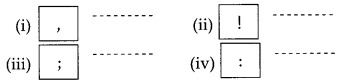Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 10 Marathi Solutions Kumarbharti Chapter 2 बोलतो मराठी… Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Class 10th Marathi Kumarbharti Chapter 2 बोलतो मराठी Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Std 10 Marathi Chapter 2 Question Answer
Marathi Kumarbharti Std 10 Digest Chapter 2 बोलतो मराठी… Textbook Questions and Answers
प्रश्न, पुढील उताश वाचा आणि दिलेल्या सूचनांनुसार ती करा:
कृती १: (आकलन)
प्रश्न 1.
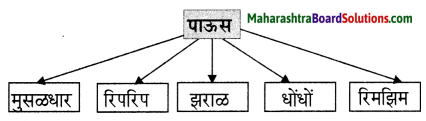
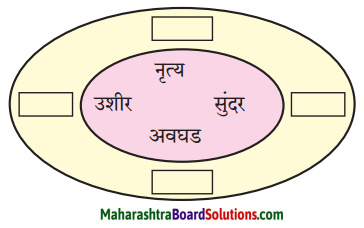
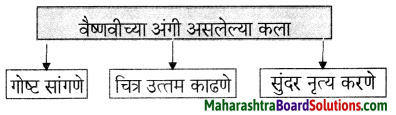
आकृत्या पूर्ण करा :
(i)

उत्तर :

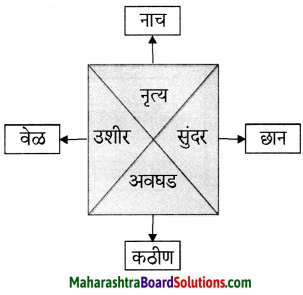
(ii)

उत्तर :

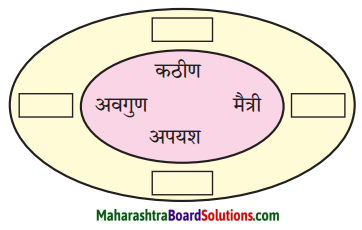
(iii)
उत्तर :

