Forms of Business Organisation – II 11th OCM Chapter 5 Solutions Maharashtra Board
Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Organisation of Commerce and Management 11th Textbook Solutions Chapter 5 Forms of Business Organisation – II Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
Class 11 OCM Chapter 5 Exercise Solutions
1. (A) Select the correct option and rewrite the sentence
Question 1.
Departmental Organisation is financed through …………………… appropriations made by the legislature.
(a) annual budget
(b) monthly budget
(c) quarterly budget
Answer:
(a) annual budget
Question 2.
A ………………. is an autonomous corporate body created by the special Act of the parliament or State legislature.
(a) Statutory corporation
(b) government company
(c) MNC
Answer:
(a) Statutory corporation

Question 3.
A statutory corporation is answerable to ……………… or state assembly whosoever creates it.
(a) Parliament
(b) public
(c) employees
Answer:
(a) Parliament
Question 4.
In government company minimum …………………. % paid up capital is held by government.
(a) 51
(b) 41
(c) 31
Answer:
(a) 51
Question 5.
The shares of government company are purchased in the name of ………………
(a) President of India
(b) Chief Minister
(c) Defence Minister
Answer:
(a) President of India
Question 6.
Government on the advice of ………………… appoints auditor of government company.
(a) Comptroller and Auditor General of India
(b) auditor
(c) chartered accountant
Answer:
(a) Comptroller and Auditor General of India
Question 7.
A government company is a ………………… entity separate from the government.
(a) natural
(b) legal
(c) human
Answer:
(b) legal
Question 8.
……………… company has public accountability.
(a) MNC
(b) Private
(c) Government
Answer:
(c) Government
Question 9.
MNCs are powerful ……………….. entities.
(a) economical
(b) political
(c) social
Answer:
(a) economical
1. (B) Match the pairs
Question 1.
| Group A |
Group B |
| (a) BHEL |
(1) Special Legislature |
| (b) Statutory Corporation |
(2) 49% paid up capital by Government |
| (c) Departmental Organisation |
(3) Service Motive |
| (d) Private Sector |
(4) Railway |
| (e) Public Sector |
(5) Profit motive |
|
(6) 51% paid up capital by Government |
Answer:
| Group A |
Group B |
| (a) BHEL |
(6) 51% paid up capital by Government |
| (b) Statutory Corporation |
(1) Special Legislature |
| (c) Departmental Organisation |
(4) Railway |
| (d) Private Sector |
(5) Profit motive |
| (e) Public Sector |
(3) Service Motive |
1. (C) Give one word / phrase / term
Question 1.
Organisations which are owned by individual or group of individuals.
Answer:
Private Sector Organisations
Question 2.
Organisations which are owned by government.
Answer:
Public Sector Organisations
Question 3.
The sector which aims at profit maximization.
Answer:
Private sector
Question 4.
The sector which aims at providing reliable services to customers.
Answer:
Public sector Organisation
Question 5.
Organisations which are owned, financed, managed and controlled by government or combination of governments.
Answer:
Public sector Organisation
Question 6.
The organisation which is owned, managed, controlled and financed by government.
Answer:
Departmental Organisation
Question 7.
The oldest form of business organisation under public sector.
Answer:
Departmental Organisation
Question 8.
The organisation which performs it’s all activities as an integral part for government only.
Answer:
Departmental Organisation
Question 9.
The organisation which is financed through annual budget appropriations made by the legislature.
Answer:
Departmental Organisation
Question 10.
The organisation in which there is direct and absolute control of government over the enterprise.
Answer:
Departmental Organisation
Question 11.
An autonomous corporate body created by the Special Act of the parliament or state legislature with defined powers, functions and duties.
Answer:
Statutory Corporation

Question 12.
An organisation which is answerable to parliament or state assembly whosoever creates it.
Answer:
Statutory Corporation
Question 13.
An organisation which is not subject to the budget, accounting and audit controls by the government.
Answer:
Statutory Corporation
1. (D) State True or False
Question 1.
Private sector organisations are owned by individual or group of individuals.
Answer:
True
Question 2.
Public sector organisations are owned by government.
Answer:
True
Question 3.
Private sector aims at providing reliable services to customers.
Answer:
False
Question 4.
Public sector was undertaken as a part of industrial policy, 1956.
Answer:
True
Question 5.
Departmental organisation is the oldest form of business organisation under public sector.
Answer:
True
Question 6.
Departmental organisation performs its all activities separately from government.
Answer:
False
Question 7.
The Minister-in-charge of ministry is the head of departmental organisation.
Answer:
True
Question 8.
There is always problem of red tapism and bureaucracy in departmental organisation.
Answer:
True
Question 9.
There is large scope for the initiative and skill in departmental organisation.
Answer:
False
Question 10.
In departmental organisation there is flexibility in operations.
Answer:
False
1. (E) Find the odd word out
Question 1.
Indian Post, Indian Railway, Bank of India, Air India.
Answer:
Bank of India
Question 2.
Life Insurance Corporation, Reserve Bank of India, Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited, ONGC.
Answer:
Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited
Question 3.
Pepsi, Coca Cola, Dabur, Proctor & Gamble.
Answer:
Dabur
Question 4.
Tata Motors, Hindustan Aeronautics Limited, Steel Authority of India Limited, Gas Authority of India Limited.
Answer:
Tata Motors
1. (F) Complete the sentences
Question 1.
A Government company is a ………………… entity separate from the government.
Answer:
Legal
Question 2.
………………… is owned, managed, controlled and financed by government.
Answer:
Departmental Organisation
Question 3.
A ………………… has defined powers, functions and duties.
Answer:
Statutory corporation
Question 4.
All government companies are registered under ………………… Act, 2013.
Answer:
Companies
Question 5.
MNCs are powerful ………………… entities.
Answer:
economical
1. (G) Answer in one sentence
Question 1.
What is Government Company?
Answer:
The Company which is registered under Companies Act, 2013 having minimum 51% of paid up share capital held by central government or any state government or partly by central government and partly by one or more state governments is known as Government company.
Question 2.
What is Departmental Organisation?
Answer:
It is the oldest form of business organisation. Departmental Organisation performs its all activities as an integral part for government only.
Question 3.
What is Statutory Corporation?
Answer:
Statutory Corporation is an autonomous corporate body created by the special act of the parliament or state legislature with defined powers, functions and duties.

Question 4.
What is Multinational Corporation?
Answer:
A multinational corporation is a business organisation that operates in many different countries at the same time.
Question 5.
What is Public Sector?
Answer:
Public sector organisations are those organisations which are setup by the government with the main object of providing essential services to the general public.
Question 6.
What is Private Sector?
Answer:
Private sector business which are owned by private individuals or group of individuals are termed as private sector organisation.
1. (H) Correct the underlined word and rewrite the following sentences
Question 1.
Statutory Corporation is a natural person created by Special Act.
Answer:
Statutory Corporation is an artificial person created by special act.
Question 2.
A Statutory Corporation is not answerable to parliament or state assembly.
Answer:
A statutory corporation is answerable to parliament or state assembly.
Question 3.
MNC have existence only in single country.
Answer:
MNC have existence in many countries.
Question 4.
Departmental Organisation has separate existence from government.
Answer:
Departmental Organisation has no separate existence from government.
Question 5.
Private sector aims at providing essential services to customers.
Answer:
Public sector aims at providing essential services to customers.
2. Explain the following terms/concepts
Question 1.
Public Sector Organisation.
Answer:
- It is owned, managed, controlled and financed by government.
- It includes – Departmental Organisation, Statutory Corporation and Government Companies.
- Its main objective is to provide services to society.
- It is managed by government officials or Board of Director.
- It is large in size and operates on large scale.
Question 2.
Private Sector Organisation.
Answer:
- It is owned, managed, controlled and financed by individuals or group of individuals.
- It includes – Sole Trading Concern, Joint Hindu Family Firm, Partnership Firm, Joint Stock Company and Co-operative Society.
- Its main objective is to maximise profit.
- It is managed by the owner himself or by their elected representatives.
- It generally operate in industrial and commercial areas only.
Question 3.
Departmental Organisation.
Answer:
- It is owned, managed, controlled and financed by government.
- It is managed by government officials of concerned ministry.
- They do not have autonomy in decision making.
