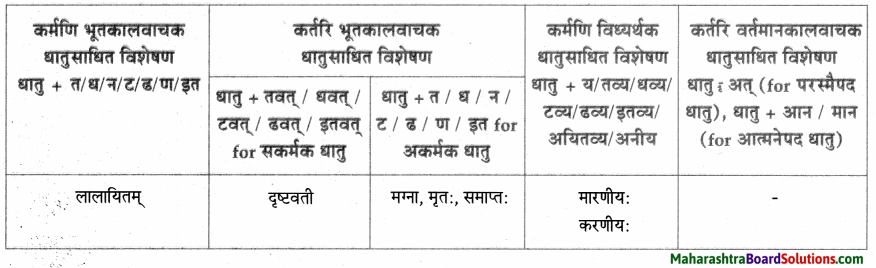
Class 9th Sanskrit Aamod Chapter 14 काव्यशास्त्रविनोदः Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 9 Sanskrit Solutions Aamod Chapter 14 काव्यशास्त्रविनोदः Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Std 9 Sanskrit Chapter 14 Question Answer
Sanskrit Aamod Std 9 Digest Chapter 14 काव्यशास्त्रविनोदः Textbook Questions and Answers
भाषाभ्यास:
श्लोकः 1
1. एकवाक्येन उत्तरत।
प्रश्न अ.
विपर्ययः कस्मिन् शब्दे दृश्यते ?
उत्तरम् :
विपर्ययः ‘साक्षराः’ इति पदे दृश्यते।
प्रश्न आ.
विपर्यय: कस्मिन् शब्दे न दृश्यते ?
उत्तरम् :
विपर्ययः ‘सरस’ इति पदे न दृश्यते।
प्रश्न इ.
मानवाः कीदृशाः भवेयुः?
उत्तरम् :
मानवा: साक्षराः भवेयुः।

प्रश्न ई.
मानवाः कीदृशाः न भवेयु:?
उत्तरम् :
मानवा: राक्षसाः न भवेयुः।
2. कोष्टकं पूरयत।
प्रश्न 1.
कोष्टकं पूरयत।
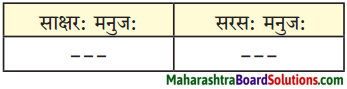
(सरसत्वम्, राक्षसत्वम्, विपरीतत्वम्)
उत्तरम् :
1. राक्षसत्वम्
2. सरसत्वम्

3. समानार्थकशब्द लिखत ।
राक्षसः, सरसः
प्रश्न 1.
समानार्थकशब्द लिखत ।
राक्षसः, सरसः
उत्तरम् :
- राक्षस: – असुरः।
- सरस: – रसपूर्णः।
4. सन्धिविग्रहं कुरुत।
प्रश्न 1.
अ) विपरीतोऽपि = …………..
आ) विपरीताश्चेत् = प्रलोकः
उत्तरम् :
अ) विपरीतोऽपि – विपरीतः + अपि।
आ) विपरीताश्चेत् – विपरीताः + चेत्।

श्लोकः 2
2. 1. एकवाक्येन उत्तरत।
प्रश्न अ.
वृक्षाग्रवासी कः?
उत्तरम् :
पक्षिराजः वृक्षाग्रवासी।नारिकेलं वृक्षाग्रवासी।
प्रश्न आ.
कः पक्षिराजः?
उत्तरम् :
गरुडः पक्षिराजः अस्ति ।
प्रश्न इ.
क: त्रिनेत्रधारी?
उत्तरम् :
शङ्करः त्रिनेत्रधारी। नारिकेलं त्रिनेत्रधारी।

प्रश्न ई.
कः शूलपाणिः ?
उत्तरम् :
शङ्करः शूलपाणिः।
प्रश्न उ.
क: जलं बिभर्ति ?
उत्तरम् :
घट: मेघः च जलं बिभर्तः। नारिकेलं जलं बिभर्ति।
प्रश्न ऊ.
कः त्वम्वस्त्रं धारयति ?
उत्तरम् :
सिद्धयोगी त्वम्वस्त्र धारयति। नारिकेलं त्वग्वस्वं धारयति।
2. शब्दसमूहस्य कृते एकं संक्षेपशब्द लिखत ।
प्रश्न 1.
अ) यः वृक्षस्य अग्रभागे निवसति – ……………
आ) पक्षिणां राजा – ……………
इ) यस्य त्रीणि नेत्राणि – …………..
ई) शूलं पाणौ यस्य सः – ……………
उ) यः त्वग्वस्त्रं धारयति – …………….
उत्तरम् :
अ) यः वृक्षस्य अग्रभागे निवसति – वृक्षाग्रवासी।
आ) पक्षिणां राजा – पक्षिराजः।
इ) यस्य त्रीणि नेत्राणि – त्रिनेत्रधारी।
ई) शूलं पाणौ यस्य सः – शूलपाणिः।
उ) य: त्वग्वस्त्रं धारयति . त्वग्वस्त्रधारी।

3. योग्यं पर्यायं चिनुत –
प्रश्न 1.
अ. पक्षिराजः वृक्षाग्रे (वसति/न वसति)।
आ. घटः त्रीणि नेत्राणि (धारयति/न धारयति)।
इ. शूलपाणिः जलं (बिभर्ति न बिभर्ति)।
ई. नारिकेलं त्वग्वस्त्रं (धारयति/न धारयति)।
उत्तरम् :
अ. पक्षिराज: वृक्षाग्रे वसति।
आ. घट: त्रीणि नेत्राणि न धारयति।
इ. शूलपाणि: जलं न बिभर्ति।
ई. नारिकेलं त्वग्वस्वं धारयति।

4. समानार्थकशब्दयुग्मं चिनुत लिखत च।
पक्षिराजः, शूलपाणिः, जलम्, मेघः, शङ्करः, वृक्षः, सिद्धयोगी, गरुडः, तरुः, तोयम्, जलदः, तपस्वी।
प्रश्न 1.
पक्षिराजः, शूलपाणिः, जलम्, मेघः, शङ्करः, वृक्षः, सिद्धयोगी, गरुडः, तरुः, तोयम्, जलदः, तपस्वी।
उत्तरम् :
- पक्षिराज: – गरुडः।
- शूलपाणिः – शङ्करः।
- जलम् – तोयम्।
- मेष: – जलदः।
- वृक्षः – तरुः।
- सिद्धयोगी – तपस्वी।
श्लोकः 3.
1. कः कं वदति? ‘पत्रं लिख।’
प्रश्न 1.
कः कं वदति? ‘पत्रं लिख।’
उत्तरम् :
पिता पुत्रं वदति।

