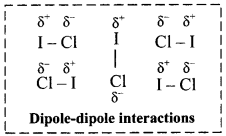
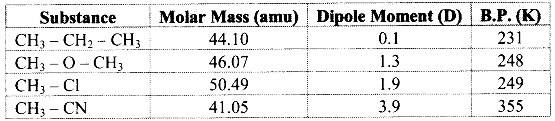
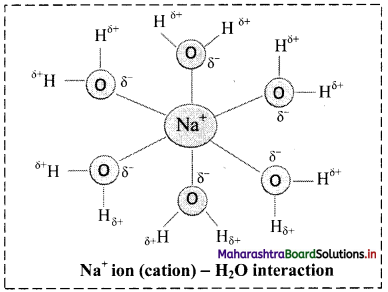
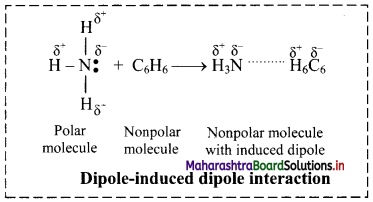
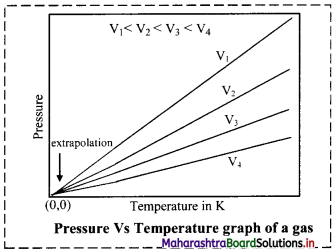
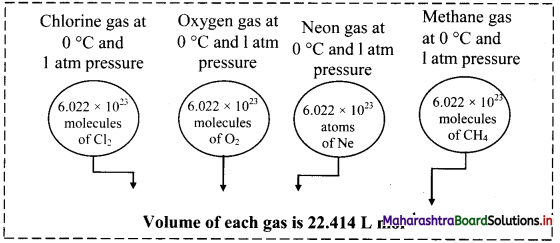
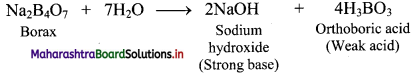
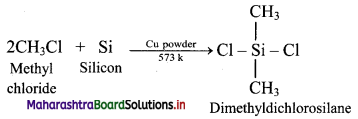
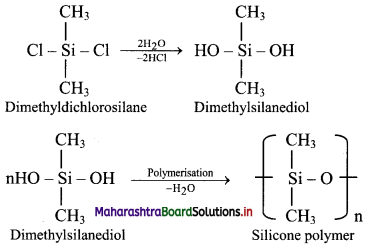
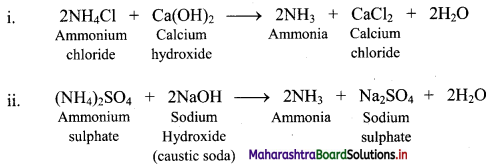
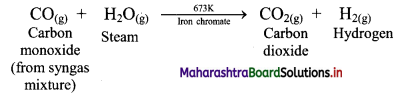
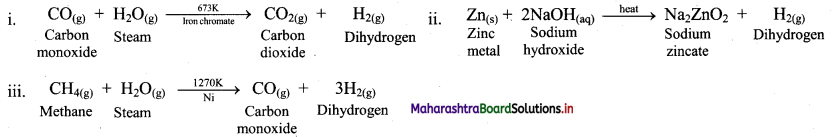
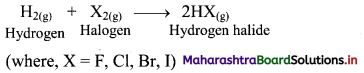
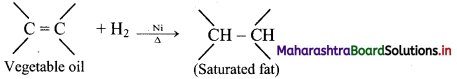
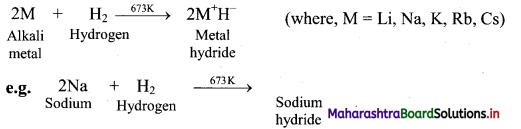
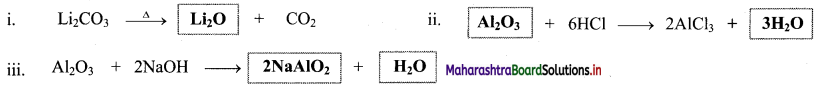
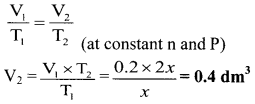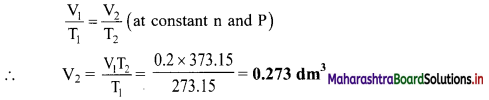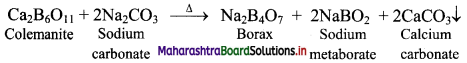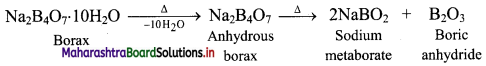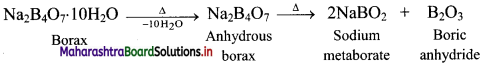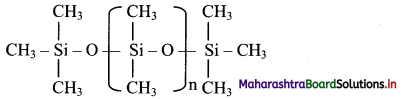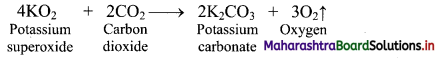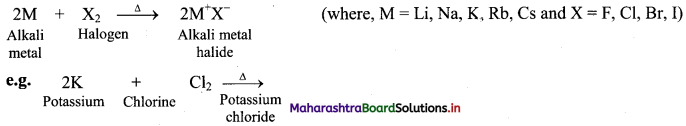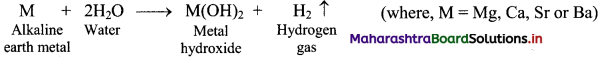Balbharati Maharashtra State Board Class 11 Information Technology Important Questions Chapter 1 Basics of Information Technology Important Questions and Answers.
Maharashtra State Board 11th Information Technology Important Questions Chapter 1 Basics of Information Technology
1. Fill in the Blanks.
Question 1.
______________ encompasses all of the technologies that we use in order to create, collect, process, protect and store information.
Answer:
Information Technology
Question 2.
______________ refers to hardware, software (computer programs), and computer networks.
Answer:
Information Technology
Question 3.
Full form of ICT is ______________
Answer:
Information and Communication Technology
Question 4.
______________ concept involves transfer and use of all kinds of information.
Answer:
Information and Communication Technology
Question 5.
______________ is the foundation of economy and a driving force of social changes in the 21st century.
Answer:
Information and Communication Technology

Question 6.
______________ can be any character, text, word, number or raw facts.
Answer:
Data
Question 7.
______________ is data formatted in a manner that allows it to be utilized by human beings in some significant way.
Answer:
Information
Question 8.
The word Computer is derived from a Latin word ______________
Answer:
Computare
Question 9.
An electronic device which accepts input from the user, processes it according to the instructions given to it and gives the required result in the form of output, is a ______________
Answer:
Computer
Question 10.
A ______________ can process data, images, audio, video and graphics.
Answer:
Computer
Question 11.
______________ accepts data or instructions by way of input.
Answer:
Computer
Question 12.
______________ stores data.
Answer:
Computer
Question 13.
______________ can process data as required by the user.
Answer:
Computer
Question 14.
______________ gives results in the form of output.
Answer:
Computer
Question 15.
______________ controls all operations inside a computer.
Answer:
Computer
Question 16.
______________ is a specification detailing of how a set of software and hardware technology standards interact to form a computer system.
Answer:
Computer Architecture

Question 17.
______________ refers to how a computer system is designed and how it works.
Answer:
Computer Architecture
Question 18.
______________ helps users to enter data and commands into a computer system.
Answer:
Input unit
Question 19.
The main function of ______________ devices is to direct commands and data into computer.
Answer:
Input
Question 20.
______________ is an input device that enters numbers and characters.
Answer:
Keyboard
Question 21.
A ______________ can be an input device for entering directions and commands.
Answer:
Mouse
Question 22.
Full form of CPU is ______________
Answer:
Central Processing Unit
Question 23.
After receiving data and commands from users, a computer system has to process it according to the instructions provided. Here, it has to rely on a component called the ______________
Answer:
Central Processing Unit
Question 24.
The ______________ further uses these three elements Arithmetic and Logic Unit, Control Unit and Memory Unit.
Answer:
Central Processing Unit
Question 25.
Full form of ALU is ______________
Answer:
Arithmetic and Logic Unit
Question 26.
______________ part of the CPU performs arithmetic operations.
Answer:
Arithmetic and Logic Unit
Question 27.
______________ can even perform logical functions like the comparison of data.
Answer:
Arithmetic and Logic Unit

Question 28.
______________ is the back bone of computers.
Answer:
Control Unit
Question 29.
______________ is responsible for coordinating tasks between all components of a computer system.
Answer:
Control Unit
Question 30.
The ______________ collects data from input units and sends it to processing units depending on its nature.
Answer:
Control Unit
Question 31.
______________ transmits processed data to output units to facilitate users.
Answer:
Control Unit
Question 32.
Once a user enters data using input devices, the computer system stores this data in its ______________
Answer:
Memory Unit
Question 33.
The ______________ uses a set of pre-programmed instructions to further transmit this data to other parts of the CPU.
Answer:
Memory Unit
Question 34.
______________ is internal memory of the computer.
Answer:
Primary Memory
Question 35.
______________ is also known as main memory.
Answer:
Primary Memory
Question 36.
______________ holds the data and instruction on which computer is currently working.
Answer:
Primary Memory
Question 37.
RAM stands for ______________
Answer:
Random Access Memory
Question 38.
______________ is known as read/write memory.
Answer:
Random Access Memory
Question 39.
______________ is generally referred to as main memory of the computer system.
Answer:
Random Access Memory
Question 40.
______________ is a temporary memory.
Answer:
Random Access Memory
Question 41.
______________ is also called as Volatile Memory.
Answer:
Random Access Memory

Question 42.
ROM stands for ______________
Answer:
Read Only Memory
Question 43.
______________ is a Permanent Type memory.
Answer:
Read Only Memory
Question 44.
______________ cannot be overwritten by the computer.
Answer:
Read Only Memory
Question 45.
______________ is also called Non-Volatile Memory.
Answer:
Read Only Memory
Question 46.
______________ is an external memory of the computer.
Answer:
Secondary Memory
Question 47.
______________ is used to store the huge amount of different programs and information.
Answer:
Secondary Memory
Question 48.
______________ basically reproduce the data formatted by the computer for user’s benefit.
Answer:
Output Unit
Question 49.
______________ is a binary digit that holds only one of two values.
Answer:
Bit
Question 50.
A group of 4 bits is called a ______________
Answer:
Nibble
Question 51.
A group of 8 bits is called a ______________
Answer:
Byte
Question 52.
A ______________ is the smallest unit, which can represent a data item or a character.
Answer:
Byte
Question 53.
1 Byte is ______________
Answer:
8 Bits

Question 54.
1 KiloByte (KB) is ______________
Answer:
1,024 Bytes
Question 55.
1 MegaByte (MB) is ______________
Answer:
1,024 KiloBytes
Question 56.
1 GigaByte (GB) is ______________
Answer:
1,024 MegaBytes
Question 57.
1 TeraByte (TB) is ______________
Answer:
1,024 GigaBytes
Question 58.
1 PetaByte (PB) is ______________
Answer:
1,024 TeraBytes
Question 59.
1 ExaByte (EB) is ______________
Answer:
1,024 PetaBytes
Question 60.
______________ comprises of the physical components that a computer system requires to function.
Answer:
Computer hardware
Question 61.
A set of instructions given to the computer is known as a ______________
Answer:
Program
Question 62.
Program or set of programs are called as ______________
Answer:
Software
Question 63.
______________ is a generic term used to describe computer programs.
Answer:
Software
Question 64.
______________ refers to the software which releases code in public domain for anyone to use.
Answer:
Open source software
Question 65.
Full form of FOSS ______________
Answer:
Free Open Source Software Policy
Question 66.
______________ and it enabled them to save some millions of rupees each year in licensing costs.
Answer:
Free Open Source Software Policy
Question 67.
In case of ______________, user has to purchase the software before using it.
Answer:
Closed Source Software
Question 68.
______________ is a program or group of programs designed for end users.
Answer:
Application Software

Question 69.
______________ is also called end-user programs.
Answer:
Application Software
Question 70.
______________ is a set of instructions required for a computer to work.
Answer:
System Software
Question 71.
______________ is a program that allows different applications and various components of hardware.
Answer:
Linux Operating System
Question 72.
A computer would not be able to function correctly without an ______________
Answer:
Operating System
Question 73.
An ______________ is a software program that empowers the computer hardware to communicate and operate with the computer software.
Answer:
Operating System
Question 74.
The ______________ boots up the computer and makes sure that everything is operational.
Answer:
Operating System
Question 75.
The ______________ is also what runs the cell phone and most of the electronic devices.
Answer:
Operating System
Question 76.
The ______________ usually come preloaded on any computer, tablet, laptop or cell phone that user buy.
Answer:
Operating System
Question 77.
Full form of DOS is ______________
Answer:
Disk Operating System
Question 78.
______________ is a series of operating systems that are designed by Microsoft.
Answer:
Windows
Question 79.
______________ is the most commonly used operating system.
Answer:
Windows
Question 80.
Apple Corporation’s registered operating system is called ______________
Answer:
Mac OS
Question 81.
______________ is an open-source operating system created by Google.
Answer:
Chrome OS

Question 82.
______________ is an open-source, portable, multi- multiprogramming, operating system.
Answer:
Linux
Question 83.
______________ is a free and open-source operating system for mobile phones provided by Google.
Answer:
Android
Question 84.
______________ is used by Nokia phones. This is closed source OS.
Answer:
Asha
Question 85.
______________ is a closed source operating system for smartphone and tablet devices.
Answer:
Blackberry
Question 86.
______________ is Apple’s closed source operating system for Apple’s iPhone, iPod Touch, iPad and second-generation Apple TVs.
Answer:
Iphone Operating System
Question 87.
______________ Phone is developed by Microsoft as a closed source operating system for mobile phones.
Answer:
Windows
Question 88.
______________ is used as the predominantly backbone of the Internet.
Answer:
Linux
Question 89.
______________ is one of the most popular GNU/Linux distribution.
Answer:
Ubuntu
Question 90.
Full form of GUI is ______________
Answer:
Graphical User Interface
Question 91.
Full form of CLI ______________
Answer:
Command Line Interface
Question 92.
The ______________ is when the user interacts with the computer using images, icons, and dialog boxes.
Answer:
Graphical User Interface
Question 93.
The ______________ option is used for quick search of the application.
Answer:
Search
Question 94.
The ______________ folder is where all the personal documents and settings are stored.
Answer:
Home
Question 95.
The ______________ is when user interacts with the computer using text.
Answer:
Command Line Interface
Question 96.
The ______________ are programs that are run when user types command name.
Answer:
Commands
Question 97.
______________ is Free and Open Source.
Answer:
Linux

