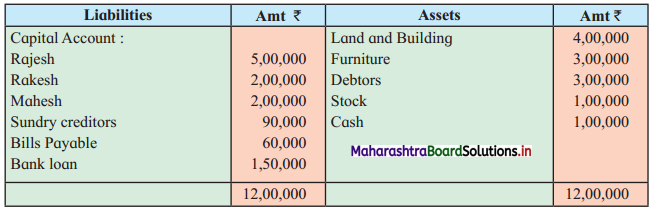
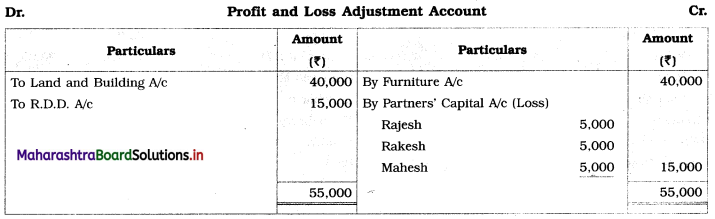
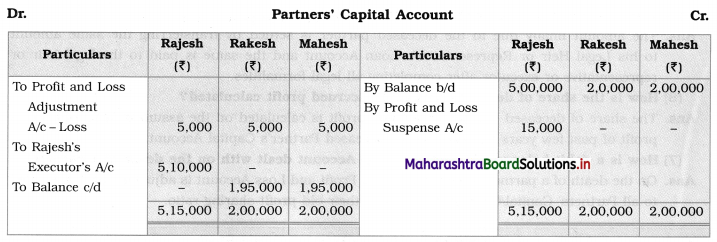
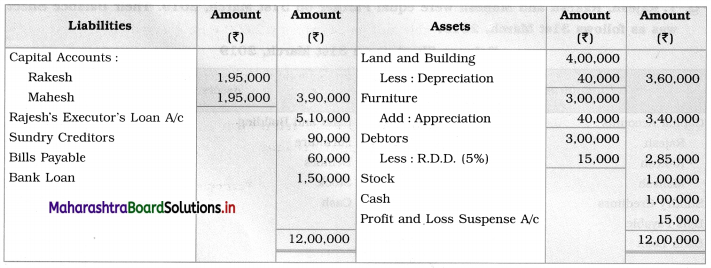
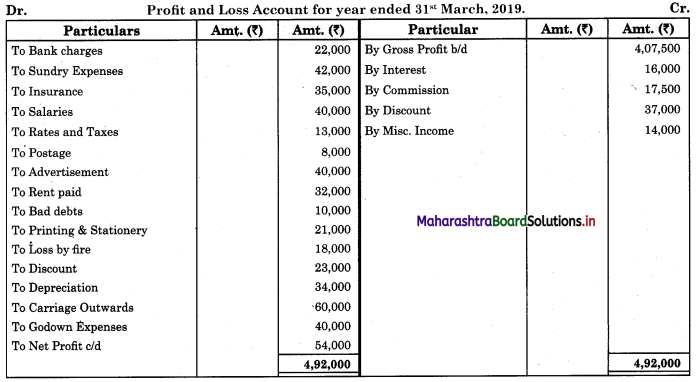
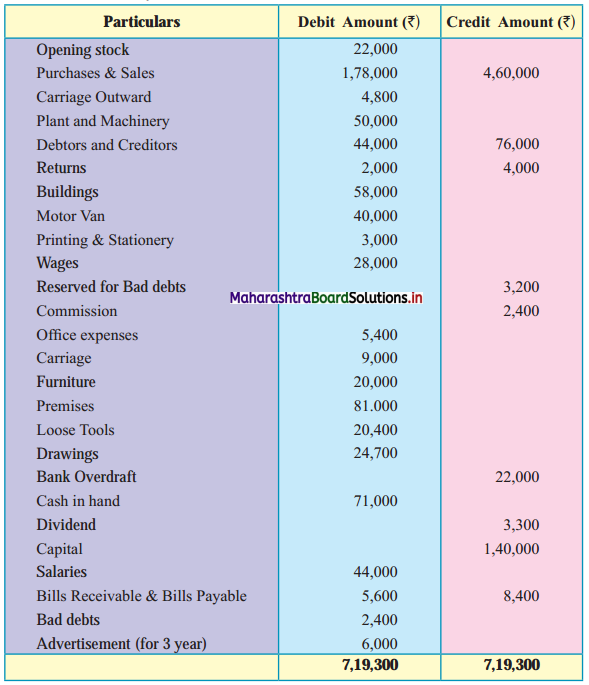
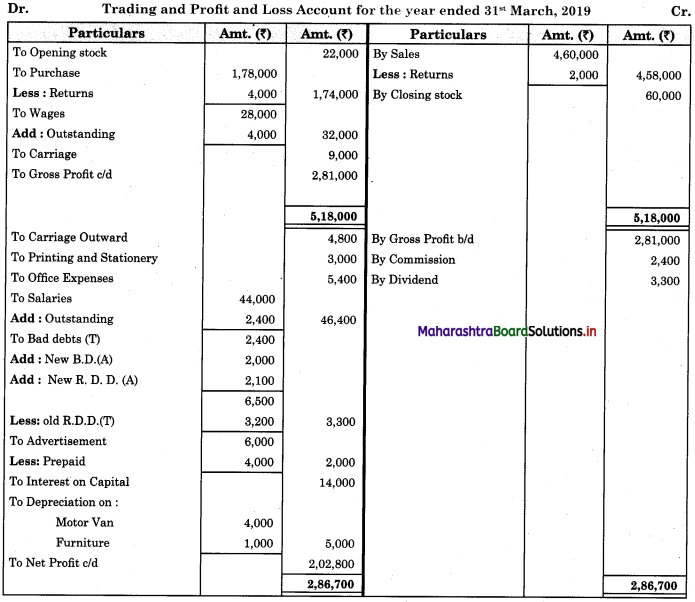
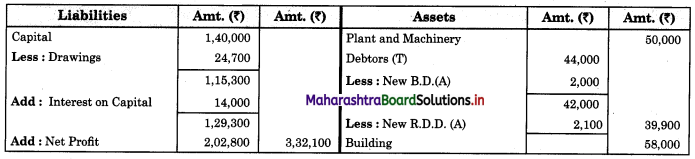
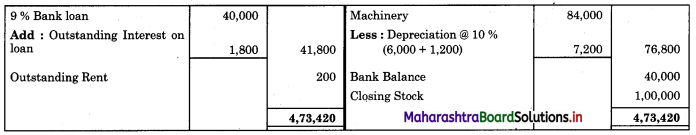
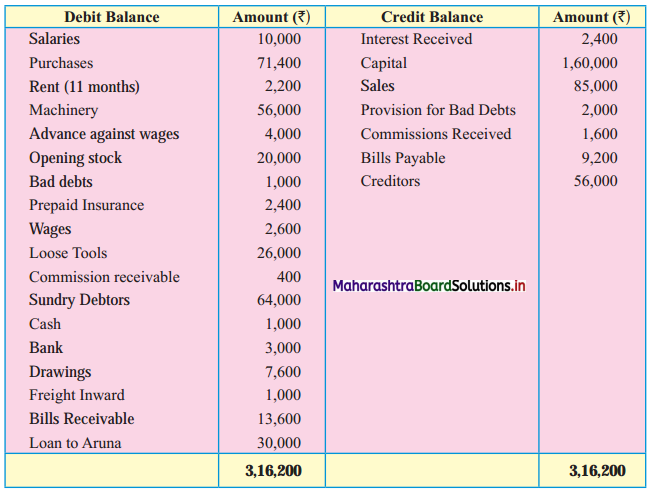
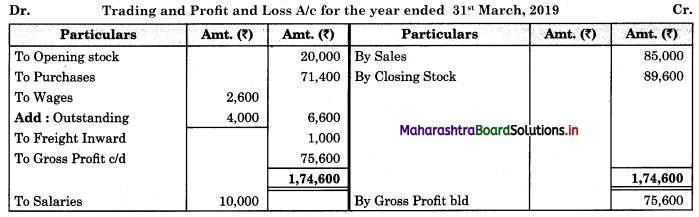
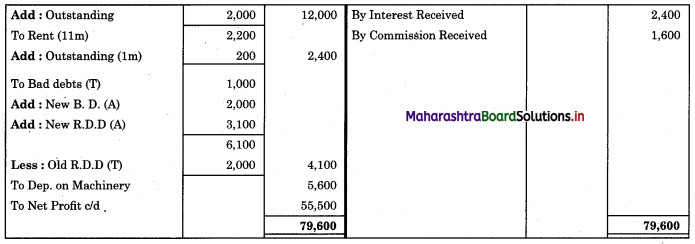
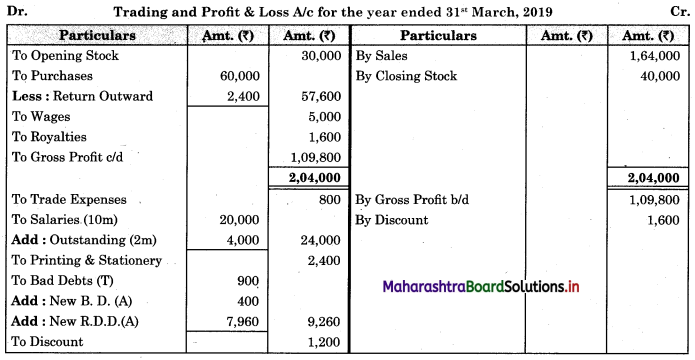
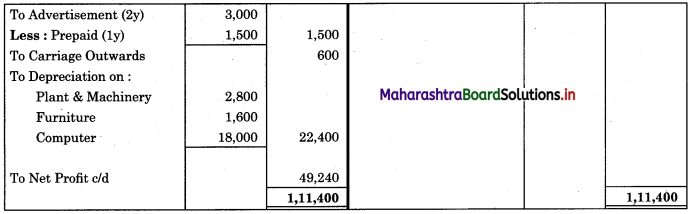
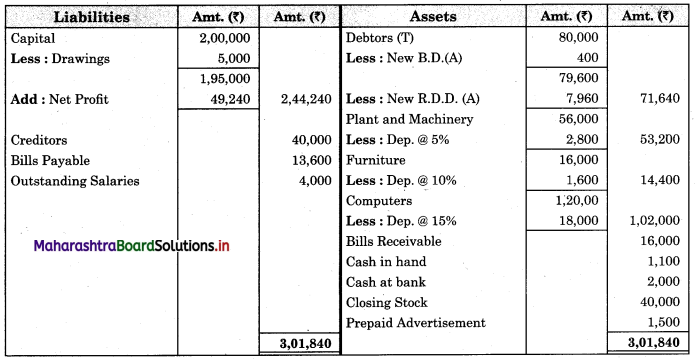
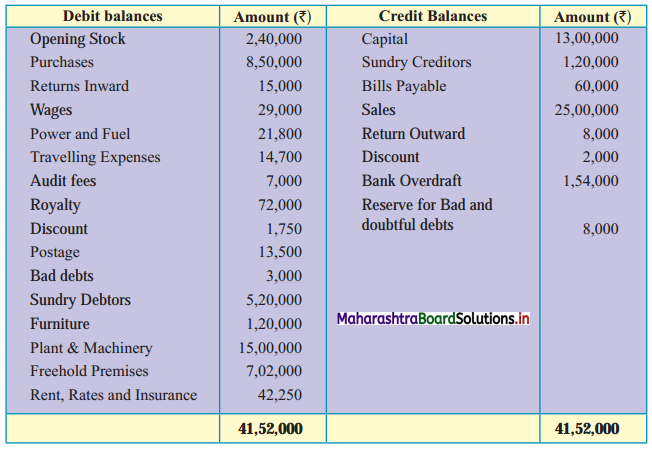
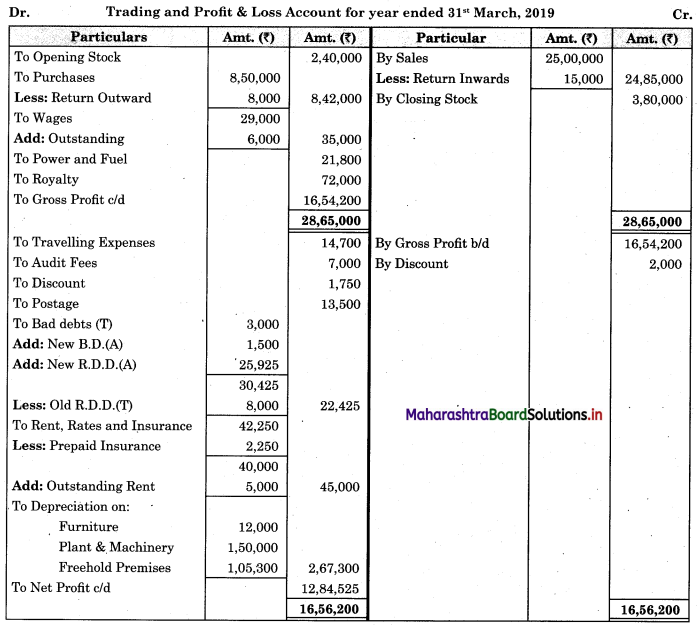
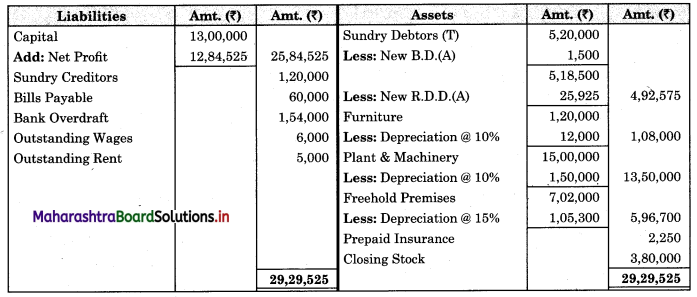
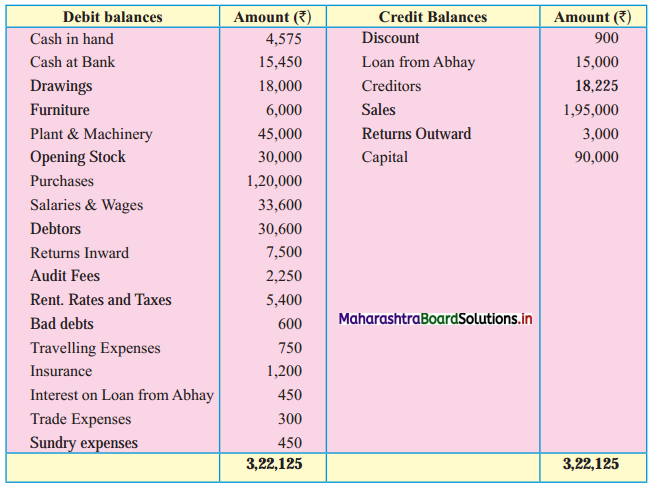
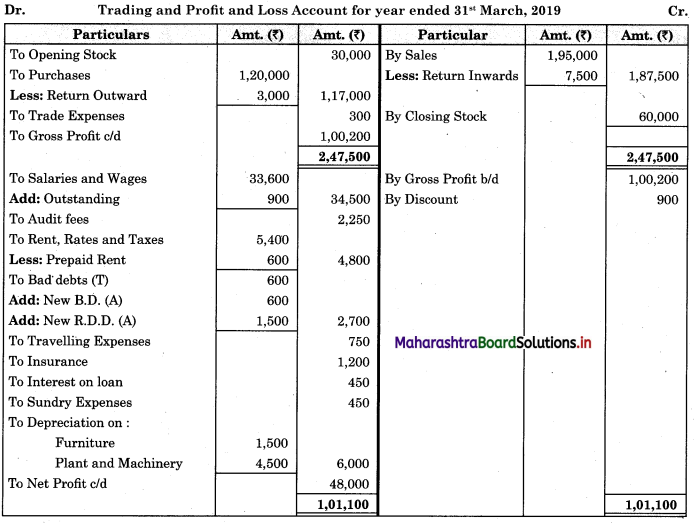
