Number Work Class 5 Problem Set 5 Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Balbharti Maharashtra Board Class 5 Maths Solutions Chapter 2 Number Work Problem Set 5 Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Std 5 Maths Chapter 2 Number Work
Question 1.
Write the place value of the underlined digit.
(1) 78, 95,210
(2) 14, 95,210
(3) 3,52,749
(4) 50,000
(5) 89, 99,988
Answer:
(1) Here, the underlined digit 7 is in ten lakhs place.
So, its place value is 70,00,000 (70 lakhs)
![]()
(2) Here, the underlined digit 4 is in lakhs place.
So, its place value is 4,00,000 (4 lakhs)
(3) Here, the underlined digit 5 in ten thousands place.
So, its place value is 50,000 (50 thousands)
(4) Here, the underlined digit ‘0’ is in the unit place.
Hence, its place value is 0 (zero)
(5) Here, the underlined digit 9 is in ten thousands place
So, its place value is 90,000 (90 thousands)
Question 2.
Write the numbers in their expanded form.
(1) 56, 43, 215
(2) 70, 815
(3) 8, 35, 999
(4) 8, 88, 889
(5) 92, 32, 992
Answer:
(1) 56,43,215: 50,00,000 + 6,00,000 + 40,000 + 3,000 + 200 + 10 + 5
(2) 70,815 : 70,000 + 800 + 10 + 5
(3) 8,35,999 : 8,00,000 + 30,000 + 5,000 + 900 + 90 + 9
(4) 8,88,889 : 8,00,000 + 80,000 + 8,000 + 800 + 80 + 9
(5) 92,32,992: 90,00,000 + 2,00,000 + 30,000 + 2,000 + 900 + 90 + 2
Question 3.
Write the place name and place value of each digit in the following numbers.
(1) 35, 705
Answer:
Digit 3 is in ten thousands place, its place value is 30,000
Digit 5 is in thousands place, its place value is 5,000
Digit 7 is in hundreds place, its place value is 700
Digit 0 is in ten place, its place value is 0
Digit 5 is in units place, its place value is 5
![]()
(2) 7, 82, 899
Answer:
Digit 7 is in lakhs place, its place value is 7.0. 000
Digit 8 is in ten thousands place, its place value is 80,000
Digit 2 is in thousands place, its place value is 2,000
Digit 8 is in hundreds place, its place value is 800
Digit 9 is- in ten place, its place value is 90 Digit 9 is in units place, its place value is 9
(3) 82, 74, 508
Answer:
Digit 8 is in ten lakhs place, its place value is 80,00,000
Digit 2 is in lakhs place, its place value is 2.0. 000
Digit 7 is in ten thousands place, its place value is 70,000
Digit 4 is in thousands place, its place value is 4,000
Digit 5 is in hundreds place, its place value is 500
Digit 0 is in ten place, its place value is 0
Digit 8 is in units place, its place value is 8
Question 4.
The expanded form of the number is given. Write the number.
(1) 60, 000 + 4000 + 600 + 70 + 9
(2) 9, 00, 000 + 20,000 + 7000 + 800 + 5
(3) 20,00,000 + 3,00,000 + 60,000 + 9000 + 500 + 10 + 7
(4) 7,00,000 + 80,000 + 4000 + 500
(5) 80,00,000 + 50,000 + 1000 + 600 + 9
Answer:
(1) The number is 64,679
(2) The number is 9,27,805
(3) The number is 23,69,517
(4) The number is 7,84,500
(5) The number is 80,51,609
![]()
An interesting dice game
Prepare a table with the name of each player, as shown below.
In front of each name, there are boxes to make seven-digit numbers.
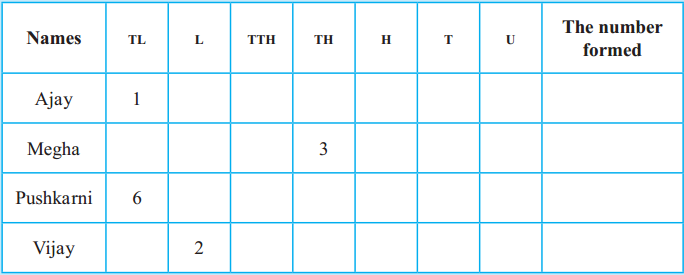
Game 1 :
The first player throws the dice and writes that number in any one of the boxes in front of his/her name. You can write only one number in each box and once it is written, you cannot change its place. The other players do the same till all the boxes are filled and each one gets a seven-digit number. The one with the largest number is the winner.
