Std 9 Hindi Chapter 9 Vardan Mangunga Nahi Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 9 Hindi Solutions Lokbharti Chapter 9 वरदान माँगूँगा नही Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Hindi Lokbharti 9th Digest Chapter 9 वरदान माँगूँगा नही Questions And Answers
Hindi Lokbharti 9th Std Digest Chapter 9 वरदान माँगूँगा नही Textbook Questions and Answers
संभाषणीय
प्रश्न 1.
गणतंत्र-दिवस’ के अवसर पर जनतांत्रिक शासन प्रणाली पर अपना मंतव्य प्रकट कीजिए।
उत्तर:
मान्यवर अतिथिगण, प्रधानाचार्य, अध्यापक, अध्यापिकाएँ, और मेरे सभी सहपाठियों को मेरा नमस्कार। गणतंत्र दिवस पर अपने विचार व्यक्त करने का एक महान अवसर देने के लिए मैं सर्वप्रथम आपको धन्यवाद देता हूँ।
आज गणतंत्र दिवस को मनाने के लिए हम यहाँ एकत्रित हए हैं। हम सभी के लिए यह एक महान और शुभ अवसर है। हमें एक-दूसरे को बधाई देनी चाहिए और अपने राष्ट्र के विकास और समृद्धि के लिए भगवान से दुआ करनी चाहिए। हम लोग 1950 से ही हर वर्ष 25 जनवरी को भारत का गणतंत्र दिवस मनाते आ रहे हैं। इसी दिन २६ जनवरी 1950 को भारत का संविधान लागू हुआ था।
भारत एक लोकतांत्रिक देश है। अत: यहाँ पर शासन करने के लिए कोई राजा या रानी नहीं है। यहाँ की जनता ही यहाँ की शासक है। इस देश में रहने वाले हर एक नागरिक के पास बराबर का अधिकार है । बिना हमारे वोट के कोई भी मुख्यमंत्री या प्रधानमंत्री नहीं बन सकता है। देश को सही दिशा में नेतृत्व प्रदान करने के लिए हमें अपना सबसे अच्छा प्रधानमंत्री या कोई भी दूसरा नेता चुनने का हक है।
लोकतंत्र अर्थात् जन-प्रतिनिधि एक ऐसा तंत्र है, जिसमें जनकल्याण की भावना से सभी कार्य संपन्न किए जाते हैं। जनकल्याण की भावना एक-एक करके इस शासन तंत्र के द्वारा हमारे सामने कार्य रूप में दिखाई पड़ने लगती है। लोकतंत्र का महत्त्व इस दृष्टि से भी होता है कि लोकतंत्र में सबकी भावनाओं का सम्मान होता है और सबको अपनी भावनाओं को स्वतंत्र रूप से प्रकट करने का पूरा अवसर मिलता है। इसी प्रकार किसी भी तानाशाही का लोकतंत्र करारा जवाब देता है।
हमारे देश ने बहुत विकास किया है और विश्व के शक्तिशाली देशों में गिना जाने लगा है। विकास के साथ कुछ कमियाँ भी खड़ी हुई हैं; जैसे-असमानता, गरीबी, बेरोजगारी, भ्रष्टाचार, अशिक्षा आदि। अपने देश को विश्व का एक बेहतरीन देश बनाने के लिए समाज की समस्याओं को सुलझाने के लिए हमें आज प्रतिज्ञा लेने की जरूरत है। धन्यवाद, जय हिन्द!
![]()
आसपास
प्रश्न 1.
