Class 10th Sanskrit Aamod Chapter 4 अमूल्यं कमलम् Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 10 Sanskrit Solutions Amod Chapter 4 अमूल्यं कमलम् Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Std 10 Sanskrit Chapter 4 Question Answer
Sanskrit Amod Std 10 Digest Chapter 4 अमूल्यं कमलम् Textbook Questions and Answers
भाषाभ्यास:
1. पूर्णवाक्येन उत्तरं लिखत ।
प्रश्न अ.
सुदासः कः आसीत् ?
उत्तरम् :
सुदास: उद्यानपाल: आसीत्।
प्रश्न आ.
पद्यं कदा व्यकसत्?
उत्तरम् :
पद्यं शिशिर-ऋतौ व्यकसत्।
![]()
प्रश्न इ.
पद्यं कीदृशम्?
उत्तरम् :
पद्मं व्योम्नि बालसूर्यबिम्बम् इव आसीत्।
प्रश्न ई.
पद्यं विक्रेतुं सुदासः कुत्र स्थितः?
उत्तरम् :
पा विक्रेतुं सुदास: राजसद्मनः पुरतः स्थितः।
प्रश्न उ.
श्रेष्ठी कमलार्थ कियत् मूल्यं दातुम् इच्छति?
उत्तरम् :
श्रेष्ठी कमलार्थ दश सुवर्णनाणकानि दातुम् इच्छति।
प्रश्न ऊ.
महात्मा कुत्र उपविष्टः आसीत् ?
उत्तरम् :
उद्याने वटवृक्षस्य अधस्तात् एकस्मिन् अश्मखण्डे महात्मा उपविष्टः आसीत्।
![]()
2. माध्यमभाषया उत्तरत ।
प्रश्न अ.
सुदासः किमर्थं कमल विक्रेतुं न इच्छति?
उत्तरम् :
‘अमूल्यं कमलम्’ ही कथा बौद्ध कथासाहित्यातून घेतलेली आहे. भगवान बुद्धांच्या अलौकिक शिकवणीचे या कथांमधून दर्शन घडते. कथेचे शीर्षक सदाचार आणि सत्संगतीचे महात्म्य योग्यप्रकारे सूचित करते. त्यातून मिळणारे समाधान व मनःशांती ही संपत्ती आणि भौतिक सुखांपेक्षा श्रेष्ठ तसेच मौल्यवान असते. ‘अमूल्यं कमलम्’ सुदास नावाचा एक माळी होता. एकदा त्याच्या तलावात हिवाळा असून सुद्धा एक सुंदर कमळ उमलले.
त्याने विचार केला की, ‘हा तर परमेश्वराचा महिमा आहे की, कडाक्याच्या थंडीत मला इतक्या सुंदर फुलाचा लाभ झाला.’ त्या ऋतूत कमळाचे फूल अभावाने फुलत असल्यामुळे त्याला वाटले, ते विकून आपल्याला चांगली किंमत मिळेल, तेव्हा ते फूल विकण्यासाठी तो राजवाड्यासमोर उभा राहिला.
एक श्रीमंत व्यापारी तिथे आला आणि भगवान सुगताच्या पूजेसाठी ते कमळ विकत घेण्याची इच्छा त्याने प्रकट केली. सुदास एक सुवर्णमुद्रा घेऊन ते फूल विकण्यास तयार झाला. तेवढ्यात दुसरा एक श्रीमंत व्यापारी, जो भगवान सुगतांच्या दर्शनासाठी चालला होता, तिथे उपस्थित झाला. तो त्या कमळासाठी दहा सुवर्णमुद्रा द्यायला तयार झाला. त्यावर पहिला व्यापारी शंभर सुवर्णमुद्रा देऊ लागला.
दोन्ही व्यापाऱ्यांमधील चढाओढ पाहून सुदासाने विचार केला, ‘हे दोघे ज्या व्यक्तीसाठी एवढ्या चढत्या दराने कमळ विकत घेऊ इच्छितात, तर ती व्यक्ती निश्चितच थोर असेल. तेच मला कमळाचे सर्वात जास्त मूल्य देतील.’ अशा विचाराने सुदासाने जाहीर केले की, तो कमळ विकू इच्छित नव्हता.
is a storyextracted from Buddhist legends that highlights the divine teachings of lord Buddha. The title rightly suggests that righteousness and a good company leading to contentment and peace of mind, is superior and priceless compared to money and worldly pleasures.
सुदास was a gardener. Once a beautiful lotus bloomed in his lake, in spite of being winter season. He thought, “It is greatness of the god that I am blessed to have the beautiful flower even during severe cold.” As lotuses were rare in that season, he thought he would earn good amount by selling it.
So he stood in front of the royal palace to sell the flower. A rich merchant came there and wished to buy that flower for worshipping lord सुगत. सुदास agreed to sell it for one gold coin. At the same time, another rich merchant, who was going to see lord arrived there and asked for the lotus. He was ready to pay ten gold coins for the same flower. Over that the first merchant raised the value to 100 gold coins.
Hearing the arguments between the two merchants, are thought, If these two are willing to buy the lotus for a person at such high value, then that person must be really very great. He would rather give me the highest price. Thus, he declared that he did not wish to sell the lotus.
![]()
प्रश्न आ.
सुदासः सुगतचरणाभ्यां कमलं किमर्थं समर्पितवान् ?
उत्तरम् :
‘अमूल्यं कमलम्’ ही कथा बौद्ध कथासाहित्यातून घेतलेली आहे. भगवान बुद्धांच्या अलौकिक शिकवणीचे या कथांमधून दर्शन घडते. कथेचे शीर्षक सदाचार आणि सत्संगतीचे महात्म्य योग्यप्रकारे सूचित करते. त्यातून मिळणारे समाधान व मनःशांती ही संपत्ती आणि भौतिक सुखांपेक्षा श्रेष्ठ तसेच मौल्यवान असते.
सुदासाने ठरवले की ते कमळ व्यापाऱ्यांना विकायचे नाही. त्याने विचार केला की, ज्याच्यासाठी सर्वाधिक मूल्य देऊन दोघे व्यापारी कमळ विकत घेऊ इच्छित होते, ती व्यक्ती सर्वात जास्त किंमत देईल. त्यामुळे जिथे भगवान बुद्ध राहत होते त्या उद्यानात सुदास गेला, भगवान वटवृक्षाखाली एका दगडावर बसलेले होते.