Question 98.
______________ Operating System is free from viruses.
Answer:
Linux
Question 99.
______________ Operating Systems can update themselves.
Answer:
Proprietary
Question 100.
______________ is a collection of software for a Linux distribution on the server.
Answer:
Repositories
Question 101.
The ______________ manager updates the operating system as well as other softwares periodically.
Answer:
Package
Question 102.
______________ is a group of interconnected computers or devices to have communication within themselves.
Answer:
Computer Network
Question 103.
A ______________ consists of a collection of computers, printers and other equipment that is connected together.
Answer:
Computer Network
Question 104.
Full form of LAN is ______________
Answer:
Local Area Network
Question 105.
Full form of MAN is ______________
Answer:
Metropolitan Area Network
Question 106.
Full form of WAN is ______________
Answer:
Wide Area Network
Question 107.
______________ type of network covers the smallest area.
Answer:
Local Area Network
Question 108.
______________ covers an area larger than LAN.
Answer:
Metropolitan Area Network
Question 109.
______________ type of network comprises the largest of all.
Answer:
Wide Area Network
Question 110.
In ______________ usage area is limited to areas such as an office building, home, hospital, schools, etc.
Answer:
Local Area Network
Question 111.
______________ covers a short distance, and so the error and noise are minimized.
Answer:
Local Area Network
Question 112.
______________ type of network is easy to setup.
Answer:
Local Area Network
Question 113.
In ______________ data transmits at a very fast rate as the number of computers linked are limited.
Answer:
Local Area Network
Question 114.
______________ is a less expensive hardware and maintenance cost is also low.
Answer:
Local Area Network
Question 115.
______________ connects two or more separate computers that reside in the same or different cities.
Answer:
Metropolitan Area Network
Question 116.
Full for of ISP is ______________
Answer:
Internet Service Provider
Question 117.
______________ covers a large geographical area and may serve as an ISP.
Answer:
Metropolitan Area Network
Question 118.
______________ type of network is hard to design and maintain.
Answer:
Metropolitan Area Network
Question 119.
______________ is a computer network that extends over a large geographical area.
Answer:
Wide Area Network
Question 120.
In ______________ type of network the technology is high speed and relatively expensive.
Answer:
Wide Area Network

Question 121.
A Communication medium used for ______________ is Telephone Network or Satellite Link.
Answer:
Wide Area Network
Question 122.
______________ is the design of a computer network.
Answer:
Network Architecture
Question 123.
A ______________ network has no dedicated servers.
Answer:
Peer-to-Peer
Question 124.
______________ type of architecture is most suitable for larger network.
Answer:
Client-Server
Question 125.
A computer which is seeking any resource from another computer is a ______________ computer.
Answer:
Client
Question 126.
If a computer has a resource which is served to another computer, it is a ______________ computer.
Answer:
Server
Question 127.
______________ means connecting computer to any other computer anywhere in the world.
Answer:
Internet
Question 128.
The ______________ is generally defined as a global network connecting millions of computers.
Answer:
Internet
Question 129.
The ______________ is a massive network of networks, a networking infrastructure.
Answer:
Internet
Question 130.
With the help of the ______________, one can easily be in touch with anyone in the whole world by sending electronic mail, by chatting.
Answer:
Internet
Question 131.
It can be said that ______________ provides a very strong connection or network between computers globally.
Answer:
Internet
Question 132.
Full form of ARPANET is ______________
Answer:
Advanced Research Projects Agency Network
Question 133.
The first workable prototype of the internet came in the late 1960’s with the creation of ______________
Answer:
Advanced Research Projects Agency Network
Question 134.
______________ used packet switching to allow multiple computers to communicate on a single network.
Answer:
Advanced Research Projects Agency Network
Question 135.
Full form of TCP/IP is ______________
Answer:
Transmission Control Protocol and Internet Protocol
Question 136.
______________ communications model that set standards for how data could be transmitted between multiple networks.
Answer:
Transmission Control Protocol and Internet Protocol
Question 137.
Full form of WWW is ______________
Answer:
World Wide Web
Question 138.
Tim Berners-Lee invented the ______________
Answer:
World Wide Web
Question 139.
A ______________ is a set of rules that governs the communications between computers on a network.
Answer:
Protocol
Question 140.
______________ breaks down the message into packets and sends them out into the network.
Answer:
Transmission Control Protocol & Internet Protocol

Question 141.
Full form of DNS is ______________
Answer:
Domain Name System
Question 142.
______________ translates network address into terms understood by humans and vice-versa.
Answer:
Domain Name System
Question 143.
DHCP stands for ______________
Answer:
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
Question 144.
______________ can automatically assign internet addresses to computers and users.
Answer:
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
Question 145.
FTP stands for ______________
Answer:
File Transfer Protocol
Question 146.
______________ is used to transfer and manipulate files on the internet.
Answer:
File Transfer Protocol
Question 147.
Full form of HTTP is ______________
Answer:
Hyper Text Transfer Protocol
Question 148.
______________ is an internet-based protocol for sending and receiving web pages.
Answer:
Hyper Text Transfer Protocol
Question 149.
Full form of IMAP is ______________
Answer:
Internet Message Access Protocol
Question 150.
______________ is used for receiving e-mail messages from server on the Internet.
Answer:
Internet Message Access Protocol
Question 151.
______________ maintains a copy of all the emails on server.
Answer:
Internet Message Access Protocol
Question 152.
Full form of IRC is ______________
Answer:
Internet Relay Chat
Question 153.
______________ facilitates communication in the form of text.
Answer:
Internet Relay Chat
Question 154.
POP3 stands for ______________
Answer:
Post Office Protocol Version 3
Question 155.
______________ is used for receiving e-mail from remote mail servers.
Answer:
Post Office Protocol Version 3
Question 156.
______________ is used for sending e-mail messages to the Server on the Internet.
Answer:
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol
Question 157.
Full form of ITES is ______________
Answer:
IT Enabled Services
Question 158.
IT Enabled Services (ITES), also called as ______________
Answer:
Web Enabled Services
Question 159.
______________ covers the entire amount of operations which exploit Information Technology for improving efficiency of an organization.
Answer:
IT Enabled Services
Question 160.
______________ can develop interactive websites using knowledge of HTML, PHP and various other programming languages.
Answer:
Web Designer
Question 161.
It is possible to have career as a ______________ with the scripting skills.
Answer:
Software Developer
Question 162.
After getting knowledge about Database management one can work as a ______________
Answer:
Database Manager
Question 163.
______________ are responsible for ensuring that networks are watertight.
Answer:
Information Security Analyst
Question 164.
______________ using computerized accounting software can successfully handle accounting work.
Answer:
Professional Accountant
Question 165.
______________ after getting IT knowledge one can advise and guide others in investing the money in various investment schemes.
Answer:
Financial Advisor
Question 166.
It is possible to become a successful ______________ using one’s own creation and innovation.
Answer:
Animator

Question 167.
Perhaps one of the trendiest and most fun jobs in the sector, a ______________
Answer:
Games Developer
Question 168.
As a career opportunity, to become an ______________, one should be good in tools such as Kdenlive, Audacity.
Answer:
Audio/Video Editor
Question 169.
______________ is the study and practice of environmentally sustainable computing or IT.
Answer:
Green Computing
Question 170.
The goals of ______________ are similar to green chemistry.
Answer:
Green Computing
Question 171.
______________ is important for all classes of systems, ranging from handheld systems to largescale data centers.
Answer:
Green Computing
Question 172.
Full form of IOT is ______________
Answer:
Internet of Things
Question 173.
The ______________ is the network of physical devices, vehicles, home appliances, and other items embedded with electronics, software, sensors, actuators, and connectivity.
Answer:
Internet of Things
Question 174.
______________ is the delivery of computing services over the internet.
Answer:
Cloud Computing
Question 175.
______________ is the process of examining data sets in order to draw conclusions about the information.
Answer:
Data Analytics
Question 176.
______________ technologies and techniques are widely used in commercial industries to enable organizations to make more-informed business decisions.
Answer:
Data Analytics
Question 177.
______________ is intelligence demonstrated by machines, in contrast to the natural intelligence displayed by humans and other animals.
Answer:
Artificial Intelligence
Question 178.
Computer science defines ______________ research as the study of “intelligent agents”.
Answer:
Artificial Intelligence
Question 179.
______________ is the scientific study of algorithms and statistical models that computer systems use to effectively perform a specific task.
Answer:
Machine Learning
Question 180.
______________ refers to data sets that are too large or complex for traditional data-processing application software.
Answer:
Big Data
Question 181.
______________ is a growing list of records, called blocks, which are linked using cryptography.
Answer:
Blockchain
2. True or False.
Question 1.
Information Technology encompasses all of the technologies that we use in order to create, collect, process, protect and store information.
Answer:
True
Question 2.
Programmers refer to hardware, software (computer programs), and computer networks.
Answer:
False
Question 3.
The full form of ICT is Information and Communication Technology:
Answer:
True
Question 4.
The Computer Science concept involves the transfer and use of all kinds of information.
Answer:
False
Question 5.
Information and Communication Technology is the foundation of the economy and a driving force of social changes in the 21st century.
Answer:
True

Question 6.
Data can be any character, text, word, number, or raw facts.
Answer:
True
Question 7.
The virus is data formatted in a manner that allows it to be utilized by human beings in some significant way.
Answer:
False
Question 8.
The word Computer is derived from the Latin word Komptom.
Answer:
False
Question 9.
An electronic device that accepts input from the user, processes it according to the instructions given to it, and gives the required result in the form of output, is a Typewriter.
Answer:
False
Question 10.
A computer can process data, images, audio, video, and graphics.
Answer:
True
Question 11.
Computer accepts data or instructions by way of input.
Answer:
True
Question 12.
Computer stores data.
Answer:
True
Question 13.
The computer can process data as required by the user.
Answer:
True
Question 14.
The computer gives results in the form of output.
Answer:
True
Question 15.
Machine controls all operations inside a computer.
Answer:
False
Question 16.
Computer Architecture is a specification detailing how a set of software and hardware technology standards interact to form a computer system.
Answer:
True
Question 17.
Website refers to how a computer system is designed and how it works.
Answer:
False
Question 18.
Storage Unit helps users to enter data and commands into a computer system.
Answer:
False
Question 19.
The main function of hardware devices is to direct commands and data into computers.
Answer:
False
Question 20.
The keyboard is an input device that enters numbers and characters.
Answer:
True
Question 21.
A Mouse can be an input device for entering directions and commands.
Answer:
True
Question 22.
The full form of CPU is Central Processing Unit.
Answer:
True
Question 23.
After receiving data and commands from users, a computer system has to process it according to the instructions provided. Here, it has to rely on a component called the Arithmetic and Logic Unit.
Answer:
False
Question 24.
The Central Processing Unit further uses these three elements Arithmetic and Logic Unit, Control Unit, and Memory Unit.
Answer:
True

Question 25.
The full form of ALU is the Arithmetic and Logic Unit.
Answer:
True
Question 26.
The Control Unit part of the CPU performs arithmetic operations.
Answer:
False
Question 27.
Arithmetic and Logic Unit can even perform logical functions like the comparison of data.
Answer:
True
Question 28.
The arithmetic and Logic Unit is the backbone of computers.
Answer:
False
Question 29.
The Control unit is responsible for coordinating tasks between all components of a computer system.
Answer:
True
Question 30.
The Control Unit collects data from input units and sends it to processing units depending on its nature.
Answer:
True
Question 31.
Control Unit transmits processed data to output units to facilitate users.
Answer:
True
Question 32.
Once a user enters data using input devices, the computer system stores this data in its Control Unit.
Answer:
False
Question 33.
The memory unit uses a set of pre-programmed instructions to further transmit this data to other parts of the CPU.
Answer:
True
Question 34.
Secondary Memory is the internal memory of the computer.
Answer:
False
Question 35.
Secondary Memory is also known as main memory.
Answer:
False
Question 36.
Secondary Memory holds the data and instructions on which computer is currently working.
Answer:
False
Question 37.
RAM stands for Random Access Memory.
Answer:
True
Question 38.
Random Access Memory is known as reading/write memory.
Answer:
True
Question 39.
Random Access Memory is generally referred to as the main memory of the computer system.
Answer:
True
Question 40.
Random Access Memory is a temporary memory.
Answer:
True
Question 41.
Read-Only Memory is also called Volatile Memory.
Answer:
False
Question 42.
ROM stands for Read-Only Memory.
Answer:
True
Question 43.
Random Access Memory is a Permanent Type of memory.
Answer:
False
Question 44.
Random Access Memory cannot be overwritten by the computer.
Answer:
False
Question 45.
Random Access Memory is also called Non-Volatile Memory.
Answer:
False
Question 46.
Secondary Memory is an external memory of the computer.
Answer:
True
Question 47.
Secondary Memory is used to store a huge amount of different programs and information.
Answer:
True
Question 48.
Does the input Unit basically reproduce the data formatted by the computer for the user’s benefit?
Answer:
False
Question 49.
A bit is a binary digit that holds only one of two values.
Answer:
True