- They do not have separate legal entity distinct from government.
- It is funded through annual budget of the government.
Question 4.
Statutory Corporation.
Answer:
- It is formed under a Special Act of Parliament or State Legislature.
- It is managed by Board of Director who are appointed by the government.
- They enjoy autonomy in decision making.
- They have separate legal entity distinct from government.
- It is funded by the government initially and also in need of additional capital.
Question 5.
Government Company.
Answer:
- It is a company where 51% of the paid up capital is held by Central Government or State Government jointly or individually.
- It is managed by Board of Directors appointed by Government and Shareholders.
- It is formed and registered under Companies Act, 2013.
- They can borrow funds by issuing shares to the public or through debentures, deposits, etc.
Question 6.
Multinational Corporation.
Answer:
- It is a business organisation that operates in many different countries.
- It conducts business activities in more then one country.
- It is controlled through centrally located head office.
- They are also called as transnational or international corporations.
- Example : Bata India, Infosys, Tata Motors, etc.
3. Study the following case/situation and express your opinion
1. There is X company in which capital contribution by different entities are as follows : Madhya Pradesh Government 35%, Maharashtra Government 35% and Government of India 30% of company.
Question 1.
Find out type of this company.
Answer:
‘X’ company is a Government Company.
Question 2.
Tell any two features of this company.
Answer:
Separate legal entity and Registration under the Companies Act, 2013 are the features of “X Government Company.
Question 3.
Give an example of this type of company.
Answer:
Hindustan Machine Tools (HMT), State Trading Corporation (STC), are the examples of the Government Company.
2. There is a company which is having a registered office in Singapore and such company is having branch offices in Varanasi (India) and Hambantota (Sri Lanka). This company provides cellular services to host countries through their respective branch offices.
Question 1.
Find out type of organisation.
Answer:
This type of organisation is called as Multinational Corporation.
Question 2.
Comment on it.
Answer:
Multinational Corporation means the companies which undertake business activities in more than one country. So this company is registered in Singapore and having branches in India and Sri Lanka.
Question 3.
Name the business organisation, which is self-financed, delegates authority and run by government as an integral part of it.
Answer:
It is a Departmental Organisation.
Question 4.
State any two merits of this organisation.
Answer:
No separate legal entity and Government employees are the merits of Departmental Organisation.
3. A central government passes a statute in the parliament and forms a business organisation which is having autonomy in administration and this organisation is answerable to legislature.
Question 1.
Which type of organisation is this?
Answer:
It is a Statutory Corporation.
Question 2.
Give any three Features of this organisation.
Answer:
Corporate body, No political interference, Own staffing system are the features of Statutory Corporation.

Question 3.
Give any one example of this type of organisation.
Answer:
“Life Insurance Corporation of India” is the example of Statutory Corporation.
4. Distinguish between the following
Question 1.
Private Sector Organisation and Public Sector Organisation.
Answer:
|
Private Sector Organisation |
Public Sector Organisation |
| (1) Meaning |
Private enterprises are owned managed, controlled and financed by individuals or groups of individuals. Thus, ownership and management is with private organisations. |
Public enterprises are owned, managed and controlled by the state on behalf of the people. |
| (2) Management |
It is managed by industrialists through board of directors and other specialized executives. |
It is managed by government officials or board of directors. |
| (3) Size of Entity |
They are usually of small or medium size depending on volume of operation. |
They are usually large in sized and they operate on large scale. |
| (4) Capital provider |
Capital is contributed by owner from their own resources and borrowings from financial institutions. |
The capital of public sector organisation is contributed by government. |
| (5) Decision making |
Decision making is quick as very few officials are involved in decision making process. |
Decision making is delayed due to bureaucratic hurdles. |
| (6) Business area |
It generally operates in industrial and commercial areas only. |
It operates in utility services areas like – railways, post, etc. and also in industrial and commercial areas. |
| (7) Main motive |
Main motive of private sector organisation is to earn a profit. |
Main motive of public sector organisation is to provide services to society. |
| (8) Flexibility |
They are more flexible in nature as their policies can be modified as and when the need arises. |
There is no flexibility in their operations as any change or modification requires the approval of thp Government. |
| (9) Political Interference |
In private enterprises, there is no political interference and therefore executive enjoys complete autonomy and freedom of operations. |
Public enterprises working is always affected by political interference. There is constant danger of undue interference by political parties and their leaders. |
| (10) Competition |
Private enterprises operate in cut throat competition. |
Public enterprises are generally monopolies or oligopolies (only two sellers in market.) |
| (11) Economic Equalities |
Private sector increases economic inequalities. |
Public Enterprises reduce economic inequalities. |
| (12) Regional Balance |
Private enterprise increase regional imbalance because it wants to enjoy the advantages of location of industries. |
Public enterprises tries to reduce the regional imbalance as it intends to bring about balanced regional development. |
| (13) Efficiency |
Private Enterprises are more efficient due to profit maximisation, division of labour and specialisation. |
Public enterprises lack initiative, flexibility and efficiency because profit motive is absent. |
| (14) Constituents |
Sole Trading Concern, Joint Hindu Family Firm, Partnership Firm, Joint Stock Companies, Co-operative Society are different forms private sector. |
Departmental Organisation, Statutory Corporations and Government companies are types of public sector. |
Question 2.
Departmental Organisation and Statutory Corporation.
Answer:
|
Departmental Organisatio |
Statutory Corporation |
| Meaning |
The organisation which is owned, managed, controlled, financed and operated by government is known as Departmental Organisation. |
The company which is formed under a special Act of Parliament or State Legislature is known as Statutory Corporation. |
| Management |
It is managed by government officials of the concerned ministry. |
It is managed by board of directors nominated by government. |
| Legal Status |
There is no separate legal status distinct from the government. |
Statutory company has a separate legal status distinct from the government. |
| Borrowing Power |
Departmental undertaking cannot borrow from public. It has to depend on budget allocated by the government. |
Statutory Company can borrow from public by issue of shares and debentures. |
| Control |
It is controlled by the concerned ministry. |
It is controlled by government by the Act of Parliament or State Legislature. |
| Capital |
Capital of departmental organisation comes from annual budget appropriations of the government. |
Capital for statutory company comes from Central or State Government. |
| Formation |
It is formed through Executive decision taken by the concerned ministry. |
It is formed by passing a Special Act in the Parliament or in the State Legislature. |
| Suitability |
It is suitable for defence and public utility undertakings such as infrastructure projects, e.g. Railways, Post & Telegraph, Defence, etc. |
It is suitable for public utilities, development projects, service industry like banking and finance and other industrial and commercial undertakings e.g. UTI, LIC, RBI, ONGC, Air India etc. |
| Staff |
Employees appointed are Government servants. They are subject to the same discipline and enjoy the same privileges as meant for civil servants. |
Employees can be recruited independently. They are not civil servants. The corporation can have its own rule of recruitment and scale of remuneration. |
| Flexibility |
It has low flexibility in its operation. |
It has moderate flexibility in its operation. |
| Autonomy |
It does not have autonomy in decision making. |
It has autonomy in decision making. |
Question 3.
Government Company and Multinational Corporation.
Answer:
|
Government Company |
Multinational Corporation |
| Meaning |
Government Company means company where minimum 51% of the paid up capital is held by the Central or State Government jointly or individually. |
Multinational Corporation is a company which is incorporated in one country and has business units in several countries. |
| Capital |
The capital is contributed by the Central Government or State Government or even by general public. |
The capital is contributed by the shareholders or financial institutions in several countries. |
| Management and Control |
Government Company is managed by Board of Directors appointed by government and shareholders. |
Multinational corporation is managed by a parent company. It manages affairs of the subsidiary from the respective home country. |
| Establishment |
Government companies are formed and registered under provisions of Companies Act, 2013. |
Multinational corporations have to seek permission from the government and host countries. |
| Borrowing power |
Government companies can borrow funds by the way of debt or issuing shares to the public. |
Multinational corporation use resources of different countries. |
| Area of Operations |
Government company operates within the local boundaries of a nation. |
MNC operates in several countries, having headquarters in one country. |
| Motive |
Government companies are service oriented and hence take interest in the social welfare activities of the country. |
MNCs are profit motivated rather than service oriented. |
| Accountability |
Government Company has to take its annual reports in the Parliament where its working is discussed and debated. Though it has autonomy in financial matters, it is indirectly accountable to the publics. |
MNC is accountable to the taxation authorities in host countries and have to follow procedures such as Income Tax law procedure, FEMA, EXIM Policy etc. and as such will have to obey the laws of the host countries. |
| Currency |
They have to deal with single currency. |
They have to deal with multiple currencies and exchange rates. |
| Resource availability |
Government company uses resources of government and its employees are government employees and are permanent. |
MNCS use resources of different countries and their employees are on contract basis. |
| Trust and Public Confidence |
Government company enjoy more public confidence as they have government backing and support. |
MNCS do not have government backing and support in host countries. |
| Example |
Steel Authority of India Ltd., State Trading Corporation, Indian Oil Corporation, BHEL, HMT, etc. |
Hindustan Lever Ltd., Colgate Palmolive India Ltd; Coca Cola, IBM Computers, Sony, etc. |
Question 4.
