Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 10 Marathi Solutions Aksharbharati Chapter 13 हिरवंगार झाडासारखं Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Class 10th Marathi Aksharbharati Chapter 13 हिरवंगार झाडासारखं Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Std 10 Marathi Chapter 13 Question Answer
Marathi Aksharbharati Std 10 Digest Chapter 13 हिरवंगार झाडासारखं Textbook Questions and Answers
(१) चौकटी पूर्ण करा.
(अ) कवीने झाडाला दिलेली उपमा
(आ) पानझडीनंतरचे, नवी वस्त्रे धारण करणारे झाड म्हणजे
(इ) कवीच्या मते उत्साही आयुष्य म्हणजे
(ई) अलगद उतरणारे थेंब
उत्तरः
(उ) फुटते शरीरभर पालवी याचा अर्थ
(अ) कवीने झाडाला दिलेली उपमा – ध्यानस्थ ऋषी
(आ) पानझडीनंतरचे, नवी वस्त्रे धारण करणारे झाड म्हणजे – नवी नवरी
(इ) कवीच्या मते उत्साही आयुष्य म्हणजे – फुलासारखं टवटवीत
(ई) अलगद उतरणारे थेंब – दव।
(उ) फुटते शरीरभर पालवी याचा अर्थ – नवउत्साह
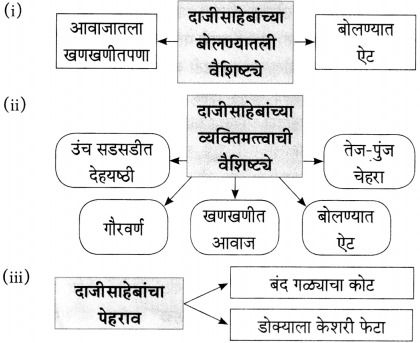
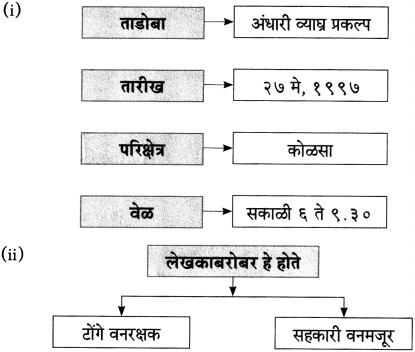
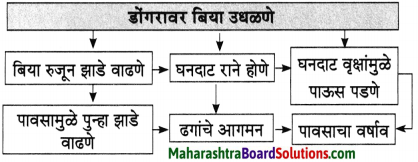
(२) आकृती पूर्ण करा.

उत्तरः
(३) एका वाक्यात उत्तरे लिहा.
(अ) झाडाच्या जीवनाचं गाणं कशात दडलेलं असतं?
(आ) झाडाच्या मुळावर घाव घातल्यावर त्याची प्रतिक्रिया काय असते?
उत्तरः
ते घाव झाड मुकाट्याने सहन करते.
(४) ‘पानझडीनंतर’ हे उत्तर येईल असा प्रश्न तयार करा.
उत्तर:
झाड नवीन वस्त्र केव्हां धारण करते?
![]()
(५) खालील ओळींचा तुम्हांला कळलेला अर्थ लिहा.
(अ) हसावं कसं सळसळत्या पानासारखं.
उत्तरः
झाडांच्या पानांची हवेने होणारी सळसळ विलक्षण असते.
सर्व दुःखे बाजूला ठेवून पानांच्या सळसळीसारखे हसले पाहिजे अशी कवीची भावना आहे. सळसळणारी पाने एकत्र असतात. त्याचप्रमाणे इतरांनाही हसण्यात सामील करून घेता आले पाहिजे. आनंदी जीवन जगण्यासाठी हे गुण अंगी बाणवावेत असा कवीने सुंदर संदेश दिला आहे. सळसळणारी पाने हवेमुळे, पक्ष्यांच्या मंजुळ गाण्यामुळे उत्साही असतात. असेच उत्साहाने, आनंदाने जीवनात हसत रहावे, प्रफुल्लित रहावे अशी कवीची भावना आहे.
(आ) जगावं कसं तर? हिरवंगार झाडासारखं.