2. एकवाक्येन उत्तरत।
प्रश्न अ.
केन आज्ञा दत्ता?
उत्तरम् :
तातेन आज्ञा दत्ता।
प्रश्न आ.
केन आज्ञा न लजिता ।
उत्तरम् :
पुत्रेण आज्ञा न लङ्घिता।

प्रश्न इ.
पत्रं केन लिखितम् ?
उत्तरम् :
पुत्रेण पत्रं लिखितम्।
3. विशेषण-विशेष्य-अन्वितिं पूरयत ।
प्रश्न 1.
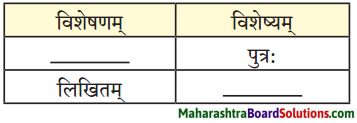
उत्तरम् :
1. कथितः
2. पत्रम्
4. सन्धिविग्रहं कुरुत।
प्रश्न 1.
ममाज्ञया, पितुराज्ञा
उत्तरम् :
- ममाज्ञया – मम + आज्ञया।
- पितुराज्ञा – पितुः + आज्ञा।
5. श्लोकात् ‘क्त’ प्रत्ययान्तरूपाणि (क.भू.धा.वि.)
चिनुत लिखत च।
उत्तरम् :
- कथितम्
- लिखितम्
- लक्षिता

श्लोकः 4.
1. क्रमानुसारं रचयत।
प्रश्न 1.
अ. त्रि-अक्षरयुक्ते शब्दे ‘य’ मध्ये तिष्ठति ।
आ. शब्दस्य आरम्भे ‘न’ विद्यते।
इ. शब्दस्य अन्ते अपि ‘न’ विद्यते।
उत्तरम् :
आ. शब्दस्य आरम्भे ‘न’ विद्यते,
अ. त्रि-अक्षरयुक्ते शब्दे ‘य’ मध्ये तिष्ठति।
इ. शब्दस्य अन्ते अपि ‘न’ विद्यते।
2. प्राप्तम् उत्तरम् – [ ] [ ] [ ]
प्रश्न 1.
प्राप्तम् उत्तरम् – [ ] [ ] [ ]
3. सन्धिं कुरुत।
प्रश्न 1.
अ. तस्य + आदिः (अ + आ) ………….
आ. तस्य + अन्तः (अ + अ) ………..
इ. तव + अपि (अ + अ) ………..
ई. अपि + अस्ति (इ + अ) ……….
उत्तरम् :
अ. तस्यादिर्न – तस्य + आदि: + न।
आ. तस्यान्तः – तस्य + अन्तः।
इ. तवाप्यस्ति – तव + अपि + अस्ति।
ई. ममाप्यस्ति – मम + अपि + अस्ति।

4. श्लोकात् षष्ठ्यन्तपदानि चिनुत लिखत च।
प्रश्न 1.
श्लोकात् षष्ठ्यन्तपदानि चिनुत लिखत च।
श्लोकः 5.
1. तालिकापूर्ति कुरुत।
प्रश्न 1.
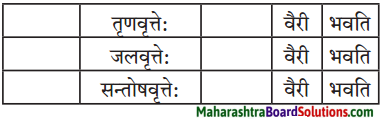
मञ्जूषा-(सज्जनस्य,धीवरः,लुब्धकः,मृगस्य,मीनस्य, पिशुन:)
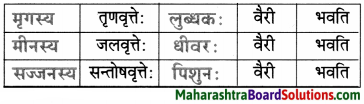
उत्तरम् :
2. अधोदत्तवाक्यानि श्लोकस्थ-समानार्थक-शब्दैः पुन: लिखत।
प्रश्न अ.
हरिणः शष्पाणि भक्षयति तथापि व्याधः तस्य शत्रुः भवति।
उत्तरम् :
मृगः शष्पाणि भक्षयति तथापि लुब्धकः तस्य वैरी भवति।
प्रश्न आ.
मत्स्य: जलं पिबति तथापि धीवरः तस्य रिपुः भवति।
उत्तरम् :
मीन : तोयं पिबति तथापि धीवर: तस्य वैरी भवति।

प्रश्न इ.
सत्पुरुषः निःस्पृहः वर्तते तथापि दुर्जनः तस्य अरि: भवति।
उत्तरम् :
सज्जन : निस्पृहः वर्तते तथापि पिशुन: तस्य वैरी भवति।
श्लोकः 6.
1. एकवाक्येन उत्तरत।
प्रश्न अ.
कस्याः नद्याः वर्णनं सुभाषिते वर्तते?
उत्तरम् :
गङ्गानद्या: वर्णनं सुभषिते वर्तते।
प्रश्न आ.
शतचन्द्रं नभस्तलं कुत्र शोभते ?
उत्तरम् :
गढ़ानद्या: चञ्चलतरे वारिणि शतचन्द्रं नभस्तलं शोभते।
2. विशेषणैः जालरेखाचित्रं पूरयत ।
प्रश्न 1.
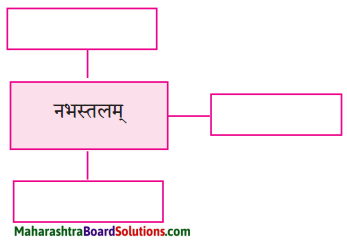
उत्तरम् :
- प्रतिबिम्बितम्
- शतचन्द्रम्
- तारकायुक्तम्

