
e. In the anticodon loop of tRNA, three unpaired nucleotides are present called as anticodon which pair with codon present on mRNA.
f. The specific amino acids are attached at the 3′ end in acceptor stem of clover leaf of tRNA.
Role of transfer RNA: It helps in elongation of polypeptide chain during the process called translation.
Question (J)
What is metabolism? How metabolic pool is formed in the cell.
Answer:
- Metabolism is the sum of the chemical reactions that take place within each cell of a living organism and provide energy for vital processes and for synthesizing new’ organic material.
- Metabolic pool in the cell is formed due to glycolysis and Krebs cycle.
- The catabolic chemical reaction of glycolysis and Krebs cycle provides ATP and biomolecules. These biomolecules form the metabolic pool of the cell.
- These biomolecules can be utilized for synthesis of many important cellular components.
- The metabolites can be added or withdrawn from the pool according to the need of the cell.

Question 6.
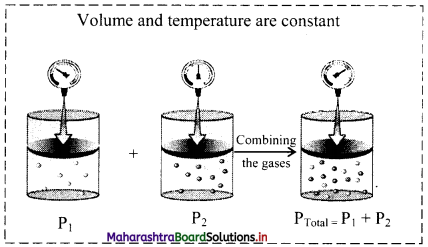
If double stranded DNA has 14% C (cytosine) what percent A (adenine), T (thymine) and G (guanine) would you expect?
Answer:
A purine always pairs with pyrimidine.
Adenine pairs with thymine and cytosine pairs with guanine.
Therefore, as per the given data If cytosine = 14% then guanine = 14%.
According to Chargaff s rule,
(C+G) = 14+ 14 = 28%
Therefore, (A+T) = 72%
So, A= 36%, T= 36%, G = 14%.
Question 7.
Name
1. The reagent used for testing for reducing sugar.
2. The form in which carbohydrate is transported in a plant.
3. The term that describes all the chemical reactions taking place in an organism.
Answer:
1. Benedict’s reagent
2. Sucrose
3. Metabolism
Practical / Project:
Question 1.
Perform an experiment to study starch granules isolated from potato.
Answer:
Isolation of starch granules from potato:
- Peal the potato with a clean knife.
- Grind the potato till the homogenous mixture is formed.
- Then strain the mixture through a cheese cloth into a beaker.
- Keep it standing for some time.
- Throw the supernatant and fill the beaker containing starch with water.
- Stir it well and again allow the starch to settle.
- After sometime, again through the supernatant.
- Repeat this for 2-3 times.
- Collect the white starch in the watch glass and keep it in the oven for drying.
To study the isolated starch granules:
1. Examination under microscope:
Examine starch granules under microscope by using a mixture of equal volumes of glycerol and distilled water.
Result: The potato starch granules appears transparent granules. They are irregularly shaped.
2. Using Iodine solution:
Boil a little amount of starch with water. Cool it. Add iodine solution to it.
Result: The solution changes colour to blue. This indicates the presence of starch.
Question 2.
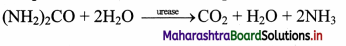
Study the action of enzyme urease on urea.
Answer:
Urease is an enzyme which exists in a dimer form. It has two active sites which are highly specific and only bind to urea or hydroxy urea. The active sites of urease contain nickel atoms. Urease catalyzes the hydrolysis of substrate urea into carbon dioxide and ammonia. It attacks the nitrogen and carbon bond in amide compounds and forms alkaline product like ammonia.
11th Biology Digest Chapter 6 Biomolecules Intext Questions and Answers
Can you recall? (Textbook Page No. 59)
(i) Which are different cell components?
Answer:
a. The three main components of any cell are: Cell membrane, Cytoplasm, Nucleus.
b. The components present in both plant and animal cells are: Endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, golgi apparatus, lysosomes, mitochondria, vacuoles.
c. The components present in plant cell and not in animal cell: Cell wall and plastids.
d. The components present in animal cell and not in plant cell: Cilia and flagella.