प्रश्न 2.
विनोद करणाऱ्या नव्याने पुढील वाक्याचा लावलेला अर्थ लिय :
तुम्हांला मी उत्तप्या बनवू का?
उत्तर :
मी तुमचे उत्तायामप्ये गपांतर वर का?
प्रश्न 3.
क्यों वो वाक्यातून विपरीत अर्य व्यक्त होतो. त्यामागील कारण तिहा.
उत्तर :
मराठी शब्दाचा व अर्थ बाजूला साशन त्या शब्दाला असलेला परभाषेतला अर्थ घेऊन वाक्ये तयार केली जातात, त्यामुळे विपरीत अर्थ व्यसा होतो.
उतारा क्र.१ : (पाठापुस्तक पृष्ठ क्र. २)
परवा वर्तमानपत्रात एक विनोद आता सेना.
बायको : “तुम्हांला, मी उत्तप्पा बनयू का?”
नवा : “नको. मी माणूसब टीक आहे. आली मोठी जादूगार !”
आता इथे विनोद निमांग झाला आहे. कारण ‘बनवणे हे क्रियापद निशे शोभणारे नाही. ते हल्ली हिंदी भाषेतून आपल्या स्वयंपाकपरा नको शार्क पुसतं आहे. मराठीत पोळया लारपे, भानी कोहगीत टाकणे, कडी करपे, पान संपणे, कुकर लायगे अशा वेगवेगळ्या क्रियांसाठी वेगवेगळे शब्दप्रयोग आहेत; पण हल्ती सगळे पदार्थ करत ‘बनवते’ जातात. मादीन ‘बनये’ म्हणजे ‘फायगे’ असा अर्थ खरं तर स्व आहे, त्यामुळे माणसायं माझ्ट आणि पुन्हा माकडाचा माणूस बनवणारा जादूगार, विनोद करणाऱ्या नवऱ्याला आठवला, तर आश्चर्य नाही.
मराठी रंगाचे शब्दप्रयोग ही आपल्या भाषेची श्रीमंती आहे. माठीत मारणे हे एक क्रियापद घेतले, ता ते किती वेगवेगळ्या प्रकारे वापरले जाते. हे लक्षात घेण्याजोगी आहे. जसे, गप्पा मारणे, उड्या मारगे, पापा मारणे, दिनकी मारणे, शिट्टी मारणे, पाकीट मारणे, वेवणावर ताव मारणे, (पोहताना) हातपाय मारणे. माझ्या मारपे इत्यादी, ‘मारणे’ भणजे मार देणे’ हा अचं यात कोठेही आलेला नाही. हीच तर भाषेची गंमत असते.
सन्दप्रयोगाप्रमाणे भावना हीदेखील भाषेनी खास शैली असते. ‘यस्ता खाणे ‘मचे वास्ता हा साक्षापदार्थ नाही. हे माहीत आहे ना? तसेच कंतम्नान घालणे’ समाचार युदाणाविषयीच्या यातायामप्ये असतो. कंठस्नान पाणगे महावे गयाखातून ‘अंघोळ थालगे’, असा शब्दशः अ. नाही, ‘घांदयाला यांदा सावणे’ (सहकार्य करणे) आणि ‘खांदा देणे’ (प्रेताला खांदा देणे) यांतला फरकही लक्षात घ्यायला कदा, एकाऐवजी दुसरे क्रियापद वापरले, तर अर्थाचा अर्थ होईल. अशी अनेक उदाहरणे देता येतील. त्यासाठी शब्दकोश वापरम्पाची सकप कापला की, ‘अक्कलवान’ म्हणजे शार; पण ‘अकलेचा कांदा’ म्हणजे ‘अतिशहाणा’ हे माहीत नसेल, तर कोण आपले खो कौतुक करतोय की फिरकी घेतोय, हेच आपल्याला कळणार नाही.
क्रियापद बापाताना त्यापूर्वी नामाला कोमता प्रत्यप लावायचा असतो, हे नीट माहीत नाले तरीदेखील अर्थाचा गोंधळ होतो. उदा., अंगाला लावणे आणि अंगावर घेणे, शिला हसगे (तिची नेष्टा करणे या अर्थी) आणि तिच्याशी हसणे (सहजपणे हमाणे) गांन प्रत्यय महत्त्वाचा आहे. हल्ली सार्वजनिक समारंभांमध्ये आगि वाहिन्यांवर प्रत्ययांची जागा अनेकदा कुकलेली असते. उदा., “तुझी मदत करणे’ याऐवजी ‘तुला मदत करणे’ हवे. “न्यांचे पन्यवाद’ पाऐवजी त्यांना पन्यवाद” असे म्हणायला हवे.
पायेमध्ये अनेक शब्द सतत पेत असतात, कारण तो नदीसारखी प्रणाली असते. आपणही संगणकासंबंधी अनेक नवे इंग्रजी शब्द मातत्याने आत्मसात केले आहेत. मराठीने आजवर संस्कृत, फारसी, अरबी, कन्नड़, इंग्रजी अशा अनेक भाषांमपले शब्द आपले मानले आहेत. ‘टेबल’ हा शब्द आता आपल्याला पाका वाटत नाही; पण गरज असताना इतर भाषांमपले शब्द आणि नेही जैं केली’ म्हणण्यातून काय नवीन अर्थ करतो? लाऐवजी ‘मी अभ्यास केला’ मम चोय नाही का?
नोंद : प्रस्तुत पुस्तकातील स पहिष्णा कृति-स्वाध्याय आहे. लामुळे या पाठातील स्वाध्यायात संपूर्ण वारा दिलेला आहे. यापुढे | मात्र प्रत्येक पाठातील स्वाध्यापांत संपूर्ण मारा न देता सान्याचे सुरवातीचे काही शब्द व शेवटचे काही शब्द दिलेले आहेत. विद्याभ्यांनी पाठयपुस्तकातून पूर्ण उतारा वाचावा.
मीक्षेत १३० ते १५० शब्दांचा उतारा दिला जाईल. इये विवाथ्यांच्या सोयीसाठी थोडा मोठा सारा दिलेला आहे. कारण त्यामुळे अधिक कृती देता येणे शक्य झाले आहे.

