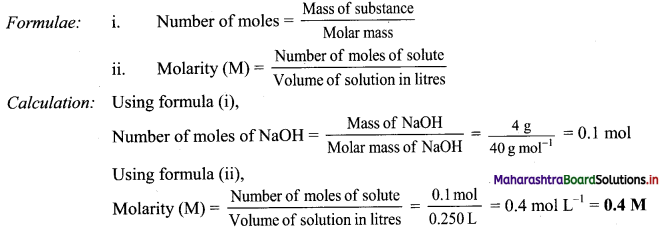
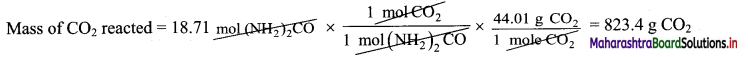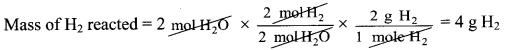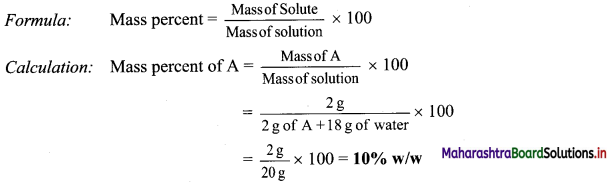Balbharti Maharashtra State Board 11th Biology Important Questions Chapter 9 Morphology of Flowering Plants Important Questions and Answers.
Maharashtra State Board 11th Biology Important Questions Chapter 9 Morphology of Flowering Plants
Question 1.
Explain how angiosperms are classified into different types based on habitat.
Answer:
Angiosperms can be classified into following types based on habitat:
- Hydrophytes – Growing in aquatic habitat e.g. Hydrilla
- Xerophytes – Growing in regions with scanty or no rainfall like desert e.g. Opimtia
- Psammophytes – Growing in sandy soil e.g. Elymus
- Lithophytes – Growing on rock e.g. Couchidium, Cladopus, Dalzellia, Paphiopedilum orchids, rock felt fem.
- Halophytes – Growing in saline soil e.g. Mangrove plants like Rhizophora

Question 2.
Draw neat and labelled diagram of a typical angiospermic plant. Classify its vegetative and reproductive structures.
Answer:
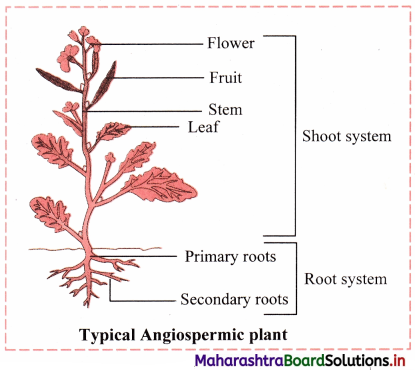
| Vegetative structures in angiospermic plant |
Reproductive structures in angiospermic plant |
| Root, Stem, Leaf |
Flowers, Fruits, Seeds |
Question 3.
Label the various regions of a typical root in the given figure and explain them in detail.
Answer:
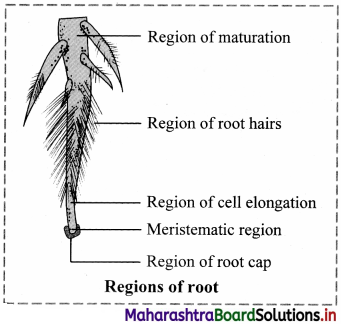
A typical root possesses the following regions:
1. Root cap:
a. A parenchymatous multicellular structure in the form of cap, present over young growing root apex is known as root cap.
b. Cell of root cap secrete mucilage for lubricating passage of root through the soil.
c. Cells of root cap show presence of starch granules which help in graviperception and geotropic movement of root.
d. Usually single root cap is present in plants. But in plants like Pandanus or screw pine multiple root caps are present.
e. In hydrophytes, root caps are replaced by root pocket e.g. Pistia, Eichhornia etc.
f. Due to presence of root cap the growing apex of root.
2. Meristematic region or region of cell division:
a. The apex of the root is a growing point about 1 mm in length protected by root cap. This region is called as region of cell division or meristematic region.
b. The structure is developed by compactly arranged thin walled actively dividing meristematic cells.
c. These cells bring about longitudinal growth of root.
3. Region of elongation:
a. This region of cells is present just above zone of cell division.
b. The cells are newly formed and show rapid elongation to bring about increase in length of the root.
c. The cells help in absorption of mineral salts.
4. Region of root hair or region of absorption:
a. A region of root hair / absorption/piliferous zone is made up of numerous hair like outgrowths.
b. The epiblema or piliferous layer produces tubular elongated unicellular structures known as root hair.
c. They are in close contact with soil particles and increase surface area for absorption of water.
d. Root hair are short lived or ephimeral and are replaced after every 10 to 15 days.
5. Region of maturation/region of differentiation:
a. It is the uppermost major part of the root.
b. The cells of this region are quite impermeable to water due to thick wall.
c. The cells show differentiation and form different types of tissues.
d. This region helps in fixation of plant and conduction of absorbed substances.
e. Development of lateral roots also takes place from this region.

Question 4.
What are the primary functions of root?
Answer:
Primary functions of root are, fixation or anchorage of plant body in the soil, absorption of water and minerals from soil and conduction of absorbed materials up to the stem base, etc.
Question 5.
Which type of root system is found in plants like maize, wheat and sugarcane? Explain in detail.
Answer:
- Adventitious root system is found in plants like maize, wheat and sugarcane.
- Adventitious root develops from any part other than radicle.
- Such roots may develop from the base of the stem, nodes or from leaves.
- In monocots, radicle is short lived.
- A thick cluster of equal sized roots arise from the base of a stem. It is also known as fibrous root system as they look like fibre. The growth of roots is superficial.
- Adventitious roots in some plants are used for vegetative propagation. E.g. Euphorbia, Carapichea ipecacuanha (Ipecac) etc.
Question 6.
What are metamorphosed roots?
Answer:
When roots have to perform some special type of function in addition to or instead of their normal function they develop some structural changes. Such roots are called as metamorphosed roots.
Question 7.
Complete the given chart and explain the modification of tap root for storage of food.
Answer:
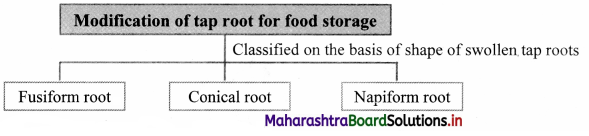
1. Modification of tap root for storage of food:
a. WTien tap root stores food it becomes swollen, fleshy and also develops definite shape.
b. Main or primary root is the main storage organ but sometimes hypocotyl part of embryo axis also joins the main root. Secondary roots remain thin.
c. On the basis of shape, swollen tap roots are classified as Fusiform, Conical and Napiform.
2. Fusiform root:
The fusiform root is swollen in the middle and tapering towards both ends forming spindle shaped structure, e.g. Radish (Raphanus sativus)
3. Conical root:
The conical root is broad at its morphological base and narrows down towards its apex. e.g. Carrot (Daucus car ota)
4. Napiform root:
In napiform root, base of root is highly swollen, almost spherical in shape and abruptly narrows down towards its apex. e.g. Beet (Beta vulgaris)
Question 8.
Identify the type of swollen tap root in the figures given below.
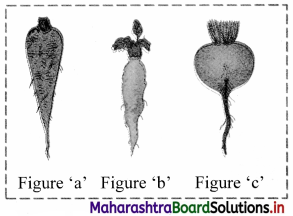
Answer:
Figure ‘a’: Conical root;
Figure ‘b’: Fusiform root;
Figure ‘c’: Napiform root
Question 9.
Answer the following questions:
1. Identify the label ‘X’ in the given figure of respiratory roots. Give its function.
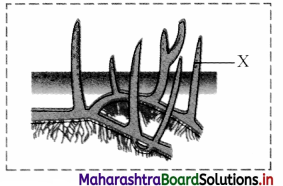
2. Give any tw o examples of plants in which respiratory roots are present.
Answer:
1. X: Lenticels
In respiratory roots or pneumatophores, gaseous exchange occurs through lenticels.
2. Examples of plants in which respiratory roots are present:
Rhizophora, Avicennia, Sormeratia, Heritiera fames (sundri), etc.
Question 10.
Identify the types of modified adventitious roots in the figures given below and explain in detail.
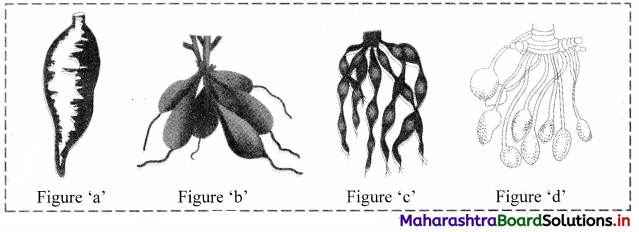
Answer:
1. Figure ‘a’ indicates simple tuberous root.
a. Simple tuberous roots become swollen and do not show definite shape.
b. They are produced singly.
c. The roots arise from nodes over the stem and penetrate into the soil, e.g. sweet potato or shakarkand (Ipomoea batatas).
2. Figure ‘b’ indicates fasciculated tuberous roots.
a. A cluster of roots arising from one point which becomes thick and fleshy due to storage of food is known as fasciculated tuberous root.
b. These clusters are seen at the base of the stem, e.g. Dahlia, Asparagus, etc.
3. Figure ‘c’ indicates Moniliform roots.
a. Some adventitious roots get swollen at regular intervals.
b. These gives them the appearance of beads of a necklace. Such roots are called as Moniliform roots, e.g. Spinacia oleracea (Indian Spinach).
4. Figure ‘d’ indicates Nodulose roots.
The cluster of long slender roots become enlarged at the tips forming nodules is known as nodulose roots, e.g. Arrow root (Maranta), Amhaldi or mango ginger (Curcuma amada).