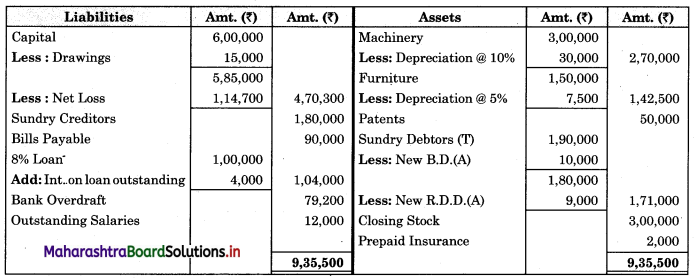
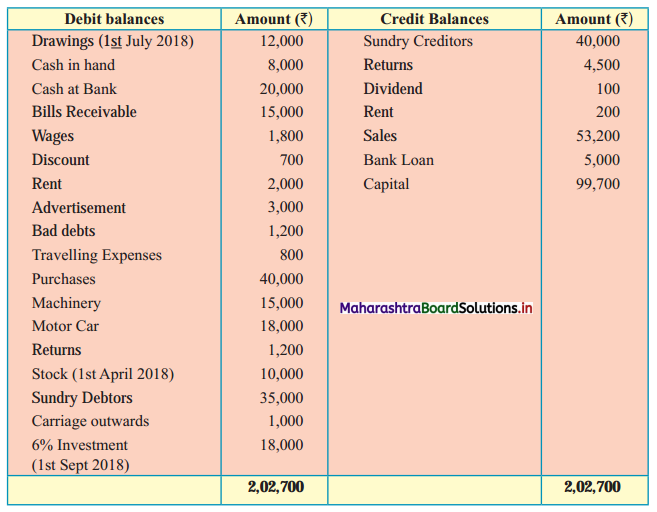
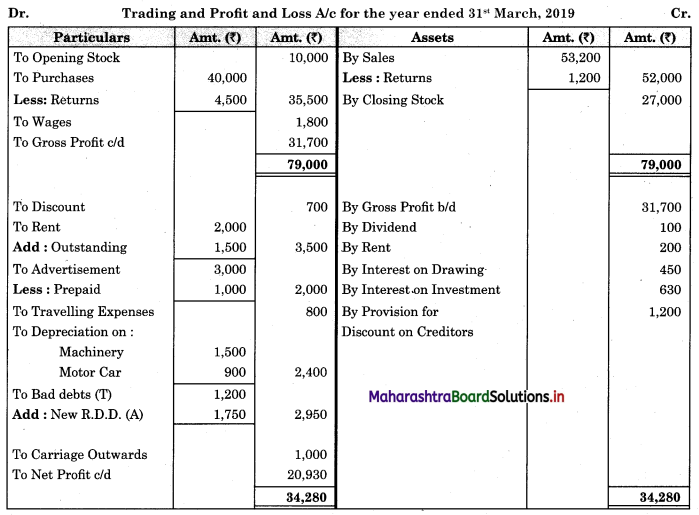
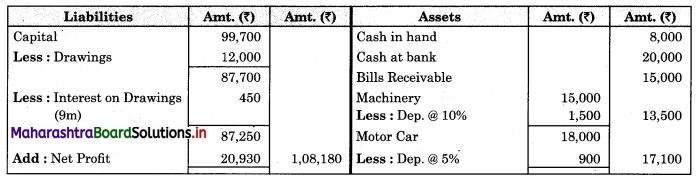
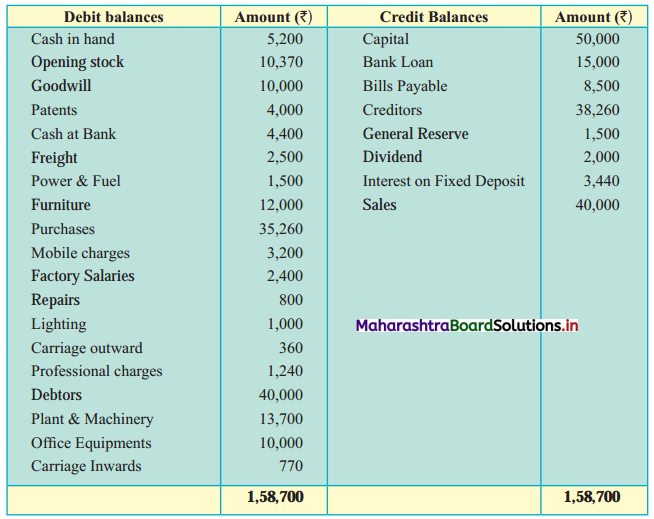
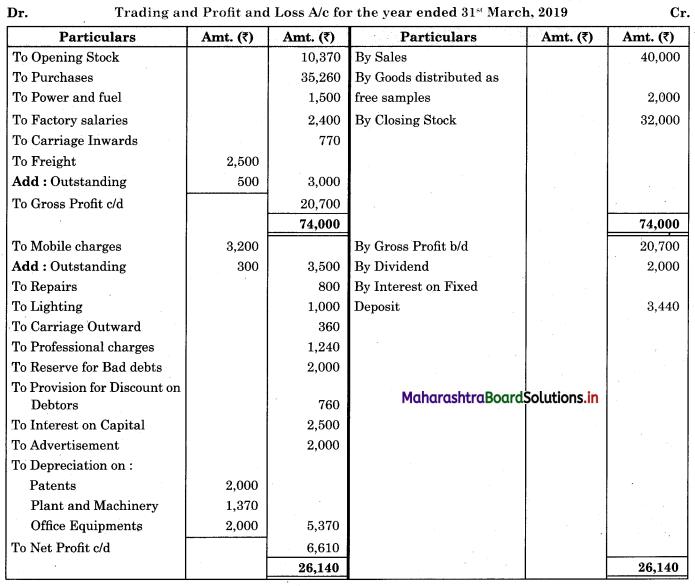
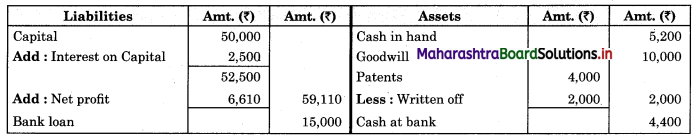
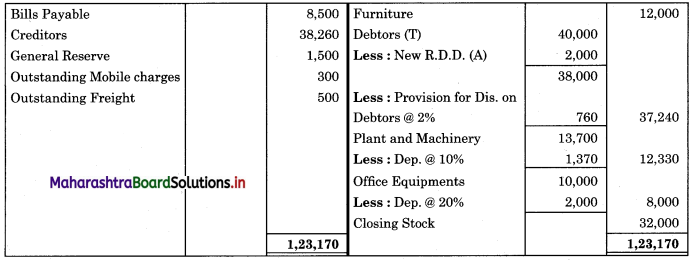
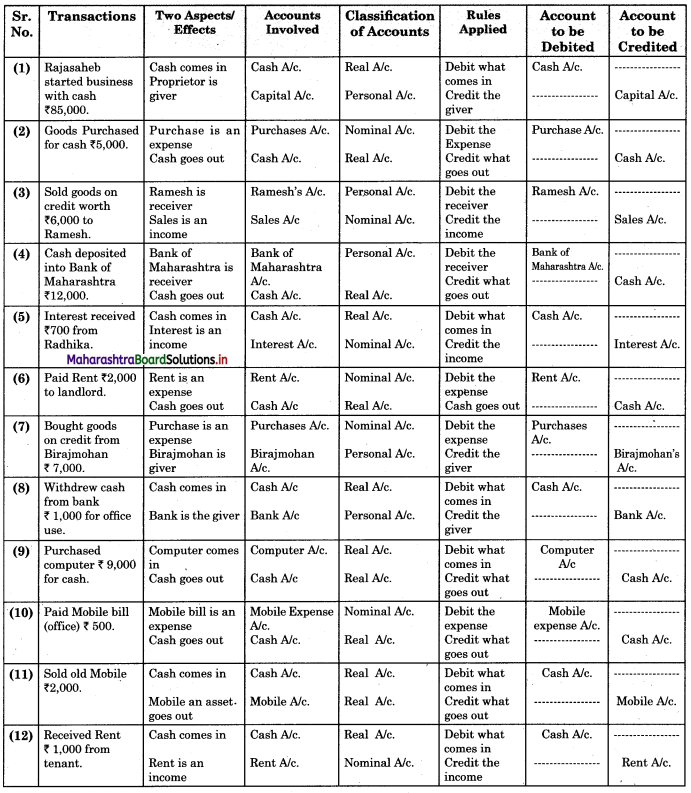
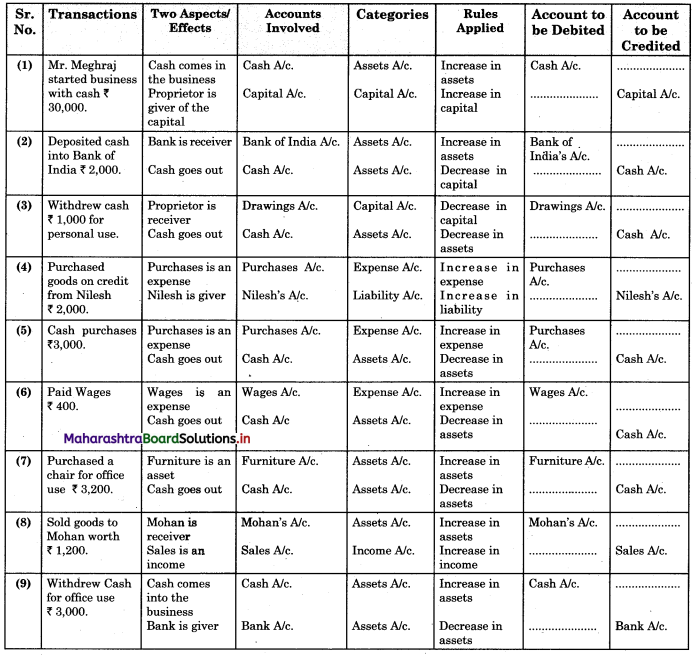
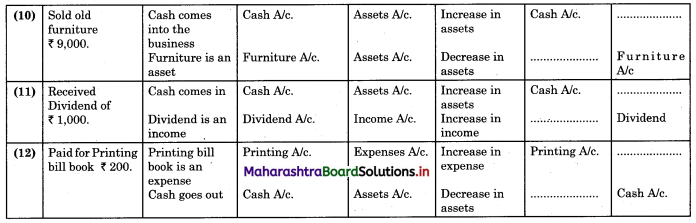
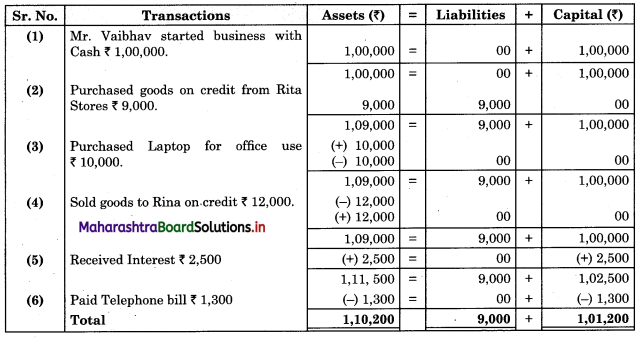
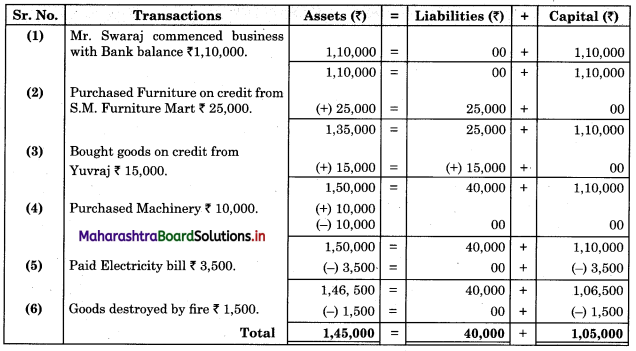
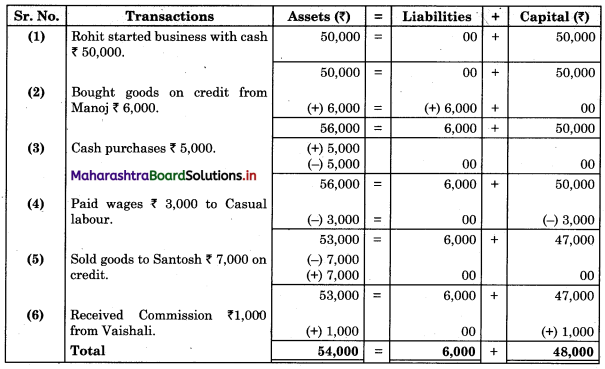
Subsidiary Books 11th BK Commerce Chapter 5 Solutions Maharashtra Board
Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Bookkeeping and Accountancy 11th Solutions Chapter 5 Subsidiary Books Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