Departmental Organisation and Multinational Corporation.
Answer:
|
Departmental Organisation |
Multinational Corporation |
| Meaning |
The organisation which is owned, managed, controlled, financed and operated by government is known as Departmental Organisation. |
Multinational Corporation is a company which is incorporated in one country and has business units in several countries. |
| Management |
Departmental Organisation is managed by government officials of the concerned ministry. |
Multinational Corporation is managed by parent company. It manages affairs of the subsidiary from the respective home country. |
| Legal status |
There is no separate legal status distinct from the government. |
It has separate legal status. |
| Borrowing power |
Departmental undertaking cannot borrow from public. It has to depend on budget allocated by the government. |
Multinational corporation use resources of different countries. |
| Control |
Departmental Organisations are controlled by the concerned ministry. |
Multinational corporations are controlled by respective parent companies and mostly home strategic. |
| Capital |
Capital of the Departmental Organisation comes from annual budget appropriations of the government. |
The capital is contributed by the shareholders or financial institutions in several countries. |
| Ownership |
Departmental undertaking is fully owned by the Government. |
Ownership of MNC is in hands of shareholder’s of the company. |
| Privileges & Concessions |
It receives highest government concessions and privileges. |
MNC do not have any concessions. They have to pay duties and taxes. |

Question 5.
Government Company and Statutory Corporation.
Answer:
|
Government Company |
Statutory Corporation |
| Meaning |
Government Company means company where minimum 51% of the paid up capital is held by the Central or State Government jointly or individually. |
The company which is formed under a special Act of Parliament or State Legislature is known as Statutory Corporation. |
| Capital |
The capital is contributed by the Central Government or State Government or even by general public and financial institutions. |
Capital for the statutory corporation comes from Central or State government. |
| Managemen |
Government Company is managed by Board of Directors appointed by government and shareholders. |
Statutory Corporation is managed by Board of Directors nominated by government. |
| Control |
These companies are controlled by government or shareholders. |
Statutory corporation is controlled by government by the Act of Parliament or State Legislature. |
| Establishment |
Government companies are formed and registered under provisions of Companies Act, 2013. |
The statutory corporation is established by special Act of the Parliament or State Legislature. |
| Borrowing power |
Government companies can borrow funds by the way of debt or issuing shares to the public. |
tatutory corporation can borrow from public by issue of bonds. |
| Privileges & Concessions |
It has no privileges and concessions by government. |
It enjoys moderate privileges and concessions. |
| Suitability |
It is suitable for industrial and commercial undertakings, e.g. BHEL, SAIL, HMT, Indian Oil Corporation, Indian Refineries, Madras Refineries, Gujarat Refineries, etc. |
It is suitable for public utilities, development projects, service industry like banking and finance and other industrial and commercial undertakings e.g. UTI, LIC, RBI, ONGC, Air India etc. |
| Political Interference |
It has less political interference in management of company as it has its own Board of Director. |
It has more political interference as it is controlled by State and Central Government. |
| Flexibility |
Government companies are more flexible in operations of business. They can change line of business as per market trend. |
Statutory company are rigid in operations they are formed for the particular purpose. |
| Accountability |
It is accountable to public. |
It is accountable to State and Central Government. |
| Autonomy |
It has full autonomy as its incorporated under Companies Act, 2013. |
It has theoretical autonomy as its established with certain purpose by Central or State Government. |
Question 6.
Departmental Organisation and Government Company.
Answer:
|
Departmental Organisation |
Government Company |
| Meaning |
The organisation which is owned, managed, controlled, financed and operated by Government is known as Departmental Organisation. |
Government Company means company where minimum 51% of the paid up capital is held by the Central or State Government jointly or individually. |
| Management |
Departmental Organisation is managed by government officials of the concerned ministry. |
Government Company is managed by Board of Directors appointed by government and shareholders. |
| Legal Status |
There is no separate legal status distinct from the government. |
A Government company has legal status separate from the Government. |
| Borrowing power |
Departmental undertaking cannot borrow from public. It has to depend on budget allocated by the government. |
Government companies can borrow funds by the way of debt or issuing shares to the public. |
| Control |
Departmental Organisations is controlled by the concerned ministry. |
These companies are controlled by government or shareholders. |
| Capital |
Capital of the departmental Organisation comes from annual budget appropriations of the government. |
The capital is contributed by the Central Government or State Government or even by general public and financial institution. |
| Formation |
It is formed through Executive decision taken by the concerned ministry. |
It is formed through registration under Companies Act, 2013. |
| Privileges & Concessions |
It receives highest government concessions and privileges. |
It has no privileges and concessions by government. |
| Suitability |
It is suitable for defence and public utility undertakings such as infrastructure projects, e.g. Railways, Post & Telegraph, Defence, etc. |
It is suitable for industrial and commercial undertakings, e.g. BHEL, SAIL, HMT, Indian Oil Corporation, Indian Refineries, Madras Refineries, Gujarat Refineries, etc. |
| Staff |
Employees appointed are Government servants. They are subject to the same discipline and enjoy the same privileges as meant for civil servants. |
Employees can be recruited independently and it does not have to necessarily follow civil service rules. |
| Political Interference |
It has high political interference with regards to the management. |
As compared to departmental organisation it has less political interference. |
| Flexibility |
It is rigid in operations as its managed through officers of the government. |
It is more flexible in operations as managed by Board of Directors. |
| Motive |
It is majorly concern with providing service to the people. |
It is concern with giving with profit making and service to the people. |
| Accountability |
Highly accountability to the respective the Minister in charge as they render their service. |
Low accountability to the people as they render their service. |
| Autonomy |
There is no autonomy as its owned, managed controlled, financed by government. |
It has full autonomy as per provisions to Companies Act, 2013. |
Question 7.
Statutory Corporation and Multinational Corporation.
Answer:
|
Statutory Corporation |
Multinational Corporation |
| Meaning |
The company which is formed under a Special Act of Parliament or State Legislature is known as Statutory Corporation. |
Multinational corporation is a company which is incorporated in one country and has business units in several countries. |
| Capital |
Capital for the statutory corporation comes from Central or State government. |
The capital is contributed by the shareholders or financial institutions in several countries. |
| Management |
Statutory Corporation is managed by Board of Directors nominated by government. |
Multinational Corporation is managed by parent company and it manages affairs of the subsidiary from the respective home country. |
| Control |
Statutory Corporations are controlled by government by the Act of Parliament or State Legislature. |
Multinational Corporations are controlled by respective parent companies. |
| Establishment |
The Statutory Corporation is established by Special Act of the parliament or State Legislature. |
Multinational Corporations have to seek permission from the Government and host countries. |
| Borrowing power |
Statutory company can borrow from public by issue of shares and debentures. |
Multinational Corporation use resources of different countries. |
| Area of Operations |
Statutory corporation operates within the local boundaries of a nation. Hence, the area of operations is not large. |
MNC operates in several countries, having headquarters in one country. Hence, the area of operations is large. |
| Motive |
Statutory Corporation are service oriented and hence take interest in the social welfare activities of the country. |
MNCs are profit motivated rather than service oriented. They render service in those areas where the opportunities for profit maximisation are more. |
| Accountability |
Statutory corporation has to take its annual reports in the Parliament where its working is discussed and debated. |
MNC is accountable to the taxation authorities in host countries and have to follow procedures such as Income Tax law procedure, FEMA, EXIM Policy etc. and as such will have to obey the laws of the host countries. |
| Currency |
They have to deal with single currency. |
They have to deal with multiple currencies and exchange rates. |
| Resource availability |
Employees can be recruited independently. They are not civil servants. The corporation can have its own rule of recruitment and scale of remuneration. |
MNC’s use resources of different countries and their employees are on contract basis. |
| Trust and Public Confidence |
Statutory corporation enjoy more public confidence as they have government backing and support. |
MNC’s do not have government backing and support in host countries. |
| Example |
UTI, LIC, RBI, ONGC, Air India, etc. |
Hindustan Lever Ltd., Colgate Palmolive India Ltd; Coca Cola, IBM Computers, Sony, etc. |
5. Answer in brief
Question 1.
