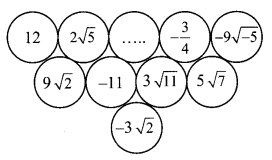
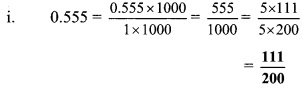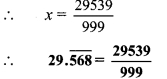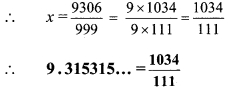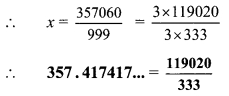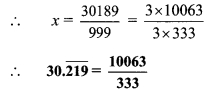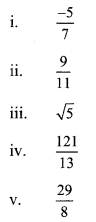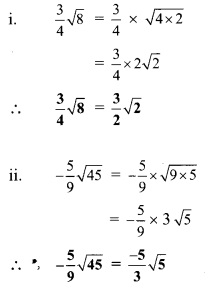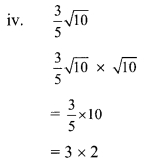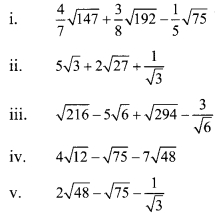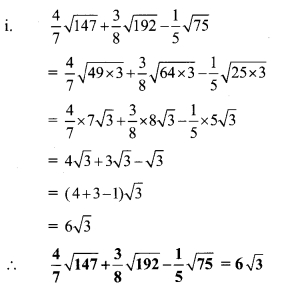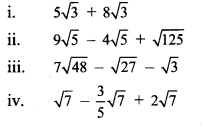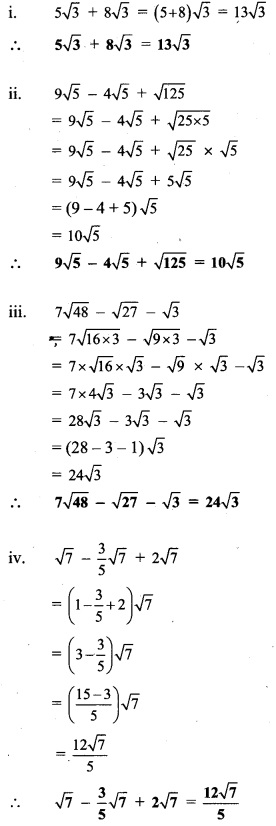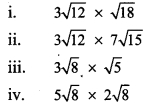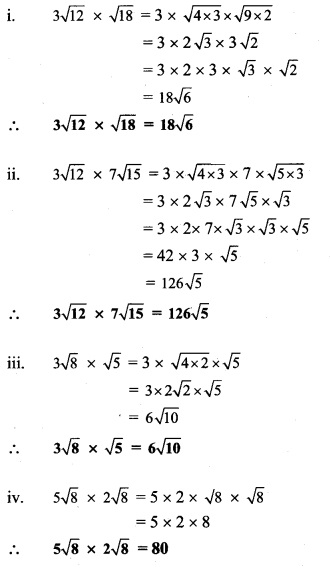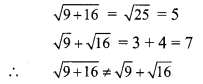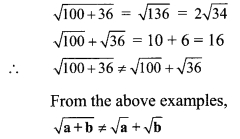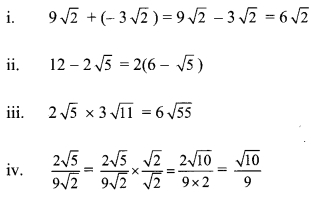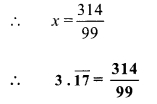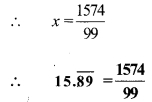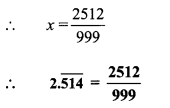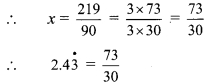Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 9 Maths Solutions covers the Practice Set 3.1 Algebra 9th Class Maths Part 1 Answers Solutions Chapter 3 Polynomials.
9th Standard Maths 1 Practice Set 3.1 Chapter 3 Polynomials Textbook Answers Maharashtra Board
Class 9 Maths Part 1 Practice Set 3.1 Chapter 3 Polynomials Questions With Answers Maharashtra Board
Question 1.
State whether the given algebraic expressions are polynomials? Justify.
i. y + \(\frac { 1 }{ y }\)
ii. 2 – 5√x
iii. x2 + 7x + 9
iv. 2m-2 + 7m – 5
v. 10
Answer:
i. No, because power of v in the term 5√x is -1 (negative number).
ii. No, because the power of x in the term 5√x is
i. e. 0.5 (decimal number).
iii. Yes. All the coefficients are real numbers. Also, the power of each term is a whole number.
iv. No, because the power of m in the term 2m-2 is -2 (negative number).
v. Yes, because 10 is a constant polynomial.
Question 2.
Write the coefficient of m3 in each of the given polynomial.
i. m3
ii. \(\sqrt [ -3 ]{ 2 }\) + m – √3m3
iii. \(\sqrt [ -2 ]{ 3 }\)m3 + 5m2 – 7m -1
Answer:
i. 1
ii. -√3
iii. – \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\)
Question 3.
