Class 9 English Chapter 1.4 Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 9 English Solutions My English Coursebook Chapter 1.4 The Story of Tea Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
The Story of Tea Poem 9th Std Question Answer
My English Coursebook Std 9 Digest Chapter 1.4 The Story of Tea Textbook Questions and Answers
Warming up!
Chit-chat:
- Can you make tea?
- How do you make tea?
- What brand do you like?
- At home, who makes tea/coffee for everybody?
- Have you seen a tea-plantation?
- What was it like?
![]()
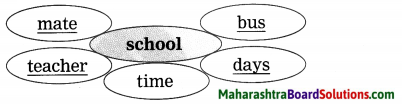
Write the names of as many beverages as you can within two minutes. What do the following beverages remind you of? Draw word webs to show your associations.
Question 1.
Write the names of as many beverages as you can within two minutes. What do the following beverages remind you of? Draw word webs to show your associations.
Answer:
English Workshop:
1. List all the names of Geographical places mentioned in the passage.
Question 1.
List all the names of Geographical places mentioned in the passage.
Answer:
Assam, China, Cambod, Darjiling, Nilgiris.
![]()
2. Make smaller words using the letters in the given words. (At least 5 words each)
Question 1.
Make smaller words using the letters in the given words. (At least 5 words each)
- actually
- refreshing
- immediately
- investigations
- meditation
- enjoyable
- loneliness
- friendship
Answer:
- actually – act, all, tall, call, ally.
- refreshing – fresh, refresh, ring, sing, fin.
- immediately – dial, ate, die, mat, date.
- investigation – invest, nation, station, nest, vest.
- meditation – tan, edition, meat, edit.
- enjoyable – enjoy, able, joy, enables, noble.
- loneliness – lone, one, line, nine, less.
- friendship – friend, ship, end, fried, find
- powdered – pod, were, red, owe, power
- hospitality – hospital, spit, pity, host, hit.
![]()
3. From the passage, copy correctly any three sentences that begin with ‘How’.
Question 1.
From the passage, copy correctly any three sentences that begin with ‘How’.
4. Find the meanings of the following from a good dictionary :
Question 1.
Find the meanings of the following from a good dictionary :
- infusion
- restorative
- inscriptions
- radicals
- connoisseurs
5. List the words related to
(a) agriculture
(b) chemistry from this passage.
Question 1.
List the words related to
(a) agriculture
(b) chemistry from this passage.
![]()
6. Complete the following sentences with the help of the passage:
Question 1.
Complete the following sentences with the help of the passage:
(a) Camellia sinensis is an evergreen plant that grows in
(b) The teas we buy are usually classified according to
(c) In many countries around the world, tea drinking is an
(d) Our body produces chemicals called
Answer:
(a) Camellia sinensis is an evergreen plant that grows in tropical and sub-tropical climates.
(b) The teas we buy are usually classified according to the size of their leaves.
(c) In many countries around the world, tea drinking is an
(d) Our body produces chemicals called
7. Prepare a flow chart to show the growth and journey of tea from the plantation to our homes. Use information from the lesson.
Question 1.
Prepare a flow chart to show the growth and journey of tea from the plantation to our homes. Use information from the lesson.
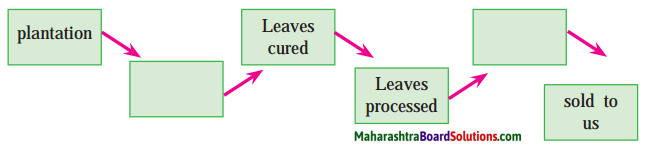
Answer:
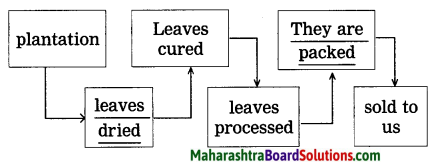
Language Study:
8. From the passage, find all the words or pairs of words that begin with ‘tea’.
Examples: teapot, tea plants.
When two words come together to form a new word, the new word is called a compound word. What words do you see in the following compounds – evergreen, blood pressure, every day?
Note that some compound words are written as one word (teapot), some with a hyphen between them (tea-making) and some as two separate words (tea club).
![]()
9. Sometimes the form of a verb in a sentence names the action but does not change according to tense, number or person. Such a form is known as a non-finite form or an ui1lnitii. An infinitive is used with or without ‘to’.
Examples: How did people first begin to drink tea? Can you name the beverage?
Underline the infinitive in the following sentences.
It was funny to read words that stood still.
Can I read the book?
They could help one another with the homework and talk about it.
To be or not to be – that is the question.