Class 11 Commerce BK Chapter 5 Exercise Solutions
Objective Type Questions & Answers
1. Answer the following questions in one sentence.
Question 1.
What are Subsidiary Books?
Answer:
Subdivision of journals on the basis of nature of transactions is known as Subsidiary Books.
Question 2.
What is a Cash Book?
Answer:
The subsidiary book in which details of cash are received in the form of cash, cheques, drafts, etc., and details of payment made in the form of cash, cheques, drafts, etc. is called a cash book.
![]()
Question 3.
State the meaning of ‘Contra entry’.
Answer:
The accounting entries which appear on both the sides of cash book are called contra entries.
Question 4.
State the meaning of the imprest system of Petty Cash Book.
Answer:
Imprest System of Petty cash book is a system in which head cashier gives fixed (imprest) amount to the petty cashier at the beginning of month/fortnight to meet the expenses of that period. Later on the shortfall after meeting the expenses is reimbursed by the head cashier.
Question 5.
Which transactions are recorded in Purchase Book?
Answer:
Goods purchased on credit for resale are only recorded in the Purchase Book.
Question 6.
Which sales are recorded in Sales Book?
Answer:
Credit sales of goods are recorded in Sales Book.
Question 7.
Which transactions are recorded in the Journal Proper?
Answer:
Journal Proper is meant for recording opening entries, closing entries, adjustment entries, transfer entries, and rectification entries.
![]()
Question 8.
Who is a Petty Cashier?
Answer:
A cashier in charge of recording transactions in a petty cash book is known as Petty Cashier.
2. Give a word/term or phrase for each of the following statements:
Question 1.
A person who maintains Petty Cash Book.
Answer:
Petty Cashier
Question 2.
A bank account which the businessman prefers to open.
Answer:
Current Account
Question 3.
Petty Cash Book in which the payment side is ruled in suitable columns.
Answer:
Analytical Petty Cash Book
![]()
Question 4.
Subsidiary book in which only credit purchases of goods are recorded.
Answer:
Purchase Book
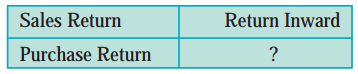
Question 5.
Subsidiary book in which return of goods sold on credit is recorded.
Answer:
Sales Return Book
Question 6.
The entry is recorded on both sides of the cash book.
Answer:
Contra Entry
Question 7.
Name the account which encourages personal savings.
Answer:
Saving Account
Question 8.
A note was issued by the buyer to the seller giving full details of goods returned.
Answer:
Debit Note
![]()
Question 9.
A note was issued by the seller on receipt of defective goods from the customer.
Answer:
Credit Note
Question 10.
Name the bank account on which overdraft facility is given to the Account holder.
Answer:
Current Account
3. Select the most appropriate answers from the alternatives given below and rewrite the sentences.
Question 1.
Cash column of Cash Book can never have ____________ balance.
(a) credit
(b) debit
(c) zero
(d) none of the above
Answer:
(a) credit
Question 2.
Any entry recorded on both sides of Cash Book is known as ____________ entry.
(a) opening
(b) rectifying
(c) transfer
(d) contra
Answer:
(d) contra
Question 3.
The source document for recording in Sales book is ____________
(a) Inward Invoice
(b) Outward Invoice
(c) Voucher
(d) Cash Memo
Answer:
(b) Outward Invoice
![]()
Question 4.
Credit purchase of Machinery is recorded in the ____________
(a) Purchase Book
(b) Cash Book
(c) Journal Proper
(d) Returns Outward Book
Answer:
(c) Journal Proper
Question 5.
Sub-division of journal is known as ____________ book.
(a) Subsidiary
(b) Purchase Return
(c) Purchase
(d) Journal Proper
Answer:
(a) Subsidiary
Question 6.
Additional cash introduced in business is recorded in ____________
(a) Purchase Book
(b) Cash Book
(c) Journal Proper
(d) Returns Inwards Book
Answer:
(b) Cash Book
Question 7.
Entry for bad debts is recorded in the ____________
(a) Sales Book
(b) Purchase Book
(c) Cash Book
(d) Journal Proper
Answer:
(d) Journal Proper
Question 8.
Direct deposit made by the customer into our bank is recorded in the ____________ side of the Cash Book.
(a) payments
(b) credit
(c) receipts
(d) both
Answer:
(c) receipts
![]()
Question 9.
The person who draws the cheque and signs on it is the ____________
(a) drawer
(b) drawee
(c) payee
(d) all of the above
Answer:
(a) drawer
Question 10.
A fixed amount is deposited for a fixed period in ____________ deposit account.
(a) Current
(b) Savings
(c) Fixed
(d) Recurring
Answer:
(c) Fixed
4. State whether the following statements are True or False with reasons:
Question 1.
Journal is a book of secondary entry.
Answer:
This statement is False.
Journal is a book of prime entry.
Question 2.
Assets sold on credit are entered in Sales Journal.
Answer:
This statement is False.
Assets sold on credit are entered in Journal Proper.
Question 3.
Cash and credit purchases are entered in Purchase Book.
Answer:
This statement is False.
Only credit purchases are entered in Purchase Book.
![]()
Question 4.
Cash sales are entered in Sales Journal.
Answer:
This statement is False.
Cash sales are entered in the cash book.
Question 5.
Cash Book records transactions relating to receipts and payments of cash.
Answer:
This statement is True.
Cashbook is prepared for cash transactions only. All incomes are receipts and they are recorded on the debit side of Cashbook. All expenses are payments recorded to the credit side.
5. Do you agree with the following statements.
Question 1.
Trade discount is recorded in Cash Book.
Answer:
Disagree
Question 2.
Petty Cash Book is a book with having a record of big payments.
Answer:
Disagree
Question 3.
Cash received is entered on the debit side of the Cash Book.
Answer:
Agree
Question 4.
Transactions recorded on both debit and credit side of Cash Book is known as Contra Entry.
Answer:
Agree
![]()
Question 5.
Credit purchase of machinery is entered in Purchase Journal.
Answer:
Disagree
6. Complete the following sentences:
Question 1.
Cash Book is a ____________ Journal.
Answer:
Subsidiary
Question 2.
In Journal Proper, only ____________ discount is recorded.
Answer:
Cash
Question 3.
Return of goods purchased on credit to the suppliers will be entered in ____________ Journal.
Answer:
Purchase return
Question 4.
Assets sold on credit are entered in ____________
Answer:
Journal proper
![]()
Question 5.
Double column Cash Book records transactions relating to cash and ____________
Answer:
Bank
Question 6.
Credit purchases of goods are recorded in ____________
Answer:
Purchase Book
Question 7.
Cash Book does not record the ____________ Transactions.
Answer:
Credit
Question 8.
Credit balance shown by a bank column in Cash Book is ____________
Answer:
Overdraft
Question 9.
Petty Cash Book is used for recording ____________ expenses.
Answer:
Petty
Question 10.
In Purchase Book goods purchased on ____________ are recorded.
Answer:
Credit
7. Correct the following sentences and rewrite them the same.
Question 1.
Cash purchases of goods are recorded in the Purchase book.
Answer:
Cash purchases of goods are recorded in Cashbook.
Question 2.
Cash Book records cash transactions as well as credit transactions.
Answer:
Cash Book records only cash transactions.
![]()
Question 3.
Small and large business records all transactions in subsidiary books.
Answer:
Large business records all transactions in subsidiary books.
Question 4.
The person who maintains the Petty Cash Book is called Chief Cashier.
Answer:
The person who maintains the Petty Cash Book is called Petty Cashier.
8. Calculate the following.
Question 1.
Cash purchases for ₹ 1,60,000 at 10% T.D. and 5% C.D. What is the amount of Net purchases?
Answer:
Gross Price = ₹ 1,60,000
Less: 10% T.D. = ₹ 16,000
Net Price = ₹ 1,44,000
Less: 5% C.D. = ₹ 7,200
Net Purchases = ₹ 1,36,800
Question 2.
Purchased goods from Harish for ₹ 12,000 @ 7% T.D. What is the amount of Trade discount?
Answer:
Trade Discount = Purchases Price × Percentage of T.D.
= 12,000 × \(\frac{7}{100}\)
= ₹ 840
Question 3.
Sold 50 Shirts at ₹ 300 per shirt and 40 Trousers at ₹ 600 each. What is the amount of sales?
Answer:
(1) 50 Shirts × ₹ 300 = ₹ 15,000
(2) 40 Trousers × ₹ 600 = ₹ 24,000
Total Sales = ₹ 39,000
![]()
Question 4.
Sold 30 Jackets at ₹ 500 per Jacket at 8% Trade discount, What is the amount of Trade discount?
Answer:
Sales Value = 30 Jackets × ₹ 500 = ₹ 15,000
Trade Discount = 15,000 × \(\frac{8}{100}\) = ₹ 1,200
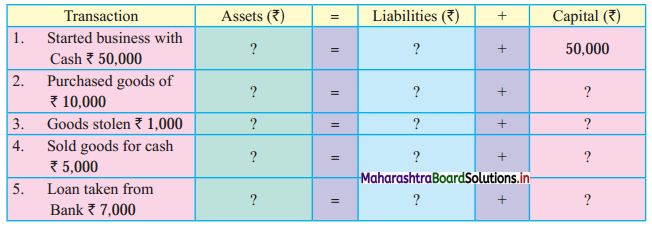
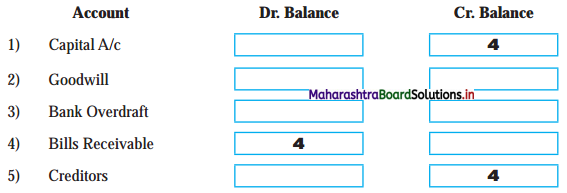
9. Complete the following Table.
Question 1.

Answer:
2,000
Question 2.

Answer:
45,000
Question 3.

Answer:
1,84,000
![]()
Question 4.

Answer:
1,10,000
Question 5.
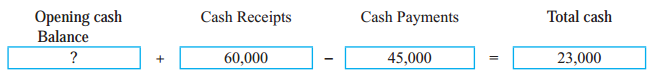
Answer:
8,000
Question 6.

Answer:
1,40,000
Question 7.

Answer:
1,10,000
Question 8.
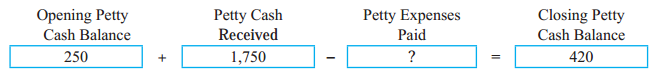
Answer:
1,580
![]()
Question 9.
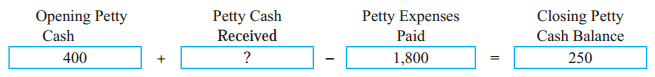
Answer:
1,650
Question 10.