Question 11.
Explain various types of adventitious roots which are modified for mechanical support.
Answer:
1. Prop roots / Columnar roots:
a. These roots arise from horizontal branches of tree like Banyan tree (Ficus benghalensis) and grow vertically downwards till they penetrate the soil.
b. These prop roots show secondary growth, become thick, act like pillars to provide mechanical support to the heavy branches.
2. Stilt roots:
a. These roots normally arise from a few lower nodes of a weak stem in some monocots, shrubs and small trees.
b. They show obliquely downward growth penetrating soil and provide mechanical support to the plant.
c. In the members of family Poaceae, the plants like Maize, Jowar, Sugarcane etc. produce stilt root in whorl around the node.
d. These roots provide additional support to the plant body.
e. In Screw pine or Pandanus (Kewada), stilt roots arise only from the lower surface of obliquely growing stem for additional support. These roots show multiple root caps.
3. Climbing roots:
Different climbers with weak stem produce roots at their nodes by means of which they attach themselves to support and thereby raise themselves above the ground.
e.g. Betel leaf or Pan, black pepper or Piper nigrum (Kali Mirch), Pothos or money plant.
4. Clinging roots:
a. These tiny roots develop along intemodes, show disc at tips, which exude sticky substance.
b. This substance enables plant to get attached with walls of buildings.
c. They do not damage substratum, e.g. English Ivy (Hedera helix).
5. Plank roots/Buttress:
a. These roots often develop at the base of large trees and form plank like extensions around stem.
b. These roots provide additional support, e.g. Silk cotton, Peepal, etc.
6. Buoyant roots:
Roots developed at the nodes of aquatic herbs like (Jussiaea repens), become highly inflated and spongy providing buoyancy and helping the plant to float.
Question 12.
What are sucking roots? Explain with the help of examples.
Answer:
Sucking roots or Haustoria:
1. These are the specialised microscopic sucking roots developed by parasitic plants to absorb nourishment from the host.
2. Viscum album is a partial parasite. It develops haustoria which penetrate into xylem of host plant for absorption of food.
3. In Cuscuta reflexa or Dodder (Amarvel) haustoria penetrates vascular strand and suck food from phloem, water and minerals from xylem. Cuscuta is leafless plant with yellow stem. It is a total parasite.
Question 13.
Enlist the important characteristics of stem.
Answer:
Characteristics of stem:
- Stem is the ascending part of the plant body which develops from plumule and reproductive units.
- It is usually positively phototropic, negatively geotropic and negatively hydrotropic.
- It shows different types of buds (axillary, apical, accessory, etc.).
- It is differentiated into nodes and intemodes.
- At nodes it produces dissimilar organs such as leaves and flowers and similar organs such as branches.
- Young stem is green and capable of photosynthesis.
Question 14.
Sketch and label a typical stem structure and write its primary functions.
Answer:
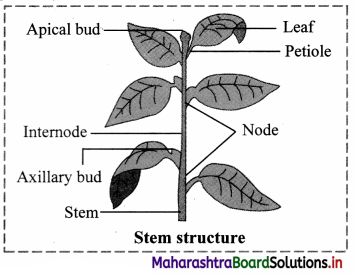
The primary functions of the stem are to produce and support branches, leaves, flowers and fruits; conduction of water and minerals and transportation of food to plant parts.

Question 15.
What is underground stem? When does it produce aerial shoots?
Answer:
In some herbaceous plants the stem which develops below soil surface is called underground stem. The underground stem remains dormant during unfavourable condition and on the advent of favourable condition produces aerial shoots.
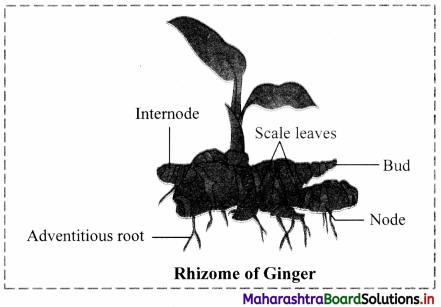
Question 16.
Draw neat and labelled diagram of rhizome of ginger.
Answer:
Question 17.
Potato which we eat is an underground part of a plant, however it can not be considered as root. Justify the given statement.
Answer:
- Potato is a stem tuber.
- It is an underground stem, modified for storage of food material.
- Special underground branches of stem at their tips becomes swollen due to storage of food which is mostly starch.
- Stem tuber shows distinct nodes, but not intemodes hence it is classified as stem.
- At nodal part, it shows scale leaves with axillary buds, which are commonly called as ‘eyes’.
- Under favourable conditions, ‘eyes’ can produce aerial shoots.
- Potato tuber can be propagated vegetatively. [Note: In stem tuber, internodes are present but they are not very distinct.]
Question 18.
What are tunicated and compound tunicated bulbs?
Answer:
1. Tunicated bulb:
When fleshy scale leaves are arranged on stem in concentric manner, bulb is called as tunicated bulb or layered bulb. E.g. Onion
2. Compound tunicated bulb:
When fleshy scale leaves arranged on stem, partially overlap each other by their margins only, such bulb is called compound tunicated or scaly bulb. e.g. Garlic
Question 19.
Which type of modified stem is present in Colocasia and Amorphophallus? Explain with the help of neat and labelled diagram.
Answer:
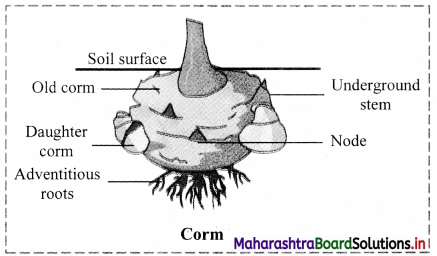
- In Colocasia and Amorphophallus corm is present, which is an underground stem modified for storage of food.
- Corm is swollen underground spherical or subspherical vertically growing stem.
- It is condensed structure with circular or ring like nodes.
- It shows presence of axillary buds and scales.
- Adventitious buds are produced which help in vegetative propagation.
- Adventitious roots are produced at lower part of the stem.

Question 20.
1. What are sub aerial stems?
2. Explain the different types of sub aerial stems. Give atleast one example of each.
Answer:
1. Subaerial stems:
a. These are generally weak or straggling stems growing over the ground and need support for perpetuation.
b. Sometimes these stems are found to grow beneath the soil surface also. Thus, they show contact with both air and soil.
c. Subaerial stems are meant for perennation and vegetative propagation.
d. Scale leaves and axillary buds are present over stem surface. Axillary buds develop into aerial shoots.
2. Types of subaerial stems:
a. Trailer:
1. The shoot spreads over the ground without striking adventitious roots.
The branches are either flat i.e. procumbent or partly vertical i.e. decumbent.
e. g. Euphorbia, Tridax etc. [Any one example]
b. Runner:
1. They are special narrow, prostrate or horizontal green branches which develop at the base of erect shoots known as crown.
2. Runners spread in all directions to produce new crowns with bunch of adventitious roots.
3. Presence of nodes with scale leaves and axillary buds is observed.
e.g. Cynodon (Lawn grass) Centella (Hydrocotyl / Brahmi), Oxalis etc. [Any one example]
c. Stolons:
1. The slender lateral branch arising from the base of main axis is known as stolon.
2. In some plants it is above ground (wild strawberry).
3. Primarily stolon shows upward growth in the form of ordinary branch, but when it bends and touches the ground terminal bud grows into new shoot and develops adventitious roots.
e.g. Wild Strawberry, Jasmine, Mentha, etc. [Any one example]
d. Sucker:
1. It is non-green, runner like branch of stem.
2. It grows horizontally below soil initially and then comes above the soil surface obliquely to produce a new plant.
3. Sucker can be termed as underground runner.
e. g. Chrysanthemum, Banana etc. [Any one example]
e. Offset:
1. These are one intemode long runners in rosette plants at ground or water level.
2. Offset helps in vegetative propagation.
e.g. Water hyacinth or Jal kumbhi (Eichhornia) and Pistia. [Any one example]
Question 21.
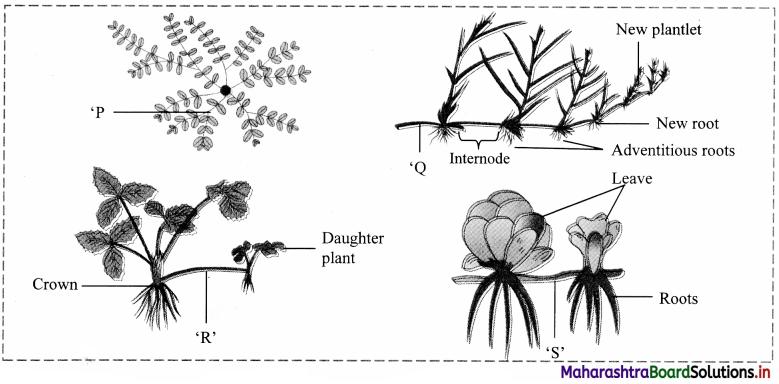
Observe the given figures and identify P, Q, R and S representing the different types of sub aerial shoot.
 Answer:
Answer:
‘P’: Trailer ‘Q’: Runner ‘R’: Stolon ‘S’: Offset
Question 22.
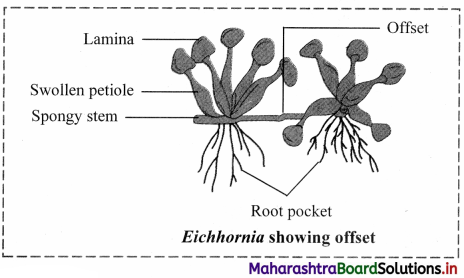
Draw neat and labelled diagram of Eichhornia showing offset.
Answer:

Question 23.
What are metamorphosed stems?
Answer:
Stem or its vegetative part develops various modifications to carry out specialized functions. Such modified stems are called as metamorphosed stems.
Question 24.
Describe the aerial modifications of stem.
Answer:
Different aerial modifications shown by stem are as follows:
1. Stem tendrils:
a. Tendrils are thin, wiry, photosynthetic, leafless coiled structures.
b. They give additional support to developing plant.
c. Tendrils have adhesive glands for fixation.
d. Apical bud in Vitis quadrangularis gets modified into tendril. The further growth is carried out by axillary bud.
e. In Passiflora axillary bud gets modified in tendril.
f. Extra axillary bud is the one which grows outside the axil. This bud in cucurbita gets modified into tendril.
g. Normally floral buds are destined to produce flowers. But in plants like Antigonon they produce tendrils.
2. Thorn:
a. It is modification of apical or axillary bud.
b. Thom is hard pointed and mostly straight structure (except Bougainvillea where it is curved and useful for climbing).
c. It provides protection against browsing animals and also helps in reducing transpiration.
d. Apical bud develops into thorn in Carrisa whereas axillary bud develops into thorn in Duranta, Citrus, Bougainvillea, etc.
3. Phylloclade:
a. Modification of stem into leaf like photosynthetic organ is known as phylloclade.
b. Being stem it possesses nodes and internodes.
c. It is thick, fleshy and succulent, contains mucilage for retaining water e.g. Opuntia, Casuarina (Cylindrical shaped phylloclade) and Muehlenbeckia (ribbon like phylloclade).
4. Cladodes:
a. The branches of limited growth i.e. one intemode long and performing photosynthetic function are called as cladodes.
b. True leaves are reduced to spine or scales to reduce rate of transpiration, e.g. Asparagus.
5. Cladophylls:
These are leaf like structures bore in the axil of scale leaf. It has floral bud and scale leaf in the middle i.e. upper half is leaf and lower half is stem. e.g. Ruscus.
6. Bulbils:
a. In plants like Dioscorea, etc. axillary bud becomes fleshy and rounded due to storage of food called as bulbil.
b. When it falls off it produces new plant and help in vegetative propagation.
Question 25.
Observe the given figures oi Asparagus, Vitis quadrangularis and Passiflora. Which of the following is labelled incorrectly?
Answer:
Figure ‘a’ is incorrectly labelled.
It represents Cladode oi Asparagus.
Question 26.
How does thorn in Carissa differ from that of Duranta?
Answer:
In Carrisa, apical bud develops into thorn, whereas in Duranta, axillary bud develops into thorn.
Question 27.
Enlist the general characteristics of a leaf.
Answer:
General characteristics of a leaf:
- Leaves are the most important appendages as they carry out photosynthesis and also help to remove excess amount of water from plant body through transpiration.
- Leaves are exogenous in origin and develops from leaf primordium.
- Leaf is dorsiventrally flattened lateral appendage of stem, produced at nodal region.
- Leaf is thin, expanded and green due to presence of photosynthetic pigments, i.e. chlorophyll.
- Axil of leaf shows presence of axillary bud.
- Leaf shows limited growth, does not show apical bud or a growing point.
Question 28.
Give an account of various parts of a typical dicot leaf.
Answer:
A typical dicot leaf shows presence of three main parts Leaf base or Hypopodium, Petiole or Mesopodium and Leaf lamina/blade or Epipodium.
1. Leaf base or Hypopodium:
a. The point by which leaf remains attached to the stem is known as leaf base.
b. The nature of leaf base varies in different plants. It may be pulvinus (swollen), sheathing or ligulate, etc.
Question 29.
How simple leaf differs from a compound leaf?
Answer:
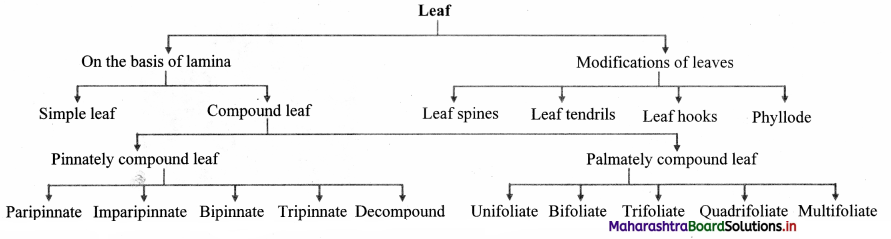
The leaf with entire lamina is called simple leaf, whereas leaf in which leaf lamina is divided into many leaflets is called as compound leaf.