Write the polynomial in x using the given information. [1 Mark each]
i. Monomial with degree 7
ii. Binomial with degree 35
iii. Trinomial with degree 8
Answer:
i. 5x7
ii. x35 – 1
iii. 3x8 + 2x6 + x5
Question 4.
Write the degree of the given polynomials.
i. √5
ii. x°
iii. x2
iv. √2m10 – 7
v. 2p – √7
vi. 7y – y3 + y5
vii. xyz +xy-z
viii. m3n7 – 3m5n + mn
Answer:
i. √5 = √5 x°
∴ Degree of the polynomial = 0
ii. x°
∴Degree of the polynomial = 0
iii. x2
∴Degree of the polynomial = 2
iv. √2m10 – 7
Here, the highest power of m is 10.
∴Degree of the polynomial = 10
v. 2p – √7
Here, the highest power of p is 1.
∴ Degree of the polynomial = 1
vi. 7y – y3 + y5
Here, the highest power of y is 5.
∴Degree of the polynomial = 5
vii. xyz + xy – z
Here, the sum of the powers of x, y and z in the term xyz is 1 + 1 + 1= 3,
which is the highest sum of powers in the given polynomial.
∴Degree of the polynomial = 3
viii. m3n7 – 3m5n + mn
Here, the sum of the powers of m and n in the term m3n7 is 3 + 7 = 10,
which is the highest sum of powers in the given polynomial.
∴ Degree of the polynomial = 10
Question 5.
Classify the following polynomials as linear, quadratic and cubic polynomial. [2 Marks]
i. 2x2 + 3x +1
ii. 5p
iii. √2 – \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)
iv. m3 + 7m2 + \(\sqrt [ 5 ]{ 2 }\)m – √7
v. a2
vi. 3r3
Answer:
Linear polynomials: ii, iii
Quadratic polynomials: i, v
Cubic polynomials: iv, vi
Question 6.
Write the following polynomials in standard form.
i. m3 + 3 + 5m
ii. – 7y + y5 + 3y3 – \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)+ 2y4 – y2
Answer:
i. m3 + 5m + 3
ii. y5 + 2y4 + 3y3 – y2 – 7y – \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)
Question 7.
Write the following polynomials in coefficient form.
i. x3 – 2
ii. 5y
iii. 2m4 – 3m2 + 7
iv. – \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\)
Answer:
i. x3 – 2 = x3 + 0x2 + 0x – 2
∴ Coefficient form of the given polynomial = (1, 0, 0, -2)
ii. 5y = 5y + 0
∴Coefficient form of the given polynomial = (5,0)
iii. 2m4 – 3m2 + 7
= 2m4 + Om3 – 3m2 + 0m + 7
∴ Coefficient form of the given polynomial = (2, 0, -3, 0, 7)
iv. – \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\)
∴Coefficient form of the given polynomial = (- \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\))
Question 8.
Write the polynomials in index form.
i. (1, 2, 3)
ii. (5, 0, 0, 0 ,-1)
iii. (-2, 2, -2, 2)
Answer:
i. Number of coefficients = 3
∴ Degree = 3 – 1 = 2
∴ Taking x as variable, the index form is x2 + 2x + 3
ii. Number of coefficients = 5
∴ Degree = 5 – 1=4
∴ Taking x as variable, the index form is 5x4 + 0x3 + 0x2 + 0x – 1
iii. Number of coefficients = 4
∴Degree = 4 – 1 = 3
∴Taking x as variable, the index form is -2x3 + 2x2 – 2x + 2
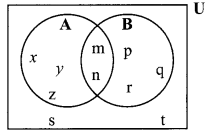
Question 9.
Write the appropriate polynomials in the boxes.
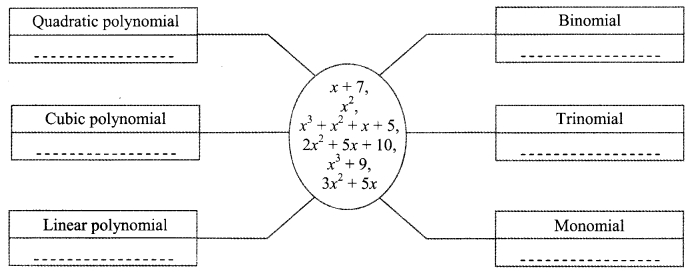
Answer:
i. Quadratic polynomial: x2; 2x2 + 5x + 10; 3x2 + 5x
ii. Cubic polynomial: x3 + x2 + x + 5; x3 + 9
iii. Linear polynomial: x + 7
iv. Binomial: x + 7; x3 + 9; 3x2 + 5x
v. Trinomial: 2x2 + 5x + 10
vi. Monomial: x2
Question 1.
Write an example of a monomial, a binomial and a trinomial having variable x and degree 5. ( Textbook pg. no. 3)
Answer:
Monomial: x5
Binomial: x5 + x
Trinomial: 2x5 – x2 + 5
Question 2.
Give example of a binomial in two variables having degree 5. (Textbook pg. no. 38)
Answer:
x3y2 + xy
Class 9 Maths Digest