3. विशेषणं लिखत।
प्रश्न 1.
विशेषणं लिखत।
1. …………. वारिणि।
2. ……………नभस्तलम्।
उत्तरम् :
1. चञ्जलतरे वारिणि।
2. तारकायुक्तम् नभस्तलम्।
4. गङ्गा इति शब्दस्य अमरपङ्क्तिं लिखत।
प्रश्न 1.
गङ्गा इति शब्दस्य अमरपङ्क्तिं लिखत।
उत्तरम् :
गङ्गा – जाह्नवी, भागीरथी जहुतनया, विष्णुपदी।
श्लोकः 7.
1. रिक्तस्थानं पूरयत।
प्रश्न 1.
अ. त्वं धनिनां ………………………. मुहुः न ईक्षसे।
आ. त्वं मृषा चाटून् न ……………. ।
इ. त्वं एषां ………………. न शृणोषि।
ई. त्वं तान् प्रति …………….. न धावसि।
उ. त्वं काले बालतृणानि …………..।
ऊ. त्वं …………….. निद्रासि।
ऋ. हे कुरङ्ग, तद् …………………. ब्रूहि।
ऋ. भवता किं नाम तपः …………………….।

2. प्रश्ननिर्माणं कुरुत।
प्रश्न अ.
त्वं धनिनां वक्त्रं मुहुः न ईक्षसे।
उत्तरम् :
त्वं किं मुहुः न ईक्षसे?
प्रश्न आ.
त्वं निद्रागमे निद्रासि।
उत्तरम् :
त्वं कदा निद्रासि?
3. समानार्थकशब्दं चिनुत लिखत च।
वदनम्, असत्यम्, शष्पम्, स्वापः, मृगः, पश्यसि
प्रश्न 1.
समानार्थकशब्दं चिनुत लिखत च।
वदनम्, असत्यम्, शष्पम्, स्वापः, मृगः, पश्यसि
उत्तरम् :
- वक्त्रम् – मुखम, तुण्डम्, वदनम्।
- मृषा – असत्यम्, मिथ्या।
- तृणम् – शष्पम्।
- निद्रा – स्वापः, शयनम्।
- मृगः – हरिणः।
- ईक्षसे – पश्यसि।

4. श्लोकात् षष्ठ्यन्तपदे चिनुत लिखत च।
प्रश्न 1.
श्लोकात् षष्ठ्यन्तपदे चिनुत लिखत च।
उत्तरम् :
तस्य, तव, मम
Sanskrit Aamod Class 9 Textbook Solutions Chapter 14 काव्यशास्त्रविनोदः Additional Important Questions and Answers
एकवाक्येन उत्तरत।
प्रश्न 1.
सरसत्वं कदा न मुञ्चति?
उत्तरम् :
‘सरस’ इति पदस्य अक्षराणां क्रम: विपरीतं क्रियते चेत् अपि तस्य सरसत्वं न मुञ्चति।
प्रश्न 2.
‘साक्षरा’ इति पदं विपरीतं क्रियते चेत् किं भवति?
उत्तरम् :
‘साक्षरा’ इति पदं विपरीतं क्रियते चेत् ‘राक्षसा’ इति भवति।
प्रश्न 3.
गङ्गायाः वारिणि किं शोभते?
उत्तरम् :
गङ्गायाः वारिणि तारकायुक्तं शतचन्द्रं नभस्तलं शोभते।

प्रश्न 4.
मृगाः किं खादन्ति?
उत्तरम् :
मृगाः तृणानि खादन्ति।
प्रश्न 5.
मीनाः कुत्र विहरन्ति?
उत्तरम् :
मीनाः जले विहरन्ति।
प्रश्न 6.
सज्जनानां का वृत्तिः?
उत्तरम् :
सन्तोषः इति सज्जनानां वत्तिः।
प्रश्न 7.
अस्याः प्रहेलिकाया: उत्तरं किम् ?
उत्तरम् :
‘नयन’ इति अस्याः प्रहेलिकायाः
प्रश्न 8.
पुत्रेण कस्य आज्ञा न लचिता?
उत्तरम् :
पुत्रेण पितु: आज्ञा न लड़िता।

प्रश्न 9.
कुरङ्गः किं न ईक्षते?
उत्तरम् :
कुरङ्गः धनिनां वक्त्रं न ईक्षते।
प्रश्न 10.
कुरङ्गः किं न शृणोति?
उत्तरम् :
कुरङ्ग: गर्ववचः न शृणोति।
प्रश्न 11.
कुरङ्गः किं खादति?
उत्तरम् :
कुरङ्गः बालतृणानि खादति।
प्रश्न 12.
कुरङ्गः किं न बूते?
उत्तरम् :
कुरङ्गः मृषा चाटून् न बूते।

लकारं लिखत।
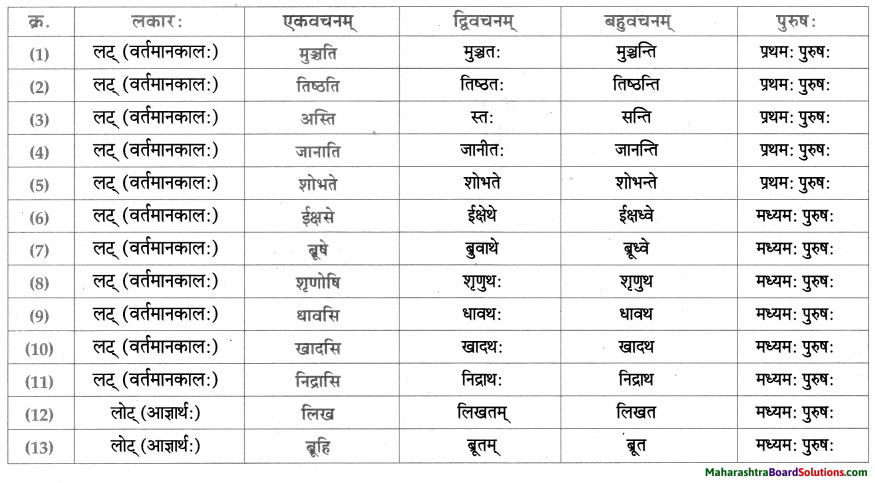
- मुशति – मुच्-मुक् धातुः षष्ठगण: उभयपदम् अत्र परस्मैपदं लट्लकार : प्रथमपुरुष: एकवचनम्।
- ईक्षसे – ईक्ष् धातुः प्रथमगण; आत्मनेपदं लट्लकार: मध्यमपुरुषः एकवचनम्।
- खादसि – खाद् धातुः प्रथमगणः परस्मैपदं लट्लकार: मध्यमपुरुष: एकवचनम्।
- पे – दूधातुः द्वितीयगण: उभयपदम् अत्र आत्मनेपदं लट्लकार: मध्यमपुरुष: एकवचनम्।
- शृणोषि – शु धातुः पञ्चमगणः परस्मैपदं लट्लकार: मध्यमपुरुष: एकवचनम्।
- धावसि – धाव् धातुः प्रथमगणः परस्मैपदं लट्लकार: मध्यमपुरुषः एकवचनम्।
- शोभते – शुभ् धातुः प्रथमगण: आत्मनेपदं लट्लकार: प्रथमपुरुषः एकवचनम्
- तिष्ठति – ‘स्था-तिष्ठ्’ धातुः प्रथमगण: परस्मैपदं लट्लकार: प्रथमपुरुषः एकवचनम्।
- जानाति – ‘ज्ञा’ धातुः नवमगण: उभयपदम् अत्र परस्मैपदं लट्लकार: प्रथमपुरुष: एकवचनम्।
- लिख – लिख् धातुः षष्ठगणः परस्मैपद लोट्लकार: मध्यमपुरुष: एकवचनम्
विभक्त्यन्तपदानि।
- प्रथमा – वृक्षाप्रवासी, पक्षिराजः, त्रिनेत्रधारी, त्वग्वसधारी, सिद्धयोगी, घटः, मेघः, वैरिणः, पिशुनाः, तृणम्, जलम्, सन्तोषः, प्रतिबिम्बितम्, तारकायुक्तम्, शतचन्द्रम्, नभस्तलम्।
- द्वितीया – वक्त्रम्, चाटून, तान, बालतृणानि।
- तृतीया – आशया, भवता।
- षष्ठी – सज्जनानाम्, वृत्तीनाम्, धनिनाम्, एषाम्।
- सप्तमी – जगति, चञ्चलतरे, वारिणि।