Question 50.
A group of 4 bits is called a Nibble.
Answer:
True
Question 51.
A group of 8 bits is called a Kilobyte.
Answer:
False
Question 52.
A Byte is the smallest unit, which can represent a data item or a character.
Answer:
True
Question 53.
1 Byte is 8 Bits.
Answer:
True
Question 54.
1 KiloByte (KB) is 1,024 Bytes.
Answer:
True
Question 55.
1 MegaByte (MB) is 1 Terabyte.
Answer:
False
Question 56.
1 GigaByte (GB) is 1024 bites.
Answer:
False
Question 57.
1 TeraByte (TB) is 1,024 GigaBytes.
Answer:
True
Question 58.
1 PetaByte (PB) is 1,024 TeraBytes.
Answer:
True
Question 59.
1 ExaByte (EB) is 1024 Megabytes.
Answer:
False
Question 60.
The program comprises the physical components that a computer system requires to function.
Answer:
False
Question 61.
A set of instructions given to the computer is known as hardware.
Answer:
False
Question 62.
Program or set of programs are called Hardware.
Answer:
False
Question 63.
Hardware is a generic term used to describe computer programs.
Answer:
False
Question 64.
Open-source software refers to the software which releases code in the public domain for anyone to use.
Answer:
True
Question 65.
Full form of FOSS Free Open Source Software Policy.
Answer:
True
Question 66.
Free Open Source Software Policy and it enabled them to save some millions of rupees each year in licensing costs.
Answer:
True
Question 67.
In the case of Closed source software, a user has to purchase the software before using it.
Answer:
True
Question 68.
The machine is a program or group of programs designed for end-users.
Answer:
False
Question 69.
Hardware is also called end-user programs.
Answer:
False
Question 70.
Pen Drive is a set of instructions required for a computer to work.
Answer:
False
Question 71.
Linux Operating system is a program that allows different applications and various components of the hardware.
Answer:
True
Question 72.
A computer would not be able to function correctly without an operating system.
Answer:
True
Question 73.
An operating system is a software program that empowers the computer hardware to communicate and operate with the computer software.
Answer:
True
Question 74.
The operating system boots up the computer and makes sure that everything is operational.
Answer:
True
Question 75.
The operating system is also what runs the cell phone and most electronic devices.
Answer:
True
Question 76.
The operating systems usually come preloaded on any computer, tablet, laptop, or cell phone that the user buys.
Answer:
True
Question 77.
The full form of DOS is Disk Operating System.
Answer:
True
Question 78.
Linux is a series of operating systems that are designed by Microsoft.
Answer:
False

Question 79.
Windows is the most commonly used operating system.
Answer:
True
Question 80.
Apple Corporation’s registered operating system is called Mac OS.
Answer:
True
Question 81.
Chrome OS is an open-source operating system created by Google.
Answer:
True
Question 82.
Linux is an open-source, portable, multi-multiprogramming, operating system.
Answer:
True
Question 83.
Asha is a free and open-source operating system for mobile phones provided by Google.
Answer:
False
Question 84.
Android is used by Nokia phones. This is a closed source OS.
Answer:
False
Question 85.
Blackberry is a closed source operating system for smartphone and tablet devices.
Answer:
True
Question 86.
Windows is Apple’s closed source operating system for Apple’s iPhone, iPod Touch, iPad, and second-generation Apple TVs.
Answer:
False
Question 87.
IOS Phone is developed by Microsoft as a closed source operating system for mobile phones.
Answer:
False
Question 88.
Linux is used as the predominant backbone of the Internet.
Answer:
True
Question 89.
Ubuntu is one of the most popular GNU/Linux distributions.
Answer:
True
Question 90.
The full form of GUI is Graphical User Interface.
Answer:
True
Question 91.
Full form of CLI Command Line Interface.
Answer:
True
Question 92.
The graphical user interface is when the user interacts with the computer using images, icons, and dialog boxes.
Answer:
True
Question 93.
The Home option is used for a quick search of the application.
Answer:
False
Question 94.
The Search folder is where all the personal documents and settings are stored.
Answer:
False
Question 95.
The Command is when the user interacts with the computer using text.
Answer:
False
Question 96.
The command-line interface is programs that are run when a user types the command name.
Answer:
False
Question 97.
Proprietary is Free and Open Source.
Answer:
False
Question 98.
Linux Operating System is free from viruses.
Answer:
True
Question 99.
Repositories Operating Systems can update themselves.
Answer:
False
Question 100.
The repository is a collection of software for a Linux distribution on the server.
Answer:
True
Question 101.
The Package manager updates the operating system as well as other software periodically.
Answer:
True
Question 102.
Local Area Network is a group of interconnected computers or devices to have communication within themselves.
Answer:
False
Question 103.
A Metropolitan Area Network consists of a collection of computers, printers, and other equipment that is connected together.
Answer:
False
Question 104.
The full form of LAN is the Local Area Network.
Answer:
True
Question 105.
The full form of MAN is Metropolitan Area Network.
Answer:
True
Question 106.
The full form of WAN is a Wide Area Network.
Answer:
True
Question 107.
Wide Area Network type of network covers the smallest area.
Answer:
False

Question 108.
Metropolitan Area Network covers an area larger than LAN.
Answer:
True
Question 109.
Local Area Network type of network comprises the largest of all.
Answer:
False
Question 110.
In Local Area Network, usage area is limited to areas such as an office building, home, hospital, schools, etc.
Answer:
True
Question 111.
Metropolitan Area Network covers a short distance, and so the error and noise are minimized.
Answer:
False
Question 112.
Local Area Network type of network is easy to set up.
Answer:
True
Question 113.
In Local Area Network data transmits at a very fast rate as the number of computers linked is limited.
Answer:
True
Question 114.
Local Area Network is less expensive hardware and maintenance cost is also low.
Answer:
True
Question 115.
Metropolitan Area Network connects two or more separate computers that reside in the same or different cities.
Answer:
True
Question 116.
Full for of ISP is Internet Service Provider.
Answer:
True
Question 117.
Metropolitan Area Network covers a large geographical area and may serve as an ISP.
Answer:
True
Question 118.
Metropolitan Area Network type of network is hard to design and maintain.3
Answer:
True
Question 119.
A Wide Area Network is a computer network that extends over a large geographical area.
Answer:
True
Question 120.
In the Wide Area Network type of network, the technology is high speed and relatively expensive.
Answer:
True
Question 121.
A Communication medium used for Wide Area networks is Telephone networks or Satellite Link.
Answer:
True
Question 122.
Client-Server is the design of a computer network.
Answer:
False
Question 123.
A Peer-to-Peer network has no dedicated servers.
Answer:
True
Question 124.
Client-Server type of architecture is most suitable for larger networks.
Answer:
True
Question 125.
A computer that is seeking any resource from another computer is a Client computer.
Answer:
False
Question 126.
If a computer has a resource that is served to another computer, it is a client computer.
Answer:
False
Question 127.
Memory means connecting a computer to any other computer anywhere in the world.
Answer:
False

Question 128.
The Internet is generally defined as a global network connecting millions of computers.
Answer:
True
Question 129.
The Internet is a massive network of networks, a networking infrastructure.
Answer:
True
Question 130.
With the help of the Internet, one can easily be in touch with anyone in the whole world by sending electronic mail, by chatting.
Answer:
True
Question 131.
It can be said that services provide a very strong connection or network between computers globally.
Answer:
False
Question 132.
The full form of ARPANET is Advanced Research Projects Agency Network.
Answer:
True
Question 133.
The first workable prototype of the internet came in the late 1960s with the creation of HTML.
Answer:
False
Question 134.
Packets used packet switching to allow multiple computers to communicate on a single network.
Answer:
False
Question 135.
The full form of TCP/IP is Transmission Control Protocol and Internet Protocol.
Answer:
True
Question 136.
HTML communications model that set standards for how data could be transmitted between multiple networks.
Answer:
False
Question 137.
The full form of WWW is World Wide Web.
Answer:
True
Question 138.
Tim Berners-Lee invented the World Wide Web.
Answer:
True
Question 139.
A DNS is a set of rules that governs the communications between computers on a network. Protocol.
Answer:
False
Question 140.
Transmission Control Protocol & Internet Protocol breaks down the message into packets and sends them out into the network.
Answer:
True
Question 141.
The full form of DNS is Domain Name System.
Answer:
True
Question 142.
Protocol translates network address into terms understood by humans and vice-versa.
Answer:
False
Question 143.
DHCP stands for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol.
Answer:
True
Question 144.
DNS can automatically assign internet addresses to computers and users.
Answer:
False
Question 145.
FTP stands for File Transfer Protocol.
Answer:
True
Question 146.
HTTP is used to transfer and manipulate files on the internet.
Answer:
False

Question 147.
The full form of HTTP is HyperText Transfer Protocol.
Answer:
True
Question 148.
HyperText Transfer Protocol is an internet-based protocol for sending and receiving web pages.
Answer:
True
Question 149.
The full form of IMAP is Internet Message Access Protocol.
Answer:
True
Question 150.
FTP is used for receiving e-mail messages from servers on the Internet.
Answer:
False
Question 151.
HTTP maintains a copy of all the emails on the server.
Answer:
False
Question 152.
The full form of IRC is Internet Relay Chat.
Answer:
True
Question 153.
FTP facilitates communication in the form of text.
Answer:
False
Question 154.
POP3 stands for Post Office Protocol Version 3.
Answer:
True
Question 155.
Post Office Protocol Version 3 is used for receiving e-mail from remote mail servers.
Answer:
True
Question 156.
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol is used for sending e-mail messages to the Server on the Internet.
Answer:
True
Question 157.
The full form of ITES is IT Enabled Services.
Answer:
True
Question 158.
IT Enabled Services (ITES), also called as Information Technology.
Answer:
False
Question 159.
IT Enabled Services covers the entire amount of operations that exploit Information Technology for improving the efficiency of an organization.
Answer:
True
Question 160.
Database Manager can develop interactive websites using knowledge of HTML, PHP, and various other programming languages.
Answer:
False
Question 161.
It is possible to have a career as a Financial Advisor with scripting skills.
Answer:
False
Question 162.
After getting knowledge about Database management one can work as a Web Designer.
Answer:
False
Question 163.
Professional Accountant is responsible for ensuring that networks are watertight.
Answer:
False
Question 164.
Information Security Analyst using computerized accounting software can successfully handle accounting work.
Answer:
False
Question 165.
Software developers after getting IT knowledge one can advise and guide others in investing the money in various investment schemes.
Answer:
False
Question 166.
It is possible to become a successful Animator using one’s own creation and innovation.
Answer:
True
Question 167.
Perhaps one of the trendiest and most fun jobs in the sector, a games developer.
Answer:
True
Question 168.
As a career opportunity, to become an Audio/Video Editor, one should be good at tools such as Kdenlive, Audacity.
Answer:
True
Question 169.
Internet of Things is the study and practice of environmentally sustainable computing or IT.
Answer:
False

Question 170.
The goals of Cloud Computing are similar to green chemistry.
Answer:
False
Question 171.
Green computing is important for all classes of systems, ranging from handheld systems to large-scale data centers.
Answer:
True
Question 172.
The full form of IoT is the Internet of Things.
Answer:
True
Question 173.
Data Analytics is the network of physical devices, vehicles, home appliances, and other items embedded with electronics, software, sensors, actuators, and connectivity.
Answer:
False
Question 174.
Artificial Intelligence is the delivery of computing services over the internet.
Answer:
False
Question 175.
Machine Learning is the process of examining data sets in order to draw conclusions about the information.
Answer:
False
Question 176.
Data analytics technologies and techniques are widely used in commercial industries to enable organizations to make more informed business decisions.
Answer:
True
Question 177.
Artificial Intelligence is intelligence demonstrated by machines, in contrast to the natural intelligence displayed by humans and other animals.
Answer:
True
Question 178.
Computer science defines Blockchain research as the study of “intelligent agents”.
Answer:
False
Question 179.
Machine Learning is the scientific study of algorithms and statistical models that computer systems use to effectively perform a specific task.
Answer:
True
Question 180.
Big Data refers to data sets that are too large or complex for traditional data-processing application software.
Answer:
True
Question 181.
Blockchain is a growing list of records, called blocks, which are linked using cryptography.
Answer:
True
3. Multiple Choice Question (Single Choice)
Question 1.
______________ encompasses all of the technologies that we use in order to create, collect, process, protect and store information.
(A) Information Technology
(B) Hardware
(C) Software
(D) System
Answer:
(A) Information Technology
Question 2.
______________ refers to hardware, software (computer programs), and computer networks.
(A) Hardware
(B) Software
(C) Information Technology
(D) Computer Programs
Answer:
(C) Information Technology
Question 3.
Full form of ICT is ______________
(A) Information and Computer Technology
(B) Internet and Communication Technology
(C) Information and Communication Technology
(D) Information and Carrier Technology
Answer:
(C) Information and Communication Technology
Question 4.
______________ concept involves transfer and use of all kinds of information.
(A) Information and Computer Technology
(B) Internet and Communication Technology
(C) Information and Communication Technology
(D) Information and Carrier Technology
Answer:
(C) Information and Communication Technology
Question 5.
______________ is the foundation of economy and a driving force of social changes in the 21st century.
(A) Information and Computer Technology
(B) Internet and Communication Technology
(C) Information and Communication Technology
(D) Information and Carrier Technology
Answer:
(C) Information and Communication Technology

Question 6.
______________ can be any character, text, word, number or raw facts.
(A) Character
(B) Data
(C) Text
(D) Facts
Answer:
(B) Data
Question 7.
______________ is data formatted in a manner that allows it to be utilized by human beings in some significant way
(A) Information
(B) Information Technology
(C) System
(D) Programming
Answer:
(A) Information
Question 8.
The word Computer is derived from a Latin word ______________
(A) Computare
(B) Audio
(C) Video
(D) Graphics
Answer:
(A) Computare
Question 9.
An electronic device that accepts input from the user, processes it according to the instructions given to it, and gives the required result in the form of output, is a ______________
(A) Audio
(B) Video
(C) Graphics
(D) Computer
Answer:
(D) Computer
Question 10.
A ______________ can process data, images, audio, video and graphics.
(A) Audio
(B) Video
(C) Graphics
(D) Computer
Answer:
(D) Computer
Question 11.
______________ accepts data or instructions by way of input.
(A) Audio
(B) Video
(C) Graphics
(D) Computer
Answer:
(D) Computer
Question 12.
______________ stores data.
(A) Audio
(B) Video
(C) Graphics
(D) Computer
Answer:
(D) Computer
Question 13.
______________ can process data as required by the user.
(A) Audio
(B) Video
(C) Graphics
(D) Computer
Answer:
(D) Computer
Question 14.
______________ gives results in the form of output.
(A) Audio
(B) Video
(C) Graphics
(D) Computer
Answer:
(D) Computer
Question 15.
______________ controls all operations inside a computer.
(A) Audio
(B) Video
(C) Graphics
(D) Computer
Answer:
(D) Computer
Question 16.
______________ is a specification detailing of how a set of software and hardware technology standards interact to form a computer system.
(A) Computer Architecture
(B) Hardware
(C) Software
(D) System
Answer:
(A) Computer Architecture
Question 17.
______________ refers to how a computer system is designed and how it works.
(A) Computer Architecture
(B) Hardware
(C) Software
(D) System
Answer:
(A) Computer Architecture
Question 18.
______________ helps users to enter data and commands into a computer system.
(A) Keyboard
(B) Mouse
(C) Input Unit
(D) Input
Answer:
(C) Input Unit
Question 19.
The main function of ______________ devices is to direct commands and data into computer.
(A) Keyboard
(B) Mouse
(C) Input Unit
(D) Input
Answer:
(D) Input
Question 20.
______________ is an input device that enters numbers and characters.
(A) Keyboard
(B) Mouse
(C) Input Unit
(D) Input
Answer:
(A) Keyboard

