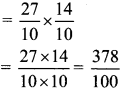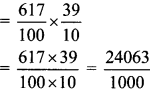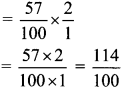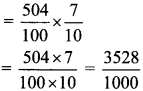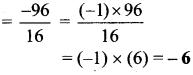Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 7 Maths Solutions covers the 7th Std Maths Practice Set 17 Answers Solutions Chapter 4 Angles and Pairs of Angles.
Angles and Pairs of Angles Class 7 Maths Chapter 4 Practice Set 17 Solutions Maharashtra Board
Std 7 Maths Practice Set 17 Solutions Answers
Question 1.
Write the measures of the supplements of the angles given below:
i. 15°
ii. 85°
iii. 120°
iv. 37°
v. 108°
vi. 0°
vii. a°
Solution:
i. Let the measure of the supplementary angle be x°.
∴ 15 + x = 180
∴ 15 + x – 15 = 180 – 15
….(Subtracting 15 from both sides)
∴ x = 165
∴ The measures of the supplement of an angle of 15° is 165°.
ii. Let the measure of the supplementary angle be x°.
∴ 85 + x = 180
∴ 85 + x – 85 = 180 – 85
….(Subtracting 85 from both sides)
∴ x = 95
∴ The measures of the supplement of an angle of 85° is 95°.
iii. Let the measure of the supplementary angle be x°.
∴ 120 + x = 180
∴ 120 + x – 120 = 180 – 120
….(Subtracting 120 from both sides)
∴ x = 60
∴ The measures of the supplement of an angle of 120° is 60°.
iv. Let the measure of the supplementary angle be x°.
∴ 37 + x = 180
∴ 37 + x – 37 = 180 – 37
….(Subtracting 37 from both sides)
∴ x = 143
∴ The measures of the supplement of an angle of 37° is 143°.
v. Let the measure of the supplementary angle be x°.
∴ 108 + x = 180
∴ 108 + x – 108 = 180 – 108
….(Subtracting 108 from both sides)
∴ x = 72
∴ The measures of the supplement of an angle of 108° is 72°.
vi. Let the measure of the supplementary angle be x°.
∴0 + x = 180
∴ x = 180
∴ The measures of the supplement of an angle of 0° is 180°.
vii. Let the measure of the supplementary angle be x°.
∴ a + x = 180
∴ a + x – a = 180 – a
….(Subtracting a from both sides) x = (180 – a)
∴ The measures of the supplement of an angle of a° is (180 – a)°.
Question 2.
The measures of some angles are given below. Use them to make pairs of complementary and supplementary angles.
m∠B = 60°
m∠N = 30°
m∠Y = 90°
m∠J = 150°
m∠D = 75°
m∠E = 0°
m∠F = 15°
m∠G = 120°
Solution:
i. m∠B + m∠N = 60° + 30°
= 90°
∴∠B and ∠N are a pair of complementary angles.
ii. m∠Y + m∠E = 90° + 0°
= 90°
∴∠Y and ∠E are a pair of complementary angles.
iii. m∠D + m∠F = 75° + 15°
= 90°
∴∠D and ∠F are a pair of complementary angles.
iv. m∠B + m∠G = 60° + 120°
= 180°
∴∠B and ∠G are a pair of supplementary angles.
v. m∠N + m∠J = 30° + 150°
= 180°
∴∠N and ∠J are a pair of supplementary angles.
Question 3.
In ΔXYZ, m∠Y = 90°. What kind of a pair do ∠X and ∠Z make?
Solution:
In ΔXYZ,
m∠X + m∠Y + m∠Z = 180° ….(Sum of the measure of the angles of a triangle is 180°)
∴m∠X + 90 + m∠Z = 180
∴m∠X + 90 + m∠Z – 90 = 180 – 90 ….(Subtracting 90 from both sides)
∴m∠X + m∠Z = 90°
∴∠X and ∠Z make a pair of complementary angles.
Question 4.
The difference between the measures of the two angles of a complementary pair is 40°. Find the measures of the two angles.
Solution:
Let the measure of one angle be x°.
∴Measure of other angle = (x + 40)°
x + (x + 40) = 90 …(Since, the two angles are complementary)
∴ 2x + 40 – 40 = 90 – 40 ….(Subtracting 40 from both sides)
∴2x = 50
∴x = \(\frac { 50 }{ 2 }\)
∴x = 25
∴x + 40 = 25 + 40
= 65
∴The measures of the two angles is 25° and 65°.
Question 5.
₹PTNM is a rectangle. Write the names of the pairs of supplementary angles.

Solution:
Since, each angle of the rectangle is 90°.
∴ Pairs of supplementary angles are:
i. ∠P and ∠M
ii. ∠P and ∠N
iii. ∠P and ∠T
iv. ∠M and ∠N
v. ∠M and ∠T
vi. ∠N and ∠T
Question 6.
If m∠A = 70°, what is the measure of the supplement of the complement of ∠A?
Solution:
Let the measure of the complement of ∠A be x° and the measure of its supplementary angle be y°.
m∠A + x = 90°
∴70 + x = 90
∴70 + x – 70 = 90 – 70 ….(Subtracting 70 from both sides)
∴x = 20
Since, x and y are supplementary angles.
∴x + y = 180
∴20 + y = 180
∴20 + y – 20 = 180 – 20 ….(Subtracting 20 from both sides)
∴y = 160
∴The measure of supplement of the complement of ∠A is 160°.
Question 7.
If ∠A and ∠B are supplementary angles and m∠B = (x + 20)°, then what would be m∠A?
Solution:
Since, ∠A and ∠B are supplementary angles.
∴m∠A + m∠B = 180
∴m∠A + x + 20 = 180
∴m∠A + x + 20 – 20 = 180 – 20 ….(Subtracting 20 from both sides)
∴m∠A + x = 160
∴m∠A + x – x = 160 – x ….(Subtracting x from both sides)
∴m∠A = (160 – x)°
∴The measure of ∠A is (160 – x)°.
Maharashtra Board Class 7 Maths Chapter 4 Angles and Pairs of Angles Practice Set 17 Intext Questions and Activities
Question 1.
Observe the figure and answer the following questions. (Textbook pg. no. 26)
T is a point on line AB.
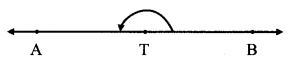
- What kind of angle is ∠ATB?
- What is its measure?
Solution:
- Straight angle
- 180°
Std 7 Maths Digest