कृती २ : (आवलन)
प्रश्न 1.
उताऱ्याच्या आधाने पुढील चोवटी पूर्ण करा :

उत्तर :


प्रश्न 2.
हल्ली आढळून पेणाऱ्या आपल्या लोकांच्या दोन चुकीच्या भाषिक सक्यो सांगा.
उत्तर :
- वेगवेगळ्या कृतांसाठी वेगवेगळे शब्द वापरात असताना, स्या कोंसाठी केवळ एकच शब्द बोलला जातो.
- गरज नसताना अन्य भाषांतील शब्दांचा वापर केला जातो.
कृती ३ : (व्याकरण)
प्रश्न 1.
वेगवेगळ्या अर्थछटा व्यक्त करण्यासाठी चापाले नागारे तुम्हांला माहीत असलेले क्रियापद सोदाहरण लिहा. (फमा ४ अर्थछटा)
उत्तर :
- महापालिकेने एकान दिवसात तीनशे बेकायदेशीर यांपकामे पाडलि.
- छपरावर वाळत घातलेले पापड कानळ्यांनी खालि पाडले.
- चक्कीवरून दळण आणताना गोपू पीच पाहत पाहतच घरी आला.
- विरोधी पक्षाच्या उमेदवाराने मंत्र्याला प्रचंड बहुमानाने पाडले.
प्रश्न 2.
‘वाटणे’ हे क्रियापद नापल नेगवेगळ्या अर्थाची दोन वाक्ये तपार कता.
उत्तर :
- मी केलेल्या त्या नुकीनी मला साल वाटली. (बाटणे : भावना जापत्य)
- पास झाल्याबद्दल रश्मीचे पेढे वारले. (वाटणे : देण्याची कृती)

कृती ४ : (स्वयत/ अभिव्यक्ती)
प्रश्न 1.
भाषा सतत बदलत असले, याची कारणमीमांसा दया.
उत्तर :
एखाच्या परिस्तात राहणाव्या लोगांचा एक समाज बनतो. त्यांची पापा एकच असते. विख्यातले शब्द, वाश्य पढवण्याचे नियम हे ती भाषा बोलणाऱ्या सगळयांना ठाऊक असतात. मात्र, प्रत्येक पिढीमध्ये त्या त्या ठिकागाच्या भाषेमध्ये यूक्ष्मपणे बदला सेन जसजसा लोकांचा विकास होतो, तसतशी त्यांची भाषामुपा विकसित होत जाते. आधुनिक काळात अनेक गमार एकमेकांच्या अबळ नांदतात. एकमेकांत मिसळतात. या मेगवेगळ्या समाजांचा प्रभाव एकमेकांच्या भाषेवर पडतो. प्रांक भाषा अशी बदलत राहते. म्हणून कोणतीही भाषा कपीही स्थिर नलो. तीन सातवाने बदल होत राहतो. काळ बदलतो, तशी लोकांची जगण्याची रीन बदलते.
त्यामुळे भाषेतले शब्द बदलतात. जुने शब्द लोप पावतात, जवान शब्दांची भर पडते. अन्य भाषांमपीत शब्द-संकल्पना स्थानिक भाषेत सामावले जातात, स्थानिक भाषेतील शब्द-संकल्पना अन्य भाषांमध्ये शिरतात. अशा प्रकारे प्रत्येक भाषा प्रत्येक क्षणी बदलत असते.
प्रश्न 2.
स्वत:च्या भाषेवर प्रभुत्व मिळवणे म्हणजे स्वा:च्या भाषेचा सन्मान करणे होय’, हे विधान समजावून सांगा.
उत्तर :
स्वत:च्या भाषेवा सन्मान आपण कसा करणार? सर्वात प्रथम म्हणजे मी माझी स्वाःची भाषा उत्तम रितीने आत्यपान कौन. माझे सन विचार, भावना माझ्या भाषेत कसोशीने व्यक्त करम्पाना प्रयत्न कनीन, माझी भाषा उत्तम येण्यासाठी मी माझ्या भाषेतील वर्तमानपत्रे, नियतकालिके पांचे नियमित वाचन करीन. माझ्या पायेतीत अनमोलन साहित्याचा आस्वाद घेत रडीन, भाषा चांगल्या रितीने आत्मपान करण्यासाठी शब्दकोश, व्युत्पत्ती कोश यांसारख्या पोशांचा वेळोवेळी मनापासून उपयोग करीत. यामुळे माझे माझ्या भाषेवरील प्रमुख वाडेल. अशा प्रकारे स्वत:च्या भाषेवरीत प्रभुत्व बाहरणे म्हणजे त्या भाषेचा सन्मान करणे होय.
Marathi Kumarbharti Class 10 Textbook Solutions Chapter 2 बोलतो मराठी… Additional Important Questions and Answers
प्रश्न. पुढील उतारा वाचा आणि दिलेल्या मूचनांनुसार कृती करा :
कृती १ : (आकलन)
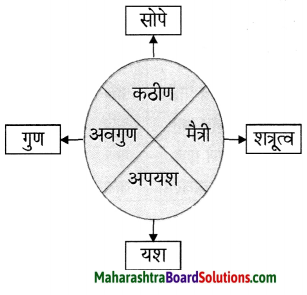
प्रश्न 1.
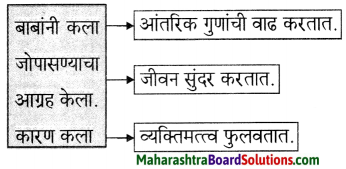
आकृत्या पूर्ण करा:
उत्तर :