Question 21.
A ______________ can be an input device for entering directions and commands.
(A) Keyboard
(B) Mouse
(C) Input Unit
(D) Input
Answer:
(B) Mouse
Question 22.
Full full for CPU is ______________
(A) Central Processing Unit
(B) Computer Processing Unit
(C) Central Programmer Unit
(D) Computer Programmer Unit
Answer:
(A) Central Processing Unit
Question 23.
After receiving data and commands from users, a computer system has to process it according to the instructions provided. Here, it has to rely on a component called the ______________
(A) Central Processing Unit
(B) Arithmetic and Logic Unit
(C) Control Unit
(D) Memory Unit
Answer:
(A) Central Processing Unit
Question 24.
The ______________ further uses these three elements Arithmetic and Logic Unit, Control Unit and Memory Unit.
(A) Central Processing Unit
(B) Arithmetic and Logic Unit
(C) Control Unit
(D) Memory unit
Answer:
(A) Central Processing Unit
Question 25.
Full form of ALU is ______________
(A) Asian Learning Unit
(B) Arithmetic and Logic Unit
(C) Arithmetic Learning Unit
(D) Arithmetic Lesson unit
Answer:
(B) Arithmetic and Logic Unit
Question 26.
______________ part of the CPU performs arithmetic operations.
(A) Central Processing Unit
(B) Arithmetic and Logic Unit
(C) Control Unit
(D) Memory unit
Answer:
(B) Arithmetic and Logic Unit
Question 27.
______________ can even perform logical functions like the comparison of data.
(A) Central Processing Unit
(B) Arithmetic and Logic Unit
(C) Control Unit
(D) Memory unit
Answer:
(B) Arithmetic and Logic Unit
Question 28.
______________ is the backbone of computers.
(A) Central Processing Unit
(B) Arithmetic and Logic Unit
(C) Control Unit
(D) Memory Unit
Answer:
(C) Control Unit
Question 29.
______________ responsible for coordinating tasks between all components of a computer system.
(A) Central Processing Unit
(B) Arithmetic and Logic Unit
(C) Control Unit
(D) Memory unit
Answer:
(C) Control Unit
Question 30.
The ______________ collects data from input units and sends it to processing units depending on its nature.
(A) Central Processing Unit
(B) Arithmetic and Logic Unit
(C) Control Unit
(D) Memory Unit
Answer:
(C) Control Unit
Question 31.
______________ transmits processed data to output units to facilitate users.
(A) Central Processing Unit
(B) Arithmetic and Logic Unit
(C) Control Unit
(D) Memory Unit
Answer:
(C) Control Unit

Question 32.
Once a user enters data using input devices, the computer system stores this data in its ______________
(A) Central Processing Unit
(B) Arithmetic and Logic Unit
(C) Control Unit
(D) Memory unit
Answer:
(D) Memory Unit
Question 33.
The ______________ uses a set of pre-programmed instructions to further transmit this data to other parts of the CPU.
(A) Central Processing Unit
(B) Arithmetic and Logic Unit
(C) Control Unit
(D) Memory Unit
Answer:
(D) Memory Unit
Question 34.
______________ is internal memory of the computer.
(A) Primary memory
(B) Random Access Memory
(C) Read-Only Memory
(D) Secondary Memory
Answer:
(A) Primary memory
Question 35.
______________ is also known as main memory.
(A) Primary memory
(B) Random Access Memory
(C) Read-Only Memory
(D) Secondary Memory
Answer:
(A) Primary memory
Question 36.
______________ holds the data and instruction on which computer is currently working.
(A) Primary memory
(B) Random Access Memory
(C) Read-Only Memory
(D) Secondary Memory
Answer:
(A) Primary Memory
Question 37.
RAM stands for ______________
(A) Random Access Memory
(B) Read Access Memory
(C) Ram Access Memory
(D) Random Access Machine
Answer:
(A) Random Access Memory
Question 38.
______________ is known as read/write memory.
(A) Primary memory
(B) Random Access Memory
(C) Read-Only Memory
(D) Secondary Memory
Answer:
(B) Random Access Memory
Question 39.
______________ is generally referred to as main memory of the computer system.
(A) Primary memory
(B) Random Access Memory
(C) Read-Only Memory
(D) Secondary Memory
Answer:
(B) Random Access Memory
Question 40.
______________ is a temporary memory.
(A) Primary memory
(B) Random Access Memory
(C) Read-Only Memory
(D) Secondary Memory
Answer:
(B) Random Access Memory
Question 41.
______________ is also called as Volatile Memory.
(A) Primary memory
(B) Random Access Memory
(C) Read-Only Memory
(D) Secondary Memory
Answer:
(B) Random Access Memory
Question 42.
ROM stands for ______________
(A) Read-Only Memory
(B) Read Only Machine
(C) Rom Only Memory
(D) Ram Only Memory
Answer:
(A) Read-Only Memory
Question 43.
______________ is a Permanent Type memory.
(A) Primary memory
(B) Random Access Memory
(C) Read-Only Memory
(D) Secondary Memory
Answer:
(C) Read-Only Memory
Question 44.
______________ cannot be overwritten by the computer.
(A) Primary memory
(B) Random Access Memory
(C) Read-Only Memory
(D) Secondary Memory
Answer:
(C) Read-Only Memory
Question 45.
______________ is also called Non-Volatile Memory.
(A) Primary memory
(B) Random Access Memory
(C) Read-Only Memory
(D) Secondary Memory
Answer:
(C) Read-Only Memory
Question 46.
______________ is an external memory of the computer.
(A) Primary memory
(B) Random Access Memory
(C) Read-Only Memory
(D) Secondary Memory
Answer:
(D) Secondary Memory
Question 47.
______________ is used to store the huge amount of different programs and information.
(A) Primary memory
(B) Random Access Memory
(C) Read-Only Memory
(D) Secondary Memory
Answer:
(D) Secondary Memory

Question 48.
______________ basically reproduce the data formatted by the computer for user’s benefit.
(A) Output unit
(B) Bit
(C) Nibble
(D) Byte
Answer:
(A) Output unit
Question 49.
______________ is a binary digit that holds only one of two values.
(A) Output unit
(B) Bit
(C) Nibble
(D) Byte
Answer:
(B) Bit
Question 50.
A group of 4 bits is called a ______________
(A) Output unit
(B) Bit
(C) Nibble
(D) Byte
Answer:
(C) Nibble
Question 51.
A group of 8 bits is called a ______________
(A) Output unit
(B) Bit
(C) Nibble
(D) Byte
Answer:
(D) Byte
Question 52.
A ______________ is the smallest unit, which can represent a data item or a character.
(A) Output unit
(B) Bit
(C) Nibble
(D) Byte
Answer:
(D) Byte
Question 53.
1 Byte is ______________
(A) 8 Bits
(B) 1,024 Bytes
(C) 1,024 KiloBytes
(D) 1,024 MegaBytes
Answer:
(A) 8 Bits
Question 54.
1 KiloByte (KB) is ______________
(A) 8 Bits
(B) 1,024 Bytes
(C) 1,024 KiloBytes
(D) 1,024 MegaBytes
Answer:
(B) 1,024 Bytes
Question 55.
1 MegaByte (MB) is ______________
(A) 8 Bits
(B) 1,024 Bytes
(C) 1,024 KiloBytes
(D) 1,024 MegaBytes
Answer:
(C) 1,024 KiloBytes
Question 56.
1 GigaByte (GB) is ______________
(A) 8 Bits
(B) 1,024 Bytes
(C) 1,024 KiloBytes
(D) 1,024 MegaBytes
Answer:
(D) 1,024 MegaBytes
Question 57.
1 TeraByte (TB) is ______________
(A) 1,024 GigaBytes
(B) 1,024 TeraBytes
(C) 1,024 PetaBytes
(D) MegaBytes
Answer:
(A) 1,024 GigaBytes
Question 58.
1 PetaByte (PB) is ______________
(A) 1,024 GigaBytes
(B) 1,024 TeraBytes
(C) 1,024 PetaBytes
(D) MegaBytes
Answer:
(B) 1,024 TeraBytes
Question 59.
1 ExaByte (EB) is ______________
(A) 1,024 GigaBytes
(B) 1,024 TeraBytes
(C) 1,024 PetaBytes
(D) MegaBytes
Answer:
(C) 1,024 PetaBytes
Question 60.
______________ comprises of the physical components that a computer system requires to function.
(A) Computer hardware
(B) Program
(C) Software
(D) Open source software
Answer:
(A) Computer hardware
Question 61.
A set of instructions given to the computer is known as a ______________
(A) Computer hardware
(B) Program
(C) Software
(D) Open source software
Answer:
(B) Program
Question 62.
Program or set of programs are called as ______________
(A) Computer hardware
(B) Program
(C) Software
(D) Open source software
Answer:
(C) Software
Question 63.
______________ is a generic term used to describe computer programs.
(A) Computer hardware
(B) Program
(C) Software
(D) Open source software
Answer:
(C) Software
Question 64.
______________ refers to the software which releases code in public domain for anyone to use.
(A) Computer hardware
(B) Program
(C) Software
(D) Open source software
Answer:
(D) Open source software
Question 65.
Full form of FOSS ______________
(A) Free Open Source Software Policy
(B) Free Open System Source Policy
(C) Free Open Source System Policy
(D) First Open Source Software Policy
Answer:
(A) Free Open Source Software Policy

Question 66.
______________ and it enabled them to save some millions of rupees each year in licensing costs.
(A) Free Open Source Software Policy
(B) Free Open System Source Policy
(C) Free Open Source System Policy
(D) First Open Source Software Policy
Answer:
(A) Free Open Source Software Policy
Question 67.
In case of ______________, user has to purchase the software before using it.
(A) Free Open Source Software Policy
(B) Free Open System Source Policy
(C) Free Open Source System Policy
(D) Closed Source Software
Answer:
(D) Closed Source Software
Question 68.
______________ is a program or group of programs designed for end-users.
(A) Application Software
(B) System Software
(C) Linux Operating system
(D) Operating system
Answer:
(A) Application Software
Question 69.
______________ is also called end-user programs.
(A) Application Software
(B) System Software
(C) Linux Operating system
(D) Operating system
Answer:
(A) Application Software
Question 70.
______________ is a set of instructions required for a computer to work.
(A) Application Software
(B) System Software
(C) Linux Operating system
(D) Operating system
Answer:
(B) System Software
Question 71.
______________ is a program that allows different applications and various components of hardware.
(A) Application Software
(B) System Software
(C) Linux Operating System
(D) Operating system
Answer:
(C) Linux Operating System
Question 72.
A computer would not be able to function correctly without an ______________
(A) Application Software
(B) System Software
(C) Linux Operating System
(D) Operating System
Answer:
(D) Operating System
Question 73.
An ______________ is a software program that empowers the computer hardware to communicate and operate with the computer software.
(A) Application Software
(B) System Software
(C) Linux Operating System
(D) Operating System
Answer:
(D) Operating System
Question 74.
The ______________ boots up the computer and makes sure that everything is operational.
(A) Application Software
(B) System Software
(C) Linux Operating System
(D) Operating System
Answer:
(D) Operating System
Question 75.
The ______________ is also what runs the cell phone and most of the electronic devices.
(A) Application Software
(B) System Software
(C) Linux Operating system
(D) Operating System
Answer:
(D) Operating System
Question 76.
The ______________ usually come preloaded on any computer, tablet, laptop or cell phone that user buy.
(A) Application Software
(B) System Software
(C) Linux Operating System
(D) Operating System
Answer:
(D) Operating System
Question 77.
Full form of DOS is ______________
(A) Disk Operating System
(B) Disk Open System
(C) Dynamic Operating System
(D) Dynamic Open System
Answer:
(A) Disk Operating System
Question 78.
______________ is a series of operating systems that are designed by Microsoft.
(A) Windows
(B) Mac OS
(C) Chrome OS
(D) Linux
Answer:
(A) Windows
Question 79.
______________ is the most commonly used operating system.
(A) Windows
(B) Mac OS
(C) Chrome OS
(D) Linux
Answer:
(A) Windows
Question 80.
Apple Corporation’s registered operating system is called ______________
(A) Windows
(B) Mac OS
(C) Chrome OS
(D) Linux
Answer:
(B) Mac OS
Question 81.
______________ is an open-source operating system created by Google.
(A) Windows
(B) Mac OS
(C) Chrome OS
(D) Linux
Answer:
(C) Chrome OS
Question 82.
______________ is an open-source, portable, multi-multiprogramming, operating system.
(A) Windows
(B) Mac OS
(C) Chrome OS
(D) Linux
Answer:
(D) Linux
Question 83.
______________ is a free and open source operating system for mobile phones provided by Google.
(A) Android
(B) Asha
(C) Blackberry
(D) IOS
Answer:
(A) Android
Question 84.
______________ is used by Nokia phones. This is closed source OS.
(A) Android
(B) Asha
(C) Blackberry
(D) IOS
Answer:
(B) Asha
Question 85.
______________ is a closed source operating system for smartphone and tablet devices.
(A) Android
(B) Asha
(C) Blackberry
(D) IOS
Answer:
(C) Blackberry
Question 86.
______________ is Apple’s closed source operating system for Apple’s iPhone, iPod Touch, iPad and second-generation Apple TVs.
(A) Android
(B) Asha
(C) Blackberry
(D) iPhone Operating System
Answer:
(D) Iphone Operating System
Question 87.
______________ Phone is developed by Microsoft as a closed source operating system for mobile phones.
(A) Windows
(B) Android
(C) Linux
(D) Ubuntu
Answer:
(A) Windows

