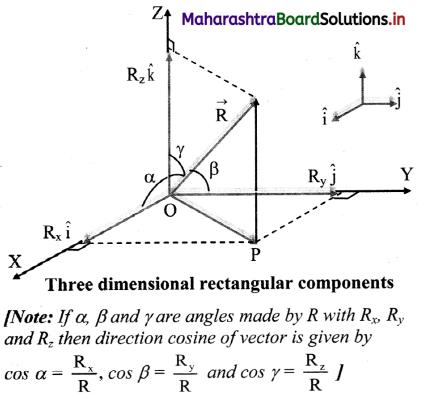
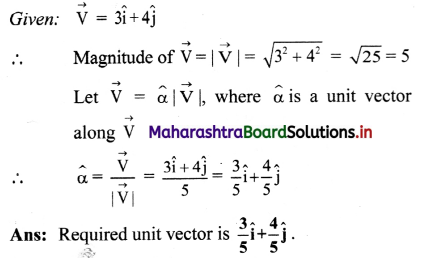
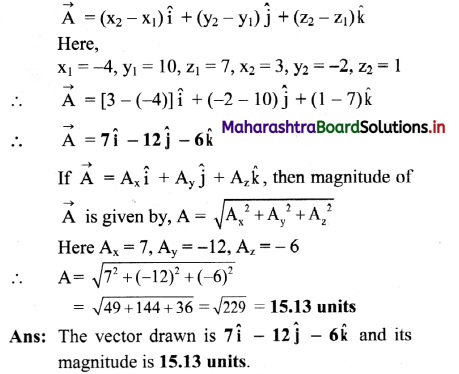
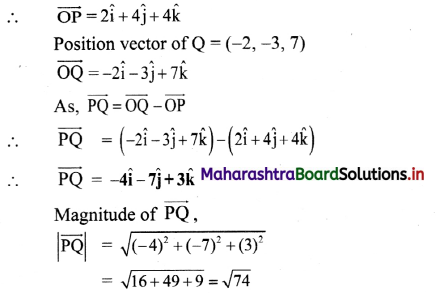
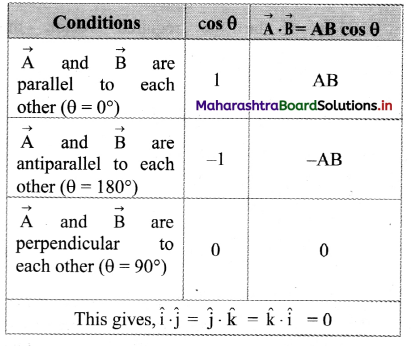
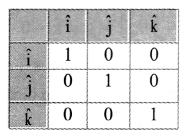
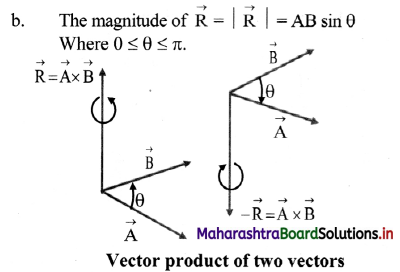
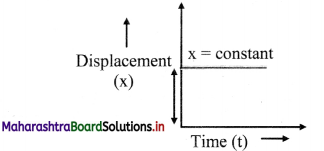
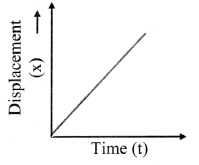
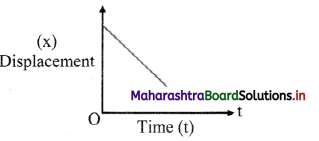
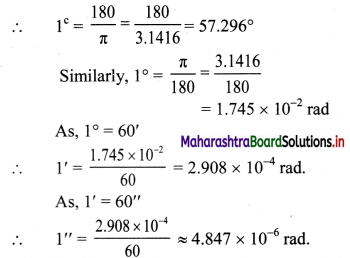
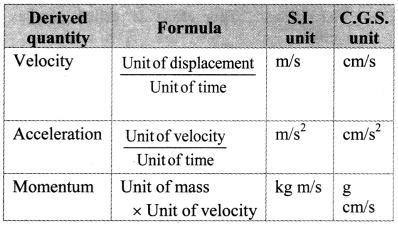
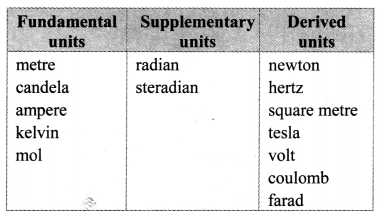
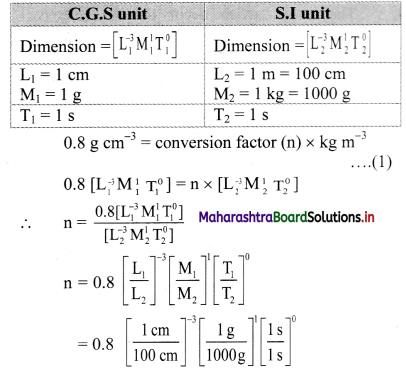
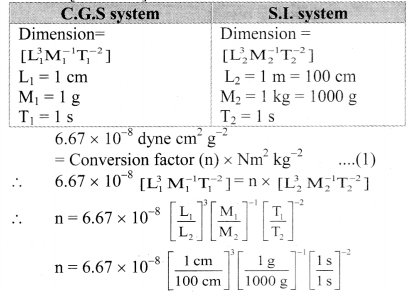
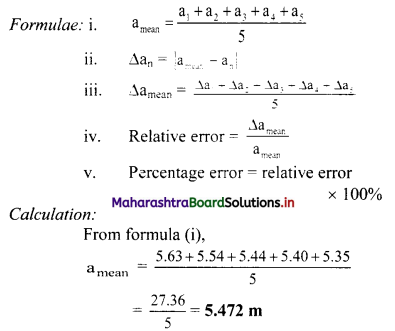
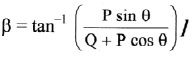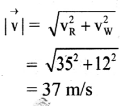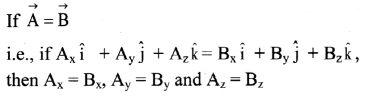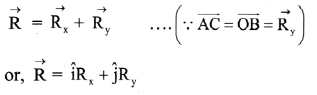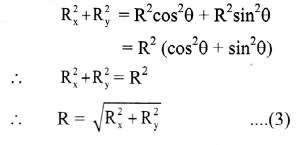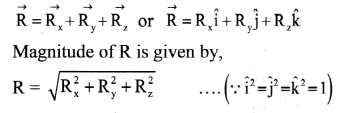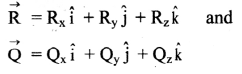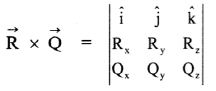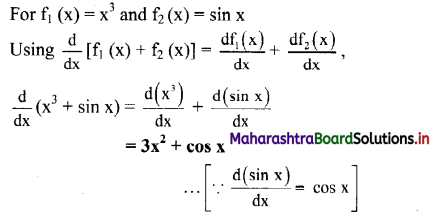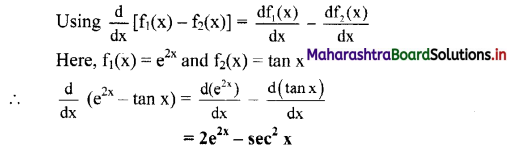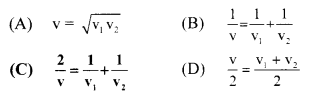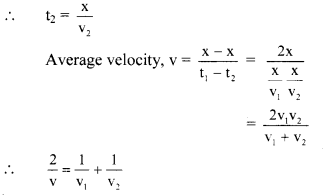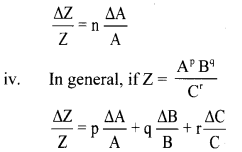Balbharti Maharashtra State Board 11th Physics Important Questions Chapter 4 Laws of Motion Important Questions and Answers.
Maharashtra State Board 11th Physics Important Questions Chapter 4 Laws of Motion
Question 1.
‘Rest and motion are relative concepts.’ Explain the statement with an example.
Answer:
- A body can be described to be at rest or in motion with respect to a system of co¬ordinate axes known as the frame of reference.
- A body is in motion if it changes its position with respect to a fixed reference point in a frame of reference. On the other hand, a body is at rest if it does not change its position with respect to a fixed reference point in a frame of reference.
- An object can be said to be at rest with respect to a frame of reference while the same object can be said to be in motion with respect to a different frame of reference.
Example: In a running train, all the travellers in the train are in a state of rest if the train is taken as the frame of reference. On the other hand, all the travellers in the train are in a state of motion if ground (or platform) is taken as the frame of reference. - Thus, motion and rest always need a frame of reference to be described. Hence, rest and motion are relative concepts.
Question 2.
Explain how acceleration and initial velocity decides trajectory of a motion.
Answer:
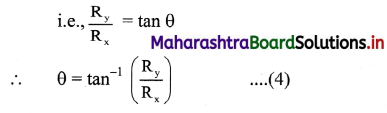
- The resultant motion is linear if:
- initial velocity \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{u}}\) = 0 (starting from rest) and acceleration \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{a}}\) is in any direction.
- initial velocity \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{u}}\) ≠ 0 and acceleration a is in line with the initial velocity (same or opposite direction).
- The resultant motion is circular if initial velocity \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{u}}\) ≠ 0 and acceleration \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{a}}\) is perpendicular to the velocity throughout.
- The resultant motion is parabolic if the initial velocity \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{u}}\) is not in line with the acceleration \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{a}}\) and \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{a}}\) = constant.
e.g., trajectory of a projectile motion. - Similarly, various other combinations of initial velocity and acceleration will result into more complicated motions.
![]()
Question 3.
State Newton’s first law of motion.
Answer:
Statement: Every inanimate object continues to be in a state of rest or of uniform unaccelerated motion along a straight line, unless it is acted upon by an external, unbalanced force.
Question 4.
An astronaut accidentally gets separated out of his small spaceship accelerating in inter stellar space at a constant rate of 100 m s-2. What is the acceleration of the astronaut the instant after he is outside the spaceship? (Assume that there are no nearby stars to exert gravitational force on him.) (NCERT)
Answer:
- Assuming absence of stars in the vicinity, the only gravitational force exerted on astronaut is by the spaceship.
- But this force is negligible.
- Hence, once astronaut is out of the spaceship net external force acting on him can be taken as zero.
- From the first law of motion, the acceleration of astronaut is zero.
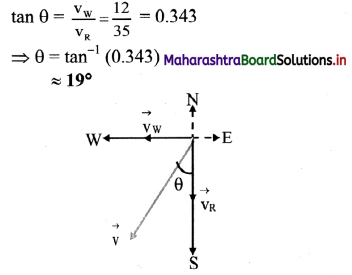
Question 5.
Give the magnitude and direction of the net force acting on:
- a drop of rain falling down with a constant speed.
- a cork of mass 10 g floating on water.
- a kite skilfully held stationary in the sky.
- a car moving with a constant velocity of 30 kmh-1 on a rough road.
- a high speed electron in space far from all gravitating objects, and free of electric and magnetic fields. (NCERT)
Answer:
- The drop of rain falls down with a constant speed, hence according to the first law of motion, the net force on the drop of rain is zero.
- Since the 10 g cork is floating on water, its weight is balanced by the up thrust due to water. Therefore, net force on the cork is zero.
- As the kite is skilfully held stationary in the sky, in accordance with first law of motion, the net force on the kite is zero.
- As the car is moving with a constant velocity of 30 km/h on a road, the net force on the car is zero.
- As the high-speed electron in space is far from all material objects, and free of electric and magnetic fields, it doesn’t accelerate and moves with constant velocity. Hence, net force acting on the electron is zero.
Question 6.
State Newton’s second law of motion and its importance.
Answer:
Statement: The rate of change of linear momentum of a rigid body is directly proportional to the applied (external unbalanced) force and takes place in the direction of force.
\(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{F}}=\frac{\mathrm{d} \overrightarrow{\mathrm{p}}}{\mathrm{dt}}\)
Where, \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{F}}\) = Force applied
p = m\(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{v}}\) = linear momentum
Importance of Newton’s second law:
- It gives mathematical formulation for quantitative measure of force as rate of change of linear momentum.
- It defines momentum instead of velocity as the fundamental quantity related to motion.
- It takes into consideration the resultant unbalanced force on a body which is used to overcome Aristotle’s fallacy.
Question 7.
Explain why a cricketer moves his hands backwards while holding a catch. (NCERT)
Answer:
- In the act of catching the ball, by drawing hands backward, cricketer allows longer time for his hands to stop the ball.
- By Newton’s second law of motion, force applied depends on the rate of change of momentum.
- Taking longer time to stop the ball ensures smaller rate of change of momentum.
- Due to this the cricketer can stop the ball by applying smaller amount of force and thereby not hurting his hands.
Question 8.
Large force always produces large change in momentum on a body than a small force. Is this correct?
Answer:
No. From Newton’s second law, we have.
\(\frac{\mathrm{dP}}{\mathrm{dt}}=\mathrm{F}\) …. (i)
dP = Fdt …. (ii)
From equation (ii), we can infer that a small force acting for a longer time can produce same change in momentum of a body as a large force acting in the same direction for a short time. Hence, the given statement is incorrect.
Question 9.
Newton’s first law is contained in the second law. Prove it.
Answer:
- From Newton’s second law of motion, we have, \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{F}}=\frac{\mathrm{d} \overrightarrow{\mathrm{p}}}{\mathrm{dt}}=\frac{\mathrm{d}}{\mathrm{dt}}(\mathrm{m} \overrightarrow{\mathrm{v}})\)
- For a given body, mass m is constant.
∴ \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{F}}=\mathrm{m} \frac{\mathrm{d} \overrightarrow{\mathrm{v}}}{\mathrm{dt}}=\mathrm{m} \overrightarrow{\mathrm{a}}\) - If \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{F}}\) = zero, \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{v}}\) is constant. Hence if there is no force, velocity will not change. This is nothing but Newton’s first law of motion.
Question 10.