प्रश्न 2.
उत्तर :

प्रश्न 3.
पाठाच्या आधारे पुढील चौकी पूर्ण करा :

उत्तर :

कृती २ : (आकलन)
प्रश्न 1.
कंसातील योग्य शब्द योजून रिकाम्या चौकटी भरा :
(कलेवर, सूतकताई, पुण्यात, मोरांबा)

उत्तर :

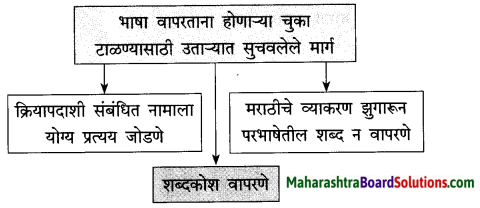
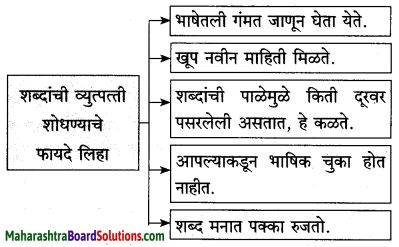
प्रश्न 2.
लेखिकांच्या मते, भाषेवरील प्रेमासाठी पुढील कृती केल्या पाहिजेत :
(i) …….. (ii) ……… (iii) ………. (iv) ……….
उत्तर :
(i) भाषेतली शक्तिस्थळे जाणून घेतली पाहिजेत.
(ii) भाषेचा योग्य सन्मान राखायला हवा.
(iii) भाषेशी जिव्हाळ्याचे नाते राखायला हवे.
(iv) भाषेचे ज्ञानही मिळवायला हवे.
कृती ३ : (व्याकरण)
प्रश्न 1.
‘सम + आरंभ = समारंभ’ या प्रकारातील संधीची आणखी दोन उदाहरणे लिहा.
उत्तर :
(i) अन् + आदर = अनादर
(ii) सत् + आचार = सदाचार
प्रश्न 2.
‘शब्दरूपे’ या प्रकारच्या समासाची दोन उदाहरणे विग्रहासह लिहा.
उत्तर :
(i) शालागृह : शाळेचे गृह, षष्ठी तत्पुरुष.
(ii) विद्यार्थिदशा : विदयार्थ्याची दशा, षष्ठी तत्पुरुष.

कृती ४ : (स्वमत / अभिव्यक्ती)
प्रश्न 1.
लेखिकांनी मराठी भाषेचा केलेला सन्मान तुमच्या शब्दांत लिहा.
उत्तर :
लेखिकांनी मराठी भाषेला श्रीमंत म्हटले आहे. होय, माझी मराठी श्रीमंत आहे. मला या गोष्टीचा प्रचंड अभिमान वाटतो.
माझ्या भाषेकडे बारकाईने पाहा. विविध ढंगांचे शब्दप्रयोग ही माझ्या भाषेची खासियत आहे. अनेकदा एकच शब्द अनेकानेक अर्थछटा प्रकट करतो. ‘चालणे’ हे साधे क्रियापद बघा. प्रत्यक्ष पायांनी चालणे या अर्थाशिवाय आणखी अनेक अर्थछटा ‘चालणे’ या क्रियापदादवारे व्यक्त करता येतात. उदाहरणार्थ, लुट्लट्र चालणे, लबाडी चालणे, नोटा-नाणी चालणे, एखादे तत्त्व चालणे, एखादया रितीनुसार चालणे, घड्याळ चालणे वगैरे वगैरे. अशी किती वाक्ये सांगू? वाक्प्रचार हा माझ्या भाषेचा खास गोडवा आहे. माझ्या भाषेने अनेक भाषांमधील शब्द स्वत:च्या हृदयात सामावून घेतले आहेत. म्हणून माझी भाषा अधिकाधिक श्रीमंत होत चालली आहे.
प्रश्न 2.
मराठी भाषेबद्दलच्या तुमच्या भावना स्पष्ट करा.
उत्तर :
आपण सर्वजण सतत एकमेकांना काहीतरी सांगण्याचा प्रयत्न करतो. म्हणजे आपले मनच आपण इतरांसमोर प्रकट करीत असतो. याचा अर्थ, कोणतीही भाषा म्हणजे ती बोलणाऱ्या माणसांचे मन असते.
आपले समृद्ध जीवन आपल्या भाषेत व्यक्त होते तेव्हा ती भाषा समृद्ध होते. पण हे असे केव्हा होईल? तर जेव्हा माझे मन मी पूर्णांशाने, अगदी बारीक-सारीक तपशिलांसह माझ्या भाषेत व्यक्त करू शकेन तेव्हाच. अशा प्रकारे मन व्यक्त करण्याचे सामर्थ्य माझ्या भाषेत नक्कीच आहे. माझ्या भाषेत खास मराठी वळणाचे शब्दप्रयोग आहेत. वाक्प्रचार ही तर माझ्या मराठीची खासियत आहे. अनेकदा एकच शब्द अनेक अर्थछटा सहज प्रकट करू शकतो. माझ्या भाषेत अनेक भाषांमधील शब्द सामावले गेले आहेत. त्यामुळे मी माझे सर्व भाव खुलवून मांडू शकतो. सूक्ष्मपणे मांडू शकतो. इतकी श्रीमंत भाषा ही माझी भाषा आहे, हे माझे भाग्यच आहे.
प्रश्न 3.
‘तुम्ही शहाणे आहात,’ या वाक्यातील ‘शहाणे’ या शब्दाच्या अर्थछटा लिहा.
उत्तर :
‘तुम्ही शहाणे आहात,’ असे अनेकदा म्हटले जाते. त्या वेळी ऐकणाऱ्याच्या समजूतदारपणावर, त्याच्या विवेकावर बोलणाऱ्याचा विश्वास असतो. आई आपल्या मुलांना हे उद्गार ऐकवते, तेव्हा तिच्या मनात आपल्या मुलांबद्दल अशीच खात्री असते.
मात्र प्रत्येक वेळेला ‘तुम्ही शहाणे आहात,’ या वाक्याचा असा सरळ, प्रांजळ व निष्कपट अर्थ असतोच, असे नाही. काही व्यक्ती मुळातच लबाड असतात. चूक लपवण्यासाठी बुद्धीचा दुरुपयोग करतात. कधी कधी तर काही माणसांना खरोखरच साधी, सोपी गोष्टही कळत नाही. कितीही समजावून सांगितले, तरी त्यांना ते समजतच नाही. मग त्यांना ‘तुम्ही शहाणे आहात,’ असे ऐकवावे लागते. येथे ‘शहाणे’ हा शब्द वापरलेला असला तरी आपण मनातल्या मनात ‘तुम्ही मूर्ख आहात,’ असेच म्हणत असतो.

प्रश्न 4.
गरज नसताना इतर भाषांमधील शब्द वापरून बोलू नये,’ या लेखिकेच्या मताबाबत तुमचे मत सोदाहरण लिहा.
उत्तर :
परभाषेतून आपल्या भाषेत अनेक नवीन शब्द आले आहेत, ते केव्हाच मराठी झाले आहेत. ते मराठी शब्द नाहीत, अशी कोणाला शंकाही येणार नाही.
मात्र काही वेळा परभाषेतील शब्द अकारण वापरले जातात. आणि तेसुद्धा आपल्या भाषेत त्यासाठी अत्यंत सार्थ, समर्पक शब्द असताना! अलीकडे “ती पिवळीवाली दया,” “तो पांढरावाला पट्टा दाखवा’ अशी वाक्ये सर्रास ऐकू येतात. वास्तविक पाहता ‘पिवळी बॅग’ आणि ‘पिवळीवाली बॅग’ यांत कोणता फरक आहे? ‘पिवळी बॅग’ या शब्दप्रयोगातून आधीपासूनच योग्य अर्थ व्यक्त होत असताना ‘पिवळीवाली’ हा नवीन शब्दप्रयोग का करावा? मराठीत आपण असे बोलतच नाही. मराठीत ‘वाला’ हा प्रत्यय फक्त नामाला जोडला जातो. “पिवळी’ हे विशेषण आहे. मराठीत विशेषणाला किंवा सर्वनामाला ‘वाला’ हा प्रत्यय जोडण्याची प्रथाच नाही. शिवाय त्या नवीन शब्दप्रयोगाने अर्थामध्ये कोणतीही भर पडत नाही. म्हणून गरज नसताना परभाषेतील शब्द वापरून बोलू नये, हे लेखिकांचे मत योग्यच आहे.
व्याकरण व भाषाभ्यास
कृतिपत्रिकेतील प्रश्न ४ (अ) आणि (आ) यांसाठी…
अ. व्याकरण घटकांवर आधारित कृती:
समास
समासात कमीत कमी दोन शब्द असतात. हे दोन शब्द एकत्र करून जो जोडशब्द तयार होतो, त्यास सामासिक शब्द म्हणतात. या सामासिक शब्दाची फोड करून दाखवणाऱ्या पद्धतीला विग्रह म्हणतात.
उदा., शब्द + शब्द = सामासिक शब्द – विग्रह
(१) प्रति + दिन = प्रतिदिन – प्रत्येक दिवशी
(२) विदया + आलय = विदयालय – विदयेचे आलय (घर) .
(३) राम + लक्ष्मण = रामलक्ष्मण – राम आणि लक्ष्मण
(४) नील + कंठ = नीलकंठ – निळा आहे ज्याचा कंठ तो (शंकर)
समासाचे प्रकार :
1. समासातील शब्दांना ‘पद’ म्हणतात.
पहिला शब्द → पहिले पद.
दुसरा शब्द → दुसरे पद. समासातील कोणते पद महत्त्वाचे किंवा प्रधान आणि कमी महत्त्वाचे किंवा गौण आहे, यावरून समासाचे चार प्रकार पडतात. [प्रधान पद +/गौण पद -]
समासाचे चार मुख्य प्रकार होतात :
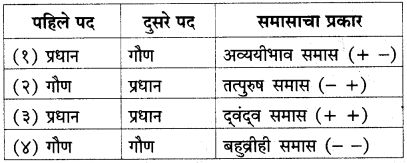
[या इयत्तेत आपल्याला अव्ययीभाव, तत्पुरुष (विभक्ती व द्विगू) आणि द्वंद्व हे समास शिकायचे आहेत.]
(१) अव्ययीभाव समास :
- ज्या समासातील पहिले पद प्रधान असते व सामासिक – शब्द क्रियाविशेषण अव्ययाचे कार्य करतो, त्यास अव्ययीभाव समास म्हणतात.
उदा., आजन्म, दररोज, बिनचूक, यथाशक्ती, बेशिस्त, दारोदार, प्रतिदिन इत्यादी.
(२) तत्पुरुष समास :
(१) विभक्ती तत्पुरुष :
ज्या समासातील दुसरे पद प्रधान असून, ज्या सामासिक शब्दांमधील विभक्ती प्रत्यय गाळलेले असतात, त्यास विभक्ती तत्पुरुष समास म्हणतात.
उदा., तोंडपाठ (तोंडाने पाठ), क्रीडांगण (क्रीडेसाठी अंगण), विदयालय (विदयेचे आलय), घरकाम (घरातील काम) इत्यादी.
(२) द्विगू समास :
ज्या समासातील दुसरे पद प्रधान असून, पहिले पद संख्याविशेषण असते, त्यास द्विगू समास म्हणतात. उदा., त्रिभुवन, चौकोन, पंचपाळे, दशदिशा, नवरात्र इत्यादी.
(३) वंद्व समास :
ज्या समासातील दोन्ही पदे प्रधान असतात, त्यास द्वंद्व समास म्हणतात.
उदा., आईवडील, खरेखोटे, केरकचरा इत्यादी.
द्वंद्व समासाचे प्रकार :
(१) इतरेतर द्वंद्व : ज्या सामासिक शब्दाचा विग्रह करताना ‘आणि’, ‘व’ या उभयान्वयी अव्ययांचा उपयोग करतात, त्यास इतरेतर द्वंद्व समास म्हणतात. उदा., आईवडील (आई आणि वडील); रामलक्ष्मण (राम आणि लक्ष्मण)
(२) वैकल्पिक वंद्व : ज्या सामासिक शब्दाचा विग्रह करताना ‘किंवा’, ‘अथवा’ या उभयान्वयी अव्ययांचा वापर केला जातो, त्यास वैकल्पिक वंद्व समास म्हणतात. (यात बहुधा परस्परविरोधी पदे असतात.) उदा., खरेखोटे (खरे किंवा खोटे), सुखदुःख (सुख किंवा दुःख) इत्यादी.
(३) समाहार वंद्व : ज्या सामासिक शब्दात अनेक गोष्टींचा समावेश असतो व ज्याचा विग्रह करताना ‘वगैरे, इतर’ या शब्दांचा वापर केला जातो, त्यास समाहार दवंदव समास म्हणतात. उदा., गप्पागोष्टी (गप्पा, गोष्टी वगैरे), मीठभाकर (मीठ, भाकर व इतर पदार्थ) इत्यादी.

१. समास :
पुढील सामासिक शब्दांचा विग्रह करा :
प्रश्न 1.
आजन्म
उत्तर:
आजन्म – जन्मापासून
प्रश्न 2.
मोरपीस
उत्तर :
मोरपीस – मोराचे पीस
प्रश्न 3.
त्रिभुवन
उत्तर :
त्रिभुवन – तीन भुवनांचा समूह
प्रश्न 4.
खरेखोटे
उत्तर :
खरेखोटे – खरे किंवा खोटे
प्रश्न 5.
विटीदांडू .
उत्तर :
विटीदांडू – विटी आणि दांडू
प्रश्न 6.
गुरेवासरे.
उत्तर :
गुरेवासरे – गुरे, वासरे वगैरे.

२. शब्दसिद्धी :
प्रश्न 1.
‘अति’ हा उपसर्ग लागलेले चार उपसर्गघटित शब्द लिहा.
उत्तर :
- अतिशहाणा
- अतिसुंदर
- अतिआनंद (अत्यानंद)
- अतिआवश्यक (अत्यावश्यक).
प्रश्न 2.
‘वान’ हा प्रत्यय लागलेले चार प्रत्ययघटित शब्द लिहा.
उत्तर :
- गुणवान
- धनवान
- गाडीवान
- अक्कलवान.
प्रश्न 3.
सामान्यरूप :
पुढील शब्दांतील सामान्यरूपे ओळखा :
(i) भाषेची
उत्तर :
भाषे
(ii) घरात (मार्च ‘१९)
उत्तर :
घरा
(iii) विनोदाने
उत्तर :
विनोदा
(iv) महोत्सवाला
उत्तर :
महोत्सवा
(v) जिभेला (मार्च ‘१९).
उत्तर :
जिभे.

प्रश्न 4.
वाक्प्रचार :
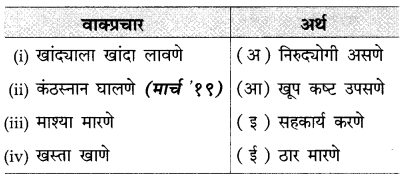
वाक्प्रचार व अर्थ यांच्या जोड्या लावा :
उत्तर :
(i) खांदयाला खांदा लावणे – सहकार्य करणे.
(ii) कंठस्नान घालणे – ठार मारणे.
(iii) माश्या मारणे – निरुदयोगी असणे.
(iv) खस्ता खाणे – खूप कष्ट उपसणे.
आ. भाषिक घटकांवर आधारित कृती
१. शब्दसंपत्ती :
प्रश्न 1.
समानार्थी शब्द लिहा :
(i) कंठ
उत्तर :
कंठ = गळा
(ii) मयूर
उत्तर :
मयूर = मोर
(iii) नदी
उत्तर :
नदी = सरिता
(iv) पाऊस.
उत्तर :
पाऊस = पर्जन्य.
प्रश्न 2.
उत्तर :

प्रश्न 3.
पुढे दिलेल्या अनेकवचनी नामांचे एकवचनी रूप लिहून त्यांचा वापर करून प्रत्येकी एक वाक्य तयार करा :
(i) रस्ते
उत्तर :
रस्ते – रस्ता.
वाक्य : डोंगरावरचा रस्ता वळणदार आहे.
(ii) वेळा
उत्तर :
वेळा – वेळ.
वाक्य : परीक्षेची वेळ जवळ आली.
(iii) भिंती
उत्तर :
भिंती – भिंत.
वाक्य : रंग लावलेली भिंत छान दिसते.
(iv) विहिरी
उत्तर :
विहिरी – विहीर.
वाक्य : आमची विहीर खूप खोल आहे.
(v) घड्याळे
उत्तर :
घड्याळे – घड्याळ.
वाक्य : बाबांनी मला नवीन घड्याळ आणले.
(vi) माणसे.
उत्तर :
माणसे – माणूस.
वाक्य : पावसात एकही माणूस घराबाहेर पडला नाही.

प्रश्न 4.
गटात न बसणारा शब्द ओळखून चौकट पूर्ण करा :
(i) ऐट, डौल, रूबाब, चैन.
उत्तर :
चैन
(ii) कपाळ, हस्त, ललाट, भाल.
उत्तर :
हस्त
(iii) विनोद, नवल, आश्चर्य, विस्मय.
उत्तर :
विनोद
(iv) संपत्ती, संपदा, कांता, दौलत.
उत्तर :
कांता
(v) प्रख्यात, प्रज्ञा, नामांकित, प्रसिद्ध.
उत्तर :
प्रज्ञा
प्रश्न 5.
पुढील शब्दसमूहाबद्दल एक शब्द लिहा :
(i) पसरवलेली खोटी बातमी
उत्तर :
अफवा
(ii) ज्याला मरण नाही असा
उत्तर :
अमर
(iii) समाजाची सेवा करणारा
उत्तर :
समाजसेवक
(iv) संपादन करणारा
उत्तर :
संपादक
प्रश्न 6.
पुढील शब्दांतील अक्षरांपासून चार अर्थपूर्ण शब्द लिहा :
उत्तर :

प्रश्न 7.
लेखननियम :
अचूक शब्द ओळखा :
(i) भाशातज्ञ/भाषातज्ञ/भाषातज्ज्ञ/भाशातज्ज्ञ.
उत्तर :
भाषातज्ज्ञ
(ii) साहित्यिक/साहीत्यिक/साहित्यीक/साहीत्यीक. उत्तरे :
उत्तर :
साहित्यिक.

प्रश्न 8.
विरामचिन्हे :
पुढील विरामचिन्हे ओळखा :
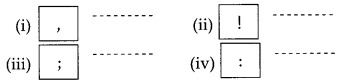
उत्तर :

प्रश्न 9.
पारिभाषिक शब्द :
पुढील इंग्रजी पारिभाषिक शब्दांना मराठी प्रतिशब्द लिहा :
(i) Event
उत्तर :
घटना
(ii) Drama
उत्तर :
नाटक
(iii) Yard
उत्तर :
आवार
(iv) Mobile
उत्तर :
भ्रमणध्वनी

प्रश्न 10.
अकारविल्हे/भाषिक खेळ :
पुढील शब्द अकारविल्हेनुसार लिहा :
(i) भाषा → मराठी → क्रियापद → भाव.
उत्तर :
क्रियापद → भाव → भाषा → मराठी.
(ii) गणित → भूगोल → भाषा → इतिहास (मार्च ‘१९).
उत्तर :
इतिहास → गणित → भाषा → भूगोल.
बोलतो मराठी… शब्दार्थ
- व्युत्पत्ती – शब्दाचे मूळ शोधण्याचे शास्त्र.
बोलतो मराठी… वाक्प्रचार व त्यांचे अर्थ
- पाकीट मारणे : पैशाचे पाकीट शिताफीने चोरणे.
- ताव मारणे : भरपूर खाणे.
- माश्या मारणे : रिकामटेकडेपणाने वेळ घालवणे.
- खस्ता खाणे : खूप कष्ट करणे.
- कंठस्नान घालणे : गळा कापून ठार मारणे.
- खांदयाला खांदा लावणे : सहकार्य करणे.
- खांदा देणे : प्रेत वाहून नेण्यात सहभागी होणे.
- अकलेचा कांदा असणे : अतिशहाणा असणे.
- एखाद्याला हसणे : एखादयाची थट्टा करण्याच्या हेतूने हसणे.
Marathi Kumarbharti Std 10 Digest Pdf भाग-१
![]()
![]()


![]()


![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()