Class 7 Hindi Chapter 4 Shabd Sampada Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 7 Hindi Solutions Sulabhbharati Chapter 4 शब्द संपदा Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Std 7 Hindi Chapter 4 Shabd Sampada Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Hindi Sulabhbharti Class 7 Solutions Chapter 4 शब्द संपदा Textbook Questions and Answers
निम्नलिखित प्रश्नों के तीन-चार वाक्यों में उत्तर लिखिए।
Question 1.
‘भाषा’ का क्या अर्थ है, इसके कारण क्या हुआ है?
Answer:
‘भाषा’ का अर्थ है – सार्थक शब्दों का व्यवस्थित क्रमबद्ध संयोजन। इसके कारण दुनिया की सभी ज्ञानशाखाओं का विकास हुआ। यही सभी प्रगति की जड़ में है।
Question 2.
भाषा समृद्ध कैसे होती है?
Answer:
हिंदी में ऐसे हजारों शब्द हैं जो संस्कृत, अरबी, फारसी, अंग्रेजी, पुर्तगाली से आए हैं। कुछ ऐसे भी हैं जो दो भिन्न भाषाओं के मेल से बने हैं। अन्य अनेक भाषाओं के शब्दों के आने से भाषा समृद्ध होती है।
Question 3.
शब्दों के बारे में लेखक के विचार बताइए।
Answer:
लेखक के अनुसार शब्दों का संसार बड़ा विचित्र होता है। यही मनुष्य को ज्ञान से और मनुष्य को मनुष्य से जोड़ते हैं। शब्द निर्जीव होते हैं। मनुष्य उन्हें अर्थ देकर जीवंत बनाते हैं। जब शब्द जीवंत हो जाते हैं, तो उनमें मनुष्य के गुण दोष आने लगते हैं। वे भी मनुष्य की तरह किसी अन्य भाषा के शब्दों को मित्र तो किसी को शत्रु बना लेते हैं। कुछ मिलनसार होते हैं, तो कुछ अड़ियल होते हैं; जो किसी से नहीं मिलते हैं। यही हमारे चरित्र, बुद्धिमत्ता, समझ और संस्कार दर्शाते हैं।
Question 4.
वाचन-संस्कृति बढ़ाने से होने वाले लाभ लिखिए।
Answer:
वाचन-संस्कृति बढ़ाने से स्वयं की शब्द संपदा में वृद्धि होती है। शब्द संपदा की वृद्धि होने पर हमारी समझ बढ़ती है कि किस समय, किसके सामने, किस प्रकार के शब्दों का प्रयोग करना चाहिए। इससे हमारे चरित्र, बुद्धिमत्ता, समझ, संस्कार समृद्ध, सुंदर व सुगठित होते हैं।
![]()
स्वयं अध्ययन
Answer:
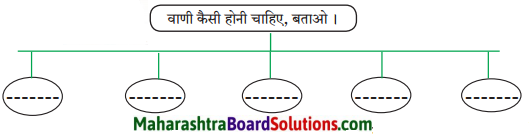
हमारी वाणी शिष्ट होनी चाहिए। कहा गया है ‘सत्यं ब्रूयात्’ यानी सत्य से युक्त वाणी बोलनी चाहिए। “प्रिय बूयात्’ प्रिय बोलना चाहिए। अहंकार रहित वाणी बोलनी चाहिए। जिसे सुनकर सुननेवाला भी सुखी हो जाए और अपने मन को भी शांति मिले। विवेक पूर्ण वाणी बोलनी चाहिए अर्थात कहाँ, किससे और कैसी वाणी बोलनी चाहिए उसका पूर्ण विचार करके बोलना चाहिए। बड़ों के लिए आदरार्थक शब्दों का प्रयोग करना चाहिए साथ ही सत्य यदि अप्रिय हो, तो नहीं बोलना ही हितकर होता है।
जरा सोचो…..
‘यदि तुम पशु-पक्षियों की बोलियाँ समझ पाते तो…’ विषय पर आधारित संवाद लिखिए। (संवाद लेखन)
Answer:
आशीष – आयुष, क्या तुमने प्रातः भ्रमण कर लिया?
आयुष – हाँ, भ्रमण तो कर लिया पर अभी और करना था। तब तक एक करुण स्वर ने…..
