Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 7 Maths Solutions covers the 7th Std Maths Practice Set 50 Answers Solutions Chapter 14 Algebraic Formulae – Expansion of Squares.
Algebraic Formulae – Expansion of Squares Class 7 Maths Chapter 14 Practice Set 50 Solutions Maharashtra Board
Std 7 Maths Practice Set 50 Solutions Answers
Question 1.
Expand:
i. (5a + 6b)²
ii. \(\left(\frac{\mathrm{a}}{2}+\frac{\mathrm{b}}{3}\right)^{2}\)
iii. (2p – 3q)²
iv. \(\left(x-\frac{2}{x}\right)^{2}\)
v. (ax + by)²
vi. (7m – 4)²
vii. \(\left(x+\frac{1}{2}\right)^{2}\)
viii. \(\left(a-\frac{1}{a}\right)^{2}\)
Solution:
i. (5a + 6b)²
Here, A = 5a and B = 6b
(5a + 6b)² = (5a)² + 2 × 5a × 6b + (6b)²
…. [(A + B)² = A² + 2AB + B²]
∴ (5a + 6b)² = 25a² + 60ab + 36b²
ii. \(\left(\frac{\mathrm{a}}{2}+\frac{\mathrm{b}}{3}\right)^{2}\)
Here A = \(\frac { a }{ 2 }\) and B = \(\frac { b }{ 3 }\)
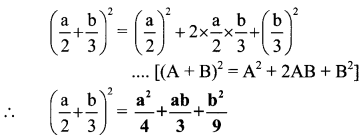
iii. (2p – 3q)²
Here, a = 2p and b = 3q
(2p – 3q)² = (2p)² – 2 × (2p) × (3q) + (3q)²
…. [(a – b)² = a² – 2ab + b²]
∴ (2p – 3q)² = 4p² – 12pq + 9q²
iv. \(\left(x-\frac{2}{x}\right)^{2}\)
Here a = x and b = \(\frac { 2 }{ x }\)
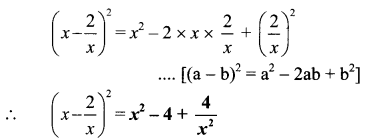
v. (ax + by)²
Here, A = ax and B = by
(ax + by)² = (ax)² + 2 × ax × by + (by)²
…. [(A + B)² = A² + 2AB + B²]
∴ (ax + by)² = a²x² + 2abxy + b²y²
vi. (7m – 4)²
Here, a = 7m and b = 4
(7m – 4)² = (7m)² – 2 × 7m × 4 + 4²
…. [(a – b)² = a² – 2ab + b²]
∴ (7m – 4)² = 49m² – 56m + 16
vii. \(\left(x+\frac{1}{2}\right)^{2}\)
Here a = x and b = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)
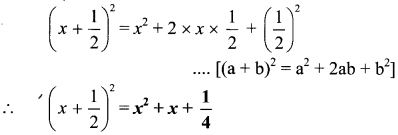
viii. \(\left(a-\frac{1}{a}\right)^{2}\)
Here A = a and B = \(\frac { 1 }{ a }\)
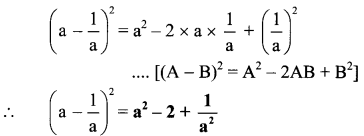
Question 2.
Which of the options given below is the square of the binomial
(A) \(64-\frac{1}{x^{2}}\)
(B) \(64+\frac{1}{x^{2}}\)
(C) \(64-\frac{16}{x}+\frac{1}{x^{2}}\)
(D) \(64+\frac{16}{x}+\frac{1}{x^{2}}\)
Solution:
(C) \(64-\frac{16}{x}+\frac{1}{x^{2}}\)
Hint:
= \(\left(8-\frac{1}{x}\right)^{2}=8^{2}-2 \times 8 \times \frac{1}{x}+\left(\frac{1}{x}\right)^{2}\) …[(a – b)² = a² – 2ab + b²]
= \(64-\frac{16}{x}+\frac{1}{x^{2}}\)
Question 3.
Of which of the binomials given below is the m²n² + 14mnpq + 49p²q² the expansion?
(A) (m + n) (p + q)
(B) (mn – pq)
(C) (7mn + pq)
(D) (mn + 7pq)
Solution:
(D) (mn + 7pq)
Hint:
Here, square root of the first term = mn
Square root of the last term = 7pq
∴ Required binomial = (mn + 7pq)²
Question 4.
Use an expansion formula to find the values of:
i. (997)²
ii. (102)²
iii. (97)²
iv. (1005)²
Solution:
i. (997)² = (1000 – 3)²
Here, a = 1000 and b = 3
(1000 – 3)² = (1000)² – 2 x 1000 x 3 + 3²
…. [(a – b)² = a² – 2ab + b²]
= 1000000 – 6000 + 9
= 994009
∴ (997)² = 994009
ii. (102)² = (100 + 2)²
Here, a = 100 and b = 2
(100 + 2)² = (100)² + 2 x 100 x 2 + 2²
…. [(a + b)² = a² + 2ab + b²]
= 10000 + 400 + 4
= 10404
∴ (102)² = 10404
iii. (97)² = (100 – 3)²
Here, a = 100 and b = 3
(100 – 3)² = (100)² – 2 x 100 x 3 + 3²
…. [(a – b)² = a² – 2ab + b²]
= 10000 – 600 + 9
= 9409
∴ (97)² = 9409
iv. (1005)² = (1000 + 5)²
Here, a = 1000 and b = 5 (1000 + 5)²
= (1000)² + 2 x 1000 x 5 + 5²
…. [(a + b)² = a² + 2ab + b²]
= 1000000+ 10000 + 25
= 1010025
∴ (1005)² = 1010025
Maharashtra Board Class 7 Maths Chapter 14 Algebraic Formulae – Expansion of Squares Practice Set 50 Intext Questions and Activities
Question 1.
Use the given values to verify the formulae for squares of binomials. (Textbook pg. no. 92)
i. a = -7, b = 8
ii. a = 11,b = 3
iii. a = 2.5,b = 1.2
Solution:
i. (a + b)² = (-7 + 8)²
= 1²
= 1
a² + 2ab + b² = (-7)² + 2 x (-7) x 8 + 8²
= 49 – 112 + 64
= 1
∴(a + b)² = a² + 2ab + b²
(a – b)² = (-7 – 8)²
= (-15)²
= 225
a² – 2ab + b² = (-7)² – 2 x (-7) x 8 + (8)²
= 49 + 112 + 64
= 225
∴(a – b)² = a² – 2ab + b²
ii. (a + b)² = (11 + 3)²
= 14²
= 196
a² + 2ab + b² = 11² + 2 x 11 x 3 + 3²
= 121 + 66 + 9
= 196
∴(a + b)² = a² + 2ab + b²
(a – b)² = (11 – 3)² = 8²
= 64
a² – 2ab + b² = 11² – 2 x 11 x 3 + 3²
= 121 – 66 + 9
= 64
∴(a – b)² = a² – 2ab + b²
iii. (a + b)² = (2.5 + 1.2)²
= 3.7²
= 13.69
a² + 2ab + b² = (2.5)² + 2 x 2.5 x 1.2 + (1.2)²
= 6.25 + 6 + 1.44
= 13.69
∴(a + b)² = a² + 2ab + b²
(a – b)² = (2.5 – 1.2)²
= 1.32
= 1.69
a² – 2ab + b² = (2.5)² – 2 x 2.5 x 1.2 + (1.2)²
= 6.25 – 6 + 1.44
= 1.69
∴(a – b)² = a² – 2ab + b²-
Std 7 Maths Digest