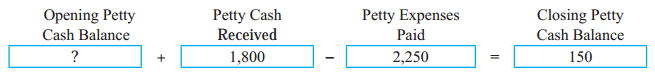
Answer:
600
Practical Problems
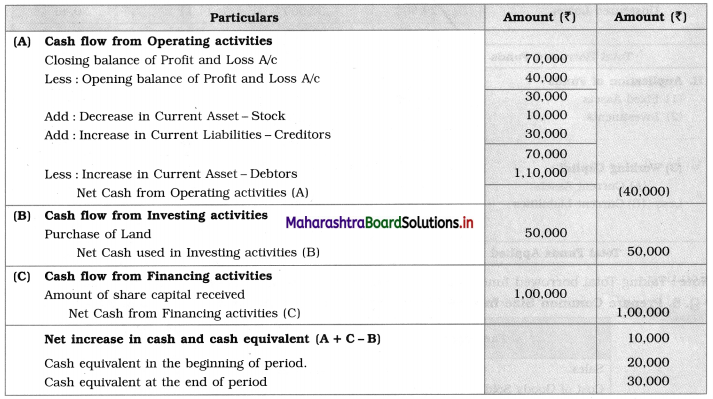
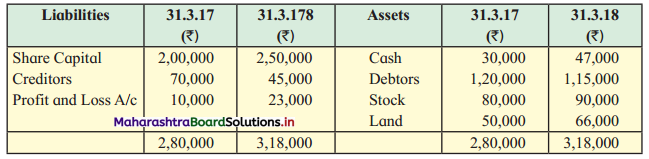
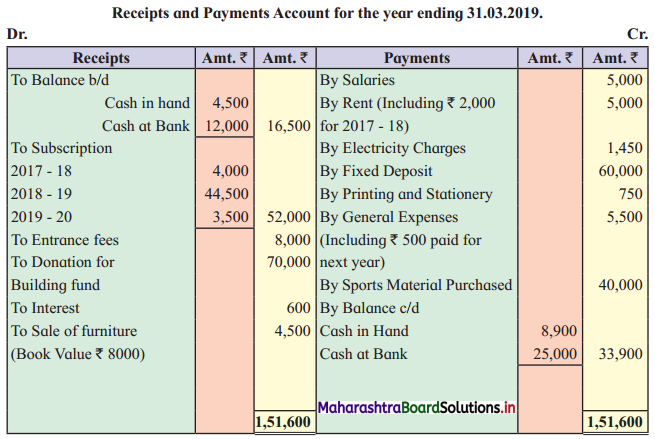
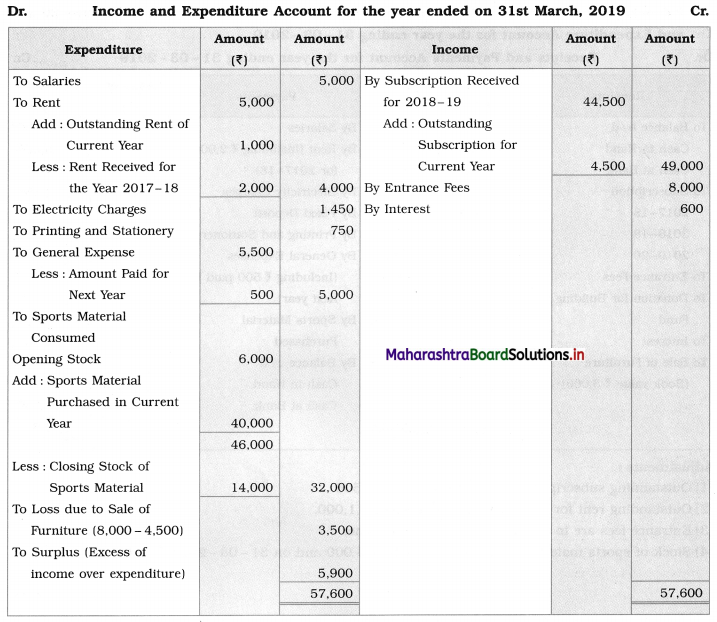
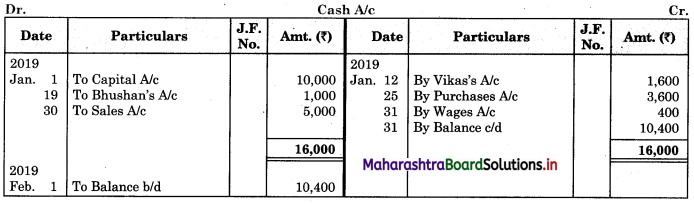
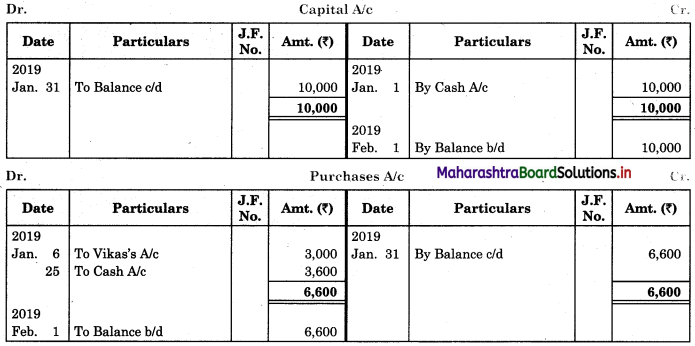
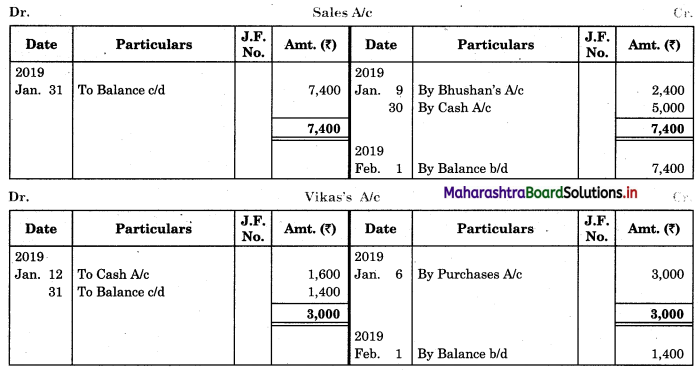
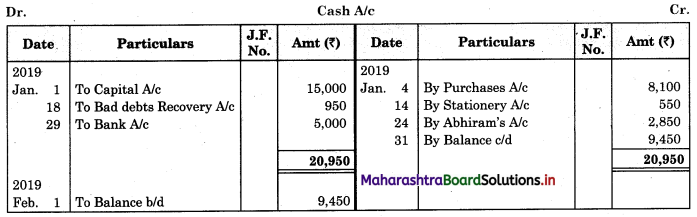
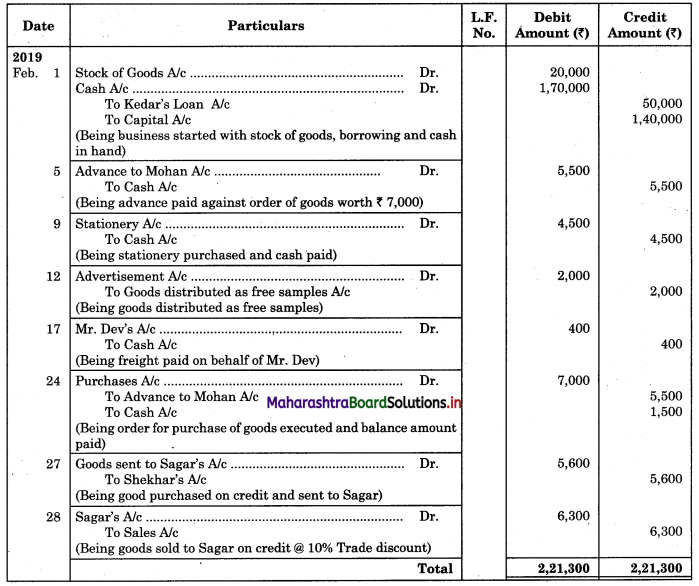
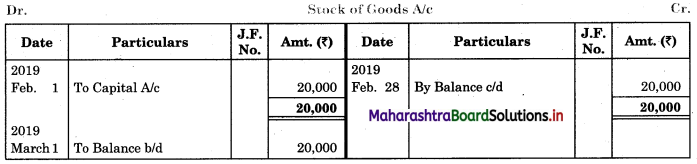
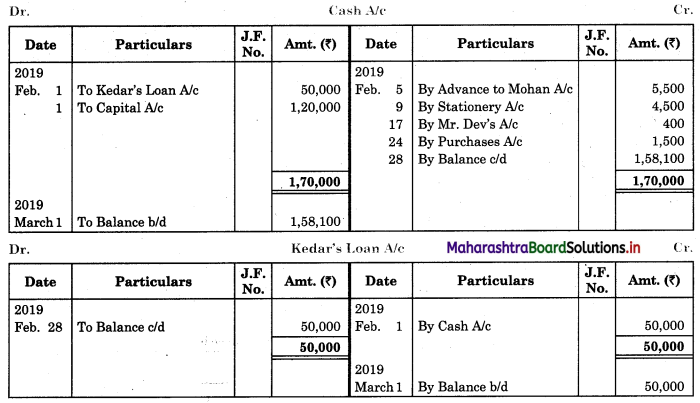
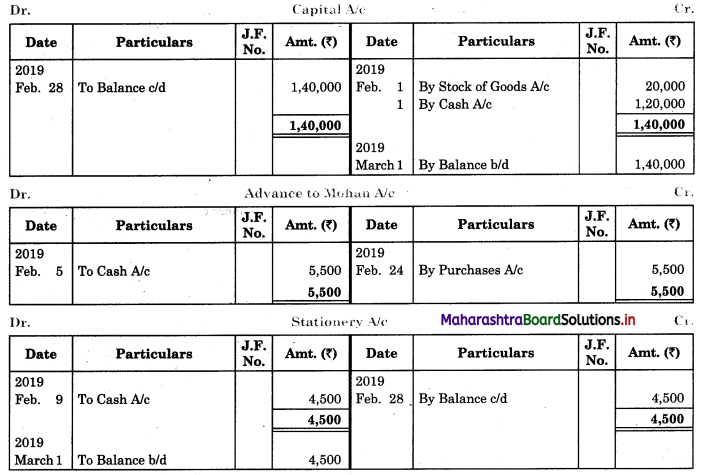
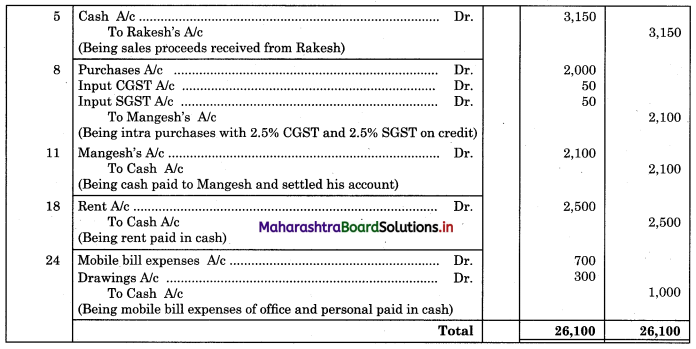
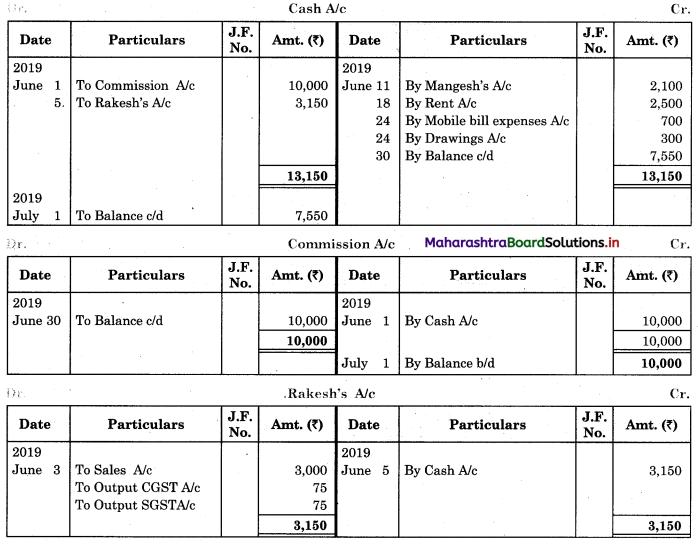
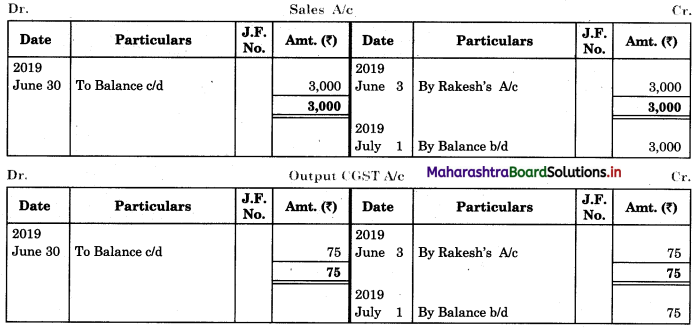
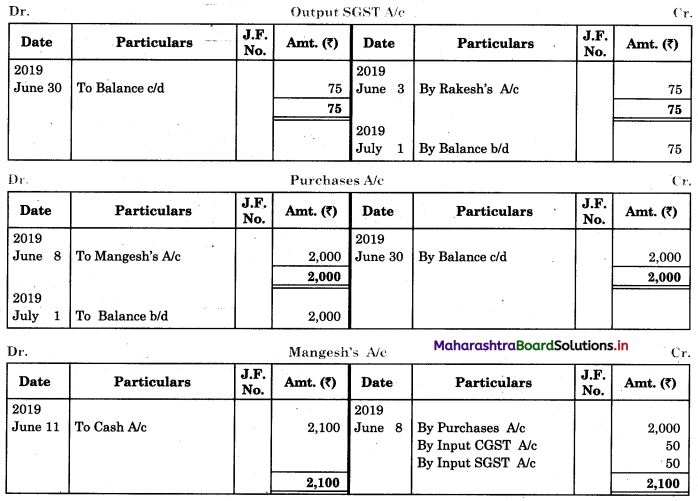
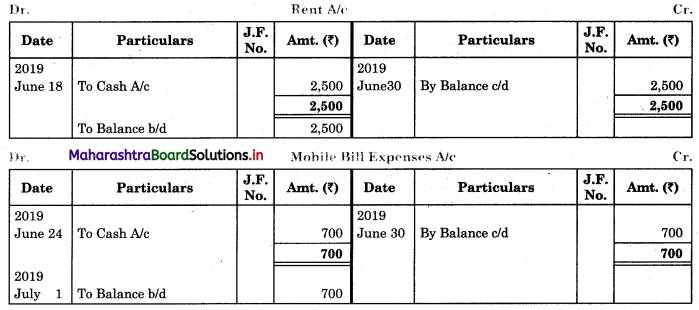
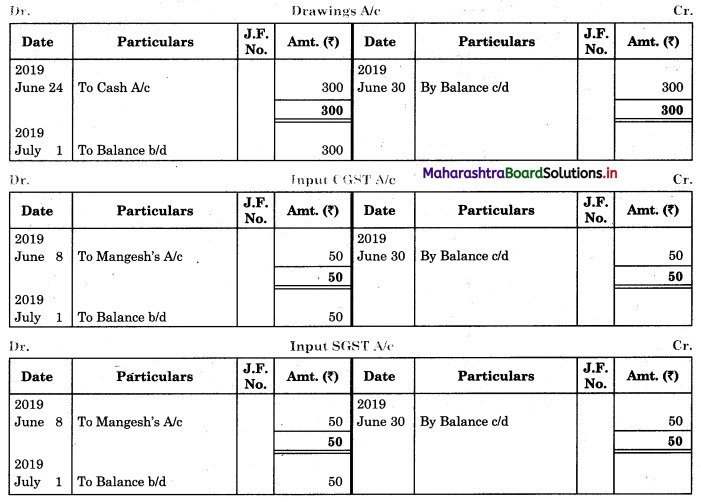
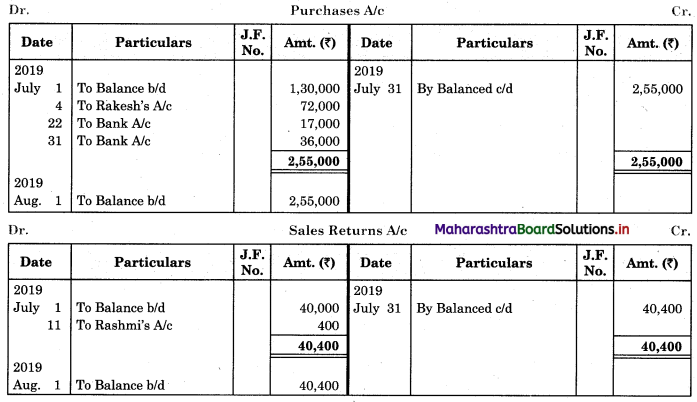
Question 1.
