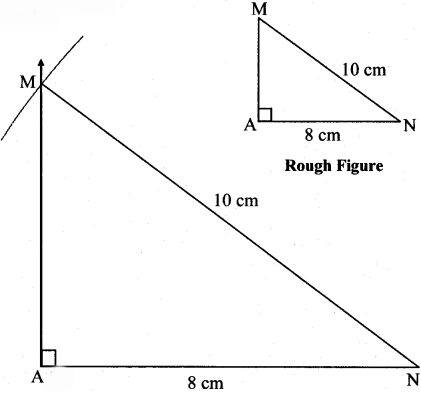
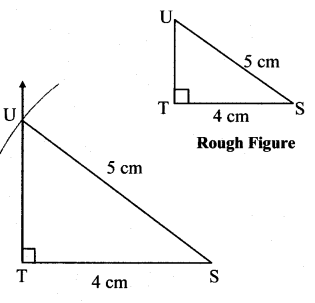
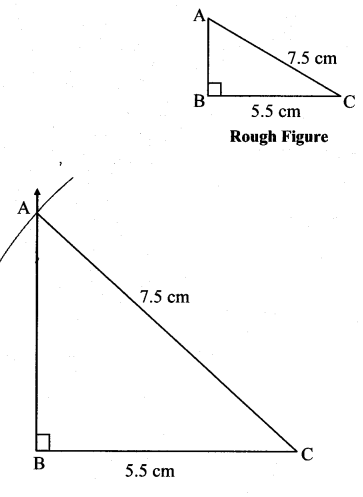
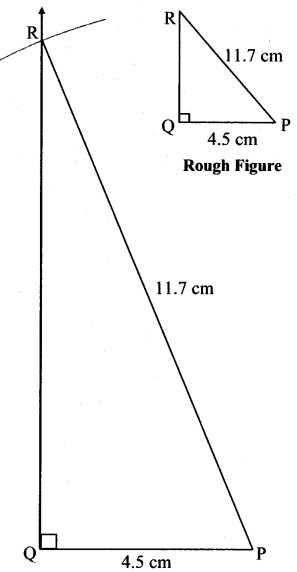
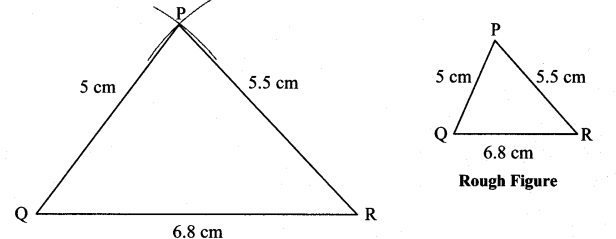
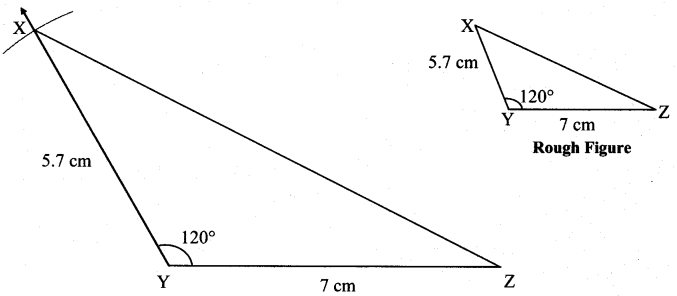
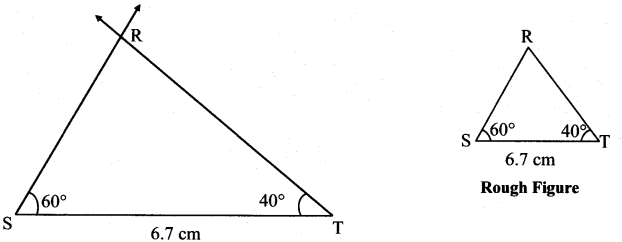
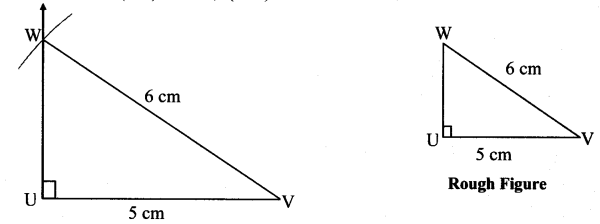
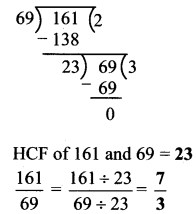Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 7 Maths Solutions covers the 7th Std Maths Practice Set 7 Answers Solutions Chapter 1 Geometrical Constructions.