Question 30.
Identify the type of pinnately compound leaves in the figures given below and give one example of each.
Answer:
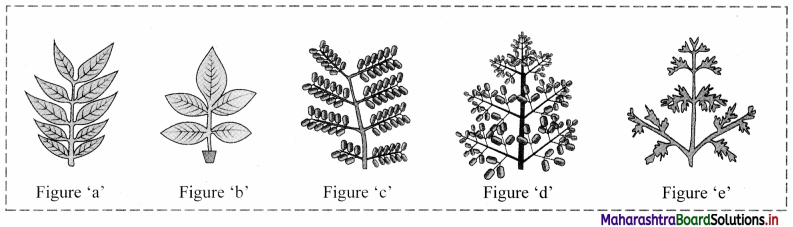
Figure ‘a’: Paripinnately compound leaves (e.g. Cassia)
Figure ‘b’: Imparipinnately compound leaves (e.g. Rosa)
Figure ‘c’: Bipinnately compound leaves (e.g. Caesalpinia)
Figure ‘d’: Tripinnately compound leaves (e.g. Moringa)
Figure ‘e’: Decompound leaves (e.g. Coriandrum)
Question 31.
Explain how leaves modify to perform different functions other than photosynthesis and gaseous exchange.
Answer:
Leaves show different types of modification as follows:
1. Leaf spines:
Sometimes entire leaf is modified into spines (Opuntia) or margin of leaf becomes spiny (Agave) or stipule modifies into spine (Acacia, Zizyphus) to check the rate of transpiration and to protect plant from grazing.
2. Leaf tendril:
In some weak stems, leaf, leaflet or other part modifies to produce thin, green, wiry, coiled structure called as leaf tendril. It helps in climbing and provides additional support.
3. Leaf hooks:
In plants like Bignonia unguis-cati (Cat’s nail) the terminal three leaflet get modified into three! stiff curve and pointed hooks used to cling over the bark of tree.
4. Phyllode:
When petiole of leaf becomes flat, green and leaf like it is called as phyllode. In Acacia auriculoformis the normal leaf is bipinnately compound and falls off soon. The petiole modifies itself into phyllode. It is a xerophytic adaptation.
Question 32.
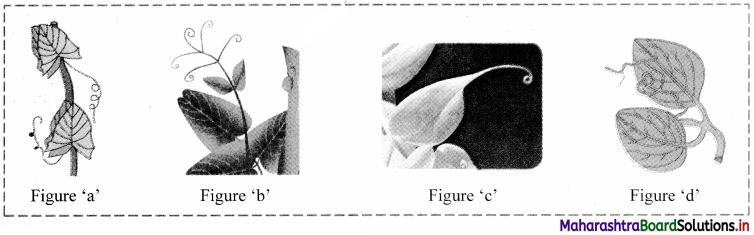
Identify different types of tendril in the figures given below and give one example of each.
Answer:
Figure ‘a’: Whole leaf tendril (e.g. Lathyrus)
Figure ‘b’: Leaflet tendril (e.g. Pisum sativum)
Figure ‘c’: Leaf tip tendril (e.g. Gloriosa)
Figure ‘d’: Stipular tendril (e.g. Smilax)
Question 33.
Define phyllotaxy. Why do leaves show phyllotaxy?
Answer:
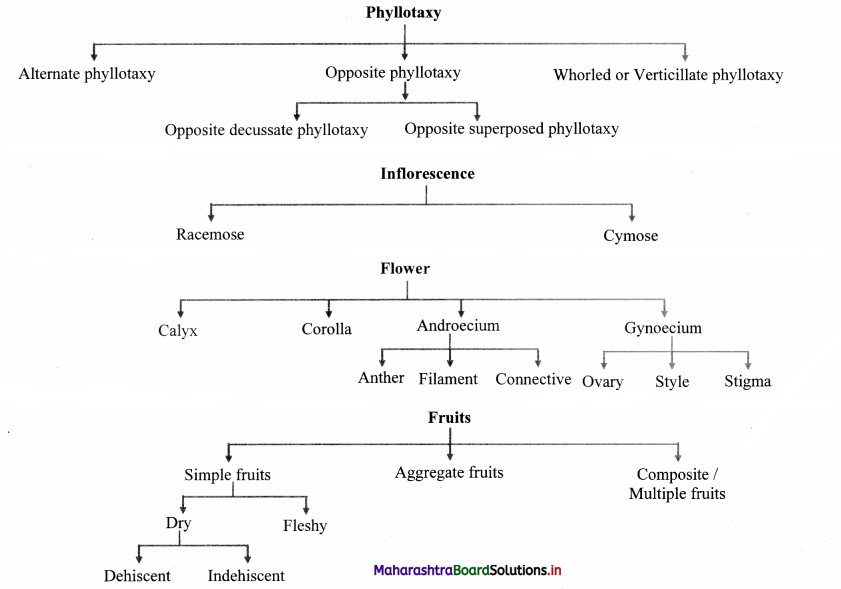
Phyllotaxy:
1. Arrangement of leaves on the stem and branches in a specific manner is known as phyllotaxy.
2. It enables leaf to get sufficient light for photosynthesis.

Question 34.
Which type of phyllotaxy is show n by leaves of Mango, Nerium and Jamun?
Answer:
- Phyllotaxy shown by leaves of Mango is alternate phyllotaxy. In this type, single leaf from each node.
- Phyllotaxy shown by leaves of Nerium is whorled phyllotaxy. In this type, many leaves arise from each node
and form a whorl.
- Phyllotaxy shown by leaves of Jamun is opposite superposed phyllotaxy. In this type, a pair of opposite leaves are arranged one above the other in the same plane.
Question 35.
What are pinnately compound and palmately compound leaves? Give any two examples of each.
Answer:
1. Pinnately compound: Leaflets are present laterally on a common axis called rachis, which represents the midrib of the leaf. e.g. Cassia, Rose, Caesalpinia, Moringa, Coriandrum, etc. [Any two examples]
2. Palmately compound: In this all the leaflets are attached at the tip of petiole.
e.g. Citrus, Zorina, Oxalis, Marsilea, Bombax [Any two examples] [Note: Another example of palmately compound leaf (Bifoliate) is Balanites roxburghii.]
Question 36.
Define inflorescence.
Answer:
A specialised axis or branch over which flowers are produced or borne in definite manner is known inflorescence.
Question 37.
Write significance of inflorescence.
Answer:
Significance of inflorescence:
- Inflorescence makes a flower more conspicuous to attract the insects and birds for pollination.
- It provides more chances for cross pollination.
- An insect can pollinate many flowers in inflorescence in a single visit.
- In an inflorescence, flowers open successively and not simultaneously. This improves chances of pollination as flowering period is longer.
Question 38.
Define flower.
Answer:
Flower is highly modified and condensed shoot meant for sexual reproduction.

Question 39.
Complete the table by giving the meaning of following terminologies related to flower.
Answer:
| 1. Complete flower: Presence of all four floral whorls |
Incomplete flower: Absence of any one of the floral whorls. |
| 2. Pedicellate flower: Flower with pedicel |
Sessile flower: Flower without pedicel |
| 3. Bracteate flower: Flower with bract at the base of pedicel |
Ebracteate flower: Flower without bract |
| 4. Perfect flower: Both androecium and gynoecium are present, also called as dicliny or bisexual flower. |
Imperfect flower: Any one reproductive whorl is present also called as monocliny or unisexual flower. |
| 5. Actinomorphic flower: The flower can be cut in any plane passing through the centre in order to obtain two identical halves. Flowers show radial symmetry, e.g. Sunflower |
Zygomorphic flower: The flower can be cut only along one plane passing through the centre in order to obtain two identical halves. Flowers show bilateral symmetry e.g. Sweet Pea flower. |
| 6. Unisexual flower: It can be either staminate (male)/ pistillate (female) flower |
Neuter flower: When both reproductive whorls are absent, it is said to be neuter flower |
| 7. Monoecious plant: Male and female reproductive flowers are borne on same plant, e.g. Maize |
Dioecious plant: Only one type of unisexual flowers are present on plant, e.g. Ray floret of sunflower |
Question 40.
Mango is called as polygamous plant. Why?
Answer:
Mango produces all types of flowers like staminate, bisexual and neuter, hence it is called as polygamous plant.
Question 41.
What is insertion of floral whorls?
Answer:
The position and arrangement of rest of the floral whorls (calyx, corolla, androecium) with respect to gynoecium on the thalamus is known as insertion of floral whorls. .
Question 42.
With help of neat and labelled diagrams explain the classification of flowers based on the position of ovary on the thalamus.
Answer:
Classification of flowers based on the position of ovary on the thalamus.
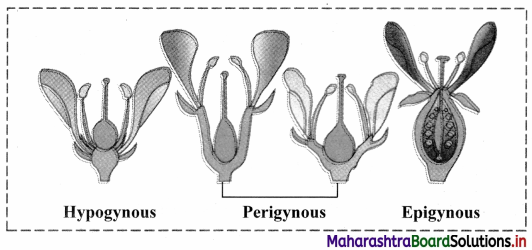
1. Hypogynous flower:
When the convex or conical thalamus is present in flower, ovary occupies the highest position while other floral parts are below ovary. Ovary is said to be superior and flower is called as hypogynous flower, e.g. Brinjal, Mustard, China rose etc. It is denoted as G in floral formula.
2. Perigynous flower:
When cup shaped or saucer shaped thalamus is present in a flower, ovary and other floral parts occupy about same position. Such an ovary is said to be semi- superior or semi-inferior. All floral whorls are at the rim of thalamus. Flower is called as perigynous. e.g. Rose, etc. It is denoted as G- in floral formula.
3. Epigynous flower:
When thalamus completely encloses ovary and may show fusion with wall; the other floral parts occupy superior position and ovary becomes inferior. Such flower is called as epigynous flower, e.g. Ray florets of Sunflower, Guava, Cucumber etc. It is denoted as G in floral formula.
Question 43.
What is thalamus?
Answer:
Thalamus:
1. The upper, swollen, condensed, knob-like part of the pedicel is called thalamus. It is also called receptacle or torus.
2. In a typical flower, the thalamus consists of four compactly arranged nodes and three highly condensed intemodes.
3. From each node of thalamus, whorl of modified leaves is produced.