त्यांच्या चेहऱ्यावर विलक्षण तेज होते. केवळ सुगतांकडे बघता क्षणी सुदासाचे मन भक्तिरसाने भरुन गेले. त्याने स्वत:ला भगवानांच्या चरणी वाहून घेतले. कमळासाठी जे सर्वोच्च मूल्य घेण्याच्या उद्देशाने तो आला होता, ते कमळ त्याने निरिच्छवृत्तीने भगवानांच्या चरणी अर्पण केले.
भगवानांच्या केवळ दर्शनाने सुदास प्रचंड प्रभावित झाला होता. त्याच्या सगळ्या इच्छा-आकांक्षा संपुष्टात आल्या होत्या. त्यामुळे त्याने ते कमळ भक्तिपूर्ण मनाने भगवानांना अर्पण केले.
‘अमूल्यं कमलम्’ is a story extracted from Buddhist legends that highlights the divine teachings of lord Buddha. The title rightly suggests that righteousness and a good company leading to contentment and peace of mind, is superior and priceless compared to money and worldly pleasures.
सुदास decided not to sell the lotus to the merchants. Because he thought, for whom these two were willing to buy the lotus at highest rates, he would pay more than them. So सुदास reached the garden where lord बुद्ध was staying.
He was seated on a piece of rock below a banyan tree. His face was adorned with great lustre. He had great aura. Just by looking at him, सुदास’s mind was filled with devotion. He surrendered himself at the feet of lords and forgetting about the highest value for the lotus, he offered it at the feet of the lord.
Just by the sight of the lord, सुदास was highly influenced. He had no more desires now. So he offered the lotus to the lord with heartfelt devotion.
![]()
3. क: कं वदति?
प्रश्न अ.
‘भद्र, भगवान् सुगतः सम्प्रत्येतस्मिन्नगरे वसति ।’
उत्तरम् :
सार्थवाहः सुदासं वदति।
प्रश्न आ.
‘अहं दश सुवर्णनाणकानि यच्छामि ।’
उत्तरम् :
श्रेष्ठी सुदासं वदति।
प्रश्न इ.
‘एष महाभागः एकं सुवर्णनाणकम् एतस्यार्थे दातुमिच्छति ।’
उत्तरम् :
सुदासः श्रेष्ठिनं वदति।
प्रश्न ई.
‘वत्स, किमिच्छसि ?’
उत्तरम् :
भगवान् गौतमबुद्धः सुदासं वदति।
![]()
प्रश्न उ.
‘नमो भगवते ।’
उत्तरम् :
सुदास: भगवन्तं गौतमबुद्ध वदति।
4. प्रश्ननिर्माणं कुरुत।
प्रश्न अ.
सुगत एवाधिकतम मूल्यं मह्यं दद्यात् ।
उत्तरम् :
सुगत एवाधिकतम मूल्यं कस्मै दद्यात्?
प्रश्न आ.
भगवत: वदनं धाम्ना राजते स्म ।
उत्तरम् :
भगवत: वदनं केन राजते स्म?
![]()
5. सन्धिविग्रहं कुरुत ।
प्रश्न अ.
कश्चिदुद्यानपालः
उत्तरम् :
कश्चिदुद्यानपालः – कश्चित् + उद्यानपालः।
प्रश्न आ.
चरणयोरय॑म्
उत्तरम् :
चरणयोरय॑म् – चरणयोः + अर्घ्यम्।
प्रश्न इ.
सोऽवदत्
उत्तरम् :
सोऽवदत् – स: + अवदत्।
प्रश्न ई.
इत्यब्रवीत् ।
उत्तरम् :
इत्यब्रवीत् भगवान् – इति + अब्रवीत् + भगवान् ।
![]()
6. समानार्थकशब्दान् लिखत ।
प्रश्न 1.
समानार्थकशब्दान् लिखत ।
तडागः, नीरजम्, सार्थवाहः, अर्णवः, धनवान् ।
उत्तरम् :
- तडागः – पद्माकरः, कासारः, सरः, सरसी, सरोवरः।
- नौरजम् – पद्मम, सरसिजम, कमलम्, सहस्रपत्रम्, शतपत्रम्, कुशेशयम्।
- सार्थवाहः – वणिक्, श्रेष्ठी।
- अर्णवः – सागरः, रत्नाकरः, समुद्रः।
- धनवान् – धनाढ्य, श्रीमान्, धनिकः, सधनः।
7. विरुद्धार्थकशब्दान् लिखत ।
प्रश्न 1.
विरुद्धार्थकशब्दान् लिखत ।
विपुलम्, बहुमूल्यम्, क्रेतुम् ।।
उत्तरम् :
- विपुलम् × अल्पम्।
- बहुमूल्यम् × अल्पमूल्यम्।
- क्रेतुम् × विक्रेतुम्।
![]()
8. मेलनं कुरुत।
प्रश्न 1.
मेलनं कुरुत।
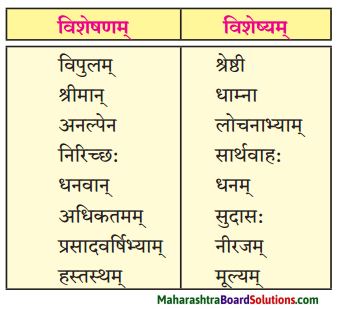
उत्तरम् :
| विशेषणम् | विशेष्यम् |
| विपुलम् | धनम् |
| श्रीमान् | सार्थवाहः |
| अनल्पेन | धाम्ना |
| निरिच्छ: | सुदासः |
| धनवान् | श्रेष्ठी |
| अधिकतमम् | मूल्यम् |
| प्रसादवर्षिभ्याम् | लोचनाभ्याम् |
| हस्तस्थम् | नीरजम् |
9. अमरकोषात् शब्दं प्रयुज्य वाक्यं पुनर्लिखत ।
प्रश्न अ.
नूनं स: सुगतः एव अधिकतम मूल्यं दद्यात् ।
उत्तरम् :
नूनं स: बुद्धः / सर्वज्ञः / धर्मराजः / तथागत: एव अधिकतम मूल्यं दद्यात्।
प्रश्न आ.
तडागे शिशिर-ऋतौ एकं पद्यं व्यकसत् ।
उत्तरम् :
तडागे शिशिर-ऋतौ एकं सहस्रपत्रं / कमलं / शतपत्रं / कुशेशयं व्यकसत्।
![]()
प्रश्न इ.
विपुलं धनं प्राप्नुयाम् ।
उत्तरम् :
विपुलं द्रव्यं । वित्तं / स्थापतेयं / रिक्थं / ऋक्थं / वसुः प्राप्नुयाम्।
10. सूचनानुसारं कृती: कुरुत ।
प्रश्न अ.
तयोः विवादं श्रुत्वा सुदासो व्यमृशत् । (पूर्वकालवाचक-त्वान्त-अव्ययं निष्कासयत।)
उत्तरम् :
तयोः विवादम् अशृणोत् सुदासो व्यमृशत् च।
प्रश्न आ.
