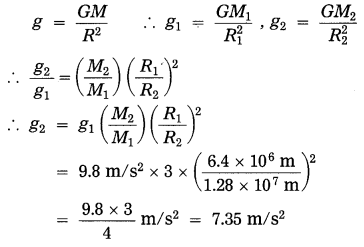
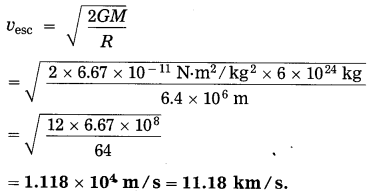
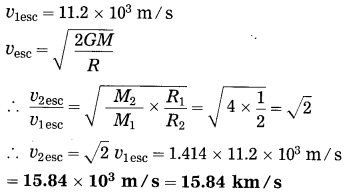
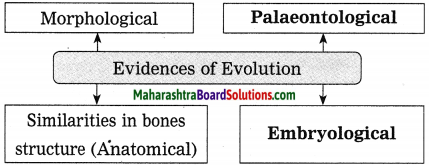
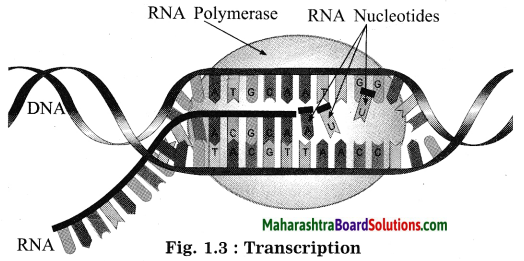
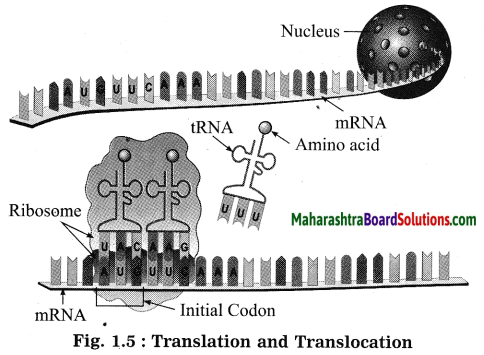
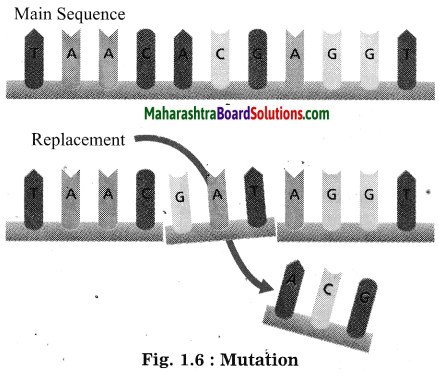
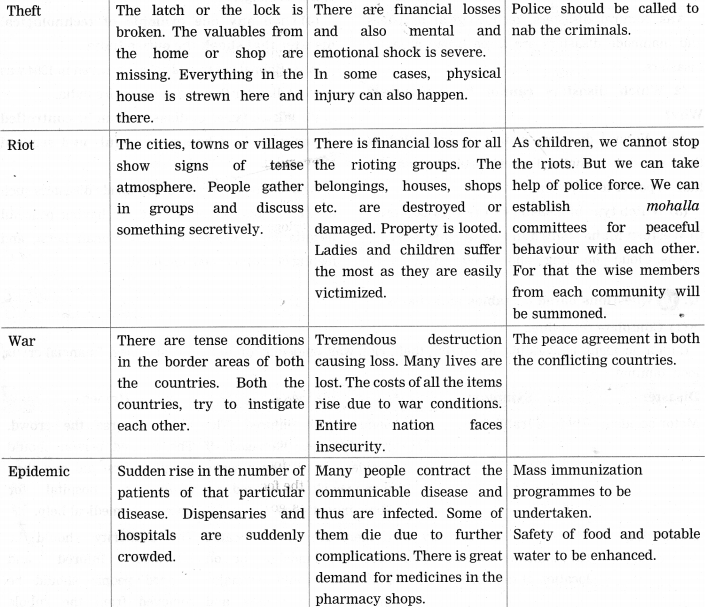
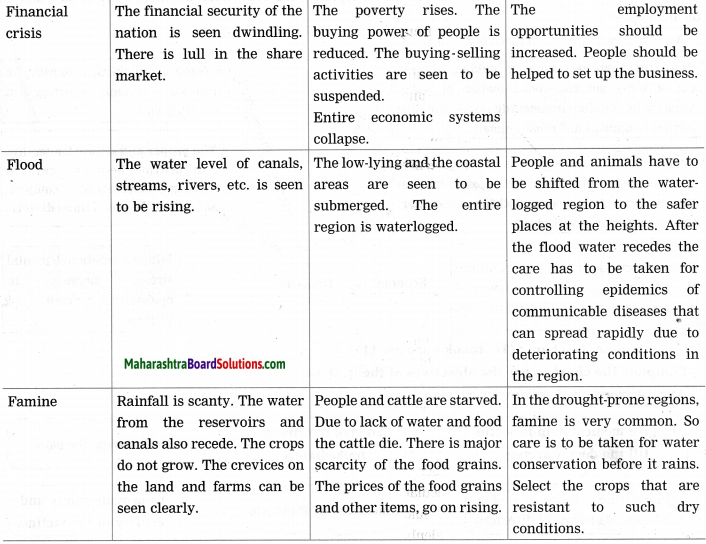
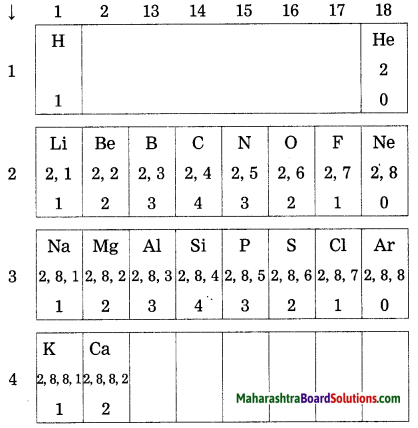
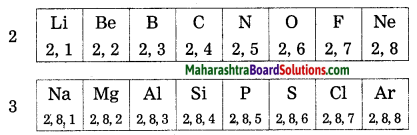
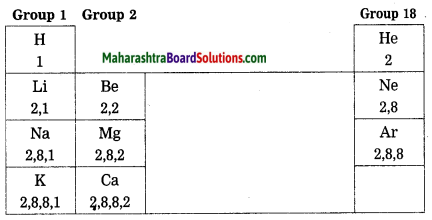
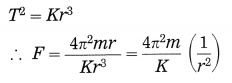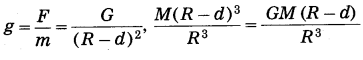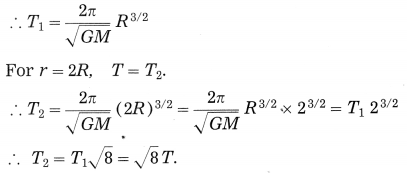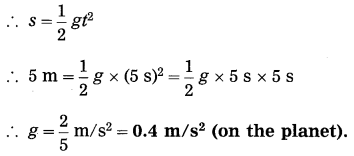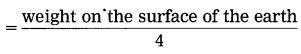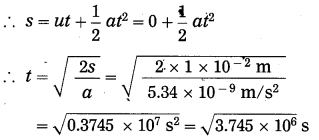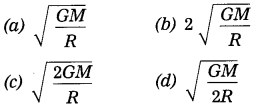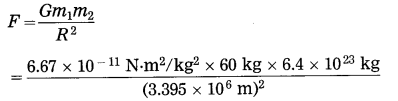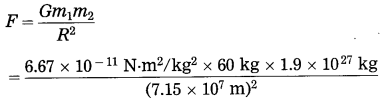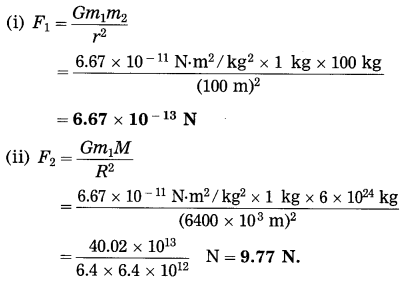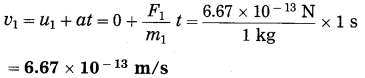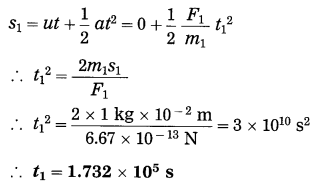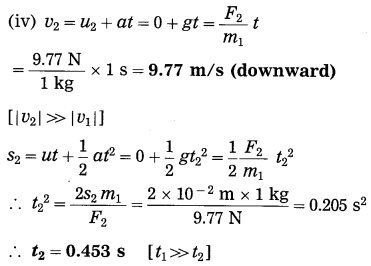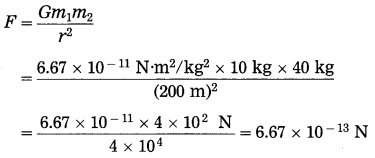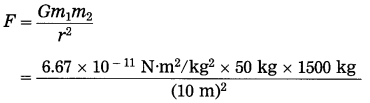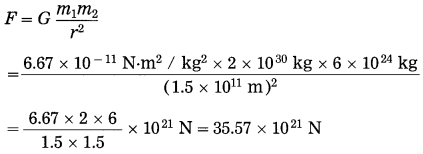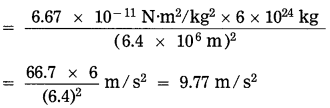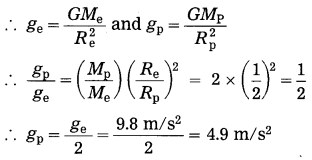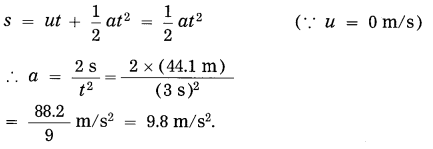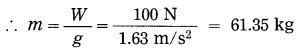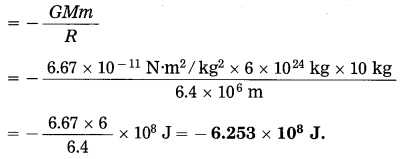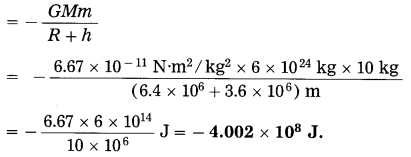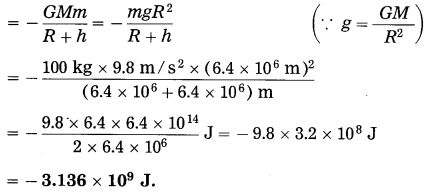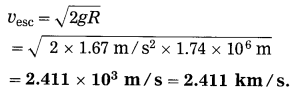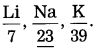Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 10 Science Solutions Part 2 Chapter 7 Introduction to Microbiology Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Std 10 Science Part 2 Chapter 7 Introduction to Microbiology Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Class 10 Science Part 2 Chapter 7 Introduction to Microbiology Question Answer Maharashtra Board