Geometrical Constructions Class 7 Maths Chapter 1 Practice Set 7 Solutions Maharashtra Board
Std 7 Maths Practice Set 7 Solutions Answers
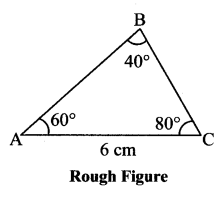
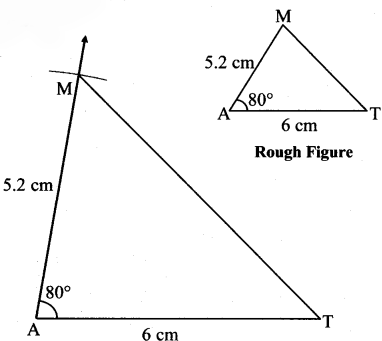
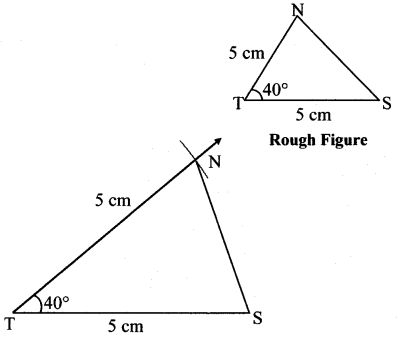
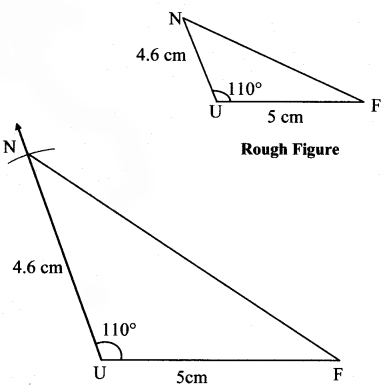
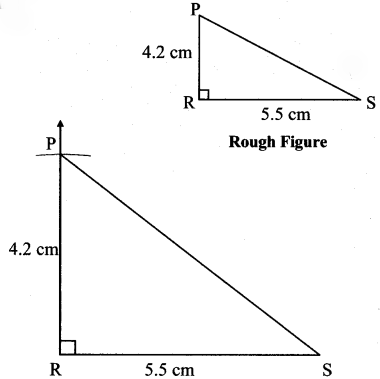
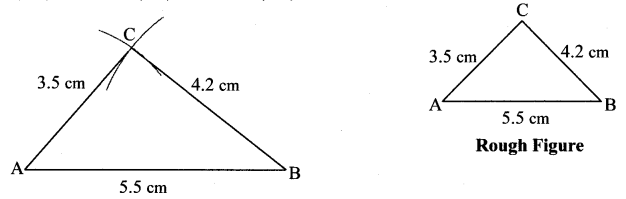
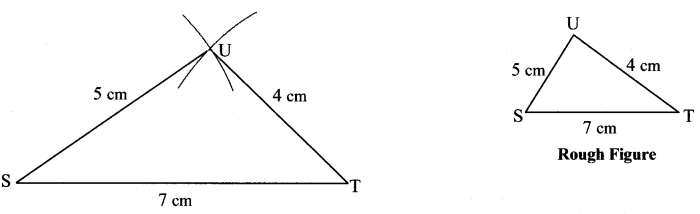
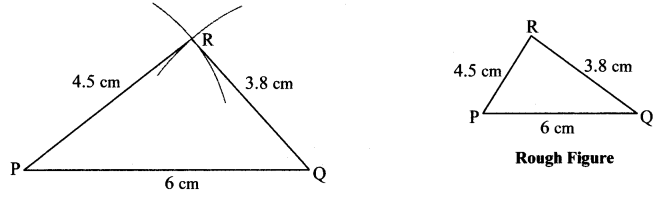
Question 1.