त्वं किम् इच्छसि ? (त्वम्’ इत्यस्य स्थाने ‘भवान्’ इति योजयत ।)
उत्तरम् :
भवान् किम् इच्छति?
प्रश्न इ.
मे आत्मा कृतार्थतां लभताम् । (लङ्लकारे वाक्यं परिवर्तयत ।)
उत्तरम् :
लोट्लकारः
प्रश्न ई.
शिशिर-ऋतौ पद्यं व्यकसत् । (बहुवचने लिखत।)
उत्तरम् :
शिशिर-ऋतौ पद्यानि व्यकसन्।
![]()
प्रश्न उ.
सुदासः सुगतचरणाभ्यां कमलं समर्पितवान् । (वाच्यपरिवर्तनं कुरुत ।)
उत्तरम् :
सुदासेन सुगतचरणाभ्यां कमलं समर्पितम्।
प्रश्न ऊ.
अहं विपुलं धनं प्राप्नुयाम् । (लकारं लिखत ।)
उत्तरम् :
विधिलिङ्लकार:
Sanskrit Amod Class 10 Textbook Solutions Chapter 4 अमूल्यं कमलम् Additional Important Questions and Answers
अवबोधनम् ।
(क) उचितं कारणं चित्वा वाक्यं पुनर्लिखत।
प्रश्न 1.
सुदास: राजसद्यनः पुरतः स्थितः यतः ”
(अ) सः सरसिजं विक्रेतुम् इच्छति स्म।
(ब) सः राजानं द्रष्टुम् इच्छति स्म।
उत्तरम् :
(अ) सः सरसिजं विक्रेतुम् इच्छति स्म।
प्रश्न 2.
सार्थवाहः सुदासाय शतसुवर्णनाणकानि दातुम् उद्युक्तः यतः
(अ) स सुदासस्य साहाय्य कर्तुम् इच्छति स्म।
(ब) सः सुदासात् कमलं क्रेतुम् इच्छति स्म।
उत्तरम् :
(ब) सः सुदासात् कमल क्रेतुम् इच्छति स्म।
![]()
प्रश्न 3.
सुदासः नीरजं सुगतचरणाभ्यां समर्पितवान् यत:
(अ) सुगतः सुदासाय अधिकं धनं यच्छति।
(ब) सुदासस्य मनसि भक्तिरस: अजायत।
उत्तरम् :
(ब) सुदासस्य मनसि भक्तिरसः अजायत।
प्रश्न 4.
सुदासेन कमलार्थ किमपि मूल्यं न स्वीकृतम् यतः
(अ) भगवतः चरणकमलस्पर्शेण एव तस्य आत्मा कृतार्थतां लभताम्।
(ब) श्रेष्ठी कमलार्थ बहुमूल्यम् अयच्छत्।
उत्तरम् :
(अ) भगवत: चरणकमलस्पर्शेण एव तस्य आत्मा कृतार्थतां लभताम्।
(ख) उचित पर्यायं चित्वा वाक्यं पुनलिखत।
प्रश्न 1.
- आसीत् ……….. नाम कश्चिदुद्यानपाल:। (सुदासः / सुगत:)
- शिशिर-प्रती एक …………. व्यकसत्। (पद्यम्/जपाकुसुमम्)
- अहो महिमा ………….. (परमात्मनः / मानवस्य)
- स: तद् विक्रेतुं ………. पुरतः स्थितः। (देवालयस्य/राजसद्मनः)
- पूजार्थमिदं कमलम् ………… (विक्रीणे / अभ्यर्थये)
- अहं दश …………. यच्छामि। (रूप्यकाणि / सुवर्णनाणकानि)
उत्तरम् :
- सुदासः
- पढा
- परमात्मनः
- राजसदानः
- अभ्यर्थये
- सुवर्णनाणकानि
![]()
प्रश्न 2.
1. महात्मा वटवृक्षस्य अवस्तात् समुपविष्टः आसीत्। (अश्मखण्डे/मृगाजिने)
2. सः हस्तस्थं भगवतः चरणयो: अयम् अकरोत्। (जपाकुसुमं/नीरज)
उत्तरम् :
1. अश्मखण्डे
2. नीरज
(ग) ककं वदति?
प्रश्न 1.
एकेन सुवर्णनाणकेन।
उत्तरम् :
सुदासः सार्थवाह वदति।
प्रश्न 2.
अहं शतं सुवर्णनाणकानि प्रयच्छामि।
उत्तरम् :
सार्थवाह: सुदासं वदति।
![]()
प्रश्न 3.
नैतद् भो विक्रेतुमिच्छामि।
उत्तरम् :
सुदास : सार्थवाहश्रेष्ठिनौ वदति।
प्रश्न 4.
केवलं भगवत: चरणकमलस्पर्शेण आत्मा मे कृतार्थता लभताम्।
उत्तरम् :
सुदास: भगवन्तं गौतमबुद्ध वदति।
प्रश्न 5.
तथास्तु।
उत्तरम् :
भगवान् गौतमबुद्धः सुदासं वदति।
(घ) पूर्णवाक्येन उत्तरत।
प्रश्न 1.
सुदास: किमर्थ राजसद्मनः पुरतः स्थितः?
उत्तरम् :
सुदासः पद्यं विक्रेतुं राजसद्मनः पुरतः स्थितः।
![]()
प्रश्न 2.
एषः गद्यांश: कस्मात् पाठात् उद्धृतः?
उत्तरम् :
एषः गद्यांश: ‘अमूल्यं कमलम्’ इति पाठात् उद्धृतः।
प्रश्न 3.
सुदासः कुत्र प्राप्तः?
उत्तरम् :
यत्र भगवत: सुगतस्य निवास: तदुद्यानं सुदासः प्राप्तः।
प्रश्न 4.
भगवतः वदनं केन राजते स्म?
उत्तरम् :
भगवतः वदनम् अनल्पेन धाम्ना राजते स्म।
![]()
प्रश्न 5.
सुदासः केन कृतार्थतां लभताम्?
उत्तरम् :
सुदासः केवलं भगवतः चरणकमलस्पर्शेण कृतार्थतां लभताम्।
प्रश्न 6.
भगवतः सुगतस्य अन्यत् नाम किम्?
उत्तरम् :
भगवतः सुगतस्य अन्यत् नाम भगवान् गौतमबुद्धः आसीत्।
(च) वाक्यं पुनर्लिखित्वा सत्यम् / असत्यम् इति लिखत।
प्रश्न 1.