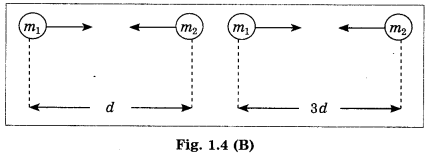
Question 1.
Rewrite the following statements using correct of the options and explain the completed statements.
(gluconic acid, coagulation, amino acid, 4% acetic acid, clostridium, lactobacilli)
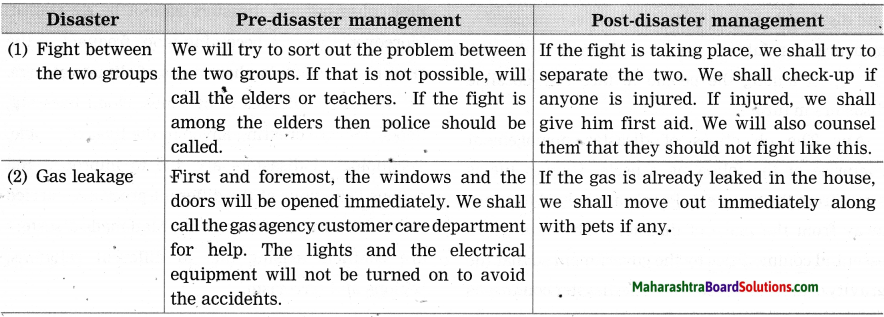
a. Process of ……. of milk proteins occurs due to lactic acid.
Answer:
Process of Coagulation of milk proteins occurs due to lactic acid.
Explanation: The lactobacilli are the bacteria carrying out fermentation of the milk. In this process, the lactose sugar in the milk is converted into lactic acid. This lactic acid causes coagulation of the proteins present in the milk.
b. Harmful bacteria like ………. in the intestine are destroyed due to probiotics.
Answer:
Harmful bacteria like Clostridium in the intestine are destroyed due to probiotics.
Explanation: In probiotics, there are lactobacilli which are useful. They control other bacteria present in the alimentary canal and also their metabolism. These bacteria thus stop the action of Clostridium which is a harmful bacteria.
c. Chemically, vinegar is …………
Answer:
Chemically, vinegar is 4% Acetic acid.
Explanation: Chemically vinegar is 4% acetic acid. It is a good preservative of the food and thus while using it as additive to the food, it is called vinegar.
d. Salts which can be used as supplement of calcium and iron are obtained from ……………. acid.
Answer:
Salts which can be used as supplement of calcium and iron are obtained from Gluconic acid.
Explanation: The microbe Aspergillus niger is used on the source material of glucose and corn steep liquor to produce amino acid called Gluconic acid. Gluconic acid is used for the production of minerals used as supplement for calcium and iron.
![]()
Question 2.