State Newton’s third law of motion
Answer:
Statement: To every action (force) there is always an equal and opposite reaction force).
Question 11.
State the importance of Newton’s third law of motion.
Answer:
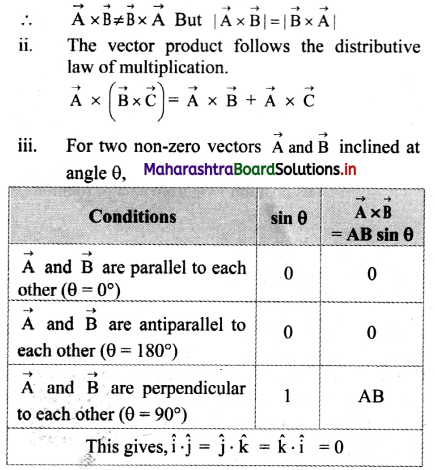
- Newton’s third law of motion defines action and reaction as a pair of equal and opposite forces acting along the same line.
- Action and reaction forces always act on different objects.
Question 12.
State the consequences of Newton’s third law of motion.
Answer:
- Two interacting bodies exert forces which are always equal in magnitude, have the same line of action and are opposite in direction, upon each other. Thus, forces always occur in pairs.
- If a body A exerts an action force \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{F}}_{\mathrm{BA}}\) on body B, then body B also exerts an equal and opposite reaction force \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{F}}_{\mathrm{AB}}\) on body A, simultaneously.
- Body A experiences the force \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{F}}_{\mathrm{AB}}\) only and
body B experiences the force \overrightarrow{\mathrm{F}}_{\mathrm{BA}} only. - Both the forces, action and reaction act at the same instant.
- Both the forces always act on different bodies. Hence, they never cancel each other.
- Both the forces do not necessarily arise due to contact i.e., they can be non-contact forces. Example: Repulsive forces between two magnets.
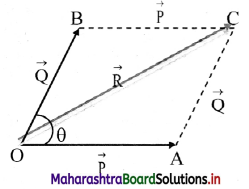
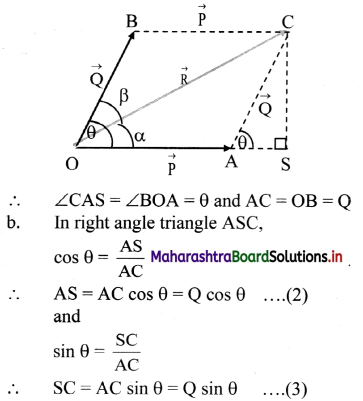
![]()
Question 13.
If a constant force of 800 N produces an acceleration of 5 m/s2 in a body, what is its mass? If the body starts from rest, how much distance will it travel in 10 s?
Solution:
Given: F = 800 N, a = 5 m/s2, u = 0, t = 10 s
To find: mass (m), distance travelled (s)
Formulae:
i. F = ma
ii. s = ut + \(\frac{1}{2} \mathrm{at}^{2}\)
Calculation:
From formula (i),
∴ m = \(\frac{\mathrm{F}}{\mathrm{a}}=\frac{800}{5}\) = 160 kg
From formula (ii),
s = \(\frac{1}{2}\) × 5 × (10)2 [∵ u = 0]
∴ s = 250 m
Answer:
Mass of the body is 160 kg and the distance travelled by the body is 250 m.
Question 14.
A constant force acting on a body of mass 3 kg changes its speed from 2 m s-1 to 3.5 m/s in 25 s. The direction of motion of the body remains unchanged. What is the magnitude and direction of the force? (NCERT)
Solution:
Given: u = 2 ms-1, m = 3 kg,
v = 3.5 m s-1, t = 25s
To find: Force (F)
Formula: F = ma
Calculation: Since, v = u + at
∴ 3.5 = 2 + a × 25
a = \(\frac{3.5-2}{25}\) = 0.06 m s-2
From formula,
F = 3 × 0.06 = 0.18 N
Since, the applied force increases the speed of the body, it acts in the direction of the motion.
Answer:
The applied force is 0.18 N along the direction of motion.
Question 15.
A constant retarding force of 50 N is applied to a body of mass 20 kg moving initially with a speed of 15 ms-1. How long does the body take to stop? (NCERT)
Solution:
Given: m = 20 kg, u = 15ms-1, v = 0,
F = – 50 N (retarding force)
To find: Time (t)
Formula: v = u + at
Calculation: Since, F = ma
∴ a = \(\frac{\mathrm{F}}{\mathrm{m}}=\frac{-50}{20}\) = -2.5 m s-2
From formula,
0 = 15 + (-2.5) × t
∴ t = 6s
Answer:
Time taken to stop the body is 6 s.
Question 16.
A hose pipe used for gardening is ejecting water horizontally at the rate of 0.5 m/s. Area of the bore of the pipe is 10 cm2. Calculate the force to be applied by the gardener to hold the pipe horizontally stationary.
Solution:
Let ejecting water horizontally be considered as the action force on the water, then the water exerts a backward force (called recoil force) on the pipe as the reaction force.

Where, V = volume of water ejected
A = area of cross section of bore = 10 cm2
ρ = density of water = 1 g/cc
l = length of the water ejected in time t
\(\frac{\mathrm{d} l}{\mathrm{dt}}\) = v = velocity of water ejected
= 0.5 m/s = 50 cm/s
F = \(\frac{\mathrm{dm}}{\mathrm{dt}} \mathrm{v}\)
= (Aρv) v
= Aρv2
= 10 × 1 × 502
∴ F = 25000 dyne = 0.25 N
Answer:
The gardener must apply an equal and opposite force of 0.25 N.
Question 17.
What does the term frame of reference mean?
Answer:
A system of co-ordinate axes with reference to which the position or motion of an object is described is called a frame of reference.
Question 18.
Explain the terms inertial and non-inertial frame of reference.
Answer:
- Inertial frame of reference:
- A frame of reference in which Newton ‘s first law of motion is applicable is called inertia/frame of reference.
- A body moves with a constant velocity (which can be zero) in the absence of a net force. The body does not accelerate.
- Example: A rocket in inter-galactic space (gravity free space between galaxies) with all its engine shut.
- Non-inertial frame of reference:
- A frame of reference in which an object suffers acceleration in absence of net force is called non-inertial frame of reference.
- The body undergoes acceleration.
- Example: If a car just start its motion from rest, then during the time of acceleration the car will be in a non-inertial frame of reference.
Question 19.
State the limitations of Newton’s laws of motion.
Answer:
- Newton’s laws of motion are not applicable in a non-inertial (accelerated) frame of reference.
- Newton’s laws are only applicable to point objects.
- Newton’s laws are only applicable to rigid bodies.
- Results obtained by applying Newton’s laws of motion for objects moving with speeds comparable to that of light do not match with the experimental results and Einstein special theory of relativity has to be used.
- Newton’s laws of motion fail to explain the behaviour and interaction of objects having atomic or molecular sizes, and quantum mechanics has to be used.
Question 20.
Name the different types of fundamental forces in nature.
Answer:
Fundamental forces in nature are classified into four types:
- Gravitational force
- Electromagnetic force
- Strong nuclear force
- Weak nuclear force
Question 21.
Define gravitational force. Give its examples.
Answer:
Force of attraction between two (point) masses separated by a distance is called as gravitational force.
F = \(\mathrm{G} \frac{\mathrm{m}_{1} \mathrm{~m}_{2}}{\mathrm{r}^{2}}\)
where ‘G’ is constant called the universal gravitational constant = 6.67 × 10-11 Nm2/kg2
Examples:
- The motion of moon, artificial satellites around the earth and motion of planets around the sun is due to gravitational force of attraction.
- The concept of weight of a body in the earth’s gravitational field is due to gravitational force exerted by the earth on a body.
Question 22.
Write down the main characteristics of gravitational force.
Answer:
Characteristics of gravitational force:
- It is always attractive.
- It is the weakest of the four basic forces in nature.
- Its range is infinite.
- Structure of the universe is governed by this force.
Question 23.
Write a note on electromagnetic (EM) force.
Answer:
Electromagnetic force:
- The attractive and repulsive force between electrically charged particles is called electromagnetic force.
- It can be attractive or repulsive.
- It is stronger than the gravitational force.
- Example: force of friction, normal reaction, tension in strings, collision forces, elastic forces, fluid friction etc. are electromagnetic in nature.
- Reaction forces are a result of the action of electromagnetic forces.
- Since majority of forces are electromagnetic in nature, our life is practically governed by these forces.
Question 24.
Write a note on strong and weak nuclear force.
Answer:
- Strong nuclear force: The strong force which binds protons and neutrons (nucleons) together in the nucleus of an atom is called strong nuclear force.
Characteristics of strong nuclear force:- It is a very strong attractive force.
- It is a short range force of the order of 10-14 m.
- it is charge independent.
- Weak nuclear force: The force of interaction between subatomic particles which results in the radioactive decay of atoms is called weak nuclear force.
Characteristics of weak nuclear force:
- It acts between any two elementary particles (pair of subatomic particles).
- It is a stronger force than gravitational force.
- It is much weaker than electromagnetic force or strong nuclear force.
- It is a short range force of the order of 10-16m.
Question 25.
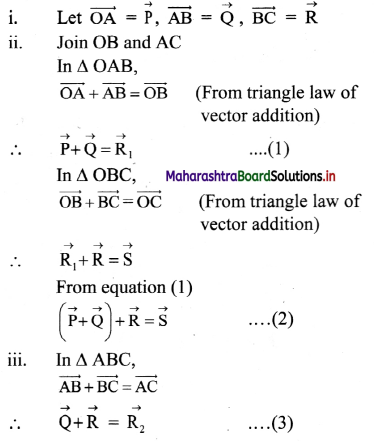
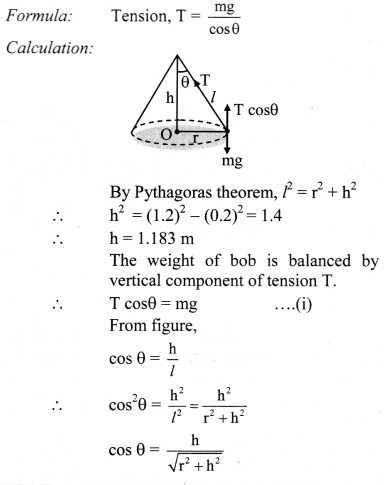
Three identical point masses are fixed symmetrically on the periphery of a circle. Obtain the resultant gravitational force on any point mass M at the centre of the circle. Extend this idea to more than three identical masses symmetrically located on the periphery. How far can you extend this concept?
Solution:
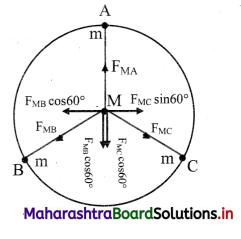
i. Consider three identical points A, B and C of mass m on the periphery of a circle of radius r. Mass M is at the centre of the circle.
Gravitational forces on M due to these masses are attractive and are given as,
In magnitude, \(\mathrm{F}_{\mathrm{MA}}=\mathrm{F}_{\mathrm{MB}}=\mathrm{F}_{\mathrm{MC}}=\frac{\mathrm{GMm}}{\mathrm{r}^{2}}\)
ii. Forces \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{F}}_{\mathrm{MB}}\) and \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{F}}_{\mathrm{MC}}\) are resolved along \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{F}}_{\mathrm{MA}}\) and perpendicular to \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{F}}_{\mathrm{MA}}\). Components perpendicular to \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{F}}_{\mathrm{MA}}\) cancel each other. Components along \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{F}}_{\mathrm{MA}}\) are,
FMB cos 60° = FMC cos 60° = \(\frac{1}{2} F_{M A}\) each.
Magnitude of their resultant is FMA and its direction is opposite to that of FMA. Thus, the
resultant force on mass M is zero. For any even number of equal masses, the force due to any mass m is balanced (cancelled) by diametrically opposite mass. For any odd number of masses, the components perpendicular to one of them cancel each other while the components parallel to one of these add up in such a way that the resultant is zero for any number of identical masses m located symmetrically on the periphery.
As the number of masses tends to infinity, their collective shape approaches circumference of the circle, which is nothing but a ring. Thus, the gravitational force exerted by a ring mass on any other mass at its centre is zero.
iii. This concept can be further extended to three-dimensions by imagining a uniform hollow sphere to be made up of infinite number of such rings with a common diameter. Thus, the gravitational force for any mass kept at the centre of a hollow sphere is zero.
Question 26.
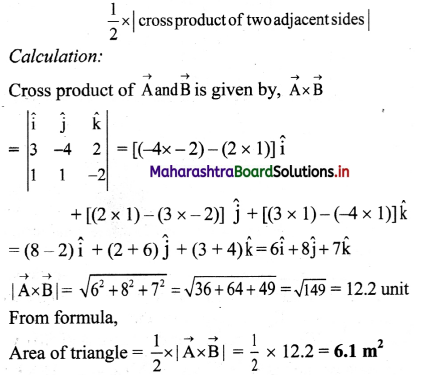
A car of mass 1.5 ton is running at 72 kmph on a straight horizontal road. On turning the engine off, it stops in 20 seconds. While running at the same speed, on the same road, the driver observes an accident 50 m in front of him. He immediately applies the brakes and just manages to stop the car at the accident spot. Calculate the braking force.
Solution:
Given: m = 1.5 ton = 1500 kg,
u = 72 kmph = 72 × \(\frac{5}{18} \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}\)m/s = 20 m
s-1 (on turning engine off),
v = 0, t = 20 s, s = 50 m
To find: Braking force (F)
Formula:
i. v = u + at
ii. v2 – u2 = 2as
iii. F = ma
Calculation:
On turning the engine off,
From formula (i),
a = \(\frac{0-20}{20}\) = -1 m s-2
This is frictional retardation (negative acceleration).
After seeing the accident,
From formula (ii),
a1 = \(\frac{0^{2}-20^{2}}{2(50)}\) = -4 m s-2
This retardation is the combined effect of braking and friction
∴ braking retardation =4 – 1 = 3 m s-2
From formula (iii), the braking force, F = 1500 × 3 = 4500 N
Answer:
The braking force is 4500 N.