State any four features of Departmental Organisation.
Answer:
Features of Departmental Organizations:
(i) Delegation of Authority : All major policy decisions are taken by the ministry. The day-to-day working is looked after by the staff consisting of civil servants of IAS, IPS cadres.
(ii) Organizational Structure : The internal organizational structure is of line type. The department is headed by minister who is responsible for the working of the department. Then there is Board of Directors or Managing Committee who are assisted by Chief Executive, Executive Assistant, Supervisory and General Staff. This is termed as bureaucracy style or military style of organisation.
(iii) Government Employees : The employees of departmental organization are civil servants and they are selected through Union Public Service Commission. Staff selection Board, Railway Recruitment Board etc. and as such they are treated as Government employees.
(iv) Financed by the Government: The funds are arranged for their operation from Government treasury. This enterprise cannot borrow money from the public without Government consent.
Question 2.
State any four features of Statutory Corporation.
Answer:
Features of Statutory Corporation:
(i) No political Interference : It enjoys freedom from political, parliamentary and government interference in day-to-day management.
(ii) Own Staffing System: They recruit their own employees and they are not government servant. Employees terms and services are not governed by civil services rules.
(iii) No Political Interference : It enjoys freedom from political, parliamentary and government interference in day to day management of its affairs.
(iv) Financial Autonomy : Statutory Corporations are financially autonomous. After getting the prior permission from the Government, it can even borrow money within and outside the country.
(v) Independent Identity : They have an independent identity different from the government. Though, the overall business policies are formulated by the government, they have administrative autonomy and hence operational flexibility.
Question 3.
State any two demerits of Multinational Corporation.
Answer:
Demerits of Multinational Corporation:
(i) Danger for Domestic Industries : Multinational Corporations have vast economic power so they are danger to domestic industries which are still in process of development. Domestic industries not so powerful to face the challenges of Multinational Corporation.
(ii) C reate Problem for Environment: Profit is sole objective of multinational corporation. Such companies damage environment of developing countries. To lower the price of goods they dump lower standard quality product which harms local soil, water and air.
(iii) O utsourcing of Job: Normally MNCs outsource the job work due to lower cost, due to this their liabilities towards employees are reduced.
(iv) Misuse of Mighty Status : Multinational Corporations have powerful financial strength because of huge capital. They can afford to bear losses for a long while in the hope of earning huge profits. They have ended local competition and achieved monopoly. This may be unfair.

Question 4.
State any four merits of Government Company.
Answer:
Merits of Government Company:
(i) Profitability and Accountability : It works on business principles and follows commercial approach. Though not profit oriented like private sector, it does make reasonable profit which is used for public welfare, modernisation, renovation and development. Moreover, its performance can be evaluated by the Parliament as it has public accountability.
(ii) Internal Autonomy: Government Company enjoys financial and administrative autonomy. Its dependence on Government authority is minimum. It has its own capital structure, financial plan, borrowing powers and so on.
(iii) Government Ownership ; The ownership of the government company rests with Central or State Government who owns major capital of the company and as such looks after its management and control. Government always promotes public welfare.
(iv) Foreign Capital and Technical Know how : As the government provides 51% of the capital, the rest 49% can be raised through foreign investment. By seeking foreign capital, Government companies bring advanced technology and technical know how.
6. Justify the following statements
Question 1.
Departmental Organisations are run for providing public services.
Answer:
- Departmental Organisations are the oldest forms of public enterprises.
- Indian railways, post office, defence, All India Radio are the Departmental Organisations.
- Indian Railways give services to public.
- Main objective of Departmental Organisations is to provide services to public.
- Private sector aims at profit maximization while public sector aims to providing reliable services to customers.
- Thus, Departmental Organisations are run for providing public services.
Question 2.
There is direct control of Government on departmental organisation.
Answer:
- Departmental organisations are run by the Government.
- Departmental organisations are financed through annual budget of Government.
- Revenues of departmental organisation is directly paid to Government treasury.
- Departmental organisation has no separate existence from Government.
- The staff of enterprises is treated equally with other civil servants.
- Thus, there is direct control of Government on departmental organisation.
Question 3.
There is no political interference in statutory corporation.
Answer:
- A Statutory corporation is an autonomous corporate body.
- Statutory corporation is an artificial person created by law and it has an independent legal entity.
- Employees are not government servants.
- A statutory corporation enjoys financial autonomy or independence.
- A statutory corporation comes into existence by following particular act, therefore, there is no political interference in formation.
- Thus, all statutory corporations are free from political interference.
Question 4.
There is professional management in statutory corporation.
Answer:
- A statutory corporation is able to manage its affairs with independence and flexibility.
- Management of statutory corporation is done without any government interference.
- The statutory corporation is relatively free from red tapism.
- There is less file work and less formality to be completed before taking decisions.
- Board of directors of statutory corporation consists of business experts and the representatives of various groups such as labour, consumers, etc. who are nominated by the government.
- Thus, there is professional management in statutory corporation.
Question 5.
MNC helps to end local monopolies.
Answer:
Multinational corporation helps to end local monopolies.
- Multinational corporations lead to competition in the host countries.
- Local monopolies of host countries either start improving their products or reduces their prices.
- Multinational corporation put an end to exploitative practices of local monopolists.
- As a matter of fact, MNCs compel domestic companies to improve their efficiency and quality.
- Thus, MNC helps to end local monopolies.
Question 6.
MNC has worldwide existence.
Answer:
- As multinational corporation is operating on a global basis.
- Multinational corporation have marketing operations in several countries operating through a network and branches.
- They have production facilities in several countries.
- Advanced Technology and international business operations are done by MNC.
- It brings in much needed foreign capital for the rapid development.
- Multinational corporation integrate economies of various nations with the world economy.
- Thus, MNC has worldwide existence.
Question 7.
MNC has mighty economic powers.
Answer:
- As MNC is operating on a global basis, they have huge physical and financial assets.
- In terms of assets and turnover, many MNCs are bigger than national economies of several countries.
- Multinational corporations are powerful economic entities.
- Multinational corporation keep on adding to their economic power through constant mergers and acquisitions of companies in host countries.
- Thus, MNC has mighty economic powers.
7. Attempt the following
Question 1.
Merits of Departmental Organisation.
Answer:
Merits of Departmental Organization:
1. Qualified Staff : Departmental organizations are properly managed and supervised by the qualified government staff.
2. Proper Use of Funds : The Departmental organizations provide public utilities or basic necessities. Government Department works under the control and supervision of the concern ministry. Charges for misuse of funds are less in departmental organization.
3. Social Welfare : Government undertakes socio-economic activities to promote social welfare. Providing essential comlhodities to people at reasonable price is top priority of the state. Thus, socio-economic objectives are achieved with Government control.
4. Public Accountability : The concerned minister incharge of the government organisation is answerable to the Parliament or Assembly. The elected representatives of people can raise the question about the working of this enterprises on behalf of public at large.

Question 2.
Demerits of Departmental Organisation.
Answer:
Demerits of Departmental Organisation:
(i) Delay in Action : In Departmental organisation there is always centralization of authorities. Such excessive centralization of authority leads to delay in action.
(ii) Inefficiency and Corruption : There is lot of inefficiency and corruption in departmental organisation.
(iii) Less Scope for Initiative : The working of this organization suffers from lack of continuity and stability because the policies of the department are decided by the ministers.