Match the pairs.
| ‘A’ group | ‘B’ group |
| (1) Xylitol | (a) Pigment |
| (2) Citric acid | (b) To impart sweetness |
| (3) Lycopene | (c) Microbial restrictor |
| (4) Nycin | (d) Protein binding emulsifier |
| (e) To impart acidity |
[Note: In examination match the column question will ham 2 components in Column ‘A’ with 4 alternatives in Column ‘B’.]
Answer:
(1) Xylitol – To impart sweetness
(2) Citric acid – To impart acidity
(3) Lycopene – Pigment
(4) Nycin – Microbial restrictor.
Question 3.
Answer the following:
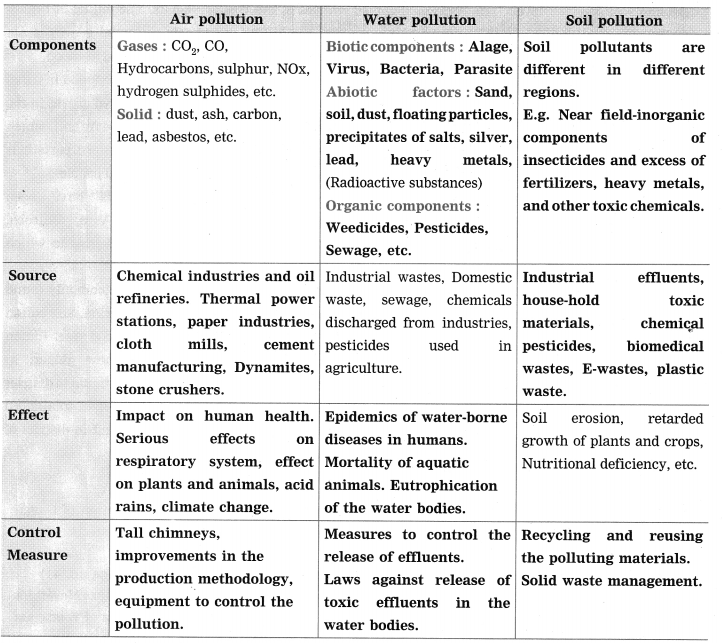
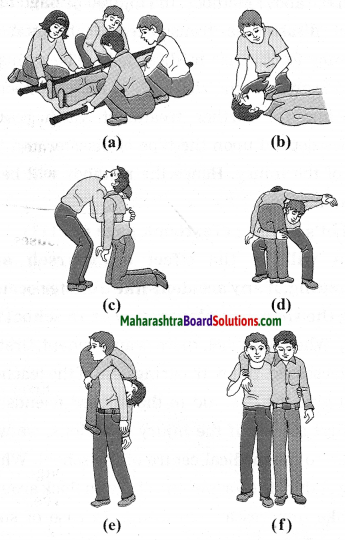
a. Which fuels can be obtained by microbial processes? Why is it necessary to increase the use of such fuels?
Answer:
- Microbial anaerobic decomposition of urban agricultural and industrial waste forms the gaseous fuel in the form of methane gas.
- Alcohol is another clean form of energy which is used in the form of ethanol. It is obtained by the fermentation of molasses by treating it with Saccharomyces-yeast.
- By photoreduction of water with the help of bacteria, hydrogen gas is released in the process of bio-photolysis of water. This hydrogen gas is said to be the fuel of the future.
- The conventional fuels are exhaustible. After few hundred years, they will be over completely. Moreover, these fossil fuels cause lot of air pollution due to emission of carbon dioxide. The fuels obtained by the microbial processes are not polluting. Therefore, it is necessary to increase the use of eco-friendly fuels.
b. How can the oil spills of rivers and oceans be cleaned?
Answer:
- The oil spills in rivers or oceans are caused by crude oil or petroleum hydrocarbons.
- This crude oil is highly toxic to the flora and fauna of the aquatic environment.
- By using mechanical means the oil spill can be removed, but this is very difficult.
- The biological way to remove this pollution is done by using culture of microbes like Pseudomonas spp. and Alcanovorax borkumensis.
- They have the ability to destroy the pyridines and other chemicals present in the hydrocarbons.
- These bacteria are called as hydrocarbono-clastic bacteria (HCB) which decompose the hydrocarbons and bring about the reaction of carbon with oxygen.
- In the process CO2 and water are formed. In this way the oil spills are cleaned, by releasing HCB at the place of oil spills.
c. How can the soil polluted by acid rain be made fertile again?
Answer:
- The soil polluted by the acid rain is made fertile again by using bacteria.
- Acidophillium spp. and Acidobacillus ferroxidens are the bacteria which have the capacity to use sulphuric acid as their energy source.
- Since this sulphuric acid present in the acid rain, can be controlled by these bacteria.
- In this way, bacteria can control the soil pollution occurring due to acid rain, making the soil fertile again.
d. Explain the importance of bio pesticides in organic farming.
Answer:
- By using bio pesticides, soil pollution is minimized. Otherwise by using chemical pesticides and fertilizers there is large scale soil pollution.
- When chemical pesticides are used in agriculture, there is contamination of soil by fluoroacetamide – like chemicals.
- These are harmful to other plants, animals as well as for-human beings. They may cause skin diseases in humans.
- By using bacterial and fungal toxins the pests and pathogens can be destroyed. Such toxins are directly incorporated in the plant materials.
E.g. Spinosad is a biopesticide produced as a by-product of fermentation.
e. What are the reasons for increasing the popularity of probiotic products?
Answer:
- Probiotic substances are mostly milk products containing live bacteria. Such probiotics are very good for health.
- The useful colonies of bacteria are produced in the alimentary canal of human beings due to the probiotics.
- Probiotics decrease the population of harmful microbes like. Clostridium from our digestive tract.
- The immunity is enhanced due to regular intake of probiotics in the diet.
- The ill-effects of harmful substances formed during metabolic activities are reduced by the probiotics.
- If someone takes the antibiotic treatment, then his or her useful intestinal bacterial flora becomes inactive or is eradicated. In such cases, probiotics restore the bacterial flora and make the person well again.
All these facts have made probiotics a popular choice for people.
f. How the bread and other products produced using baker’s yeast are nutritious?
Answer:
- In order to make the bread the baker’s yeast – Saccharomyces cerevisiae is added to the flour for the fermentation process.
- In commercial bakery, compressed yeast is used while in domestic settings dry, granular form of yeast is used.
- The flour prepared by using commercial yeast contains various useful contents like carbohydrates, fats, proteins, various vitamins, and minerals.
- The anaerobic fermentation also increases the nutritive content of the flour.
- Due to this, bread and other products produced with the help of yeast become nutritive.
g. Which precautions are necessary for proper decomposition of domestic waste?
Answer:
The domestic waste should be properly segregated into biodegradable (wet waste) and non-biodegradable (dry waste). After segregation, these wastes should be stored separately into two different containers. The non-biodegradable substances should he either reused or sent for recycling. The biodegradable substances are decomposed naturally.
The decomposition process can be done at house-hold level too in a pot or a tank. This decomposition will yield a rich manure. The pot should be covered by a thin layer of soil and it should be kept in a dark but airy place.
