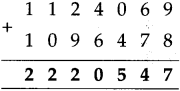
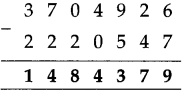
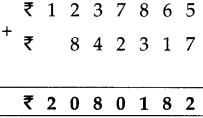
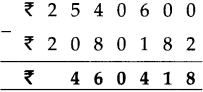
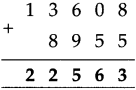
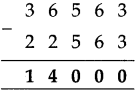
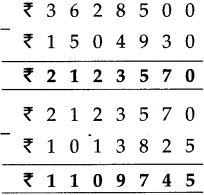
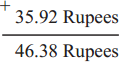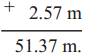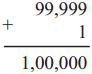Number Work Class 5 Problem Set 2 Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Balbharti Maharashtra Board Class 5 Maths Solutions Chapter 2 Number Work Problem Set 2 Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Std 5 Maths Chapter 2 Number Work
Question 1.
Using the digits 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 write ten each of two-, three-, four- and five-digit numbers. Read the numbers.
Answer:
| Two-digit numbers |
Reading a number |
| 37 |
Thirty-seven |
| 80 |
Eighty |
| 49 |
Forty-nine |
| 65 |
Sixty-five |
| 28 |
Twenty-eight |
| 54 |
Fifty-four |
| 92 |
Ninety-two |
| 71 |
Seventy-one |
| 16 |
Sixteen |
| 22 |
Twenty-two |
| Three-digit numbers |
Reading a number |
| 504 |
Five hundred and four |
| 386 |
Three hundred eighty-six |
| 430 |
Four hundred thirty |
| 891 |
Eight hundred ninety-one |
| 615 |
Six hundred fifteen |
| 267 |
Two hundred sixty-seven |
| 900 |
Nine hundred |
| 173 |
One hundred seventy-three |
| 766 |
Seven hundred sixty-six |
| 258 |
Two hundred and fifty-eight |
| Four-digit numbers |
Reading a number |
| 3,817 |
Three thousand eight hundred and seventeen |
| 4,059 |
Four thousand fifty-nine |
| 9,611 |
Nine thousand six hundred and eleven |
| 7,413 |
Seven thousand four hundred thirteen |
| 5,608 |
Five thousand six hundred and eight |
| Four-digit numbers |
Reading a number |
| 2,009 |
Two thousand and nine |
| 6,420 |
Six thousand four hundred and twenty |
| 1,357 |
One thousand three hundred and fifty-seven |
| 8,172 |
Eight thousand one hundred and seventy-two |
| 6,156 – |
Six thousand one hundred and fifty-six |
| Five-digit numbers |
Reading a number |
| 41,309 |
Forty-one thousand, three hundred and nine |
| 68,527 |
Sixty-eight thousand five hundred and twenty seven |
| 50,348 |
Fifty thousand three hundred and forty eight |
| 76,052 |
Seventy-six thousand and fifty-two |
| 21,546 |
Twenty-one thousand five hundred and forty-six |
| 10,358 |
Ten thousand three hundred and fifty-eight |
| 94,215 |
Ninety-four thousand two hundred and fifteen |
| 36,104 |
Thirty-six thousand one hundred and four |
| 89,157 |
Eighty-nine thousand one hundred and fifty-seven |
| 72,560 |
Seventy-two thousand five hundred and sixty |

Question 2.
Fill in the blanks in the table below.
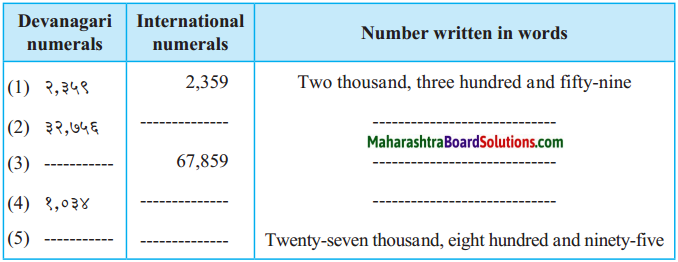
Answer:
|
Devnagari numerals |
International numerals |
Number written in words |
| (1) |
२,३५९ |
2,359 |
Two thousand three hundred and fifty nine |
| (2) |
३२,७५६ |
32,756 |
Thirty two thousand seven hundred and fifty Six |
| (3) |
६७,८५९ |
67,859 |
Sixty seven thousand eight hundred and fifty Nine |
| (4) |
१,०३४ |
1,034 |
One thousand and thirty four |
| (5) |
२७,८९५ |
27,895 |
Twenty seven thousand eight hundred and ninety five |
Question 3.
As a part of the ‘Avoid Plastic Project’, Zilla Parishad schools made and provided paper bags to provision stores and greengrocers. Read the talukawise numbers of the bags and write the numbers in words.