![]()
Question 27.
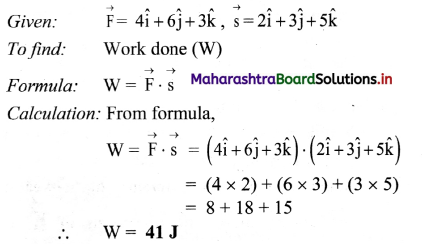
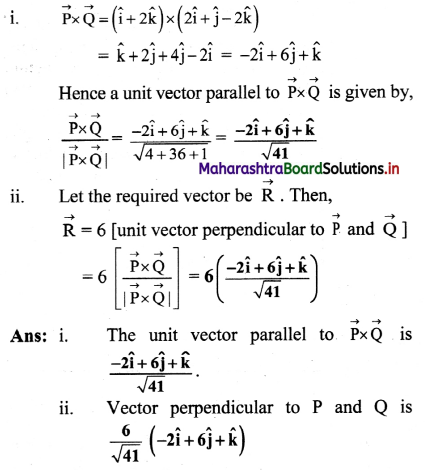
A body constrained to move along the z-axis of a coordinate system is subject to a constant force F given by \(\overrightarrow{\mathbf{F}}=(-\hat{\mathbf{i}}+2 \hat{\mathbf{j}}+3 \hat{\mathbf{k}})\) N where \(\hat{\mathbf{i}}\), \(\hat{\mathbf{j}}\), \(\hat{\mathbf{k}}\) are unit vectors along the x, y and z axis of the system respectively. What is the work done by this force in moving the body a distance of 4 m along the z-axis? (NCERT)
Solution:
Given: \(\overrightarrow{\mathbf{F}}=(-\hat{\mathbf{i}}+2 \hat{\mathbf{j}}+3 \hat{\mathbf{k}})\) N, \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{s}}=4 \hat{\mathrm{k}}\)
To find: work done (W)
Formula: W = \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{F}} \cdot \overrightarrow{\mathrm{s}}\)
Calculation: From formula,
W = \((-\hat{\mathrm{i}}+2 \hat{\mathrm{j}}+3 \hat{\mathrm{k}}) \cdot(4 \hat{\mathrm{k}})\)
= \(12 \hat{\mathrm{k}} \cdot \hat{\mathrm{k}}\) = 12 J
Answer:
The work done by the force is in moving the body 12 J.
Question 28.
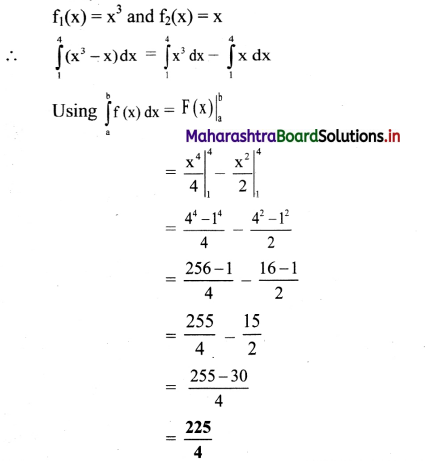
Over a given region, a force (in newton) varies as F = 3x2 – 2x + 1. In this region, an object is displaced from x1 = 20 cm to x2 = 40 cm by the given force. Calculate the amount of work done.
Solution:
Given: F = 3x2 – 2x + 1, x1 = 20 cm = 0.2 m,
x2 = 40 cm = 0.4 m.
To find: Work done (W)
Formula: W = \(\int_{A}^{B} \vec{F} \cdot \overrightarrow{d s}\)
Calculation:
From formula,
W = \(\int_{x_{1}}^{x_{2}} F \cdot d x=\int_{0.2}^{0.4}\left(3 x^{2}-2 x+1\right) d x\)
= [x3 – x2 + x]0.4
= [0.43 – 0.42 + 0.4] – [0.23 – 0.22 + 0.2]
= 0.304 – 0.168 = 0.136 J
The work done is 0.136 J.
Question 29.
A position dependent force f = 7 – 2x + 3x2 newton acts on a small body of mass 2 kg and displaces from x = 0 m to x = 5 m, calculate the work done.
Solution:
Given: F = 7 – 2x + 3x2, x = 0 at A and x = 5 at B.
To find: Work done (W)
Formula: W = \(\int_{A}^{B} \vec{F} \cdot \overrightarrow{d s}\)
Calculation: From formula,
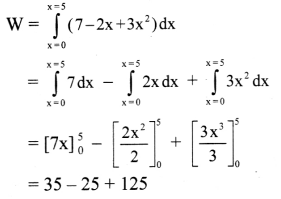
∴ W = 135 J
Answer:
The work done is 135 J.
Question 30.
State the principle of work-energy theorem in case of a conservative force and explain.
OR
Show that work done on a body by a conservative force is equal to the change in its kinetic energy
Answer:
Principle: Decrease in the potential energy due to work done by a conservative force is entirely converted into kinetic energy. Vice versa, for an object moving against a conservative force, its kinetic energy decreases by an amount equal to the work done against the force.
Work-energy theorem in case of a conservative force:
- Consider an object of mass m moving with velocity u experiencing a constant opposing force F which slows it down to v during displacement s.
- The equation of motion can be written as, v2 – u2 = -2as (negative acceleration for
opposing force.)
Multiplying throughout by \(\frac{\mathrm{m}}{2}\), we get,
\(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{2}\)mu2 – \(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{2}\)mv2 = (ma)s …. (1) - According to Newton’s second law of motion,
F = ma … (2) - From equations (1) and (2), we get,
\(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{2}\)mu2 – \(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{2}\)mv2 = F.s - But, \(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{2}\)mv2= Kf = final K.E of the body,
\(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{2}\)mu2 = Ki = initial K.E of the body. and, work done by the force = F.s
∴ work done by the force = kf – ki
= decrease in K.E of the body. - Thus, work done on a body by a conservative force is equal to the change in its kinetic energy.
Question 31.
Explain the work-energy theorem in case of an accelerating conservative force along with a retarding non-conservative force.
Answer:
- Consider an object dropped from some point at height h.
- While coming down its potential energy decreases.
∴ Work done = decrease in P.E of the body. - But, in this case, some part of the energy is used in overcoming the air resistance. This part of energy appears in some other forms such as heat, sound, etc. Thus, the work is not entirely converted into kinetic energy. In this case, the work-energy theorem can mathematically be written as,
∴ ∆ PE = ∆ K.E. + Wair resistance
∴ Decrease in the gravitational P.E. = Increase in the kinetic energy + work done against non-conservative forces.
Question 32.
A liquid drop of 1.00 g falls from height of cliff 1.00 km. It hits the ground with a speed of 50 m s-1. What is the work done by the unknown force? (Take g = 9.8 m/s2)
Solution:
Given: m = 1.0 g = 1.0 × 10-3 kg,
h = 1 km = 103 m, v = 50 ms-1
To find: Work done (Wf)
Formula: Wf = ∆ K.E – Wg
Calculation:
i. The change in kinetic energy of the drop
∆ K.E = (K.E.)final (K.E.)initial
∴ ∆ K.E. = \(\frac{1}{2} \mathrm{mv}^{2}-0\)
= \(\frac{1}{2} \times 1.0 \times 10^{-3} \times(50)^{2}\)
∴ ∆ K.E.= 1.25 J
ii. Work done by the gravitational force is,
Wg = mgh = 1.0 × 10-3 × 9.8 × 103 = 9.8 J
∴ Wg = 9.8J
From formula,
Wf = ∆K.E. – Wg = 1.25 – 9.8
Wf = -8.55 J
Answer:
Work done by the unknown force is – 8.55 J.
Question 33.
A body of mass 0.5 kg travels in a straight line with velocity y = ax3/2, where a = 5 m1/2s-1. What is the work done by the net force during its displacement from x = 0 to x = 2m? (NCERT)
Solution:
Given: M = 0.5 kg, y = ax3/2,
where a = 5 m-1/2s-1
Let v1 and v2 be the velocities of the body, when x = 0 and x = 2 m respectively. Then,
v1 = 5 × 03/2 = 0, v2 = 5 × 23/2 = \(10 \sqrt{2}\) m
To find: Work done (W)
Formula: Work done = Increase in kinetic energy
W = \(\frac{1}{2} \mathrm{M}\left(\mathrm{v}_{2}^{2}-\mathrm{v}_{1}^{2}\right)\)
Calculation: From formula,
W = \(\frac{1}{2}\) × 0.5 × [latex](10 \sqrt{2})^{2}-0^{2}[/latex]
∴ W = 50J
Answer:
Work done by the net force on the body is 50 J.
Question 34.
A particle of mass 12 kg is acted upon by a force f = (100 – 2x2) where f is in newton and ‘x’ is in metre. Calculate the work done by this force in moving the particle x = 0 to x = -10 m. What will be the speed at x = 10 m if it starts from rest?
Solution:
Given: F = 100 – 2x2
at A, x = 0 and at B, x = -10 m
To find: Work done (W), speed (v)
Formulae:
i. W = \(\int_{A}^{B} \vec{F} \cdot d s\)
ii. W = K.E. = \(\frac{1}{2} \mathrm{mv}^{2}\)
Calculation:
From formula (i),
W = \(\int_{A}^{B} \vec{F} \cdot \overline{d s}=\int_{x=0}^{x=-10} F d x\)

Answer:
- Work done by the force on the particle is 333.3 J.
- The speed of the particle at x = 10 will be 7.45 m/s.
Question 35.
Define free body diagram. In the figure given below, draw the free body diagrams for mass of 2 kg, 4 kg and 5 kg and hence state their force equations.
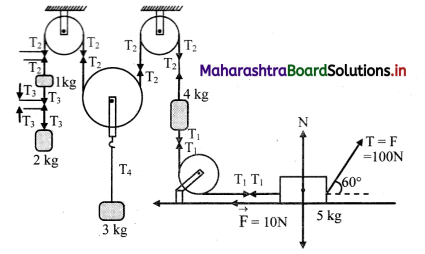
Answer:
i. The diagram showing the forces acting on only one body at a time along-with its acceleration is called a free body diagram.
ii. The free body diagram for the mass of 2 kg is
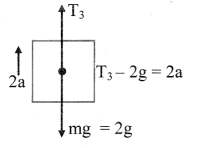
Free body diagram for 2 kg mass
The force equation is given as,
2a = T3 – 2g
iii. The free body diagram for the mass of 4 kg is,
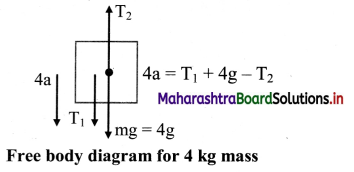
The force equation is given as, 4a = T1 + 4g – T2
iv. The free body diagram for the mass of 5kg is,
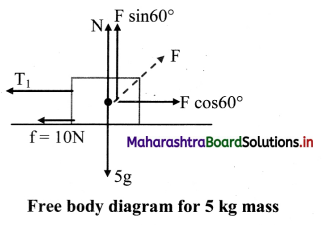
The force equation for the mass of 5 kg is given as,
N + F sin 60° = 5g, along the vertical direction.
T1 + 10 = F cos 60°, along the horizontal direction (Considering the mass is in equilibrium).
Question 36.
Figure shows a fixed pulley. A massless inextensible string with masses m1 and m2 > m1 attached to its two ends is passing over the pulley. Such an arrangement is called an Atwood machine. Calculate accelerations of the masses and force due to the tension along the string assuming axle of the pulley to be frictionless.
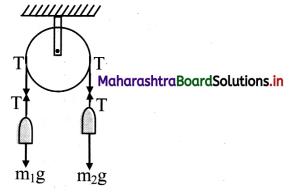
Solution:
Method I: As m2 > m1, mass m2 is moving downwards and mass m1 is moving upwards.
Net downward force = F = (m2) g – (m1) g
= (m2 – m1)g
the string being inextensible, both the masses travel the same distance in the same time. Thus, their accelerations are equal in magnitude (one upward, other downward). Let it be a.
Total mass in motion, M = m2 + m1
∴ a = \(\frac{F}{M}=\left(\frac{m_{2}-m_{1}}{m_{2}+m_{1}}\right) g\) …. (i)
For mass m1, the upward force is the force due to tension T and downward force is mg. It has upward acceleration a. Thus, T – m1g = m1a
∴ T = m1(g + a)
Using equation (i), we get,
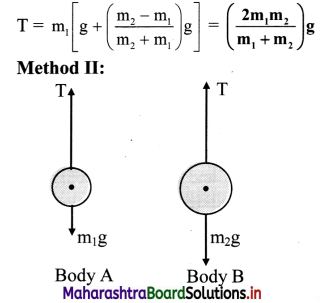
From the free body equation for the first body,
T – m1g = m1a .. (i)
From the free body equation for the second body,
m2g – T = m2a … (ii)
Adding (i) and (ii), we get,
a = \(\left(\frac{\mathrm{m}_{2}-\mathbf{m}_{1}}{\mathrm{~m}_{2}+\mathrm{m}_{1}}\right) \mathbf{g}\) ….(iii)
Solving equations. (ii) and (iii) for T, we get,
T = m2(g – a) = \(\left(\frac{2 m_{1} m_{2}}{m_{1}+m_{2}}\right) g\)
Question 37.
Write a note on elastic collision.
Answer:
- Collision between two bodies in which kinetic energy of the entire system is conserved along with the linear momentum is called as elastic collision.
- In an elastic collision,
\(\mathrm{m}_{1} \overrightarrow{\mathrm{u}_{1}}+\mathrm{m}_{2} \overrightarrow{\mathrm{u}_{2}}=\mathrm{m}_{1} \overrightarrow{\mathrm{v}_{1}}+\mathrm{m}_{2} \overrightarrow{\mathrm{v}}_{2}\) - In an elastic collision,
\(\sum \mathrm{K} \cdot \mathrm{E}_{\text {‘initial }}=\sum \mathrm{K} \cdot \mathrm{E}_{\text {. final }}\) - An elastic collision is impossible in daily life.