Question 88.
______________ is used as the predominantly backbone of the Internet.
(A) Windows
(B) Android
(C) Linux
(D) Ubuntu
Answer:
(C) Linux
Question 89.
______________ is one of the most popular GNU/Linux distribution.
(A) Windows
(B) Android
(C) Linux
(D) Ubuntu
Answer:
(D) Ubuntu
Question 90.
Full form of GUI is ______________
(A) Graphical User Interface
(B) Graphic Using Internet
(C) Game Using Internet
(D) Game User Internet
Answer:
(A) Graphical User Interface
Question 91.
Full form of CLI ______________
(A) Command Line Internet
(B) Command Line Interface
(C) Central Line Interface
(D) Computer Line Interface
Answer:
(B) Command Line Interface
Question 92.
The ______________ is when the user interacts with the computer using images, icons, and dialog boxes.
(A) Graphical User Interface
(B) Command Line Interface
(C) Search
(D) Home
Answer:
(A) Graphical User Interface
Question 93.
The ______________ option is used for quick search of the application.
(A) Graphical User Interface
(B) Command Line Interface
(C) Search
(D) Home
Answer:
(C) Search
Question 94.
The ______________ folder is where all the personal documents and settings are stored.
(A) Graphical User Interface
(B) Command Line Interface
(C) Search
(D) Home
Answer:
(D) Home
Question 95.
The ______________ is when user interacts with the computer using text.
(A) Graphical User Interface
(B) Command Line Interface
(C) Search
(D) Home
Answer:
(B) Command Line Interface
Question 96.
The ______________ are programs that are run when user types command name.
(A) Commands
(B) Graphical User Interface
(C) Search
(D) Home
Answer:
(A) Commands
Question 97.
______________ is Free and Open Source.
(A) Linux
(B) Proprietary
(C) Repositories
(D) Package
Answer:
(A) Linux
Question 98.
______________ Operating System is free from viruses.
(A) Linux
(B) Proprietary
(C) Repositories
(D) Package
Answer:
(A) Linux
Question 99.
______________ Operating Systems can update themselves.
(A) Linux
(B) Proprietary
(C) Repositories
(D) Package
Answer:
(B) Proprietary
Question 100.
______________ is a collection of software for a Linux distribution on the server.
(A) Linux
(B) Proprietary
(C) Repositories
(D) Package
Answer:
(C) Repositories
Question 101.
The ______________ manager updates the operating system as well as other softwares periodically.
(A) Linux
(B) Proprietary
(C) Repositories
(D) Package
Answer:
(D) Package
Question 102.
______________ is a group of interconnected computers or devices to have communication within themselves.
(A) Computer Network
(B) Local Area Network
(C) Wide Area Network
(D) Metropolitan Area Network
Answer:
(A) Computer Network
Question 103.
A ______________ consists of a collection of computers, printers and other equipment that is connected together.
(A) Computer Network
(B) Local Area Network
(C) Wide Area Network
(D) Metropolitan Area Network
Answer:
(A) Computer Network
Question 104.
Full form of LAN is ______________
(A) Local Area Network
(B) Local Access Network
(C) Live Area Network
(D) Live Access Network
Answer:
(A) Local Area Network
Question 105.
Full form of MAN is ______________
(A) Metropolitan Area Network
(B) Metropolitan Access network
(C) Mobile Area Network
(D) Mobile Access Network
Answer:
(A) Metropolitan Area Network
Question 106.
Full form of WAN is ______________
(A) Wide Area Network
(B) World Area Network
(C) Wonder Area Network
(D) Wide Access Network
Answer:
(A) Wide Area Network
Question 107.
______________ type of network covers the smallest area.
(A) Computer Network
(B) Local Area Network
(C) Wide Area Network
(D) Metropolitan Area Network
Answer:
(B) Local Area Network

Question 108.
______________ covers an area larger than LAN.
(A) Computer Network
(B) Local Area Network
(C) Wide Area Network
(D) Metropolitan Area Network
Answer:
(D) Metropolitan Area Network
Question 109.
______________ type of network comprises the largest of all.
(A) Computer Network
(B) Local Area Network
(C) Wide Area Network
(D) Metropolitan Area Network
Answer:
(C) Wide Area Network
Question 110.
In ______________ usage area is limited to areas such as an office building, home, hospital, schools, etc.
(A) Computer Network
(B) Local Area Network
(C) Wide Area Network
(D) Metropolitan Area Network
Answer:
(B) Local Area Network
Question 111.
______________ covers a short distance, and so the error and noise are minimized.
(A) Computer Network
(B) Local Area Network
(C) Wide Area Network
(D) Metropolitan Area Network
Answer:
(B) Local Area Network
Question 112.
______________ type of network is easy to setup.
(A) Computer Network
(B) Local Area Network
(C) Wide Area Network
(D) Metropolitan Area Network
Answer:
(B) Local Area Network
Question 113.
In ______________ data transmits at a very fast rate as the number of computers linked are limited.
(A) Computer Network
(B) Local Area Network
(C) Wide Area Network
(D) Metropolitan Area Network
Answer:
(B) Local Area Network
Question 114.
______________ is a less expensive hardware and maintenance cost is also low.
(A) Computer Network
(B) Local Area Network
(C) Wide Area Network
(D) Metropolitan Area Network
Answer:
(B) Local Area Network
Question 115.
______________ connects two or more separate computers that reside in the same or different cities.
(A) Computer Network
(B) Local Area Network
(C) Wide Area Network
(D) Metropolitan Area Network
Answer:
(D) Metropolitan Area Network
Question 116.
Full for of ISP is ______________
(A) Internet Service Provider
(B) International Service Provider
(C) Indian Server Provider
(D) Internet Server Provider
Answer:
(A) Internet Service Provider
Question 117.
______________ covers a large geographical area and may serve as an ISP.
(A) Computer Network
(B) Local Area Network
(C) Wide Area Network
(D) Metropolitan Area Network
Answer:
(D) Metropolitan Area Network
Question 118.
______________ type of network is hard to design and maintain.
(A) Computer Network
(B) Local Area Network
(C) Wide Area Network
(D) Metropolitan Area Network
Answer:
(D) Metropolitan Area Network
Question 119.
______________ is a computer network that extends over a large geographical area.
(A) Computer Network
(B) Local Area Network
(C) Wide Area Network
(D) Metropolitan Area Network
Answer:
(C) Wide Area Network
Question 120.
In ______________ type of network the technology is high speed and relatively expensive.
(A) Computer Network
(B) Local Area Network
(C) Wide Area Network
(D) Metropolitan Area Network
Answer:
(C) Wide Area Network
Question 121.
A Communication medium used for ______________ is Telephone Network or Satellite Link.
(A) Computer Network
(B) Local Area Network
(C) Wide Area Network
(D) Metropolitan Area Network
Answer:
(C) Wide Area Network
Question 122.
______________ is the design of a computer network.
(A) Network architecture
(B) Peer-to-Peer
(C) Client-Server
(D) Client
Answer:
(A) Network Architecture
Question 123.
A ______________ network has no dedicated servers.
(A) Network architecture
(B) Peer-to-Peer
(C) Client-Server
(D) Client
Answer:
(B) Peer-to-Peer
Question 124.
______________ type of architecture is most suitable for larger network.
(A) Network architecture
(B) Peer-to-Peer
(C) Client-Server
(D) Client
Answer:
(C) Client-Server
Question 125.
A computer which is seeking any resource from another computer is a ______________ computer.
(A) Network architecture
(B) Peer-to-Peer
(C) Client-Server
(D) Client
Answer:
(D) Client

Question 126.
If a computer has a resource which is served to another computer, it is a ______________ computer.
(A) Server
(B) Peer-to-Peer
(C) Client-Server
(D) Client
Answer:
(A) Server
Question 127.
______________ means connecting computer to any other computer anywhere in the world.
(A) Internet
(B) Local Area Network
(C) Wide Area Network
(D) Metropolitan Area Network
Answer:
(A) Internet
Question 128.
The ______________ is generally defined as a global network connecting millions of computers.
(A) Internet
(B) Local Area Network
(C) Wide Area Network
(D) Metropolitan Area Network
Answer:
(A) Internet
Question 129.
The ______________ is a massive network of networks, a networking infrastructure.
(A) Internet
(B) Local Area Network
(C) Wide Area Network
(D) Metropolitan Area Network
Answer:
(A) Internet
Question 130.
With the help of the ______________, one can easily be in touch with anyone in the whole world by sending electronic mail, by chatting.
(A) Internet
(B) Local Area Network
(C) Wide Area Network
(D) Metropolitan Area Network
Answer:
(A) Internet
Question 131.
It can be said that ______________ provides a very strong connection or network between computers globally.
(A) Internet
(B) Local Area Network
(C) Wide Area Network
(D) Metropolitan Area Network
Answer:
(A) Internet
Question 132.
Full form of ARPANET is ______________
(A) Advanced Research Projects Agency Network
(B) Advanced Research Project Area Network
(C) Advanced Research Project Access Network
(D) Advance Recovery Project Area Network
Answer:
(A) Advanced Research Projects Agency Network
Question 133.
The first workable prototype of the internet came in the late 1960’s with the creation of ______________
(A) Advanced Research Projects Agency Network
(B) Transmission Control Protocol and Internet Protocol
(C) World Wide Web
(D) Local Area Network
Answer:
(A) Advanced Research Projects Agency Network
Question 134.
______________ used packet switching to allow multiple computers to communicate on a single network.
(A) Advanced Research Projects Agency Network
(B) Transmission Control Protocol and Internet Protocol
(C) World Wide Web
(D) Local Area Network
Answer:
(A) Advanced Research Projects Agency Network
Question 135.
Full form of TCP/IP is ______________
(A) Transmission Control Protocol and Internet Protocol
(B) Transfer Control Protocol and Internet Protocol
(C) Transmission Control Password and Internet Password
(D) Transfer Control Process and Internet Password
Answer:
(A) Transmission Control Protocol and Internet Protocol
Question 136.
______________ communications model that set standards for how data could be transmitted between multiple networks.
(A) Advanced Research Projects Agency Network
(B) Transmission Control Protocol and Internet Protocol
(C) World Wide Web
(D) Local Area Network
Answer:
(B) Transmission Control Protocol and Internet Protocol
Question 137.
Full form of WWW is ______________
(A) World Wide Website
(B) Web Wide World
(C) World Wide Web
(D) Wide Web World
Answer:
(C) World Wide Web
Question 138.
Tim Berners-Lee invented the ______________
(A) Advanced Research Projects Agency Network
(B) Transmission Control Protocol and Internet Protocol
(C) World Wide Web
(D) Local Area Network
Answer:
(C) World Wide Web
Question 139.
A ______________ is a set of rules that governs the communications between computers on a network.
(A) Protocol
(B) Transmission Control Protocol & Internet Protocol
(C) Domain Name System
(D) Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
Answer:
(A) Protocol
Question 140.
______________ breaks down the message into packets and sends them out into the network.
(A) Protocol
(B) Transmission Control Protocol & Internet Protocol
(C) Domain Name System
(D) Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
Answer:
(B) Transmission Control Protocol & Internet Protocol

Question 141.
Full form of DNS is ______________
(A) Domain Name System
(B) Dynamic Name System
(C) Domain Name Service
(D) Dynamic Name Service
Answer:
(A) Domain Name System
Question 142.
______________ translates network address into terms understood by humans and vice-versa.
(A) Protocol
(B) Transmission Control Protocol & Internet Protocol
(C) Domain Name System
(D) Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
Answer:
(C) Domain Name System
Question 143.
DHCP stands for ______________
(A) Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
(B) Domain Host Configuration Protocol
(C) Dynamic Host Configuration Process
(D) Domain Host Configuration Process
Answer:
(A) Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
Question 144.
______________ can automatically assign internet addresses to computers and users.
(A) Protocol
(B) Transmission Control Protocol & Internet Protocol
(C) Domain Name System
(D) Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
Answer:
(D) Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
Question 145.
FTP stands for ______________
(A) File Transfer Protocol
(B) File Transfer Process
(C) File Time Pass
(D) File Time Protocol
Answer:
(A) File Transfer Protocol
Question 146.
______________ is used to transfer and manipulate files on the internet.
(A) File Transfer Protocol
(B) HyperText Transfer Protocol
(C) Internet Message Access Protocol
(D) Internet Relay Chat
Answer:
(A) File Transfer Protocol
Question 147.
Full form of HTTP is ______________
(A) Hyper Text Transfer Protocol
(B) Hyper Test Transfer Protocol
(C) Hyper Transfer Text
(D) Hyper Text Transfer Process
Answer:
(A) Hyper Text Transfer Protocol
Question 148.
______________ is an internet-based protocol for sending and receiving web pages.
(A) File Transfer Protocol
(B) Hyper Text Transfer Protocol
(C) Internet Message Access Protocol
(D) Internet Relay Chat
Answer:
(B) Hyper Text Transfer Protocol
Question 149.
Full form of IMAP is ______________
(A) Internet Message Access Protocol
(B) Internet Message Access Process
(C) Internet Message Access Program
(D) Information Message Access Protocol
Answer:
(A) Internet Message Access Protocol
Question 150.
______________ is used for receiving e-mail messages from server on the Internet.
(A) File Transfer Protocol
(B) HyperText Transfer Protocol
(C) Internet Message Access Protocol
(D) Internet Relay Chat
Answer:
(C) Internet Message Access Protocol
Question 151.
______________ maintains a copy of all the emails on server.
(A) File Transfer Protocol
(B) Hyper Text Transfer Protocol
(C) Internet Message Access Protocol
(D) Internet Relay Chat
Answer:
(C) Internet Message Access Protocol
Question 152.
Full form of IRC is ______________
(A) Internet Relay Chat
(B) International Relay Chat
(C) Internet Regional Chat
(D) Internet Random Chat
Answer:
(A) Internet Relay Chat
Question 153.
______________ facilitates communication in the form of text.
(A) File Transfer Protocol
(B) Hyper Text Transfer Protocol
(C) Internet Message Access Protocol
(D) Internet Relay Chat
Answer:
(D) Internet Relay Chat
Question 154.
POP3 stands for ______________
(A) Post Office Protocol Version 3
(B) Post Office Process Version 3
(C) Protocol Office Post Version 3
(D) Process Office Protocol Version 3
Answer:
(A) Post Office Protocol Version 3
Question 155.
______________ is used for receiving e-mail from remote mail servers.
(A) File Transfer Protocol
(B) Hyper Text Transfer Protocol
(C) Internet Message Access Protocol
(D) Post Office Protocol Version 3
Answer:
(D) Post Office Protocol Version 3
Question 156.
______________ is used for sending e-mail messages to the Server on the Internet.
(A) File Transfer Protocol
(B) Hyper Text Transfer Protocol
(C) Internet Message Access Protocol
(D) Simple Mail Transfer Protocol
Answer:
(D) Simple Mail Transfer Protocol
Question 157.
Full form of ITES is ______________
(A) IT Enabled Services
(B) IT Encrypted Service
(C) IT Essential Service
(D) IT Safe Service
Answer:
(A) IT Enabled Services