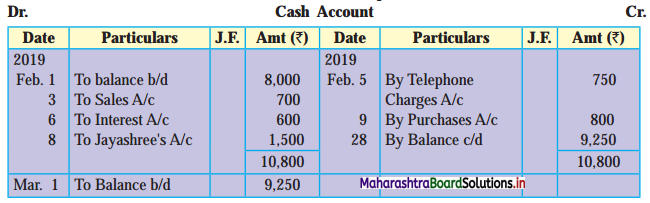
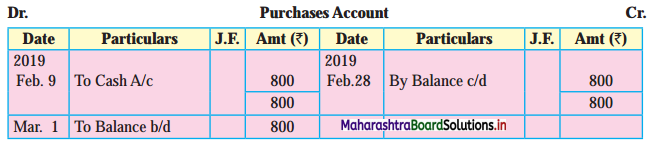
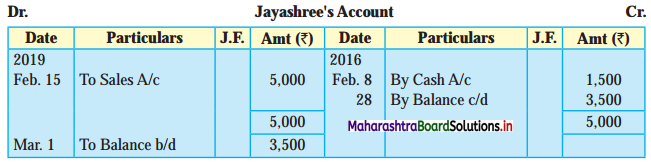
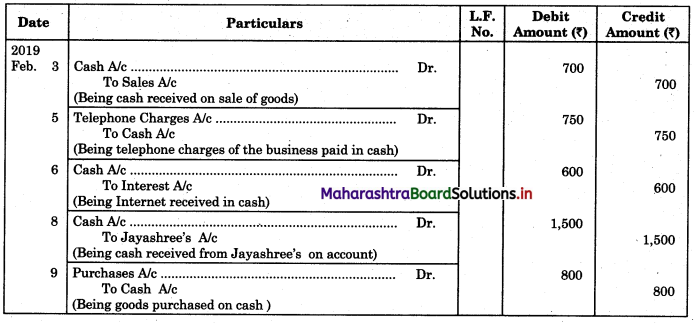
Prepare a two-column Cash Book with the help of the following information for January 2018.
| January 2018 | Amt (₹) | |
| 01 | Started business with cash | 1,20,000 |
| 03 | Cash paid into Bank of Baroda | 50,000 |
| 05 | Purchased goods from Sakshi on credit | 20,000 |
| 06 | Sold goods to Divakar and received a bearer cheque | 20,000 |
| 10 | Paid to Sakshi cash | 20,000 |
| 14 | Cheque received on December 06, 2018, deposited into Bank | |
| 18 | Sold goods to Shivaji on credit | 12,000 |
| 20 | Cartage paid in cash | 500 |
| 22 | Received cash from Shivaji | 12,000 |
| 27 | Commission received | 5,000 |
| 30 | Drew cash for personal use | 2,000 |
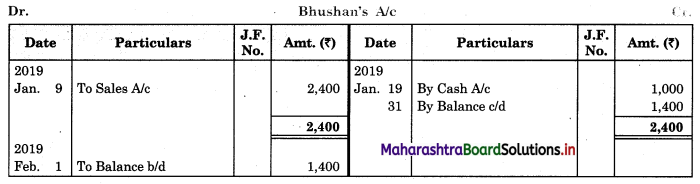
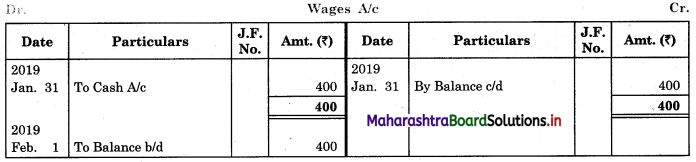
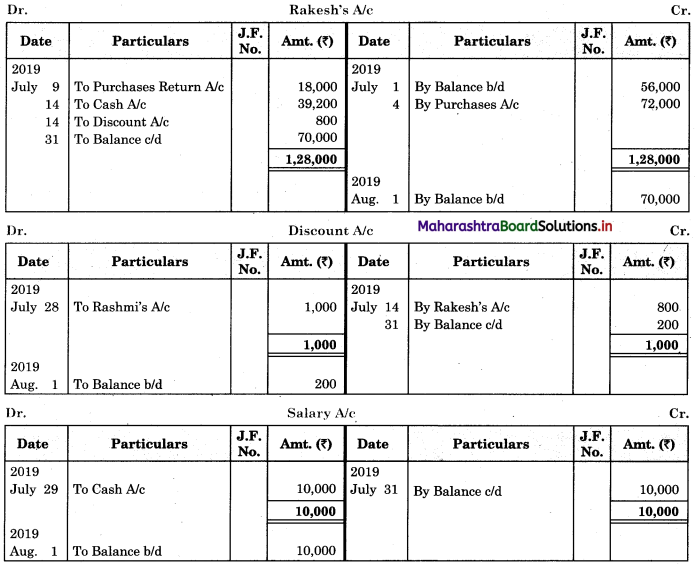
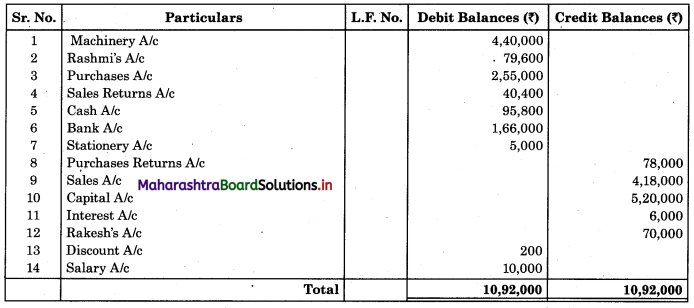
Solution:
In the books of ____________
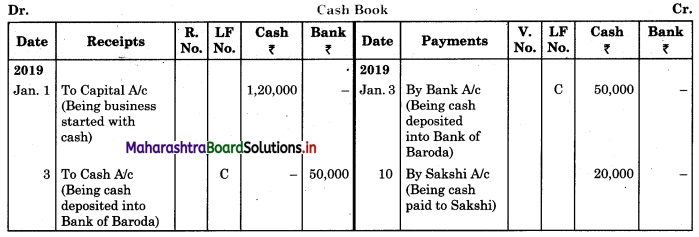
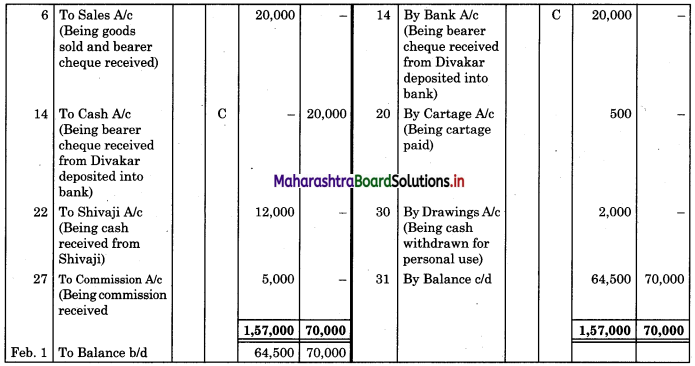
Note: Transactions dated 5th and 18th are credit transactions, hence not to be recorded in the cash book.
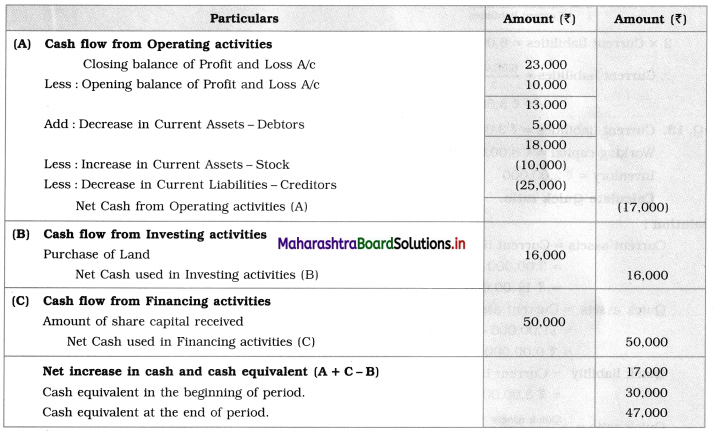
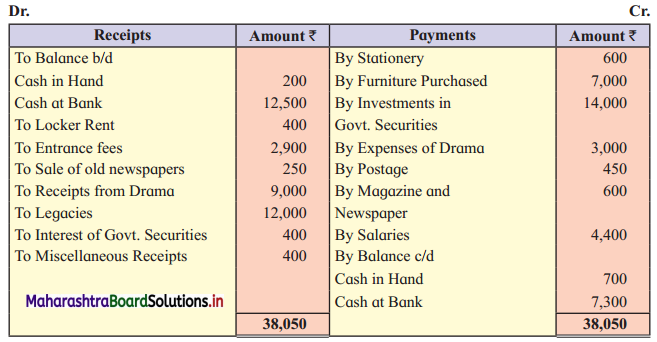
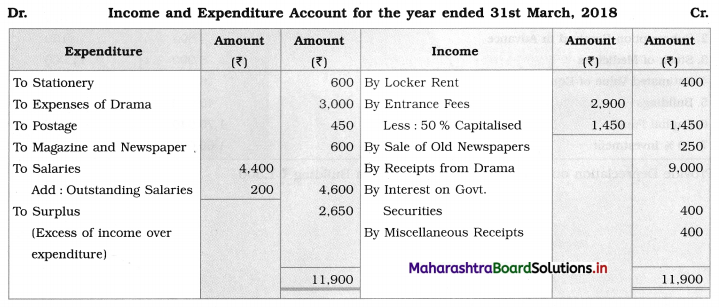
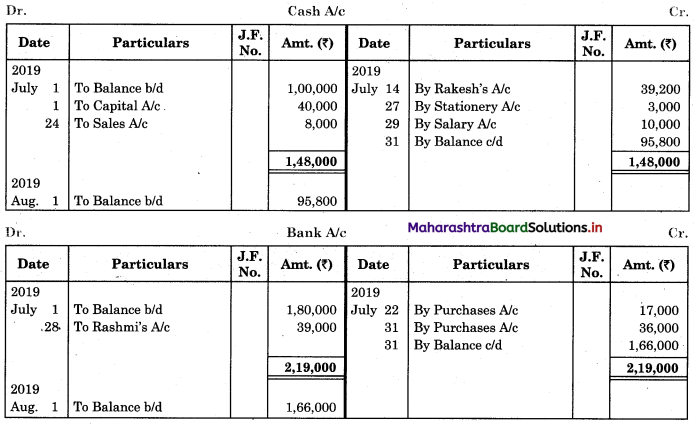
Question 2.