Answer:
| Talukas |
No. of Bags |
Numbers in words |
| Kopargaon |
12,740 |
Twelve thousand seven hundred and forty |
| Shevgaon |
28,095 |
Twenty-eight thousand and ninety-five |
| Karjat |
31,608 |
Thirty-one thousand six hundred and eight |
| Sangamner |
10,792 |
Ten thousand seven hundred and ninety-two |

Question 4.
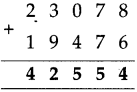
How many rupees do they make?
(1) 20 notes of 1000 rupees, 5 notes of 100 rupees and 14 notes of 10 rupees.
(2) 15 notes of 1000 rupees, 12 notes of 100 rupees, 8 notes of 10 rupees and 5 coins of 1 rupee.
Answer:
Question 5.
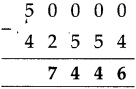
Write the biggest and the smallest five-digit numbers that can be made using the digits 4, 5, 0, 3, 7 only once.
Answer:
Biggest five digit number is 75,430 Smallest five digit number is 30,457
Question 6.
The names of some places and their populations are given below. Use this information to answer the questions that follow.
Tala : 40,642
Gaganbawada : 35,777
Bodhwad : 91,256
Moregaon : 87,012
Bhamragad : 35,950
Velhe : 54,497
Ashti : 76,201
Washi : 92,173
Morwada : 85,890
(1) Which place has the greatest population? What is its population?
(2) Which place, Morwada or Moregaon, has the greater population?
(3) Which place has the smallest population? How much is it?
Answer:
(1) Washi has the greatest population. Population of Washi is 92,173
(2) Moregaon has the greater population.
(3) Gaganbawada has the smallest population. Its population is 35,777

Introducing six-digit numbers
Teacher : How much, do you think, is the price of a four-wheeler?
Ajay : Maybe about six or seven lakh rupees.
Teacher : Do you know exactly how much one lakh is?
Ajay : It’s a lot, isn’t it? More than even ten thousand, right?
Teacher : Yes, indeed ! Let’s find out just how much. What is 999 + 1?
Ajay : One thousand.
Teacher : You have learnt to write 99000, too. Now, if you add 1000 to that, you will get one hundred thousand. That’s what we call one lakh.
Vijay : 9999+1 is 10,000 (ten thousand). We had made the ten thousands place for it. Can we make a place for one lakh too in the same way?
Teacher : Yes, of course. Carry out the addition 99,999 + 1 and see what you get.
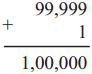
Here we keep carrying over till we have to make a place for the ‘lakh’ on the left of the ten thousands place. And we write the last carried over one in that place. The sum we get is read as ‘one lakh’.
Vijay : Kishakaka bought a second-hand car for two and a half lakh rupees.
Ajay : How much is two and a half lakh?
Teacher : One lakh is 100 thousand. So, half a lakh is 50 thousand. Because, half of 100 is 50.

Vijay : That means two and a half lakh is 2 lakh 50 thousand.
Teacher : Now write this number in figures.
Vijay : 2,50,000.
Teacher : We have seen that a hundred thousand is 1 lakh. If we have 1000 notes of 100 rupees, how many rupees would they make?
Vijay : 1000 notes of 100 rupees would make 1 lakh rupees.

Reading six-digit numbers
(1) 2,35,705 : two lakh thirty-five thousand seven hundred and five
(2) 8,00,363 : eight lakh three hundred and sixty-three
(3) 3,07,899 : three lakh seven thousand eight hundred and ninety-nine
(4) 9,00,049 : nine lakh forty-nine
(5) 5,30,735 : five lakh thirty thousand seven hundred and thirty-five
Writing six-digit numbers in figures
(1) Eight lakh, nine thousand and forty-three : There are 8 lakhs in this number. There are no ten thousands, so we write 0 in that place. As there are 9 thousands, we write 9 in the thousands place. We write 0 in the hundreds place as there are no hundreds. Forty-three is equal to 4 tens and 3 units, so in the tens and units places we write 4 and 3 respectively. In figures : 8,09,043.
When writing numbers in figures, write the digit in the highest place first and then, in each of the next smaller places, write the proper digit from 1 to 9. Write 0, if there is no digit in that place. For example, if the number eight lakh, nine thousand and forty-three is written as ‘89043’, it is wrong. It should be written as 8,09,043. Here, we have to write zero in the ten thousands place.
(2) Four lakh, twenty thousand, five hundred : In this figure, there aren’t any thousands in the thousands place, so we write 0 in it. Since there are five hundreds, we write 5 in the hundreds place. There are no tens and units, hence, we write 0 in those places. In figures : 4,20,500.
Roman Numerals Problem Set 2 Additional Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Fill in the blanks in the table below:
Answer:
|
Devnagari numerals |
International numerals |
The number written in words |
| (1) |
५,५१८ |
5,518 |
Five thousand five hundred and eighteen |
| (2) |
४९,८०९ |
49,809 |
Forty-nine thousand eight hundred and nine |
| (3) |
७,२५६ |
7,256 |
Seven thousand two hundred and fifty-six |