The non-biodegradable things such as plastic articles, glass pieces, metal objects, unused 5 medicines, e-waste should never be thrown in wet wastes. The toxic substances and the insecticides if added to wet waste, will never allow the natural decomposition process. Therefore, only after taking proper precautions we can aim at proper decomposition of domestic wastes.
h. Why is it necessary to ban the use of plastic bags?
Answer:
Plastic is a non-biodegradable substance. It cannot be degraded back into its original constituents. It remains just like that for many hundreds of years. It causes solid waste pollution in any environment wherever it is thrown indiscriminately. If burnt, it releases very toxic gases. If dumped in landfills it obstructs the other decomposition processes.
If thrown in water bodies, it causes harm to aquatic life. Cattle graze on plastic unknowingly and are killed by it as it clogs inside their alimentary canal. The gutters and rain water drains get clogged due to plastic bags and this causes cities to submerge in water during heavy rains. Nowadays, the fishermen get more than half of plastic if they cast their net in the sea.
People use the plastic bags indiscriminately without any thought towards their environmental impact. There are better alternatives for plastic bags such as cloth bags which can be reused again and again. Therefore, it is absolutely necessary to ban the use of plastic bag.
![]()
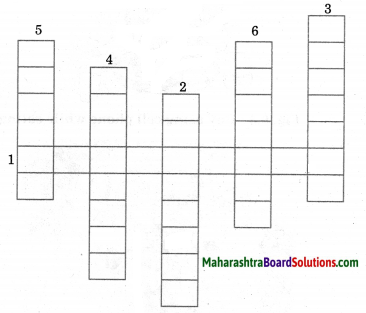
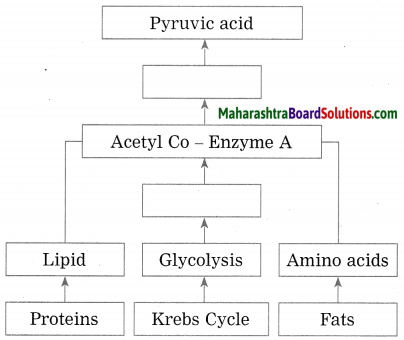
Question 4.
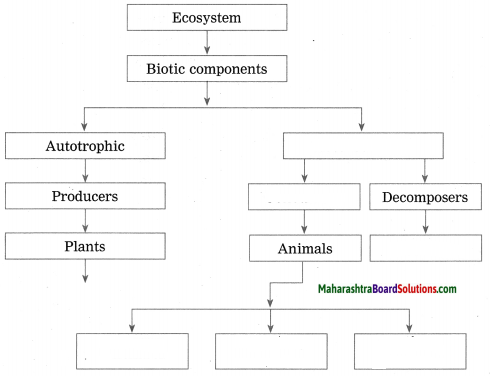
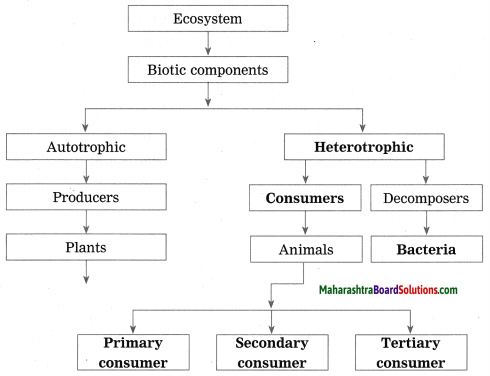
Complete the following conceptual picture.
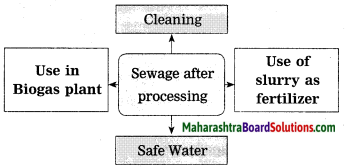
Answer:
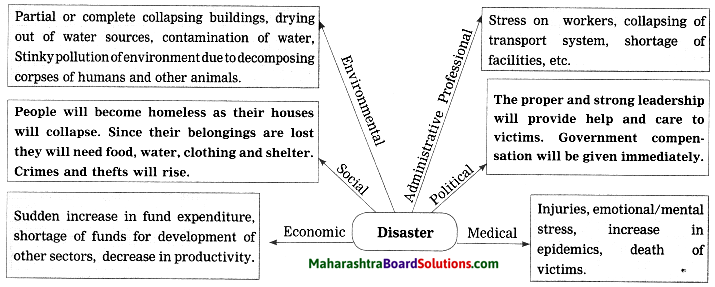
Question 5.
Give scientific reasons.
a. Use of mutant strains has been increased in industrial microbiology.
Answer:
- By using industrial microbiology, the commercial use of microbes is done.
- In such experiments, various economic, social and environment related processes and products are included.
- In this, fermentation processes are used to make bread, cheese, wines, enzymes, nutrients, etc.
- Different types of antibiotics are also made by using processes of industrial microbiology.
- In pollution control and solid waste management, the industrial microbiology becomes helpful.
- In farming too biotechnology is used to produce BT crops.
b. Enzymes obtained by microbial process are mixed with detergents.
Answer:
- When detergents are mixed with microbial enzymes, they start working more efficiently.
- The cleaning process takes place at lesser temperatures.
- Therefore, for better results, enzymes obtained by microbial process are mixed with detergents.
c. Microbial enzymes are used instead of chemical catalysts in chemical industry. (March 2019)
(OR)
Microbial enzymes are said to be eco-friendly.
Answer:
- Microbial enzymes are active at low temperature, pH and pressure.
- Due to this property, the energy is saved. The costlier erosion-proof instruments need not be used.
- In enzymatic reactions, the unnecessary byproducts are not formed as the reactions are highly specific.
- The expenses on purification of the product are minimized as no unnecessary products are formed.
- The elimination and decomposition of waste material is avoided and enzymes can be reused again. Hence, microbial enzymes which are eco¬friendly are used in chemical industry.
Question 6.
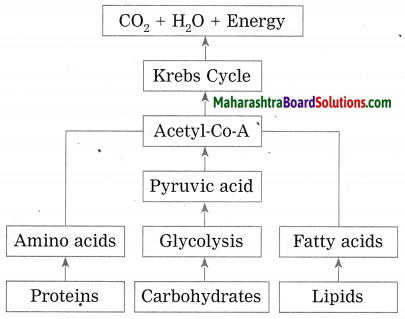
Complete the following conceptual picture with respect to its uses. (Board’s Model Activity Sheet)
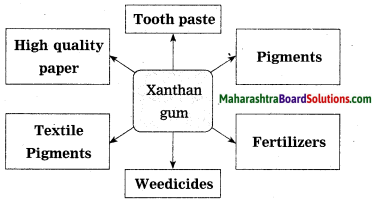
Answer:
Question 7.