प्रश्ननिर्माणं कुरुत।
प्रश्न 1.
- पितुः आज्ञा न लाविता।
- पत्रं लिख।
- बालतृणानि खादसि।
- त्वं मृषा चाटून् न बूषे।
- तारकायुक्तं शतचन्द्रं नभस्तलं शोभते।
- गङ्गायाः वारिणि नभस्तलं प्रतिबिम्बितम्।
उत्तरम् :
- कस्य आज्ञा न लविता?
- किं लिख?
- त्वं किं खादसि?
- त्वं किं न बूषे?
- कीदृशं नभस्तलं शोभते?
- नभस्तलं कुत्र प्रतिबिम्बितम्?

पद्यांशं पठित्वा जालरेखाचित्रं पूरयत।
प्रश्न 1.
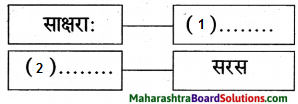
उत्तरम् :
1. राक्षसाः
2. सरस
प्रश्न 2.
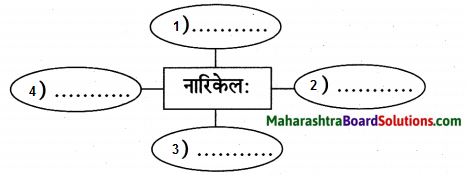
उत्तरम् :
- वक्षाग्रवासी
- जलं बिभ्रन्
- त्वग्वस्त्रधारी
- त्रिनेत्रधारी

प्रश्न 3.
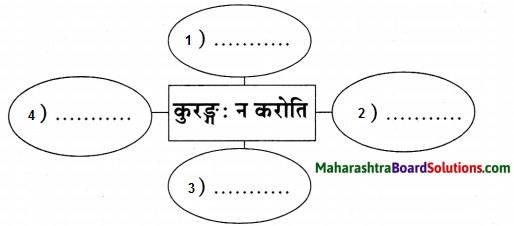
उत्तरम् :
- धनिनां वक्त्रस्य ईक्षणम्,
- धनिनां गर्ववचस: श्रवणम्,
- धनिनां प्रति आशया धावनम्,
- मृषा चाटूभाषणम्
समानार्थकशब्दं योजयित्वा वाक्यं पुनर्लिखत।
- पुत्र – पत्रं लिख। तनय, पत्रं लिख।
- नभस् – नभः शोभते। गगनं शोभते।
- वैरिन – जगति वैरी निष्कारणम् अस्ति। जगति शत्रुः निष्कारणम् अस्ति।

व्याकरणम् :
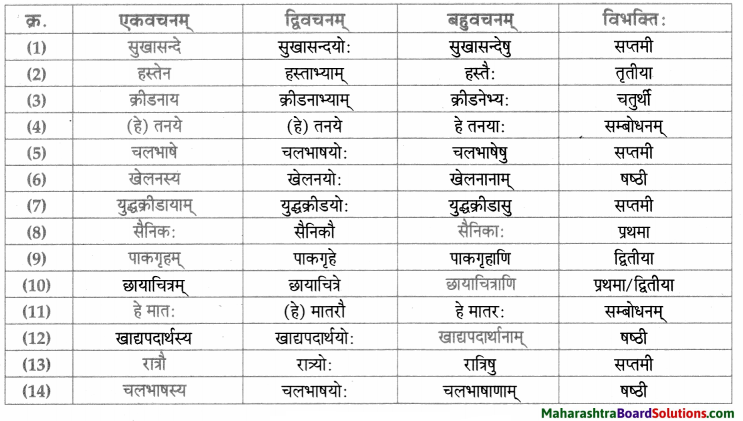
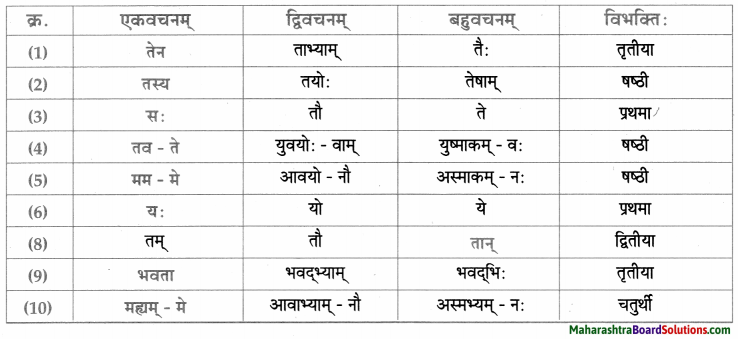
नाम – तालिका।
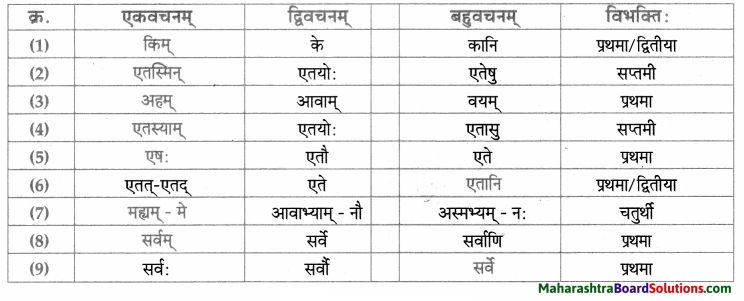
सर्वनाम – तालिका।

