Balbharti Yuvakbharati English 12th Digest Chapter 1.4 Big Data-Big Insights Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Class 12 English Chapter 1.4 Big Data-Big Insights Question Answer Maharashtra Board
12th Std English Chapter 1.4 Brainstorming Question Answer
Yuvakbharati English Navneet 12th Digest PDF Free Download Maharashtra Board
Question 1.
Give business suggestions to the respective industry/company for the following situations. You have received data that –
Answer:
(a) Many passengers prefer morning flights between 7 am and 9 am from Mumbai to Delhi.
Suggestion: Increase the number of flights between 7 am and 9 am.
(b) Many students are opting for UPSC/ MPSC Exams.
Suggestion: Increase the number of examination centres as well as job opportunities.
(c) Many people go for a morning walk to Kamla Nehru Park.
Suggestion: Open the gates of the Park earlier and close them only at noon. Also, clean the Park the previous night before closing or very early in the morning. Keep security guards in the mornings to maintain discipline.
(d) Many people buy clothes from miracle.com an online shopping site.
Suggestion: Increase the variety and brands in clothes. Give discounts and incentives to new and regular customers. Start various schemes.
(e) The viewership on television is more between 8 pm and 10 pm.
Suggestion: Telecast serials with the highest TRPs and socially important ads (like eye donation, polio drops, etc.) at this time.
![]()
Question 2.
People get information from various sources: Can you name a few?
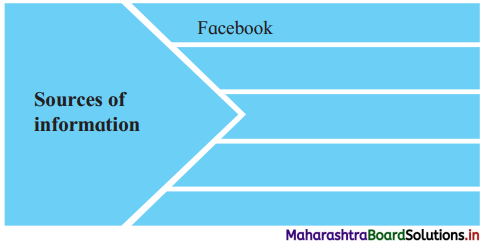
Answer:
Sources of Information:
- Internet
- Dictionary
- Encyclopedia
(A1)
Question 1.
YouTube has many videos on various things. Listen to the uses and health benefits of ‘Lemon’ and share them with your friends.
(A2)
(i) Make pointwise notes from the lesson regarding the uses of Big Data in the following application. Do not write complete sentences.
Question (a)
‘Location Tracking’.
Answer:
- Used by Google Maps and GPS to identify and track location of a place.
- Geographic positioning, radio frequency identification sensors data about traffic conditions on particular route.
- Can plan route according to travel time, transportation of the goods.
- Companies reduce risks in transport improves speed, reliability in delivery.
![]()
Question (b)
Health Care Industry.
Answer:
Uses of Big Data:
Various apps, smartwatches, gadgets, etc. collect data about various functions of our body.
- Data analyzed and feedback provided.
- Doctors can have a better diagnosis of any ailment effects of any drug.
- Past data of patients maintained suggestions, solutions for their problems given.
- Helps in monitoring the outbreaks of epidemics, diseases.
Question (c)
Education Industry.
Answer:
- Get information about the study patterns of students – can now prepare customized and dynamic learning programmes according to need of individual students.
- Every student’s comprehension level is different – course material designed to cater to different requirements of the students. One-size-fits-all pitfall avoided.
- Students’ choices, difficulties, results, etc. are available.
- Strengths and weaknesses gauged -guidance while choosing career.
Question (ii)
When you are asked for personal details on social media, mention precautions that you will take.
Answer:
When I am asked for personal details on social media, I first try to find out who wants them and why. I never reveal credit/ debit card pin numbers, even if it is a bank asking me. I never give my mobile/adhaar card numbers either. I also keep my social media accounts private and visible only to friends. Only after checking and re-checking do I give any details, for I know that there are many cases of exploitation going on.
Question (iii)
Do you think all the data we receive is used for positive things? If ‘No’, make a list of the negative things which can be done with the help of Big Data.
Answer:
Negative things which can be done with the help of Big Data:
- Loss of privacy-Big Data has all information about us.
- Misuse of personal information
- Leaking of information-this leads to thefts, blackmail, cheating, and so on.
- Data may fall into wrong hands, and a person may be harassed.
- Unsolicited calls and emails based on your internet history.