My English Coursebook 9th Class Solutions Chapter 1.4 The Story of Tea Additional Important Questions and Answers
Read the following passage and do the activities:
Simple Factual Activity:
Question 1.
Complete the sentences using the information given in the passage:
(Answers are directly given.)
Answer:
- The most popular beverage in the world is tea.
- Tea plants require at least 100-125 cm of rainfall a year.
- World’s famous tea estates are located on hill slopes.
Question 2.
Complete the following sentences using the information given in the passage :
(Answers are directly given.)
Answer:
- Most people agree that tea is a refreshing drink.
- Emperor Shennong was called the father of Chinese agriculture and medicine.
- Bodhidharma found that chewing tea leaves acted as a stimulant.
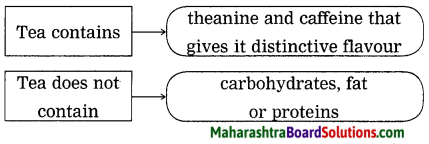
- Tea got its distinctive flavour by its theanine as well as caffeine.
![]()
Question 3.
Write whether the following statements are True or False :
(Answers are directly given.)
Answer:
- The first Indian tea was sent to England for public sale in 1823. – False
- Tea became a fashionable and popular drink in Europe. – True
- Our body produces chemicals called free radicals. – True
- The word ‘chai’ is now sometimes used in English to refer to China tea. – False
Question 4.
Complete the following sentences with the help of the information given in the passage :
(Answers are directly given.)
Answer:
- In many countries around the world, tea drinking is an important social occasion.
- Tea ceremonies give people the time to relax and enjoy the taste and smell of tea.
- For many people tea is a popular drink to have with friends.
- Koreans still have tea ceremonies on the occasions of special birthdays and anniversaries.
![]()
Question 5.
Choose the correct alternatives and complete the following sentences :
(Answers are directly given.)
Question a.
In Russia, tea is made and served in ………….. .
(a) cups
(b) pots
(c) samovars
Answer:
(c) samovars
Question b.
In Japan, tea is made using ……………… .
(a) a bamboo whisk
(b) sugar
(c) green tea
Answer:
(a) a bamboo whisk
![]()
Question c.
In India, tea is served as a token of ……………….. .
(a) love
(b) hospitality
(c) affection
Answer:
(b) hospitality
Question d.
In China, tea is made in small ………………. teapots.
(a) clay
(b) metal
(c) glass
Answer:
(a) clay
Complex Factual Activities:
Question 1.
Which geographical conditions (features) are required for growing tea plants?
Answer:
Tea plants require tropical and sub-tropical climates. They need at least 100-125 cm of rainfall and acidic soils. They grow well on hill slopes at elevations of up to 1500 metres where they acquire a richer flavour at that height.
![]()
Question 2.
Why are tea plants pruned?
Answer:
The tea plants are pruned and kept at height of about three feet to make it possible for them to ; pluck the tea leaves easily.
Question 3.
How is tea the beverage made?
Answer:
Tea is made by brewing, that is by infusing tea leaves in boiling water.
![]()
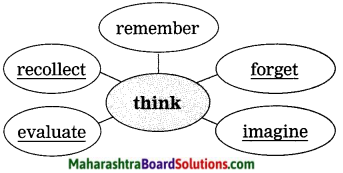
Question 4.
Complete the web:
(Answer are directly given.)
Answer:
Question 5.
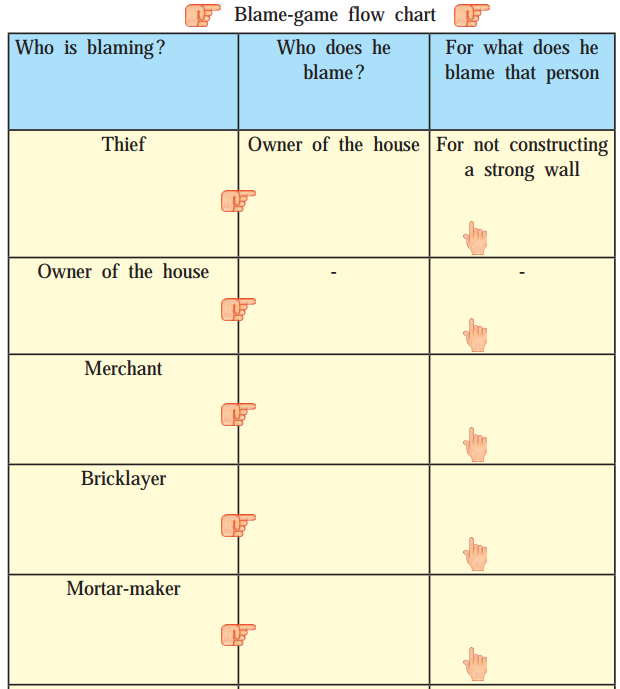
Who was Emperor Shennong? Why did he carry out further investigations about tea?