(iv) Instability : The working of this organisation suffers from lack of continuity and stability, because the policies of the department are decided by the Ministers.
(v) Delayed : The executives at the lower level have to depend on higher authority for all the decisions. They can’t take, their own decisions.
Question 3.
Merits of Statutory Corporation.
Answer:
Merits of Statutory Corporation:
(i) Professional Management: Statutory Corporations are managed professionally. The directors and other executives are highly trained and specialize in their respective fields. This leads to efficiency in working.
(ii) Rapid Decisions : Statutory Corporations enjoy autonomy. They can take quick decisions. There is less file work and less formalities to be completed before taking decisions.
(iii) Efficient Staff : In Statutory Corporation, employees are given fair wages, better working conditions and proper training and development programs are initiated for the employees. As a result, employer-employee relations are very cordial and staff is highly motivated to perform better.
(iv) Motivated Staff: In Statutory Corporations, employees are given fair wages, better working conditions and proper training and development programmes are initiated for the employees. As a result, employer- employee relations are very cordial and staff is highly motivated to perform better.
Question 4.
Demerits of Statutory Corporation.
Answer:
Demerits of Statutory Corporation:
Though statutory corporations are autonomous bodies and enjoy flexibility in their working, they have certain limitations which are as follows:
(i) Clashes Amongst Interests : All or majority directors of Statutory Corporations are appointed by the Government from different fields. As there are many members it is quite possible that their interests may clash. The smooth functioning of the corporation may be hampered.
(ii) Autonomy on Paper Only : Ministers, government officials and political parties often interfere with the working and decision making policies which affects the autonomy and flexibility of it.
(iii) Rigid Structure : Though statutory corporation have operational flexibility, they are subject to many rules and regulations. Any changes in the constitution, objects, powers, duties, etc., require amendments to be passed in the parliament which is difficult task. This reduces its flexibility.
(iv) Lack of Initiative : The statutory corporation have no profit motive. There is no competition among them. So employees do not take initiative to increase the profit.
Question 5.
Features of Government Company.
Answer:
Features of Government Company:
The Government Company may be registered as public or private limited companies. These companies are established for purely business purpose and to compete with the private sector.
Following are the features of Government Company:
(i) Free from Procedural Controls: The Government companies have a right to formulate their independent policies and even make necessary changes in them. It enjoys freedom from budgetary, accounting and audit controls which are applicable to Government undertakings.
(ii) Majority of Government Directors : All or majority of directors of such companies are appointed by the Government from different fields. They may be experts from banking sector, insurance sector, who manage the day to day business affairs.
(iii) Public Accountability : The annual accounts of the company are tabled before Parliament or State Legislature for review and discussion. Thus, Government Company is accountable and answerable to the Parliament or State Legislature through the concerned Minister.
(iv) Registration under the Companies Act: The Government Company is registered under the Companies Act, 2013 and its formation, working, management and winding up a business is governed by provisions of- the Act. Government has power to modify or change certain provisions laid down in the Act.
Question 6.
Demerits of Government Company.
Answer:
Demerits of Government Company:
Though Government Company enjoys various benefits due to Government ownership and autonomy, it has following limitations:
(i) Inefficiency and Corruption : The Directors have no financial stake in the company and as a result they are indifferent towards working of the company. Due to limited autonomy and petty politics, the efficiency of the enterprise is affected. It results in corruption.
(ii) Lack of Professional view : There is lack of devotion, dedication and systematic approach. In fact, there is no professional approach in various operations and working of the company.
Thus, from the above points it could be seen that there is lot of government and political interference in the Government company which brings about its inefficiency and ineffectiveness.
(iii) Domination of Ministers and Politicians : The ministers of the concerned departments are in charge of the Government Company. In view of Government ownership, political interference is quite common. The Directors try to serve and achieve their political motives rather than realisation of business goals as they are nominated for political gains and not on merits.
(iv) Red Tapism and Delay : The bureaucratic management delays in taking decision and implementing. There is no time frame and the employees are not devoted. There is often delay in preparing various documents and forwarding the same for taking action. Thus, delay, red tape, corruption, avoidance of work and shirking from the responsibility is common sight in Government Company.
Question 7.
Features of Multinational Corporation.
Answer:
Features of Multinational Corporation:
Following are the features of Multinational Corporation:
(i) Advanced and Sophisticated Technology : Multinational company has large capital and sophisticated technology and infrastructure. As a result it undertakes diversified and multifarious activities including manufacturing, marketing, financial, research and development.
(ii) Legal Existence : MNCs are registered in their home country as per their laws and as such they enjoy separate legal status. It can sue and be sued, enter into contracts and own property in their own name.
(iii) Government: MNCs have to bring about the necessary changes in their functioning based upon the laws prevailing in the countries of their operations. For e.g. advertisement about various products on TV is given in local languages in India and in national language Hindi, to cover maximum target audience. In some cases they have to change the menu to suit local demands for e.g. McDonalds had to change its menu for its business in India.
(iv) Origin: The MNCs have origin in one country and the country to which they belong is called home country. The country in which they operate their business activities is called host country. These companies are registered in their home country and have a place of business in different countries of the world. The head office controls the operations of different branches through a network of internet. They also appoint their representatives in host countries for smooth business operations.
Question 8.
Merits of Multinational Corporation.
Answer:
Merits of Multinational Corporation:
Following are the merits of Multinational Corporation.
(i) Proper use of Idle Resources : The national income of host country increases as MNCs use idle physical and human resources with latest technologies.
(ii) Inflow of Foreign Capital: Multinational corporations bring much needed foreign capital for the rapid development of developing countries. This capital is useful for growth of domestic country.
(iii) Promotion of International Brotherhood and Culture: MNCs integrate economies of various nations with the world economy and promote international brotherhood and culture with peace and prosperity in the world.
(iv) End of Local Monopolies : In global market, Multinational Corporations end local monopolies of host . countries improving their products and reduces prices.
(v) Technical Development: Multinational corporations gives lot of importance to research and development activities. They are also fully equipped and have necessary infrastructure. The research and development is undertaken for finding out new product, new system, and new technology of doing business in an economical way.
8. Answer the following in details
Question 1.
Explain Departmental Organization and its features.
Answer:
(A) Meaning:
Departmental organizations are oldest form of public enterprises. These are run by Government departments headed by a minister who guides and controls the activities of the undertaking e.g. Indian Railways, all India Radio, Indian Post, Defence etc. A Departmental organization is organized, financed and controlled by Government like any other Government department. Under this type of organization, no distinction is made between public sector and traditional Government functions.
(B) Features of Departmental Organizations:
(i) Delegation of Authority : All major policy decisions are taken by the ministry. The day-to-day working is looked after by the staff consisting of civil servants of IAS, IPS cadres.
(ii) Organizational Structure : The internal organizational structure is of line type. The department is headed by minister who is responsible for the working of the department. Then there is Board of Directors or Managing Committee who are assisted by Chief Executive, Executive Assistant, Supervisory and General Staff. This is termed as bureaucracy style or military style of organisation.
(iii) Government Employees : The employees of departmental organization are civil servants and they are selected through Union Public Service Commission. Staff selection Board, Railway Recruitment Board etc. and as such they are treated as Government employees.
(iv) Financed by the Government: The funds are arranged for their operation from Government treasury. This enterprise cannot borrow money from the public without Government consent.
(v) Useful for Secret: matters like defence, atomic energy, etc.
(vi) No Legal Status : A government department does not enjoy an independent legal status. It is dependent on the Government. It cannot be taken to court without the consent of the Government. Thus, the above are the features of Departmental Organization.
(vii) Government Sanction for Expansion : Public Enterprises need to take the sanction of the Government for expansion and diversification of business or for changing the policies, etc.
(viii) Examples of Departmental Organisation : Ordinance factories, Railways, Broadcasting, Post and Telegraph, BHEL, Indian Drug and Pharmaceuticals Ltd. Hindustan Aeronautics Ltd. Army Clothing Factory, Gun Factory and so on.
(ix) Run by Government : Different procedures like accounting, auditing and budgeting are at par with Government department.
(x) Managed by Government : The Departmental organization is managed by Government officials of the concern ministry.
(xi) Accounting Control : The organisation is subject to accounting and audit procedures and controls as applicable to government departments or to the concerned ministry.