![]()
(A3)
Question 1.
Guess the meaning of the following idioms and phrases and use them in sentences of your own. One is done for you.
One-size-fits-all – suitable for or used in all circumstances
The wrist watches have adjustable belts, so one – size – fits – all.
Question (a)
‘Once in a blue moon’:
Answer:
Meaning: very rarely.
Sentence: Our English teacher is very strict and smiles only once in a blue moon.
Question (b)
‘One man army’ :
Answer:
Meaning: A ‘one-man army’ is someone who can do, or thinks he can do, everything by himself and without assistance.
(A4)
Do as directed.
Question (a)
Advertisers are one of the biggest players in Big Data.
1. Begin the sentence with ‘Very few ……………’
2. Use ‘bigger than’ and rewrite the sentence.
Answer:
1. Very few players in Big data are as big as advertisers.
2. Very few players in Big Data are bigger than advertisers.
![]()
Question (b)
No other diagnosis is as good as the diagnosis done with the help of Big Data.
1. Use ‘best’ and rewrite the sentence.
2. Use ‘better than’ and rewrite the sentence.
Answer:
1. The diagnosis done with the help of Big data is the best diagnosis.
2. No other diagnosis is better than the diagnosis done with the help of Big Data.
Question (c)
These internet giants provide the greatest data about people.
1. Begin the sentence with ‘No other ……………’
2. Use ‘greater than’ and rewrite the sentence.
Answer:
1. No other networking services provide greater data about people than these internet giants.
2. No other networking services provide greater data about people than these internet giants. OR These internet giants provide greater data about people than any other networking services.
Question (ii)
Read the sentence from the text.
New insights have enabled the banks and finance companies to come up with suitable plans.
Answer:
New insights have enabled either the banks or the finance companies to come up with suitable plans.
Question (a)
New insights have enabled the banks and finance companies to come up with suitable plans. (Rewrite using ‘either … or’.)
Answer:
New insights have enabled either the banks or the finance companies to come up with suitable plans.
![]()
Question (b)
Whatever activity we do online is recorded, monitored and analysed. (Rewrite using ‘either … or’.)
Answer:
Whatever activity we do online is either recorded, monitored or analysed.
Question (c)
Weather sensors and satellites help us to understand the weather and help in weather forecasting. (Rewrite using ‘either … or’.)
Answer:
Weather sensors and satellites help us to either understand the weather or help in weather forecasting.
(A5)
Question (i)
Interview the students of your class regarding the career they would like to pursue and the reason for selecting that particular career. Collect the data and analyse the information you have collected. Answer:
(Sample questions)
Hi, Rohan. I would like to ask you a few questions regarding the career you would like to pursue and the reason for selecting that particular career. Are you ready? Thanks.
- Which are your favourite subjects?
- Have you decided on the career you would like to pursue?
- Why have you selected that particular career?
- What are the exams you have to pass or the qualifications you must have to pursue this career?
- What type of work does it involve?
- What are the job opportunities?
- Will you have chances of business travel?
- Is the salary structure good?
- Is your family happy with your choice?
- Is this your final choice, or are you still in the process of deciding?
Thanks, Rohan. I have learnt a lot from this interview today. Bye.
![]()
Question (ii)
To listen well is as powerful a means of influence as to talk well and is essential to all true conversations.
Form a group and have a group discussion on the topics:
(a) Social Media – Curse or Boon (If used carefully and judiciously, a boon if misused, or people become addicts, then a curse)
(b) Women Empowerment and Equality (very important today-gender equality a must-the hand that rocks the cradle rules the world-however, women must not take advantage of this change-must be judicious in the use of the powers given)
(c) Climate Change (one of the biggest problems of today-must be taken very seriously-must change lifestyles-reduce consumption- recycle-carbon footprint)
(A6)
Question 1.
Find out job opportunities in the following areas and the skills required for them.