Answer:
Emperor Shennong was the father of Chinese agriculture and medicine. On drinking the boiled water of tea leaves, he was amazed by the rich flavour and the refreshing quality of the infusion he was so excited that he decided to carry out further investigation.
Question 6.
Arrange the following sentences in proper order of their occurrence :
1. Japanese priests studying under Buddhist teachers in China carried tea seeds and leaves to Japan.
2. Turkish traders began to bargain for tea on the border of Mongolia.
3. Bodhidharma, a Buddhist monk introduced tea among his disciples in China.
4. The Chinese Emperor Hui Tsung failed to notice that Mongolia had actually taken over his empire.
Answer:
3. Bodhidharma, a Buddhist monk introduced tea among his disciples in China.
1. Japanese priests studying under Buddhist teachers in China carried tea seeds and leaves to Japan.
2. Turkish traders began to bargain for tea on border of Mongolia.
4. The Chinese Emperor Hui Tsung failed to notice that Mongolia had actually taken over his empire.
![]()
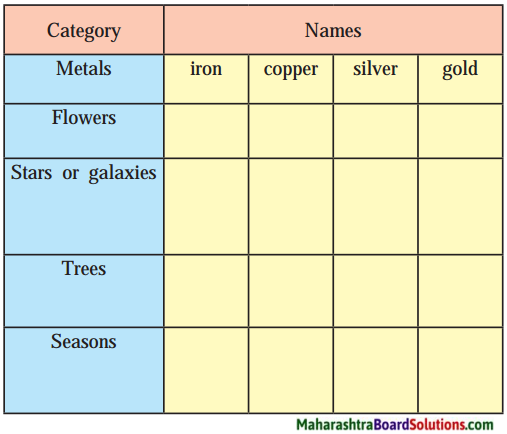
Question 7.
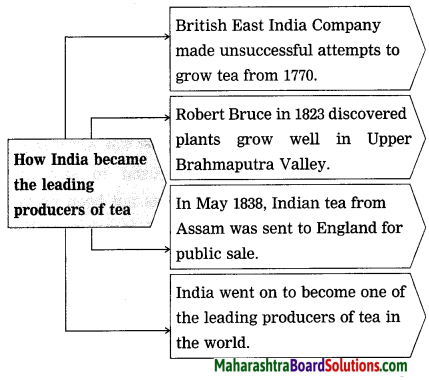
Complete the web :
(Answers are directly given.)
Answer:
Question 8.
Guess the origin of the Marathi word ‘Chaim’:
Answer:
Instead of earlier word ‘t’u’ Chinese started using ‘ch’a’ to describe tea. The word ‘Ch’a’ was close to the Hindi word ‘chai’ and was used all over India. Then slightly changed word ‘chaha’ was used in Marathi. It was the combination of the words ‘ch’a’ and ‘chai’ in Marathi version.
![]()
Question 9.
Complete the following choosing information from the passage :
Answer:

Question 10.
How do Indians like to have their tea?
Answer:
Most Indians like to have their tea hot with a good deal of milk and sugar in it. In the rainy season, tea is brewed with ginger to give it additional medicinal properties. Some others add spices like cardamom, cloves or mace to add to its taste and flavour. They have their morning and evening tea after spicy snacks. Some connoisseurs enjoy delicately flavoured jasmine tea, green tea, lemon tea and even iced tea.
![]()
Activities based on vocabulary:
Question 1.
Match the words in Column ‘A’ with their meaning in Column ‘B’:
| ‘A’ | ‘B’ |
| 1. aromatic | (a) any liquid for drinking |
| 2. brew | (b) the hot regions of the world |
| 3. beverage | (c) fragrant |
| 4. tropical | (d) to make tea etc. by boiling |
Answer:
| ‘A’ | ‘B’ |
| 1. aromatic | (c) fragrant |
| 2. brew | (d) to make tea etc. by boiling |
| 3. beverage | (a) any liquid for drinking |
| 4. tropical | (b) the hot regions of the world |
Question 3.
List the qualities of the special type of tea.
Answer:
unique in taste, aroma, strength, flavour.
![]()
Question 4.