उत्तर:
हिरवंगार झाडासारखं’ या कवितेत कवी ‘जॉर्ज लोपीस’ यांनी मानवाचे जीवन झाडाशी किती सुसंगत आहे याचे उत्तम दर्शन घडवले आहे. झाडाचे अनेक गुण जीवनात आचरण्यासारखे आहेत, हा उपयुक्त संदेश त्यांनी कवितेतून दिला आहे. जीवनात ‘मौन’ अनेकवेळा उपयुक्त असते. झाडही ऋषीसारखे मौन धरून तपश्चर्या करीत असते. ‘मौन’ धरून तपश्चर्या करणे हा झाडाचा गुण उपयुक्त ठरतो. झाड पक्ष्यांना आसरा देते, पण त्यांच्याकडून कोणतीही अपेक्षा ठेवीत नाही. मानवाने विना अपेक्षेने दुसऱ्यांना सहकार्य केले पाहिजे. झाडासारखे दातृत्व अंगी बाणले पाहिजे. झाड कितीही संकटे, वादळे आली तरी घट्ट पाय रोवून उभे असते. माणसानेही कठीण प्रसंगी न घाबरता घट्टपणे उभे राहून संकटांशी सामना केला पाहिजे. झाडाचा हिरवेगारपणा, प्रफुल्लितपणा, ताजेपणा बघून आयुष्यात प्रफुल्लित राहिले पाहिजे. नकारात्मकतेची मरगळ झटकून हिरवेगार झाडासारखे ताजेतवाने जगावे असे कवी म्हणतो. मुळावर घाव घातला तरी झाडाची सहनशीलता ढळत नाही. सहनशीलता हा गुण झाडाकडून घ्यावा. हिरव्यागार झाडासारखे अनेक गुणांना आत्मसात करून जगावे असा संदेश कवी देत आहे.
(६) काव्यसौंदर्य.
(अ) खालील ओळींचे रसग्रहण करा.
‘झाडांच्या पानावरून वहीच्या पानावर अलगद उतरतात दवांचे टपोरे थेंब’
(आ) ‘झाडाचे मानवी जीवनातील स्थान’, याविषयी तुमचे विचार लिहा.
उत्तरः
झाडांचे मानवी जीवनातील स्थान अतुलनीय आहे. संपूर्ण पर्यावरण झाडांवर अवलंबून आहे. निसर्गाचे संतुलन राखण्यात झाडे अग्रेसर आहेत. झाडांमुळे फळे, फुले, औषधे तर मिळतांतच; पण थकलेल्या जीवाला सावली मिळते. झाडांमुळे पाऊस पडतो. झाडे मानवी जीवनातील ‘श्वास’ च आहेत. त्यावाचून आपले जीवन जगणे अशक्य आहे.
![]()
(इ) ‘झाडापासून आनंदी जगणे शिकावे’, या विधानातील विचार स्पष्ट करा.
उत्तरः
झाड कोणत्याही परिस्थितीत घट्ट पाय रोवून उभे असते. वाऱ्याच्या झुळूकीबरोबर पानांच्या सळसळाटीने हसते. पक्ष्यांच्या मंजुळ गाण्याबरोबर जीवनाचे गाणे गाते. आपल्या विशाल सावलीत मुसाफिरांना कवेत घेते. पावसाळ्यात हिरवेगार ताजेतवाने होऊन न्हाऊन निघते. पानझडीनंतर नव्या नवरीसारखा नवीन वेष धारण करते. दातृत्व हा झाडाचा मोठाच गुण आहे. फळे, फुले बहरली की झाडे ती दुसऱ्यांच्या पदरात दान करते. संपूर्ण आयुष्य हिरवगार होऊन जगते. अशाच प्रकारे माणसानेही सहनशीलता, सहकार्याची वृत्ती, कठीण प्रसंगातही घट्ट पाय रोवून ठेवण्याची वृत्ती जोपासली तर त्याचेही जीवन आनंदाने भरून जाईल.
Marathi Akshar Bharati Class 10 Textbook Solutions Chapter 13 हिरवंगार झाडासारखं Additional Important Questions and Answers
प्रश्न १.खालील कवितेच्या आधारे दिलेल्या सूचनेनुसार कृती करा,
कृती १: आकलन कृती
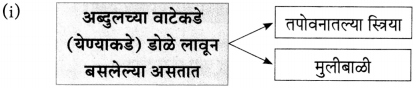
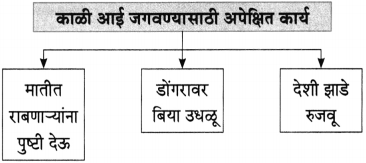
(१) आकृतिबंध पूर्ण करा.
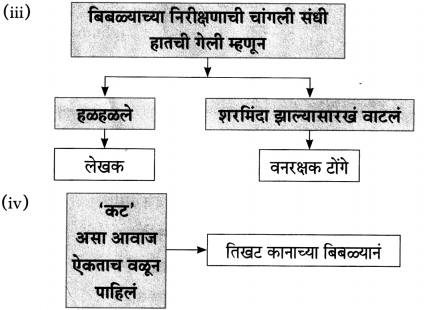
(iii) चौकटी पूर्ण करा.