(a) Clinical Data Management
(b) Network Operations
(c) Data Processing
(d) Data Operations and Research
(e) Data Entry Operation
Yuvakbharati English 12th Digest Chapter 1.4 Big Data-Big Insights Additional Important Questions and Answers
Global Understanding:
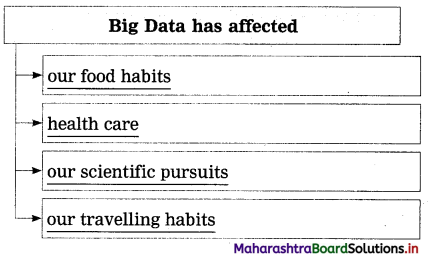
Question 1.
Complete the web:
(The answers are given directly and underlined.)
Answer:
![]()
Question 2.
Complete the following:
Answer:
- Big Data analytics is used to give insights that were previously incomprehensible.
- Big Data is so massive that it challenges the current computing technologies.
- It’s not the amount of data that is important but what the [organizations do with the data is what matters.
- Big Data analytics is the complex process of examining large and varied data sets or Big Data to uncover information.
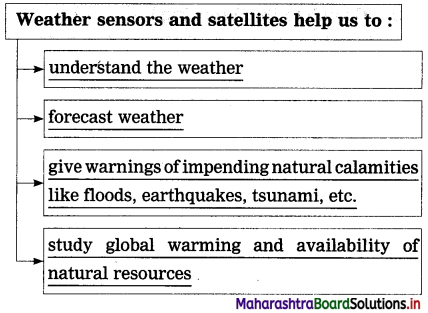
Question 3.
Complete the web:
(The answers are given directly and underlined.)
Answer:
Question 4.
Complete the following:
(The answers are given directly and underlined.)
Answer:

Question 5.
Write whether you agree or disagree with the following statements:
- Today, the majority of equity trading takes place via data algorithms.
- Big Data analytics cannot help in studying the investment patterns of people.
- Big Data is useful in High-Frequency Trading.
- Big Data cannot predict possible spikes on servers.
Answer:
- Agree
- Disagree
- Agree
- Disagree
![]()
Question 6.
Describe the ways used to create a huge database in sports.
Answer:
A huge data has been created over a period of time from the recording of matches, training sessions and workouts.
Question 7.
The database collected can help a sportsperson. Explain how.
Answer:
The data enables a sportsperson to study his own performance as well as that of the other players worldwide. It also helps in improving individual as well as team performance.
Question 8.
State the use of video analytics.
Answer:
Video analytics help one to see each and every performance minutely.
Question 9.
Name the Internet Giants mentioned in the extract.
Answer:
Facebook, Google, Twitter.
Question 10.
Pick out the False sentences, if any, and correct them:
1. Every student’s level of understanding is the same.
2.Big Data has brought about a big negative change in the education industry.
3. Designing the course material to cater to different requirements of the students is a good idea.
4. Big Data has provided a solution to the ‘one-size-fits-all’ pitfall.
Answer:
False sentences:
1. Every student’s level of understanding is the same.
2. Big Data has brought about a big negative change in the education industry.
Corrected sentences:
1. Every student’s level of understanding is different.
2. Big data has brought about a big positive change in the education industry.
![]()
Complex Factual:
Question 1.
Complete the following describing the sources of the collection of data:
(The answers are given directly and underlined.)
Answer:
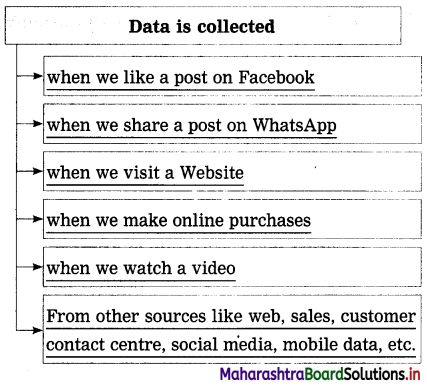
Question 2.
Mention the ways to reduce risk in transport.
Answer:
Big Data has been useful in identifying and tracking the exact location of a place. GPS and Google Maps make use of Big Data. With geographic positioning and radio frequency identification sensors we get the up-to-date data about traffic, congestion on a particular route, information if the route is closed or if it is a one-way route, understanding accident prone areas, etc. Thus, we can plan our own route according to the travel time and the transportation of goods.