Question 44.
With the help of a diagram explain the floral parts of a typical flower.
Answer:
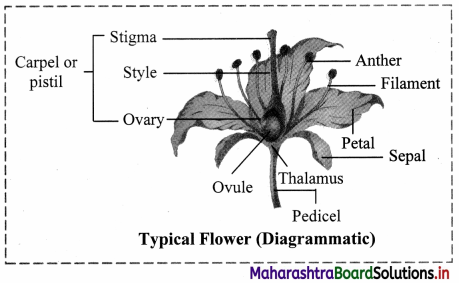
Floral parts of a typical flower:
1. Calyx (K):
a. It is outermost floral whorl and individual members are known as
sepals.
b. Sepals are usually green in colour and perform photosynthesis.
c. If all the sepals are united, the condition is gamosepalous and if they are free, the condition is called as polysepalous.
d. Gamosepalous calyx is found in China rose and polysepalous calyx is found in Brassica.
e. The main function of sepals is to protect inner floral parts in bud condition.
f. Sometimes sepals become brightly coloured (petaloid sepals) and attract insects for pollination,
e.g. Mussaenda etc.
g. Sepals modify into hairy structures called as pappus. Such calyx helps in dispersal of fruit, e.g. Tridex.
2. Corolla (C):
a. It is second floral whorl from outer side and variously coloured.
b. The individual member is called as petal.
c. Petals may be sweet to taste, possess scent, odour, aroma or fragrance etc.
d. The condition in which petals are free is said to be polypetalous (e.g. Rose) and if they are fused it is called as gamopetalous (e.g. Datura).
e. The main function of corolla is to attract different agencies for pollination.
3. Perianth (P):
a. Many times, calyx and corolla remain undifferentiated. Such member is known as tepal.
b. The whorl of tepals is known as Perianth.
c. It protects other floral whorls.
d. If all the tepals are free the condition is called as polyphyllous and if they are fused the condition is called as gamophyllous.
e. Sepaloid perianth shows green tepals, while petaloid perianth shows brightly coloured tepals. e.g. Lily, Amaranthus, Celosia, etc.
f. Petaloid tepal helps in pollination and sepaloid tepals can perform photosynthesis.
4. Androecium (A):
a. It is third floral whorl from outer side.
b. Androecium is male reproductive part of a flower.
c. The individual member is known as stamen.
d. If all the stamens are free the condition is polyandrous and synandrous if they are fused.
e. Typical stamen shows three different parts:
1. Anther: It is terminal in position. Anther produces pollen grains. It is usually dithecous (two anther lobes), tetralocular/tetra sporangiate (four pollen sacs) structure, e.g. Datura.
In some plants it is monothecous (single lobed), bilocular or bisporangiate structure e.g. Hibiscus.
2. Filament: It is a stalk of stamen and bears anther at its tip. It raises anther to a proper height for easy dispersal of pollen grains.
3. Connective: It is in continuation with the filament. It is similar to mid rib and connects two anther lobes together and also with the filament.
5. Gynoecium (G):
a. It is the female reproductive part of a flower and innermost in position.
b. It is also known as pistil.
c. The individual member of gynoecium is known as carpel.
d. The number of carpels may be one to many.
e. If all the carpels are fused the condition is described as syncarpous and if they are free the condition is described as apocarpous.
f. The polycarpellary gynoecium can be bicarpellary (two carpels e.g. Datura), tricarpellary (three carpels e.g. Cucurbita), pentacarpellery (five carpels e.g. Hibiscus) and so on.
g. A typical carpel consists of three parts stigma, style and ovary.
1. Stigma is a terminal part of carpel which receives pollen grains during pollination. It helps in
germination of pollen grain. Stigma shows variation in structure to suit the pollinating agent.
2. Style is narrow thread like structure that connects ovary with stigma.
3. Ovary is basal swollen fertile part of the carpel. Ovules are produced in ovary on a soft fertile tissue called placenta.

Question 45.
Explain the term Epicalyx.
Answer:
Epicalyx:
- Epicalyx is an additional whorl of sepal like structures formed by bracteole which occurs on the outside of calyx.
- These are 5-8 in number.
- It is a characteristic feature of family Malvaceae.
- They are protective in function, e.g. Ladies finger
Question 46.
Match the columns.
| Column I (Tvpe of calyx) |
Column II (Nature of sepals) |
Column III (Example) |
| 1. Caducous |
(a) Sepals remain even after fruit formation |
1. Brinjal, Pea |
| 2. Deciduous |
(b) Sepals fall off as soon as the flower bud opens |
2. Lotus, Mustard |
| 3. Persistent |
(c) Sepals survive till (withering of petals) fruit formation |
3. Argemone (Poppy) |
Answer:
| Column I (Type of calyx) |
Column II (Nature of sepals) |
Column III (Example) |
| 1. Caducous |
(b) Sepals fall off as soon as the flower bud open |
3. Argemone (Poppy) |
| 2. Deciduous |
(c) Sepals survive till (withering of petals) fruit formation |
2. Lotus, Mustard |
| 3. Persistent |
(a) Sepals remain even after fruit formation |
1. Brinjal, Pea |
Question 47.
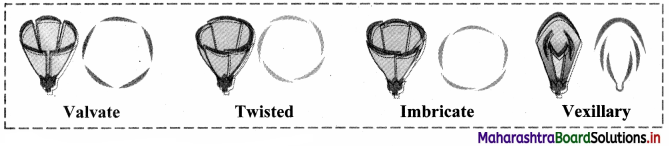
Define aestivation and explain its different types.
Answer:
Aestivation:
1. The mode of arrangement of sepals, petals or tepals in a flower with respect to the members of same whorl is known as aestivation.
2. Different types of aestivation are as follows:
a. Valvate: Margins of sepals or petals remain either in contact or lie close to each other but do not overlap, e.g. Calyx of Datura, Calotropis.
b. Twisted: Margins of each sepal or petal is directed inwards and is overlapped. While the other margin is directed outwards and overlap the margin of adjacent, e.g. Corolla of China rose, Cotton etc.
c. Imbricate: One of the sepals or petals is internal and is overlapped at both the margins. One is external i.e. both of its margin overlap adjacent member. Rest of the sepals / petals have one inner or overlapped margin and outer or overlapping margin, e.g. Cassia, Bauhinia, etc.
d. Vexillary: Corolla is butterfly shaped and consists of five petals. Outermost and largest is known as standard or vexillum, two lateral petals are wings and two smaller fused forming boat shaped structures keel. e.g. Pisum sativum
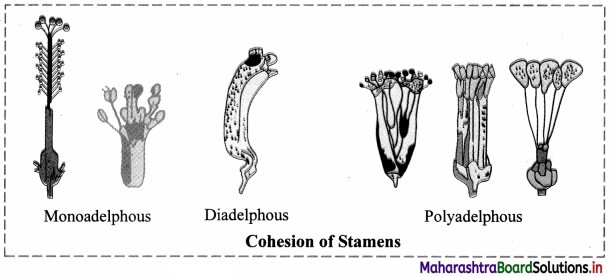
Question 48.
Answer the following:
1. Define the term Adelphy.
2. Give three types of stamens based on adelphy. Draw a diagram of each type.
Answer:
Adelphy:
1. When stamens are united by filaments and anthers are free, the condition is called adelphy.
2. Three types of stamens based on adelphy:
Monadelphous stamens, Diadelphous stamens, Polyadelphous stamens.

Question 49.
Define the following terms and give one example of each:
- Epipetalous stamens
- Epiphyllous stamens
- Syngenesious stamens
- Synandrous stamens
Answer:
- Epipetalous stamens: When the stamens are united to petals they are described as epipetalous stamen. E.g. Datura
- Epiphyllous stamens: When the stamens are united to tepals they are described as epiphyllous stamens. E.g. Lily
- Syngenesious stamens: When anthers are united and filaments are free, such stamens are called as syngenesious stamens. E.g. Sunflower
- Synandrous stamens: When both anthers and filaments are fused, such stamens are called as synandrous stamens. E.g. Cucurbita
Question 50.
Define placentation. Explain its types.
Answer:
1. Placentation: The mode of arrangement of ovules on the placenta within the ovary is called placentation.
2. Types of placentation:
a. Marginal: Ovules are placed on the fused margins of unilocular ovary, e.g. Pea, Bean etc.
b. Axile: Ovules are placed on the central axis of a multilocular ovary, e.g. China rose, Cotton, etc.
c. Parietal: Ovules are placed on the inner wall of unilocular ovary of multicarpellary syncarpus ovary,
e. g. Papaya, Cucumber, etc.
d. Basal: Single ovule is present at the base of unilocular ovary, e.g. Sunflower, Rice, Wheat.
e. Free central: Ovules are borne on central axis which is not attached to ovary wall, e.g.Argemone, Dianthus.
Question 51.
What are parthenocarpic fruits? Give any two examples.
Answer:
Fruits which are produced from ovary without fertilization are called as parthenocarpic fruits, e.g. Cultivated Banana and Grapes.
Question 52.
How true fruit differs from false fruit or pseudofruit? Give one example of each.
Answer:
The fruit which develops only from ovary is called as true fruit or eucarp. e.g. Mango. The fruit which develops from other than ovary floral part is called as false fruit or pseudocarp
Question 53.
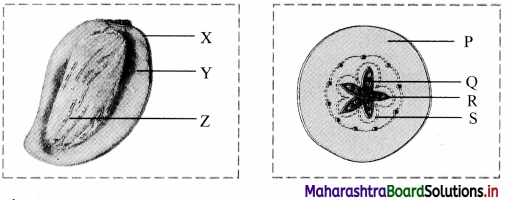
Identify the parts of mango and apple fruit in the given figures.
 Answer:
Answer:
1. parts of mango fruit:
X: Epicarp
Y: Mesocarp
Z: Endocarp
2. Part of apple fruit:
P: Thalamus
Q: Seed
R: Endocarp
S: Mesocarp