- However, in many situations, the interatomic and intermolecular collisions are considered to be elastic.
Question 38.
Write a note on inelastic collision.
Answer:
- A collision is said to be inelastic if there is a loss in the kinetic energy during collision, but linear momentum is conserved.
- In an inelastic collision, m1u1 + m2u2 = m1v1 + m2v2.
- In an inelastic collision,
\(\sum \mathrm{K} \cdot \mathrm{E}_{\text {.initial }} \neq \sum \mathrm{K} \cdot \mathrm{E}_{\text {.final }}\) - The loss in kinetic energy is either due to internal friction or vibrational motion of atoms causing heating effect.
Question 39.
Define perfectly inelastic collision. Give an example of it.
Answer:
- Collision in which the colliding bodies stick together after collision and move with a common velocity is called perfectly inelastic collision.
- The loss in kinetic energy is maximum in perfectly elastic collision.
- Example: Lump of mud thrown on a wall sticks to the wall due to the loss of kinetic energy.
Question 40.
In case of an elastic head on collision between two bodies, derive an expression for the final velocities of the bodies in terms of their masses and velocities before collision.
Answer:
Head on elastic collision of two spheres:
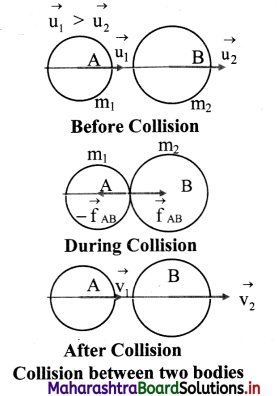
i. Consider two rotating smooth bodies A and B of masses m1 and m2 respectively moving
along the same straight line.
ii. Let \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{u}}_{1}\) = initial velocity of the sphere A before collision.
\(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{u}}_{2}\) = initial velocity of the sphere B before collision.
\(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{v}}_{1}\) = velocity of the sphere A after collision.
\(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{v}}_{2}\) = velocity of the sphere B after collision.
iii. After the elastic collision, the spheres separate and move along the same straight line without rotation.
iv. According to the law of conservation of momentum,
m1\(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{u}}_{1}\) + m2\(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{u}}_{2}\) = m1\(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{v}}_{1}\) + m2\(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{v}}_{2}\) ….(i)
According to the law of conservation of energy (as kinetic energy is conserved during elastic collision),
![]()
v. Since kinetic energy is a scalar quantity, the terms involved in the above equations are scalars.
vi. The equation (1) can be written in scalar form as,
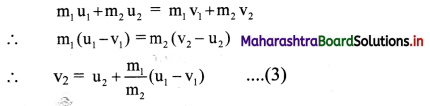
vii. Also the equation (2) can be written as,
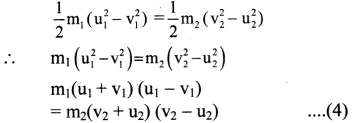
viii. Now dividing equation (4) by (3) we get,
(u1 + v1) = (u2 + v2)
∴ u1 + v1 = u2 + v2
∴ v2 = u1 – u2 + v1 … (5)
ix. Comparing equation (3) and (5),
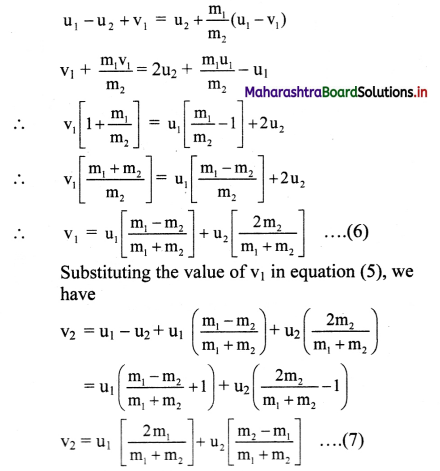
Equations, (6) and (7), represent the final velocities of two spheres after collision.
Question 41.
Are you aware of elasticity of materials? Is there any connection between elasticity of materials and elastic collisions?
Answer:
(Students should answer the question as per their understanding).
Question 42.
Two bodies undergo one-dimensional, inelastic, head-on collision. State an expression for their final velocities in terms
of their masses, initial velocities and coefficient of restitution.
Answer:
If e is the coefficient of restitution, the final velocities after an inelastic, head on collision are given as,
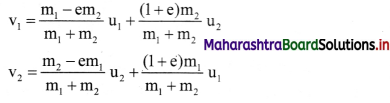
Question 43.
Two bodies undergo one-dimensional, inelastic, head-on collision. State an expression for the loss in the kinetic energy.
Answer:
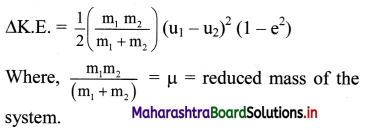
ii. As e < 1, (1 – e2) is always positive. Thus, there is always a loss of kinetic energy in an inelastic collision.
![]()
Question 44.
Two bodies undergo one-dimensional, inelastic, head-on collision. Obtain an expression for the magnitude of impulse.
Answer:
i. When two bodies undergo collision, the linear momentum delivered by the first body to the second body must be equal to the change in momentum or impulse of the second body and vice versa.
∴ Impulse,
|J| = |∆p1| = |∆p2|
= |m1v1 – m1u1| = |m2v2 – m2u2| ….(1)
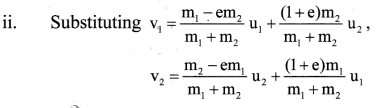
In equation (1) and solving, we get,
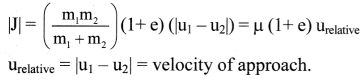
Question 45.
Two bodies undergo one-dimensional, perfectly inelastic, head-on collision. Derive an expression for the loss in the kinetic energy.
Answer:
i. Let two bodies A and B of masses m1 and m2 move with initial velocity \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{u}}_{1}\) and \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{u}}_{2}\), respectively such that particle A collides head on with particle B i.e., u1 > u2.
ii. If the collision is perfectly inelastic, the particles stick together and move with a common velocity \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{v}}\) after the collision along the same straight line.
loss in kinetic energy = total initial kinetic energy – total final kinetic energy.
iii. By the law of conservation of momentum,
m1u1 + m2u2 = (m1 + m2)v
∴ v = \(\frac{\mathrm{m}_{1} \mathrm{u}_{1}+\mathrm{m}_{2} \mathrm{u}_{2}}{\mathrm{~m}_{1}+\mathrm{m}_{2}}\)
iv. Loss of Kinetic energy,
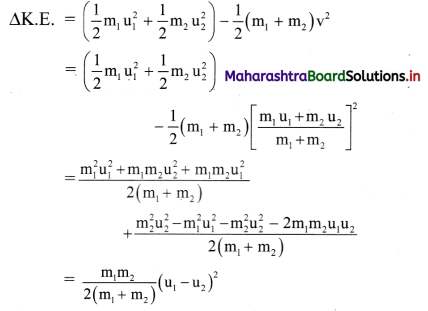
iv. Both the masses and the term (u1 – u2)2 are positive. Hence, there is always a loss in a perfectly inelastic collision. For a perfectly inelastic collision, as e = 0, the loss is maximum.
Question 46.
Distinguish between elastic and inelastic collision.
Answer:
| No. | Elastic Collision | Inelastic Collision |
| i. | In an elastic collision, both momentum and kinetic energy are conserved. | In an inelastic collision, momentum is conserved but kinetic energy is not conserved. |
| ii. | The total kinetic energy after collision is equal to the total kinetic energy before collision. | The total kinetic energy after the collision is not equal to the total kinetic energy before collision. |
| iii. | Coefficient of restitution (e) is equal to one. | Coefficient of restitution (e) is less than one. For a perfectly inelastic collision coefficient of restitution is equal to zero. |
| iv. | Bodies do not stick together in elastic collision. | Bodies stick together in a perfectly inelastic collision. |
| v. | Sound, heat and light are not produced. | Sound or light or heat or all of these may be produced. |
Question 47.
Explain elastic collision in two dimensions.
Answer:
i. Suppose a particle of mass mi moving with initial velocity \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{u}_{1}}\), undergoes a non head-on collide with another particle of mass m2 and initial velocity \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{u}_{2}}\).
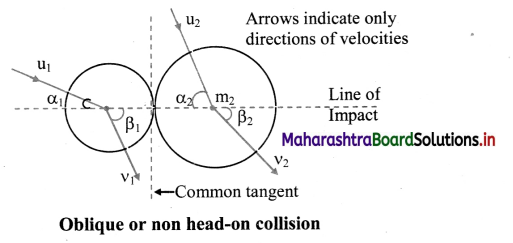
ii. Let us consider two mutually perpendicular directions; Common tangent at the point of impact, along which there is no force (or no change of momentum).
Line of impact which is perpendicular to the common tangent through the point of impact, in the two-dimensional plane of initial and final velocities.
iii. Applying the law of conservation of linear momentum along the line of impact, we have, m1u1 cos α1 + m2u2 cos α2 = m1v1 cos β1 + m2v2 cos β2
As there is no force along the common tangent,
m1u1 sin α1 = m1u1 sin β1 and m2u2 sin α2 = m2v2 sin β2
iv. Coefficient of restitution (e) along the line of impact is given as

Question 48.
Two bodies undergo a two-dimensional collision. State an expression for the magnitude of impulse along the line of impact and the loss in kinetic energy.
Answer:
i. For two bodies undergoing a two-dimensional collision, the magnitude of impulse along the line of impact is given as, Magnitude of the impulse, along the line of impact,
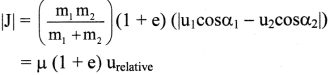
ii. The loss in the kinetic energy is given as Loss in the kinetic energy = ∆ (K.E.)
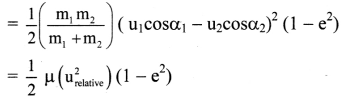
Question 49.
0ne marble collides head-on with another identical marble at rest. If the collision is partially inelastic, determine the ratio of their final velocities in terms of coefficient of restitution e.
Solution:
According to conservation of momentum,
m1u1 + m2u2 = m1v1 + m2v2
As m1 = m2, we get, u1 + u2 = v1 + v2
∴ If u2 = 0, we get, v1 + v2 = u1 ….. (i)
Coefficient of restitution,

Question 50.
A 10 kg mass moving at 5 m/s collides head- on with a 4 kg mass moving at 2 m/s in the same direction. If e = \(\frac{1}{2}\), find their velocity after impact.
Solution:
Given: m1 = 10 kg, m2 = 4 kg
u1 = 5 m/s, u2 = 2 m/s, e = \(\frac{1}{2}\)
To find: Velocity after impact (v1 and v2)
Formulae:
i. m1u1 + m2u2 = m1v1 + m2v2
ii. e = \(\left(\frac{v_{2}-v_{1}}{u_{1}-u_{2}}\right)\)
Calculation:
From formula (i),
10 × 5 + 4 × 2 = 10v1 + 4v2
∴ 5v1 + 2v2 = 29 … (1)
From formula (ii),
v2 – v1 = e(u1 – u2) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) (5 – 2) = \(\frac{3}{2}\)
∴ 2v2 – 2v1 = 3 … (2)
Solving (1) and (2), we have
∴ v1 = \(\frac{26}{7}\) m/s and v2 = \(\frac{73}{14}\) m/s
Answer:
The respective velocities of the two masses are \(\frac{26}{7}\) m/s and \(\frac{73}{14}\) m/s.
Question 51.
A metal ball falls from a height 1 m on a steel plate and jumps upto a height of 0.81 m. Find the coefficient of restitution.
Solution:
As the ball falls to the steel plate P.E changes to kinetic energy.
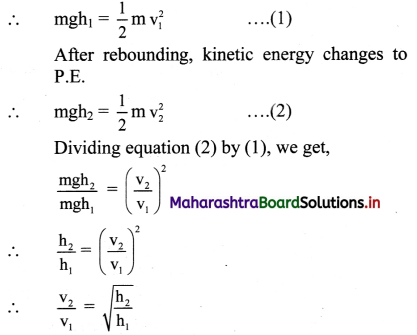
As ground is stationary, both its initial and final velocities are zero.
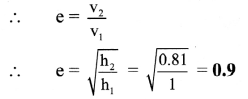
Question 52.
Two bodies of masses 5 kg and 3 kg moving in the same direction along the same straight line with velocities 5 m s-1 and 3 m s-1 respectively suffer one-dimensional elastic collision. Find their velocities after the collision.
Solution:
Given: m1 = 5kg, u1 = 5ms-1, m2 = 3kg, u2 = 3 m s-1
To find: velocities after collision (v1 and v2)
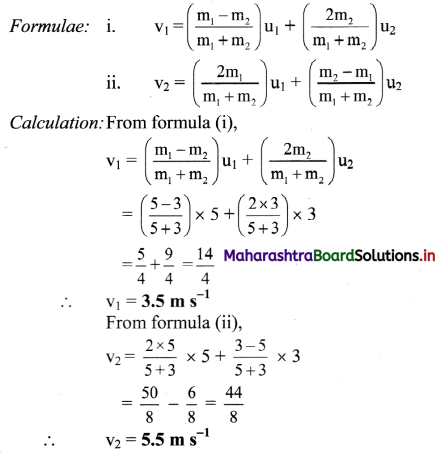
Answer:
The velocities of the two bodies after collision are 3.5 m/s and 5.5 m/s.
Question 53.
A 20 g bullet leaves a machine gun with a velocity of 200 m/s. If the mass of the gun is 20 kg, find its recoil velocity. If the gun fires 20 bullets per second, what force is to be applied to the gun to prevent recoil?
Solution:
Given: m1 = 20g = 0.02 kg, m2 = 20 kg, v1 = 200 m/s, t = \(\frac{1}{20}\) s,
To find: Recoil velocity (v2), applied force (F)
Formulae:
i. v2 = \(-\frac{\mathrm{m}_{1} \mathrm{v}_{1}}{\mathrm{~m}_{2}}\)
ii. F = ma
Calculation: From formula (i),
∴ v2 = \(-\frac{0.02}{20} \times 200\)
= -0.2 m/s
Negative sign shows that the machine gun moves in a direction opposite to that of the bullet.
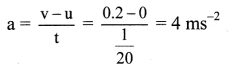
From formula (ii),
∴ F = m2 × a = 20 × 4 = 80N
Answer:
The recoil velocity of gun is 0.2 m/s and the required force to prevent recoil is 80 N.
Question 54.
A shell of mass 3 kg is dropped from some height. After falling freely for 2 seconds, it explodes into two fragments of masses 2 kg and 1 kg. Kinetic energy provided by the explosion is 300 J. Using g = 10 m/s2, calculate velocities of the fragments. Justify your answer if you have more than one options.
Solution:
Total mass = m1 + m2 = 3 kg
Initially, when the shell falls freely for 2 seconds, v = u+ at = 0 + 10(2) = 20 ms-1 = u1 = u2
According to conservation of linear momentum,
m1u1 + m2u2 = m1v1 + m2v2

There are two possible answers since the positions of two fragments can be different as explained below.
Case 1: v1 = 30 m s-1 and v2 = 0 with the lighter fragment 2 above.
Case 2: v1 = 10 m s-1 and v2 = 40 m s-1 with the lighter fragment 2 below, both moving downwards.
Question 55.
Bullets of mass 40 g each, are fired from a machine gun at a rate of 5 per second towards a firmly fixed hard surface of area 10 cm2. Each bullet hits normal to the surface at 400 m/s and rebounds in such a way that the coefficient of restitution for the collision between bullet and the surface is 0.75. Calculate average force and average pressure experienced by the surface due to this firing.
Solution:
For the collision,
u1 = 400 m s-1, e = 0.75
For the firmly fixed hard surface, u2 = v2 = 0
e = 0.75 = \(\frac{v_{1}-v_{2}}{u_{2}-u_{1}}=\frac{v_{1}-0}{0-400}\)
∴ v1 = -300 m/s.
Negative sign indicates that the bullet rebounds in exactly opposite direction.
Change in momentum of each bullet = m(v1 – u1)
The same momentum is transferred to the surface per collision in opposite direction.
∴ Momentum transferred to the surface, per collision,
p = m (u1 – v1) = 0.04(400 – [-300]) = 28 Ns
The rate of collision is same as rate of firing.
∴ Momentum received by the surface per second, \(\frac{\mathrm{dp}}{\mathrm{dt}}\) = average force experienced by the surface = 28 × 5 = 140 N
This is the average force experienced by the surface of area A = 10 cm2 = 10-3 m2
∴ Average pressure experienced,
P = \(\frac{\mathrm{F}}{\mathrm{A}}=\frac{140}{10^{-3}}\) = 1.4 × 105 N m-2
∴ P ≈ 1.4 times the atmospheric pressure.
Answer:
The average force and average pressure experienced by the surface due to the firing is 140 N and 1.4 × 105 N m-2 respectively.
Question 56.
A shell of mass 0.020 kg is fired by a gun of mass 100 kg. If the muzzle speed of the shell is 80 m s-1, what is the recoil speed of the gun? (NCERT)
Solution:
Given: m1 = 0.02 kg, m2 = 100 kg, v1 = 80 m s-1
To find: Recoil speed (v2)
Formula: m1u1 + m2u2 = m1v1 + m2v2
Calculation: Initially gun and shell are at rest.
∴ m1u1 + m2u2 = 0
Final momentum = m1v1 – m2v2
Using formula,
0 = 0.02 (80) – 100(v2)
∴ v2 = \(\frac{0.02 \times 80}{100}\) = 0.016 ms-1
Answer:
The recoil speed of the gun is 0.016 m s-1.
Question 57.
Two billiard balls each of mass 0.05 kg moving in opposite directions with speed 6 m s-1 collide and rebound with the same speed. What is the impulse imparted to each bail due to the other? (NCERT)
Solution:
Given: m = 0.05 kg. u = 6 m/s, v = -6 m/s
To find: Impulse (J)
Formula: J = m (v – u)
calculation: From formula,
J = 0.05 (-6 – 6) = -0.6 kg m s-1
Answer:
Impulse received by each ball is -0.6 kg m s-1.
Question 58.
A bullet of mass 0.1 kg moving horizontally with a velocity of 20 m/s strikes a target and brought to rest in 0.1 s. Find the impulse and average force of impact.
Solution:
Given: m = 0.1 kg, u = 20 m/s, t = 0.1 s
To find: Impulse (J), Average force (F)
Formulae:
i. J = mv – mu
ii. F = \(m \frac{(v-u)}{t}\)
Calculation:
From formula (i).
J = m(v – u) = 0.1 (0 – 20) = -2 Ns
From formula (ii),
F = \(\frac{m(v-u)}{t}=\frac{2}{0.1}=20 N\)
Answer:
Magnitude of impulse is 2 Ns, average force of impact is 20 N.
![]()
Question 59.
A batsman deflects a ball by an angle of 45° without changing its initial speed which is equal to 54 km/h. What is the impulse imparted to the ball? (Mass of the ball is 0.15 kg) (NCERT)
Answer:
Let the point B represents the position of bat. The ball strikes the bat with velocity v along the path AB and gets deflected with same velocity along BC. such that ∠ABC = 45°
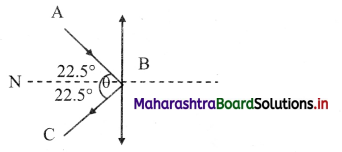

Thus, impulse imparted to the ball is 4.157 kg ms-1
Question 60.
A cricket ball of mass 150 g moving with a velocity of 12 m/s is turned back with a velocity of 20 m/s on hitting the bat. The force of the ball lasts for 0.01 s. Find the average force exerted on the ball by the bat.
Solution:
m = 0.150 kg, v = 20 m/s,
u = -12 m/s and t = 0.01 s
To find: Average force (F)
Formula: F = \(\frac{m(v-u)}{t}\)
Calculation: From formula,
F = \(\frac{0.150[20-(-12)]}{0.01}\) = 480 N
Answer:
The average force exerted on the ball by the bat is 480 N.
Question 61.
Mass of an Oxygen molecule is 5.35 × 10-26 kg and that of a Nitrogen molecule is 4.65 × 10-26 kg. During their Brownian motion (random motion) in air, an Oxygen molecule travelling with a velocity of 400 m/s collides elastically with a nitrogen molecule travelling with a velocity of 500 m/s in the exactly opposite direction. Calculate the impulse received by each of them during collision. Assuming that the collision lasts for
1 ms, how much is the average force experienced by each molecule?
Solution:
Let, m1 = mO = 5.35 × 10-26 kg,
m2 = mN = 4.65 × 10-26 kg,
∴ u1 = 400 ms-1 and u2 = -500 ms-1 taking direction of motion of oxygen molecule as the positive direction.
For an elastic collision,
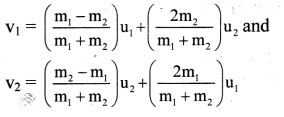

Hence, the net impulse or net change in momentum is zero.
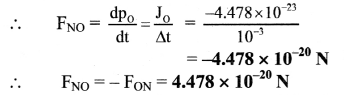
Answer:
The average force experienced by the nitrogen molecule and the oxygen molecule are
-4.478 × 10-20 N and 4.478 × 10-20 N.
Question 62.
Explain rotational analogue of the force. On what factors does it depend? Represent it in vector form.
Answer:
- Rotational analogue of the force is called as moment of force or torque.
- It depends on the mass of the object, the point of application of the force and the angle between direction of force and the line joining the axis of rotation with the point of application.
- In its mathematical form, torque or moment of a force is given by
\(\vec{\tau}=\overrightarrow{\mathrm{r}} \times \overrightarrow{\mathrm{F}}\)
where \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{F}}\) is the applied force and \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{r}}\) is the position vector of the point of application of the force from the axis of rotation.
Question 63.
Illustrate with an example how direction of the torque acting on any object is determined.
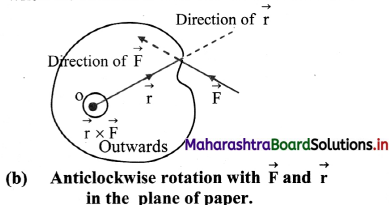
Answer:
i. Consider a laminar object with axis of rotation perpendicular to it and passing through it as shown in figure (a).
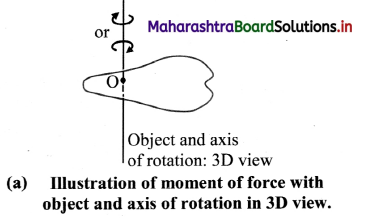
ii. Figure (b) indicates the top view of the object when the rotation is in anticlockwise direction
iii. Figure (c) shows the view from the top, if rotation is in clockwise direction.
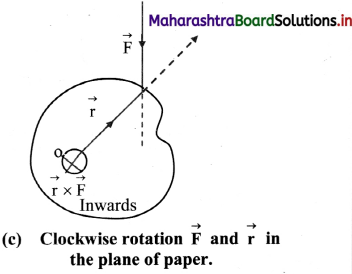
iv. The applied force \(\vec{F}\) and position vector \(\vec{r}\) of the point of application of the force are in the plane of these figures.
v. Direction of the torque is always perpendicular to the plane containing the vectors \(\vec{r}\) and \(\vec{F}\) and can be obtained from the rule of cross product or by using the right-hand thumb rule.
vi. In Figure (b), it is perpendicular to the plane of the figure and outwards while in the figure (c), it is inwards.
Question 64.
State the equation for magnitude of torque and explain various cases of angle between the direction of \(\overrightarrow{\mathbf{r}}\) and \(\overrightarrow{\mathbf{F}}\).
Answer:
Magnitude of torque, \(\tau\) = r F sin θ
where θ is the smaller angle between the directions of \(\overrightarrow{\mathbf{r}}\) and \(\overrightarrow{\mathbf{F}}\).
Special cases:
- If θ = 90°, \(\tau\) = \(\tau\)max = rF. Thus, the force should be applied along normal direction for easy rotation.
- If θ = 0° or 180°, \(\tau\) = \(\tau\)min = 0. Thus, if the force is applied parallel or anti-parallel to \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{r}}\), there is no rotation.
- Moment of a force depends not only on the magnitude and direction of the force, but also on the point where the force acts with respect to the axis of rotation. Same force can have different torque as per its point of application.
Question 65.
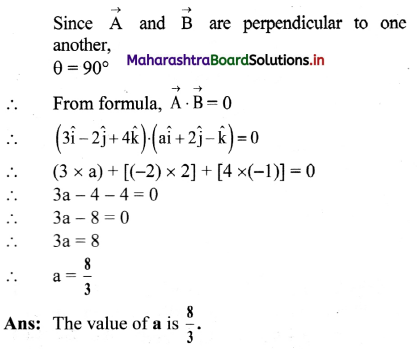
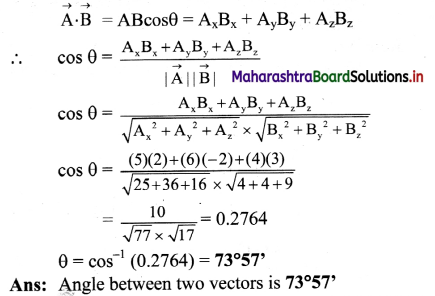
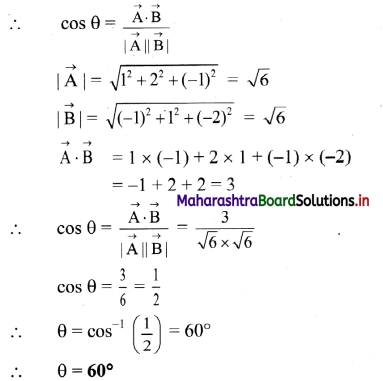
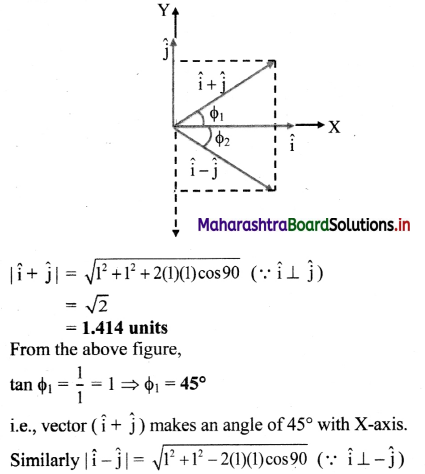
A force \(\overrightarrow{\mathbf{F}}=\mathbf{3} \hat{\mathbf{i}}+\hat{\mathbf{j}}-\mathbf{4} \hat{\mathbf{k}}\) is applied at a point (3, 4, -2). Find its torque about the point (-1, 2, 4).
Solution:
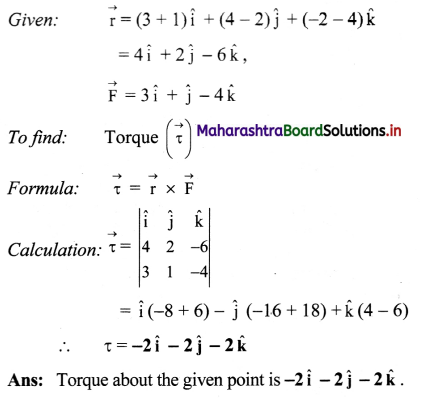
![]()
Question 66.
Define couple. Show that moment of couple is independent of the points of application of forces.
Answer:
A pair of forces consisting of two forces of equal magnitude acting in opposite directions along different lines of action is called a couple.
- Figure shows a couple consisting of two forces \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{F}}_{1}\) and \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{F}}_{2}\) of equal magnitudes and opposite directions acting along different lines of action separated by a distance r.
- Position vector of any point on the line of action of force \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{F}}_{1}\) from the line of action of force \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{F}}_{2}\) is \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{r}}_{12}\). Similarly, the position vector of any point on the line of action of force \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{F}}_{2}\) from the line of action of force \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{F}}_{1}\) is \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{r}}_{21}\).