If we have ordered something online we can track the location of our goods in transit, we can also track the condition of the goods. All this has immensely helped the logistics companies to reduce risks in transport, improve speed and reliability in delivery.
![]()
Question 3.
Complete the following:
(The answers are given directly and underlined.)
Answer:
- Big Data helps to predict and prevent cybercrimes, card fraud detection, archival of audit trails, etc.
- Banks can predict future attempts of frauds by analyzing the past data of their customers and the data on previous brute force attacks.
- SEC is using Big Data to monitor financial markets for possible illegal trades and suspicious activities.
- Big Data algorithms are used to make trading decisions.
Question 4.
List the ways in which sensors help a person.
Answer:
Sensors help a person:
- to understand the game from close quarters
- to understand field conditions
- to understand the weather conditions
- to understand individual performances
Inference/Interpretation/ Analysis:
Question 1.
Discuss and write how Big data is increasing in volume, variation, velocity, veracity and value.
Answer:
When we like a post on Facebook or share a post on WhatsApp, visit any website, make online purchases, or watch videos, the variety of activity we do online is recorded, monitored and analysed. So a huge amount of data is collected. Data is also collected swiftly from different sources, for example web, sales, customer contact centre, social media, mobile data and so on.
Big Data analytics is used to give insights that were previously incomprehensible. As more and more people use the Internet, social media, make online purchases, use mobile phones, and are generally more active online, Big data is increasing in volume, variation, velocity, veracity and value in leaps and bounds.
![]()
Question 2.
Do you think Big Data has improved the quality of life? Give reasons for your answer.
Answer:
Big Data has certainly improved the quality of life. Through various apps, we can maintain our body weight and exercise levels, and remain healthy. Our heart rate, sleep patterns, etc. can be monitored and any changes can be immediately reported to the doctor, who can then prescribe the correct treatment as soon as possible.
Age-related diseases like diabetes and arteriosclerosis can be treated at the early stages. Thus, we can lead healthier and more active lives. Big Data is also being used to. predict and monitor epidemics, thus ensuring that they affect as few people as possible.
Question 3.
Write some ways of the condition of the goods.
Answer:
When we order something online, we are given a tracking number. By logging into the website of the company and entering this tracking number in the given slot, we can find out the location and condition of the goods.
Question 4.
Can we understand the economy of the country by the data on Banking and Finance? Explain.
Answer:
Yes, we can. With the Big Data analytics the study of investment patterns of the people can be done. We can analyse the bank deposits made, the loans taken and the equity trading.
We can find out the business across borders. We can find out how many industries have come up, and what the industrial economy is. From all this information, we understand the economy of the country.
![]()
Question 5.
Explain, giving an example, the technique used by Netflix and YouTube to increase viewership.
Answer:
Netflix and YouTube know through Big Data just what a person has viewed and his/her behaviour online. Based on this information, the person will be shown different recommendations. For example, if a person has viewed a couple of horror films from start to end, Netflix will know that the viewer is interested in horror films.
Accordingly, Netflix will recommend a few more horror films. The viewer is pleased with this easy access to his/her favourite genre, and continues to be a customer, thus increasing Netflix revenue.
Question 6.
Discuss a solution provided by Big Data.
Answer:
Through Big Data we have information about the study patterns of students, and we can now prepare customized and dynamic learning programmes according to the need of an individual student.
Personal Response:
Question 1.
Industries can be benefited from data. Explain with an example.
Answer:
Industries can benefit from the huge amount of data available. For example, in the tourism industry, through Big Data travel agencies and hotels can identify the times when there are more crowds and hence more demand for a certain tourist spot.
They can accordingly make arrangements for more flights, trains, buses, tours, labour, essential items, etc. Hotels can use big data to compile and analyse information about their main competitors so that they are aware of what other hotels or businesses are offering customers.
Question 2.
Do you have any app on your phone that monitors your health? Describe it in brief.
Answer:
Yes, I have an app that helps me to measure the calories I have eaten and I can thus plan my meals. It also records my weight and tells me whether it has gone up or down. There is a very clear graph too which gives me complete information of the ups and downs in my weight. I have managed to lose a few kilos with the help of this app and feel much healthier now.