(ii) What is the role of each component of cell?
Answer:
The role of each component of a cell is as follows:
a. Cell membrane: Cell membrane separates the cytoplasmic contents from external environment.
b. Cytoplasm: Site for metabolic activities and organelles.
c. Nucleus: It is the control center of the cell. Genetic material is present in the nucleus.
d. Endoplasmic reticulum: It produces, processes and transports proteins and lipids.
e. Ribosomes: Ribosome is the site for protein synthesis.
f. Golgi apparatus: It is involved in modifying, sorting and packing of proteins for secretion. It also transports lipids around the cell.
g. Lysosomes: It is involved in digestion of worn out organelles and waste removal.
h. Mitochondria: It is responsible for production of energy.
i. Vacuoles: It has various functions like storage, waste disposal, protection and growth.
j. Cell wall: It provides strength and support to the cell.
k. Plastids: They are responsible for production and storage of food. It also contains photosynthetic pigments (Chloroplasts).
l. Cilia and flagella: Help in motility.
Can you tell? (Textbook Page No. 62)
What are carbohydrates?
Answer:
- The word carbohydrates mean ‘hydrates of carbon’.
- They are also called saccharides.
- They are biomolecules made from just three elements: carbon, hydrogen and oxygen with the general formula Cx(H20)y.
- They contain hydrogen and oxygen in the same ratio as in water (2:1).
- Carbohydrates can be broken down (oxidized) to release energy.
Can you tell? (Textbook Page No. 62)
(i) Enlist the natural sources, structural units and functions of the following polysaccharides.
a. Starch
b. Cellulose
c. Glycogen
Answer:
a. Starch:
1. Natural Sources: Cereals (wheat, maize, rice), root vegetables (potato, cassava etc.)
2. Structural units: Starch consist of two types of molecules – Amylose and amylopectin.
3. Functions: It acts as a reserve food and supply energy.
b. Cellulose:
1. Natural sources: Plant fibers (cotton, flax, hemp, jute, etc.), wood.
2. Structural units: It is made from p glucose molecules.
3. Functions: It in a major component of cell wall. It provides structural support.
c. Glycogen:
1. Natural sources: Fruits, starchy vegetables, whole grain foods.
2. Structural units: It consists of linear chains of glucose residues. The glucose is linked linearly by a (1 → 4) glycosidic bonds and branches are linked to the linear chain by a (1 → 6) glycosidic bonds.
3. Functions: It is stored in liver and muscles and it readily provides energy when the blood glucose level decreases.

(ii) The exoskeleton of insects is made up of chitin. This is a ________.
(A) mucoprotein
(B) lipid
(C) lipoprotein
(D) polysaccharide
Answer:
polysaccharide
(iii) List names of structural polysaccharides.
Answer:
Arabinoxylans, cellulose, chitin, pectin.
(iv) Write a note on oligosaccharide and glycosidic bond.
Answer:
Oligosaccharides:
a. A carbohydrate polymer comprising of two to six monosaccharide molecules is called oligosaccharide.
b. They are linked together by glycosidic bond.
c. They are classified on the basis of monosaccharide units:
Disaccharides: These are the sugars containing two monosaccharide units and can be further hydrolysed into smaller components. E.g.: Sucrose, maltose, lactose, etc.
Trisaccharides: These contain three monomers. E.g. Raffmose.
Tetrasaccharides: These contain four monomers. E.g.: Stachyose.
Glycosidic bond:
a. Glycosidic bond is a covalent bond that forms a linkage between two monosaccharides by a dehydration reaction.
b. It is formed when a hydroxyl group of one sugar reacts with the anomeric carbon of the other.
c. Glycosidic bonds are readily hydrolyzed by acid but resist cleavage by base.
d. There are two types of glycosidic bonds: a-glycosidic bond and P-glycosidic bond.
Can you tell? (Textbook Page No. 63)
What are lipids? Classify them and give at least one example of each.
Answer:
Lipids:
Lipids are a group of heterogeneous compounds like fats, oils, steroids, waxes, etc.
They are macro-biomolecules.
These are group of substances with greasy consistency with long hydrocarbon chain containing carbon, hydrogen and oxygen.
Lipids are classified into:
1. Saturated fatty acids: They contain single chain of carbon atoms with single bonds.
E.g. Palmitic acid, stearic acid
2. Unsaturated fatty acids: They contain one or more double bonds between the carbon atoms of the hydrocarbon chain.
a. Simple lipids: These are esters of fatty acids with various alcohols.
E.g. Fats, wax.
b. Compound lipids: These are ester of fatty acids containing other groups like phosphate (Phospholipids), sugar (glycolipids), etc.
E.g. Lecithin
c. Sterols: They are derived lipids. They are composed of fused hydrocarbon rings (steroid nucleus) and a long hydrocarbon side chain.
E.g. Cholesterol, phytosterols.