Match the words in Column ‘A’ with their meaning in column ‘B’:
| ‘A’ | ‘B’ |
| 1. investigation | (a) a scientific examination for finding the truth. |
| 2. stimulant | (b) a drink made by leaving shrubs (leaves), etc. in boiling water. |
| 3. infusion | (c) making you strong and healthy again. |
| 4. restorative | (d) a substance (tea) that helps you to stay awake. |
Answer:
| ‘A’ | ‘B’ |
| 1. investigation | (a) a scientific examination for finding the truth. |
| 2. stimulant | (d) a substance (tea) that helps you to stay awake. |
| 3. infusion | (b) a drink made by leaving shrubs (leaves), etc. in boiling water. |
| 4. restorative | (c) making you strong and healthy again. |
![]()
Question 5.
Match the verbs in ‘A’ with the related phrases/words in ‘B’ from the passage:
| ‘A’ | ‘B’ |
| 1. reduce | (a) viruses in our body |
| 2. control | (b) us live longer |
| 3. fight | (c) the risk of cancer |
| 4. help | (d) blood pressure |
Answer:
| ‘A’ | ‘B’ |
| 1. reduce | (c) the risk of cancer |
| 2. control | (d) blood pressure |
| 3. fight | (a) viruses in our body |
| 4. help | (b) us live longer |
Question 6.
Write the words related to ‘medicine’ from the passage :
Answer:
cancer, blood pressure, viruses, antioxidants, free radicals, system, body, health, damage.
Question 7.
List the things from the passage that are used for making tea.
Answer:
powdered green tea, bamboo whisk, milk, sugar, ginger, spices like cardamom, cloves, mace, jasmine, lemon.
![]()
Activities based on contextual grammar:
Question 1.
Underline the adverbs from the following sentences :
(Answers are directly underlined.)
Answer:
- Can you name the most widely consumed beverage in the world, after water?
- The tree plants grow slowly.
Question 2.
Underline the infinitives in the following sentence:
(Answers are directly given.)
Answer:
- It was funny to read words that stood still.
- Do I have to read the book?
- Turkish traders began to bargain for tea.
- A servant was boiling some water for the king to drink.
Question 3.
Find the subject and the object from the following sentences :
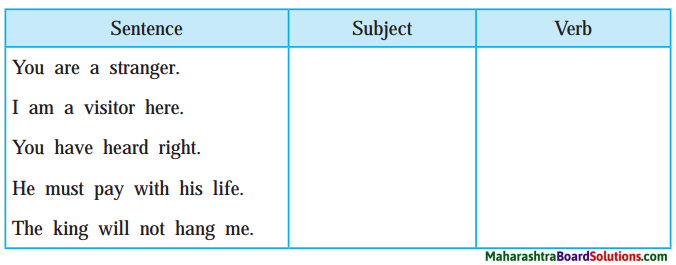
1. The water immediately changed colour.
2. He carried out further investigations.
Answer:
1. Subject: The water: Object: colour
2. Subject: He; Object: investigations.
![]()
Question 4.
Underline the infinitives in the following sentences :
(Answers are directly underlined.)
Answer:
- The word ch’a’ is used in English to refer to China tea.
- Tea may be able to reduce the risk of cancer.
Question 5.
Choose the proper article from the given brackets to complete the sentences.
(Answers are directly given.)
Answer:
1. He has to attend an important meeting. (a, an)
2. He was looking at the setting sun. (the, a, an)
Question 6.
Replace the underlined words with another words and rewrite the sentences :
Question a.
The ceremonies give people the time to relax.
Answer:
The ceremonies give people the time to enjoy.
![]()
Question b.
For many people tea is a popular drink.
Answer:
For many people tea is a refreshing drink.
Question c.
Make any question using the wh-words given below:
- Where
- What
- Who
- When
Answer:
- Where is our friend, Amar?
- What shall we do now?
- Who was there with you just now?
- When will you meet me again?
![]()
Question 7.
Read the sentences and fill in the blanks with correct prepositions given in the brackets :
(Answers are directly given.)
Answer:
- Tea is served in a small clay pot. (in, on, with)
- The tea is mixed with boiled water using cloves, (for, with, at)
- They still have tea ceremonies for important occasions, (for, to, in)
- Some people use mace to add to its taste. (for, to, with)
Question 8.
Arrange the following words in correct order to frame sentences :
1. is tea cup of a offered guests to.
2. brewed ginger is Tea with.
Answer:
1. A cup of tea is offered to guests.
2. Tea is brewed with ginger.
![]()
Do as directed :
Question 1.
We have three different tea-growing regions in India. (Frame a Wh-question to get the underlined word as an answer.)
Answer:
How many different tea-growing regions are there in India?
Question 2.
Choose the correct form of the verb from the brackets :
(Answers are directly given.)