Question 54.
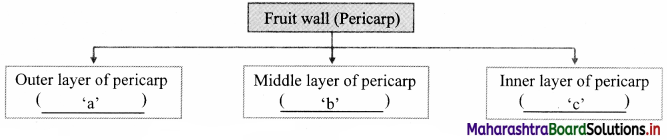
Identify terms a,b,and c in the given chart.
Answer:
a: Epicarp
b: Mesocarp
c: Endocarp
Question 55.
What are simple fruits? Explain its different types.
Answer:
1. Fruits which develop from one ovary of one flower are called as simple fruits.
2. Types of simple fruits on the basis of their pericarp:
a. Dry fruits: These fruits have thin pericarp. It is further divided into two types:
1. Dehiscent dry fruits: Pericarp becomes dry, thin and fruit opens at maturity, e.g. Capsule (Lady’s finger) and legume (Pea)
2. Indehiscent dry fruits: Fruit does not open.
e.g. Achene (Mirabilis), Caryopsis (Maize) and Cypsela (Sunflower)
b. Fleshy fruits: These fruits have thick pericarp. It is further divided into two types based on nature endocarp:
1. Drupe: In these fruits, endocarp is hard and stony, e.g. Mango
2. Berry: In these fruits, endocarp is fleshy and fruit is many seeded, e.g. Tomato
Question 56.
What are aggregate fruits? Enlist the types of aggregate fruits.
Answer:
The fruit which develops from a single flower with many ovaries of polycarpellary, apocarpous gynoecium is known as aggregate fruit or etaerio.
Types of aggregate fruits:
Etario of achenes (e.g. Strawberry), etario of berries (e.g. Custard apple), etario of follicles (e.g. Calotropis)
Question 57.
Write a short note on composite fruits.
Answer:
1. The fruits which develop from many ovaries of many flowers of a complete inflorescence are called composite fruits, (e.g. fig) and from catkin inflorescence are called sorosis (e.g. Pineapple).
2. Fruits which develops from hypanthodium inflorescence are called syconus.
Question 58.
Match the columns with column II.
| Column I |
Column II |
| 1. Composite fruit |
(a) Custard apple |
| 2. Parthenocarpic fruit |
(b) Cultivated Banana |
| 3. Aggregate fruit |
(c) Mango |
|
(d) Pineapple |
Answer:
| Column I |
Column II |
| 1. Composite fruit |
(d) Pineapple |
| 2. Parthenocarpic fruit |
(b) Cultivated Banana |
| 3. Aggregate fruit |
(a) Custard apple |

Question 59.
Describe the structure of a seed.
Answer:
Structure of a seed:
- Seed is a reproductive unit that developed from fertilized mature ovule.
- The seed is made up of seed coat, embryo with or without endosperm and one or two cotyledons.
- Outer most covering of a seed is called seed coat.
- It shows outer layer called as testa and inner layer called as tegmen.
- Hilum is a scar on the seed coat through which seed attach to the fruit.
- Embryo of a seed is enclosed within seed coat.
- Embryonal axis consists of radicle and plumule.
- The part of embryonal axis between cotyledon and plumule is epicotyl, while the part between cotyledons and radicle is hypocotyl.
- The nutritive tissue in a seed called endosperm.
[Note: Dicotyledonous seed is a non-endospermic or exalbuminous, as it lacks endosperm at maturity.]
[Note: Students can scan the given Q.R code to study the structure of dicotyledonous and monocotyledonous seed.]
Question 60.
Describe the family Fabaceae with suitable floral diagram.
Answer:
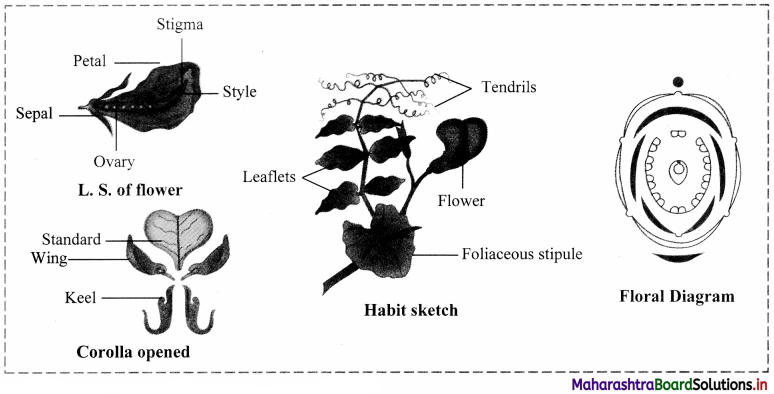
- Example: Pea plant (Pisum sativum)
- Habit: Tree, shrubs, herbs.
- Root: Root with root nodules.
- Stem: Erect or climber.
- Leaves: Alternate phyllotaxy, Pinnately compound leaves.
- Inflorescence: Racemose
- Flower: Zygomorphic, bisexual, complete.
- Calyx: Sepals five, gamosepalous, imbricate aestivation.
- Corolla: Petals five, polypetalous, consisting of a larger posterior petal vexillum, two lateral petals wings and two anterior ones forming a keel, vexillary aestivation.
- Androecium: Stamens ten, diadelphous.
- Gynoecium: Ovary superior, monocarpellary, unilocular with many ovules, marginal placentation. Fruit: Legume.
- Seed: Non-endospermic
Question 61.
Apply your knowledge
Question 1.
Tendrils are seen in the following plants. Identify whether they are stem tendrils or leaf tendrils,
- Vitis
- Smilax
- Lathyrus
- Passiflora
- Cucurbita
- Gloriosa
Answer:
Stem tendrils → Vitis, Passiflora, Cucurbita
Leaf tendrils → Smilax, Lathyrus, Gloriosa

Question 2.
Which type of roots are shown by halophytes growing in Sundarbans in West Bengal?
Answer:
Pneumatophores
Question 3.
Find out from internet the state flower of Sikkim. Write about the type of roots shown by this plant.
Answer:
Dendrobium is the state flower of Sikkim. It shows epiphytic roots.
Epiphytic roots:
- Epiphytic plants like Vanda, Dendrobium grow on branches of trees in dense rain forests and are unable to obtain moisture from soil.
- Such plants produce epiphytic roots which hang in the air.
- The roots are provided with a spongy membranous absorbent covering of the velamen tissue.
- The cells of velamen tissue are hygroscopic and have porous walls, thus they can absorb moisture from air.
- Epiphytic roots can be silvery white or green and are without root cap.
Question 62.
Quick Review:
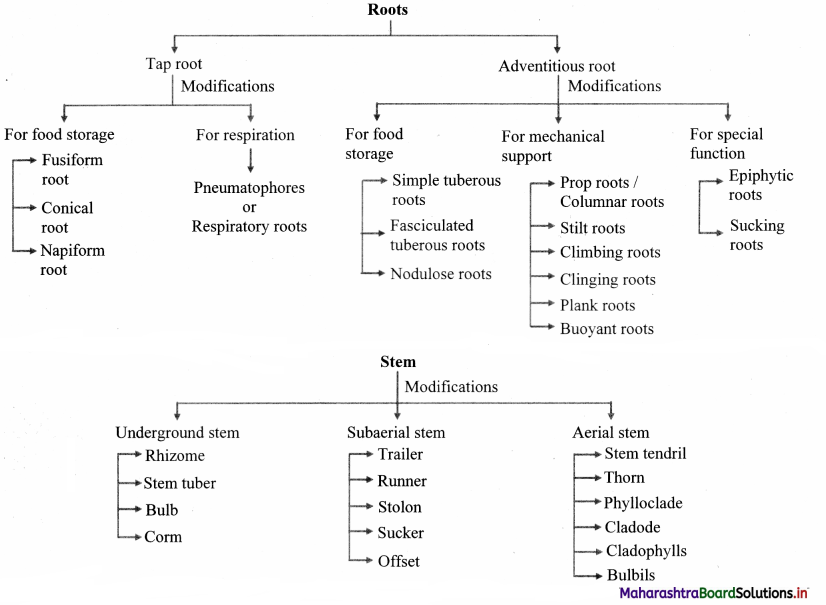

Question 63.
Exercise:
Question 1.
Draw neat and labelled diagram of tap root showing different regions.
Answer:
A typical root possesses the following regions:
1. Root cap:
a. A parenchymatous multicellular structure in the form of cap, present over young growing root apex is known as root cap.
b. Cell of root cap secrete mucilage for lubricating passage of root through the soil.
c. Cells of root cap show presence of starch granules which help in graviperception and geotropic movement of root.
d. Usually single root cap is present in plants. But in plants like Pandanus or screw pine multiple root caps are present.
e. In hydrophytes, root caps are replaced by root pocket e.g. Pistia, Eichhornia etc.
f. Due to presence of root cap the growing apex of root is
2. Meristematic region or region of cell division:
a. The apex of the root is a growing point about 1 mm in length protected by root cap. This region is called as region of cell division or meristematic region.
b. The structure is developed by compactly arranged thin walled actively dividing meristematic cells.
c. These cells bring about longitudinal growth of root.
3. Region of elongation:
a. This region of cells is present just above zone of cell division.
b. The cells are newly formed and show rapid elongation to bring about increase in length of the root.
c. The cells help in absorption of mineral salts.
4. Region of root hair or region of absorption:
a. A region of root hair / absorption/piliferous zone is made up of numerous hair like outgrowths.
b. The epiblema or piliferous layer produces tubular elongated unicellular structures known as root hair.
c. They are in close contact with soil particles and increase surface area for absorption of water.
d. Root hair are short lived or ephimeral and are replaced after every 10 to 15 days.
5. Region of maturation/region of differentiation:
a. It is the uppermost major part of the root.
b. The cells of this region are quite impermeable to water due to thick wall.
c. The cells show differentiation and form different types of tissues.
d. This region helps in fixation of plant and conduction of absorbed substances.
e. Development of lateral roots also takes place from this region.
Question 2.
Write a short note on root cap.
Answer:
Root cap:
a. A parenchymatous multicellular structure in the form of cap, present over young growing root apex is known as root cap.
b. Cell of root cap secrete mucilage for lubricating passage of root through the soil.
c. Cells of root cap show presence of starch granules which help in graviperception and geotropic movement of root.
d. Usually single root cap is present in plants. But in plants like Pandanus or screw pine multiple root caps are present.
e. In hydrophytes, root caps are replaced by root pocket e.g. Pistia, Eichhornia etc.
f. Due to presence of root cap the growing apex of root.
Question 3.
Name the region of a root which is located just above the zone of a cell division.
Answer:
Region of elongation:
a. This region of cells is present just above zone of cell division.
b. The cells are newly formed and show rapid elongation to bring about increase in length of the root.
c. The cells help in absorption of mineral salts.
Question 4.
Name any two plants in which root caps are replaced by root pockets.
Answer:
In hydrophytes, root caps are replaced by root pocket e.g. Pistia, Eichhornia etc.