‘जीत के लिए संघर्ष जरूरी है।’ विषय पर प्रतियोगिता में सहभागी टीम के साथ चर्चा कीजिए।
उत्तरः
किसी ने क्या खूब कहा है:
किश्ती तूफ़ान से निकल सकती है,
बुझता हुआ चिराग़ फिर से जल सकता है।
उम्मीद न हार, न अपने इरादे बदल,
ये तक़दीर है, तक़दीर किसी भी वक्त बदल सकती है।
मनुष्य के जीवन में पल-पल परिस्थितियाँ बदलती रहती हैं। जीवन में सफलता-असफलता, हानि-लाभ, जय-पराजय के अवसर मौसम के समान हैं, कभी कुछ स्थिर नहीं रहता। हमारे जीवन में सुख भी है, दुख भी है, अच्छाई भी है, बुराई भी है। जहाँ अच्छा वक्त हमें खुशी देता है, वहीं बुरा वक्त हमें मजबूत बनाता है। हम अपनी जिंदगी की सभी घटनाओं पर नियंत्रण नहीं रख सकते, पर उनसे निपटने के लिए सकारात्मक सोच के साथ सही तरीका तो अपना ही सकते हैं।
कई लोग अपनी पहली असफलता से इतना परेशान हो जाते हैं कि अपने लक्ष्य को ही छोड़ देते हैं। कभी-कभी तो अवसाद में चले जाते हैं। अब्राहम लिंकन भी अपने जीवन में कई बार असफल हुए और अवसाद में भी गए किन्तु उनके साहस और सहनशीलता के गुण ने उन्हें सर्वश्रेष्ठ सफलता दिलाई। अनेकों चुनाव हारने के बाद 52 वर्ष की उम्र में अमेरिका के राष्ट्रपति चुने गए।
संघर्ष ही जीवन है। जीवन संघर्ष का ही दूसरा नाम है। इस सष्टि में छोटे-से-छोटे प्राणी से लेकर बड़े-से-बड़े प्राणी तक, सभी किसी-न-किसी रूप में संघर्षरत हैं। जिसने संघर्ष करना छोड़ दिया, वह मृतप्राय हो गया। जीवन में संघर्ष है प्रकृति के साथ, स्वयं के साथ, परिस्थितियों के साथ। जो तरह-तरह के संघर्षों का सामना करने से कतराते हैं, वे जीवन से भी हार जाते हैं, जीवन भी उनका साथ नहीं देता। जब हम संघर्ष करते हैं, तभी हमें अपने बल व सामर्थ्य का पता चलता है। संघर्ष करने से ही आगे बढ़ने का हौसला मिलता है और अंतत: हम अपनी मंजिल को हासिल कर लेते हैं।
लेखनीय
प्रश्न 1.
‘जीवन में परिश्रम का महत्त्व पर’, अपने विचार व्यक्त
उत्तरः
जीवन में सफलता कौन नहीं चाहता। हर व्यक्ति अपने जीवन में सफलता की ऊँचाई प्राप्त करना चाहता है। ये संसार भी ऐसे लोगों को ही याद रखता है जो इस दुनिया में सफल हुए हैं, जिन्होंने अपने-अपने क्षेत्रों में विजय पताका फहराई है। एक बात तो पूरी तरह स्पष्ट है, संसार में हर व्यक्ति की जीतने की इच्छा होती है, लेकिन जीतना इतना आसान नहीं है। जीतने के लिए कीमत होती है। अपने जीवन का एक लम्बा समय और उस लम्बे समय में किया हुआ अथाह परिश्रम।
परिश्रम वह मूलमंत्र है जो खजानों को खोल देता है. पर्वतों को चीर देता है, सारी दुनिया को मुट्ठी में कर लेता है और असफलता को फूंक मार कर उड़ा देता है। जरूरत है लगन, आस्था और अथक प्रयास की। जिस प्रकार कुएँ के पत्थर पर रस्सी के बार-बार आने-जाने से निशान पड़ जाते हैं उसी तरह परिश्रम द्वारा कठिन से कठिन कार्यों को भी सरल बनाया जा सकता है। कहा भी गया है
‘करत-करत अभ्यास ते जड़मति होत सुजान।’
एक चीज़ को लक्ष्य बनाकर उस दिशा में प्रयत्न करना होता है। नियमित रूप से लगातार परिश्रम करना पड़ता है। हमारा मन भटकाने के लिए बहुत सारी चीजें सामने आएँगी पर उन पर ध्यान न देते हुए पूरी एकाग्रता से किया हुआ परिश्रम ही मनुष्य को सफलता दिला सकता है। इतिहास इस बात का साक्षी है कि मनुष्य ने कठोर परिश्रम द्वारा असंभव कार्य को संभव कर दिखाया है। परिश्रम मनुष्य के स्वास्थ्य के लिए भी आवश्यक है। शारीरिक और मानसिक परिश्रम के उचित तालमेल से व्यक्ति का तन और मन दोनों स्वस्थ रह सकता है। इसलिए परिश्रम से भागना बिल्कुल मूर्खता है।
विद्यार्थी को विद्यार्जन में, खिलाड़ी को अपने खेल में, कलाकार को अपनी कला में, गायक को अपने गीत में, एक सामान्य व्यक्ति को अपने पेशे में निरंतरता लानी है, तो परिश्रम ही एकमात्र रास्ता है। परिश्रम से बचकर कोई और रास्ता ढूँढ़ना समय की बरबादी है। जीवन में सफलता और परिश्रम एक-दूसरे से सिक्के के दो पहलू की तरह जुड़े हुए हैं। इसलिए जीत की इच्छा रखने वाले को कठोर परिश्रम के लिए हमेशा तैयार रहना चाहिए।
![]()
श्रवणीय:
प्रश्न 1.
किसी अवकाश प्राप्त सैनिक से उनके अनुभव सुनिए और उनसे प्रेरणा लीजिए ।
पाठ से आगे:
प्रश्न 1.
कविवर्य रवींद्रनाथ टैगोर की कविता पढ़िए।
पाठ के आँगन में…
1. सूचना के अनुसार कृतियाँ पूर्ण कीजिए:
प्रश्न (क)
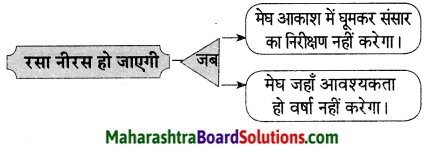
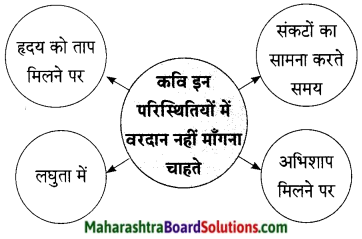
कवि इन परिस्थितियों में वरदान नहीं माँगना चाहते –
उत्तर:
प्रश्न (ख)
आकृति पूर्ण कीजिए।

उत्तर:

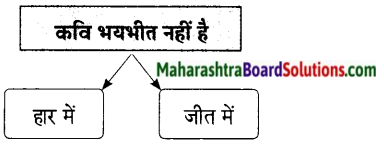
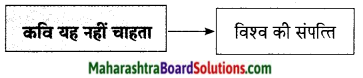
प्रश्न 2.
आकृति पूर्ण कीजिए।

उत्तर:
![]()
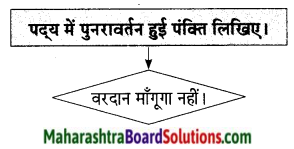
2. पदूय में पुनरावर्तन हुईं पक्ति लिखिरा
प्रश्न 1.
पदूय में पुनरावर्तन हुईं पक्ति लिखिरा
3. रेखांकित वाक्यांशों के स्थान पर उचित मुहावरा लिखिए।
प्रश्न 1.
रुग्ण शय्या पर पड़ी माता जी को देखकर मोहन का धीरज धीरे-धीरे समाप्त हो रहा था। (तिल-तिल मिटना, जिस्म टूटना)
उत्तरः
रुग्ण शय्या पर पड़ी माता जी को देखकर मोहन का धीरज तिल-तिल मिट रहा था।
भाषा बिंदु
प्रश्न 1.
निम्नलिखित अशुद्ध वाक्यों को शुद्ध करके फिर से लिखिए।
- लता कितनी मधुर गाती है।
- तितली के पास सुंदर पंख होते हैं।
- यह भोजन दस आदमी के लिए है।
- कश्मीर में कई दर्शनीय स्थल देखने योग्य है।
- उसने प्राण की बाजी लगा दी।
- तुमने मीट्टी से कीया प्यार।
- यह है न पसीने का धारा।
- आओ सिंहासन में बैठो।
- तुम हँसो कि फूले-फले देश।
- यह गंगा का है नवल धार।
उत्तरः
- शुदध वाक्य
- लता कितना मधुर गाती है।
- तितली के पंख सुंदर होते हैं।
- यह भोजन दस आदमियों के लिए है।
- कश्मीर में कई दर्शनीय स्थल हैं।
- उसने प्राणों की बाजी लगा दी।
- तुमने मिट्टी से किया प्यार।
- यह है न पसीने की धारा।
- आओ, सिंहासन पर बैठो।
- तुम हँसो ताकि फूले-फले देश।
- गंगा की यह नवल धार है।
![]()
Hindi Lokbharti 9th Answers Chapter 9 वरदान माँगूँगा नही Additional Important Questions and Answers
(क) पद्यांश पढ़कर दी गई सूचना के अनुसार कृतियाँ कीजिए।
कृति (1) आकलन कृति
प्रश्न 1.
समझकर लिखिए।
उत्तर:
प्रश्न 2.
आकृति पूर्ण कीजिए।
उत्तर:
कृति (2) आकलन कृति
प्रश्न 1.
आकृति पूर्ण कीजिए।
उत्तर:
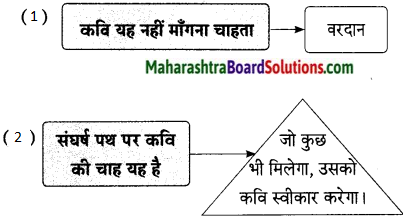
![]()
प्रश्न 2.
समझकर लिखिए।
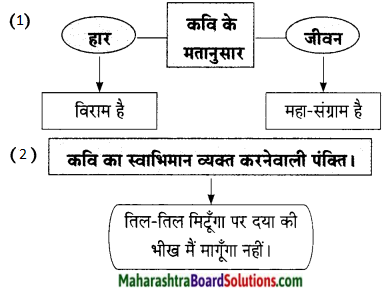
‘जीवन-महा-संग्राम है।’ इस का अर्थ है-
उत्तरः
जीवनपथ पर चारों ओर दुख एवं संकट-ही-संकट है। अत: जीवन रूपी पथ पर चलते समय उनके साथ संघर्ष करना पड़ता है। यही जीवन का महासंग्राम है।
कृति (3) भावार्थ
निम्नलिखित पद्यांश का भावार्थ लिखिए।
प्रश्न 1.
यह हार एक ……………….. वरदान माँगूंगा नहीं।
भावार्थ:
कवि स्वाभिमानी हैं अत: वह ईश्वर से दया की भीख नहीं माँगना चाहते। वे कहते हैं यह जीवन एक बड़ा युद्ध है। इस युद्ध में हार भी हो सकती है और जीत भी हो सकती है । यदि जीवन में हार का सामना करना पड़ेगा तो भी वह घबराएँगे नहीं। वे कहते हैं कि जीवन में मिली हार बहुत दिन नहीं ठहरती । अत: जीवनरूपी महासंग्राम में आने वाले दुख एवं संघर्षों से वह भयभीत नहीं होंगे, वह तिल-तिल मिटेंगे यानी जब तक शरीर में प्राण है तब तक वह सघर्षों का सामना करेंगे परंतु संघर्षों से बाहर निकलने के लिए वह ईश्वर से दया की भीख कदापि नहीं माँगेंगे। वे कहते हैं कि मैं ईश्वर से कभी वरदान नहीं माँगूंगा।
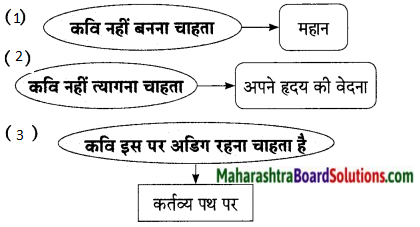
(ख) पद्यांश पढ़कर दी गई सूचना के अनुसार कृतियाँ कीजिए।
कृति (1) आकलन कृति
प्रश्न 1.
सूचना के अनुसार कृतियाँ कीजिए।
उत्तर:
![]()
कृति (2) आकलन कृति
प्रश्न 1.
समझकर लिखिए।
उत्तर:
1.
2.

3.

कृति (3) भावार्थ
निम्नलिखित पद्यांश का भावार्थ लिखिए।
प्रश्न 1.
लघुता न ………………….. वरदान माँगूंगा नहीं।
भावार्थः
कवि अपने आप को बहुत ही लघु यानी छोटा मानते हैं। आखिर ईश्वर के सामने सभी लघु ही होते हैं। ईश्वर महान होता है। इस तथ्य को स्वीकार कर कवि कहते हैं, “मेरी लघुता को छूने का प्रयास मत करो यानी मेरे दुख-दर्द दूर करने का विचार तू त्याग दे; इस संसार में तुम सबसे श्रेष्ठ हो। अत: तुम महान बने रहो। मैं अपने हृदय में निर्मित वेदना को व्यर्थ त्यागूंगा नहीं और उसे मेरे हृदय से निकालने के लिए मैं तुमसे वरदान नहीं माँगूंगा।’
![]()
मौलिक सजन
प्रश्न 1.
निम्नलिखित शब्दों के आधार पर कहानी लिखिए तथा उसे शीर्षक दीजिए।
उत्तरः
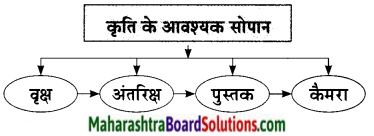
स्मृतियों के साथ अंतरिक्ष की ओर
खुशी के मारे उसके पाँव जमीन पर नहीं पड़ रहे थे। नासा से बाहर आते ही उसने घर का नंबर मिलाया।
“पापा!” उससे बोला नहीं गया।
“हमारी बेटी ने किला फतह कर लिया! है न?”
‘हाँ, पापा!” वह चहकी, ‘मैंने नासा में प्रवेश पानेवाली परीक्षा
पास कर ली है। मेरिट में पहले नंबर पर हैं।”
‘शाबाश! मुझे पता था हमारी बेटी लाखों में एक है!”
“पापा, पंद्रह मिनट के ब्रेक के बाद एक औपचारिक इंटरव्यू और होना है। उसके फौरन बाद मुझे ‘नासा अंतरिक्ष प्रवेश कार्ड’ दिया जाएगा। मम्मी को फोन देना”
“तुम्हारी मम्मी सब्जी लेने गई है। आते ही बात कराता हूँ। आल द बेस्ट, बेटा!” उसकी आँखें भर आई। पापा की छोटी-सी नौकरी थी, लेकिन उन्होंने बैंक से कर्जा लेकर अपनी दोनों बेटियों को उच्च शिक्षा दिलवाई थी। मम्मी-पापा की आँखों में तैरते सपनों को हकीकत में बदलने का अवसर आ गया था। उसे याद आए अपने वह बचपन के दिन, वह बरगद का वृक्ष, जिसके नीचे बैठकर वह लगातार अंतरिक्ष की ओर देखा करती थी।
उसी वृक्ष के नीचे बैठकर वह अंतरिक्ष संबंधी पुस्तकें पढ़ा करती थी। उसे याद आया, वह कैमरा, जो उसके पापा ले आए थे। उसी कैमरे को आँखों के सामने पकड़कर वह अंतरिक्ष की ओर देखती थी। बचपन की वह यादें, वह वृक्ष, पुस्तक और कैमरा मानो उसे पुकार-पुकार कर कहे रहे थे – दिव्या तुम सचमुच दिव्य हो, अब तुम अंतरिक्ष का भ्रमण करने निकलोगी। क्या हमें साथ लेकर नहीं चलोगी?
![]()
पद्य-विश्लेषण
- कविता का नाम – वरदान माँगूंगा नहीं
- कविता की विधा – गीत
- पसंदीदा पंक्ति – चाहे हृदय को ताप दो। चाहे मुझे अभिशाप दो। कुछ भी करो कर्तव्य पथ से किंतु भागूंगा नहीं। वरदान माँगूंगा नहीं।
- पसंदीदा होने का कारण – प्रस्तुत पंक्ति मुझे बेहद पसंद है क्योंकि उसमें प्रतिकूल परिस्थितियों में भी कर्तव्य पथ पर अडिग रहने की बात की गई है।
- कविता से प्राप्त संदेश या प्रेरणा – प्रस्तुत कविता से प्रेरणा मिलती है कि व्यक्ति को अपने कर्तव्य पथ पर अटल रहना चाहिए।
आने वाले संकटों का हँसते हए सामना करने की भावना रखनी चाहिए। व्यक्ति के हौसलें बुलंद होने चाहिए। व्यक्ति में आत्मविश्वास होना चाहिए कि वह आने वाली प्रतिकूल परिस्थितियों का अकेले सामना कर सके और अपने कर्तव्य पथ से कदापि पीछे नहीं हटे। व्यक्ति को तूफानों का सामना करने का साहस स्वयं रखना चाहिए।
वरदान माँगूँगा नही Summary in Hindi
कवि-परिचय:
जीवन-परिचय: जनकवि शिवमंगल सिंह ‘सुमन’ जी, प्रगतिवादी कविता के स्तंभ कवि थे। उनकी कविताओं में जनकल्याण, प्रेम, रचनात्मक विद्रोह के स्वर मुख्य रूप से मुखरित हुए हैं। वे अपने समय के सामूहिक चेतना के संरक्षक के रूप में कार्यरत रहे।