Answer:
- A new flush appears on the plant every seven to ten days, (appear/appears)
- Tea plants require at least 100-125 cm of rainfall a year, (require/requires)
- Each of these regions is famous for the special type of tea. (is/are)
- It is said that the tea plants grow slowly. (are/is)
Personal Response :
Question 1.
What are botanical names? How are they decided?
Answer:
Botanical names are actually scientific names. These names are according to binomial (two words) naming system. The first name tells us the genus of a plant and the second name is the species of the plant. Throughout the world there should be only one uniform name, that is why the scientific naming system is used.
![]()
Question 2.
What is the difference between legends or stories and history?
Answer:
Legends or stories may not be true but history tells you the facts and true events of the past. History is the written or recorded or spoken events of the past. They are concerned with the real persons, places, arts, etc. that really existed in the past whereas legends are mostly imaginary and passed down from generations to generations in the form of story telling. So they are likely to change but the events in history are generally unchangeable.
Question 3.
What is the difference between ‘claim’ and ‘fact’?
Answer:
The word ‘claim’ is used to say that something is true although it has not been proved or approved by all people totally. Fact means reality. It is used to refer that a particular situation or incident existed and considered to be true and that it can be proved as real.
Question 4.
Do you have any ceremonies associated with food items?
Answer:
There are no any ceremonies directly associated with particular food items. While celebrating marriage ceremony, house warming ceremony, anniversaries, etc. variety of food items are served by the hosts and people enjoy different food items with different flavours and tastes. When people celebrate the festivals of Holi, Diwali, Makar Sankrant etc. people particularly prepare and enjoy food items like puran poli, sweets, laddoos, tilgul, kheer, etc.
![]()
Question 5.
What is your favourite beverage? Tell your reasons :
Answer:
My favourite beverage is coffee. I love to have it because of its rich flavour and unique taste. I feel refreshed when I drink hot, slightly bitter coffee with brown colour.
Do as directed :
Question 1.
Complete the words by using correct letters :
- j u _ c e
- d _ i n k
- s _ o p e
- w o _ l d
Answer:
- j u i c e
- d r i n k
- s l o p e
- w o r l d
![]()
Question 2
Copy the following sentences in your notebook:
1. Japan, China, Russia and Korea have special tea ceremonies and traditions.
2. Can you name the most widely consumed beverage in the world, after water?
Question 3.
Put the following words in alphabetical order :
1. evergreen, acidic, flavour, beverage.
2. emperor, elevation, enable, establish.
Answer:
1. acidic, beverage, evergreen, flavour.
2. elevation, emperor, enable, establish.
Question 4.
Punctuate the following sentences :
1. are there any wild animals in this forest Sahil asked the tour guide
2. what a fantastic landscape it is the visitor exclaimed.
Answer:
1. “Are there any wild animals in this forest?” Sahil asked the tour guide.
2. “What a fantastic landscape it is !” the visitor exclaimed.
![]()
Question 5.
Spot the error and rewrite the correct sentences:
1. How and when did people first began to drink tea?
2. We has three very distinct and different tea growing regions in India.
Answer:
1. How and when did people first begin to drink tea?
2. We have three very distinct and different tea-growing regions in India.
Question 6.
Write related words as shown in the example :
(Answer is directly given.)
Answer:
Question 7.
Complete the following word-chain of nouns. Add four words, each beginning with the last letter of the previous word :
proteins → ……………. → …………… → …………….. → …………….
Answer:
proteins → sugar → remand → dream → mop.
![]()
Do as directed :
Question 1.
Make your own meaningful sentence by using the phrase ‘to look for’.
Answer:
Amav lost his pen in his school and now he is looking for it in his home.
Question 2.
Add a prefix or suffix to make new words and use any one of the root word in your own sentence :
1. confident
2. absent.
Answer:
1. confidence
2. absence.
Sentence: Ramesh was very confident when he began to give his speech.
![]()
Question 3.
Add a clause to expand the sentence meaningfully:
We know
Answer:
We know that trees are very important for all of us.
Language Study:
Question 1.
Compound word :
Find all the words or pairs of words that begin with ‘tea’.
Answer:
teapot, tea plants, tea gardens, tea-estates, tea leaves, tea seeds, tea-tasting, tea whisking, tea minded, tea growing, tea club, tea ceremony, tea kettle, tea lovers.
![]()
Question 2.
Underline the infinitive in the following sentences :
(The answers are underlined directly.)
Answer:
- It was funny to read words that stood still.
- To be or not to be – that is the question.
- Can I read the book?
- They could help one another with the homework and talk about it.
My English Coursebook Std 9 Digest Pdf Unit 1