Prepare a two-column Cash Book from the following transaction for the year July 2018.
| July 2018 | Amt (₹) | |
| 01 | Cash in hand | 17,500 |
| 01 | Cash at Bank | 5,000 |
| 03 | Purchased goods for cash | 3,000 |
| 05 | Received cheque from Arun | 10,000 |
| 08 | Sold goods for cash | 8,000 |
| 10 | Arun’s cheque deposited into the bank | – |
| 12 | Purchased goods and paid by cheque | 20,000 |
| 15 | Paid establishment expenses through bank | 1,000 |
| 18 | Cash Sales | 7,000 |
| 20 | Deposited into bank | 10,000 |
| 24 | Paid General Expenses | 500 |
| 27 | Received commission by Cross cheque | 6,000 |
| 29 | Paid Rent | 2,000 |
| 30 | Withdrew cash for personal use | 1,200 |
| 31 | Wages paid | 6,000 |
Solution:
In the books of ____________
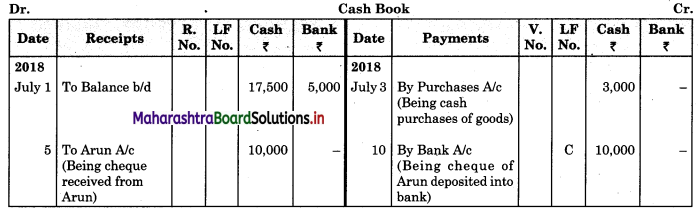
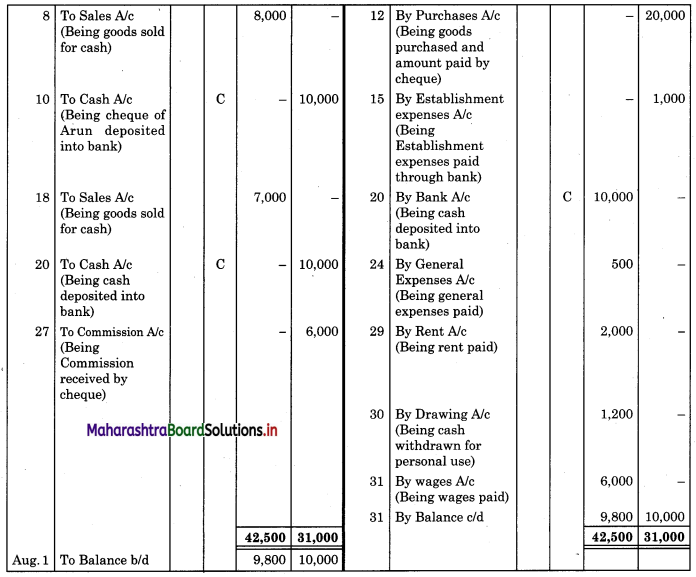
![]()
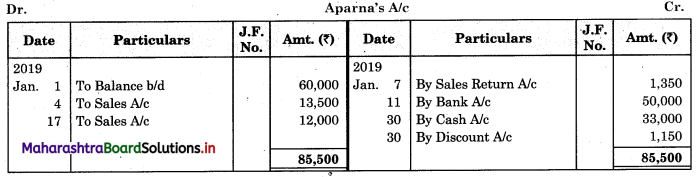
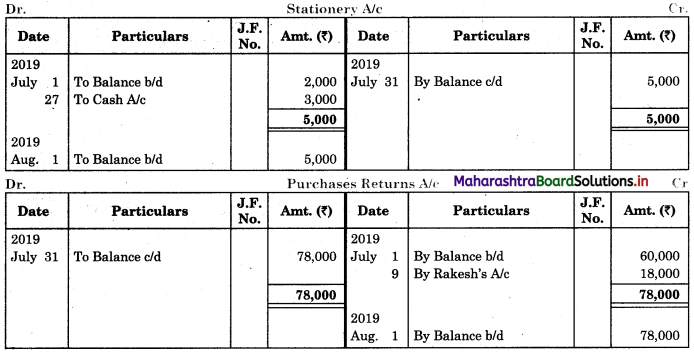
Question 3.
Record the following transactions in the Cash Book of M/s Kamal Traders. Balance for the month of July 2018: Cash in hand ₹ 2,000 and balance in Bank Current account ₹ 8,000.
| July 2018 | Amt (₹) | |
| 03 | Cash Sales | 2,300 |
| 05 | Purchased goods and amount paid by cheque | 6,000 |
| 08 | Cash Sales | 10,000 |
| 12 | Paid General Expenses | 700 |
| 15 | Sold goods and amount received by Cheque and deposited into Bank | 20,000 |
| 18 | Purchased Motor Car paid by Cheque | 15,000 |
| 20 | Cheque received from Mrunal deposited into Bank | 10,000 |
| 22 | Cash Sales | 7,000 |
| 25 | Mrunal’s cheque returned dishonoured | |
| 28 | Paid Rent | 2,000 |
| 29 | Paid Telephone expenses by cheque | 500 |
| 31 | Cash is withdrawn from Bank for personal use | 2,000 |
Prepare a two-column Cash Book.
Solution:
In the books of M/s Kamal Traders
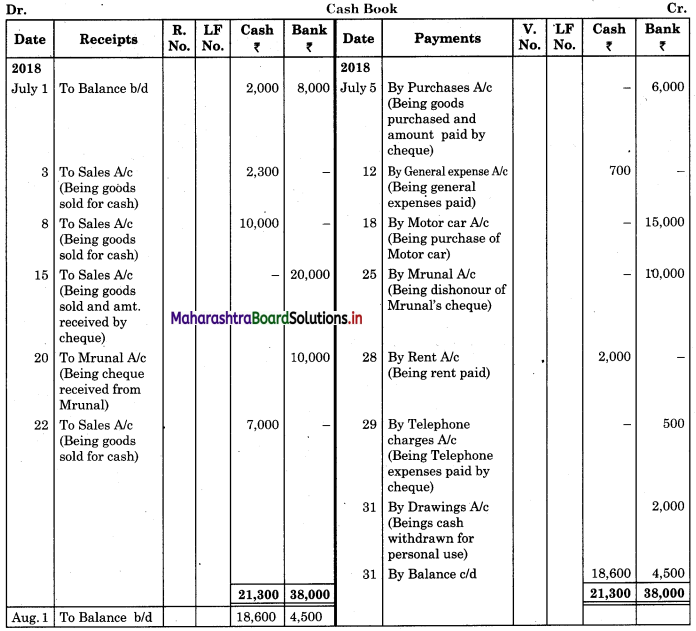
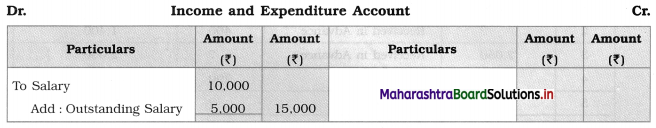
Question 4.
Prepare Analytical Petty Cash Book from the following transactions in the books of Swarali General Stores, Kolhapur. The imprest amount is ₹ 1,500 received from the main cashier.
| 2018 January | Amt (₹) | |
| 01 | Paid Cartage | 50 |
| 02 | Telephone Charges | 40 |
| 02 | Bus Fare | 20 |
| 03 | Postage | 30 |
| 04 | Refreshment to Employees | 80 |
| 06 | Courier Charges | 30 |
| 08 | Refreshment to Customers | 50 |
| 10 | Cartage | 35 |
| 15 | Taxi Fare to Manager | 70 |
| 18 | Purchased Stationery | 65 |
| 20 | Bus Fare | 10 |
| 22 | Xerox Charges | 30 |
| 25 | Internet Charges | 35 |
| 27 | Postage Stamps | 200 |
| 29 | Repair on Furniture | 105 |
| 30 | Cleaning Expenses | 115 |
| 31 | Miscellaneous Expenses | 100 |
Solution:
Analytical Petty Cash Book of Swarali General Stores
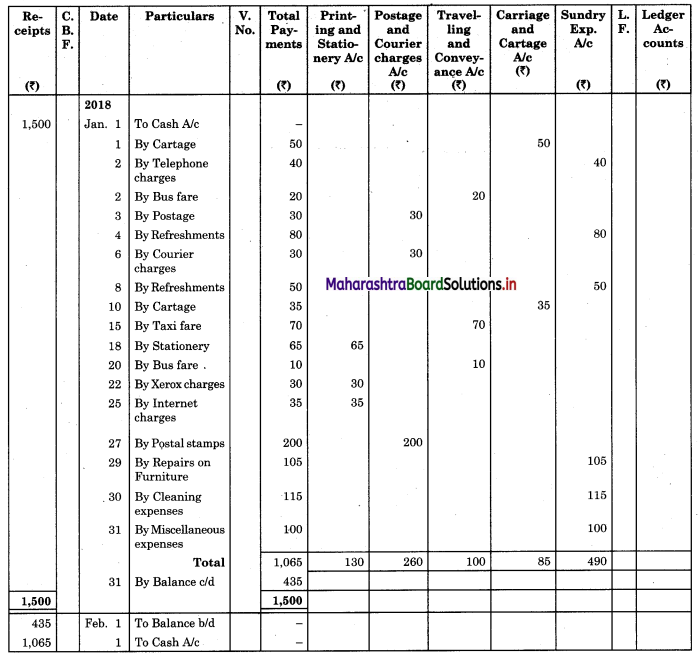
Question 5.
From the following information prepare Columnar Petty Cash Book kept on imprest system in the books of Manisha Books Stall, Beed.
| 2018 April | Amt (₹) | |
| 01 | Opening petty cash balance | 200 |
| 02 | Received a bearer cheque to make up the imprest amount | 1,200 |
| 03 | Gave a tip to peon | 40 |
| 04 | Purchased stationery | 150 |
| 05 | Paid Taxi Fare | 35 |
| 06 | Purchased Stamp pad | 140 |
| 07 | Paid Cartage | 40 |
| 08 | Paid Bus Fare | 30 |
| 11 | Paid to sweeper | 50 |
| 13 | Purchased a box of pencils | 40 |
| 14 | Paid Mobile charges | 35 |
| 15 | Gave it to Sohan on account | 250 |
| 19 | Paid for Refreshment to staff | 150 |
| 20 | Paid Railway Fare | 30 |
| 21 | Paid Carriage | 65 |
Solution:
Analytical Petty Cash Book of Manish a Books Stall, Beed
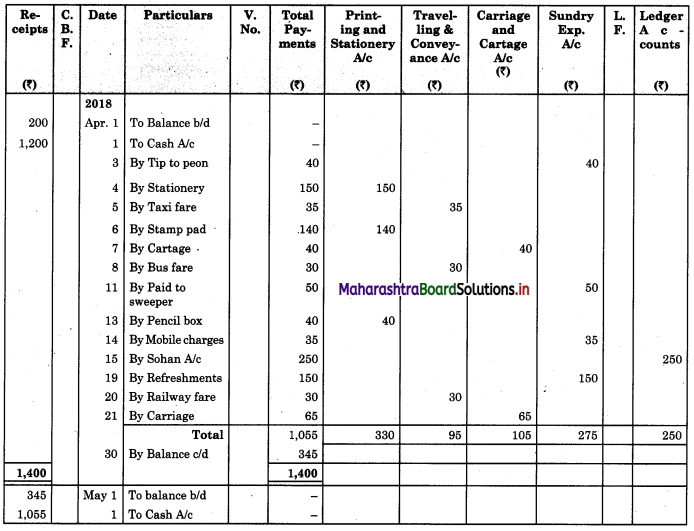
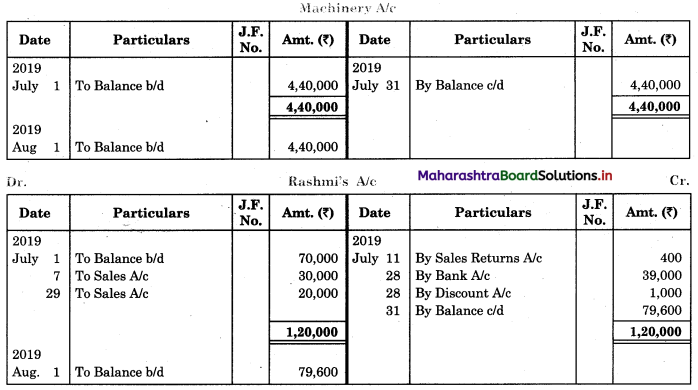
Question 6.