प्रमुख कृतियाँ: काव्य संग्रह – हिल्लोल, जीवन के गान, युग का मेल, मिट्टी की बारात, विश्वास बढ़ता ही गया, वाणी की व्यथा आदि।
गद्य रचनाएँ – महादेवी की काव्य साधना, गीतिकाव्य उद्भव और विकास’ ।
पद्य-परिचय:
गीत: स्वर, पद और ताल से युक्त गीत हिंदी साहित्य की महत्त्वपूर्ण विधाओं में से एक है। इसमें गेयता होती है। गीत मनुष्य मात्र की भाषा है। गीतों के माध्यम से मानव जीवन में ऊर्जा एवं ताजगी का संचार होता है।
प्रस्तावना: प्रस्तुत गीत के माध्यम से कवि ने स्वाभिमान के बल पर सुख-दुख में समभाव रखकर कर्तव्य पथ पर सतत बढते रहने की प्रेरणा प्रदान की है।
सारांश:
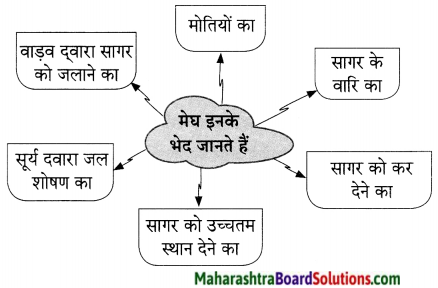
‘वरदान माँगूंगा नहीं’ इस कविता में कवि कहते हैं कि जीवन एक महासंग्राम है। हमें इस जीवनरूपी महासंग्राम का सामना करने के लिए सदैव तैयार रहना चाहिए। कवि विपरीत परिस्थितियों में भी कर्तव्य पथ पर अडिग रहने की सलाह देते हैं। कवि जीवन में आनेवाले संघर्षों को अपने आत्मविश्वास, प्रयास व परिश्रम द्वारा दूर करने की सलाह देते हैं।
![]()
शब्दार्थ:
- विराम – ठहराव
- महा-संग्राम – बड़ा युद्ध |
- स्मृति – यादें
- खंडहर – (यहाँ) खंडित आकांक्षा
- लघुता – छोटापन
- वेदना – व्यथा, पीड़ा
- ताप – गर्मी
- अभिशाप – श्राप
मुहावरे:
तिल-तिल मिटना – धीरे धीरे समाप्त होना।
भावार्थ:
यह हार एक ………….. वरदान माँगूंगा नहीं।
कवि स्वाभिमानी हैं अत: वह ईश्वर से दया की भीख नहीं माँगना चाहते। वे कहते हैं यह जीवन एक बड़ा युद्ध है। इस युद्ध में हार भी हो सकती है और जीत भी हो सकती है । यदि जीवन में हार का सामना करना पड़ेगा तो भी वह घबराएँगे नहीं । वे कहते हैं कि जीवन में मिली हार बहुत दिन नहीं ठहरती । अत: जीवनरूपी महासंग्राम में आने वाले दुख एवं संघर्षों से वह भयभीत नहीं होंगे, वह तिल-तिल मिटेंगे यानी जब तक शरीर में प्राण है तब तक वह सघर्षों का सामना करेंगे परंतु संघर्षों से बाहर निकलने के लिए वह ईश्वर से दया की भीख कदापि नहीं माँगेंगे। वे कहते हैं कि मैं ईश्वर से कभी वरदान नहीं माँगूंगा ।
Hindi Lokbharti 9th Digest Answers Pdf पहली इकाई
- चाँदनी रात Question Answer
- बिल्ली का बिलुंगड़ा Question Answer
- कबीर (पूरक पठन) Question Answer
- किताबें Question Answer
- जूलिया Question Answer
- ऐ सखि ! (पूरक पठन) Question Answer
- डाॅक्टर का अपहरण Question Answer
- वीरभूमि पर कुछ दिन Question Answer
- वरदान माँगूँगा नही Question Answer
- रात का चौकीदार (पूरक पठन) Question Answer
- निर्माणों के पावन युग में Question Answer