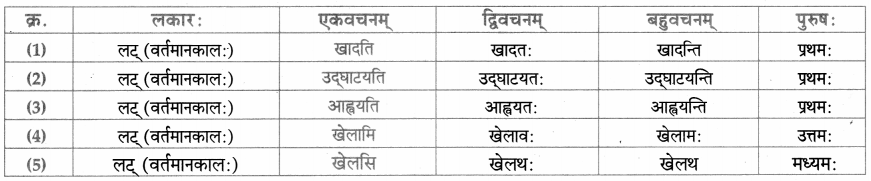
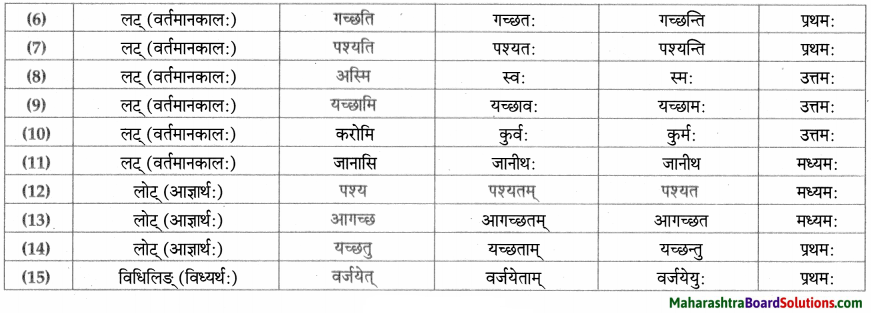
धातु – तालिका।
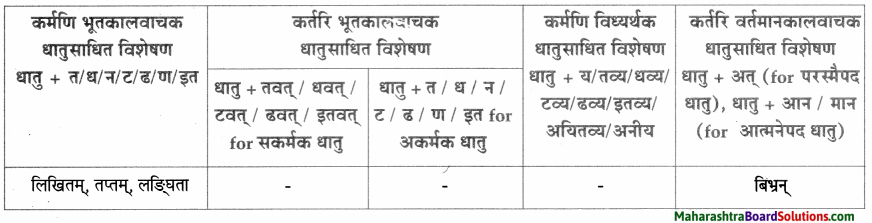
समासाः।
| समस्तपदम् |
अर्थ: |
समासविग्रहः |
समासनाम |
| पक्षिराजः |
king of birds |
पक्षिणां राजा। |
षष्ठी तत्पुरुष समास। |
| मृगमीनसज्जनानाम् |
of deers, fishes and noble ones |
मृगा: च मौना: च सज्जनाः च, तेषाम्। |
इतरेतर द्वन्द्व समास। |
| लुब्धकधीवरपिशुना: |
hunters, fishermen and wicked ones |
लुब्धकाः च धीवरा: च पिशुनाः च, तैः। |
इतरेतर द्वन्द्व समास। |
| नभस्तलम् |
surface of sky |
नभस: तलम्। |
षष्ठी तत्पुरुष समास। |

धातुसाधितविशेषणानि।
| धातुसाधित – विशेषणम् |
विशेष्यम् |
| लिखितम् |
पत्रम् |
| लङ्घिता |
आज्ञा |
| बिभ्रन् |
मेघः |
| तप्तम् |
तपः |
काव्यशास्त्रविनोदः Summary in Marathi and English
प्रस्तावना :
काव्यशास्त्रविनोद म्हणजे काव्य आणि शास्त्र यांच्याद्वारे केलेले मनोरंजन.
हा शब्द –
‘काव्यशास्त्रविनोदेन कालो गच्छति धीमताम्।
व्यसनेन च मूर्खाणां निद्रया कलहेन वा।।’
या श्लोकात आला आहे. याचा अर्थ असा – बुद्धिमान लोक काव्य आणि शास्त्र यांद्वारे मनोरंजन करण्यात वेळ वापरतात. तर मूर्ख लोक व्यसन, झोप, भांडण यांत वेळ घालवतात. संस्कृत भाषा सुभाषितांनी नटलेली आहे. काही सुभाषिते इतकी चमत्कृतीपूर्ण असतात की ती समजण्यासाठी आपल्या बुद्धीला ताण द्यावा लागतो. ती सुभाषिते समजायला अवघड असली तरी मनोरंजकसुद्धा असतात.
टीप : – या पद्यातील श्लोक हे माध्यमभाषेत भाषांतरासाठी आहेत आणि त्यांचे स्पष्टीकरणसुद्धा अपेक्षित आहे.
काव्यशास्त्रविनोद means amusement derived from poetry and science. This phrase is a part of the shlok
‘काव्यशास्त्रविनोदेन कालो गच्छति धीमताम्।
व्यसनेन च मूर्खाणां निद्रया कलहेन वा।।’
This means wise people spend their time in deriving amusment through poetry and scriptures but foolish spend their time in addiction, sleep or quarrel. We know that Sanskrit abounds in subhashitas.
Some Subhashitas are so marvellous that understanding them requires us to tickle over brain cells. These are not only challenging but also amusing at times. Note:- These shlokas are for writing the meaning in medium of answer and explanation to them is also expected.