आशीष – करुण स्वर?
आयुष – हाँ, मित्र यह चिड़िया अचानक मेरे सामने आकर गिर पड़ी।
आशीष – क्या हुआ है इसे?
आयुष – पता नहीं यार! यह मेरे सामने गिरी और छटपटाते हुए ची… चौं… कर रही थी।
आशीष – शायद तुम ठीक कह रहे हो; पर कौए को इससे क्या दुश्मनी हो सकती है जो वह इसे मारेगा?
आयुष – वह तो यह चिड़िया ही बता सकती है। शायद यह कुछ कहना चाहती है। परंतु हम इसकी भाषा नहीं समझ पा रहे हैं।
आशीष – चलो इसे साथ ले चलते हैं।
विचार मंथन
‘कथनी मीठी खाँड़-सी’ इस विषय पर आधारित एक अनुच्छेद लिखिए। (अनुच्छेद-लेखन)
Answer:
‘कथनी’ का अर्थ है हमारा कथन अर्थात हमारी वाणी। हमारी वाणी मीठी होनी चाहिए। एकदम गुड़ के समान। कहने का आशय यह है कि हम जो भी बोले उसका प्रभाव सुनने वाले के ऊपर अच्छा व सकारात्मक हो। एक बार मुख से शब्द निकल जाए तो वह वापस नहीं आता है। वाणी के कारण दोस्त और दुश्मन बनते हैं।
मधुर वाणी को औषधि के समान माना गया है। जिसे सुनकर सुनने वाला शांत एवं आनंदित हो जाता है तथा अपने मन को भी परम सुख की अनुभूति होती है। तभी तो कहा गया है। “ऐसी वाणी बोलिए, मन का आपा खोय। औरन को शीतल करे, आपहू शीतल होय।।”
![]()
सुनो तो जरा:
भारत के संविधान की उद्देशिका सुनो और दोहराओ।
‘बातै हाथी पाइए, बातै हाथी पाँव’ विषय पर अनुच्छेद लिखिए। (अनुच्छद-लखन)
Answer:
बात से हम सब कुछ हासिल कर सकते हैं। ‘बातै हाथी पाइए’ का अर्थ है – बात से हाथी प्राप्त करना। यदि आप को बोलने की कला आती है, तो आपकी हर बात पूरी हो सकती हैं। बड़ी-से-बड़ी इच्छाएँ आपकी पूरी हो सकती हैं। इसके विपरीत यदि बात करने नहीं आता है, तो कहीं भी आप समस्या उपस्थित कर सकते हैं। जो कार्य आसानी से संपन्न हो सकता है।
वह काम बिगड़ भी सकता है। यही नहीं यदि आपने किसी को कटु वाणी बोल दी, तो वह आग बबूला भी हो सकता है। संभवतः वह आपको मार-मार कर हाथी पाँव जैसा भी बना सकता है। अत: बात करते समय हमेशा सतर्क रहना चाहिए। सोच-समझकर बात करनी चाहिए। आपकी बात का सुनने वाले पर क्या प्रभाव पड़ेगा? यह विचार करके ही बोलना चाहिए।
खोजबीन
हजारी प्रसाद द्विवेदी की ‘कबीर ग्रंथावली’ से पाँच दोहे दंडकर सुंदर अक्षरों में लिखिए। (कविता लेखन)
Answer:
(१) दुख में सुमिरन सब करे, सुख में करे न कोय।
जो सुख में सुमिरन करे, दुख काहे को होय।।१।।
(२) तिनका कबहुँ ना निंदिये, जो पाँव तले होय।
कबहुँ उड़ आँखों पड़े, पौर घनेरी होय।।२।।
(३) गुरु गोविंद दोऊ खड़े, काके लागूं पाय।
बलिहारी गुरु आपनो, गोबिंद दियो बताय।।३।।
(४) जाति न पूछो साधुकी, पूछि लीजिए ज्ञान।
मोल करो तलवार का, पड़ी रहन दो म्यान ।।४।।
(५) माया मरी न मन मरा, मर-मर गया शरीर।
आशा तृष्णा ना मरी, कह गए दास कबीर।।५।।
![]()
अध्ययन कौशल:
जानकारी प्राप्त करने के विविध संदर्भ स्रोतों के बारे में पढ़ो और उनका संकलन करो।