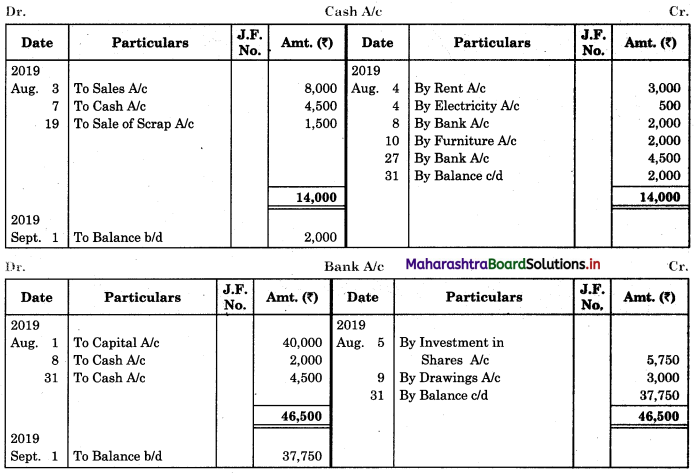
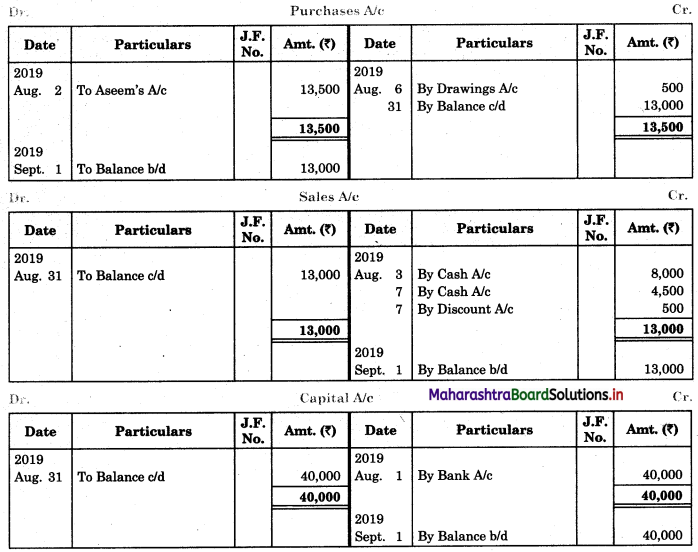
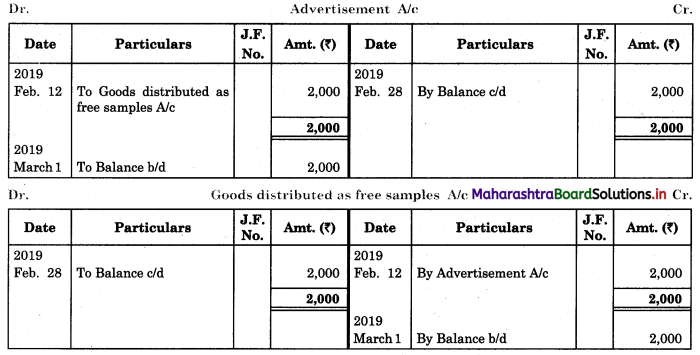
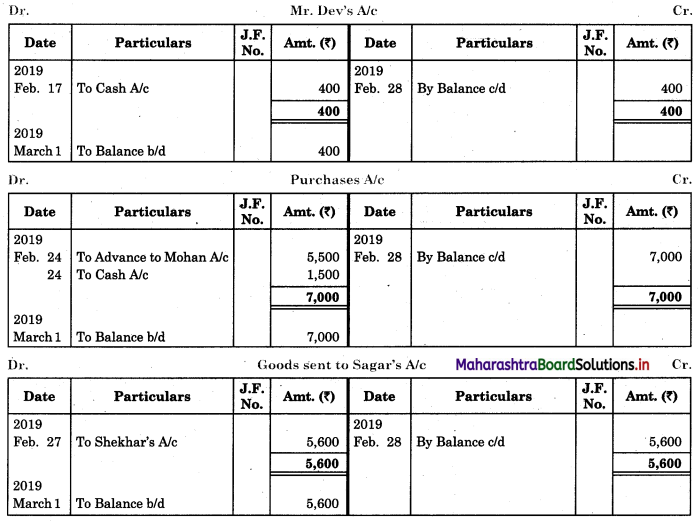
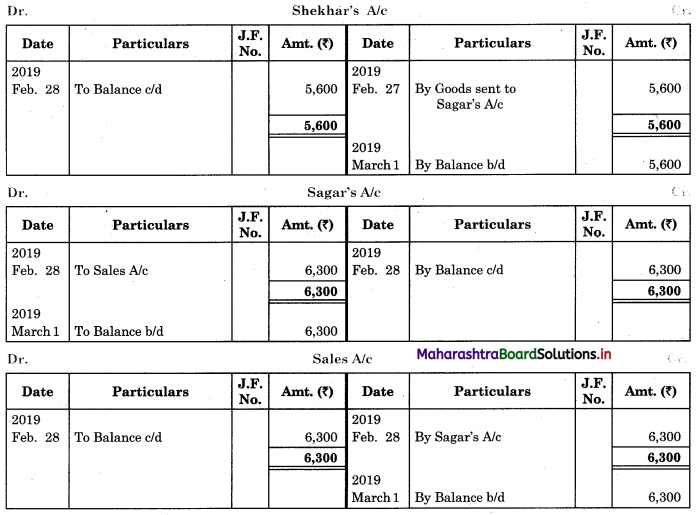
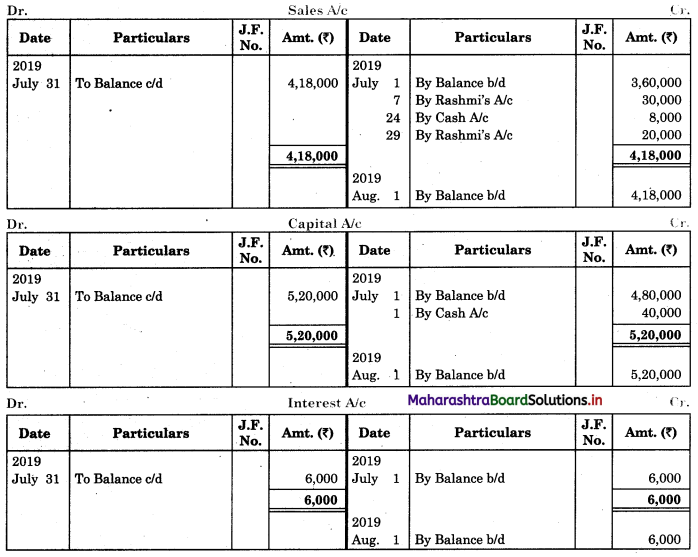
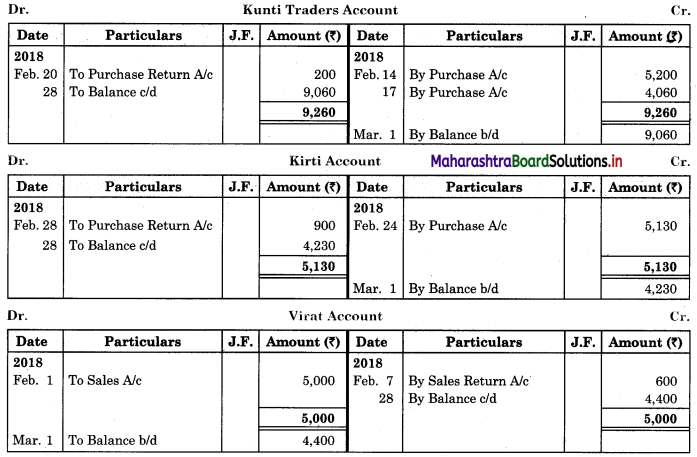
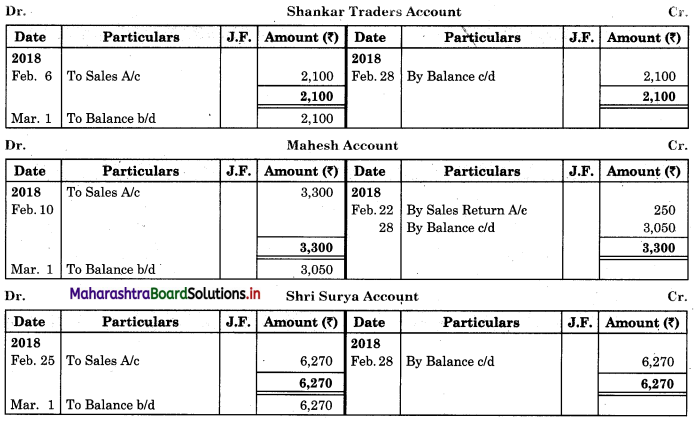
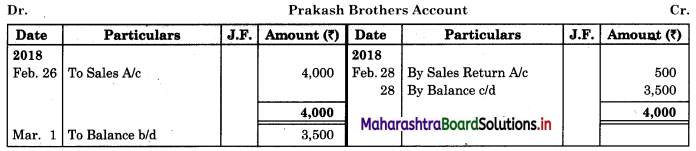
Prepare proper Subsidiary Books and post them to the ledger from the following transactions for the month of February 2018.
| 2018 February | Amt (₹) | |
| 01 | Goods sold to Virat | 5,000 |
| 04 | Purchased goods from Khushboo Traders | 2,480 |
| 06 | Sold goods to Shankar Traders | 2,100 |
| 07 | Virat returned goods | 600 |
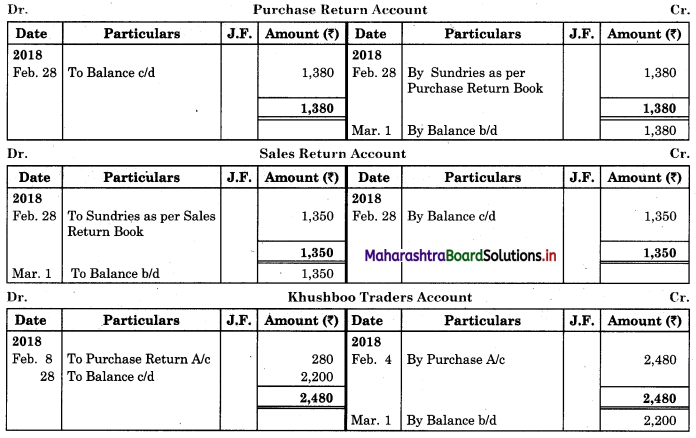
| 08 | Returns goods to Khusboo Traders | 280 |
| 10 | Sold goods to Mahesh | 3,300 |
| 14 | Purchased from Kunti Traders | 5,200 |
| 15 | Furniture purchased from Arun | 3,200 |
| 17 | Bought goods from Kunti Traders | 4,060 |
| 20 | Return goods to Kunti Traders | 200 |
| 22 | Return goods from Mahesh | 250 |
| 24 | Purchased goods from Kirti less 10% T.D. | 5,700 |
| 25 | Sold goods to Shri Surya goods less 5% T.D. | 6,600 |
| 26 | Sold goods to Prakash Brothers | 4,000 |
| 28 | Return goods to Kirti less 10% T.D. | 1,000 |
| 28 | Prakash Brothers returned goods | 500 |
Solution:
In the books of ____________
Purchase Book
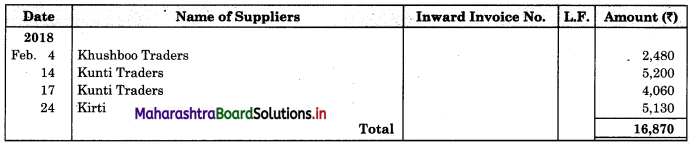
Sales Book
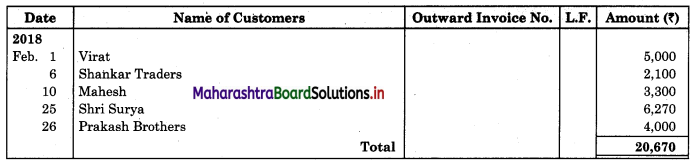
![]()
Purchase Return Book
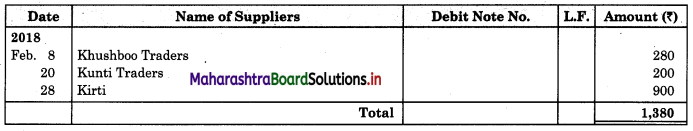
Sales Return Book
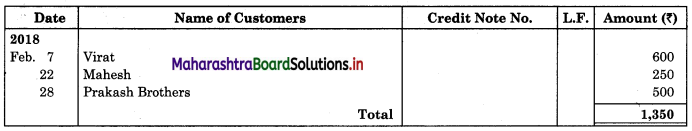
In the books of ____________
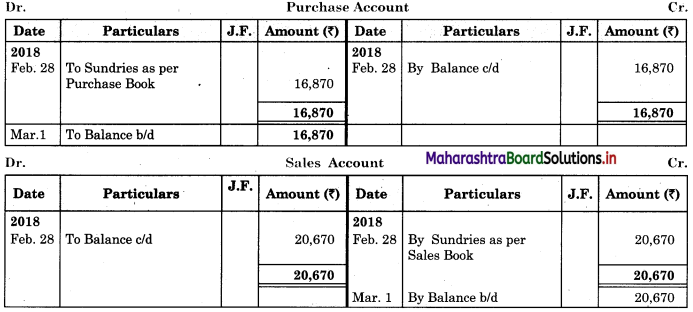
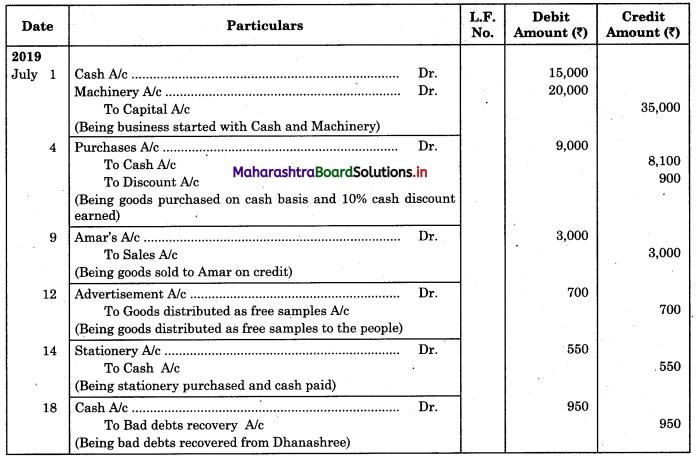
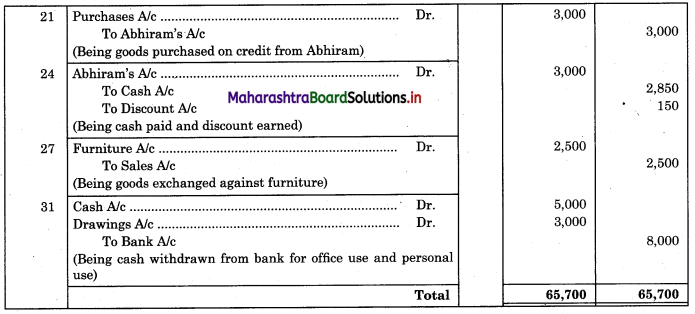
Question 7.