Find out (Textbook Page No. 63)
(i) Why do high cholesterol level in the blood cause heart diseases?
Answer:
a. When there is high level of cholesterol in the blood, the cholesterol builds up on the walls of arteries causing a condition called atherosclerosis (a form of heart disease).
b. Because of this the arteries are narrowed and the blood flow to the heart is slowed down.
c. The blood carries oxygen to the heart, but because of this condition enough blood and oxygen does not reach to the heart and causes heart diseases.
d. If the condition increases, the supply of oxygen and blood is completely cut off to the heart and this can lead to heart attack.
(ii) Polyunsaturated fatty acids are believed to decrease blood cholesterol level. How?
Answer:
a. The liver converts polyunsaturated fatty acids into ketones instead of cholesterol.
b. Therefore, polyunsaturated fatty acids are transported directly to tissues for oxidation without leaving behind any lipoprotein in the form of cholesterol as it is seen in the case of saturated fatty acids.
c. Thus, polyunsaturated fatty acids are believed to decrease blood cholesterol level.
Can you tell? (Textbook Page No. 64)
Which of the following is a simple protein?
(A) nucleoprotein
(B) mucoprotein
(C) chromoprotein
(D) globulin
Answer:
Globulin
Can you tell? Textbook Page No. 64)
What are conjugated proteins? How do they differ from simple ones? Give one example of each.
Answer:
1. Conjugated proteins consist of a simple protein attached with some non-protein substance. The non-protein group is called prosthetic group.
2. The conjugated protein functions in interaction with other chemical group whereas simple proteins contain only amino acids and no other chemical group attached to it.
3. Example of conjugated protein is haemoglobin. Globin is the protein and iron containing pigment and haem is the prosthetic group.
Can you tell? (Textbook Page No. 64)
All Proteins are made up of the same amino acids; then how proteins found in human beings and animals may be different from those of other?
Answer:
The proteins found in human beings and animals may be different from those of others because the ratio of amino acids present in the protein differs.