Question 2.
Solve the following:
(1) In an election, the First candidate received 58,735 votes, the Second candidate received 65,500, the Third candidate received 85,450 and the Fourth candidate got 09,689 votes. Read the numbers of the votes and write the numbers in words.
Answer:
First candidate – 58,735 – Fifty-eight thousand seven hundred and thirty-five
Second candidate – 65,500 – Sixty-five thousand five hundred
Third candidate – 85,450 – Eighty-five thousand four hundred and fifty
Fourth candidate – 09,689 – Nine thousand six hundred and eighty-nine
Question 3.
How many rupees do they make?
*(1) 10 notes of 2,000 rupees, 5 notes of 100 rupees and 14 notes of 10 rupees.
Solution:
10 notes of 2,000 rupees = 10 x 2,000 ₹ 20,000
5 notes of 100 rupees = 5 x 100 = ₹ 500
14 notes of 10 rupees = 14 x 10 = ₹ 140
Total = ₹ 20,640

∴ They make, twenty thousand, six hundred and forty.

*(2) 7 notes of 2,000 rupees, 12 notes of loo rupees, 8 notes of 10 rupees and 5 coins of 1 rupee
Solution:
7 notes of 2,000 rupees = 7 x 2,000 = ₹ 14,000
12 notes of 100 rupees = 12 x 100 = ₹ 1,200
8 notes of 10 rupees = 8 x 10 = ₹ 80
5 coins of 1 rupee = 5 x 1 = ₹ 5
Total = ₹ 15,285
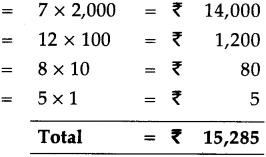
∴ They make, fifteen thousand, two hundred and eighty five.
(3) 4 notes of 2,000 rupees, 6 notes of 100 rupees and 12 notes of 10 rupees
Solution:
4 notes of 2,000 rupees = 4 x 2,000 = ₹ 8,000
6 notes of 100 rupees = 6 x 100 = ₹ 600
12 notes of 10 rupees = 12 x 10 = ₹ 120
Total = ₹ 8,720
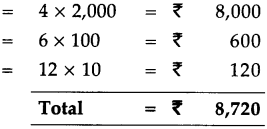
∴ They make, eight thousand, seven hundred and twenty.

(4) 5 notes of 2,000 rupees, 9 notes of 500 rupees, 8 notes of 100 rupees, 7 notes of 50 rupees, 6 notes of 20 rupees and 5 note of 10 rupees
Solution:
5 notes of 2,000 rupees 5 x 2,000 = ₹ 10,000
9 notes of 500 rupees = 9 x 500 = ₹ 4,500
8 notes of 100 rupees = 8 x 100 = ₹ 800
7 notes of 50 rupees = 7 x 50 = ₹ 350
6 notes of 20 rupees = 6 x 20 = ₹ 120
5 notes of 10 rupees = 5 x 10 = ₹ 50
Total = ₹ 15,820
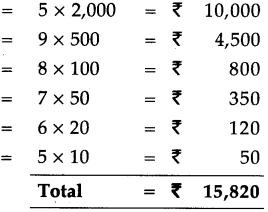
∴ They make, fifteen thousand, eight hundred and twenty.
*Question 4.
Write the biggest and the smallest numbers using all the given digits in every number. Use each digit only once.
(1) 4, 8, 0, 2, 6, 5;
(2) 2, 6, 7, 1, 4;
(3) 5, 9, 6, 1, 4, 3;
(4) 9, 4, 1, 3, 6;
(5) 5, 3, 0, 0, 2
Answer:
(1) Biggest six digit number is 8,65,420 Smallest six digit number is 2,04,568
(2) Biggest five digit number is 76,421 Smallest five digit number is 12,467
(3) Biggest six digit number is 9,65,431 Smallest six digit number is 1,34,569
(4) Biggest five digit number is 96,431 Smallest five digit number is 13,469
(5) Biggest five digit number is 53,200 Smallest five digit number is 20,035
Class 5 Maths Solution Maharashtra Board
![]()
![]()
![]()