- Torque or moment of the couple is then given mathematically as
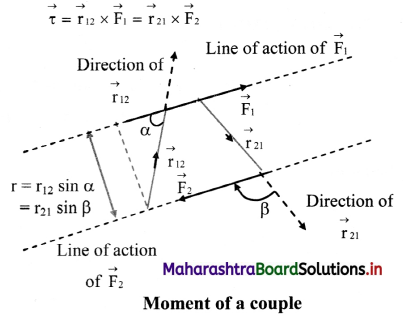
- From the figure, it is clear that r12 sinα = r21 sin β = r.
- If \(\left|\overrightarrow{\mathrm{F}}_{1}\right|=\left|\overrightarrow{\mathrm{F}}_{2}\right|\) = F, the magnitude of torque is given by
\(\tau=\mathrm{r}_{12} \mathrm{~F}_{1} \sin \alpha\) = \(r_{21} F_{2} \sin \beta=r F\) - It clearly shows that the torque corresponding to a given couple, i.e., the moment of a given couple is constant, i.e., it is independent of the points of application of forces.
Question 67.
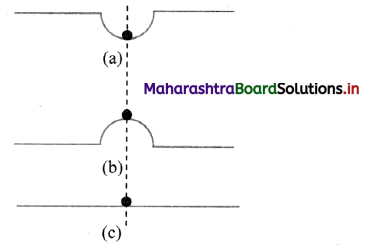
The figure below shows three situations of a ball at rest under the action of balanced forces. Is the bail in mechanical equilibrium? Explain how the three situations differ.
Answer:
- In all these cases, as the ball is at rest under the action of balanced forces i.e, there is no net force acting on it. Hence, it is in mechanical equilibrium.
However, potential energy-wise, the three situations show the different states of mechanical equilibrium. - Stable equilibrium: In situation (a), potential energy of the system is at its local minimum. If it is disturbed slightly from its equilibrium position and released, it tends to recover its position. In this situation, the ball is most stable and is said to be in stable equilibrium.
- Unstable equilibrium: In situation (b), potential energy of the system is at its local maximum. If it is slightly disturbed from its equilibrium position, it moves farther from that position. This happens because initially, if disturbed, it tries to achieve the configuration of minimum potential energy. In this situation, the ball is said to be in unstable equilibrium.
- Neutral equilibrium: in situation (e), potential energy of the system is constant over a plane and remains same at any position. Thus, even if the ball is disturbed, it still remains in equilibrium, practically at any position. In this situation, the ball is in neutral equilibrium.
Question 68.
Two weights 5 kg and 8 kg are suspended from a uniform rod of length 10 m and weighing 3 kg. The distances of the weights from one end are 2 m and 7 m. Find the point at which the rod balances.
Solution:
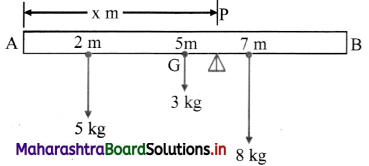
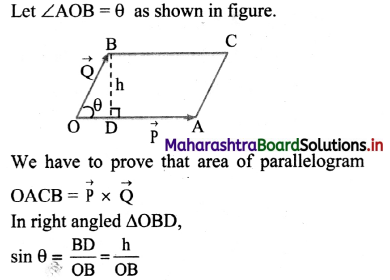
Let the rod balance at a point P, x m from the end A of the rod AB. The suspended weight and the centre of gravity of the rod G is shown in the figure.
P = 5 + 3 + 8 = 16kg
Taking moments about A,
16 × x = 5 × 2 + 3 × 5 + 8 × 7
16x = 10 + 15 + 56 = 81
∴ x = \(\frac{81}{16}\) = 5.1 m
Answer:
The rod balances at 5.1 m from end A.
Question69.
A metre stick is balanced on a knife edge at its centre. When two coins, each of mass 5 g are put one on top of the other at the 12.0 cm mark, the stick is found to be balanced at 45.0 cm. What is the mass of the metre stick? (NCERT)
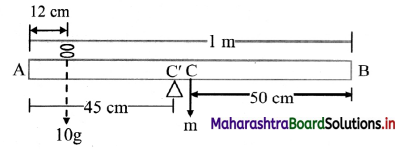
Consider the metre scale AB. Let its mass be concentrated at C at 50 cm. mark. Upon placing coins, balancing point of the scale and the coins system is shifted to C’ at 45 cm mark.
For equilibrium about C’
10(45 – 12) = m (50 – 45)
m = \(\frac{10 \times 33}{5}\) = 66g
Answer:
The mass of the metre scale is 66 g.
Question 70.
The diagram shows a uniform beam of length 10 m, used as a balance. The beam is pivoted at its centre. A 5.0 N weight is attached to one end of the beam and an empty pan weighing 0.25 N Is attached to the other end of the beam.
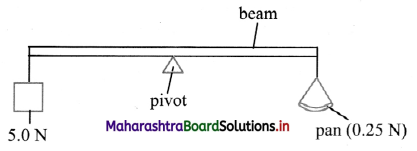
i. What is the moment of couple at pivot?
ii. If pivot is shifted 2 ni towards left, then what will be moment of couple at new position?
Answer:
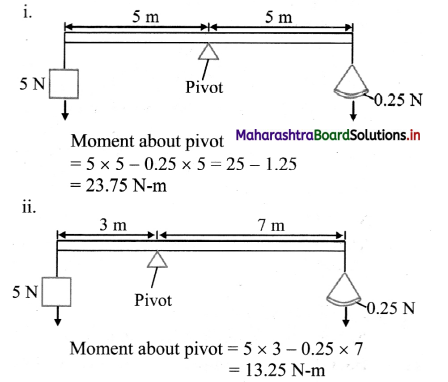
Answer:
- The moment of couple at center is 23.75 N-m.
- The moment of couple at new position is 13.25 N-m.
∴ For equilibrium,
40 × x = 20 × 0.5
∴ x = \(\frac{1}{4}\) = 0.25 m
Hence, the total distance walked by the person is 1.25 m.
Ans
The person can walk 1.25 m before the plank topples.
![]()
Question 71.
Define centre of mass.
Answer:
Centre of mass of a body is a point about which the summation of moments of masses in the system is zero.
Question 72.
Derive an expression for the position of centre of mass of a system of n particles and for continuous mass distribution.
Answer:
System of n particles;
i. Consider a system of n particles of masses m1, m2, …, mn having position vectors \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{r}_{1}}\), \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{r}_{2}}\),….., \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{r}_{n}}\) from the origin O.
The total mass of the system is,
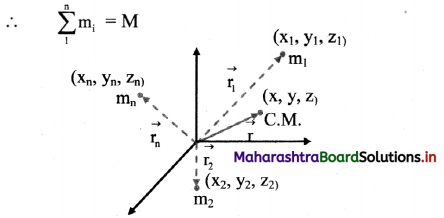
Centre of mass for n particles
ii. Position vector \(\vec{r}\) of their centre of mass from the same origin is then given by
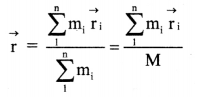
iii. If the origin is at the centre of mass, \(\overrightarrow{\mathbf{r}}\) = 0
∴ \(\sum_{1}^{\mathrm{n}} \mathrm{m}_{\mathrm{i}} \overrightarrow{\mathrm{r}}_{\mathrm{i}}\) = 0,
iv. In this case, \(\sum_{1}^{n} m_{i} \vec{r}_{i}\) gives the moment of masses (similar to moment of force) about the centre of mass.
v. If (x1, x2, …… xn), (y1, y2, …..yn), (z1, z2, …. zn) are the respective x, y and z – coordinates of (r1, r2,…….. rn) then x,y and z – coordinates of the centre of mass are given by,
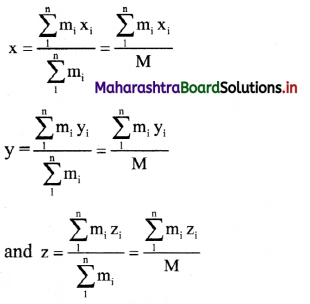
vi. Continuous mass distribution: For a continuous mass distribution with uniform density, the position vector of the centre of mass is given by,
r = \(\frac{\int \vec{r} d m}{\int d m}=\frac{\int \vec{r} d m}{M}\)
Where \(\int \mathrm{dm}=\mathrm{M}\) is the total mass of the object.
vii. The Cartesian coordinates of centre of mass are
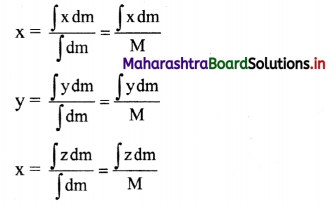
Question 73.
State the expression for velocity of the centre of mass of a system of n particles and for continuous mass distribution.
Answer:
Let v1, v2,…..vn be the velocities of a system of point masses m1, m2, … mn. Velocity of the centre of mass of the system is given by
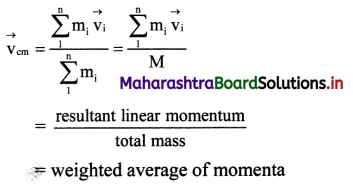
x, y and z components of \(\overrightarrow{\mathbf{v}}\) can be obtained similarly.
For continuous distribution, \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{v}}_{\mathrm{cm}}\) = \(\frac{\int \vec{v} \mathrm{dm}}{\mathrm{M}}\)
Question 74.
State the expression for acceleration of the centre of mass of a system of n particles and for continuous mass distribution.
Answer:
Let a1, a2,…. an be the accelerations of a system of point masses m1, m2 … mn.
Acceleration of the centre of mass of the system is given by
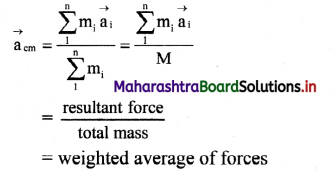
x, y and z components of can be obtained similarly.
For continuous distribution, \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{a}}_{\mathrm{cm}}\) = \(\frac{\int \vec{a} d m}{\mathrm{M}}\)
Question 75.
State the characteristics of centre of mass.
Answer:
- Centre of mass is a hypothetical point at which entire mass of the body can be assumed to he concentrated.
- Centre of mass is a location, not a physical quantity.
- Centre of mass is particle equivalent of a given object for applying laws of motion.
- Centre of mass is the point at which applied force causes only linear acceleration and not angular acceleration.
- Centre of mass is located at the centroid, for a rigid body of uniform density.
- Centre of mass is located at the geometrical centre, for a symmetric rigid body of uniform density.
- Location of centre of mass can be changed only by an external unbalanced force.
- Internal forces (like during collision or explosion) never change the location of centre of mass.
- Position of the centre of mass depends only upon the distribution of mass, however, to describe its location we may use a coordinate system with a suitable origin.
- For a system of particles, the centre of mass need not coincide with any of the particles.
- While balancing an object on a pivot, the line of action of weight must pass through the centre of mass and the pivot. Quite often, this is an unstable equilibrium.
- Centre of mass of a system of only two particles divides the distance between the particles in an inverse ratio of their masses, i.e., it is closer to the heavier mass.
- Centre of mass is a point about which the summation of moments of masses in the system is zero.
- If there is an axial symmetry for a given object, the centre of mass lies on the axis of symmetry.
- If there are multiple axes of symmetry for a given object, the centre of mass is at their point of intersection.
- Centre of mass need not be within the body.
Example: jumper doing fosbury flop.
![]()
Question 76.
The mass of moon is 0.0 123 times the mass of the earth and separation between them is 3.84 × 108 m. Determine the location of C.M as measured from the centre of the earth.
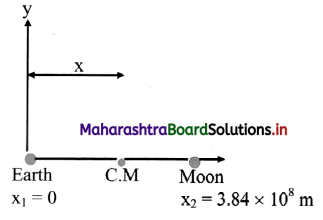
Solution:

Answer:
The location of centre of mass as measured from the center of the earth is 4.67 × 106 m.
Question 77.
Three particles of masses 3 g, 5 g and 8 g are situated at point (2, 2, 2), (-3, 1, 4) and (-1, 3, -2) respectively. Find the position vector of their centre of mass.
Solution:
m1 = 3 g, m2 = 5 g, m3 = 8 g, x1 = 2, y1 = 2, z1 = 2
x2 = -3, y2 = 1, z2 = 4,
x3 = -1, y3 = 3, z3 = -2
Let (X, Y, Z) be co-ordinates of C.M., then
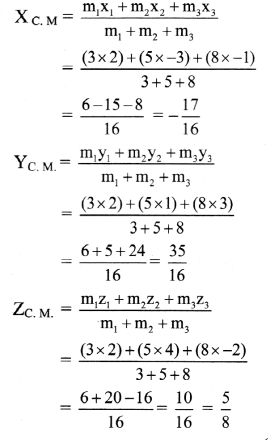
The co-ordinates of the C.M. are \(\left(-\frac{17}{16}, \frac{35}{16}, \frac{5}{8}\right)\)
Answer:
The position vector of the C.M. is \(-\frac{17}{16} \hat{\mathbf{i}}+\frac{35}{16} \hat{\mathbf{j}}+\frac{5}{8} \hat{\mathbf{k}}\)
Question 78.
In the HCl molecule, the separation between the nuclei of the two atoms is about 1.27 Å (1 Å = 10-10 m). Find the approximate location of the CM of the molecule, given that a chlorine atom is about 35.5 times as massive as a hydrogen atom and nearly all the mass of an atom is concentrated in its nucleus. (NCERT)
Solution:
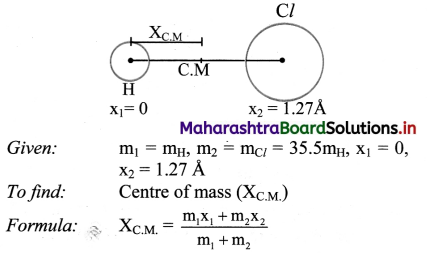
Claculation: From formula
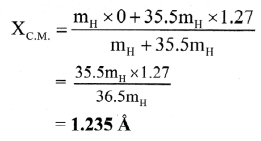
Answer:
The location of centre of mass from the nucleus of hydrogen atom is 1.235 A.
Question 79.
Three thin walled uniform hollow spheres of radii 1 cm, 2 cm and 3 cm are so located that their centres are on the three vertices of an equilateral triangle ABC having each side 10 cm. Determine centre of mass of the system.
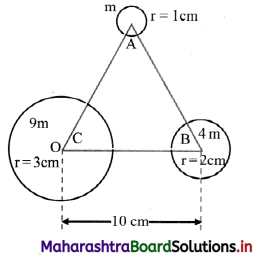
Solution:
Mass of a thin walled uniform hollow sphere is proportional to its surface area. (as density is constant) hence proportional to r2.
Thus, if mass of the sphere at A is mA = m, then mB = 4m and mC = 9m. By symmetry of the spherical surface, their centres of mass are at their respective centres, i.e., at A, B and C. Let us choose the origin to be at C, where the largest mass 9m is located and the point B with mass 4m on the positive x-axis. With this, the co-ordinates of C are (0, 0) and that of B are (10, 0). If A of mass m is taken in the first quadrant, its co-ordinates will be \([5,5 \sqrt{3}]\)

Question 80.
Locate the centre of mass of three particles of mass m1 = 1 kg, m2 = 2 kg and m3 = 3 kg at the corner of an equilateral triangle of each side of 1 m.
Solution:
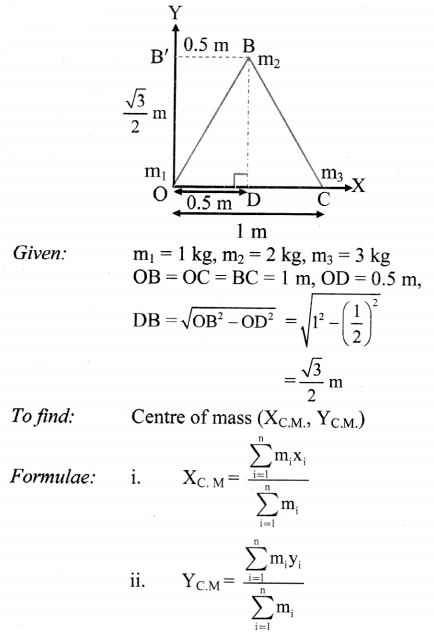

Answer:
The centre of mass of the system of three particles lies at \(\left(\frac{2}{3} m, \frac{\sqrt{3}}{6} m\right)\) with respect to the particle of mass 1 kg as the origin.
![]()
Question 81.
A letter ‘E’ is prepared from a uniform cardboard with shape and dimensions as shown in the figure. Locate its centre of mass.
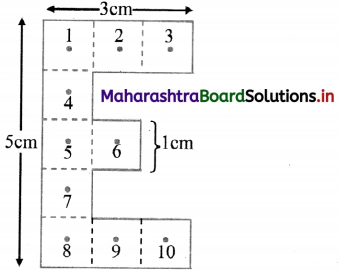
Solution:
As the sheet is uniform, each square can be taken to be equivalent to mass m concentrated at its respective centre. These masses will then be at the points labelled with numbers 1 to 10, as shown in figure. Let us select the origin to be at the left central mass m5, as shown and all the co-ordinates to be in cm.
By symmetry, the centre of mass of m1, m2 and m3 will be at m2 (1, 2) having effective mass 3m. Similarly, effective mass 3m due to m8, m9 and m10 will be at m9 (1, -2). Again, by symmetry, the centre of mass of these two (3m each) will have co-ordinates (1, 0). Mass m6 is also having co-ordinates (1, 0). Thus, the
effective mass at (1, 0) is 7m.
Using symmetry for m4, m5 and m7, there will be effective mass 3m at the origin (0, 0). Thus, effectively, 3m and 7m are separated by 1 cm along X-direction. Y-coordinate is not required.
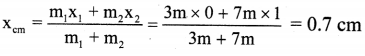
Question 82.
A hole of radius r is cut from a uniform disc of radius 2r. Centre of the hole is at a distance r from centre of the disc. Locate centre of mass of the remaining part of the disc.
Solution:
Before cutting the hole, c.în. of the full disc was at its centre. Let this be our origin O. Centre of mass of the cut portion is at its centre D. Thus, it is at a distance x1 = r form the origin. Let C be the centre of mass of the
remaining disc, which will he on the extension of the line DO at a distance x2 = x from the origin. As the disc is uniform, mass of any of its part is proportional to the area of that part.
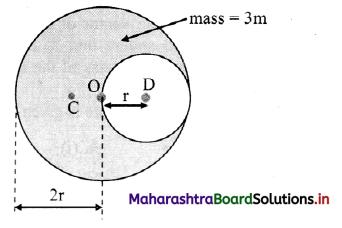
Thus, if m is the mass of the cut disc, mass of the entire disc must be 4m and mass of the remaining disc will be 3m.
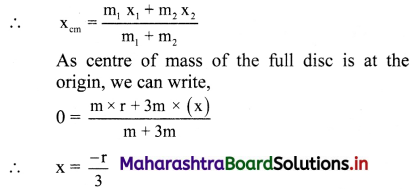
Alternate method: (Using negative mass):
Let \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{R}}\) be the position vector of the centre of mass of the uniform disc of mass M. Mass m is with centre of mass at position vector \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{r}}\) from the centre of the disc be cut out from the complete disc. Position vector of the centre of mass of the remaining disc is then given by
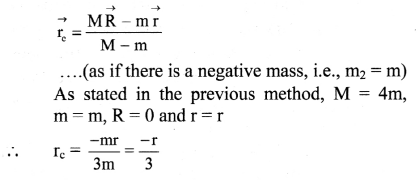
Question 83.
Define centre of gravity of a body. Under what conditions the centre of gravity and centre of mass coincide?
Answer:
- centre of gravity of a body is the point around which the resultant torque due to force of gravity on the body is zero.
- The centre of mass coincides with centre of gravity when the body is in a uniform gravitational field.
Question 84.
Explain how to find the location of centre of mass or centre of gravity of a laminar object.
Answer:
- A laminar object is suspended from a rigid support at two orientations.
- Lines are drawn on the object parallel to the plumb line as shown in the figure.
- Plumb line is always vertical, i.e., parallel to the line of action of gravitational force.
- Intersection of the lines drawn is then the point through which line of action of the gravitational force passes for any orientation. Thus, it gives the location of the c.g. or c.m.
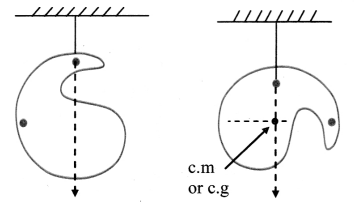
Question 85.
Why do cricketers wear helmet and pads while playing? Is it related with physics?
Answer:
Helmet and pads used by cricketers protects the head, using principles of physics.
- The framing between the interior of the helmet and pads increases the time over which the impulse acts on the head resulting into reduction of force.
(Impulse = force × time = constant) - The pads spread the force applied by the ball over a wider area reducing pressure at a point.
Question 86.
The diagram shows four objects placed on a flat surface.
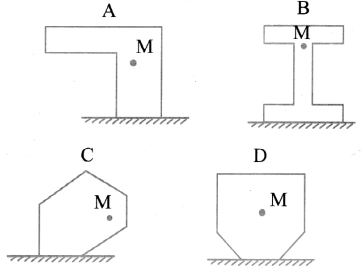
The centre of mass of each object is marked M. Which object is likely to fall over?
Answer:
Object C will fall because its centre of mass is not exactly at centre, in turn applying more force on one side of the object resulting in to unbalance force. Whereas, in other objects center of mass is exactly at center resulting into zero rotational or translational motion maintaining their equilibrium.
Question 87.
A boy is about to close a large door by applying force at A and B as shown. State with a reason, which of the two positions, A or B, will enable him to close the door with least force.
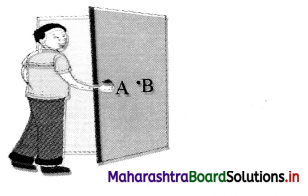
Answer:
Boy has to apply more force at point B as compared to point A, because point B is at least distance from the hinge of the door while point A is at maximum distance from hinge of the door. Opening of door applies a moment, which is. given by,
M = F × perpendicular distance
F ∝ \(\frac{1}{\text { distance }}\)
More is the distance from the axis of rotation less will be the force.
Question 88.
How is a seat belt useful for safety?
Answer:
When car hits another car or an object with high speed it applies a high impulse on the driver and due to inertia driver tends to move in forward direction towards the steering. Seat belts spreads the force over large area of the body and holds the driver and protects him from crashing at the steering.
Question 89.
According to Newton’s third law of motion for every action there is equal and opposite reaction, why two equal and opposite forces don’t cancel each other?
Answer:
Forces of action and reaction always act on different bodies, hence they never cancel each other.
Question 90.
Linear momentum depends on frame of reference, but principle of conservation of linear momentum is independent of frame of reference. Why?
Answer:
Observers in different frame find different values of linear momentum of a system, hence linear momentum depends upon frame of reference, but each would observe that the value of linear momentum does not change with time (provided the system is isolated), hence principle of conservation of linear momentum is independent of frame of reference.
Question 91.
Multiple choice Questions
Question 1.
A body of mass 2 kg moving on a horizontal surface with initial velocity of 4 m s-1 comes to rest after two seconds. If one wants to keep this body moving on the same surface with a velocity of 4 m s-1, the force required is
(A) 2 N
(B) 4 N
(C) 0
(D) 8 N
Answer:
(B) 4 N
![]()
Question 2.
What force will change the velocity of a body of mass 1 kg from 20 m s-1 to 30 m s-1 in two seconds?
(A) 1N
(B) 5 N
(C) 10 N
(D) 25 N
Answer:
(B) 5 N
Question 3.
A force of 5 newton acts on a body of weight 9.80 newton. What is the acceleration produced in m/s2?
(A) 0.51
(B) 1.96
(C) 5.00
(D) 49.00
Answer:
(C) 5.00
Question 4.
A body of mass m strikes a wall with velocity v and rebounds with the same speed. Its change in momentum is
(A) 2 mv
(B) mv/2
(C) – mv
(D) Zero
Answer:
(A) 2 mv
Question 5.
A force of 6 N acts on a body of mass 1 kg initially at rest and during this time, the body attains a velocity of 30 m/s. The time for which the force acts on a body is
(A) 10 second
(B) 8 second
(C) 7 second
(D) 5 second
Answer:
(D) 5 second
Question 6.
A bullet of mass 10 g is fired from a gun of mass 1 kg with recoil velocity of gun = 5 m/s. The muzzle velocity will be
(A) 30 km/min
(B) 60 km/min
(C) 30 m/s
(D) 500 m/s
Answer:
(D) 500 m/s
Question 7.
The velocity of rocket with respect to ground is v1 and velocity of gases ejecting from rocket with respect to ground is v2 Then velocity of gases with respect to rocket is given by
(A) v2
(B) v1 + v2
(C) v1 × v2
(D) v1
Answer:
(B) v1 + v2
Question 8.
Two bodies A and B of masses 1 kg and 2 kg moving towards each other with velocities 4 m/s and 1 m/s suffers a head on collision and stick together. The combined mass will
(A) move in direction of motion of lighter mass.
(B) move in direction of motion of heavier mass.
(C) not move.
(D) move in direction perpendicular to the line of motion of two bodies.
Answer:
(A) move in direction of motion of lighter mass.
Question 9.
Which of the following has maximum momentum?
(A) A 100 kg vehicle moving at 0.02 m s-1.
(B) A 4 g weight moving at 1000 cm s-1’.
(C) A 200 g weight moving with kinetic energy of 10-6 J
(D) A 200 g weight after falling through one kilometre.
Answer:
(D) A 200 g weight after falling through one kilometre.
Question 10.
A bullet hits and gets embedded in a solid block resting on a horizontal frictionless table. What is conserved?
(A) Momentum alone.
(B) K.E. alone.
(C) Momentum and K.E. both.
(D) P.E. alone.
Answer:
(A) Momentum alone.
![]()
Question 11.
The force exerted by the floor of an elevator on the foot of a person standing there, is more than his weight, if the elevator is
(A) going down and slowing down.
(B) going up and speeding up.
(C) going up and slowing down.
(D) either (A) and (B).
Answer:
(D) either (A) and (B).
Question 12.
If E, G and N represents the magnitudes of electromagnetic, gravitational and nuclear forces between two electrons at a given separation, then,
(A) N = E = G
(B) E < N < G (C) N > G < E (D) E > G > N
Answer:
(D) E > G > N
Qestion 13.
For an inelastic collision, the value of e is
(A) greater than 1
(B) less than 1
(C) equal to 1
(D) none of these
Answer:
(B) less than 1
Question 14.
A perfect inelastic body collides head on with a wall with velocity y. The change in momentum is
(A) mv
(B) 2mv
(C) zero
(D) none of these.
Answer:
(A) mv
Question 15.
Two masses ma and rnb moving with velocitics va and vb in opposite direction collide
elastically and after the collision ma and mb move with velocities vb and va respectively. Then the ratio mamb is
(A) \(\frac{v_{a}-v_{b}}{v_{a}+v_{b}}\)
(B) \(\frac{\mathrm{m}_{\mathrm{a}}+\mathrm{m}_{\mathrm{b}}}{\mathrm{m}_{\mathrm{a}}}\)
(C) 1
(D) \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Answer:
(C) 1
Question 16.
The frictional force acts _____.
(A) in direction of motion
(B) against the direction of motion
(C) perpendicular to the direction of motion
(D) at any angle to the direction of motion
Answer:
(B) against the direction of motion
Question 17.
A marble of mass X collides with a block of mass Z, with a velocity Y. and sticks to it. The final velocity of the system is
(A) \(\frac{\mathrm{Y}}{\mathrm{X}+\mathrm{Y}} \mathrm{Y}\)
(B) \(\frac{X}{X+Z} Y\)
(C) \(\frac{X+Y}{Z}\)
(D) \(\frac{X+Z}{X}\)
Answer:
(B) \(\frac{X}{X+Z} Y\)
Question 18.
Two balls lying on the same plane collide. Which of the following will be always conserved?