श्लोकः – 1
साक्षरा …………….. मुञ्चति ।।1।।
श्लोकः : साक्षरा विपरीताश्चेद् राक्षसा एव केवलम्।
सरसो विपरीतोऽपि सरसत्वं न मुञ्चति ।।1।।
स्पष्टीकरणम् : साक्षरा: इति पदं विपरीतक्रमेण पठितं चेत् ‘राक्षसाः’ इति भवति। परं ‘सरसः’ इति पदं यथानुक्रमं वा विपरीतक्रमेण पठितं चेत् ‘सरसः’ इत्येव भवति। अत्र कविकल्पना एवं कविकौशलं विभाति।
अनुवादः
‘साक्षर’ हा शब्द उलट केला तर ‘राक्षस’ असा होतो. पण ‘सरस’ हा शब्द उलट केला तरी तो त्याचा सरसपणा सोडत नाही.
स्पष्टीकरण – ‘साक्षर’ मनुष्य जर विपरीत असेल तर तो राक्षसाप्रमाणे वागतो. म्हणजे तो त्याच्या ज्ञानाचा विपरीत वापर करून विघातक कृत्य करतो. पण ‘सरस’ म्हणजे उत्तम प्रवृत्तीचा मनुष्य संवेदनशील असतो. त्याचे वर्तन सरळ अथवा विपरीत परिस्थितीमध्ये सुद्धा बदलणार नाही.
The word ‘साक्षराः’ (literate) if reversed, becomes ‘राक्षसा:’ that is demons. But the word ‘सरस’ which means sensitive or filled with emotion doesn’t leave its sensitivity though reversed.
Explanation – This is poetic imagination which itself is the creativity of the poet. The poet says those who have only bookish knowledge whom we refer to as ‘pothi pandits’ if he is rubbed the wrong way will become evil like demons. Just as intelligent man has created weapons using science which is the wrong usage of knowledge.
On the other hand, a connoisseur is sensitive and even in difficult conditions, he still remains happy, because the word Rasa means आनंद i.e happiness, Rasika is always happy and also makes others happy.

श्लोकः – 2
वृक्षाग्रवासी ………….. न मेघः।
श्लोकः : वृक्षानवासी न च पक्षिराज:
त्रिनेत्रधारी न च शूलपाणिः।
त्वग्वत्रधारी न च सिद्धयोगी
जलं च विभन्न घटोन मेघः।।
स्पष्टीकरणम् : सः वृक्षस्य अग्रे वसति किन्तु पक्षिराजः गरुडः न। तस्य त्रीणि नेत्राणि सन्ति किन्तु सः शूलपाणिः शङ्कर: न। सः वल्कलसदृशं वस्त्रं धारयति किन्तु स: सिद्धयोगी न। सः जलं धारयति किन्तु सः न घटः न च मेषः। अस्य उत्तरं वर्तते नारिकेलफलम्।
अनुवादः
तो वृक्षाच्या टोकावर राहतो पण पक्षीराज (गरुड) नाही. तीन डोळे आहेत पण शंकर नाही. वल्कले धारण करतो पण योगी नाही. पाणी धारण करतो पण घडा नाही व ढगही नाही.
स्पष्टीकरण – हे सुभाषित प्रहेलिका प्रकारातील आहे. प्रहेलिका म्हणजे कोडे. या कोड्याचे उत्तर आहे नारळ, नारळ झाडाच्या टोकावर असतो. त्याला तीन डोळे असतात, त्याला शेंडी असते आणि आत पाणी असते.
It lives on the top of the tree but is not the king of birds (garuda/eagle). It has three eyes but is not the one who holds the Trident (Shiva). It wears barkgarments but is not an accomplished ascetic (yogi), and it holds water but is neither a pot nor a cloud.
Explanation – This is a riddle or prahelika the answer to which is a coconut. A coconut grows on the top of the tree, it has three eyes below the tuft of coin on top, it has bark garments which is the coir and it has water in it.

श्लोकः – 3
तातेन ……………… लड़िता।।3।।
श्लोकः : तातेन कथितं पुत्र पत्रं लिख ममाज्ञया।
न तेन लिखित पत्रं पितुराज्ञा न लड्डिता ।।3।।
स्पष्टीकरणम् : तातेन कथितं, “हे पुत्र, मम आज्ञया पत्रं लिख।” तेन पुत्रेण पत्रं न लिखितम्। तथापि पितुः आशा न लकिता। अर्थसङ्गतिः न दृश्यते। यदि ‘न तेन’ इति एकपदं क्रियते ‘नतेन’ इति पदेन अर्थबोधः भवति। नतेन नाम नमस्वभावेन पुत्रेण पत्रं लिखितम्। अपि च पितुः आज्ञा न लविता।
अनुवादः
वडिलांनी मुलाला सांगितले ‘माझ्या आज्ञेने पत्र लिही!’ त्याने पत्र लिहिले नाही आणि वडिलांची आज्ञा मोडली नाही. स्पष्टीकरण – हा श्लोक ‘कूटश्लोक’ या सुभाषितप्रकाराचे उदाहरण आहे. ‘न तेन’ हा शब्द एकत्र ‘नतेन’ असा वाचला तर ‘त्या नम्र मुलाने’ असा अर्थ होतो. संस्कृत भाषेमधील विभक्तिप्रत्यय व शब्द चमत्कृती येथे दिसून येते.
The father said, “O son, write a letter by my order. He did not write the letter nor did he disobey the father’s order.
Explanation – In this shloka the word has to be read as one word ‘1’ which means ‘by the modest one.’ So, the son who was modest wrote the letter and therefore did not disobey the father’s order. This is an example of a कूटश्लोक.