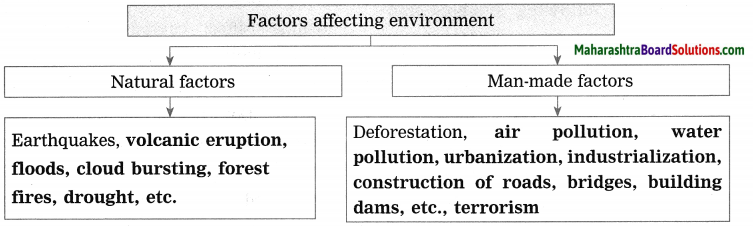
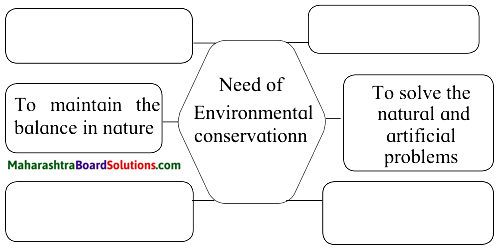
Complete the following conceptual picture related to environmental management.
Answer:
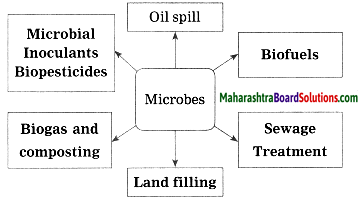
![]()
Question 8.
Answer the following questions.
a. What is the role of microbes in compost production?
Answer:
- Microbes can bring about natural decomposition of the organic compounds.
- During the biodegradation, some bacteria andmfungi bring about such decomposition and release the inorganic constituents back into the nature.
- Compost is formed in such a way by recycling process.
b. What are the benefits of mixing ethanol with petrol and diesel?
Answer:
When only diesel or petrol is used as fuel, there is increased air pollution. Morevoer, since these are non-renewable and exhaustible fuels, they will be finished in next some years. When petrol and diesel is mixed with ethanol, the proportion of CO2, CO, and hydrocarbons which are emitted in the atmosphere becomes lesser.
The particulate pollutants which otherwise are emitted through combustion of petrol and diesel are not formed when fuels are mixed with ethanol. By adding ethanol to the fuels, the cost of expensive petrol or diesel also becomes less. The ethanol burns more efficiently hence ethanol is mixed with petrol and diesel.
c. Which plants are cultivated to obtain the fuel?
Answer:
- The ethanol is obtained from wheat, maize, beet, sugarcane and molasses of sugarcane.
- For biodiesel, the soybean, rapeseed, jatropa, mahua, flaxseed, mustard, sunflower, palm, jute and some types of algae are cultivated.
d. Which fuels are obtained from biomass?
Answer:
From biomass, the biogas and biodiesel are mainly obtained. The biogas is obtained from dung of cattle. The fermentation of cattle dung gives rise to methane. From methane, methanol is obtained. Ethanol is obtained from molasses of sugarcane and some other crops. In some countries, special crops are cultivated for the biodiesel.
e. How does the bread become spongy?
Answer:
- When the dough for bread is prepared, the baker’s yeast – Saccharomyces cerevisiae is added to it.
- This yeast carries out anaerobic fermentation.
- This results in formation of CO2 and ethanol.
- The CO2 formed tries to escape out of the flour and thus the dough rise. When such dough is baked, it produces spongy bread.
Project: (Do it your self)
Project 1.
Find the ways to implement the zero garbage system at domestic level.
Project 2.
Which are the microbes that destroy the chemical pesticides in soil?
Project 3.
Collect more information about reasons for avoiding the use of chemical pesticides.
![]()
Can you recall? (Text Book Page No. 77)
Question 1.
Which different microbes are useful to us?
Answer:
Many microbes are useful to us, such as bacteria which are used for making curds from milk, yeast used to ferment the batter of bread, bacteria used for making other milk products, bacteria and fungi used for making antibiotics. The bacteria are even used for pollution control.
Question 2.
Which different products can he produced with the help of Microbes?
Answer:
Milk products, cheese, cocoa, pickles made from vegetables, wine and other beverages, bread, probiotic substances and cattle feed are produced with the help of microbes.
Use your brain power. (Text Book Page No. 79)
Question 1.
In the earlier class, you had prepared the solution of dry yeast for observation of yeast. Which substance is prepared by its use on commercial basis?
Answer:
The commercial production of bread and other bakery products need yeast. In wine and beer making also solution of yeast is required.
(Use your brain power. (Text Book Page No. 81)
Question 1.
Food materials like cold drinks, ice creams, cakes, juices are available in various colours and flavours. Whether these colours and flavours are really derived from fruits?
Answer:
The eatables can be made directly from fruits or essence of fruits. But most of the food products purchased from markets use these colours and flavours which are derived from synthetic chemicals.
Let’s Think: (Text Book Page No. 83)
Question .1
Why is it asked to segregate wet and dry waste in each home?
Answer:
The wet waste decomposes on its own as most of the matter therein is biodegradable. This waste can be converted into manure by composting. The dry waste can be picked up by the bhangarwala or kabadiwala. This waste can be reused or recycled. Therefore, if dry and wet wastes are kept separately, the solid waste management becomes much easier.
On the contrary if everything is dumped indiscriminately, it adds to the total volume of the solid wastes. This becomes unmanageable. Therefore, to reduce the problems of solid waste management, the dry and wet waste segregation must be done at every point source. This also could fetch wealth from waste.
Question 2.
What is done with the segregated waste?
Answer:
In big cities, there is a mechanism to pick up the solid waste every day or even twice a day at some places. The segregated garbage is taken by the municipal garbage trucks at the land filling sites. Here it is buried deep in the ground. The dry waste that can be reused or recycled, is sold to the recycling units.
![]()
Question 3.
Which is most appropriate method of disposal of dry waste?
Answer:
Reuse and recycle is the most appropriate method of disposal of dry waste.
Choose the correct alternative and write its alphabet against the sub-question number:
Question 1.
Enzyme ……….. obtained from fungi is used to produce vegetarian cheese.
(a) lipase
(b) protease
(c) amylase
(d) trypsin
Answer:
(b) protease
Question 2.
Milk is subjected to ………… at the beginning to destroy unwanted microbes.
(a) pasteurization
(b) fermentation
(c) coagulation
(d) decomposition
Answer:
(a) pasteurization
Question 3.
………….. like compounds are formed due to lactobacilli that gives characteristic taste to the yoghurt.
(a) Lactose
(b) Caesin
(c) Acetyldehyde
(d) All the above
Answer:
(c) Acetyldehyde
Question 4.
Methane can be obtained by …………. decomposition of urban agricultural and industrial waste.
(a) aerobic
(b) anaerobic
(c) microbial anaerobic
(d) chemical
Answer:
(c) microbial anaerobic
Question 5.
……….. gas is considered to be the fuel of future.
(a) Hydrogen
(b) Nitrogen
(c) Methane
(d) Butane
Answer:
(a) Hydrogen
Question 6.
………. are mixed with waste materials at land-filling sites for quicker decomposition.
(a) Microbes
(b) Bioreactors
(c) Fungi
(d) Worms
Answer:
(b) Bioreactors
Question 7.
…………. bacteria decompose the xenobiotic chemicals present in sewage.
(a) Hydrocarbonoclastic
(b) Decomposing
(c) E.coli
(d) Phenol oxidizing
Answer:
(d) Phenol oxidizing
![]()
Question 8.