Question 3.
Do you use GPS and Google Maps? If so, where and when?
Answer:
I drive a two-wheeler. If I have to go to a new shop/hotel or some other place, I find out the route through GPS and follow this route. I used Google Maps when I went to Goa with my family and wanted to calculate distances and use the best routes.
![]()
Question 4.
Do you spend a lot of time on Facebook, Netflix, etc.? Do you think it is addictive?
Answer:
Yes, I do spend a lot of time on Facebook. I have a large number of friends, and hence the news feed is quite a lot. I like to know what my friends are doing, where they have gone, etc. It is addictive, and since I have Facebook on my mobile phone too, I can check it at any time. This is what most of my friends do too. I know it is not good, and I am trying to control screen time. I do not subscribe to Netflix.
Question 5.
Do you think Big Data will help to bring improvements in students? Give reasons for your answer.
Answer:
Yes, Big Data will certainly help to bring improvements in students. Students can learn topics/subj ects. according to their abilities and capacity. They can choose their careers after knowing their strengths and weaknesses, their mental make-up and abilities. Thus, there will be fewer drop-outs, and students will be happy in the careers they have chosen..
Language Study:
Question 1.
Whatever activity we do online is recorded, monitored and analysed. (Rewrite using ‘as well as’….)
Answer:
Whatever activity we do online is recorded, monitored, as well as analysed.
![]()
Question 2.
The massive data available with us can really work wonders. (Rewrite using the noun form of the underlined word.)
Answer:
The availability of massive data with us can really work wonders.
Question 3.
Big Data analytics is the complex process of examining large and varied data sets or Big Data to uncover information. (Frame a wh-question to get the underlined part as the answer.)
Answer:
What is Big Data analytics?
Question 4.
Big Data helps in monitoring the outbreaks of epidemics and diseases. (Rewrite using ‘as well as …’)
Answer:
Big Data helps in monitoring the outbreaks of epidemics as well as diseases.
Question 5.
Big Data helps in monitoring the outbreaks of epidemics and diseases. (Rewrite using ‘either …or’.)
Answer:
Big Data helps in monitoring the outbreaks of either epidemics or diseases.
![]()
Question 6.
Big Data has been useful in identifying and tracking the exact location of a place. (Rewrite using ‘as well as’.)
Answer:
Big Data has been useful in identifying as well as tracking the exact location of a place.
Question 7.
Big Data has been useful in identifying and tracking the exact location of a place. (Rewrite using ‘either … or’.)
Answer:
Big Data has been useful in either identifying or tracking the exact location of a place.
Question 8.
Weather sensors and satellites help us to understand the weather and help in weather forecasting. (Rewrite using ‘as well as’.)
Answer:
Weather sensors and satellites help us to understand the weather as well as help in weather forecasting.
Question 9.
Huge amount of data is continuously being I received from them. (Change the voice.)
Answer:
We continuously receive a huge amount of data from them.
![]()
Question 10.
Big Data has enabled smooth functioning of these agencies and institutions. (Rewrite as an interrogative question.)
Answer:
Hasn’t Big Data enabled smooth functioning of these agencies and institutions?
Question 11.
Here, Big Data algorithms are used to make trading decisions. (Rewrite using a gerund in place of the underlined word.)
Answer:
Here, Big Data algorithms are used for making trading decisions.
Question 12.
Every student’s comprehension level is different. (Add a question tag.)
Answer:
Every student’s comprehension level is different, isn’t it?
Question 13.
This will also help in guiding the student regarding the best career for him. (Rewrite using the noun form of the underlined word.)
Answer:
This will also help in providing guidance to the student regarding the best career for him.
![]()
Question 14.
This would, in general, enhance progress of all students. (Rewrite beginning ‘Progress….)
Answer:
Progress of all students, would in general, be enhanced.
Vocabulary:
Question 1.
From the extract, find the antonyms of the following words :
- understandable
- tiny
- sales
- simple
Answer:
- understandable × incomprehensible
- tiny × massive (huge)
- sales × purchase
- simple × complex
Question 2.