Can you tell? (Textbook Page No. 67)
What is a nucleotide? How is it formed? Mention the names of all nucleotides.
Answer:
1. Nucleotide is a unit which consists of a sugar, phosphate and a base. Nucleotides are basic units of nucleic acids.
2. The nitrogen base and a sugar form a nucleoside. In a nucleoside, nitrogenous base is attached to the first carbon atom (C-1) of the sugar and when a phosphate group gets attached with that of the carbon (C-5) atom of the sugar molecule a nucleotide molecule is formed.
3. The names of all nucleotides are:
| Base |
Nucleotides of RNA |
Nucleotides of DNA |
| Adenine |
Adenylate |
Deoxydenylate |
| Guanine |
Guanylate |
Deoxyguanylate |
| Cytosine |
Cytidylate |
Deoxy cytidylate |
| Thymine |
– |
Deoxythymidylate |
| Uracil |
Uridylate |
– |
Can you tell? (Textbook Page No. 67)
Describe the structure of DNA molecule as proposed by Watson and Crick.
Answer:
- According to Watson and Crick, DNA molecule consists of two strands twisted around each other in the form of a double helix.
- The two strands i.e. polynucleotide chains are supposed to be in opposite direction so end of one chain having 3′ lies beside the 5′ end of the other.
- One turn of the double helix of the DNA measures about 34A.
- It consists paired nucleotides and the distance between two neighboring pair nucleotides is 3.4A.
- The diameter of the DNA molecule has been found be 20A.
Can you tell (Textbook Page No. 70)
Name the chemical found in the living cell which has necessary message for the production of all enzymes required by it.
Answer:
DNA found in the nucleus of a living cell has necessary message for the production of all enzymes required by it. DNA forms mRNA through the process of transcription. This mRNA through the process of translation forms proteins.

Can you tell? (Textbook Page No. 67)
Difference between DNA and RNA is because of
(A) sugar and base
(B) sugar and phosphate
(C) phosphate and base
(D) sugar only
Answer:
Sugar and base
Can you tell? (Textbook Page No. 67)
Differentiate between DNA and RNA.
Answer:
| DNA |
RNA |
| 1. It is a genetic material of majority of the organisms. |
It is a genetic material only of some viruses. |
| 2. It is double stranded. |
It is single stranded. |