Question 5.
Write a short note on pneumatophores.
Answer:
1. a. Plants growing in marshy region (halophytes) produce upwardly growing roots called as
pneumatophores or respiratory roots.
b. The main root system of these plants does not get sufficient air for respiration as soil is water logged.
c. Due to this, mineral absorption of plant also gets affected.
d. To overcome this problem underground roots, develop special roots which are negatively geotropic; growing vertically upward.
e. These roots are conical projections present around main trunk of plant.
f. Respiratory roots show presence of lenticels which helps in gaseous exchange.
2. Examples of plants in which respiratory roots are present:
Rhizophora, Avicennia, Sormeratia, Heritiera fames (sundri), etc.
Question 6.
Name the four types of adventitious roots modified for food storage.
Answer:
1. Figure ‘a’ indicates simple tuberous root.
a. Simple tuberous roots become swollen and do not show definite shape.
b. They are produced singly.
c. The roots arise from nodes over the stem and penetrate into the soil, e.g. sweet potato or shakarkand (Ipomoea batatas).
2. Figure ‘b’ indicates fasciculated tuberous roots.
a. A cluster of roots arising from one point which becomes thick and fleshy due to storage of food is known as fasciculated tuberous root.
b. These clusters are seen at the base of the stem, e.g. Dahlia, Asparagus, etc.
3. Figure ‘c’ indicates Moniliform roots.
a. Some adventitious roots get swollen at regular intervals.
b. These gives them the appearance of beads of a necklace. Such roots are called as Moniliform roots, e.g. Spinacia oleracea (Indian Spinach).
4. Figure ‘d’ indicates Nodulose roots.
The cluster of long slender roots become enlarged at the tips forming nodules is known as nodulose roots, e.g. Arrow root (Maranta), Amhaldi or mango ginger (Curcuma amada).
Question 7.
Explain in detail modification of tap roots for food storage.
Answer:
1. Modification of tap root for storage of food:
a. WTien tap root stores food it becomes swollen, fleshy and also develops definite shape.
b. Main or primary root is the main storage organ but sometimes hypocotyl part of embryo axis also joins the main root. Secondary roots remain thin.
c. On the basis of shape, swollen tap roots are classified as Fusiform, Conical and Napiform.
2. Fusiform root:
The fusiform root is swollen in the middle and tapering towards both ends forming spindle shaped structure, e.g. Radish (Raphanus sativus)
3. Conical root:
The conical root is broad at its morphological base and narrows down towards its apex. e.g. Carrot (Daucus car ota)
4. Napiform root:
In napiform root, base of root is highly swollen, almost spherical in shape and abruptly narrows down towards its apex. e.g. Beet (Beta vulgaris)
Question 8.
Write a short note on:
1. Stilt root
2. Climbing roots
Answer:
1. Stilt roots:
a. These roots normally arise from a few lower nodes of a weak stem in some monocots, shrubs and small trees.
b. They show obliquely downward growth penetrating soil and provide mechanical support to the plant.
c. In the members of family Poaceae, the plants like Maize, Jowar, Sugarcane etc. produce stilt root in whorl around the node.
d. These roots provide additional support to the plant body.
e. In Screw pine or Pandanus (Kewada), stilt roots arise only from the lower surface of obliquely growing stem for additional support. These roots show multiple root caps.
2. Climbing roots:
Different climbers with weak stem produce roots at their nodes by means of which they attach themselves to support and thereby raise themselves above the ground.
e.g. Betel leaf or Pan, black pepper or Piper nigrum (Kali Mirch), Pothos or money plant.

Question 9.
What is the function of prop roots in banyan tree?
Answer:
These prop roots show secondary growth, become thick, act like pillars to provide mechanical support to the heavy branches.
Question 10.
Name any two plants which show climbing roots.
Answer:
Climbing roots:
Different climbers with weak stem produce roots at their nodes by means of which they attach themselves to support and thereby raise themselves above the ground.
e.g. Betel leaf or Pan, black pepper or Piper nigrum (Kali Mirch), Pothos or money plant.
Question 11.
Identify the type of modified roots shown in the picture given below.

Answer:
Plank roots/Buttress:
a. These roots often develop at the base of large trees and form plank like extensions around stem.
b. These roots provide additional support, e.g. Silk cotton, Peepal, etc.
Question 12.
Identify the type of root marked as ‘X’ in the given picture and write a short note on it.
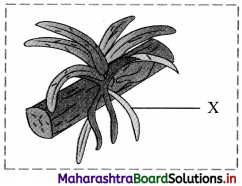
Answer:
Epiphytic roots:
1. Epiphytic plants like Vanda, Dendrobium grow on branches of trees in dense rain forests and are unable to obtain moisture from soil.
2. Such plants produce epiphytic roots which hang in the air.
3. The roots are provided with a spongy membranous absorbent covering of the velamen tissue.
4. The cells of velamen tissue are hygroscopic and have porous walls, thus they can absorb moisture from air.
5. Epiphytic roots can be silvery white or green and are without root cap.
Question 13.
Identify the type of aerial modification of stem in the given figure.

Answer:
Cladophylls:
These are leaf like structures bore in the axil of scale leaf. It has floral bud and scale leaf in the middle i.e. upper half is leaf and lower half is stem. e.g. Ruscus.

Question 14.
Write a short note on corm.
Answer:
- In Colocasia and Amorphophallus corm is present, which is an underground stem modified for storage of food.
- Corm is swollen underground spherical or subspherical vertically growing stem.
- It is condensed structure with circular or ring like nodes.
- It shows presence of axillary buds and scales.
- Adventitious buds are produced which help in vegetative propagation.
- Adventitious roots are produced at lower part of the stem.
Question 15.
Observe the type of sub aerial stem in the given picture of Eichhornia and explain it.
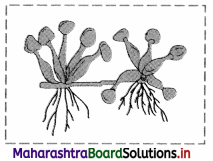
Answer:
Offset:
1. These are one intemode long runners in rosette plants at ground or water level.
2. Offset helps in vegetative propagation.
e.g. Water hyacinth or Jal kumbhi (Eichhornia) and Pistia. [Any one example]
Question 16.
Explain the type of stem modification in Opuntia.
Answer:
Phylloclade:
a. Modification of stem into leaf like photosynthetic organ is known as phylloclade.
b. Being stem it possesses nodes and internodes.
c. It is thick, fleshy and succulent, contains mucilage for retaining water e.g. Opuntia, Casuarina (Cylindrical shaped phylloclade) and Muehlenbeckia (ribbon like phylloclade).
Question 17.
Identify the structure ‘X’ in the given figure and explain it.
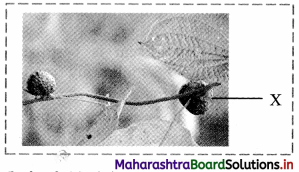
Answer:
Bulbils:
a. In plants like Dioscorea, etc. axillary bud becomes fleshy and rounded due to storage of food called as bulbil.
b. When it falls off it produces new plant and help in vegetative propagation.

Question 18.
Describe the types of stem tendrils present in different plants.
Answer:
1. Stem tendrils:
a. Tendrils are thin, wiry, photosynthetic, leafless coiled structures.
b. They give additional support to developing plant.
c. Tendrils have adhesive glands for fixation.
d. Apical bud in Vitis quadrangularis gets modified into tendril. The further growth is carried out by axillary bud.
e. In Passiflora axillary bud gets modified in tendril.
f. Extra axillary bud is the one which grows outside the axil. This bud in cucurbita gets modified into tendril.
g. Normally floral buds are destined to produce flowers. But in plants like Antigonon they produce tendrils.
Question 19.
What are cladodes?
Answer:
Cladodes:
a. The branches of limited growth i.e. one intemode long and performing photosynthetic function are called as cladodes.
b. True leaves are reduced to spine or scales to reduce rate of transpiration, e.g. Asparagus.
Question 20.
What are tendrils?
Answer:
Tendrils are thin, wiry, photosynthetic, leafless coiled structures.
Question 21.
What is sympodial growth in ginger rhizome and monopodial growth in lotus rhizome?
Answer:
1. Growth of rhizome takes place with lateral buds, such growth is known as sympodial growth, e.g. Ginger (Zingiber officinale), Turmeric (Curcuma domestica), Canna etc.
2. In plants where rhizomes grow obliquely, terminal bud brings about growth of rhizomes. This is known as monopodial growth, e.g. Nymphea, Nelumbo (Lotus), Pteris (Fern) etc.
Question 22.
In xerophytic plant like Opuntia, the stem becomes photosynthetic. Give reason.
Answer:
1. Xerophytes are the plants which grow in regions with scanty or no rainfall like desert.
2. In Xerophytes, leaves get modified into spines or get reduced in size to check the loss of water due to transpiration.
3. As the leaves are modified into spines, the stem becomes green in colour to do the function of photosynthesis.
Question 23.
Define compound leaves. Explain its two types.
Answer:
The leaf with entire lamina is called simple leaf, whereas leaf in which leaf lamina is divided into many leaflets is called as compound leaf.
1. Pinnately compound: Leaflets are present laterally on a common axis called rachis, which represents the midrib of the leaf. e.g. Cassia, Rose, Caesalpinia, Moringa, Coriandrum, etc. [Any two examples]
2. Palmately compound: In this all the leaflets are attached at the tip of petiole.
e.g. Citrus, Zorina, Oxalis, Marsilea, Bombax [Any two examples] [Note: Another example of palmately compound leaf (Bifoliate) is Balanites roxburghii.]