(xii) Accountability : The enterprise is funded by the government and hence the government controls its affairs. In other words, it is answerable to the Parliament.
(xiii) No Separate Legal Entity : A Government department does not enjoy an independent legal status. It is dependent on the Government. It cannot be taken to court without the consent of the Government.

Question 2.
Explain merits and demerits of Departmental Organization.
Answer:
(A) Meaning:
Departmental organizations are run by the Government departments headed by a minister who guides and controls the activities of the undertaking.
(B) Merits of Departmental Organization:
1. Qualified Staff : Departmental organizations are properly managed and supervised by the qualified government staff.
2. Proper Use of Funds : The Departmental organizations provide public utilities or basic necessities. Government Department works under the control and supervision of the concern ministry. Charges for misuse of funds are less in departmental organization.
3. Social Welfare : Government undertakes socio-economic activities to promote social welfare. Providing essential comlhodities to people at reasonable price is top priority of the state. Thus, socio-economic objectives are achieved with Government control.
4. Public Accountability : The concerned minister incharge of the government organisation is answerable to the Parliament or Assembly. The elected representatives of people can raise the question about the working of this enterprises on behalf of public at large.
5. Maintain Secrecy: In matters of strategic, national importance, secrecy is essential and confidentiality can be maintained in certain business activities such as defence deals, atomic plants, drugs and pharmaceuticals etc.
6. Easy Formation : These organisations are very easy to form. They do not require any special statute or registration.
7. Direct Control: These organizations are properly managed and supervised by the qualified Government Staff Minister at the top is responsible to the Parliament for its operations.
8. Direct Revenue to Government : The revenue of departmental organizations directly goes to the jr Government treasury.
9. Less Overheads : The administrative expenses are less as government only operate it.
10. Easy Finance : These organisation get the required finance by the government through direct allocation of funds from the concerned ministry.
11. Development of Public Utilities : The departmental organisation provides public utilities or basic r necessities. People require essential services and products such as Railways, Transport and Communications, Telephone services, etc. Thus, essential services are made available by the Government department at a very reasonable rate.
(C) Demerits of Departmental Organisation:
(i) Delay in Action : In Departmental organisation there is always centralization of authorities. Such excessive centralization of authority leads to delay in action.
(ii) Inefficiency and Corruption : There is lot of inefficiency and corruption in departmental organisation.
(iii) Less Scope for Initiative : The working of this organization suffers from lack of continuity and stability because the policies of the department are decided by the ministers.
(iv) Instability : The working of this organisation suffers from lack of continuity and stability, because the policies of the department are decided by the Ministers.
(v) Delayed : The executives at the lower level have to depend on higher authority for all the decisions. They can’t take, their own decisions.
(vi) Lack of Flexibility : The Departmental organization lacks flexibility in decision making. This is because there is centralization of authority.
(vii) Incurring Losses/Huge Losses : Most of the government undertakings incur heavy losses due to lack of business skills and approach as they are not professional.
(viii) Absence of Professionalism : There is lack of professionalism in the management of departmental organization. Often the decisions are taken unsystematically, moreover the data collected is often out dated and there is no proper analysis of such data. Hence, the decisions are taken hastily.
(ix) Political Interference : The Ministers, bureaucrats, Government officials interfere in the day to day working of the undertaking.
(x) Red Tapism and Bureaucracy : The Departmental organisations are controlled by government. Departmental organisations are facing delays, red tapism, corruption, lack of initiative, bureaucracy, etc.
(xi) Insensitive to Consumer Needs : The officials of this organisation are insensitive to the needs of consumers. The officials are not bothered about consumer needs and consumer satisfaction as they are more worried about their security of service in view of monopolistic position.
(xii) Lack of Autonomy : Departmental organisation lack autonomy and freedom in working and decision making.
Question 3.
Explain Statutory Corporation and its features.
Answer:
(A) Meaning:
Statutory Corporations are autonomous bodies established under special legislative Acts. A statutory corporation is formed under a Special Act of Parliament or State Legislature. The powers, duties, functions and scope of operations are laid down in the Act.
LIC, IFCI, SBI, UTI, Air India are the examples of public corporation.
Statutory Corporation is a body with a separate existence, which can sue and be sued and is responsible for its own finance. It is administered by a board appointed by public authority to which it is answerable.
(B) Features of Statutory Corporation:
(i) No political Interference : It enjoys freedom from political, parliamentary and government interference in day-to-day management.
(ii) Own Staffing System: They recruit their own employees and they are not government servant. Employees terms and services are not governed by civil services rules.
(iii) No Political Interference : It enjoys freedom from political, parliamentary and government interference in day to day management of its affairs.
(iv) Financial Autonomy : Statutory Corporations are financially autonomous. After getting the prior permission from the Government, it can even borrow money within and outside the country.
(v) Independent Identity : They have an independent identity different from the government. Though, the overall business policies are formulated by the government, they have administrative autonomy and hence operational flexibility.
(vi) Special Act : They are established under a special Act passed by the Parliament. Its objectives, powers 98and functions are regulated by the Act.
(vii) Corporate Body : Statutory Corporation is a corporate body. It has a separate legal entity distinct from its members and thereby can enter into contracts and acquire property on its own name.
(viii) Answerable to the Legislature : A statutory corporation is answerable to Parliament or State Assembly whomsoever creates it. Parliament has no right to interfere. Though the overall business policies are formulated by the government, they have administrative autonomy and hence operational flexibility.
(ix) Legal Status : As a body corporate, it has a separate legal entity, distinct from its members and thereby can enter into contracts and acquire property in its own name.
(x) Independent Accounting System : They are not subject to budget accounting and audit laws and procedures applicable to government departments. But financial reports are placed in the Parliament for discussion.
(xi) Public Accountability : It’s accounts are audited by the Comptroller and Auditor General of India. Its annual reports and results are placed in Parliament or Legislative Assembly for discussion and hence answerable for their working and results to the Parliament.
(xii) Objective : It is service oriented and not profit oriented. It works efficiently to earn profit which is used for its day to day functioning.
Question 4.
Explain merits and demerits of statutory corporation.
Answer:
(A) Introduction
Statutory Corporations are autonomous bodies established under special legislative Acts. A statutory corporation is formed under a Special Act of Parliament or State Legislature. The powers, duties, functions and scope of operations are laid down in the Act.
LIC, IFCI, SBI, UTI, Air India are the examples of public corporation.
Statutory Corporation is a body with a separate existence, which can sue and be sued and is responsible for its own finance. It is administered by a board appointed by public authority to which it is answerable.
(B) Merits of Statutory Corporation:
(i) Professional Management: Statutory Corporations are managed professionally. The directors and other executives are highly trained and specialize in their respective fields. This leads to efficiency in working.
(ii) Rapid Decisions : Statutory Corporations enjoy autonomy. They can take quick decisions. There is less file work and less formalities to be completed before taking decisions.
(iii) Efficient Staff : In Statutory Corporation, employees are given fair wages, better working conditions and proper training and development programs are initiated for the employees. As a result, employer-employee relations are very cordial and staff is highly motivated to perform better.
(iv) Motivated Staff: In Statutory Corporations, employees are given fair wages, better working conditions and proper training and development programmes are initiated for the employees. As a result, employer- employee relations are very cordial and staff is highly motivated to perform better.
(v) Service Motive : They are formed to provide public utility services and promote consumer satisfaction. It provides essential commodities to people at reasonable rates.
(vi) Easy to Raise Capital : Being owned by government, these corporations can raise required funds by floating bonds at low rate of interest.
(vii) Administrative Autonomy : Due to administrative and financial autonomy, statutory corporation take quick decisions and are flexible in its policy framing and working as per the changing business needs.
(viii) Public Accountability : These organisations enjoy public accountability, flexibility and autonomy in its working. The accounts are audited by Comptroller and Auditor General of India and final accounts are tabled before Parliament or Legislature.
(ix) Initiative and Flexibility : Statutory Corporation have an independent identity different from the government. Though, the overall business policies are formulated by the government, they have administrative autonomy and hence operational flexibility.
(x) Enjoys Economies of Scale : As these organisations are large scale undertakings which promote social welfare, it enjoys economies of large scale business operations.