| 3. Deoxyribose sugar is present. |
Ribose sugar is present. |
| 4. Nitrogen bases like Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, Thymine are present. |
Nitrogen bases like Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, Uracil are present. |
| 5. Specific base pairing is observed. |
Nitrogen bases do not form pair. |
| 6. Total number of purines is equal to total number of pyrimidine. Thus, purine to pyrimidine ratio is 1:1. |
Amount of purine and pyrimidine may or may not be equal. |
| 7. It is present in nucleus. |
It is present in nucleus and cytoplasm. |
| 8 It is responsible for determining hereditary characters and for formation of RNA. |
It takes part in protein synthesis. |
Can you tell? (Textbook Page No. 70)
Co-enzyme is ________
(A) often a metal
(B) often a vitamin
(C) always as organic molecule
(D) always an inorganic molecule
Answer:
Always as organic molecule

Can you tell? (Textbook Page No. 70)
(i) Which enzyme is needed to digest food reserve in castor seed?
(A) Amylase
(B) Diastase
(C) Lipase
(D) Protease
Answer:
Lipase
(ii) List the important properties of enzymes.
Answer:
a. Proteinaceous Nature
b. Three-Dimensional conformation
c. Catalytic property
d. Specificity of action
e. Temperature
Try this: (Textbook Page No. 70)
To demonstrate the effect of heat on the activities of inorganic catalysts and enzymes.
Answer:
1. Using MnO2 and Enzymes without any heat treatment:
Mn02 and cellular enzymes (catalase/peroxidase) causes breakdown of H202 and evolution of oxygen.
2. Using Mn02 and Enzymes after heat treatment:
Oxygen evolves in the H202 solution containing boiled and cooled Mn02. But oxygen does not evolve in the tube containing the enzyme.
3. This confirms that heat affects the enzyme and inactivates it whereas heat does not have any effect on inorganic catalyst.
11th Std Biology Questions And Answers:
![]()
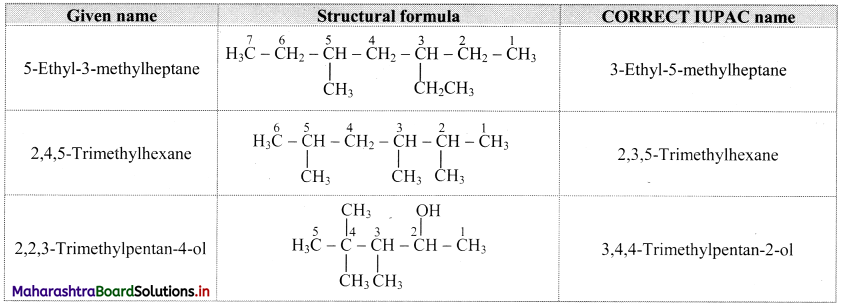
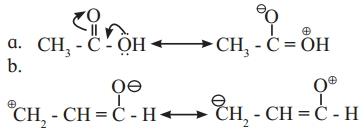
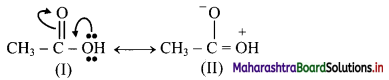
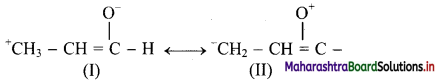
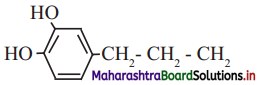
 ,
, ,
,![]()
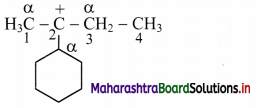
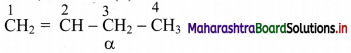
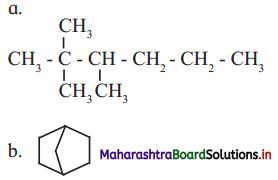
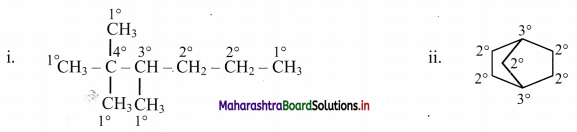
![]()

![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
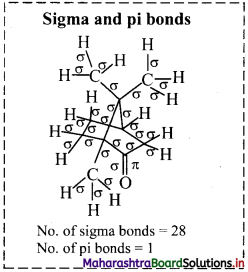

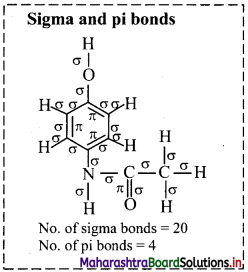
![]()
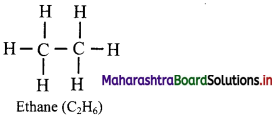
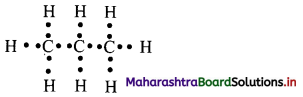
![]()


![]()
![]()















 Answer:
Answer:



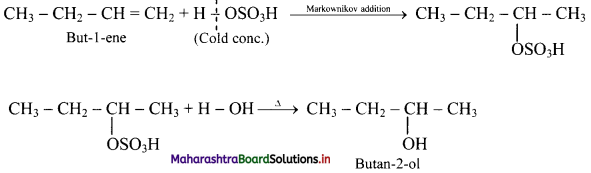
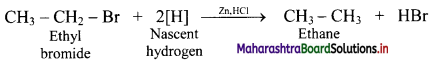
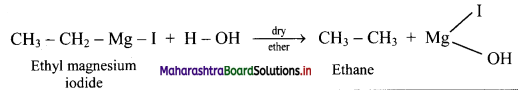
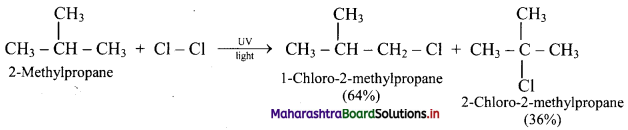
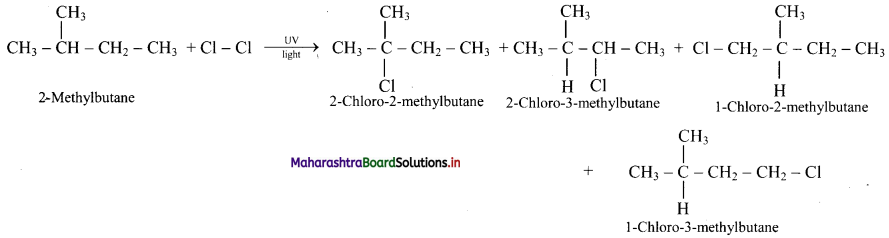
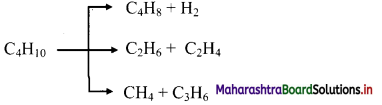
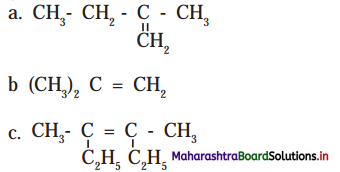
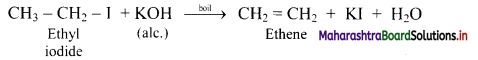
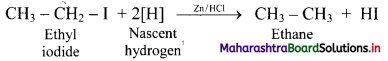
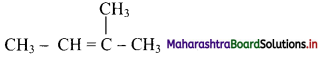
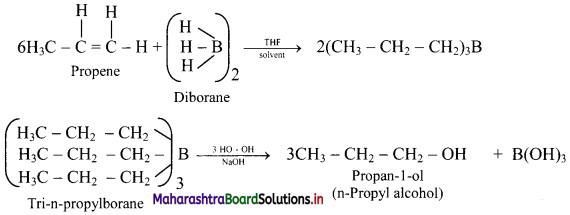
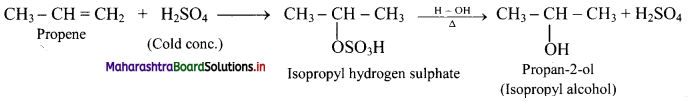
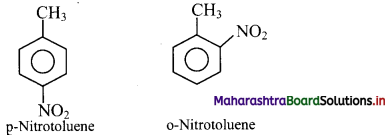
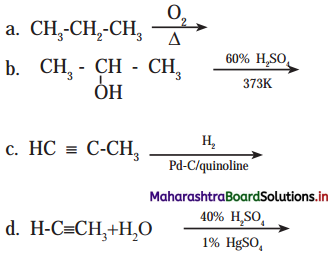
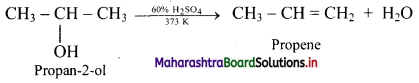
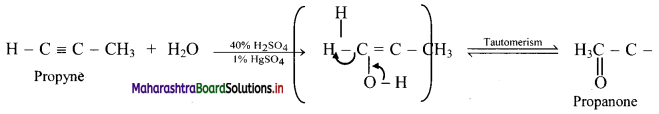



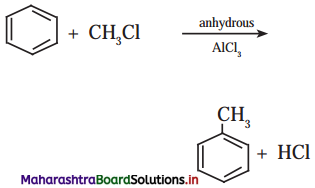
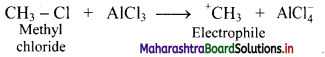


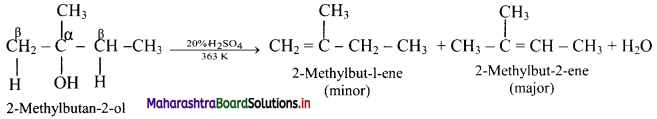
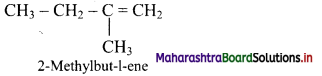
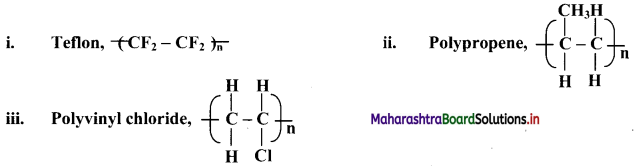
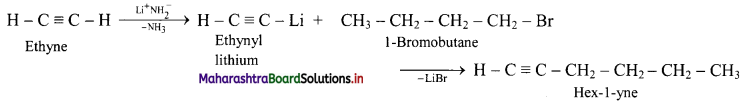

 Answer:
Answer: