Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 7 Maths Solutions covers the 7th Std Maths Practice Set 46 Answers Solutions Chapter 12 Perimeter and Area.
Perimeter and Area Class 7 Maths Chapter 12 Practice Set 46 Solutions Maharashtra Board
Std 7 Maths Practice Set 46 Solutions Answers
Question 1.
A page of a calendar is 45 cm long and 26 cm wide. What is its area?
Solution:
Area of page of a calendar = length × breadth
= 45 × 26
= 1170 sq. cm.
∴ The area of the page of the calendar is 1170 sq. cm.
Question 2.
What is the area of a triangle with base 4.8 cm and height 3.6 cm?
Solution:
Area of triangle = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) × base × height
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) × 4.8 × 3.6
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) × 17.28
= 8.64 sq. cm.
∴ The area of the triangle is 8.64 sq. cm.
Question 3.
What is the value of a rectangular plot of land 75.5 m long and 30.5 m broad at the rate of Rs 1000 per square metre?
Solution:
Area of the rectangular plot = length × breadth
= 75.5 × 30.5
= 2302.75 sq. m.
Value of the plot = area of the plot × rate per square metre = 2302.75 × 1000
= Rs 230275
∴ The value of the plot is Rs 23,02,750.
Question 4.
A rectangular hall is 12 m long and 6 m broad. Its flooring is to be made of square tiles of side 30 cm. How many tiles will fit in the entire hall? How many would be required if tiles of side 15 cm were used?
Solution:
Area of the rectangular hall = length × breadth
= 12 × 6
= 72 sq. m.
Side of the square shaped tile = 30 cm
= \(\frac { 30 }{ 100 }\) m …[1cm = \(\frac { 1 }{ 100 }\)m]
= \(\frac { 3 }{ 10 }\) m
Area of the tile = (side)²
= \(\left(\frac{3}{10}\right)^{2}\)
= \(\frac{9}{100}\) sq.m
Number of tiles required = \(\frac{\text { Area of the hall }}{\text { Area of each tile }}\)
= \(72 \div \frac{9}{100}\)
= \(72 \times \frac{100}{9}\)
= 800
∴ 800 square shaped tiles of 30 cm side will be required.
If the side of the square is reduced to half, its area will become \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\) times the original.
i. e. number of tiles required will become 4 times the original tiles.
∴ Number of tiles required = 4 × number of tiles of side 30 cm
= 4 × 800
= 3200
∴ 3200 square shaped tiles of 15 cm side will be required.
Question 5.
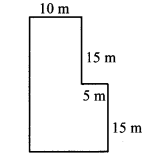
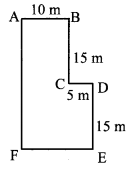
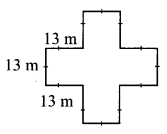
Find the perimeter and area of a garden with measures as shown in the figure alongside.
Solution:
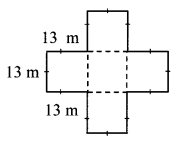
The boundary of the garden is made of 12 sides each of length 13 m.
Perimeter of the garden = sum of the lengths of all sides
= 12 × 13
= 156 m
The garden in the given figure can be divided into 5 squares each of side 13 m.
∴ Area of the garden = 5 × area of each square part
= 5 × (side)²
= 5 × (13)²
= 5 × 169
= 845 sq. m.
∴ The perimeter and area of a garden are 156 m and 845 sq. m. respectively.
Std 7 Maths Digest