Question 158.
IT Enabled Services (ITES), also called as ______________
(A) Web Enabled Services
(B) Word Enabled Services
(C) Wide Enabled Services
(D) Web Engineer Services
Answer:
(A) Web Enabled Services
Question 159.
______________ covers the entire amount of operations which exploit Information Technology for improving efficiency of an organization.
(A) File Transfer Protocol
(B) Hyper Text Transfer Protocol
(C) Internet Message Access Protocol
(D) IT Enabled Services
Answer:
(D) IT Enabled Services
Question 160.
______________ can develop interactive websites using knowledge of HTML, PHP and various
other programming languages.
(A) Web Designer
(B) Software Developer
(C) Database Manager
(D) Information Security Analyst
Answer:
(A) Web Designer
Question 161.
It is possible to have career as a ______________ with the scripting skills.
(A) Web Designer
(B) Software Developer
(C) Database Manager
(D) Information Security Analyst
Answer:
(B) Software Developer
Question 162.
After getting knowledge about Database management one can work as a ______________
(A) Web Designer
(B) Software Developer
(C) Database Manager
(D) Information Security Analyst
Answer:
(C) Database Manager
Question 163.
______________ are responsible for ensuring that networks are watertight.
(A) Web Designer
(B) Software Developer
(C) Database Manager
(D) Information Security Analyst
Answer:
(D) Information Security Analyst
Question 164.
______________ using computerized accounting software can successfully handle accounting work.
(A) Professional Accountant
(B) Financial Advisor
(C) Animator
(D) Games Developer
Answer:
(A) Professional Accountant
Question 165.
______________ after getting IT knowledge one can advise and guide others in investing the money in various investment schemes.
(A) Professional Accountant
(B) Financial Advisor
(C) Animator
(D) Games Developer
Answer:
(B) Financial Advisor
Question 166.
It is possible to become a successful ______________ using one’s own creation and innovation.
(A) Professional Accountant
(B) Financial Advisor
(C) Animator
(D) Games Developer
Answer:
(C) Animator
Question 167.
Perhaps one of the trendiest and most fun jobs in the sector, a ______________
(A) Professional Accountant
(B) Financial Advisor
(C) Animator
(D) Games Developer
Answer:
(D) Games Developer
Question 168.
As a career opportunity, to become an ______________, one should be good in tools such as Kdenlive, Audacity.
(A) Professional Accountant
(B) Financial Advisor
(C) Animator
(D) Audio/Video Editor
Answer:
(D) Audio/Video Editor
Question 169.
______________ is the study and practice of environmentally sustainable computing or IT.
(A) Green Computing
(B) Internet of Things
(C) Cloud Computing
(D) Data Analytics
Answer:
(A) Green Computing
Question 170.
The goals of ______________ are similar to green chemistry
(A) Green Computing
(B) Internet of Things
(C) Cloud Computing
(D) Data Analytics
Answer:
(A) Green Computing

Question 171.
______________ is important for all classes of systems, ranging from handheld systems to largescale data centers.
(A) Green Computing
(B) Internet of Things
(C) Cloud Computing
(D) Data Analytics
Answer:
(A) Green Computing
Question 172.
Full form of IOT is ______________
(A) Internet of Time
(B) Internet of Things
(C) International of Time
(D) Intelligent of Things
Answer:
(B) Internet of Things
Question 173.
The ______________ is the network of physical devices, vehicles, home appliances, and other items embedded with electronics, software, sensors, actuators, and connectivity.
(A) Green Computing
(B) Internet of Things
(C) Cloud Computing
(D) Data Analytics
Answer:
(B) Internet of Things
Question 174.
______________ is the delivery of computing services over the internet.
(A) Green Computing
(B) Internet of Things
(C) Cloud Computing
(D) Data Analytics
Answer:
(C) Cloud Computing
Question 175.
______________ is the process of examining data sets in order to draw conclusions about the information.
(A) Green Computing
(B) Internet of Things
(C) Cloud Computing
(D) Data Analytics
Answer:
(D) Data Analytics
Question 176.
______________ technologies and techniques are widely used in commercial industries to enable
organizations to make more-informed business decisions.
(A) Green Computing
(B) Internet of Things
(C) Cloud Computing
(D) Data Analytics
Answer:
(D) Data Analytics
Question 177.
______________ is intelligence demonstrated by machines, in contrast to the natural intelligence displayed by humans and other animals.
(A) Artificial Intelligence
(B) Machine Learning
(C) Big Data
(D) Blockchain
Answer:
(A) Artificial Intelligence
Question 178.
Computer science defines ______________ research as the study of “intelligent agents”.
(A) Artificial Intelligence
(B) Machine Learning
(C) Big Data
(D) Blockchain
Answer:
(A) Artificial Intelligence
Question 179.
______________ is the scientific study of algorithms and statistical models that computer systems use to effectively perform a specific task.
(A) Artificial Intelligence
(B) Machine Learning
(C) Big Data
(D) Blockchain
Answer:
(B) Machine Learning
Question 180.
______________ refers to data sets that are too large or complex for traditional data-processing application software.
(A) Artificial Intelligence
(B) Machine Learning
(C) Big Data
(D) Blockchain
Answer:
(C) Big Data
Question 181.
______________ is a growing list of records, called blocks, which are linked using cryptography.
(A) Artificial Intelligence
(B) Machine Learning
(C) Big Data
(D) Blockchain
Answer:
(D) Blockchain
4. Multiple Choice Two Correct Answer.
Question 1.
Computer Architecture is a specification detailing of how a set of ______________ and ______________ technology standards interact to form a computer system
(A) Software
(B) Numbers
(C) Data
(D) Commands
(E) Hardware
Answer:
(A) Software (E) Hardware
Question 2.
Input unit helps users to enter ______________ and ______________ into a computer system.
(A) Software
(B) Numbers
(C) Data
(D) Commands
(E) Hardware
Answer:
(C) Data (D) Commands
Question 3.
The main function of input devices is to ______________ and ______________ into computer.
(A) Software
(B) Numbers
(C) Direct Commands
(D) Data
(E) Hardware
Answer:
(C) Direct Commands (D) Data

Question 4.
Keyboard is an input device that enters ______________ and ______________
(A) Software
(B) Numbers
(C) Data
(D) Characters
(E) Hardware
Answer:
(B) Numbers (D) Characters
Question 5.
A Mouse can be an input device for entering ______________ and ______________
(A) Directions
(B) Commands
(C) Data
(D) Logical
(E) Comparison
Answer:
(A) Directions (B) Commands
Question 6.
After receiving ______________ and ______________ from users, a computer system has to process it according to the instructions provided. Here, it has to rely on a component called the Central Processing Unit.
(A) Directions
(B) Commands
(C) Data
(D) Logical
(E) Comparison
Answer:
(B) Commands (C) Data
Question 7.
Arithmetic and Logic Unit can even perform ______________ functions like the ______________ of data.
(A) Directions
(B) Commands
(C) Data
(D) Logical
(E) Comparison
Answer:
(D) Logical (E) Comparison
Question 8.
There are two types of memory ______________ & ______________
(A) Primary Memory
(B) Random Access Memory
(C) Secondary Memory
(D) Read Only Memory
(E) Data
Answer:
(A) Primary Memory (C) Secondary Memory
Question 9.
Primary memory is generally of two types ______________ & ______________
(A) Primary Memory
(B) Random Access Memory
(C) Secondary Memory
(D) Read Only Memory
(E) Data
Answer:
(B) Random Access Memory (D) Read Only Memory
Question 10.
Primary Memory holds the ______________ and ______________ on which computer is currently working.
(A) Primary Memory
(B) Instruction
(C) Secondary Memory
(D) Read-Only Memory
(E) Data
Answer:
(B) Instruction (E) Data
Question 11.
______________ and ______________ is often measured in Megabytes (MB) and Gigabytes (GB).
(A) Computer storage
(B) Megabytes (MB)
(C) Memory
(D) Gigabytes (GB)
(E) Data
Answer:
(A) Computer storage (C) Memory
Question 12.
Computer storage and memory is often measured in ______________ and ______________
(A) Computer storage
(B) Megabytes (MB)
(C) Memory
(D) Gigabytes (GB)
(E) Data
Answer:
(B) Megabytes (MB) (D) Gigabytes (GB)
Question 13.
A byte is the smallest unit, which can represent a ______________ item or a ______________
(A) Computer storage
(B) Character
(C) Memory
(D) Gigabytes (GB)
(E) Data
Answer:
(B) Character (E) Data
Question 14.
Computer hardware comprises of the ______________ components that a computer system requires to ______________
(A) Application Software
(B) Physical
(C) System Software
(D) Function
(E) Hardware
Answer:
(B) Physical (D) Function
Question 15.
Computer software can be classified into two types based on its utility ______________ & ______________
(A) Application Software
(B) Physical
(C) System Software
(D) Function
(E) Hardware
Answer:
(A) Application Software (C) System Software

Question 16.
Linux Operating system is a program that allows different ______________ and various components of ______________
(A) Application
(B) Physical
(C) System Software
(D) Function
(E) Hardware
Answer:
(A) Application (E) Hardware
Question 17.
An operating system is a software program that empowers the ______________ to communicate and operate with the ______________
(A) Application Software
(B) Physical
(C) Computer Hardware
(D) Function
(E) Computer Software
Answer:
(C) Computer Hardware (E) Computer Software
Question 18.
Windows is a series of ______________ that are designed by ______________
(A) Operating Systems
(B) Open-Source Operating
(C) Microsoft
(D) Google
(E) Portable
Answer:
(A) Operating Systems (C) Microsoft
Question 19.
Chrome OS is an ______________ system created by ______________
(A) Operating Systems
(B) Open-Source Operating
(C) Microsoft
(D) Google
(E) Portable
Answer:
(B) Open-Source Operating (D) Google
Question 20.
Linux is an open-source, ______________, ______________, operating system.
(A) Operating Systems
(B) Open-Source Operating
(C) Portable
(D) Google
(E) Multi-User-Multiprogramming
Answer:
(C) Portable (E) Multi-User-Multiprogramming
Question 21.
Android is a free and ______________ for mobile phones provided by ______________
(A) Operating Systems
(B) Open-Source Operating
(C) Multi- Multiprogramming
(D) Google
(E) Portable
Answer:
(B) Open-Source Operating (D) Google
Question 22.
Asha is used by ______________ phones. This is ______________ OS.
(A) Nokia
(B) Microsoft
(C) Closed Source
(D) Multitasking
(E) Multi-User
Answer:
(A) Nokia (C) Closed Source
Question 23.
Blackberry is a closed source operating system for ______________ and ______________
(A) Smartphone
(B) Tablet Devices
(C) Microsoft
(D) Multitasking
(E) Multi-User
Answer:
(A) Smartphone (B)Tablet Devices
Question 24.
Windows Phone is developed by ______________ as a ______________ for mobile phones.
(A) Nokia
(B) Microsoft
(C) Closed Source Operating System
(D) Multitasking
(E) Multi-User
Answer:
(B) Microsoft (C) Closed Source Operating System

Question 25.
UNIX was trademarked in 1969 by a group of AT&T employees at Bell Labs as a ______________ and ______________ computer operating system.
(A) Smartphone
(B) Tablet Devices
(C) Microsoft
(D) Multitasking
(E) Multi-User
Answer:
(D) Multitasking (E) Multi-User
Question 26.
The Search option is used for ______________ search of the ______________
(A) Quick
(B) Personal
(C) Application
(D) Settings
(E) Software
Answer:
(A) Quick (C) Application
Question 27.
The Home folder is where all the ______________ documents and ______________ are stored.
(A) Quick
(B) Personal
(C) Application
(D) Settings
(E) Software
Answer:
(B) Personal (D) Settings
Question 28.
Repositories is a collection of ______________ for a ______________ distribution on the server.
(A) Quick
(B) Software
(C) Application
(D) Settings
(E) Linux
Answer:
(B) Software (E) Linux
Question 29.
The Package manager updates the ______________ as well as other ______________ periodically.
(A) Operating System
(B) Softwares
(C) Application
(D) Settings
(E) Linux
Answer:
(A) Operating System (B) Softwares
Question 30.
Computer Network is a group of ______________ or ______________ to have communication within themselves.
(A) Interconnected Computers
(B) Devices
(C) High Speed
(D) Relatively Expensive
(E) Telephone Network
Answer:
(A) Interconnected Computers (B) Devices
Question 31.
In Wide Area Network type of network the technology is ______________ and ______________
(A) Interconnected Computers
(B) Devices
(C) High Speed
(D) Relatively Expensive
(E) Telephone Network
Answer:
(C) Highspeed (D) Relatively Expensive
Question 32.
A Communication medium used for WAN is ______________ or ______________
(A) Devices
(B) High Speed
(C) Relatively Expensive
(D) Telephone Network
(E) Satellite Link
Answer:
(D) Telephone Network (E) Satellite Link
Question 33.
Two of the most widely used types of network architecture are ______________ and ______________
(A) Peer-to-Peer
(B) Devices
(C) Client/Server
(D) High Speed
(E) Relatively Expensive
Answer:
(A) Peer-to-Peer (C) Client/Server
Question 34.
There are two types of machines in network, ______________ and ______________
(A) Client
(B) Devices
(C) Server
(D) High Speed
(E) Relatively Expensive
Answer:
(A) Client (C) Server
Question 35.
The first workable prototype of the ______________ came in the late 1960’s with the creation of ______________
(A) Internet
(B) Advanced Research Projects Agency Network
(C) Packet
(D) Single
(E) Network
Answer:
(A) Internet (B) Advanced Research Projects Agency Network