सदैव ध्यान में रखो
शब्दों का प्रयोग सावधानी से करना चाहिए।
भाषा की ओर
नीचे दिए गए वाक्य पढ़ो और उपयुक्त शब्द उचित जगह पर लिखो:

(१) लक्ष्मी ……. यहाँ से दस ……. दूरी पर है। (मील, मिल)
(२) …….. छोड़ दूंगा पर ……. नहीं छोडूंगा। (प्रण, प्राण)
(३) ………. को देखकर रुचिका …….. पड़ी। (हँस, हंस)
(४) शब्द ……. में ……शब्द मिलता है। (कोष, कोश)
(५) …….. रात ……. दुखियों की सेवा करना सभी का कर्तव्य है। (दीन, दिन)
(६) नदी के ………. का ……… जल समेटा नहीं जा सकता। (कुल, कूल)
(७) ………. दिवाली में जलाकर देहरी पर रख …….। (दिया, दीया)
(८) बालंक ………. से पानी ……. है। (पीता, पिता)
Answer:
(१) मिल, मील
(२) प्राण, प्रण
(३) हंस, हँस
(४) कोश, कोष
(५) दिन, दीन
(६) कूल, कुल
(७) दीया, दिया
(८) पिता, पीता
![]()
Hindi Sulabhbharti Class 7 Solutions Chapter 4 शब्द संपदा Additional Important Questions and Answers
निम्नलिखित शब्दों में से सही शब्द चुनकर रिक्त स्थानों की पूर्ति कीजिए।
(मिलनसार, विचित्र, ज्ञान, मालिका, हानिकारक, शब्द, स्वयं)
Question 1.
शब्दों का यह संसार बड़ा ……….है।
Answer:
विचित्र
Question 2.
शब्द ही मनुष्य को ………… से जोड़ते हैं।
Answer:
ज्ञान
Question 3.
हिंदी के शब्द …………… है।
Answer:
मिलनसार
Question 4.
………… के उच्चारण के पूर्व हमें सोचना चाहिए।
Answer:
शब्द
Question 5.
अनाप-शनाप शब्दों का प्रयोग हमेशा ……….. होता है।
Answer:
हानिकारक
Question 6.
प्रत्येक व्यक्ति के पास …… की शब्द संपदा होती है।
Answer:
स्वयं
Question 7.
तुम भी शब्द संपदा के ………………” हो जाओगे।
Answer:
मालिक
![]()
निम्नलिखित वाक्य सही है या गलत लिखिए।
Question 1.
ज्ञान शाखाओं का नाश भाषा के कारण हुआ।
Answer:
गलत
Question 2.
शब्द ही मनुष्य को मनुष्य से जोड़ते हैं।
Answer:
सही
Question 3.
विज्ञान की दृष्टि से अक्षर ध्वनि के चिह्न हैं।
Answer:
सही
Question 4.
तमिल भाषा के शब्द मिलनसार होते हैं।
Answer:
गलत
Question 5.
शब्द संपदा को बढ़ाने के लिए साहित्य के वाचन की जरूरत होती है।
Answer:
सही
![]()
निम्नलिखित प्रश्नों के उत्तर एक शब्द में लिखिए।
Question 1.
सार्थक शब्दों का व्यवस्थित क्रमबद्ध संयोजन क्या कहलाता है?
Answer:
भाषा
Question 2.
शब्दों को अर्थ कौन देता है?
Answer:
मनुष्य
Question 3.
न्यूटन के अनुसार सफलता के लिए कितने प्रतिशत परिश्रम की जरूरत होती है?
Answer:
९०(नब्बे)
Question 4.
शब्दों के विभिन्न अर्थों को जानने के लिए किसकी जरूरत होती है?
Answer:
शब्दकोश
Question 5.
शब्द संपदा को बढ़ाने के लिए क्या पढ़ना चाहिए?
Answer:
साहित्य
![]()
निम्नलिखित प्रश्नों के उत्तर एक वाक्य में लिखिए।
Question 1.
दुनिया के सभी ज्ञान शाखाओं का विकास किसके कारण हुआ?
