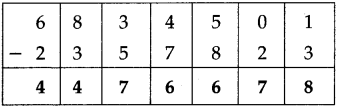
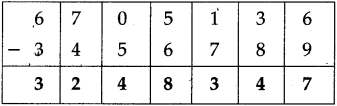
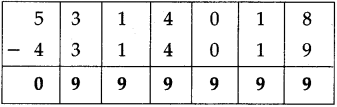
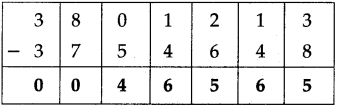
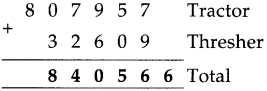
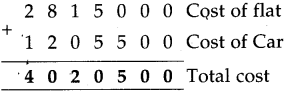
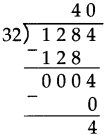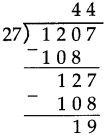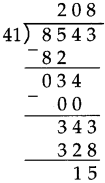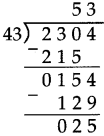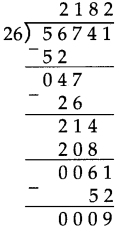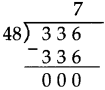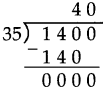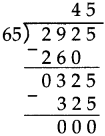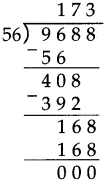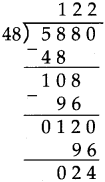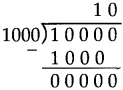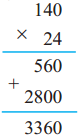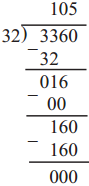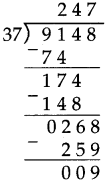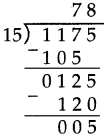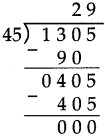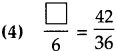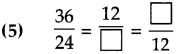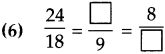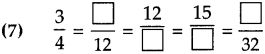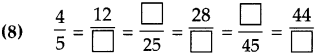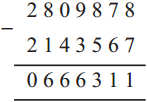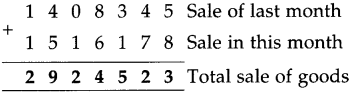Number Work Class 5 Problem Set 6 Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Balbharti Maharashtra Board Class 5 Maths Solutions Chapter 2 Number Work Problem Set 6 Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Std 5 Maths Chapter 2 Number Work
Question 1.
Write the proper symbol, ‘<’ or ‘>’ in the box.
(1) 5,705 [ < ] 15,705
(2) 22,74,705 [ ] 12,74,705
(3) 35,33,302 [ ] 35,32,302
(4) 99,999 [ ] 9,99,999
(5) 4,80,009 [ ] 4,90,008
(6) 35,80,177 [ ] 35,88,172
Answer:
(1) <
(2) >
(3) >
(4) <
(5) <
(6) <
Question 2.
Solve the problems given below.
(1) The Swayamsiddha Savings Group made 3,45,000 papads while the Swabhimani Group made 2,95,000. Which group made more papads?
Answer:
Here, 3,45,000 > 2,95,000
Hence, the Swayamsiddha saving group made more papads.
(2) Children of the Primary School in Ahmadnagar District collected 2,00,000 seeds while those in Pune District collected 3,25,000. Which children collected more seeds?
Answer:
Here, 3,25,000 > 2,00,000
Hence, Pune District children collected more seeds.
(3) The number of people who took part in the Republic Day flag hoisting ceremony was 2,01,306 in Pandharpur taluka and 1,97,208 in Malshiras taluka. In which taluka did a larger number of people participate?
Answer:
Here, 2,01,306 > 1,97,208
Hence, people of Pandharpur taluka participated in larger number
(4) At an exhibition, the Annapoorna Savings Group sold goods worth 5,12,345. The Nirman Group sold goods worth 4,12,900. This figure was 4,33,000 for the Srujan Group and 5,11,937 for the Savitribai Phule group.
Which group had the largest sales?
Which group had the smallest?
Write the sales figures in ascending order.
Answer:
Among the numbers 5,12,345; 4,12,900; 4,33,000; 5,11,937
5,12,345 is largest and 4,12,900 is smallest. Hence, Annapoorna group had the largest sale and Nirman Group had the smallest sales.
Sales in ascending order
4,12,900 < 4,33,000 < 5,11,937 < 5,12,345
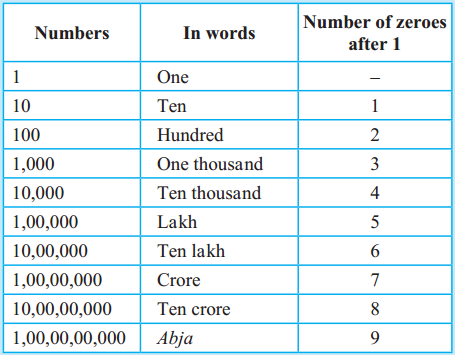
Introducing crores
99,99,999 is the biggest seven-digit number. On adding the number 1 to it, we get the smallest eight-digit number, 1,00,00,000. We read this number as ‘one crore’. The new place created to write this number is called the ‘crores’ place.
From the following examples, you can learn to read eight-digit numbers.
Number – Reading
8,45,12,706 – Eight crore forty-five lakh twelve thousand seven hundred and six
5,61,63,589 – Five crore sixty-one lakh sixty-three thousand five hundred and eighty-nine
6,09,04,034 – Six crore nine lakh four thousand and thirty-four
Something more
On the left of the crores place are the places for ten crores, abja, and ten abja in that order. The place value of each of these is ten times the value of the one on its right. According to the Census of the year 2011, the population of our country is 1,21,01,93,422. We read this as ‘one Abuja twenty-one crore one lakh ninety-three thousand four hundred and twenty-two.

Roman Numerals Problem Set 4 Additional Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Write the proper symbol, ‘<‘ or ‘>’ in the box.
(1) 68,34,170 [ ] 8,43,170
(2) 5,04,132 [ ] 5,04,123
(3) 1,01,001 [ ] 1,00,101
(4) 14,55,432 [ ] 4,54,532
Answer:
(1) >
(2) >
(3) >
(4) >
Question 2.
Write the numbers in words.
(1) 15,97,21,409
Answer:
Fifteen crore, ninety-seven lakh, twenty-one thousand, four hundred and nine
(2) 99,99,99,999
Answer:
Ninety-nine crore, ninety-nine lakh, ninety- nine thousand, nine hundred and ninety nine.
(3) 7,54,21,607
Answer:
Seven crore, fifty-four lakh, twenty-one thousand, six hundred and seven.
(4) 5,16,36,854
Answer:
Five crore, sixteen lakh, thirty-six thousand, eight hundred and fifty four.
Question 3.
Write in figures.
(1) One crore, fifteen lakh, fifty-nine thousand, seven hundred and four
Answer:
1,15,59,704
(2) Sixty-five crore, seventy lakh, fifty thousand and thirty nine
Answer:
65,70,50,039
(3) Four crore, fifty-nine lakh, fourty-three thousand, five hundred and thirty four
Answer:
4,59,43,534
(4) Eighteen crore, seventy-six lakh, fifty-four thousand and one
Answer:
18,76,54,001
Question 4.
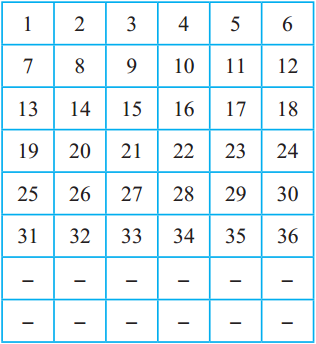
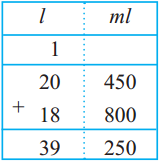
Fill in the blanks in the table below:
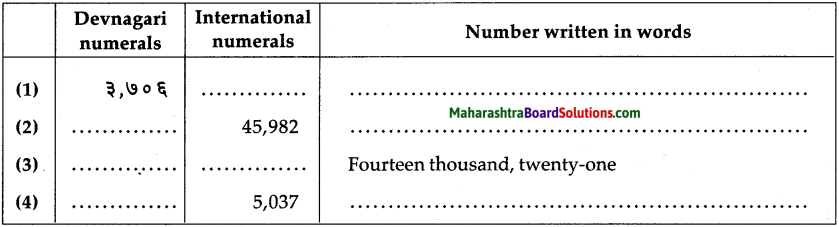
Answer:

Question 5.
Write the following numbers in words.
(1) 17,301
(2) 45,019
(3) 40,018
(4) 28,740
Answer:
(1) Seventeen thousand, three hundred and one.
(2) Forty-five thousand and nineteen.
(3) Forty thousand and eighteen
(4) Twenty-eight thousand seven hundred and forty
Question 6.
How many rupees do they make?
(1) 8 notes of rupees 2,000, 3 notes of rupees 100,11 notes of rupees 10.
Answer:
16,410
(2) 9 notes of rupees 2,000, 18 notes of rupees 100,18 notes of rupees 50,18 notes of rupees 10.
Answer:
20,880
(3) Write the smallest and the biggest five-digit numbers that can be made using the digits only once.
(a) 6, 8, 0,1, 9
(b) 3, 5,1,2, 8
Answer:
Smallest number : (i) 10,689 (ii) 12358
Biggest number : (i) 98,610 (ii) 85321
(4) Write the smallest and the biggest number from the following numbers.
(a) 35,798
(b) 39,785
(c) 39,587
(d) 35,789
Answer:
Smallest number : 35,789
Biggest number : 39,785
(5) Write the number from the given number which is neither biggest nor smallest.
(a) 45, 798
(b) 45, 789
(c) 45, 897
Answer:
45,798.
(6) Write the biggest and the smallest three-digit numbers that can be made using the digits 0,1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 only once.
Answer:
Biggest three-digit number : 987
Smallest three-digit number : 102
Question 7.
Read the numbers and write them in words.
(1) 2,65,048
(2) 1,80,794
(3) 1,06,709
(4) 8,80,006
Answer:
(1) Two lakh sixty-five thousand and forty- eight,
(2) One lakh eighty thousand seven hundred and ninety-four.
(3) One lakh six thousand seven hundred and nine.
(4) Eight lakh eighty thousand and six.
Question 8.
Read the numbers and write them in figures.
(1) Two lakh five thousand three hundred and six.
(2) Six lakh and six
(3) Nine lakh forty thousand and thirty seven.
(4) Five lakh ninety-nine thousand and fifteen.
Answer:
(1) 2,05,306
(2) 6,00,006
(3) 9,40,037
(4) 5,99,015
Question 9.
Write six, six-digit numbers using the digits 0,.3,5,7,9,1 only once with 9 lakh fifty-seven thousand in all numbers.
Answer:
(1) 9,57,301
(2) 9,57,310
(3) 9,57,103
(4) 9,57,130
(5) 9,57,013
(6) 9,57,031
Question 9.
(A) Match the columns:
| (A) |
(B) |
| (1) Nine lakh nine thousand nine |
(a) 9,09,090 |
| (2) Nine lakh june thousand nine hundred nine |
(b) 9,90,090 |
| (3) Nine lakh nine thousand ninety |
(c) 9,09,009 |
| (4) Nine lakh ninety thousand ninety |
(d) 9,09,909 |
Answer:
(1 – c),
(2 – d),
(3 – a),
(4 – b)
(B) Match the columns:
| (A) |
(B) |
| (1) Thirty-three lakh, three thousand and three |
(a) 33,30,300 |
| (2) Thirty-three lakh, thirty thousand, three hundred |
(b) 33,03,003 |
| (3) Thirty lakh, three thousand and thirty. |
(c) 30,30,003 |
| (4) Thirty lakh, thirty thousand and three |
(d) 30,03,030 |
Answer:
(1 – b),
(2 – a),
(3 – d),
(4 – c)
Question 10.
Read the numbers and write them in words.
(1) 34,87,569
(2) 70,85,039
(3) 48,07,102
(4) 67,40,960
(5) 88,00,080
(6) 40,40,004
Answer:
(1) Thirty-four lakh, eighty-seven thousand, five hundred and sixty-nine.
(2) Seventy lakh, eight-five thousand and thirty-nine.
(3) Forty-eight lakh, seven thousand, one hundred and two.
(4) Sixty-seven lakh, forty thousand, nine hundred and sixty.
(5) Eighty-eight lakh and eighty.
(6) Forty lakh, forty thousand and four.
Question 11.
Read the numbers and write them in figures.
(1) Fifty-nine lakh, seven thousand, seventeen.
(2) Twenty-two lakh, ten thousand, five hundred.
(3) Fifty-two lakh, twenty-five thousand, four hundred and fifteen.
(4) Thirty lakh, thirty thousand and thirty.
Answer:
(1) 59,07,017
(2) 22,10,500
(3) 52,25,415
(4) 30,30,030
Question 12.
Write the place value of the underlined digit.
(1) 68,03,512
(2) 3,42,157
(3) 84,52,170
(4) 79,345
(5) 38,14,093
(6) 8,10,618
(7) 35,10,387
Answer:
(1) 8,00,000
(2) 40,000
(3) 2,000
(4) 5
(5) 90
(6) 600
(7) 30,00,000
Question 13.
Write the numbers in their expanded form.
(1) 78,15,692
(2)50,95,182
(3)6,40,078
(4) 9,58,802
Answer:
(1) 70,00,000 + 8,00,000 + 10,000 + 5,000 + 600 + 90 + 2
(2) 50,00,000 + 90,000 + 5,000 + 100 + 80 + 2
(3) 6,00,000 + 40,000 + 70 + 8
(4) 9,00,000 + 50,000 + 8,000 + 800 + 2
Question 14.
Write the place name and place value of each digit in the following numbers.
(1) 27,306
(2) 1,70,425
(3) 75,68,041
(4) 55,555
Answer:
(1) 27,306
(2) 1,70,425
(3) 75,68,041
(4) 55,555
Question 15.
The expanded form of the number is given. Write the number.
(1) 70,000 + 6,000 + 500 + 40 + 8
(2) 8,00,000 +-30,000 + 5,000 + 400 + 3
(3) 60,00,000 + 2,00,000 + 70 + 4
(4) 20,00,000 + 5,00,000 + 900 + 5
Answer:
(1) 76,548
(2) 8,35,403
(3) 62,00,074
(4) 25,00,905
Question 16.
Considering the number 50,43,176.
Fill in the blanks.
(1) The digit in the ten thousand place is ……………………………………….. .
(2) Place value of 1 is ……………………………………….. .
(3) The digit in the lakhs place is ……………………………………….. .
(4) Place value of 5 is ……………………………………….. .
(5) The digit 7 is in ……………………………………….. place.
Answer:
(1) 4
(2) 100
(3) 0
(4) 50,00,000
(5) tens
Question 17.
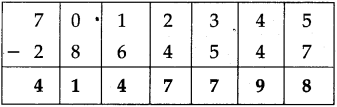
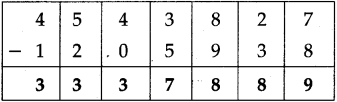
Write the proper symbols ‘<‘ or ‘>’ in the box.
(1) 12,625 [ ] 21,526
(2) 23,564 [ ] 23,546
(3) 36,60,660 [ ] 36,60,606
(4) 89,14,507 [ ] 89,15,407
Answer:
(1) <
(2) >
(3) >
(d) <
Question 18.
Solve the problems given below.
(1) Population of city A is 8,57,238 and that of city B is 8,75,461. Population of which city is more?
Answer:
city B
(2) Yearly income of Rajnikant is? 3,48,600 and that of Shashikant is? 3,46,500. Whose income is less?
Answer:
Shashikant
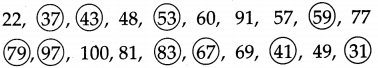
Question 19.
Profit of the four companies A, B, C, D is as follows.
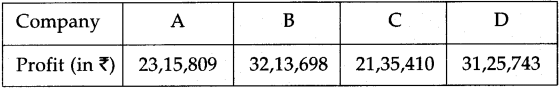
Now, answer the following questions.
(1) Which company made maximum profit?
(2) Which company made minimum profit?
(3) Write the profit of the companies in the descending order.
Answer:
(1) B
(2) C
(3) profit of company B > D > A > C
Question 20.
In a certain election, candidates : Tavade, Patel, Chauhan, and Shinde got the votes as follows.
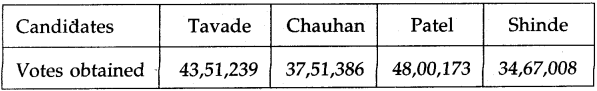
Now, answer the following questions.
(1) Who got the highest number of votes?
(2) Who got the least number of votes?
(3) Write the number of votes obtained in the ascending order.
Answer:
(1) Patel
(2) Shinde
(3) 34,67,008 < 37,51,386 < 43,51,239 < 48,00,173
Question 21.
Compare the following using >, < or = signs.
(1) 3,97,48,632 [ ] 3,97,58,632
(2) 1,50,15,178 [ ] 1,50,15,780
(3) 3,74,98,561 [ ] 96,42,748
(4) 30,49,75,831 [ ] 30,49,00,831
Answer:
(1) <
(2) <
(3) >
(4) >
Question 22.
Circle the correct answer:
(1) Mark periods 617231801 according to the Indian Number system.
(a) 61,72,31,801
(b) 16,172,31
(c) 617,231,801
Answer:
(a) 61,72,31,801
(2) Mark periods 90289164 according to the international Number system.
(a) 9,0289,164
(b) 902891,64
(c) 90,289,164
Answer:
(c) 90,289,164
(3) 1,00,00,000 is read as ……………………………….. .
(a) ten crore
(b) one crore
(c) hundred thousand
Answer:
(b) one crore
Class 5 Maths Solution Maharashtra Board
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()

![]()
![]()