Game 2 :
Use the same table, but you may write the number (you get on throwing the dice) in any box in front of anyone’s name. The one with the largest number is the winner.
Game 3 :
The rules are the same as for game 2, but the one with the smallest number is the winner.
Bigger and smaller numbers
Hamid : How do we determine the smaller or bigger number when we are dealing with six- or seven-digit numbers ?
Teacher : You have learnt how to do that with five-digit numbers. The number with the bigger ten thousands digit is the bigger number. If they are the same, we look at the thousands digits to determine the smaller or bigger number.
Now, can you tell how to compare six- or seven-digit numbers ?
![]()
Hamid : Yes, I can. First, we’ll look at the ten lakhs digits. If they are the same, we’ll look at the digits in the lakhs place. If those are equal, we look at the ten thousands place to tell the smaller or bigger number and so on. Besides, we might be able to tell which of the numbers is bigger, just by looking at the number of digits in each number. Right ?
Teacher : Absolutely ! The number with more digits is the bigger number.
Roman Numerals Problem Set 5 Additional Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Write the place value of the underlined digit.
(1) 81,67,303
Answer:
Here, the underlined digit 7 is in thousands place.
So, its place value is 7,000 (7 thousands)
(2) 41,35,062
Answer:
Here, the underlined digit 6 is in ten’s place.
So, its place value is 60 (sixty)
(3) 90,31,265
Answer:
Here, the underlined digit 3 is in ten thousands place.
So, its place value is 30,000 (30 thousands)
![]()
Question 2.
Write the numbers in their expanded form.
Answer:
(1) 51,03,640: .50,00,000 + 1,00,000 + 3,000 + 600 + 40
(2) 60,60,600: 60,00,000 + 60,000 + 600
(3) 71,45,042 : 70,00,000 + 1,00,000 + 40,000 + 5,000 + 40 + 2
Question 3.
Write the place name and place value of each digit in the following numbers.
(1) 1,88,919
Answer:
Digit 1 is in lakhs place, its place value is 1,00,000
Digit 8 is in ten thousands place, its place value is 80,000
Digit 8 is in thousands place, its place value is 8,000
Digit 9 is in hundreds place, its place value is 900
Digit 1 is in ten place, its place value is 10
Digit 9 is in units place, its place value is 9
Question 4.
The expanded form write the number.
(1) 40,00,000 + 5,00,000 + 10,000 + 3,000 + 200 + 70+8
Answer:
The number is 45,13,278
![]()
(2) 80,000 + 300 + 40 + 1
Answer:
The number is 80,341
Class 5 Maths Solution Maharashtra Board
- Roman Numerals Problem Set 1 Class 5 Maths Solutions
- Number Work Problem Set 2 Class 5 Maths Solutions
- Number Work Problem Set 3 Class 5 Maths Solutions
- Number Work Problem Set 4 Class 5 Maths Solutions
- Number Work Problem Set 5 Class 5 Maths Solutions
- Number Work Problem Set 6 Class 5 Maths Solutions












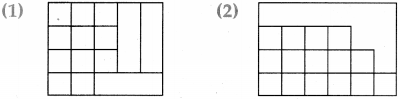
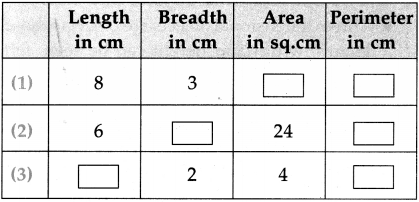
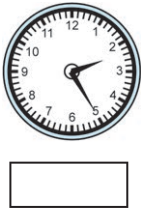





 20 minutes and 10 seconds past 7
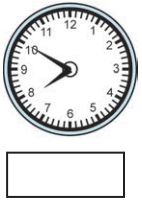
20 minutes and 10 seconds past 7 15 minutes and 40 seconds past 10
15 minutes and 40 seconds past 10