Microbes are used for ………… of environment polluted due to sewage.
(a) protection
(b) conservation.
(c) bioremediaiion
(d) decomposition
Answer:
(c) bioremediaiion
Question 9.
……….. is a powerful antibiotic against tuberculosis.
(a) Streptomycin
(b) Tetracycline
(c) Rifamycin
(d) Bacitracin
Answer:
(c) Rifamycin
Question 10.
Bacteria are used to clear the oil spills are called ………….. bacteria.
(a) phenol oxidizing
(b) electrolytic
(c) hydrocarbonoclastic
(d) decomposing
Answer:
(c) hydrocarbonoclastic
Question 11.
………… convert these salts of uranium into insoluble salts.
(a) Saccharomyces
(b) Thiobacillus
(c) Acidobacillus
(d) Geobacter
Answer:
(d) Geobacter
Question 12.
………….., a byproduct of fermentation is a biopesticide.
(a) Fluoroacetamide
(b) Vanillin
(c) Aspertame
(d) Spinosad
Answer:
(d) Spinosad
Question 13.
…………. beverage is obtained by fermentation of apple juice. (July ’19)
(a) Cider
(b) Wine
(c) Coffee
(d) Cocoa
Answer:
(a) Cider
Question 14.
Vinegar is the chemically ………… acid. (Board’s Model Activity Sheet)
(a) Citric
(b) Gluconic
(c) Glutamic
(d) Acetic
Answer:
(d) Acetic
Question 15.
In which of the following industries microbial enzymes are not used?
(a) Glass industry
(b) Cheese industry
(c) Tanning industry
(d) Paper industry
Answer:
(a) Glass industry
![]()
Question 16.
Citric acid used in production of beverages, toffees, chocolates is obtained by fermentation of …….. by Aspergillus niger.
(a) grapes
(b) sugar molasses
(c) apple
(d) coffee nuts
Answer:
(b) sugar molasses
Match the pairs:
Question 1.
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| (1) Vinegar | (a) Polylactic acid |
| (2) Xanthan gum | (b) Molasses |
| (c) Icecreams and puddings | |
| (d) Acetic acid |
Answer:
(1) Vinegar – Acetic acid
(2) Xanthan gum – Icecreams and puddings
Find the odd one out:
Question 1.
Lactobacillus acidophilus, Lactobacillus casei, Bifidobacterium bifidum, Streptococcus thermophilus
Answer:
Streptococcus thermophilus. (All others are bacteria producing probiotics.)
Question 2.
Lactobacillus lactis, Bifidobacterium bifidtim, Lactobacillus cremoris, Streptococcus thermophilus
Answer:
Bifidobacterium bifidum. (All others are bacteria used in cheese production.)
Question 3.
Dark chocolate, Miso soup, Wafers, Corn syrup
Answer:
Wafers. (All others are probiotic products.)
Question 4.
Vinegar, Soya sauce, Ketchup, Monosodium glutamate
Answer:
Ketchup. (All others are products prepared by microbial fermentation.)
Question 5.
Actinomycetes, Streptomyces, Nocardia, yeast
Answer:
Yeast. (All others have ability of decomposing rubber from garbage.)
![]()
Find the correlation:
Question 1.
Bread Baker’s yeast : : Soya sauce : ……….
Answer:
Bread Baker’s yeast : : Soya sauce : Aspergillus oryzae
Question 2.
Coffee : Caffea arabica : : Cocoa : …………
Answer:
Coffee : Coffea arabica : : Cocoa : Theobroma cacao
Question 3.
Oil slick : Alcanovorax : Rubber from garbage : …………
Answer:
Oil slick : Alcanovorax : Rubber from garbage : Actinomycetes
Question 4.
Conversion of metals into comounds : Thiobacilli : : Conversion of uranium salts …………
Answer:
Conversion of metals into comounds : Thiobacilli : : Conversion of uranium salts Geobacter.
Name the following:
Question 1.
Microbial enzymes.
Answer:
Oxidoreductases, transferases, hydrolases, lyases, isomerases, ligases.
Question 2.
Emulsifiers.
Answer:
Polysaccharides and glycolipids.
Question 3.
Microbe used in preparation of wine and cider.
Answer:
Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
Question 4.
Effective antibiotic against tuberculosis.
Answer:
Rifamycin.
Question 5.
Antibiotics.
Answer:
Penicillin, cephalosporins, monobactam, erythromycin, gentamycin, neomycin, streptomycin, tetracyclins, vancomycin.
![]()
Question 6.
Bacteria that use sulphuric acid as source of energy.
Answer:
Acidobacillus ferroxidens, Acidophillium spp.
Question 7.
Substance that makes biodegradable plastic.
Answer:
Polylactic acid.
Question 8.
Curd like food product made from sheep milk.
Answer:
Kefir.
Question 9.
Enzyme used to make vegetarian cheese.
Answer:
Protease.
Question 10.
Fungus used for making soya sauce.
Answer:
Aspergillus oryzae.
Complete the charts:
Question 1.
| Fruit | Microbe used | Name of beverage |
| ___________________________ | ___________________________ | Coffee |
| Theobroma cacao | Candida, Hansenula, Pichia, Saccharomyces | ___________________________ |
| Grapes | ___________________________ | ___________________________ |
| Apple | Saccharomyces cerevisiae | ___________________________ |
Answer:
| Fruit | Microbe used | Name of beverage |
| Caffea arabica | Lactobacillus brevis | Coffee |
| Theobroma cacao | Candida, Hansenula, Pichia, Saccharomyces | Cocoa |
| Grapes | Saccharomyces cerevisiae | Wine |
| Apple | Saccharomyces cerevisiae | Cider |
![]()
Question 2.
| Source | Microbe | Amino acid | Use |
| Sugar and beet molasses, ammonia salt | ___________________ | ___________________ | Production of monosodium glutamate (Ajinomoto). |
| ___________________ | Aspergillus niger | ___________________ | Drinks, toffees, chocolate production. |
| Glucose, corn steep liquor | ___________________ | Gluconic acid | ___________________ |
| Molasses, corn steep liquor | Lactobacillus delbrueckii | ___________________ | ___________________ |
| ___________________ | Aspergillus itaconius | Itaconic acid | ___________________ |
Answer:
| Source | Microbe | Amino acid | Use |
| Sugar and beet molasses, ammonia salt | Brevibacterium, Corynobacterium | L-glutamic acid | Production of monosodium glutamate (Ajinomoto). |
| Sugar molasses, salt | Aspergillus niger | Citric acid | Drinks, toffees, chocolate production. |
| Glucose, corn steep liquor | Aspergillus niger | Gluconic acid | Production of minerals used as supplement for calcium and iron. |
| Molasses, corn steep liquor | Lactobacillus delbrueckii | Lactic acid | Source of nitrogen, production of vitamins. |
| Molasses, corn steep liquor | Aspergillus itaconius | Itaconic acid | Paper, textile, plastic industry, gum production |
Question 3.
| Source | Microbe | Amino acid |
| (1) Sugar molasses and salt | ___________________ | Citric acid |
| (2) ___________________ | Lactobacillus delbrueckii | ___________________ |
| (3) Corn steep liquor | Aspergillus itaconius | ___________________ |
Answer:
| Source | Microbe | Amino acid |
| (1) Sugar molasses and salt | Aspergillus niger | Citric acid |
| (2) Molasses, corn steep liquor | Lactobacillus delbrueckii | Lactic acid |
| (3) Corn steep liquor | Aspergillus itaconius | Itaconic acid |
![]()
Answer the following questions:
Question 1.