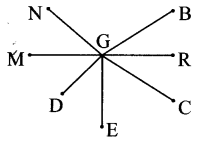
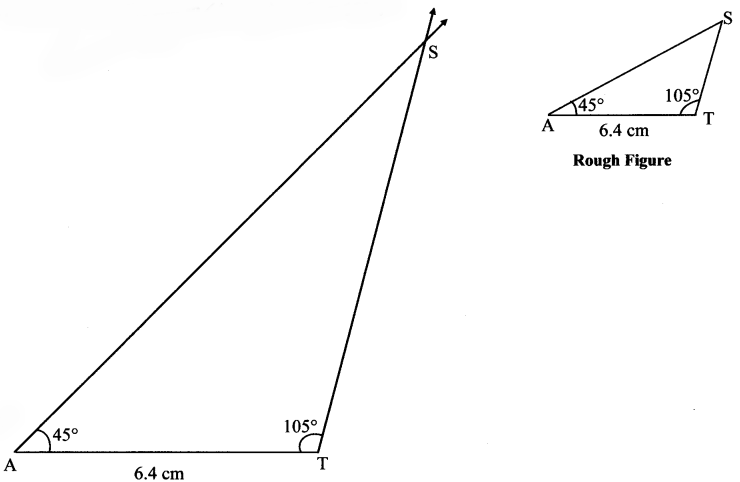
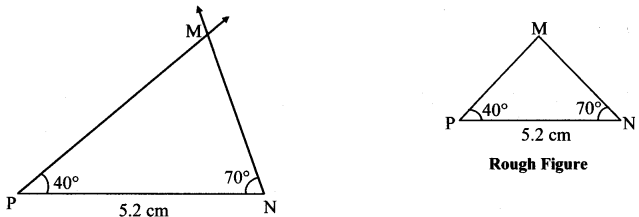
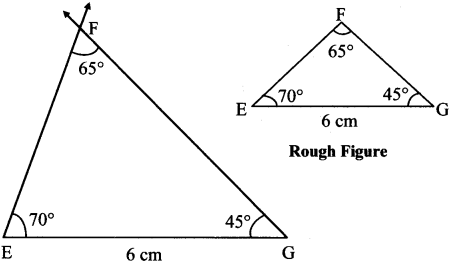
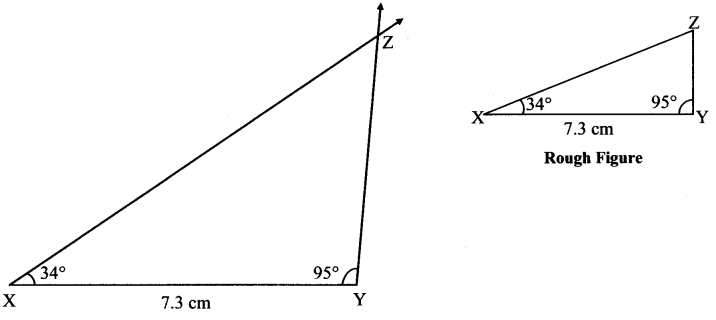
Some angles are given below. Using the symbol of congruence write the names of the pairs of congruent angles in these figures.
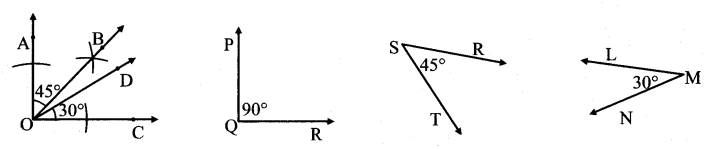
Solution:
i. ∠AOC ≅ ∠PQR
ii. ∠DOC ≅ ∠LMN
iii. ∠AOB ≅ ∠BOC ≅ ∠RST
Maharashtra Board Class 7 Maths Chapter 1 Geometrical Constructions Practice Set 7 Intext Questions and Activities
Question 1.
Observe the given angles and write the names of those having equal measures.
(Textbook pg. no. 8 and 9)
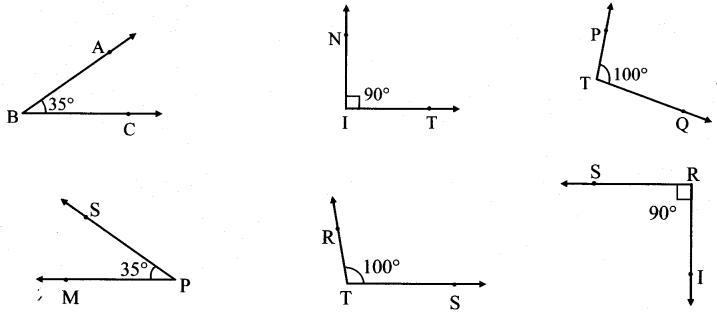
Solution:
i. ∠ABC and ∠SPM
ii. ∠NIT and ∠SRI
iii. ∠PTQ and ∠RTS
Question 2.
Observe the image shown in the adjacent figure and answer the following questions. (Textbook pg. no. 9)
- What time does this clock show?
- What is the measure of the angle between its two hands?
- At which other times is the angle between the hands congruent with this angle?
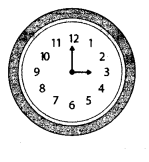
Solution:
- 3 o’ clock.
- 90°.
- 9 o’ clock.
Question 3.
Get bangles of different sizes but equal thickness and find the congruent ones among them. (Textbook pg. no. 10)
Solution:
[Students should attempt the above activities on their own.]
Question 4.
Find congruent circles in your surroundings. (Textbook pg. no. 10)
Solution:
[Students should attempt the above activities on their own.]
Question 5.
Take some round bowls and plates. Place their edges one upon the other to find pairs of congruent edges. (Textbook pg. no. 10)
Solution:
[Students should attempt the above activities on their own.]
Std 7 Maths Digest