- सुदास: मालाकार: आसीत्।
- कमलस्य विकासेन तडाग: विभूषितः ।
- पद्मं हेमन्त-ऋतौ व्यकसत्।
- पद्यं विक्रेतुं स: देवालयस्य पुरतः स्थितः ।
- श्रेष्ठी कमलार्थं शतं सुवर्णनाणकानि दातुम् इच्छति।
उत्तरम् :
- सत्यम्।
- सत्यम्।
- असत्यम्।
- असत्यम्।
- असत्यम्।
![]()
प्रश्न 2.
- भगवतः सुगतस्य निवास: देवालये आसीत्।
- उद्याने आम्रवृक्षस्य अधस्तात् महात्मा उपविष्टः आसीत्।
- सुदासः हस्तस्थं सरसिज सुगतस्य चरणयोरय॑म् अकरोत्।
- सुगतः सुदासाय कमलार्थम् अधिकमूल्यं यच्छति।
उत्तरम् :
- असत्यम्।
- असत्यम्।
- सत्यम्।
- असत्यम्।
शब्दज्ञानम् :
(क) सन्धिविग्रहः।
- सुदासो नाम – सुदास: + नाम।
- सत्यपि – सति + अपि।
- शिशिरऋतावेकम् – शिशिरऋतौ + एकम्।
- व्योम्नीव – व्योनि+इव।
- सोऽचिन्तयत् – स: + अचिन्तयत्।
- यदेतादृशे – यत् + एतादृशे।
- काले तिशीते – काले + अतिशीते।
- विभूषितो में – विभूषितः + मे।
- तडाग एतस्य – तडाग: + एतस्य।
- विक्रीयाहम् – विक्रीय + अहम्।
- स तद् – स: + तद्।
- तेनैव – तेन + एव।
- सम्प्रत्येतस्मिन्नगरे – सम्प्रति + एतस्मिन् + नगरे।
- पूजार्थमिदम् – पूजार्थम् + इदम्।
- कमलमभ्यर्थये – कमलम् + अभ्यर्थये।
- तत्कियता – तत् + कियता।
- उद्यानपालोऽब्रवीत् – उद्यानपाल: + अब्रवीत्।
- स सार्थवाह: – सः + सार्थवाहः।
- यावत्तत् – यावत् + तत्।
- क्रेतुमिच्छति – क्रेतुम् + इच्छति।
- तावदेवापरो धनवान् – तावत् + एव + अपरः + धनवान्।
- उद्यानपालोऽबूत . उद्यानपाल: + अबूत।
- एव महाभाग एकम् – एष: + महाभागः + एकम्।
- एतस्यार्थे – एतस्य + अर्थे ।
- दातुमिच्छति – दातुम् + इच्छति।
- सार्थवाहोऽभणत् . सार्थवाहः + अभणत्।
- तयोर्विवादम् – तयोः + विवादम्।
- सुदासो व्यमृशत् – सुदास: + व्यमृशत्।
- कमलमेतत् – कमलम् + एतत्।
- क्रेतुमिच्छतः – केतुम् + इच्छतः।
- स सुगत एवाधिकतमम् – सः + सुगतः + एव + अधिकतमम्।
- स उद्यानपालस्तावभाषत – सः + उद्यानपाल: + वौ + अभाषत ।
- नैतद् – 1 + एतद्।
- भो विक्रेतुमिच्छामि – भो: + विक्रेतुम् + इच्छामि।
- सुदासस्तदुद्यानम् – सुदास: + तत् + उद्यानम्।
- वटवृक्षस्याधस्तादेकस्मिन्न – वटवृक्षस्य + अधस्तात् + श्मखण्डे एकस्मिन् + अश्मखण्डे।
- समुपविष्ट आसीत्स महात्मा – समुपविष्टः + आसीत् + सः+ महात्मा।
- भगवतो वदनम् – भगवतः + वदनम्।
- तदालोकयतः – तत् + आलोकयतः।
- भक्तिरसार्णव उदतिष्ठत् – भक्तिरसार्णवः+ उदतिष्ठत् ।
- स हस्तस्थम् – सः + हस्तस्थम्।
- नमो भगवते नमः + भगवते।
- स्मयमानमुखपद्मो भगवान् – स्मयमानमुखपा : + भगवान्।
- किमिच्छसि – किम् + इच्छसि।
- किमन्यत् – किम् + अन्यत्।
- तथास्तु – तथा + अस्तु।
- यत्तस्य – यत् + तस्य।
- दर्शनमात्रेणैव – दर्शनमात्रेण + एव।
- बहुमूल्यमपेक्षमाणः – बहुमूल्यम् + अपेक्षमाणः।
- सुदासस्तद्विस्मृत्य – सुदासः + तत् + विस्मृत्य।
- तत्कमलम् – तत् + कमलम्।
![]()
(ख) त्वान्त-ल्यबन्त-तुमन्त-अव्ययानि।
1.
| त्वान्न अव्यय धातु + त्वा / ध्या / ट्वा / वा / इत्वा अयित्वा | ल्यबन्त अव्यय उपसर्ग + धातु + य / त्य | तुमन्त अव्यय धातु + तुम् / धुम् / दुम् / दुम् इतुम् / अयितुम् |
| श्रुत्वा | सशिन्त्य | विक्रेतुम, क्रेतुम् दातुम् |
2.
| त्वान्न अव्यय धातु + त्वा / ध्या / ट्वा / वा / इत्वा अयित्वा | तुमन्त अव्यय धातु + तुम् / धुम् / दुम् / दुम् इतुम् / अयितुम् |
| कृत्वा | विस्मृत्य |
![]()
(ग) विभक्त्यन्तरूपाणि।
1.
- द्वितीया – एतत्, सरसिजम्, विपुलम्, धनम्, इदम, कमलम्, नीरजमूल्यम्, पृच्छन्तम्, तम्, श्रेष्ठिनम्, एकम, सुवर्णनाणकम्, सुवर्णनाणकानि, विवादम्, अधिकतमम्, मूल्यम्, तौ।
- तृतीया – विकासेन, तेन, अध्वना, कियता, मूल्येन, एकेन, सुवर्णनाणकेन।
- चतुर्थी – महाम्, मे।
- षष्ठी – एतस्य, सरसिजस्य, परमात्मनः, राजसद्मनः, महात्मनः, तस्य, तयोः, यस्य।
- सप्तमी – तडागे, सति, शिशिरऋतौ, व्योम्नि, एतादृशे, काले, अतिशीते, एतस्मिन्, नगरे।
- सम्बोधनम् – भद्र।
2.