Which microbes are used in the baking industries? (Board’s Model Activity Sheet)
Answer:
Yeast i.e. Saccharomyces cerevisiae is used in the baking industries.
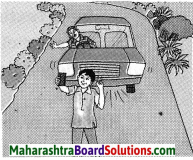
Question 2.
There is an oil layer on the water surface of river in your area. What will you do? (March 2019)
Answer:
If there is an oil layer on the water surface, we shall use hydrocarbonoclastic bacteria like Pseudomonas to clean up the oil spill.
Question 3.
(a) How are microbes used in sewage management?
(b) How is the sludge produced in this process utilized? (Board’s Model Activity Sheet)
Answer:
(a)
- In cities, the sewage is sent to processing plant and is treated with microbes.
- Microbes that carry out decomposition, are mixed with sewage. Such microbes are able to destroy, pathogens as well as decompose any compounds.
- Some microbes bring about bioremediation of environment, that are used for treating sewage pollution.
- Upon decomposition of the carbon compounds present in sewage, microbes release methane and CO2.
(b) The sludge formed in this process, is used as fertilizer.
Question 4.
Answer the following questions:
(a) What is clean technology?
Answer:
Clean technology is the method to use microbes for controlling air, soil and water pollution. These microbes can degrade the manmade chemicals.
(b) Why is it essential to ban plastic bags?
Answer:
Plastic is a non-biodegradable substance. It cannot be degraded back into its original constituents. It remains just like that for many hundreds of years. It causes solid waste pollution in any environment wherever it is thrown indiscriminately. If burnt, it releases very toxic gases. If dumped in landfills it obstructs the other decomposition processes.
If thrown in water bodies, it causes harm to aquatic life. Cattle graze on plastic unknowingly and are killed by it as it clogs inside their alimentary canal. The gutters and rain water drains get clogged due to plastic bags and this causes cities to submerge in water during heavy rains. Nowadays, the fishermen get more than half of plastic if they cast their net in the sea.
People use the plastic bags indiscriminately without any thought towards their environmental impact. There are better alternatives for plastic bags such as cloth bags which can be reused again and again. Therefore, it is absolutely necessary to ban the use of plastic bag.
Write short notes on the following:
Question 1.
Production of Yoghurt.
Answer:
- Yoghurt is one of the milk product produced from milk with the help of lactobacilli (inoculant).
- In the industrial production of yoghurt, the milk is added with condensed milk powder. This increases the protein content of the milk. Then this milk is subjected to fermentation.
- Milk is boiled and then it is cooled till it becomes lukewarm.
- Then the bacterial strains of Streptococcus thermophiles and Lactobacillus delbrueckii are added to this lukewarm milk in 1:1 proportion.
- The Streptococcus bacteria convert the milk into solution containing lactic acid. This makes the proteins to gel out. It makes the yoghurt dense.
- The lactobacilli help in the formation of acetaldehyde like compounds giving a characteristic taste to the yoghurt.
- For commercial reasons, various fruit juices are mixed with yoghurt to impart different flavours forming strawberry yoghurt, banana yoghurt, etc.
- The pasteurization is carried out to increase the shelf life of yoghurt and improve its probiotic properties.
![]()
Question 2.
Production of cheese.
Answer:
Cheese is made from cow’s milk throughout the world. The steps in the process of cheese manufacture are as follows:
- Chemical and microbiological testing of milk is done.
- Three types of bacteria, viz. Lactobacillus lactis, Lactobacillus cremoris and Streptococcus thermophilus along with some colour is added to the milk.
- It imparts sourness to the milk and it is converted into yoghurt like substance.
- The water from this yoghurt, i.e. whey is not removed to make the yoghurt denser.
- Enzyme, rennet or protease is added to the mixture to make it more denser.
- Later cutting the solid yoghurt into pieces, washing, rubbing, salting, land mixing of essential microbes, pigments and flavours is done in suitable steps.
- The pressed cheese is then cut in to pieces and stored for ripening.
Question 3.
Land-filling sites.
Answer:
- In the land-filling sites the degradable wastes are transferred. Usually such sites are in urban areas.
- The land-filling sites are away from the residential areas for the hygienic reasons. Here large pits arb dug in open spaces.
- These pits are lined with plastic sheets. Therefore, the leaching of toxic and harmful materials is avoided to reduce the chance of soil pollution due to leachates.
- Compressed waste is put in the pit and is covered with layers of soil, saw dust, leafy waste.
- Specific biochemical substances are added for speedy decomposition.
- Bioreactors which are mixtures of bacteria are mixed at some places.
- Soil microbes and other top layers decompose the waste.
- Soil slurry is used to seal the pits completely.
- After a certain period, best quality compost is formed. Such land filling sites can be reused after removal of compost.
Complete the paragraph by choosing the appropriate words given in the brackets:
Question 1.
(Nocardia, Geobacter, Ideonella sakaiensis, Pseudomonas, Alcanovorax borkumensis, hydrocarbonoclastic, Acidophillium, streptomyces)
Bacteria like ………… spp. and ………. have the ability to destroy the pyridines and other chemicals. Hence, these bacteria are used to clear the oil spills. These are called ………. bacteria. It has been observed that species like Vibrio, …………… can decompose the PET. Similarly, species of fungi like ………… have ability of decomposing rubber from garbage. Sulphuric acid is source of energy for some species of bacteria like ………… Hence, these bacteria can control the soil pollution occurring due to acid rain. …………..convert the salts of uranium into insoluble salts.
Answer:
Bacteria like Pseudomonas spp. and Alcanovorax borkumensis have the ability to destroy the pyridines and other chemicals. Hence, these bacteria are used to clear the oil spills. These are called hydrocarbonoclastic bacteria. It has been observed that species like Vibrio, Ideonella sakaiensis can decompose the PET. Similarly, species of fungi like Nocardia have ability of decomposing rubber from garbage. Sulphuric acid is source of energy for some species of bacteria like Acidophillium. Hence, these bacteria can control the soil pollution occurring due to acid rain. Geobacter convert the salts of uranium into insoluble salts.
Read the paragraph and answer the questions given below:
Remediation is the process of removing dangerous or poisonous substances from the environment, or limiting the effect that they have on it. When any biological organism is used for remediation, it is called bioremediation. When plant species are used for the purpose of remediation, it is called phytoremediation. When any microbes are used then it is named as microbial remediation. The methods of such remediation have helped to clean the environment from toxic effluents, especially sewage and crude oil. Dr. Anand Chakraborty, a scientist of Indian origin, has worked on Pseudomonas aeruginosa which have reduced the crude oil films into carbon dioxide and water.