Question 24.
Define leaf venation. What are its two types?
Answer:
Leaf venation:
1. Arrangement of veins and veinlets in leaf lamina is known as venation.
2. There are two types of leaf venation: parallel venation which is found in monocot leaves and reticulate venation which is found in dicot leaves.
Question 25.
Draw neat and labelled diagram of structure of a typical leaf.
Answer:
A typical dicot leaf shows presence of three main parts Leaf base or Hypopodium, Petiole or Mesopodium and Leaf lamina/blade or Epipodium.
1. Leaf base or Hypopodium:
a. The point by which leaf remains attached to the stem is known as leaf base.
b. The nature of leaf base varies in different plants. It may be pulvinus (swollen), sheathing or ligulate, etc.
Question 26.
Which type of venation can be observed in monocot leaf?
Answer:
There are two types of leaf venation: parallel venation which is found in monocot leaves and reticulate venation which is found in dicot leaves.
Question 27.
Enlist the types of pinnately compound leaves and give one example of each.
Answer:
Figure ‘a’: Paripinnately compound leaves (e.g. Cassia)
Figure ‘b’: Imparipinnately compound leaves (e.g. Rosa)
Figure ‘c’: Bipinnately compound leaves (e.g. Caesalpinia)
Figure ‘d’: Tripinnately compound leaves (e.g. Moringa)
Figure ‘e’: Decompound leaves (e.g. Coriandrum)
Question 28.
What is opposite decussate phyllotaxy? Give one example.
Answer:
Figure ‘c’ represents opposite decussate phyllotaxy. In this type of phyllotaxy, a pair of leaf arise from each node and the consecutive pair at right angle to the previous one. e.g. Calotropis.
Question 29.
Explain in detail androecium of an angiospermic flower.
Answer:
Androecium (A):
a. It is third floral whorl from outer side.
b. Androecium is male reproductive part of a flower.
c. The individual member is known as stamen.
d. If all the stamens are free the condition is polyandrous and synandrous if they are fused.
e. Typical stamen shows three different parts:
1. Anther: It is terminal in position. Anther produces pollen grains. It is usually dithecous (two anther lobes), tetralocular/tetra sporangiate (four pollen sacs) structure, e.g. Datura.
In some plants it is monothecous (single lobed), bilocular or bisporangiate structure e.g. Hibiscus.
2. Filament: It is a stalk of stamen and bears anther at its tip. It raises anther to a proper height for easy dispersal of pollen grains.
3. Connective: It is in continuation with the filament. It is similar to mid rib and connects two anther lobes together and also with the filament.
4. Gynoecium (G):
a. It is the female reproductive part of a flower and innermost in position.
b. It is also known as pistil.
c. The individual member of gynoecium is known as carpel.
d. The number of carpels may be one to many.
e. If all the carpels are fused the condition is described as syncarpous and if they are free the condition is described as apocarpous.
f. The polycarpellary gynoecium can be bicarpellary (two carpels e.g. Datura), tricarpellary (three carpels e.g. Cucurbita), pentacarpellery (five carpels e.g. Hibiscus) and so on.
g. A typical carpel consists of three parts stigma, style and ovary.
1. Stigma is a terminal part of carpel which receives pollen grains during pollination. It helps in
germination of pollen grain. Stigma shows variation in structure to suit the pollinating agent.
2. Style is narrow thread like structure that connects ovary with stigma.
3. Ovary is basal swollen fertile part of the carpel. Ovules are produced in ovary on a soft fertile tissue called placenta.
Question 30.
Draw neat and labelled diagram of a typical flower.
Answer:
Floral parts of a typical flower:
1. Calyx (K):
a. It is outermost floral whorl and individual members are known as
sepals.
b. Sepals are usually green in colour and perform photosynthesis.
c. If all the sepals are united, the condition is gamosepalous and if they are free, the condition is called as polysepalous.
d. Gamosepalous calyx is found in China rose and polysepalous calyx is found in Brassica.
e. The main function of sepals is to protect inner floral parts in bud condition.
f. Sometimes sepals become brightly coloured (petaloid sepals) and attract insects for pollination,
e.g. Mussaenda etc.
g. Sepals modify into hairy structures called as pappus. Such calyx helps in dispersal of fruit, e.g. Tridex.
2. Corolla (C):
a. It is second floral whorl from outer side and variously coloured.
b. The individual member is called as petal.
c. Petals may be sweet to taste, possess scent, odour, aroma or fragrance etc.
d. The condition in which petals are free is said to be polypetalous (e.g. Rose) and if they are fused it is called as gamopetalous (e.g. Datura).
e. The main function of corolla is to attract different agencies for pollination.
3. Perianth (P):
a. Many times, calyx and corolla remain undifferentiated. Such member is known as tepal.
b. The whorl of tepals is known as Perianth.
c. It protects other floral whorls.
d. If all the tepals are free the condition is called as polyphyllous and if they are fused the condition is called as gamophyllous.
e. Sepaloid perianth shows green tepals, while petaloid perianth shows brightly coloured tepals. e.g. Lily, Amaranthus, Celosia, etc.
f. Petaloid tepal helps in pollination and sepaloid tepals can perform photosynthesis.
4. Androecium (A):
a. It is third floral whorl from outer side.
b. Androecium is male reproductive part of a flower.
c. The individual member is known as stamen.
d. If all the stamens are free the condition is polyandrous and synandrous if they are fused.
e. Typical stamen shows three different parts:
1. Anther: It is terminal in position. Anther produces pollen grains. It is usually dithecous (two anther lobes), tetralocular/tetra sporangiate (four pollen sacs) structure, e.g. Datura.
In some plants it is monothecous (single lobed), bilocular or bisporangiate structure e.g. Hibiscus.
2. Filament: It is a stalk of stamen and bears anther at its tip. It raises anther to a proper height for easy dispersal of pollen grains.
3. Connective: It is in continuation with the filament. It is similar to mid rib and connects two anther lobes together and also with the filament.
4. Gynoecium (G):
a. It is the female reproductive part of a flower and innermost in position.
b. It is also known as pistil.
c. The individual member of gynoecium is known as carpel.
d. The number of carpels may be one to many.
e. If all the carpels are fused the condition is described as syncarpous and if they are free the condition is described as apocarpous.
f. The polycarpellary gynoecium can be bicarpellary (two carpels e.g. Datura), tricarpellary (three carpels e.g. Cucurbita), pentacarpellery (five carpels e.g. Hibiscus) and so on.
g. A typical carpel consists of three parts stigma, style and ovary.
1. Stigma is a terminal part of carpel which receives pollen grains during pollination. It helps in
germination of pollen grain. Stigma shows variation in structure to suit the pollinating agent.
2. Style is narrow thread like structure that connects ovary with stigma.
3. Ovary is basal swollen fertile part of the carpel. Ovules are produced in ovary on a soft fertile tissue called placenta.

Question 37.
How many carpels are present in gynoecium of Cucurbita and Hibiscus flower?
Answer:
The polycarpellary gynoecium can be bicarpellary (two carpels e.g. Datura), tricarpellary (three carpels e.g. Cucurbita), pentacarpellery (five carpels e.g. Hibiscus) and so on.
Question 38.
Enlist the different types of aestivation and placentation in a flower.
Answer:
Different types of aestivation are as follows:
a. Valvate: Margins of sepals or petals remain either in contact or lie close to each other but do not overlap, e.g. Calyx of Datura, Calotropis.
b. Twisted: Margins of each sepal or petal is directed inwards and is overlapped. While the other margin is directed outwards and overlap the margin of adjacent, e.g. Corolla of China rose, Cotton etc.
c. Imbricate: One of the sepals or petals is internal and is overlapped at both the margins. One is external i.e. both of its margin overlap adjacent member. Rest of the sepals / petals have one inner or overlapped margin and outer or overlapping margin, e.g. Cassia, Bauhinia, etc.
d. Vexillary: Corolla is butterfly shaped and consists of five petals. Outermost and largest is known as standard or vexillum, two lateral petals are wings and two smaller fused forming boat shaped structures keel. e.g. Pisum sativum
2. Types of placentation:
a. Marginal: Ovules are placed on the fused margins of unilocular ovary, e.g. Pea, Bean etc.
b. Axile: Ovules are placed on the central axis of a multilocular ovary, e.g. China rose, Cotton, etc.
c. Parietal: Ovules are placed on the inner wall of unilocular ovary of multicarpellary syncarpus ovary,
e. g. Papaya, Cucumber, etc.
d. Basal: Single ovule is present at the base of unilocular ovary, e.g. Sunflower, Rice, Wheat.
e. Free central: Ovules are borne on central axis which is not attached to ovary wall, e.g.Argemone, Dianthus.
Question 39.
Explain in detail types of fruits.
Answer:
1. Fruits which develop from one ovary of one flower are called as simple fruits.
2. Types of simple fruits on the basis of their pericarp:
a. Dry fruits: These fruits have thin pericarp. It is further divided into two types:
1. Dehiscent dry fruits: Pericarp becomes dry, thin and fruit opens at maturity, e.g. Capsule (Lady’s finger) and legume (Pea)
2. Indehiscent dry fruits: Fruit does not open.
e.g. Achene (Mirabilis), Caryopsis (Maize) and Cypsela (Sunflower)
b. Fleshy fruits: These fruits have thick pericarp. It is further divided into two types based on nature endocarp:
1. Drupe: In these fruits, endocarp is hard and stony, e.g. Mango
2. Berry: In these fruits, endocarp is fleshy and fruit is many seeded, e.g. Tomato
The fruit which develops from a single flower with many ovaries of polycarpellary, apocarpous gynoecium is known as aggregate fruit or etaerio.
Types of aggregate fruits:
Etario of achenes (e.g. Strawberry), etario of berries (e.g. Custard apple), etario of follicles (e.g. Calotropis)
1. The fruits which develop from many ovaries of many flowers of a complete inflorescence are called composite fruits, (e.g. fig) and from catkin inflorescence are called sorosis (e.g. Pineapple).
2. Fruits which develops from hypanthodium inflorescence are called syconus.

Question 40.
Give one example of each type of fruit given below:
1. Etario of berries
2. Berry
3. Etario of follicles
4. Cypsela
5. Sorosis
Answer:
The fruit which develops from a single flower with many ovaries of polycarpellary, apocarpous gynoecium is known as aggregate fruit or etaerio.
Types of aggregate fruits:
Etario of achenes (e.g. Strawberry), etario of berries (e.g. Custard apple), etario of follicles (e.g. Calotropis)
2. Berry: In these fruits, endocarp is fleshy and fruit is many seeded, e.g. Tomato
The fruit which develops from a single flower with many ovaries of polycarpellary, apocarpous gynoecium is known as aggregate fruit or etaerio.
Types of aggregate fruits:
Etario of achenes (e.g. Strawberry), etario of berries (e.g. Custard apple), etario of follicles (e.g. Calotropis)
2. Types of simple fruits on the basis of their pericarp:
a. Dry fruits: These fruits have thin pericarp. It is further divided into two types:
3. Dehiscent dry fruits: Pericarp becomes dry, thin and fruit opens at maturity, e.g. Capsule (Lady’s finger) and legume (Pea)
4. Indehiscent dry fruits: Fruit does not open.
e.g. Achene (Mirabilis), Caryopsis (Maize) and Cypsela (Sunflower)
5. The fruits which develop from many ovaries of many flowers of a complete inflorescence are called composite fruits, (e.g. fig) and from catkin inflorescence are called sorosis (e.g. Pineapple).
Question 41.
Define parthenocarpic fruit and give one example.
Answer:
Fruits which are produced from ovary without fertilization are called as parthenocarpic fruits, e.g. Cultivated Banana and Grapes.
Question 42.
Write a short note on simple fruits.
Answer:
1. Fruits which develop from one ovary of one flower are called as simple fruits.
2. Types of simple fruits on the basis of their pericarp:
a. Dry fruits: These fruits have thin pericarp. It is further divided into two types:
1. Dehiscent dry fruits: Pericarp becomes dry, thin and fruit opens at maturity, e.g. Capsule (Lady’s finger) and legume (Pea)
2. Indehiscent dry fruits: Fruit does not open.
e.g. Achene (Mirabilis), Caryopsis (Maize) and Cypsela (Sunflower)
b. Fleshy fruits: These fruits have thick pericarp. It is further divided into two types based on nature endocarp:
1. Drupe: In these fruits, endocarp is hard and stony, e.g. Mango
2. Berry: In these fruits, endocarp is fleshy and fruit is many seeded, e.g. Tomato
Question 43.
Give examples of any two types of aggregate fruits.
Answer:
The fruit which develops from a single flower with many ovaries of polycarpellary, apocarpous gynoecium is known as aggregate fruit or etaerio.
Types of aggregate fruits:
Etario of achenes (e.g. Strawberry), etario of berries (e.g. Custard apple), etario of follicles (e.g. Calotropis)
Question 44.
Complete the given chart.
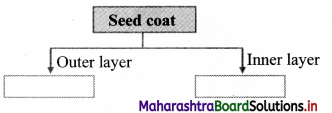
Answer:
It shows outer layer called as testa and inner layer called as tegmen.
Question 45.
Explain the family of pea plant in detail with suitable floral diagram.
Answer:
- Example: Pea plant (Pisum sativum)
- Habit: Tree, shrubs, herbs.
- Root: Root with root nodules.
- Stem: Erect or climber.
- Leaves: Alternate phyllotaxy, Pinnately compound leaves.
- Inflorescence: Racemose
- Flower: Zygomorphic, bisexual, complete.
- Calyx: Sepals five, gamosepalous, imbricate aestivation.
- Corolla: Petals five, polypetalous, consisting of a larger posterior petal vexillum, two lateral petals wings and two anterior ones forming a keel, vexillary aestivation.
- Androecium: Stamens ten, diadelphous.
- Gynoecium: Ovary superior, monocarpellary, unilocular with many ovules, marginal placentation. Fruit: Legume.
- Seed: Non-endospermic
Question 46.
Answer the following.
1. Explain the family Solanaceae with the help of floral diagram.
2. Give examples of economically important plants from family Liliaceae.
Answer:
- Example: Thom apple (Datura stramonium)
- Habit: Mostly herbs, shmbs and rarely small trees.
- Root: Tap root system
- Stem: Herbaceous, woody, erect, branched, hairy, sometimes it may be underground like in potato.
- Leaves: Alternate phyllotaxy, simple, reticulate venation.
- Inflorescence: Solitary, cymose.
- Flower: Actinomorphic, bisexual, complete.
- Calyx: Sepals five, gamosepalous, persistent, valvate aestivation.
- Corolla: Petals five, gamopetalous, valvate aestivation.
- Androecium: Stamens five, free epipetalous (adhesion).
- Gynoecium: Bicarpellary, syncarpous, superior ovary, bilocular, placenta swollen with many ovules, axile placentation.
- Fruits: Berry or capsule.
- Seeds: Many, endospermic.
2. Economically important plant from family Liliaceae:
Family Liliaceae includes many ornamental plants like tulip, Gloriosa, Medicinal plants like Aloe vera. Asparagus and source of colchicine, e.g. Colchicum autumnale.
Question 64.
Multiple Choice Questions:
Question 1.
Root is descending axis of plant body which is
(A) negatively geotropic
(B) hydrophobic
(C) negatively phototropic
(D) green and with intemodes
Answer:
(C) negatively phototropic