From the words given below, write down the ones that have been formed using prefixes:
industries, increasing, incomprehensible, unknown, examining, uncover, information, innumerable, important
Answer:
incomprehensible, unknown, uncover, innumerable
![]()
Question 3.
Find the meanings of:
1. petabytes
2. exabytes
Answer:
1. petabytes – units of information equal to one thousand million 1000 tetrabytes.
2. exabytes – units of information equal to one quintillion 1000 petabytes
Question 4.
Pick out 4 words ending in ‘ing’ from the extract.
Answer:
identifying, tracking, positioning, understanding
Question 5.
Pick out 4 nouns ending in ‘tion’ from the extract.
Answer:
location, identification, congestion, information
![]()
Question 6.
Complete the following, giving the meanings.
(The answers are given directly and underlined.)
Answer:
e.g. new insights: insights that are new.
- health-conscious people: people who are conscious of their health.
- smartwatches: watches that are smart.
- heart rate: the rate at which heart beats.
- blood pressure: the pressure of the blood.
- necessary precautions: precautions that are necessary.
- unnecessary guesswork: guesswork that is unnecessary.
Question 7.
Find adjectives from the extract having the following suffixes :
(-able, -ible, -ial, -ious, -al)
Answer:
- -able – suitable;
- -ible – possible;
- -ial – financial, social;
- -ious – suspicious, previous;
- -al-natural.
Question 8.
Match the words in Column A with the words in Column B to make collocations found in the extract:
Answer:
| A | B | Answer |
| new | crimes | new insights |
| cyber | seconds | cyber crimes |
| future | insights | future attempts |
| split | attempts | split seconds |
![]()
Question 9.
Give the adjective forms of the following words:
- giant
- interest
- create
- behaviour
Answer:
- giant – gigantic
- interest – interesting
- create – creative
- behaviour – behavioural
Question 10.
Match the words in Box A with the meanings in Box B:
Answer:
- revenue – earnings
- gigantic – huge
- enables – allows
- embedded – implanted
Question 11.
Make sentences of your own using the following expressions/words :
- leaps and bounds
- enhance
- to make optimum use of
Answer:
- leaps and bounds: Suman’s progress in studies increased by leaps and bounds after her health improved.
- enhance: We can enhance our looks by having a pleasant expression on our faces.
- to make optimum use of: Saurav decided to make optimum use of the Diwali vacation to catch up with his studies.
![]()
Oral Work:
Question 1.
Do you think people click consciously on Facebook? Discuss.
Answer:
[Points: in general, most people just press ‘like’ button on friends’ posts, many times not even reading the post-sometimes some only repeat the comment above theirs-some forwards and videos are not even seen-with so many posts and information many times there is no time to read everything]
Non-Textual Grammar
Do as directed:
Question 1.
Her family and their well-being were her highest priority. (Rewrite as an interrogative sentence.)
Answer:
Weren’t her family and their well-being her highest priority?
![]()
Question 2.
The shadows were lengthening when Smita arrived at the college. (Identify the clauses.)
Answer:
The shadows were lengthening – Main Clause
when Smita arrived at the college – Subordinate Adverb Clause of Time
Question 3.
He had to find the books and read them before the day ended.
(Rewrite using ‘not only…but also’.)
Answer:
He had not only to find the books but also read them before the day ended.
Spot the error in the following sentences and rewrite them correctly:
Question 1.
I was either scared of people’s curious looks nor their awkward questions.
Answer:
I was neither scared of people’s curious looks nor their awkward questions.
![]()
Question 2.
He was unable to participate due to a health problems.
Answer:
He was unable to participate due to a health problem.
12th Std English Questions And Answers:
- An Astrologer’s Day Class 12 Questions And Answers
- On Saying “Please” Class 12 Questions And Answers
- The Cop and the Anthem Class 12 Questions And Answers
- Big Data-Big Insights Class 12 Questions And Answers
- The New Dress Class 12 Questions And Answers
- Into the Wild Class 12 Questions And Answers
- Why We Travel Class 12 Questions And Answers
- Chapter 1.8 Voyaging Towards Excellence Class 12 Questions And Answers