- द्वितीया – तत्, उद्यानम्, हस्तस्थम्, नीरजम, तम्, कृतार्थताम्, वादिनम्, सुदासम्, कमलम्।
- तृतीया – अनल्पेन, धाम्ना, प्रसादवर्षिभ्याम, लोचनाभ्याम, चरणकमलस्पर्शेण, दर्शनमात्रेण।
- चतुर्थी – सुगतचरणाभ्याम्, भगवते।
- षष्ठी – भगवतः, सुगतस्य, वटवृक्षस्य, तस्य, आलोकयतः, सुदासस्य, में।
- सप्तमी – एकस्मिन, अश्मखण्डे, चित्ते, चरणयोः, उक्तवति, सुगते।
- सम्बोधनम् – वत्स, भगवन्।
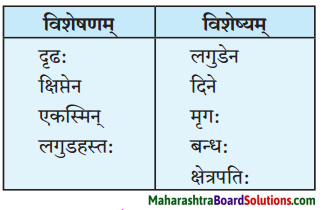
(घ) विशेषण – विशेष्य – सम्बन्धः ।
| विशेषणम् | विशेष्यम् |
| 1. अतिशीते | काले |
| 2. स्मयमानमुखपद्यः | भगवान् |
| 3. वादिनम् | सुदासम् |
![]()
(च) लकारं लिखत।
प्रश्न 1.
- आसीत् सुदास: नाम कश्चिदुद्यानपालः।
- तस्य पूजार्थमिदं कमलम् अभ्यर्थये।
- तत्कियता मूल्येन ददासि।
- उद्यानपाल: अब्रवीत्।
- तं श्रेष्ठिनम् उद्यानपाल: अबूत।
- एतौ कमलमेतत् क्रेतुम् इच्छतः।
- स सुगत एवाधिकतम मूल्यं दद्यात्।
उत्तरम् :
- लङ्लकार;
- लट्लकार:
- लट्लकारः
- लङ्लकारः
- लङ्लकार:
- लट्लकार:
- विधिलिङ्लकार:
![]()
प्रश्न 2.
1. ‘सुदासस्य चित्ते भक्तिरसार्णवः उदतिष्ठत्।
2. ‘तथास्तु’ इति अब्रवीत् भगवान् सुगतः।
उत्तरम् :
1. लङ्लकारः
2. ललकार:
(छ) प्रश्ननिर्माणं कुरुत।
प्रश्न 1.
तस्य तडागे शिशिर-ऋतौ पद्मं व्यकसत्।
उत्तरम् :
तस्य तडागे कदा पर्दा व्यकसत्?
प्रश्न 2.
स: कमल विक्रेतुं राजसानः पुरत: स्थितः।
उत्तरम् :
स: कमलं विक्रेतुं कुत्र स्थित:?
![]()
प्रश्न 3.
श्रेष्ठी दश सुवर्णनाणकानि दातुमिच्छति।
उत्तरम् :
कः दश सुवर्णनाणकानि दातुमिच्छति?
प्रश्न 4.
सुदासः उद्यानं प्राप्तः।
उत्तरम् :
कः उद्यानं प्राप्तः?
प्रश्न 5.
वटवृक्षस्य अधस्तात् अश्मखण्डे महात्मा उपविष्टः आसीत्।
उत्तरम् :
वटवृक्षस्य अधस्तात् अश्मखण्डे कः उपविष्टः आसीत्?
प्रश्न 6.
सुदासः भगवत: चरणयोः नीरजम् अयं कृतवान्।
उत्तरम् :
सुदासः भगवतः चरणयोः किम् अध्यं कृतवान् ?
![]()
प्रश्न 7.
‘तथास्तु’ इति अब्रवीत् भगवान् सुगतः।
उत्तरम् :
‘तथास्तु’ इति क: अब्रवीत्?
पृथक्करणम्
(क) क्रमेण योजयत।
प्रश्न 1.
- श्रेष्ठिनः सार्थवाहस्य च विवादः ।
- शिशिर-ऋतौ पद्मस्य विकासः।
- सुदास: विक्रयणार्थ राजसद्मनः पुरतः स्थितः।
- सुदासस्य धनप्राप्ते: इच्छा।
उत्तरम् :
- शिशिर-ऋतौ पद्यस्य विकासः ।
- सुदासस्य धनप्राप्ते: इच्छा।
- सुदासः विक्रयणार्थ राजसद्मनः पुरतः स्थितः।
- श्रेष्ठिन: सार्थवाहस्य च विवादः।
प्रश्न 2.
- सुदासस्य धनप्राप्ते: इच्छा।
- सार्थवाहस्य कमलक्रयणस्य इच्छा।
- सार्थवाहः शतं सुवर्णनाणकानि दातुं सिद्धः।
- श्रेष्ठी दश सुवर्णनाणकानि दातुमिच्छति।
उत्तरम् :
- सुदासस्य धनप्राप्ते: इच्छा।
- सार्थवाहस्य कमलक्रयणस्य इच्छा।
- श्रेष्ठी दश सुवर्णनाणकानि दातुमिच्छति।
- सार्थवाहः शतं सुवर्णनाणकानि दातुं सिद्धः ।
![]()
प्रश्न 3.
- सुगतचरणाभ्यां कमलस्य समर्पणम्।
- सुदासस्य सुगतदर्शनम्।
- सुगतस्य आशीर्वादप्रदानम्।
- सुगतदर्शनात् बहुमूल्यस्य अपेक्षायाः विस्मरणम्।
उत्तरम् :
- सुदासस्य सुगतदर्शनम्।
- सुगतदर्शनात् बहुमूल्यस्य अपेक्षायाः विस्मरणम्।
- सुगतचरणाभ्यां कमलस्य समर्पणम्।
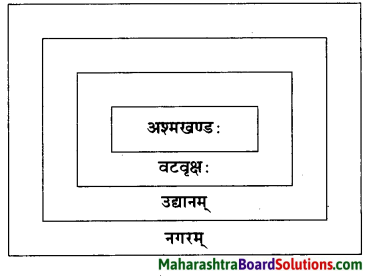
- सुगतस्य आशीर्वादप्रदानम्। स्थानाधारेण शब्दपेटिका पूरयत। (वटवृक्षः नगरम्, अश्मखण्डः, उद्यानम्)
(ख) स्थानाधारेण शब्दपेटिका पूरयत।
(वटवृक्ष: नगरम्, अश्मखण्डः, उद्यानम्)
(ख) तालिका पूरयत।
प्रश्न 1.
(मञ्जूषा – एकेन सुवर्णनाणकेन, अहं शतं सुवर्णनाणकानि प्रयच्छामि, नैतद् विक्रेतुमिच्छामि, तत् कियता मूल्येन ददासि?)