Question 2.
The root system grow out from the
(A) plumule of the embryo
(B) radicle of the embryo
(C) embryo of the seed
(D) all of these
Answer:
(B) radicle of the embryo
Question 3.
Adventitious roots develop from
(A) radicle
(B) any part of the plant body except the radicle
(C) flower
(D) embryo
Answer:
(B) any part of the plant body except the radicle
Question 4.
A fibrous root system is best adapted to perform which of the following functions?
(A) Storage of food
(B) Transport of water and organic food
(C) Absorption of water and minerals from the soil
(D) Anchorage of the plant into the soil
Answer:
(D) Anchorage of the plant into the soil
Question 5.
When the root is swollen in the middle and tapers at both ends, it will be called as root.
(A) tuberous
(B) fusiform
(C) conical
(D) napiform
Answer:
(B) fusiform
Question 6.
Pneumatophores are helpful in
(A) protein synthesis
(B) respiration
(C) transpiration
(D) carbohydrate metabolism
Answer:
(B) respiration
Question 7.
Sweet potato is a modification of
(A) leaf
(B) adventitious root
(C) tap root
(D) stem
Answer:
(B) adventitious root
Question 8.
Stilt roots are roots.
(A) primary
(B) adventitious
(C) secondary
(D) tap
Answer:
(B) adventitious
Question 9.
A spongy tissue called velamen is present in
(A) breathing roots
(B) parasitic roots
(C) tuberous roots
(D) epiphytic roots
Answer:
(D) epiphytic roots
Question 10.
Which of the following is NOT a type of adventitious root modified for storage of food?
(A) Fasciculated tuberous roots
(B) Simple tuberous root
(C) Napiform root
(D) Moniliform roots
Answer:
(C) Napiform root
Question 11.
In which of the following plants, root cap is replaced by root pocket?
(A) Pistia
(B) Pandanus
(C) Screw pine
(D) Hibiscus
Answer:
(A) Pistia
Question 12.
Which of the following is an example of stem tuber?
(A) Helianthus tuberosus
(B) Zingiber officinale
(C) Cynodon
(D) Chrysanthemum
Answer:
(A) Helianthus tuberosus

Question 13.
In stem tuber, the number of nodes and eyes is more towards
(A) rose end
(B) basal end
(C) heel
(D) both (B) and (C)
Answer:
(A) rose end
Question 14.
A rhizome differs from corm in its
(A) thickness
(B) basic organization
(C) direction of growth
(D) nature of leaves
Answer:
(C) direction of growth
Question 15.
The reduced stem of onion produces.
(A) Adventitious roots
(B) Prop roots
(C) Fusiform roots
(D) Fasciculated roots
Answer:
(A) Adventitious roots
Question 16.
Corm is ____________
(A) a horizontal underground stem.
(B) an underground root.
(C) an underground vertical stem.
(D) an aerial stem modification.
Answer:
(C) an underground vertical stem.
Question 17.
The stem modified to perform the function of leaf and with many internodes is called
(A) phylloclade
(B) cladode
(C) offset
(D) phyllode
Answer:
(A) phylloclade
Question 18.
_______ is a non-green runner like branch of stem, which develops from underground base of roots and found in Chrysanthemum.
(A) Corn
(B) Sucker
(C) Offset
(D) Tendril
Answer:
(B) Sucker
Question 19.
Ribbon shaped phylloclades are found in
(A) Ruscus
(B) Duranta
(C) Muehlenbeckia
(D) Bougainvillea
Answer:
(C) Muehlenbeckia
Question 20.
Axillary buds in Dioscorea becomes fleshy and rounded due to storage of food called as
(A) Stiphles
(B) Bulbils
(C) Offset
(D) Cladophylls
Answer:
(B) Bulbils

Question 21.
The leaves without petiole are called
(A) sessile
(B) petiolate
(C) rachis
(D) lamina
Answer:
(A) sessile
Question 22.
The type of leaves observed is mango plant is
(A) Compound leaves
(B) Bipinnately compound leaves
(C) Simple leaves with reticulate venation
(D) Simple leaves with parallel venation
Answer:
(C) Simple leaves with reticulate venation
Question 23.
In _________ , the terminal three leaflet get modified into three stiff leaf hooks.
(A) Lathyrus
(B) Pisum sativum
(C) Smilax
(D) Bignonia unguisi-cati
Answer:
(D) Bignonia unguisi-cati
Question 24.
Leaf apex is modified into tendril in
(A) Gloriosa
(B) Pea
(C) Smilax
(D) Lathyrus
Answer:
(A) Gloriosa
Question 25.
Modification of petiole into leaf-like structure is called ________ .
(A) cladode
(B) phylloclade
(C) phyllode
(D) pistillode
Answer:
(C) phyllode
Question 26.
The mode of arrangement of leaves on the stem and the branch is known as _______ .
(A) vernalization
(B) vernation
(C) venation
(D) phyllotaxy
Answer:
(D) phyllotaxy
Question 27.
Bipinnately compound leaves can be observed in
(A) Citrus
(B) Hibiscus
(C) Caesalpinia
(D) Coriandrum
Answer:
(C) Caesalpinia
Question 28.
The axis of the inflorescence is known as
(A) Thalamus
(B) Peduncle
(C) Pedicel
(D) Petiole
Answer:
(B) Peduncle
Question 29.
In racemose inflorescence
(A) growth of peduncle is infinite
(B) apical bud always terminates into flower
(C) growth of peduncle is finite.
(D) order of opening of flower is centrifugal.
Answer:
(A) growth of peduncle is infinite

Question 30.
In a typical flower thalamus consists of compactly arranged nodes and intemodes.
(A) three, two
(B) four, three
(C) three, four
(D) two, three
Answer:
(B) four, three
Question 31.
When the flower is epigynous, the ovary is said to be
(A) inferior
(B) superior
(C) semi-inferior
(D) semi-superior
Answer:
(A) inferior
Question 32.
When the gynoecium is present at the topmost position of the thalamus, the flower is known as
(A) inferior
(B) epigynous
(C) perigynous
(D) hypogynous
Answer:
(D) hypogynous
Question 33.
When all sepals are united, the condition is called as
(A) polysepalous
(B) gamosepalous
(C) polypetalous
(D) gamopetalous
Answer:
(B) gamosepalous
Question 34.
When sepals fall just after opening of the flower, they are termed as
(A) persistent
(B) caducous
(C) remnant
(D) deciduous
Answer:
(B) caducous
Question 35.
Fusion between members of a similar whorl is known as
(A) succession
(B) adhesion
(C) cohesion
(D) inflorescence
Answer:
(C) cohesion

Question 36.
Complete the analogy. Seed:ovule::Fruit:
(A) pericarp
(B) ovary
(C) embryo
(D) cotyledons
Answer:
(B) ovary
Question 37.
Which one of the following is not a fruit?
(A) Tomato
(B) Cucumber
(C) Pumpkin
(D) Potato
Answer:
(D) Potato
Question 38.
Pineapple is an example of _________ .
(A) simple dry fruit
(B) composite fruit
(C) aggregate fruit
(D) simple-fleshy fruit
Answer:
(B) composite fruit
Question 39.
Outer seed coat is called _______ .
(A) testa
(B) tegmen
(C) raphe
(D) micropyle
Answer:
(A) testa
Question 40.
Vexillum wings and keel corolla are found in family
(A) Solanaceae
(B) Fabaceae
(C) Liliaceae
(D) Malvaceae
Answer:
(B) Fabaceae
Question 65.
Competitive Corner:
Question 1.
Match the placental types (Column-I) with their examples (Column-II).
| Column-I |
Column-II |
| 1. Basal |
(p) Mustard |
| 2. Axile |
(q) China rose |
| 3. Parietal |
(r) Dianthus |
| 4. Free central |
(s) Sunflower |
Choose the correct answer from the following option: [NEET (ODISHA) – 2019J
(A) i – r, ii – s, iii – p, iv – q
(B) i – q, ii – r, iii – s, iv – p
(C) i – p, ii – q, iii – r, iv – s
(D) i – s, ii – q, iii – p, iv – r
Answer:
(D) i – s, ii – q, iii – p, iv – r
Question 2.
Placentation in which ovules develop on the inner wall of the ovary or in peripheral part is:
(A) Parietal
(B) Free central
(C) Basal
(D) Axile
Answer:
(A) Parietal
Question 3.
Pneumatophores occur in
(A) Carnivorous plants
(B) Free-floating hydrophytes
(C) Halophytes
(D) Submerged hydrophytes
Answer:
(C) Halophytes
Question 4.
Sweet potato is a modified
(A) Tap root
(B) Adventitious root
(C) Stem
(D) Rhizome
Answer:
(B) Adventitious root

Question 5.
Root hairs develop from the region of
(A) Maturation
(B) Elongation
(C) Root cap
(D) Meristematic activity
Hint: Epidermal cells from the region of maturation form very fine and delicate, thread like structures called root hairs. These root hairs absorb water and minerals from the soil.
Answer:
(A) Maturation
Question 6.
Plants which produce characteristic pneumatophores and show vivipary belong to
(A) Mesophytes
(B) Halophytes
(C) Psammophytes
(D) Elydrophytes
Hint: Plants growing in swampy areas, marshy places and salt lakes are called halophytes. Many halophytes develop respiratory roots or pneumatophores. Pneumatophores are negatively geotropic and are provided with pores called lenticels. Since they grow in oxygen-deficient soil, their seeds germinate inside the fruit, when it is still attached with the parents, exhibiting vivipary.
Answer:
(B) Halophytes
Question 7.
In Bougainvillea thorns are the modifications of
(A) Stipules
(B) Adventitious root
(C) Stem
(D) Leaf
Hint: Thom is a hard, pointed, woody and usually straight structure produced by modification of axillary bud. It provides protection against browsing animals. In Bougainvillea, thorns are modified stems.
Answer:
(C) Stem

Question 8.
Coconut fruit is a
(A) Drupe
(B) Berry
(C) Nut
(D) Capsule
Hint: Dmpe is the simple, fleshy fruit developing from the monocarpellary superior ovary. It is generally one seeded. Coconut fruit is a dmpe with fibrous mesocarp and hard endocarp
Answer:
(A) Drupe
![]()
![]()
![]()














 Answer:
Answer:






 Answer:
Answer: