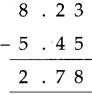Fractions Class 5 Problem Set 22 Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Balbharti Maharashtra Board Class 5 Maths Solutions Chapter 5 Fractions Problem Set 22 Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Std 5 Maths Chapter 5 Fractions
Question 1.
Add the following:
\(\text { (1) } \frac{1}{8}+\frac{3}{4}\)
Solution:
The smallest common multiple of 4 and 8 is 8. So making 8 is the common denominator of the given fractions.
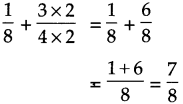
Answer:
\(\frac{7}{8}\)
![]()
\(\text { (2) } \frac{2}{21}+\frac{3}{7}\)
Solution:
21 is the multiple of 7. So making 21 as denominator of both the fractions.
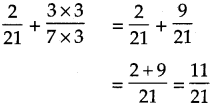
Answer:
\(\frac{11}{21}\)
\(\text { (3) } \frac{2}{5}+\frac{1}{3}\)
Solution:
Least common multiple of 5 and 3 is 15. So making common denominator of both the fractions 15.
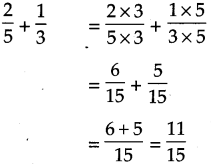
Answer:
\(\frac{11}{15}\)
\(\text { (4) } \frac{2}{7}+\frac{1}{2}\)
Solution:
Smallest common multiple of 2 and 7 is 14. So, making denominator of both the fractions 14.
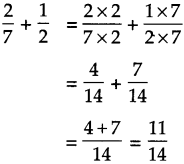
Answer:
\(\frac{11}{14}\)
![]()
\(\text { (5) } \frac{3}{9}+\frac{3}{5}\)
Solution:
Smallest common multiple of 9 and 5 is 45.
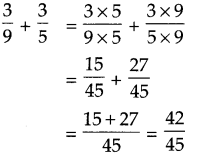
Answer:
\(\frac{42}{45}\)
Question 2.
Subtract the following:
\(\text { (1) } \frac{3}{10}-\frac{1}{20}\)
Solution:
20 is the multiples of 10. So,
![]()
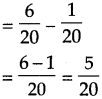
Answer:
\(\frac{5}{20}\)
\(\text { (2) } \frac{3}{4}-\frac{1}{2}\)
Solution:
4 is the multiple of 2. So,
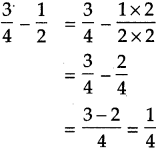
Answer:
\(\frac{1}{4}\)
![]()
\(\text { (3) } \frac{6}{14}-\frac{2}{7}\)
Solution:
14 is the multiples of 7. So,
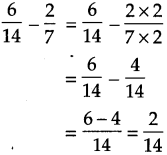
Answer:
\(\frac{2}{14}\)
\(\text { (4) } \frac{4}{6}-\frac{3}{5}\)
Solution:
Smallest common multiple of 6 and 5 is 30. So,
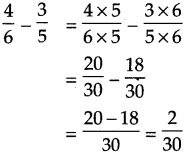
Answer:
\(\frac{2}{30}\)
\(\text { (5) } \frac{2}{7}-\frac{1}{4}\)
Solution:
Smallest common multiple of 7 and 4 is 28.
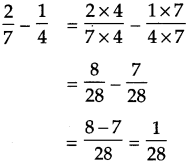
Answer:
\(\frac{1}{28}\)
![]()
A fraction of a collection and a multiple of a fraction
\(\frac{1}{4}\) of a collection of 20 dots – \(\frac{1}{2}\) of a collection of 20 dots
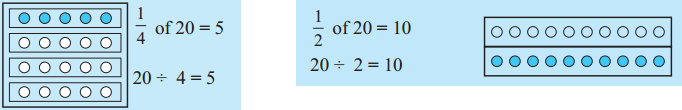
\(\frac{3}{4}\) of a collection of 20 dots

Twice 5 is 10 – \(\frac{1}{2}\) times 10
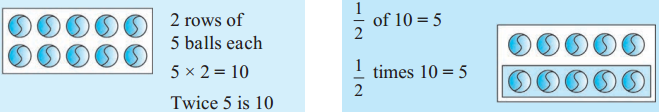
Thrice 5 – \(\frac{1}{3}\) times 15
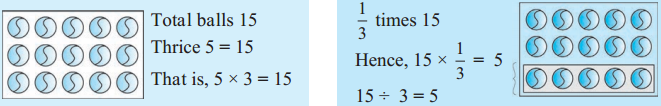
![]()
\(\frac{1}{3}\) times 15

Meena has 5 rupees. Tina has twice as many rupees. That is, Tina has 5 × 2 = 10 rupees. Meena has half as many rupees as Tina, that is, \(\frac{1}{2}\) of 10, or, 5 rupees.
Ramu has to travel a distance of 20 km. If he has travelled \(\frac{4}{5}\) of the distance by car, how many kilometres did he travel by car?
\(\frac{4}{5}\) of 20 km is 20 × \(\frac{4}{5}\). So, we take \(\frac{1}{5}\) of 20, 4 times.
\(\frac{1}{5}\) of 20 = 4. 4 times 4 is 4 × 4 = 16.
It means that 20 × \(\frac{4}{5}\) = 16.
Ramu travelled a distance of 16 kilometres by car.
Addition and Subtraction Problem Set 13 Additional Important Questions and Answers
\(\text { (1) } \frac{5}{6}+\frac{1}{12}\)
Solution:
12 is the multiple of 6
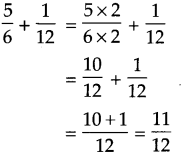
Answer:
\(\frac{11}{12}\)
![]()
\(\text { (2) } \frac{1}{9}+\frac{2}{3}\)
Solution:
Here 9 is the multiples of 3. So, making like fractions of denominator 9, we get
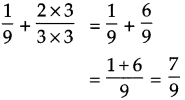
Answer:
\(\frac{7}{9}\)
Subtract the following:
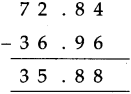
\(\text { (1) } \frac{4}{9}-\frac{2}{5}\)
Solution:
Common multiple of 9 and 5 is 45
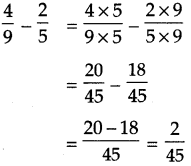
Answer:
\(\frac{2}{45}\)
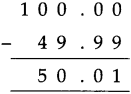
![]()
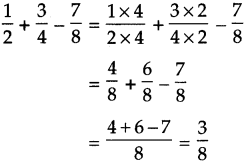
Answer:
\(\frac{3}{8}\)
Class 5 Maths Solution Maharashtra Board
- Fractions Problem Set 17 Class 5 Maths Solutions
- Fractions Problem Set 18 Class 5 Maths Solutions
- Fractions Problem Set 19 Class 5 Maths Solutions
- Fractions Problem Set 20 Class 5 Maths Solutions
- Fractions Problem Set 21 Class 5 Maths Solutions
- Fractions Problem Set 22 Class 5 Maths Solutions
- Fractions Problem Set 23 Class 5 Maths Solutions