![]()
(२) खालील प्रश्नांची उत्तरे एका वाक्यात लिहा.
(i) झाड कोणासारखे बसते? उत्तरः झाड ध्यानस्थ ऋषीसारखे बसते.
(ii) झाड कोणाचे आहे? उत्तरः झाड पक्ष्यांचे आहे.
(iii) झाडांच्या जीवनाचे एक संथ गाणे कोठे दडले आहे?
उत्तरः
पक्ष्यांच्या मंजुळ नादात झाडांच्या जीवनाचे एक संथ गाणे दडले आहे.
(iv) झाडाच्या मुळावर घाव घातला तर झाड काय करते?
उत्तरः
झाडाच्या मुळावर घाव घातला तर झाड मुकाट सहन करते.
(३) कंसातील योग्य शब्द वापरून रिकाम्या जागा भरा.
(i) …………………………… झाडांचे कुणीच नसतात तरीही झाड त्याचं असतं. (प्राणी, माणसे, पक्षी, किटक)
(ii) झाडाकडे टक लावून पाहिलं तर …………………………… विरघळतो हिरवा रंग. (शरीरभर, जमिनीवर, पाण्यात, आकाशात)
(iii) पक्ष्यांच्या …………………………… नादात झाडाचंही जीवनाचं एक संथ गाणे दडलेले असते. (मधूर, गोड, मंजुळ, सुरेल)
उत्तर:
(i) पक्षी
(ii) शरीरभर
(iii) मंजुळ.
कृती २ : आकलन कृती
(१) उत्तरे लिहा.
(i) मुळावरचे घाव मुकाट सहन करते – [झाड]
(ii) वहीच्या पानावर अलगद उतरतात – [दवाचे थेंब]
(iii) सरसावलेले असतात – [झाडाचे बाहू]
(२) ‘पालवी’ उत्तर येईल असा प्रश्न तयार करा.
उत्तरः
शरीरभर काय फुटते?
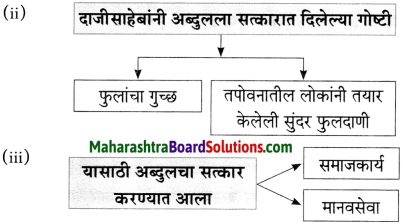
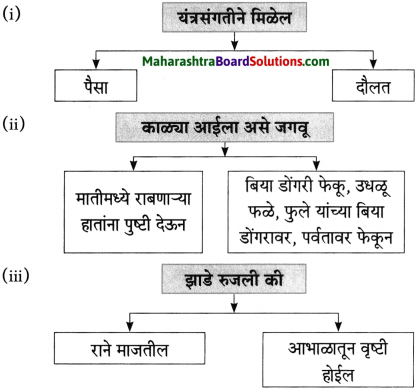
(३) आकृतिबंध पूर्ण करा.
![]()
(४) सहसंबंध लिहा.
(i) शरीरभर विरघळतो : हिरवा रंग : : क्षणभर रक्त : …………………………. .
(ii) हसावं कसं : सळसळत्या पानासारखं : : जगावं कसं तर? …………………………. .
उत्तर:
(i) हिरवेगार
(ii) हिरवंगार झाडासारखं
(५) काव्यपंक्तींचा योग्य क्रम लावा.
(i) हसावं कसं सळसळत्या पानासारखं
(ii) शरीरभर विरघळतो हिरवा रंग
(iii) झाडांच्या पानावरून वहीच्या पानावर अलगद उतरतात दवांचे टपोरे थेंब
(iv) रोजचं चिंतन करावं कसं तर झाडासारखं!
उत्तर:
(i) झाडांच्या पानावरून वहीच्या पानावर अलगद उतरतात दवांचे टपोरे थेंब
(ii) शरीरभर विरघळतो हिरवा रंग
(iii) हसावं कसं सळसळत्या पानासारखं
(iv) रोजचं चिंतन करावं कसं तर झाडासारखं!
(६) चूक की बरोबर ते लिहा.
(i) रक्त होते क्षणभर लालेलाल
(ii) जगावं कसं तर? हिरवंगार झाडासारखं
उत्तर:
(i) चूक
(ii) बरोबर
कृती ३: कवितेतील शब्दांचा अर्थ
(१) खालील कवितेतील शब्दांचा अर्थ लिहा.