उत्तरम् :
वक्त्रा संवाद मेलयत।
| सार्थवाहः | उद्यानपाल: |
| 1. अहं शतं सुवर्णनाणकानि प्रयच्छामि। | 1. एकेन सुवर्णनाणकेन। |
| 2. तत् कियता मूल्येन ददासि? | 2. नैतद् विक्रेतुमिच्छामि। |
![]()
(ग) वक्त्रा संवादं मेलयत।
प्रश्न 1.
(मञ्जूषा – भगवन् किमन्यत्?, तथास्तु, नमो भगवते, वत्स, किमिच्छसि)
| सुदासः | सुगत: |
| नमो भगवते। | तथास्तु। |
| भगवन् किमन्यत्? | वत्स, किमिच्छसि। |
भाषाभ्यासः
(क) समानार्थकशब्दाः।
- उद्यानपाल: – मालाकारः।
- व्योम्नि – आकाशे, गगने, नभसि, अन्तरिक्षे, अनन्ते, खे।
- धनम् – द्रव्यम्, वित्तम्, स्थापतेयम्, रिक्थम्, ऋक्थम्, वसुः, अर्थम्।
- अध्वना – मार्गेण, पथिना।
- सुगतः – सर्वज्ञः, बुद्धः, धर्मराजः, तथागतः, गौतमः ।
(ख) विरुद्धार्थकशब्दान् लिखत।
1. पुरतः × पृष्ठतः।
(ग) सूचमनुसारं कृती: कुरुत।
(आ) धातुसाधित – अव्ययं निष्कासयत।
प्रश्न 1.
सः सुगतस्य चरणयोरय॑म् कृत्वा प्राणमत्।
उत्तरम् :
स: सुगतस्यं चरणयोरय॑म् अकरोत् प्राणमत् च।
![]()
प्रश्न 2.
सुदासः तत् विस्मृत्य तत्कमलं समर्पितवान्।
उत्तरम् :
सुदासः तत् व्यस्मरत् तत्कमलं समर्पितवान् च।
(इ) स्म निष्कासयत ।
प्रश्न 1.
तस्य वदनम् अनल्पेन धाम्ना राजते स्म।
उत्तरम् :
तस्य वदनम् अनल्पेन धाम्ना अराजत।
(उ) वचनं परिवर्तयत।
प्रश्न 1.
एतौ कमलमेतत् क्रेतुम् इच्छतः । (एकवचने लिखत।)
उत्तरम् :
एष: कमलमेतत् केतुम् इच्छति ।
(क) लकार परिवर्तयत।
प्रश्न 1.
शिशिर-ऋतौ पचं व्यकसत्। (लट्लकारे परिवर्तयत।)
उत्तरम् :
शिशिर-ऋतौ पा विकसति।
![]()
प्रश्न 2.
सुदासस्य चित्ते भक्तिरसार्णवः उदतिष्ठत्। (विधिलिङ्लकारे परिवर्तयत।)
उत्तरम् :
सुदासस्य चित्ते भक्तिरसाणव: उत्तिष्ठेत्।
(घ) वाक्यं शुद्धं कुरुत।
प्रश्न 1.
स: राजसाना पुरत: स्थितः।
उत्तरम् :
स: राजसद्मनः पुरतः स्थितः।
प्रश्न 2.
अनल्या धाम्ना तस्य वदनं राजते।
उत्तरम् :
अनल्पेन धाम्ना तस्य वदनं राजते।
प्रश्न 3.
अहं दश सुवर्णनाणकानि यच्छामः ।
उत्तरम् :
वयं दश सुवर्णनाणकानि यच्छामः।
![]()
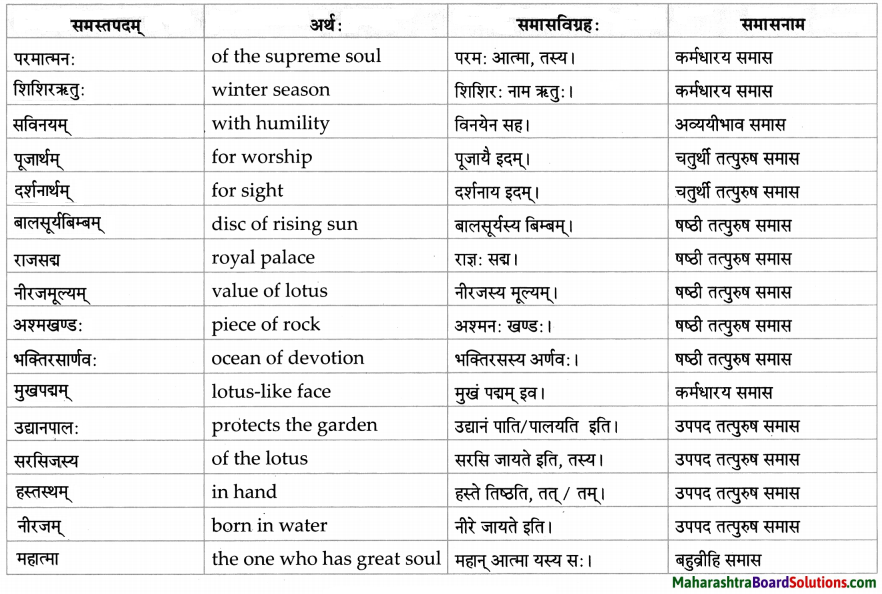
समासाः
अमूल्यं कमलम् Summary in Marathi and English
प्रस्तावना :
भारत हा अनेक तत्त्वचिंतकांचा देश आहे. भगवान गौतम बुद्ध हे त्याच महान व्यक्तिमत्त्वांपैकी एक होते. भगवान बुद्ध हे सत्य, प्रेम, ज्ञान व शांततेचा संदेश जगभरात पसरवणाऱ्या बौद्ध धर्माचे प्रवर्तक होते. भगवान बुद्धांविषयीच्या अनेक कथा प्रसिद्ध आहेत, ज्यात ते आपल्या शिष्यांना समाधानी आणि शांतीपूर्ण जीवनाचे धडे देतात.
‘अमूल्यं कमलम्’ ही कथा बौद्ध कथासाहित्यातून घेतलेली आहे. भगवान बुद्धांच्या अलौकिक शिकवणीचे या कथांमधून दर्शन घडते. कथेचे शीर्षक सदाचार आणि सत्संगतीचे महात्म्य योग्यप्रकारे सूचित करते. त्यातून मिळणारे समाधान व मन:शांती ही संपत्ती आणि भौतिक सुखांपेक्षा श्रेष्ठ तसेच मौल्यवान असते.