Question 36.
Advanced Research Projects Agency Network used ______________ switching to allow multiple computers to communicate on a ______________ network.
(A) Internet
(B) Advanced Research Projects Agency Network
(C) Packet
(D) Single
(E) Network
Answer:
(C) Packet (D) Single
Question 37.
Transmission Control Protocol & Internet Protocol breaks down the message into ______________ and sends them out into the ______________
(A) Internet
(B) Advanced Research Projects Agency Network
(C) Packets
(D) Single
(E) Network
Answer:
(C) Packets (E) Network
Question 38.
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol can automatically assign internet addresses to ______________ and ______________
(A) Computers
(B) Internet
(C) Advanced Research Projects Agency Network
(D) Users
(E) Network
Answer:
(A) Computers (D) Users
Question 39.
File Transfer Protocol is used to ______________ and ______________ files on the internet.
(A) Transfer
(B) Sending
(C) Manipulate
(D) Receiving
(E) HTML
Answer:
(A) Transfer (C) Manipulate
Question 40.
HyperText Transfer Protocol is an internet-based protocol for ______________ and ______________ web pages.
(A) Transfer
(B) Sending
(C) Manipulate
(D) Receiving
(E) HTML
Answer:
(B) Sending (D) Receiving
Question 41.
The outcome of an IT Enabled Service is in two forms ______________ & ______________
(A) Direct Improved Service
(B) Indirect Benefits
(C) Manipulate
(D) Receiving
(E) HTML
Answer:
(A) Direct Improved Service (B) Indirect Benefits
Question 42.
Web Designer can develop interactive websites using knowledge of ______________, ______________ and various other programming languages.
(A) Direct Improved Service
(B) Indirect Benefits
(C) HTML
(D) Receiving
(E) PHP
Answer:
(C) HTML (E) PHP
Question 43.
Professional Accountant using ______________ software can successfully handle ______________ work.
(A) Computerized Accounting
(B) Accounting
(C) HTML
(D) Receiving
(E) PHP
Answer:
(A) Computerized Accounting (B) Accounting
Question 44.
It is possible to become a successful Animator using one’s own ______________ and ______________
(A) Creation
(B) Handheld
(C) Innovation
(D) Data
(E) Algorithms
Answer:
(A) Creation (C) Innovation
Question 45.
Green computing is important for all classes of systems, ranging from ______________ systems to largescale ______________ centers.
(A) Creation
(B) Handheld
(C) Innovation
(D) Data
(E) Algorithms
Answer:
(B) Handheld (D) Data
Question 46.
Machine Learning is the scientific study of ______________ and ______________ models that computer systems use to effectively perform a specific task.
(A) Creation
(B) Handheld
(C) Innovation
(D) Algorithms
(E) Statistical
Answer:
(D) Algorithms (E) Statistical
Question 47.
Blockchain is a growing list of records, called ______________, which are linked using ______________
(A) Blocks
(B) Creation
(C) Handheld
(D) Innovation
(E) Cryptography
Answer:
(A) Blocks (E) Cryptography
5. Multiple Choice Three Correct Answers.
Question 1.
Information technology refers to ______________, ______________, and ______________
(A) Hardware
(B) Input Unit
(C) Output Unit
(D) Software (computer programs)
(E) Computer Networks
Answer:
(A) Hardware (D) Software (computer programs) (E) Computer networks
Question 2.
Computer Architecture is a specification detailing of how a set of ______________ and ______________ technology standards interact to form a ______________
(A) Software
(B) Hardware
(C) Computer System
(D) Input Unit
(E) Output Unit
Answer:
(A) Software (B) Hardware (C) Computer System

Question 3.
Every computer system has the following three basic components ______________, ______________ & ______________
(A) Data
(B) Commands
(C) Input Unit
(D) Central Processing Unit
(E) Output Unit
Answer:
(C) Input Unit (D) Central Processing Unit (E) Output Unit
Question 4.
Input unit helps users to enter ______________ and ______________ into a ______________
(A) Data
(B) Commands
(C) Input Unit
(D) Central Processing Unit
(E) Computer System
Answer:
(A) Data (B) Commands (E) Computer System
Question 5.
The CPU further uses these three elements ______________, ______________ & ______________
(A) Arithmetic and Logic Unit
(B) Image
(C) Control Unit
(D) Memory Unit
(E) Icons
Answer:
(A) Arithmetic and Logic Unit (C) Control Unit (D) Memory Unit
Question 6.
The graphical user interface is when the user interacts with the computer using ______________ , ______________, and ______________
(A) Images
(B) Icons
(C) Dialog Boxes
(D) Computers
(E) Printers
Answer:
(A) Images (B) Icons (C) Dialog Boxes
Question 7.
A computer network consists of a collection of ______________, ______________ and ______________ that is connected together.
(A) Computers
(B) Printers
(C) Metropolitan Area Network
(D) Wide Area Network
(E) Other equipment
Answer:
(A) Computers (B) Printers (E) Other equipment
Question 8.
______________, ______________ & ______________ are three types of network based on the geographical area they cover.
(A) Local Area Network
(B) Metropolitan Area Network
(C) Wide Area Network
(D) Web enabled services
(E) Remote services
Answer:
(A) Local Area Network (B) Metropolitan Area Network (C) Wide Area Network
Question 9.
IT Enabled Services (ITES), also called ______________ or ______________ or ______________
(A) Local Area Network
(B) Wide Area Network
(C) Web Enabled Services
(D) Remote Services
(E) Tele-Working
Answer:
(C) Web Enabled Services (D) Remote Services (E) Tele-Working
6. Match the following.
Question 1.
| Column ‘A’ |
Column ‘B’ |
| (1) Computer |
(A) Input device |
| (2) Keyboard |
(B) Computare |
| (3) Arithmetic and Logic Unit |
(C) Arithmetic Operations |
| (4) Memory Unit |
(D) Pre-programmed instructions |
Answer:
| Column ‘A’ |
Column ‘B’ |
| (1) Computer |
(B) Computare |
| (2) Keyboard |
(A) Input device |
| (3) Arithmetic and Logic Unit |
(C) Arithmetic Operations |
| (4) Memory Unit |
(D) Pre-programmed instructions |
Question 2.
| Column ‘A’ |
Column ‘B’ |
| (1) Primary Memory |
(A) Non-Volatile Memory |
| (2) RAM |
(B) Volatile Memory |
| (3) ROM |
(C) Internal memory |
| (4) Binary Digit |
(D) 0 or 1 |
Answer:
| Column ‘A’ |
Column ‘B’ |
| (1) Primary Memory |
(C) Internal memory |
| (2) RAM |
(B) Volatile Memory |
| (3) ROM |
(A) Non-Volatile Memory |
| (4) Binary Digit |
(D) 0 or 1 |
Question 3.
| Column ‘A’ |
Column ‘B’ |
| (1) 4 bits |
(A) Software |
| (2) 8 bits |
(B) Physical components |
| (3) Computer hardware |
(C) Byte |
| (4) Program or set of programs |
(D) Nibble |
Answer:
| Column ‘A’ |
Column ‘B’ |
| (1) 4 bits |
(D) Nibble |
| (2) 8 bits |
(C) Byte |
| (3) Computer hardware |
(B) Physical components |
| (4) Program or set of programs |
(A) Software |
Question 4.
| Column ‘A’ |
Column ‘B’ |
| (1) Open source software |
(A) Public domain |
| (2) Closed source software |
(B) Purchase the software |
| (3) Applications software |
(C) Operating system |
| (4) System Software |
(D) End-user programs |
Answer:
| Column ‘A’ |
Column ‘B’ |
| (1) Open source software |
(A) Public domain |
| (2) Closed source software |
(B) Purchase the software |
| (3) Applications software |
(D) End-user programs |
| (4) System Software |
(C) Operating system |
Question 5.
| Column ‘A’ |
Column ‘B’ |
| (1) Apple Corporation’s |
(A) Mac OS |
| (2) Google |
(B) Android |
| (3) Asha |
(C) Nokia Phones |
| (4) Microsoft |
(D) Windows Phone |
Answer:
| Column ‘A’ |
Column ‘B’ |
| (1) Apple Corporation’s |
(A) Mac OS |
| (2) Google |
(B) Android |
| (3) Asha |
(C) Nokia Phones |
| (4) Microsoft |
(D) Windows Phone |

Question 6.
| Column ‘A’ |
Column ‘B’ |
| (1) Ubuntu |
(A) Free from viruses |
| (2) Linux Operating System |
(B) GNU/Linux |
| (3) Repositories |
(C) Collection of Software |
Answer:
| Column ‘A’ |
Column ‘B’ |
| (1) Ubuntu |
(B) GNU/Linux |
| (2) Linux Operating System |
(A) Free from viruses |
| (3) Repositories |
(C) Collection of Software |
Question 7.
| Column ‘A’ |
Column ‘B’ |
| (1) LAN |
(A) Covers the smallest area |
| (2) MAN |
(B) The largest of all |
| (3) WAN |
(C) Covers an area larger than LAN |
Answer:
| Column ‘A’ |
Column ‘B’ |
| (1) LAN |
(A) Covers the smallest area |
| (2) MAN |
(C) Covers an area larger than LAN |
| (3) WAN |
(B) The largest of all |
Question 8.
| Column ‘A’ |
Column ‘B’ |
| (1) Peer-to-Peer Architecture |
(A) Connecting millions of computers |
| (2) Client-Server Architecture |
(B) Client and server |
| (3) Internet |
(C) World Wide Web |
| (4) Tim Berners-Lee |
(D) Same Status |
Answer:
| Column ‘A’ |
Column ‘B’ |
| (1) Peer-to-Peer Architecture |
(D) Same Status |
| (2) Client-Server Architecture |
(B) Client and server |
| (3) Internet |
(A) Connecting millions of computers |
| (4) Tim Berners-Lee |
(C) World Wide Web |
Question 9.
| Column ‘A’ |
Column ‘B’ |
| (1) Domain Name System |
(A) Sending and receiving web pages |
| (2) Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol |
(B) Transfer and manipulate files |
| (3) File Transfer Protocol |
(C) Automatically assign internet addresses |
| (4) HyperText Transfer Protocol |
(D) Translates Network Address |
Answer:
| Column ‘A’ |
Column ‘B’ |
| (1) Domain Name System |
(D) Translates Network Address |
| (2) Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol |
(C) Automatically assign internet addresses |
| (3) File Transfer Protocol |
(B) Transfer and manipulate files |
| (4) HyperText Transfer Protocol |
(A) Sending and receiving web pages |
Question 10.
| Column ‘A’ |
Column ‘B’ |
| (1) Internet Message Access Protocol |
(A) Receiving e-mail messages from the server |
| (2) Internet Relay Chat |
(B) Used for Internet chat |
| (3) Post Office Protocol Version 3 |
(C) Receiving an e-mail from remote mail servers |
| (4) Simple Mail Transfer Protocol |
(D) Sending e-mail messages to the Server |
| (5) Transmission Control Protocol & Internet Protocol |
(E) Breaks down the message into packets |
Answer:
| Column ‘A’ |
Column ‘B’ |
| (1) Internet Message Access Protocol |
(A) Receiving e-mail messages from the server |
| (2) Internet Relay Chat |
(B) Used for Internet chat |
| (3) Post Office Protocol Version 3 |
(C) Receiving an e-mail from remote mail servers |
| (4) Simple Mail Transfer Protocol |
(D) Sending e-mail messages to the Server |
| (5) Transmission Control Protocol & Internet Protocol |
(E) Breaks down the message into packets |
Question 11.
| Column ‘A’ |
Column ‘B’ |
| (1) IT Enabled Services (ITES) |
(A) HTML & PHP |
| (2) Web Designer and Developer |
(B) Web Enabled Services |
| (3) Software Developer |
(C) Scripting Skill |
| (4) Database Manager |
(D) SQL Skills |
Answer:
| Column ‘A’ |
Column ‘B’ |
| (1) IT Enabled Services (ITES) |
(B) Web Enabled Services |
| (2) Web Designer and Developer |
(A) HTML & PHP |
| (3) Software Developer |
(C) Scripting Skill |
| (4) Database Manager |
(D) SQL Skills |
Question 12.
| Column ‘A’ |
Column ‘B’ |
| (1) Information Security Analyst |
(A) Networks are watertight |
| (2) Professional Accountant |
(B) Handle accounting work |
| (3) Financial Advisor |
(C) Investing the money |
| (4) Animator |
(D) Creation and innovation |
Answer:
| Column ‘A’ |
Column ‘B’ |
| (1) Information Security Analyst |
(A) Networks are watertight |
| (2) Professional Accountant |
(B) Handle accounting work |
| (3) Financial Advisor |
(C) Investing the money |
| (4) Animator |
(D) Creation and innovation |
Question 13.
| Column ‘A’ |
Column ‘B’ |
| (1) Green Computing |
(A) Computing Services |
| (2) Internet of Things (IoT) |
(B) Network of Physical Devices |
| (3) Cloud Computing |
(C) Green Chemistry |
| (4) Data Analytics |
(D) Examining Data |
Answer:
| Column ‘A’ |
Column ‘B’ |
| (1) Green Computing |
(C) Green Chemistry |
| (2) Internet of Things (IoT) |
(B) Network of Physical Devices |
| (3) Cloud Computing |
(A) Computing Services |
| (4) Data Analytics |
(D) Examining Data |
Question 14.
| Column ‘A’ |
Column ‘B’ |
| (1) Artificial Intelligence |
(A) Blocks |
| (2) Machine Learning |
(B) Too large or complex |
| (3) Big Data |
(C) Algorithms and Statistical Models |
| (4) Blockchain |
(D) Intelligent Agents |
Answer:
| Column ‘A’ |
Column ‘B’ |
| (1) Artificial Intelligence |
(D) Intelligent Agents |
| (2) Machine Learning |
(C) Algorithms and Statistical Models |
| (3) Big Data |
(B) Too large or complex |
| (4) Blockchain |
(A) Blocks |
7. Answer Briefly.
Question 1.
Define Information Technology.
Answer:
Information Technology encompasses all of the technologies that we use in order to create, collect, process, protect and store information. Information Technology refers to “hardware, software (computer programs), and computer networks”.
Question 2.
Explain ICT.
Answer:
- The full form of ICT is Information and Communication Technology.
- The information and Communication Technology concept involves the transfer and use of all kinds of information.
- Information and Communication Technology is the foundation of the economy and a driving force of social changes in the 21st century.
Question 3.
What are Data and Information?
Answer:
Data can be any character, text, word, number, or raw facts.
Examples of Data:
Mumbai, 1234, Aditya, MG Road, Maharashtra, 9444444441, 411004
Information is data formatted in a manner that allows it to be utilized by human beings in some significant way.
Examples of Information:
Aditya, 1234, MG Road, Mumbai 400004,
Maharashtra, 944444444114.