(A) heat
(B) velocity
(C) kinetic energy
(D) linear momentum.
Answer:
(D) linear momentum.
Question 19.
A body is moving with uniform velocity of 50 km h-1, the force required to keep the body in motion in SI unit is
(A) zero
(B) 10
(C) 25
(D) 50
Answer:
(A) zero
Question 20.
A coolie holding a suitcase on his head of 20 kg and travels on a platform. then work done in joule by the coolie is
(A) 198
(B) 98
(C) 49
(D) zero
Answer:
(D) zero
Question 21.
Out of the following forces, which force is non-conservative?
(A) gravitational
(B) electrostatic
(C) frictional
(D) magnetic
Answer:
(C) frictional
Question 22.
The work done in conservative force is ____.
(A) negative
(B) zero
(C) positive
(D) infinite
Answer:
(B) zero
Question 23.
The angle between the line of action of force and displacement when no work done (in degree) is
(A) zero
(B) 45
(C) 90
(D) 120
Answer:
(C) 90
Question 24.
If the momentum of a body is doubled, its KE. increases by
(A) 50%
(B) 300%
(C) 100%
(L)) 400%
Answer:
(B) 300%
![]()
Question 25.
In perfectly inelastic collision, which is conserved?
(A) P.E. only
(B) K.E. only
(C) momentum only
(D) K.E. and momentum
Answer:
(C) momentum only
Question 26.
In case of elaine collision, which s
(A) Momentum and K.E. is conserved.
(B) Momentum conserved and K.E. not conserved,
(C) Momentum not conserved and K.E. conserved.
(D) Momentum and K.E. both not conserved,
Answer:
(A) Momentum and K.E. is conserved.
Question 27.
Pseudo force is true only in
(A) frame of reference which is at rest
(B) inertial frame of reference.
(C) frame of reference moving with constant velocity.
(D) non-inertial frame of reference
Answer:
(D) non-inertial frame of reference
Question 28.
A men weighing 90kg carries a stone of 20 kg to the top of the building 30m high. The work done by hint is (g = 9.8 m/s2)
(A) 80 J
(B) 100 J
(C) 980 J
(D) 29,400 J
Answer:
(D) 29,400 J
Question 29.
A weight lifter is holding a weight of 100 kg on his shoulders for 45 s, the amount of work done by him in joules is
(A) 4500
(B) 100
(C) 45
(D) zero
Answer:
(D) zero
Question 30.
If m is the mass of a body and E its K.E..then its linear momentum is
(A) \(\mathrm{m} \sqrt{\mathrm{E}}\)
(B) \(2 \sqrt{\mathrm{m}} \mathrm{E}\)
(C) \(\sqrt{m} E\)
(D) \(\sqrt{2 \mathrm{mE}}\)
Answer:
(D) \(\sqrt{2 \mathrm{mE}}\)
Question 31.
Torque applied is masimum when the angle between the directions of \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{r}}\) and \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{F}}\) is
(A) 90°
(B) 180°
(C) 0°
(D) 45°
Answer:
(A) 90°
Question 92.
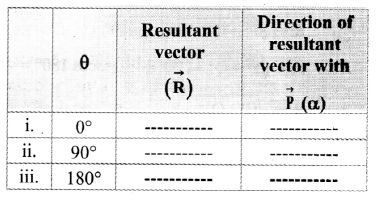
A particle moving with velocity \(\vec{v}\) is acted by three forces shown by the vector triangle PQR. The velocity of the particle will:
(A) remain constant
(B) change according to the smallest force \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{QR}}\)
(C) increase
(D) decrease
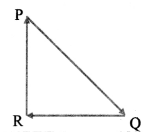
Hint: As the three forces acting on a particle represents a triangle (i.e., a closed loop)
∴ Fnet = 0
∴ m \(\vec{a}\) = 0
∴ m\(\frac{\mathrm{d} \overrightarrow{\mathrm{v}}}{\mathrm{dt}}\)
∴ v remains constant
Answer:
(A) remain constant
Question 93.
A force F = 20 + 10y acts on a particle in y-direction where F is in newton and y in meter. Work done by this force to move the particle from y = 0 to y = 1 m is:
(A) 25J
(B) 20J
(C) 30J
(D) SJ
Hint: Work done by variable force, W = \(\int_{y_{\text {initial }}}^{y_{\text {final }}} \mathrm{Fdy}\)
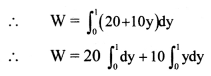
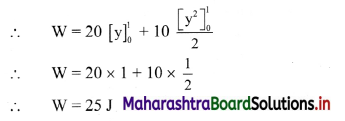
Answer:
(A) 25J
Question 94.
Body A of mass 4m moving with speed u collides with another body B of mass 2m, at rest. The collision is head on and elastic in nature. After the collision the fraction of energy lost by the colliding body A is:
(A) \(\frac{4}{9}\)
(B) \(\frac{5}{9}\)
(C) \(\frac{1}{9}\)
(D) \(\frac{8}{9}\)
Hint:
Fractional loss of K.E. of colliding bodies,
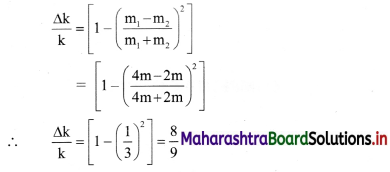
Answer:
(D) \(\frac{8}{9}\)
Question 95.
An object of mass 500 g, initially at rest, is acted upon by a variable force whose X-component varies with X in the manner shown. The velocities of the object at the points X = 8 m and X = 12 m, would have the respective values of
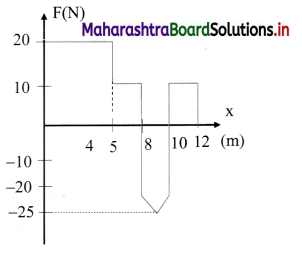
(A) 18m/s and 20.6 m/s
(B) 18 m/s and 24.4 m/s
(C) 23 m/s and 24.4 m/s
(D) 23 m/s and 20.6 m/s
Hint: From work-energy theorem
∆ K.E. = work = area under F-x graph
From x = 0 to x = 8m
\(\frac{1}{2} \mathrm{mv}^{2}\) = (5 × 20) + (3 × 10)
∴ \(\frac{1}{2} \mathrm{mv}^{2}\) = 100 + 30
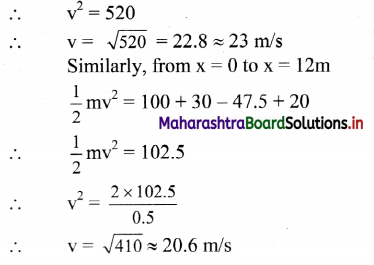
Answer:
(D) 23 m/s and 20.6 m/s
Question 96.
The centre of mass of two particles system lies
(A) at the midpoint on the line joining the two particles.
(B) at one end of line joining the two particles.
(C) on the line perpendicular in the line joining two particles.
(D) on the line joining the Iwo particles.
Answer:
(D) on the line joining the two particles.
![]()
Question 97.
A block of mass m is placed on a smooth inclined wedge ABC of inclination θ as shown in the figure. The wedge is given an acceleration ‘a’ towards the right. The relation between a and θ for the block to remain stationary on the wedge is
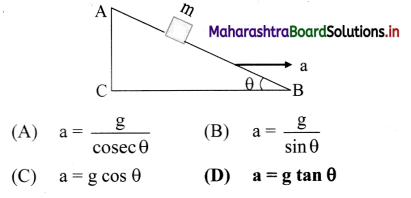
Hint:
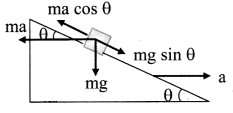
The mass of block is given to be m. It will remain stationary if forces acting on it are in equilibrium i.e., ma cos θ = mg sin θ
Here, ma = Pseudo force on block.
∴ a = g tan θ
Answer:
a = g tan θ
Question 98.
A moving block having mass m, collides with another stationary block having mass 4m. The lighter block comes to rest after collision, When the initial velocity of the lighter block is v, then the value of coefficient of restitution
(e) will
(A) 0.5
(B) 0.25
(C) 0.8
(D) 0.4
Hint:
Given: m1 = m, m2 = 4m, u1 = v, u2 = 0, v1 = 0 According to law of conservation of momentum,
m1u1 + m2u2 = m1v1 + m2v2
mv + 4m × 0 = m × 0 + 4mv2
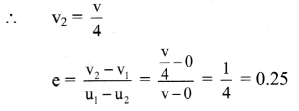
Answer:
(B) 0.25
Question 99.
In a collinear collision, a particle with an initial speed v0 strikes a stationary particle of the same mass. If the final total kinetic energy is 50% greater than the original kinetic energy, the magnitude of the relative velocity between the two particles, after collision, is:

Hint:
According to law of conservation of momentum,
mv0 = mv1 + mv2

Answer:
(D) \(\sqrt{2} \mathbf{v}_{0}\)
Question 100.
The mass of a hydrogen molecule is 3.32 × 10-27 kg. If 1023 hydrogen molecules strike, per second, a fixed wall of area 2 cm2 at an angle of 45° to the normal and rebound elastically with a speed of 103 m/s, then the pressure on the wall is nearly:
(A) 2.35 × 102 N/m2
(B) 4.70 × 102 N/m2
(C) 2.35 × 103 N/m2
(D) 4.70 × 103 N/m2
Hint:
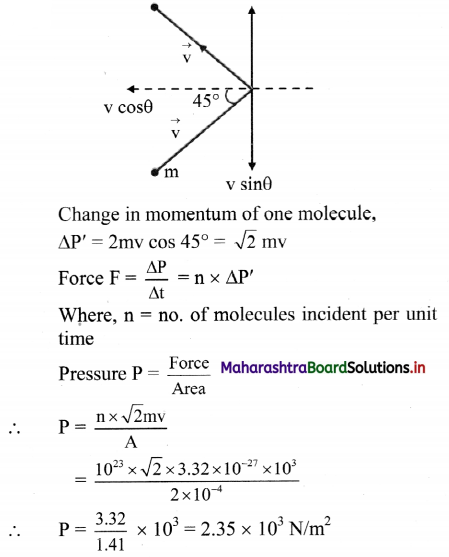
Answer:
(C) 2.35 × 103 N/m2
Question 101.
A bomb at rest explodes into 3 parts of same mass. The momentum of two parts is -3P\(\hat{\mathrm{i}}\) and 2P\(\hat{\mathrm{j}}\) respectively. The magnitude of momentum of the third part is
(A) P
(B) \(\sqrt{5} \mathrm{P}\)
(C) \(\sqrt{11} \mathrm{P}\)
(D) \(\sqrt{13} \mathrm{P}\)

Answer:
(D) \(\sqrt{13} \mathrm{P}\)
Question 102.
A sphere of mass ‘m’ moving with velocity V collides head-on on another sphere of same mass which is at rest. The ratio of final velocity of second sphere to the initial velocity of the first sphere is (e is coefficient of restitution and collision is inelastic)
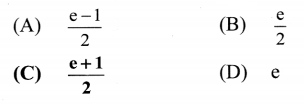
Hint:
Initial momentum = mv
Final momentum = mv1 + mv2
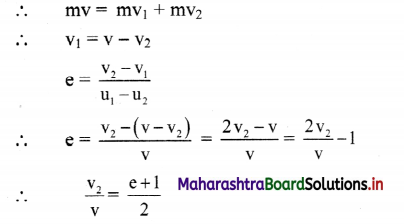
Answer:
(C) \(\frac{\mathrm{e}+1}{2}\)
Question 103.
Two blocks A and B of masses 3m and m respectively are connected by a massless and inextensible string. The whole system is suspended by a massless spring as shown in figure. The magnitudes of acceleration of A and B immediately after the string is cut, are respectively:

Hint:
Tension in spring before cutting the strip,
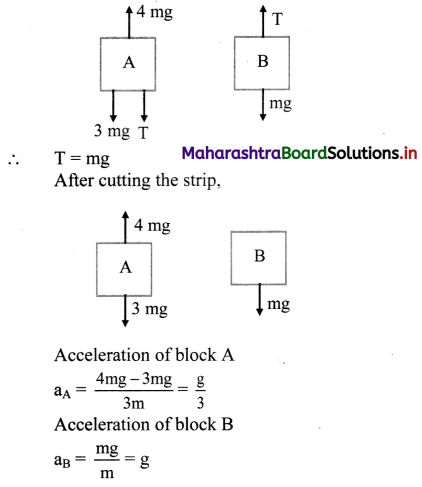
Answer:
(B) \(\frac{\mathrm{g}}{3}\), g
Question 104.
A time dependent force F = 6t acts on a particle of mass 1 kg. If the particle starts from rest, the work done by the force during the first 1 sec. will be
(A) 9 J
(B) 18 J
(C) 4.5 J
(D) 22 J
Hint:
F = 6t
m = 1 kg
∴ a = 6t
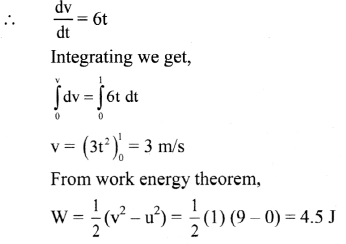
Answer:
(C) 4.5 J
Question 105.
Consider a drop of rain water having mass Ig falling from a height of 1 km. It hits the ground with a speed of 50 m/s. Take ‘g’ constant with a value 10 m/s2. The work done by the
(i) gravitational force and the
(ii) resistive force of air is:
(A) (i) -10 J
(ii) -8.25 J
(B) (i) 1.25 J
(ii) -8.25 J
(C) (i) 100 J
(ii) 8.75 J
(D) (i) 10 J
(ii) -8.75 J
Hint: Work done by gravitation force is given by (Wg)
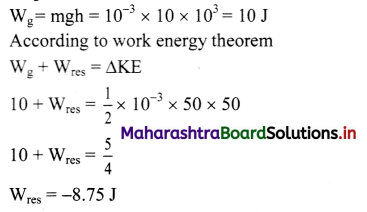
Answer:
(D) (i) 10 J
(ii) -8.75 J