Questions and Answers:
Question 1.
What is the meaning of remediation?
Answer:
Remediation is the process by which dangerous or toxic substances are removed from the environment.
Question 2.
What is the difference between phytoremediation and microbial remediation?
Answer:
When any plant species are used for remediation process, then it is called phytoremediation, whereas when any microbe species used for remediation then it is called microbial remediation.
Question 3.
Which environmental pollutant is mainly removed through bioremediation processes?
Answer:
Toxicants released through sewage and crude oil are removed by bioremediation processes.
Question 4.
What is the role of Pseudomonas aeruginosa?
Answer:
Pseudomonas aeruginosa helps in bioremediation by acting on film of crude oil and reduces it to carbon dioxide and water.
Question 5.
Why Dr. Anand Chakraborty’s work phenomenal?
Answer:
Dr. Anand Chakraborty discovered that Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteria can act on oil film which is toxic and reduce it to nontoxic products. This helps in controlling the oil pollution of marine waters which otherwise is very difficult to control.
![]()
Diagram based questions:
Question 1.
Observe the diagram and answer the following questions:
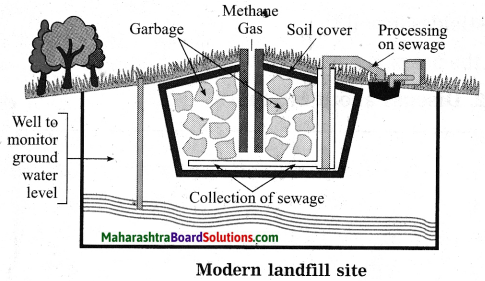
(a) Name the following method of solid waste management.
Answer:
The above diagram shows modern landfill site. This method is used for solid waste management.
(b) What type of waste is used in this method?
Answer:
In this method only degradable waste matter collected in cities can be used. Such solid waste can undergo biodegradation and hence can be managed in an eco-friendly way.
(c) What kind of useful substances can be obtained from such methods?
Answer:
From such decomposition, organic fertilizers and manure formed through composting are obtained. Methane gas is also obtained which is used as fuel.
Question 2.
Observe the Figure 7.1 and answer the following questions: (March 2019)
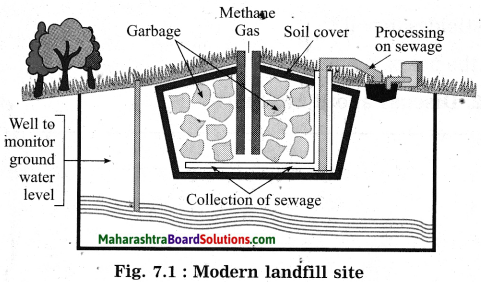
(a) Identify the process shown in the figure.
Answer:
The figure shows modern land fill site where microbial biodegradation process is carried out.
(b) Explain the process in short.
Answer:
Land-filling sites:
- In the land-filling sites the degradable wastes are transferred. Usually such sites are in urban areas.
- The land-filling sites are away from the residential areas for the hygienic reasons. Here large pits arb dug in open spaces.
- These pits are lined with plastic sheets. Therefore, the leaching of toxic and harmful materials is avoided to reduce the chance of soil pollution due to leachates.
- Compressed waste is put in the pit and is covered with layers of soil, saw dust, leafy waste.
- Specific biochemical substances are added for speedy decomposition.
- Bioreactors which are mixtures of bacteria are mixed at some places.
- Soil microbes and other top layers decompose the waste.
- Soil slurry is used to seal the pits completely.
- After a certain period, best quality compost is formed. Such land filling sites can be reused after removal of compost.
![]()
Activity based questions:
Question 1.
Collect Information Search : (Textbook page no. 84)
(i) Which materials should not be present in garbage for its proper microbial decomposition?
Answer:
If there are non-biodegradable materials in the garbage, they will not decompose. The plastic, glass, metals etc. will not undergo microbial decomposition, therefore, such items should not be- there in the garbage. The toxic matter, hazardous chemicals and e-waste should also be removed. If such materials are present in the garbage, the microbes will be killed and the entire process of decomposition will be suffered.
(ii) How the sewage generated in your house or apartment is disposed off ?
Answer:
The sewage generated in our house is carried by the drainage pipes to municipal sewage treatment plants. Here, primary, secondary and tertiary treatment is done on the sewage. The safe water is then released into the ocean.
Question 2.
Observe: (Textbook page no. 83)
Observe the garbage vans of gram panchayat and municipality. Nowadays, there is facility of decreasing the volume of garbage by compaction in those vans. Explain the advantages of this activity.
Answer:
When the garbage is compressed, its volume is reduced. The trips of the vans that pick up the garbage can be reduced due to such measures. The land filling sites can also accommodate more garbage if it is compacted.
Question 3.
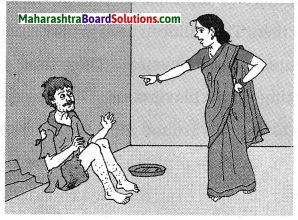
Observe the figure and answer the following:

(i) Lack of management of which factor is shown in the picture?
Answer:
The above picture shows the lack of management of sewage resulting in waste water being dumped carelessly.
(ii) How can that factor be managed with the help of microbes?
Answer:
Microbes which can destroy the pathogens of cholera, typhoid, etc. are mixed with sewage. They release methane and CO2 by decomposition of the carbon compounds present in sewage. Other microbes that decompose chemical compounds are also released. Phenol oxidizing bacteria decompose the xenobiotic chemicals present in sewage.
(iii) How are the oil spills in oceans cleared?
Answer:
Hydrocarbonoclastic bacteria like
Alcanivorax borkumensis and Pseudomonas are used to clear the oil spillage from ocean water. These bacteria decompose the hydrocarbons. They bring about the reaction of released carbon with oxygen to produced CO2 and water.
![]()
Projects: (Do it your self)
Project 1.
Search: (Textbook page no. 81)
Read the ingredients and their proportion printed on bottles of cold drinks and juices and wrappers of ice creams. Find out the natural and artificial ingredients.
Project 2.
Internet is My Friend: (Textbook page no. 85)
Collect pictures of various useful microbes. Display chart of their information in the classroom.
Project 3.
Observe the figure given on Textbook page no. 82. Discuss about bio-fuel?
10th Std Science Part 2 Questions And Answers:
- Heredity and Evolution Class 10 Questions And Answers
- Life Processes in Living Organisms Part – 1 Class 10 Questions And Answers
- Life Processes in Living Organisms Part – 2 Class 10 Questions And Answers
- Environmental management Class 10 Questions And Answers
- Towards Green Energy Class 10 Questions And Answers
- Animal Classification Class 10 Questions And Answers
- Introduction to Microbiology Class 10 Questions And Answers
- Cell Biology and Biotechnology Class 10 Questions And Answers
- Social health Class 10 Questions And Answers
- Disaster Management Class 10 Questions And Answers