Question 4.
What is Computer and Computer System?
Answer:
- The word Computer is derived from the Latin word Computare.
- An electronic device that accepts input from the user, processes it according to the instructions given to it, and gives the required result in the form of output, is a Computer.
- The computer can process data, images, audio, video, and graphics.
- Computer accepts data or instructions by way of input.
- Computer stores data.
- A computer can process data as required by the user.
- The computer gives results in the form of output.
- The computer controls all operations inside a computer.
Question 5.
What is Computer Architecture?
Answer:
- Computer Architecture is a specification detailing how a set of software and hardware technology standards interact to form a computer system.
- Computer Architecture refers to how a computer system is designed and how it works.
Question 6.
Explain Input Unit
Answer:
- Input unit helps users to enter data and commands into a computer system.
- The main function of input devices is to direct commands and data into the computer.
- The keyboard is an input device that enters numbers and characters.
- A mouse can be an input device for entering directions and commands.
Question 7.
Briefly explain the CPU and its element.
Answer:
- After receiving data and commands from users, a computer system has to process it according to the instructions provided. Here, it has to rely on a component called the Central Processing Unit.
- The Central Processing Unit further uses these three elements Arithmetic and Logic Unit, Control Unit, and Memory Unit.
- The full form of ALU is the Arithmetic and Logic Unit.
- The arithmetic and Logic Unit part of the CPU performs arithmetic operations.
- Arithmetic and Logic Unit can even perform logical functions like the comparison of data.
- The Control Unit is the backbone of computers.
- The Control Unit is responsible for coordinating tasks between all components of a computer system.
- The Control Unit collects data from input units and sends it to processing units depending on its nature.
- Control Unit transmits processed data to output units to facilitate users.
- Once a user enters data using input devices, the computer system stores this data in its Memory unit.
- The Memory unit uses a set of pre-programmed instructions to further transmit this data to other parts of the CPU.
Question 8.
Explain the types of memory.
Answer:
There are two types of memory (1) Primary Memory (2) Secondary Memory
- Primary Memory is the internal memory of the computer.
- Primary Memory is also known as main memory.
- Primary Memory holds the data and instructions on which computer is currently working.
- RAM stands for Random Access Memory.
- Random Access Memory is known as reading/write memory.
- Random Access Memory is generally referred to as the main memory of the computer system.
- Random Access Memory is a temporary memory.
- Random Access Memory is also called Volatile Memory.
- Read-Only Memory is a Permanent Type memory.
- Read-Only Memory cannot be overwritten by the computer.
- Read-Only Memory is also called Non-Volatile Memory.
- Secondary Memory is an external memory of the computer.
- Secondary Memory is used to store a huge amount of different programs and information.
Question 9.
What is the Output unit and units of memory?
Answer:
- Output units basically reproduce the data formatted by the computer for the user’s benefit.
- The bit is a binary digit that holds only one of two values.
- A group of 4 bits is called a Nibble.
- A group of 8 bits is called a Byte.
- A Byte is the smallest unit, which can represent a data item or a character.
- 1 Byte is 8 Bits.
- 1 KiloByte (KB) is 1,024 Bytes.
- 1 MegaByte (MB) is 1,024 KiloBytes.
- 1 GigaByte (GB) is 1,024 MegaBytes.
- 1 TeraByte (TB) is 1,024 GigaBytes.
- 1 PetaByte (PB) is 1,024 TeraBytes.
- 1 ExaByte (EB) is 1,024 PetaBytes.

Question 10.
Explain concepts of hardware and software.
Answer:
- Computer hardware comprises the physical components that a computer system requires to function.
- A set of instructions given to the computer is known as Program.
- Program or set of programs are called Software.
- Software is a generic term used to describe computer programs.
- Open-source software refers to the software which releases code in the public domain for anyone to use.
- The full form of FOSS is FOSS Free Open Source Software Policy.
- Free Open Source Software Policy and enabled them to save some millions of rupees each year in licensing costs.
- In the case of Closed Source Software user has to purchase the software before using it.
Question 11.
Write down the classification of software based on its utility.
Answer:
- Application software is a program or group of programs designed for end-users.
- Applications software is also called end-user programs.
- System Software is a set of instructions required for a computer to work.
- Linux Operating system is a program that allows different applications and various components of the hardware.
- A computer would not be able to function correctly without an operating system.
- An operating system is a software program that empowers the computer hardware to communicate and operate with the computer software.
- The operating system boots up the computer and makes sure that everything is operational.
- The operating system is also what runs the cell phone and most electronic devices.
- The operating systems usually come preloaded on any computer, tablet, laptop, or cell phone that the user buys.
Question 12.
Explain Operating Systems for Personal Computers and Mobile Phones.
Answer:
- The full form of DOS is Disk Operating System.
- Windows is a series of operating systems that are designed by Microsoft.
- Windows is the most commonly used operating system.
- Apple Corporation’s registered operating system is called Mac OS.
- Chrome OS is an open-source operating system created by Google.
- Linux is an open-source, portable, multi- multiprogramming, operating system.
- Android is a free and open-source operating system for mobile phones provided by Google.
- Asha is used by Nokia phones. This is a closed source OS.
- Blackberry is a closed source operating system for smartphone and tablet devices.
- IOS is Apple’s closed source operating system for Apple’s iPhone, iPod Touch, iPad, and second-generation Apple TVs.
- Windows Phone is developed by Microsoft as a closed source operating system for mobile phones.
- Linux is used as the predominant backbone of the Internet.
- Ubuntu is one of the most popular GNU/Linux distributions.
Question 13.
Explain GUI and CLI.
Answer:
- The full form of GUI is Graphical User Interface.
- Full form of CLI Command Line Interface.
- The graphical user interface is when the user interacts with the computer using images, icons, and dialog boxes.
- The Search option is used for a quick search of the application.
- The Home folder is where all the personal documents and settings are stored.
- The Command-line interface is when the user interacts with the computer using text.
- The Commands are programs that are run when a user types the command name.
Question 14.
Explain the advantages of GNU/Linux.
Answer:
- Linux is Free and Open Source.
- Linux Operating System is free from viruses.
- Proprietary Operating Systems can update themselves.
- The repository is a collection of software for a Linux distribution on the server.
- The Package manager updates the operating system as well as other software periodically.
Question 15.
Define Computer networks and different types of networks.
Answer:
- Computer Network is a group of interconnected computers or devices to have communication within themselves.
- A Computer Network consists of a collection of computers, printers, and other equipment that is connected together.
- The full form of LAN is the Local Area Network.
- The full form of MAN is Metropolitan Area Network.
- The full form of WAN is a Wide Area Network.
- Local Area Network type of network covers the smallest area.
- Metropolitan Area Network covers an area larger than LAN.
- Wide Area Network type of network comprises the largest of all.
- In Local Area Network, usage area is limited to areas such as an office building, home, hospital, schools, etc.
- Local Area Network covers a short distance, and so the error and noise are minimized.
- Local Area Network type of network is easy to set up.
- In Local Area Network data transmits at a very fast rate as the number of computers linked is limited.
- Local Area Network is less expensive hardware and maintenance cost is also low.
- Metropolitan Area Network connects two or more separate computers that reside in the same or different cities.
- Full for of ISP is Internet Service Provider.
- Metropolitan Area Network covers a large geographical area and may serve as an ISP.
- Metropolitan Area Network type of network is hard to design and maintain.
- A Wide Area Network is a computer network that extends over a large geographical area.
- In the Wide Area Network type of network, the technology is high speed and relatively expensive.
- A Communication medium used for Wide Area networks is Telephone networks or Satellite Link.

Question 16.
Explain Network Architecture.
Answer:
- Network architecture is the design of a computer network.
- A Peer-to-Peer network has no dedicated servers.
- Client-Server type of architecture is most suitable for larger networks.
- A computer that is seeking any resource from another computer is a Client computer.
- If a computer has a resource that is served to another computer, it is a Server computer.
Question 17.
What is Internet?
Answer:
- Internet means connecting a computer to any other computer anywhere in the world.
- The Internet is generally defined as a global network connecting millions of computers.
- The Internet is a massive network of networks, a networking infrastructure.
- With the help of the Internet, one can easily be in touch with anyone in the whole world by sending electronic mail, by chatting.
- It can be said that the Internet provides a very strong connection or network between computers globally.
Question 18.
Write down the history of the Internet.
Answer:
- The full form of ARPANET is Advanced Research Projects Agency Network.
- The first workable prototype of the internet came in the late 1960s with the creation of the Advanced Research Projects Agency Network.
- Advanced Research Projects Agency Network used packet switching to allow multiple computers to communicate on a single network.
- The full form of TCP/ IP is Transmission Control Protocol and Internet Protocol.
- Transmission Control Protocol and Internet Protocol communications model that set standards for how data could be transmitted between multiple networks.
- The full form of WWW is World Wide Web.
- Tim Berners-Lee invented the World Wide Web.
Question 19.
Define Protocol with examples.
Answer:
- A Protocol is a set of rules that governs the communications between computers on a network.
- Transmission Control Protocol & Internet Protocol breaks down the message into packets and sends them out into the network.
- The full form of DNS is Domain Name System.
- Domain Name System translates network address into terms understood by humans and vice-versa.
- DHCP stands for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol.
- Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol can automatically assign internet addresses to computers and users.
- FTP stands for File Transfer Protocol.
- File Transfer Protocol is used to transfer and manipulate files on the internet.
- The full form of HTTP is HyperText Transfer Protocol.
- HyperText Transfer Protocol is an internet-based protocol for sending and receiving web pages.
- The full form of IMAP is Internet Message Access Protocol.
- Internet Message Access Protocol is used for receiving e-mail messages from servers on the Internet.
- Internet Message Access Protocol maintains a copy of all the emails on the server.
- The full form of IRC is Internet Relay Chat.
- Internet Relay Chat facilitates communication in the form of text.
- POP3 stands for Post Office Protocol Version 3.
- Post Office Protocol Version 3 is used for receiving e-mail from remote mail servers.
- Simple Mail Transfer Protocol is used for sending e-mail messages to the Server on the Internet.
Question 20.
Explain the meaning of ITES.
Answer:
- The full form of ITES is IT Enabled Services.
- IT Enabled Services (ITES), also called as Web-Enabled Services.
- IT Enabled Services covers the entire amount of operations that exploit Information Technology for improving the efficiency of an organization.
Question 21.
Discuss various careers opportunities in IT.
Answer:
- Web Designer can develop interactive websites using knowledge of HTML, PHP, and various other programming languages.
- It is possible to have a career as a software developer with scripting skills.
- After getting knowledge about Database management one can work as a Database Manager.
- Information Security Analysts are responsible for ensuring that networks are watertight.
- Professional Accountant using computerized accounting software can successfully handle accounting work.
- Financial Advisor after getting IT knowledge one can advise and guide others in investing the money in various investment schemes.
- It is possible to become a successful Animator using one’s own creation and innovation.
- Perhaps one of the trendiest and most fun jobs in the sector, a games developer.
- As a career opportunity, to become an Audio / Video Editor one should be good in tools such as Kdenlive, Audacity.

Question 22.
Write down the recent trends in IT.
Answer:
- Green Computing is the study and practice of environmentally sustainable computing or IT.
- The goals of green computing are similar to green chemistry.
- Green computing is important for all classes of systems, ranging from handheld systems to large-scale data centers.
- The full form of IoT is the Internet of Things.
- The Internet of Things is the network of physical devices, vehicles, home appliances, and other items embedded with electronics, software, sensors, actuators, and connectivity.
- Cloud Computing is the delivery of computing services over the internet.
- Data Analytics is the process of examining data sets in order to draw conclusions about the information.
- Data Analytics technologies and techniques are widely used in commercial industries to enable organizations to make more informed business decisions.
- Artificial Intelligence is intelligence demonstrated by machines, in contrast to the natural intelligence displayed by humans and other animals.
- Computer science defines Artificial Intelligence research as the study of “intelligent agents”.
- Machine Learning is the scientific study of algorithms and statistical models that computer systems use to effectively perform a specific task.
- Big Data refers to data sets that are too large or complex for traditional data-processing application software.
- Blockchain is a growing list of records, called blocks, which are linked using cryptography.
![]()
![]()
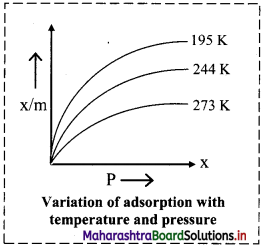
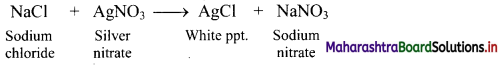
![]()
![]()
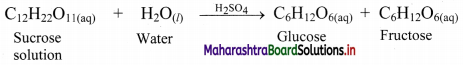
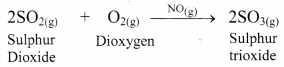
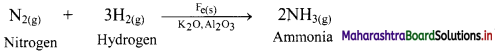
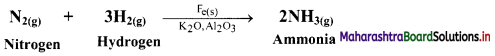
![]()
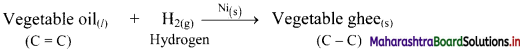
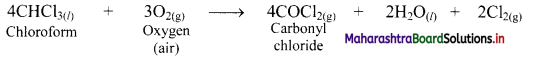
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
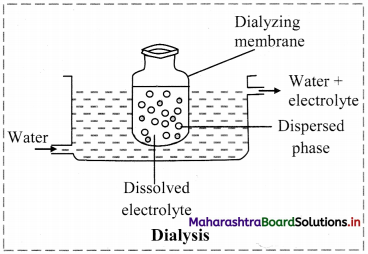
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
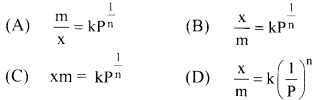
![]()
![]()
![]()