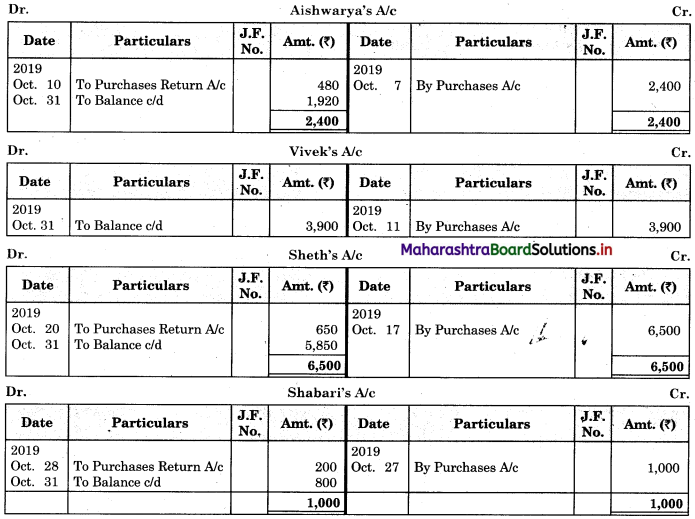
Enter the following transactions in the books of Vijay in Purchase Book, Sales Book, Purchase Returns Book and Sales Returns Book and Journal Proper for the month of August 2018.
2018 August
01 Purchased goods from Vikas Stores ₹ 18,000 at 5% Trade Discount
02 Sold goods of ₹ 9,000 to Prabhakar Traders
05 Veena sold goods of ₹ 16,000 to us at 5% Trade Discount as per our order dated 28th July, 2018.
08 Sent a Debit Note to Vikas Stores ₹ 1,600 (Gross) for goods returned.
10 Sold goods of ₹ 12,000 on credit to Shamal & Sons at 6% Trade Discount.
18 Received Credit Note from Veena ₹ 900 (Gross) for goods returned.
22 Sent Credit Note to Prabhakar Traders for ₹ 1,500 for goods returned. Received Dedit note from Shamal & Sons for ₹ 1,200 (Net) for goods returned.
23 Purchased goods of ₹ 16,600 from Priya Stores and paid for Carriage ₹ 150.
25 Purchased goods from Sadhana Stores ₹ 12,000 and sold the same to Aradhana Stores at a profit of 20% on cost.
28 Aradhana Stores returned goods of ₹ 2,400 as they were defective and the same were returned to Sadhana Stores.
31 Purchased Furniture for office use ₹ 30,000 from Art Furniture Works on credit.
Solution:
In the books of Vijay
Purchase Book
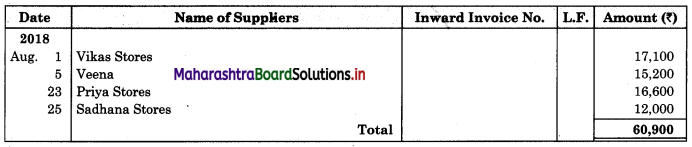
Sales Book
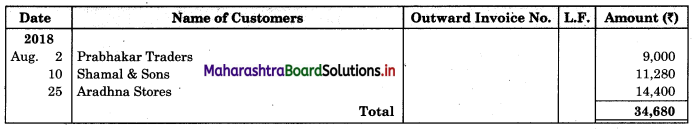
Purchase Return Book
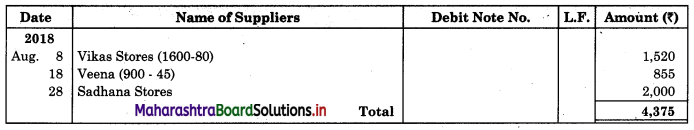
![]()
Sales Return Book
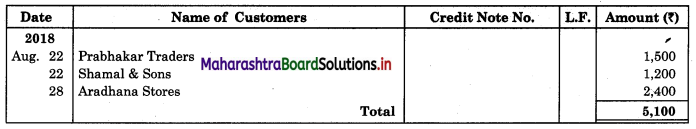
Journal Proper

Question 8.
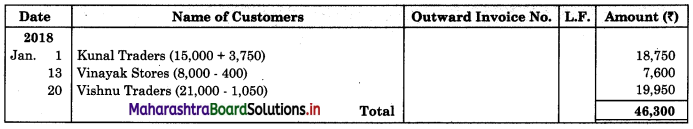
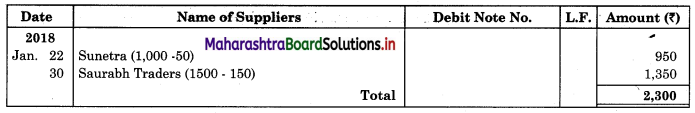
Mr. Akash gives you the following information and asks you to prepare Purchase Book, Sales Book, Purchase Returns Book and Sales Return Book for the month of January 2018.
2018 January
01 Purchased goods on credit from Dhanal Traders for ₹ 15,000 and sold the same to Kunal Traders at a profit of 25% on cost.
05 Placed an order with Sunetra for goods of ₹ 10,000 less 5% Trade discount.
08 Purchased goods of ₹ 20,000 at 10% Trade Discount from Saurabha Traders.
13 Sold goods to Vinayak Stores ₹ 8,000 at 5% Trade Discount.
15 Vinayak Stores returned goods to us ₹ 200.
18 Sunetra executed our order placed on 5th Jan. 2018.
20 Sold goods to Vishnu Traders ₹ 21,000 less 5% Trade Discount.
22 Returned goods to Sunetra ₹ 1,000 (Gross).
28 Kunal Traders returned goods to us ₹ 500
30 Returned goods to Sourabh Traders ₹ 1,500.
Solution:
In the books of Mr. Akash
Purchase Book
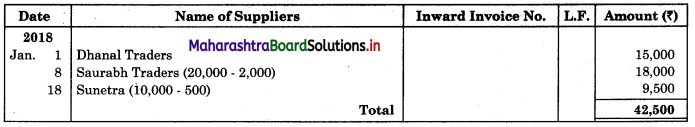
Sales Book
Purchase Return Book
![]()
Sales Return Book

Question 9.
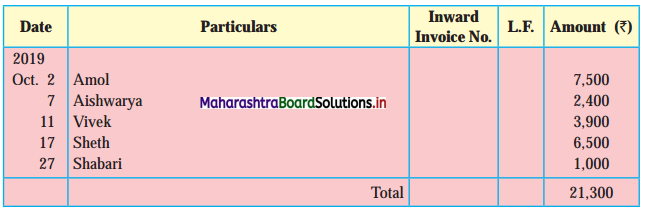
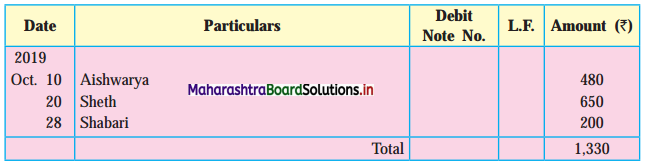
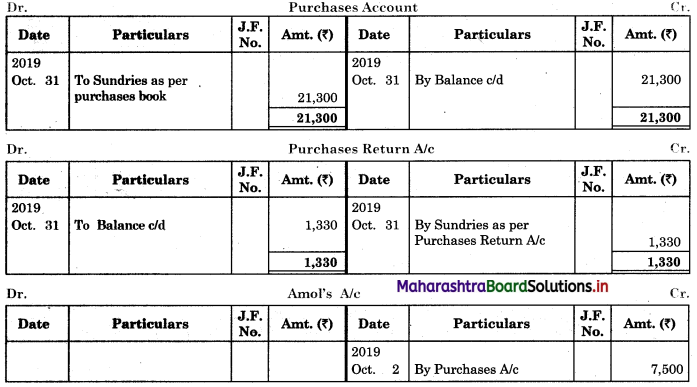
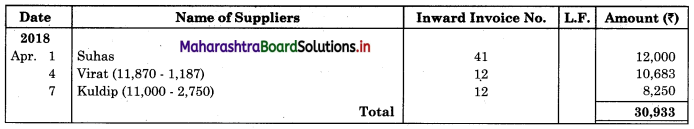
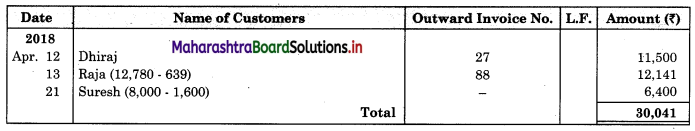
Enter the following transactions in the Subsidiary Book of Kamal Traders.
2018 April
01 Bought from Suhas goods of ₹ 12,000 as per his Invoice No. 41.
04 Purchased from Virat goods of ₹ 11,870 less 10% Trade Discount vide Bill No. 12.
07 Bought from Kuldip goods of ₹ 11,000 less 25% Trade Discount vide Bill No. 12.
08 Bought from M/s. Art Furniture Works, Furniture for ₹ 13,000 vide Invoice No. 84.
12 Sold to Dhiraj goods of ₹ 11,500 vide Sales Invoice No. 27
13 Sold to Raja goods of ₹ 12,780 less 5% Trade Discount, vide invoice No. 88
21 Sold to Suresh goods of ₹ 8,000 less 20% Trade Discount
23 Dhiraj returned goods of ₹ 500 vide our Credit note No. 14
26 Suresh returned goods of ₹ 150 (gross) vide our Credit Note No. 115
28 Returned to Suhas goods ₹ 1,200 vide our Debit Note No. 09
30 Returned to Virat goods of ₹ 1,300 (Gross) vide our Debit Note No. 10.
30 Returned to Kuldip goods of ₹ 1,100 (Gross) vide our Debit Note No. 11.
Solution:
In the books of Kamal Traders
Purchase Book
Sales Book
Purchase Return Book
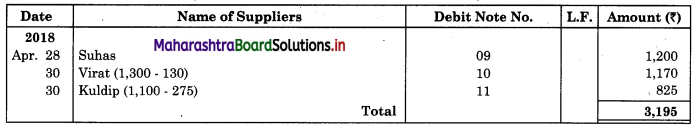
Sales Return Book

![]()
Journal Proper

Question 10.
Enter the following transactions in the Subsidiary Books of Navyug Traders:
2018 March
01 Sold to Bharat Patil goods ₹ 10,000 at 10% Trade discount.
04 Purchased from Naresh goods of ₹ 11,000 less 10% Trade discount.
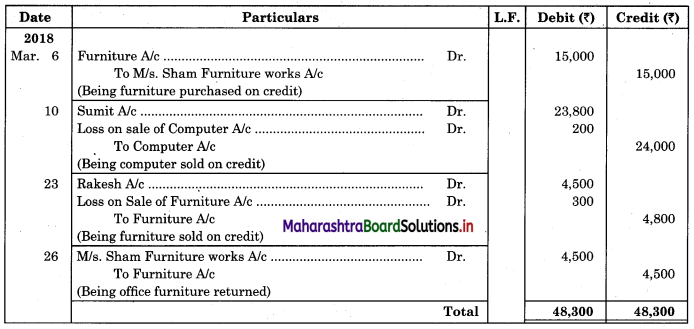
06 Purchased Furniture from M/s. Sham Furniture Works, of ₹ 15,000 for office use.
07 Bharat Patil returned 20% of the goods bought by him on 1st March above and we gave him fresh goods in exchange.
08 Sold to Sundar goods of ₹ 13,000 less 15% Trade Discount.
10 Sold to Sumit Computer for ₹ 23,800 with a book value of ₹ 24,000.
12 Placed an order with Sajan for goods of ₹ 12,000.
17 Purchased from Naresh goods of ₹ 14,000 and sold them to Kamesh for ₹ 16,000.
19 Kamesh returned us goods of ₹ 1,600 and immediately returned the same to Naresh.
23 Sold to Rakesh for ₹ 4,500 old Furniture with a book value of ₹ 4,800.
26 Returned to M/s. Sham Furniture Works, office Furniture of ₹ 4,500.
28 Sajan executed our order dated 12th March, 2018.
Solution:
In the books of Navyug Traders
Purchase Book
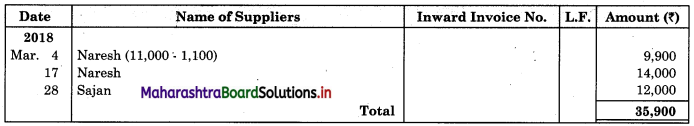
Sales Book
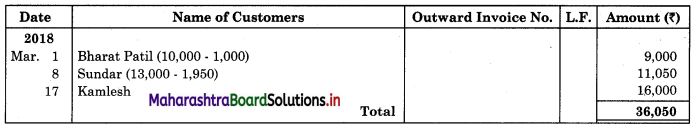
Purchase Return Book

Sales Return Book

![]()
Journal Proper
Class 11 Commerce BK Textbook Solutions Digest
- 11th Bk Chapter 1 Practical Problems
- 11th Bk Chapter 2 Practical Problems
- 11th Bk Chapter 3 Practical Problems
- 11th Bk Chapter 4 Practical Problems
- 11th Bk Chapter 5 Practical Problems
- 11th Bk Chapter 6 Practical Problems
- 11th Bk Chapter 7 Practical Problems
- 11th Bk Chapter 8 Practical Problems
- 11th Bk Chapter 9 Practical Problems
- 11th Bk Chapter 10 Practical Problems