Answer:
दुनिया के सभी ज्ञान शाखाओं का विकास भाषा के कारण हुआ।
Question 2.
किसकी ताकत की ओर हमारा ध्यान कभी नहीं जाता?
Answer:
शब्दों की ताकत की ओर हमारा ध्यान कभी नहीं जाता।
Question 3.
किन शब्दों को हमें अपने जीवन व्यवहार से निकालकर बाहर करना चाहिए?
Answer:
जो शब्द हमें निष्क्रिय करते रहते हैं। उन्हें अपने जीवन व्यवहार से निकालकर बाहर करना चाहिए।
Question 4.
शब्दों के उच्चारण के पूर्व हमें क्यों सोचना चाहिए?
Answer:
शब्दों के उच्चारण के पूर्व हमें सोचना चाहिए क्योंकि हमारे मुख से उच्चरित शब्द हमारे चरित्र बुद्धिमत्ता, समझ और संस्कारों को दर्शाते हैं।
Question 5.
परीक्षा में अच्छी श्रेणी कैसे प्राप्त होती है?
Answer:
परीक्षा में सुंदर, उपयुक्त और अर्थमय शब्दों से जो वाक्य लिखे जाते हैं; उस कारण ही अच्छी श्रेणी प्राप्त होती है।
![]()
निम्नलिखित शब्दों के विलोम शब्द लिखिए।
- आधुनिक
- उन्नति
- सार्थक
- व्यवस्थित
- निर्जीव
- निष्क्रिय
- सज्जन
- गुण
Answer:
- प्राचीन
- अवनति
- निरर्थक
- अव्यवस्थित
- सजीव
- सक्रिय
- दुर्जन
- अवगुण
![]()
निम्नलिखित शब्दों के तीन पर्यायवाची शब्द लिखिए।
- मनुष्य
- मित्र
- माँ
- पिता
Answer:
- नर, मानव, मनुज
- सखा, दोस्त, साथी
- जननी, अंबा, माता
- जनक, बापू, पितृ
![]()
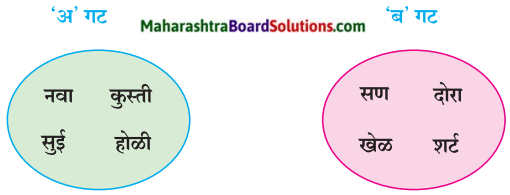
पाठ में से हिंदीतर भाषा के शब्दों को चुनकर लिखिए एवं उनका वर्गीकरण कीजिए।
Answer:
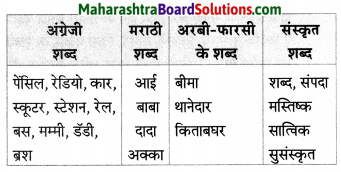
निम्नलिखित शब्दों में से अंग्रेजी और हिंदी के शब्दों को अलग कीजिए।
माई, अम्मा, बाबा, ब्रश, रेल, पेंसिल, रेडियो, अक्का, कार, अण्णा, स्कूटर, परीक्षा, दादा, बापू, स्टेशन, माँ, मम्मी, डॅडी
Answer:
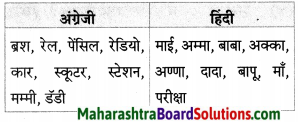
![]()
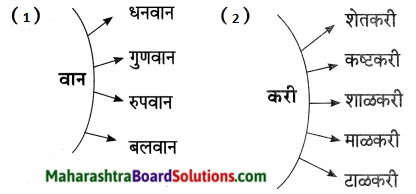
‘दार’ प्रत्यय लगाकर पाँच शब्द बनाइए।
जैसे – थाने + दार = थानेदार
Answer:
- ईमान + दार – इमानदार
- जमीन + दार – जमींदार
- दुकान + दार = दुकानदार
- समझ + दार = समझदार
- शान + दार = शानदार
दैनिक बोल चाल में प्रयुक्त शब्दों के हिंदी समानार्थी शब्द लिखिए।
Answer:
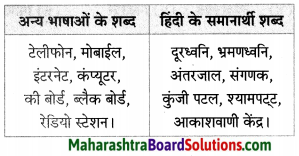
![]()
Hindi Sulabhbharati 7th Standard Digest Guide दूसरी इकाई