श्लोकः – 4
न तस्यादिर्न ……………. स पण्डितः।
श्लोकः : न तस्यादिर्न तस्यान्त; यो मध्ये तस्य तिष्ठति।
तवाप्यस्ति ममाप्यस्ति यो जानाति स पण्डितः ।।4।।
स्पष्टीकरणम् : कूटप्रश्न: अयम्।
अस्य उत्तरम् – तस्य आदिः न , तस्य अन्त:न, तस्य मध्ये यः तिष्ठति (तत्) तव अपि अस्ति, मम अपि अस्ति।
अनुवादः
त्याच्या सुरुवातीला ‘न’, त्याच्या शेवटी ‘न’ वमध्ये ‘य’ आहे. तुझ्याकडेही आहे. माझ्याकडेही आहे. जो जाणतो तो पंडित आहे.
स्पष्टीकरण – हा सुभाषिताचा ‘कूटप्रश्न’ प्रकार आहे. ‘नयन’ हे त्याचे उत्तर आहे. कारण यात ‘न’ हे अक्षर सुरुवातीला आणि शेवटी येते तसेच ‘य’ हे अक्षर मध्ये येते.
It doesn’t have a beginning nor does it have an end and it stays in the middle. You too have it and I too have it, the one who knows this is a scholar. Explanation – This is an example of prahelika where the answer is ‘नयन’ means eye’. ‘न’ is at the beginning ‘न’ is at the end and ‘य’ is in the middle which is ‘नयन’.

श्लोक: – 5
मृगमीनसज्जनानां ……………… जगति ।।5।।
श्लोकः : मृगमीनसज्जनानां तृणजलसन्तोषविहितवृत्तीनाम्।
लुब्धकधीवरपिशुना निष्कारणवैरिणो जगति ।।5।।
स्पष्टीकरणम् : मृगाः तृणानि खादन्ति। मत्स्या: जले विहरन्ति। साधवः सन्तोषं यच्छन्ति। परम् अस्मिन् जगति लुब्धकाः मृगान् धीवरा: मत्स्यान्
तथा दुष्टा: साधून निष्कारणमेव पीडयन्ति। अत्र यथासङ्ख्य – अलङ्कारः विद्यते।
अनुवादः
हरीण, मासा व सज्जन अनुक्रमे गवत, पाणी व समाधान यांवर जगतात तरीही या जगात अनुक्रमे शिकारी, कोळी व दुर्जन हे विनाकारणच त्यांचे वैरी आहेत.
स्पष्टीकरण – हा श्लोक यथासंख्य अलंकाराचे उदाहरण आहे. या अलंकारात कर्तुपदे, कर्मपदे तसेच क्रियापदे वेगवेगळ्या चरणांत गुंफलेली असतात. प्रस्तुत श्लोकात जगातील एक सत्य गोष्ट – ‘दुर्जनांचे सज्जनांना विनाकारण छळणे’ सांगितली आहे.
Deer, fish, and good people have grass, water, and satisfaction respectively for their livelihood. Yes, in this world, the hunter, fisherman and the wicked for no reason make enmity with these.
Explanation – In the Shloka, we see how the poet has beautifully used यथासंख्य अलंकार where the words मृग, तृण and लुब्धक go together मीन, जल and धीवरgo together and सज्जन, संतोष and पिशुन go together. The thought conveyed in the shloka is that people with bad intention for no reason trouble those who are innocent and who don’t otherwise harm others.

श्लोकः – 6
गङ्गायाश्चञ्चलतरे ………………. नभस्तलम्।।6।।
श्लोकः : गङ्गायाश्चलतरे वारिणि प्रतिबिम्बितम्।
शोभते तारकायुक्तं शतचन्द्रं नभस्तलम् ।।6।।
स्पष्टीकरणम् । गङ्गायाशजलतरे वारिणि प्रतिबिम्बितम् तारकायुक्तं शतचन्द्र नभस्तलम् शोभते। शतचन्द्र नभस्तलम्। इति काचन समस्या वर्तते। आकाशे चन्द्राणां शतं कथं शक्यते? इत्येषा समस्या।
समस्यापूर्तिः- गङ्गानद्याः जलं कल्लोलयुक्त विद्यते। यदा गगने तारकाः चन्द्रमा: च विलसन्ति तदा चन्द्रमसः शतं प्रतिबिम्बानि गङ्गानद्याः जले दृश्यन्ते । तदा कवि: कल्पनां करोति, ‘नभः शतचन्द्रम्’ इव दृश्यते।
अनुवादः
गंगेच्या चंचल पाण्यामध्ये प्रतिबिंबित झालेले आकाश जणू काही चांदण्यांनी व शेकडो चंद्रांनी युक्त असल्याप्रमाणे शोभून दिसत आहे.
स्पष्टीकरण – ही समस्यापूर्ती आहे. ‘शतचन्द्रं नभस्तलम्’ ही समस्या म्हणजे कोडे आहे. त्याचे उत्तर कवी असे देतो, आकाशात तर शंभर चंद्र असणे शक्य नाही, पण गंगेच्या लाटांवर जेव्हा चांदण्या व चंद्राने भरलेल्या आकाशाचे प्रतिबिंब पडते तेव्हा एकाचवेळी पाण्यात असंख्य चंद्र असल्याचे (पडल्याचे) भासते.
Hundred moons look beautiful along with stars in the sky reflected in the trembling waters of the Ganga.
Explanation – This shloka is an example of समस्यापूर्त where the last part ‘शतचन्द्रं नभस्तलम्’ is given and poets have to compose a shloka to make it meaningful. Now, this is really not possible.
So, to justify this sentence, the poet very beautifully says that the reflection of the moon is seen in the shaking waters of Ganga and this appears as if there are hundreds of moons. The reflection of the moon in the sky with many stars when seen in the trembling river water makes one see hundred moons.