India is the country of philosophical thinkers. Lord Gautam Buddha uns one of those great personalities. Lord Buddha uns the founder of Buddhism which Spreads the message of truth, love, enlightenment and peace on the earth.
Many legends of Lord Buddha are popular in which he preaches and enlightens his disciples about content and peaceful life. ‘अमूल्यं कमलम्’ is a story extracted from Buddhist legends that highlights the divine teachings of lord Buddha. The title rightly suggests that, righteousness and a good company leading to contentment and peace of mind, is superior and priceless compared to money and worldly pleasures.
![]()
परिच्छेदः 1
आसीत् सुदासो ……………….. विक्रेतुमिच्छामि इति।
अनुवादः
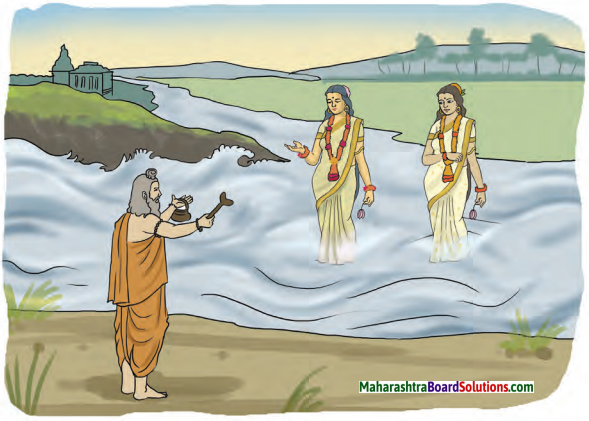
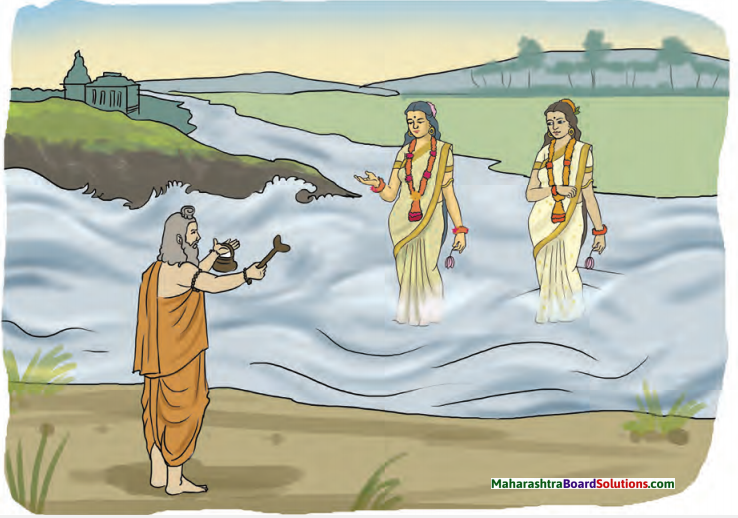
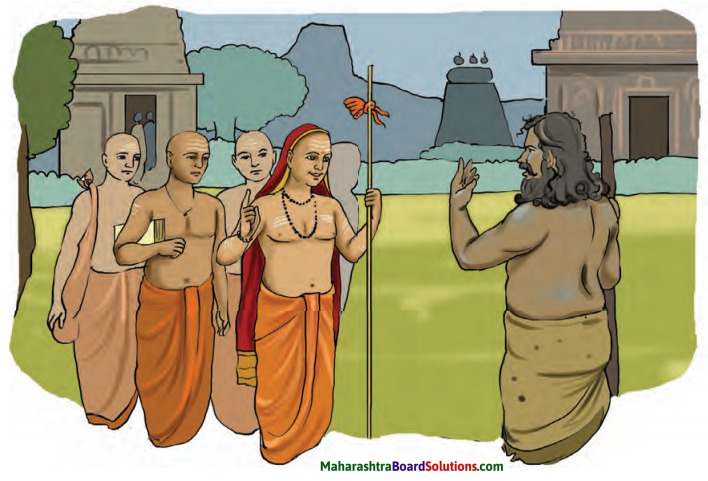
सुदास नावाचा कोणी एक माळी होता. एकदा शिशिरऋतू (हिवाळा) असूनसुद्धा आकाशात (शोभून दिसणाऱ्या) नुकत्याच उगवलेल्या सूर्यबिंबासारखे (तेजस्वी) कमळ मराठी त्याच्या सरोवरात उमलले. त्याने विचार केला, “परमात्म्याचा महिमा थोर (आहे), की एवढ्या कडाक्याच्या थंडीतसुद्धा या कमळाच्या उमलण्यामुळे माझे सरोवर सुशोभित झाले आहे. हे कमळ विकून मी पुष्कळ पैसे कमवेन”. असा विचार करून तो ते (कमळ) विकण्यासाठी राजवाड्यासमोर उभा राहिला. काही वेळानंतर, कोणी एक श्रीमंत व्यापारी त्याच मार्गान (दिशेने) आला.
तो म्हणाला, “सध्या भगवान सुगत याच शहरात राहत आहेत.” त्या महात्म्याच्या पूजेसाठी या कमळाची(मी) याचना (इच्छा) करतो. ते किती रूपयांत (मला) देशील? माळी म्हणाला, “एक सुवर्णमुद्रा (घेईन).” तेव्हा तो व्यापारी कमळ विकत घेण्याची इच्छा (व्यक्त) करत असताना दुसरा एक धनाढ्य व्यापारी सुगतांच्या दर्शनासाठी जात असताना तेथे हजर झाला. कमळाची किंमत विचारणाऱ्या त्या व्यापाऱ्याला माळी म्हणाला “हे महाशय या (कमळा) साठी एक सुवर्णमुद्रा देऊ इच्छितात.”
व्यापारी म्हणाला, “मी दहा सुवर्णमुद्रा देईन.”(पहिला) व्यापारी म्हणाला, “मी शंभर सुवर्णमुद्रा देईन.” त्या दोघांमधील विवाद ऐकून सुदासाने विचार केला. “ज्याच्यासाठी हे दोघे हे कमळ विकत घेऊ इच्छितात, तो सुगतच मला याहून अधिक मूल्य देईल.”
तेव्हा तो माळी त्या दोघांना म्हणाला, “महाशय, मी हे (कमळ) विकू इच्छित नाही.”
There was a certain gardener named सुदास, In his pond, in the winter season, there bloomed a lotus, which looked like the rising sun, in the sky. He thought, “O, the greatness of the Supreme Soul! In this severe cold, my pond is adorned by the blooming of such a lotus. By selling this lotus, I shall obtain a lot of wealth.” Thinking so, in order to sell it, he stood in front of the royal palace.