(xi) Creates Employment Opportunities : Statutory organisations generate employment opportunities for the people at large. LIC, ONGC, Air India and others employ lakhs of people in the country. This reduces government burden of providing jobs to teeming millions and as such they help government.
(xii) Enjoy Monopoly : Most of statutory organisations are monopolistic or semi-monopolistic in their areas of functioning.
(C) Demerits of Statutory Corporation:
Though statutory corporations are autonomous bodies and enjoy flexibility in their working, they have certain limitations which are as follows:
(i) Clashes Amongst Interests : All or majority directors of Statutory Corporations are appointed by the Government from different fields. As there are many members it is quite possible that their interests may clash. The smooth functioning of the corporation may be hampered.
(ii) Autonomy on Paper Only : Ministers, government officials and political parties often interfere with the working and decision making policies which affects the autonomy and flexibility of it.
(iii) Rigid Structure : Though statutory corporation have operational flexibility, they are subject to many rules and regulations. Any changes in the constitution, objects, powers, duties, etc., require amendments to be passed in the parliament which is difficult task. This reduces its flexibility.
(iv) Lack of Initiative : The statutory corporation have no profit motive. There is no competition among them. So employees do not take initiative to increase the profit.
(v) Unfair Practices : Before 1991, these corporations enjoyed monopolistic and semi monopolistic position. They were charging high prices from the consumers to cover up their inefficiencies. After 1991, due to liberalization, most of them lost their monopolistic position but skill, in practice the lack competition as they are not aware of consumer needs.
Question 5.
Explain Government Company and its features.
Answer:
(A) Meaning:
- A Government Company is one in which atleast 51% of its paid up capital is held by the Central Government and / or the State Government.
- State Trading Corporation (STC), Steel Authority of India (SAIL), Bharat Heavy Electricals Ltd (BHEL) etc. are some of the examples of Government Companies.
- These companies are registered under the Indian Companies Act, 2013 and its working is governed by the rules and regulations of the act.
- Government Companies are established for purely business purpose and to complete with the private sector. The shares of the company are purchased in the name of the President of India.
- Government Companies may be registered as public or private limited companies.
(B) Features of Government Company:
The Government Company may be registered as public or private limited companies. These companies are established for purely business purpose and to compete with the private sector.
Following are the features of Government Company:
(i) Free from Procedural Controls: The Government companies have a right to formulate their independent policies and even make necessary changes in them. It enjoys freedom from budgetary, accounting and audit controls which are applicable to Government undertakings.
(ii) Majority of Government Directors : All or majority of directors of such companies are appointed by the Government from different fields. They may be experts from banking sector, insurance sector, who manage the day to day business affairs.
(iii) Public Accountability : The annual accounts of the company are tabled before Parliament or State Legislature for review and discussion. Thus, Government Company is accountable and answerable to the Parliament or State Legislature through the concerned Minister.
(iv) Registration under the Companies Act: The Government Company is registered under the Companies Act, 2013 and its formation, working, management and winding up a business is governed by provisions of- the Act. Government has power to modify or change certain provisions laid down in the Act.
(v) Own Staff: The employees are appointed as per the rules and regulations set by the company. Its employees are not governed by respective Government.
(vi) Promotes Social Welfare : Government Companies aims to optimise national and natural resources such as land, water, electricity, etc. It produces arms, ammunition and other defence equipments. It also brings about balanced regional development and leads to equality of income.
(vii) Objective : It operates on commercial principles and as such its aim is to make profit.
(viii) Separate Legal Entity : A Government Company is a corporate body created under the Companies Act. It has all features of a company such as legal entity, common seal, limited liability, etc. It can enter into contracts and acquire property in its own name.
(ix) Exemptions : Government Company is exempted from budget, accounting and audit laws applicable to government departments. Its accounts are audited by the Government Auditor. The Government has a right to exempt the company from any provisions of Companies Act which may come in its way of providing welfare services to the public at large.
(ix) Suitability : Government Companies are suitable for conducting manufacturing and marketing activities.
Question 6.
Explain Merits and Demerits of Government Company.
Answer:
(A) Merits of Government Company:
(i) Profitability and Accountability : It works on business principles and follows commercial approach. Though not profit oriented like private sector, it does make reasonable profit which is used for public welfare, modernisation, renovation and development. Moreover, its performance can be evaluated by the Parliament as it has public accountability.
(ii) Internal Autonomy: Government Company enjoys financial and administrative autonomy. Its dependence on Government authority is minimum. It has its own capital structure, financial plan, borrowing powers and so on.
(iii) Government Ownership ; The ownership of the government company rests with Central or State Government who owns major capital of the company and as such looks after its management and control. Government always promotes public welfare.
(iv) Foreign Capital and Technical Know how : As the government provides 51% of the capital, the rest 49% can be raised through foreign investment. By seeking foreign capital, Government companies bring advanced technology and technical know how.
(v) Acquisition of Sick Units : A government company can acquire a sick unit in the private sector without rationalisation. It can be acquired by purchasing 51% of the share capital of a private company.
(vi) Concessions and Privileges : As government owns Government Company, it enjoys various concessions, privileges, subsidies, etc. It may also get orders for the products or services from various government departments and agencies. It also has access to use financial resources of the Government.
(vii) Efficiency : Government company has to compete with the private sector companies. Hence, it tries to promote efficiency at all levels and avoids wastages wherever possible. It tries to improve its services to consumers and promotes consumer satisfaction by providing quality goods at reasonable prices.
From the above points, it could be seen that the Government Company enjoys various benefits as it is owned by the Government and blends the objectives of privately owned companies with State owned control and maximise public welfare.
(viii) Professional Management: The management of Government Company is in the hands of the Board of Directors appointed by the Government. Government exercises control on various matters through Board of Directors. They are highly qualified.
(ix) Easy Formation : The formation of Government Company is easy as there is no procedural delay and legal constraints. It does not require special Act or Parliament approval. It comes into existence through executive decision of the Government.
(x) Flexibility : The objects, powers and organisational set up of a Government Company can be altered easily. The company can take prompt decisions regarding management, finance and other related matters due to flexibility in their operations.
(xi) Easy to Alter : The objects, powers and organisational set up of a Government Company can be altered easily. The company can take prompt decisions regarding management, finance and other related matters due to flexibility in their operations.
(xii) Enjoys Private and Public Objective : In a Government Company, attempt is made to combine the operating flexibility of privately owned companies with the advantage of state regulation and control in public interest.
(B) Demerits of Government Company:
Though Government Company enjoys various benefits due to Government ownership and autonomy, it has following limitations:
(i) Inefficiency and Corruption : The Directors have no financial stake in the company and as a result they are indifferent towards working of the company. Due to limited autonomy and petty politics, the efficiency of the enterprise is affected. It results in corruption.
(ii) Lack of Professional view : There is lack of devotion, dedication and systematic approach. In fact, there is no professional approach in various operations and working of the company.
Thus, from the above points it could be seen that there is lot of government and political interference in the Government company which brings about its inefficiency and ineffectiveness.
(iii) Domination of Ministers and Politicians : The ministers of the concerned departments are in charge of the Government Company. In view of Government ownership, political interference is quite common. The Directors try to serve and achieve their political motives rather than realisation of business goals as they are nominated for political gains and not on merits.
(iv) Red Tapism and Delay : The bureaucratic management delays in taking decision and implementing. There is no time frame and the employees are not devoted. There is often delay in preparing various documents and forwarding the same for taking action. Thus, delay, red tape, corruption, avoidance of work and shirking from the responsibility is common sight in Government Company.
(v) Autonomy only in Name : Though there is administrative autonomy, these companies face a lot of interference from the government in all the matters. Appointment of Directors, employees and its working, there is no autonomy. Autonomy is only on paper and not in practice.
(vi) Weak Public Accountability : Absence of Government audit is a major draw back in case of Government company which does not assure proper utilisation of funds. There is no control on misappropriation of funds which leads to weak public accountability.
(vii) Fear of Exposure : The working of Government Company like annual report is placed before the parliament or State Legislature. It is exposed to press and public criticism. Therefore, management of the government company often gets demoralized.
(viii) Lack of Expertise: The managerial key personnel of a Government Company are deputed from government departments. Such person, generally, lack expertise and commitment leading to lower operational efficiency of the Government Company.