श्लोक: – 7
यद्वक्त्रं महरीक्षसे ……………. तप्त तपः ।।7।।
श्लोकः : यद्क्वं मुहुरीक्षसे न धनिनां दूषे न चाटून मृषा
नैषां गर्ववचः शृणोषि न च तान् प्रत्याशया धावसि ।
काले बालतृणानि खादसि परं निद्रासि निद्रागमे
तन्मे बूहि कुरङ्ग कुत्र भवता किं नाम तप्तं तपः ।।7।।
स्पष्टीकरणम् : हे कुरङ्ग, यत् त्वं धनिकानां वक्वं मुहुः न ईक्षसे, मृषा चाटून न दूषे, एषां गर्ववचः न शृणोषि, प्रत्याशया च तान प्रति न धावसि काले बालतृणानि खादसि परं निद्रागमे निद्रासि। तत् मे बूहि, भवता किं नाम तपः तप्तम्? एषा कुरङ्गान्योक्तिः वर्तते। सज्जनान् उद्दिश्य एषा अन्योक्तिः।
अनुवादः
अरे हरिणा ! तू धनिकांचे तोंड पुन्हा पाहत नाहीस, उगाच खोटी स्तुती करीत नाहीस, त्यांचे गर्वपूर्ण बोलणे ऐकत नाहीस. त्यांच्या दिशेने आशेने धावत (जात) नाहीस, योग्यवेळी कोवळे गवत खातोस, झोप आल्यावर झोपतोस! मला सांग बरे असे कोणते तप तू केले आहेस?
स्पष्टीकरण – प्रस्तुत श्लोकामध्ये स्थितप्रज्ञ माणसाविषयी हरणाचे रूपक घेऊन भाष्य केले आहे. ही अन्योक्ती असून हरणाच्या रूपकातून मनस्वी माणसाला कवी विचारत आहे की, त्याने असे काय साध्य केले आहे ज्यामुळे त्याला श्रीमंत माणसांवर अवलंबून रहावे लागत नाही. मनस्वी माणसे साधे पण स्वावलंबी आयुष्य जगतात हे या अन्योक्तीतून कवीला सांगायचे आहे.
Oh deer, tell me what penance has been performed by you because of which you do not have to see the face of the rich again and again, nor speak false pleasing words, you do not have to listen to their words filled with pride, not do you have to run behind them with greed. You eat tender grass at the proper time and sleep when you are sleepy.
Explanation – In this Shloka which is अन्योक्ति, the poet is not just addressing the deer and asking the deer how it has such a carefree life but is actually asking the man who leads a carefree life what has he done to get such a life where he doesn’t have to depend on the rich for everything. Generally, one has to depend on the wealthy for everything and per this he needs to please them. But there are those who lead simple lives and don’t have to do so.

सन्धिविग्रहः
- घटोन – घट: + न।
- यो मध्ये – यः + मध्ये।
- गङ्गायाश्चञ्चलतरे – गङ्गायाः + चलतरे।
- नभस्तलम् – नभः + तलम्।
- मुहुरीक्षसे – मुहुः + ईक्षसे।
- तन्मे – तद् + मे।
- नैषाम् – न + एषाम्।
- यद्वक्त्रम् – यत् + वक्वम्।

समानार्थकशब्दाः
- तपः – तपस्या।
- दानव: – दैत्यः ।
- धनी – धनिक्, श्रीमत्, बहुधनः ।
- वच: – वाणी, भाषा।
- वारि – जलम, तोयम, आपः।
- तारका – नक्षत्रम्, तारा, ज्योतिः।
- चन्द्रः – हिमांशुः, इन्दुः, विधुः, सुधांशुः, सोमः ।
- तृणानि – शष्याणि।
- संतोषः – तुष्टिः।
- मीन: – मत्स्यः ।
- पिशुन: – दुर्जनः।
- लुब्धक: – व्याधः।
- सज्जनः – सुजनः, सत्पुरुष।
- वैरिणः – शत्रवः, रिपवः।
- कुरङ्ग – मृगः, हरिणः, सारङ्गः।
- पण्डितः – ज्ञानी, विद्वान्।
- तातः – पिता, जनक:
- पुत्रः – तनयः, सूनुः आत्मजः

विरुद्धार्थकशब्दाः
- मृषा × सत्यम्।
- धनी × निर्धनः।
- चञ्चलम् × स्थिरम्।
- सज्जनः × दुर्जनः।
- पिशुनः × सत्पुरुषः।
- निष्कारण × सकारण।
- वैरी × मित्रम्।
- आदिः × अन्तः
- पण्डित: × मूढः।
- लहिता × अनुसता।
- नतः × गर्विष्ठः, उध्दतः।
- विपरीत: × सरलः।
- सरस: × नीरसः।

शब्दार्थाः
- विपरीत – reverse order – उलट क्रमाने
- मुञ्चति – does not leave – सोडत नाही
- सरसत्वम् – best qualities – रसिकता, रसाळपणा
- साक्षरा: – literate – साक्षर
- राक्षसा: – demons – दानव
- चेत् – if – जर
- वृक्षाग्रवासी – one who resides on top of the tree – वृक्षाच्या टोकावर राहणारा
- पक्षिराज: – king of birds, eagle – पक्ष्यांचा राजा, गरुड
- त्रिनेत्रधारी: – I having three eyes, Shiva – तीन डोळे असणारा, शंकर
- सिद्धयोगी – ascetic – योगी
- शूलपाणि: – the one who holds त्रिशूल in hand – त्रिशूलधारी (शंकर)
- त्वग्वस्त्रम् – clothes of bark – वल्कल
- घट: – pot – घडा
- मेघः – cloud – ढग
- बिभ्रत् – holds – धारण करणारा
- तात: – father – वडील
- आज्ञया – by order – आज्ञेवरून
- पत्रम् – letter – पत्र
- लहिता – crossed – मोडली
- आदिः – beginning – सुरुवात
- अन्त – end – शेवट
- मध्ये – in the middle – मध्ये
- जानाति – knows – जाणतो
- पण्डित: – intelligent, scholar – हुशार
- तिष्ठति – stands – राहते
- मृगः – deer – हरीण
- सज्जनः – good person – सज्जन
- मीन: – fish – मासा
- लुब्धकः – hunter – शिकारी
- ग्धीवरः – fisherman – कोळी
- पिशुन: – wicked – दुर्जन
- निष्कारण – without reason – निष्कारण
- जगति – in the world – ह्या जगात
- वैरिणः – foes, enemies – शत्रु
- चञ्चल – unsteady – चंचल, हलणारे
- प्रतिबिम्बित – reflected – प्रतिबिंबित झालेले
- तारकायुक्त – full of stars – चांदण्यानी युक्त
- नभः – sky – आकाश
- वक्त्रम् – mouth – तोंड
- मुहु – again and again – पुनः पुनः
- चाटून् – flatter – स्तुती
- मृषा – false – खोटे
- गर्ववचः – speech filled with pride – गर्वाने बोलणे
- प्रत्याशया – with greed – आशेने
- बालतृणानि – grass – कोवळे गवत
- ब्रुहि – tell me – सांग
- कुरङ्ग – o deer – हे हरिणा
- तपः – penance – तप
Aamod Sanskrit Book 9th Class Solutions
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()