After a while, a certain rich merchant came by that very road. He spoke, “O noble man, the Lord y resides in this city now. I request this lotus for the worship of that great soul. At what price will you give it (to me)?” The gardener stated, “One gold coin.” Then, no sooner did that merchant wish to buy the lotus, than another wealthy tradesman / merchant, going to see yer, also came there.
The gardener said to the tradesman, who was asking for the price of the lotus, “This eminent person wishes to give one gold coin for this.” The tradesman replied, “l shall give ten gold coins.” The merchant spoke, “I will give a hundred gold coins.” Listening to their argument, yere deliberated, “The one, for whom these two wish to buy this lotus, that सुगत alone will give me a higher price.”
Thus, he told both of them, “Sirs, I do not wish to sell (this lotus).”
![]()
परिच्छेदः 2
अथ प्राप्तः …………………. भगवान् गौतमबुद्धः।
अनुवादः
आता सुदास, भगवान सुगत ज्या उद्यानात राहत होते, तेथे पोहोचला. तेथे वटवृक्षाखाली एका खडकावर ते महात्मा बसलेले होते. त्या दैवी पुरुषाचा चेहरा अमाप तेजाने झळकत होता. त्यांना पाहताच सुदासाच्या मनात भक्तिरसाचा सागर उफाळून आला.
हातातील कमळ भगवान सुगतांच्या पायावर अर्घ्य म्हणून समर्पित करुन, “भगवंतांना वंदन असो” असे म्हणत (त्याने) नम्रपणे अभिवादन केले. करुणाई डोळ्यांनी त्याच्याकडे पाहत कमळासारखे मुख असलेले भगवान सस्मित म्हणाले, “बाळा, तुझी काय इच्छा आहे?”
सुगतांचे हे शब्द ऐकताच आता निरिच्छ झालेला सुदास म्हणाला, “भगवन, अजून काय (असणार)? आपल्या चरणकमलांच्या केवळ स्पर्शाने माझ्या आत्म्याला कृतार्थता लाभो.” असे म्हणणाऱ्या सुदासाला ‘तसेच होवो’ असे भगवान सुगत म्हणाले.
काय तो सुगतांचा प्रभाव! त्यांच्या केवळ दर्शनाने कमळासाठी मोठ्या किमतीची अपेक्षा करणाऱ्या सुदासाने ते विसरून ते कमळ सुगतांच्या चरणावर वाहिले. हे सुगत म्हणजेच भगवान गौतम बुद्ध.
Now, सुदास reached that garden where Lord सुगत lived. There, under the banyan tree, that great soul was seated, on a rock. That divine one’s face shone with great lustre. As soon as he saw him, an ocean of devotion arose in सुदास’s heart.
Offering the lotus in his hand at the feet of Lord सुगत as homage, saying “Salutations to the Lord”, he bowed down with humility. Looking at him with eyes showering kindness (serenity), the lotus-faced Lord smilingly said, “Child, what do you wish?”.
At these words of सुगत, सुदास who was now desireless replied, “O Lord what else? By the mere touch of your feet, may my soul attain fulfilment.” To सुदास who spoke thus, the Lord सुगत uttered, “May it be so.” Othe effect of सुगत, by only the sight of whom, सुदास, having forgotten that he expected a huge price for the lotus, dedicated that lotus at the feet of सुगत. This सुगत is none other than Lord गौतम बुद्ध.
![]()
शब्दार्थाः :
- उद्यानपाल: – gardener – माळी
- विवादः – argument – वाद/भांडण
- सार्थवाह:/श्रेष्ठी – merchant/trader – व्यापारी
- महिमा – greatness – महात्म्य, मोठेपणा
- अध्वना – by the road – रस्त्याने
- परमात्मनः – of the supreme soul – परमात्म्याचे
- राजसद्मनः – of the royal palace – राजवाड्याच्या
- अतिशीते – in extreme cold – कडाक्याच्या थंडीत
- तडागे – in the lake – सरोवरामध्ये
- शिशिर ऋती – in winter season – हिवाळ्यात
- व्योम्नि – in the sky – आकाशात
- अभ्यर्थये – I request – मी विनंती करतो
- पद्यं व्यकसत् – a lotus bloomed – कमळ उमलले
- व्यमृशत् – thought – विचार केला
- दद्यात् – would give – देतील
- क्रेतुम् – to buy – विकत घेण्यासाठी
- विक्रेतुम् – to sell – विकण्यासाठी
- सत्यपि- in spite of being – असताना सुद्धा
- प्राप्तः सुदासः – सुदास reached – सुदास पोहोचला
- मुखपद – lotus-like face – मुखकमल
- भक्तिरसार्णवः – an ocean of devotion – भक्तिचा सागर
- निरिच्छ: – desireless – नि:स्पृह/निःस्वार्थ
- अपेक्षमाणः – expected अपेक्षा करणारा
- स्मयमानः – smiling – हसरा
- निरूपयन् – looking बघत असता
- समर्पितवान् – dedicated – अर्पण केले
- एवं वादिनम् – who spoke thus – असे बोलणाऱ्या
- धाम्ना – with lustre – तेजाने
- प्रसादवर्षिभ्याम् – showering kindness – करूणेचा वर्षाव करणाऱ्या
- आलोकयत: – while seeing – बघत असताना
- अश्मखण्डे – on a rock – खडकावर
- उदतिष्ठत् – arose – उत्पन्न झाला
- सविनयम् – bowed down with – विनम्र अभिवादन केले
- प्राणमत् – humility
- कृतार्थतां लभताम् – attain fulfilment – कृतार्थता लाभो
- अयं कृत्वा – offering as homage – अर्घ्य वाहून
- अवस्तात् – under/ below – खाली
Aamod Sanskrit Book 10th Class Solutions
- आद्यकृषक: पृथुवैन्यः Class 10 Question Answer
- व्यसने मित्रपरीक्षा Class 10 Question Answer
- सूक्तिसुधा Class 10 Question Answer
- अमूल्यं कमलम् Class 10 Question Answer
- स एव परमाणुः Class 10 Question Answer
- युग्ममाला Class 10 Question Answer
- संस्कृतनाट्ययुग्मम् Class 10 Question Answer
- वाचनप्रशंसा Class 10 Question Answer
- धेनोर्व्याघ्रः पलायते Class 10 Question Answer
- नदीसूक्तम् Class 10 Question Answer
- जटायुशौर्यम् Class 10 Question Answer
- आदिशङ्कराचार्यः Class 10 Question Answer
- चित्रकाव्यम् Class 10 Question Answer
- प्रतिपदं संस्कृतम् Class 10 Question Answer
- मानवताधर्मः Class 10 Question Answer