(ix) Ineffective Control of Parliament : There is lack of control of the Parliament in the working of the Government company. Parliament is not having direct control, due to which the officers shirk from responsibility and postpone decision making. It affects efficiency of Government company.
(x) Poor Labour Management Relations : The employer-employee relations in the Government companies are poor. This is the result of corrupt and inefficient management of selfish trade unions. Proper work culture is found absent in Government companies.

Question 7.
Explain Multinational Corporation and its features.
Answer:
(A) Meaning:
(i) Global enterprises or Multinational Corporations are the Corporations which under take business activities in more than one country. Any company having its head office in one country and place of business in other countries is called a Multinational Corporation.
(ii) Multinational Corporation played an important role in the Indian Economy since 1991. They have become a common feature of developing economies in the world.
A Multinational Corporation is a corporation which operates, in addition to the country in which it is incorporated, in one or more other countries.
(B) Features of Multinational Corporation:
Following are the features of Multinational Corporation:
(i) Advanced and Sophisticated Technology : Multinational company has large capital and sophisticated technology and infrastructure. As a result it undertakes diversified and multifarious activities including manufacturing, marketing, financial, research and development.
(ii) Legal Existence : MNCs are registered in their home country as per their laws and as such they enjoy separate legal status. It can sue and be sued, enter into contracts and own property in their own name.
(iii) Government: MNCs have to bring about the necessary changes in their functioning based upon the laws prevailing in the countries of their operations. For e.g. advertisement about various products on TV is given in local languages in India and in national language Hindi, to cover maximum target audience. In some cases they have to change the menu to suit local demands for e.g. McDonalds had to change its menu for its business in India.
(iv) Origin: The MNCs have origin in one country and the country to which they belong is called home country. The country in which they operate their business activities is called host country. These companies are registered in their home country and have a place of business in different countries of the world. The head office controls the operations of different branches through a network of internet. They also appoint their representatives in host countries for smooth business operations.
(v) Research & Development: MNCs give lot of importance to research and development activities. They are also fully equipped and have necessary infrastructure. The R&D is undertaken for finding out new product, new system, new technology, new methods of doing business in an economical way.
(vi) International Operations : Multinational Corporation play a significant role in world trade. Nearly 40% of the world is contributed by the multinational companies.
(vii) Target Profit Oriented : Earning profit is the main motive of MNCs. For this purpose they introduce new and novel products, launch new marketing schemes, organize trade fairs and exhibitions, does lots of publicity and adopts professional approach in all its dealings.
(viii) Huge Assets and Turnover : Multinational Corporation have huge financial strength because of huge capital and assets. This enables it to develop its business potential in developing and under developing nations where they can earn handsome profits.
(ix) Mighty Economic Power: Multinational Corporation has a huge capital and assets so they have a mighty economic power. They keep on adding to their economic power through constant mergers and acquisitions of companies in host countries.
(x) Centralized Control: Multinational Corporation is managed by parent company. It manages affairs of the subsidiary company from the respective home country. Multinational corporations are controlled by parent companies and mostly home strategic.
(xi) Area of Operation : MNCs operate in different countries of the world and deal in multiple products on a large scale. They operate in those countries where chance of maximizing profit is more. MNCs of developed nations dominate the global market and they undertake production or marketing activities and so on. For . e.g. Coca Cola, Tata Tea and so on have global presence.
(xii) Professional Management: A MNC employs professionally qualified personnel to handle huge funds, advanced technology and international operations.
Question 8.
Explain Merits and Demerits of Multinational Corporation
Answer:
(A) Introduction:
(i) Global enterprises or Multinational Corporations are the Corporations which under take business activities in more than one country. Any company having its head office in one country and place of business in other countries is called a Multinational Corporation.
(ii) Multinational Corporation played an important role in the Indian Economy since 1991. They have become a common feature of developing economies in the world.
A Multinational Corporation is a corporation which operates, in addition to the country in which it is incorporated, in one or more other countries.
(B) Merits of Multinational Corporation:
Following are the merits of Multinational Corporation.
(i) Proper use of Idle Resources : The national income of host country increases as MNCs use idle physical and human resources with latest technologies.
(ii) Inflow of Foreign Capital: Multinational corporations bring much needed foreign capital for the rapid development of developing countries. This capital is useful for growth of domestic country.
(iii) Promotion of International Brotherhood and Culture: MNCs integrate economies of various nations with the world economy and promote international brotherhood and culture with peace and prosperity in the world.
(iv) End of Local Monopolies : In global market, Multinational Corporations end local monopolies of host . countries improving their products and reduces prices.
(v) Technical Development: Multinational corporations gives lot of importance to research and development activities. They are also fully equipped and have necessary infrastructure. The research and development is undertaken for finding out new product, new system, and new technology of doing business in an economical way.
(vi) Improvement of Standard of Living : Multinational Corporations supply their product at very reasonable prices in the global market. E.g. the price of wrist watches, cell phones, etc. This helps to improve the standard of living of people of host countries.
(vii) Managerial Development : Multinational corporations have highly specialized and expert team of management. These experts are hired from different countries of the world. Also their functioning is highly professional. They adopt new technology and use huge resources.
(viii) Employment Generation : MNCs create large scale employment opportunities in host countries and . helps in reducing unemployment.
(C) Demerits of Multinational Corporation:
(i) Danger for Domestic Industries : Multinational Corporations have vast economic power so they are danger to domestic industries which are still in process of development. Domestic industries not so powerful to face the challenges of Multinational Corporation.
(ii) Create Problem for Environment: Profit is sole objective of multinational corporation. Such companies damage environment of developing countries. To lower the price of goods they dump lower standard quality product which harms local soil, water and air.
(iii) Outsourcing of Job: Normally MNCs outsource the job work due to lower cost, due to this their liabilities towards employees are reduced.
(iv) Misuse of Mighty Status : Multinational Corporations have powerful financial strength because of huge capital. They can afford to bear losses for a long while in the hope of earning huge profits. They have ended local competition and achieved monopoly. This may be unfair.
(v) Multinational Corporations Import Skilled Labour : Most companies in this position imports the skilled labour they require from other economic to meet their needs. That means the best jobs, especially in the developing world, are given to people who don’t even live in the local economy. Those wages do not offer the same economic benefits because spending occurs internationally instead of at the local level.
(vi) Interference : Multinational Corporations are gigantic organizations with huge finance and efficient management. They try to bring about expansion of business through mergers, acquisitions and amalgamations. As they are huge corporations they exert influence on political parties and try to spread political ideology of their home country.

(vii) Take away Profits to Home Country : Profits made by multinational corporations are not used in the same country from where they are earned. They are not interested in development of other countries. They do not use their profits on infrastructural development of other countries.
(viii) E ncourage Political Corruption : To get favourable terms and conditions in host country multinational corporations bribe to political parties.
(ix) Repatriation of Profiles : Multinational Corporations get huge profit. Repatriation of profit by Multinational Corporation adversely affects the foreign exchange reserves of the host country. If means that a large amount of foreign exchange goes out of host country.
OCM 11th Commerce Textbook Solutions Digest
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
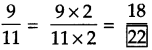
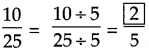

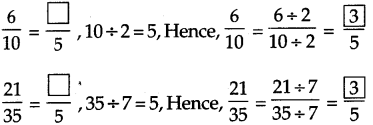
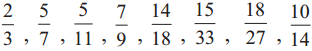

 . Therefore, 16/28 and 21/28 are the required like fractions.
. Therefore, 16/28 and 21/28 are the required like fractions.

 So let us divide each part on this strip into two equal parts. \(\frac{4}{6}\) is a fraction equivalent to \(\frac{2}{3}\). Now, as 16 is to be added to \(\frac{2}{3}\) i.e. to \(\frac{4}{6}\), we shall colour one more of the six parts on the strip. Now, the total coloured part is \(\frac{5}{6}\).
So let us divide each part on this strip into two equal parts. \(\frac{4}{6}\) is a fraction equivalent to \(\frac{2}{3}\). Now, as 16 is to be added to \(\frac{2}{3}\) i.e. to \(\frac{4}{6}\), we shall colour one more of the six parts on the strip. Now, the total coloured part is \(\frac{5}{6}\).