(i) मुसाफिर
(ii) आयुष्य
(iii) खुडणे
(iv) टवटवीत
उत्तर:
(i) प्रवासी
(ii) जीवन
(iii) तोडणे
(iv) ताजे
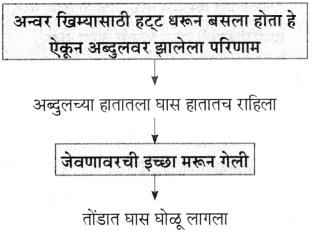
![]()
कृती ४: काव्यसौंदर्य
(१) पुढील ओळींचे अर्थसौंदर्य स्पष्ट करा.
(i) ‘झाडाचे बाहु सरसावलेले असतात मुसाफिरांना कवेत घेण्यासाठी’
उत्तरः
झाडाची सहकार्याची वृत्ती विलक्षण असते. परोपकाराची भावना त्यांच्या मनात सतत जागी असते. आपल्या सर्वदूर पसरलेल्या फांद्यांमुळे झाड कडक उन्हात वाटसरूंना गारेगार सावली देते त्यांचा थकवा दूर करतं. जणू आपले बाहू पसरवून हे झाड मुसाफिरांना म्हणजे वाटसरूंना आपल्या कवेत घेते, असे वाटते.
(ii) ‘पक्षी झाडांचे कुणीच नसतात तरीही झाड त्यांचं असतं
उत्तरः
पक्षी झाडांवर सतत येत असतात. घरटे बांधून राहतात.
काम झाले की, फळे चाखून, खाऊन पुन्हा दुसरीकडे उडून जातात. झाड त्यांना निवारा देते, अन्न देते. ऊन-पावसापासून रक्षण करते, पण जेव्हा झाडावर घाव घातले जातात, ते कापले जाते तेव्हां पक्षी स्वत:चाच विचार करून झाडावरून उडून जातात. परंतु, झाड मात्र हिरवेगार असताना येणाऱ्या पक्ष्यांना कधीही अडवत नाही, आश्रय नाकारत नाही. म्हणूनच पक्षी झाडांचे कुणीही नसून झाड त्यांचे असते असे कवी म्हणतात. पुढील काव्यपंक्तीतील तुम्हांला समजलेला विचार तुमच्या भाषेत स्पष्ट करा.
‘झाड बसते ध्यानस्थ ऋषिसारखं मौन व्रत धारण करून, तपश्चर्या करत……….
उत्तर:
झाड अचल असते. ते काहीही न बोलता एका ठिकाणी अढळ उभे असते. ऋषीमुनी जसे तपश्चर्येला ध्यान लावून बसतात. त्याचप्रमाणे झाडही मौन व्रतात उभे असते. बाह्य गोष्टींच्या सर्व परिणामांना ते बिना तक्रार सहन करत असते. पक्षी येतात जातात, झाडांच्या मुळांवरही कधी घाव बसतो. पानझड होते तरी झाड स्थिर व सहनशील असते. कठीण प्रसंगातही पाय
घट्ट रोवून ध्यानस्थ ऋषिसारखे शांत असते.
![]()
(५) झाडासारखे घट्ट पाय रोवण्यासाठी माणसाने काय काय करावे स्पष्ट करा.
उत्तरः
घट्ट पाय रोवून उभे राहणे हा झाडाचा गुण आहे. माणसानेही कोणत्याही परिस्थितीला न घाबरता सामोरे जावे. संकटांशी सामना करावा, झाडांसारखी सहनशीलता शिकावी. झाड आपल्या मुळांवर घाव बसला तरी मुकाट्याने सहन करते. आयुष्यात किती ही संकटे आली तरी सहन करून त्यातून मार्ग काढता येणे गरजेचे आहे. नव्या उमेदीने पुन्हा नव्या पालवीसारखे प्रफुल्लीत राहायला शिकावे. झाडासारखे चिंतन करावे. झाडासारखे घट्ट पाय रोवून जीवनात मुरावे.
प्रश्न २. दिलेल्या मुद्यांच्या आधारे कवितेसंबंधी पुढील कृती सोडवाः
(१) प्रस्तुत कवितेचे कवी/कवयित्री:
जॉर्ज लोपीस
(२) प्रस्तुत कवितेचा विषयः
आनंदी जीवन जगण्यासाठी माणसाने झाडाचे सर्व गुण आपल्या अंगी बाणवावेत असा विचार मांडला आहे.
(३) प्रस्तुत कवितेतील दिलेल्या ओळींचा सरळ अर्थ: मुळावर घाव घातला तरी झाड मुकाट सहन करते झाडांच्या पानावरून वहीच्या पानावर अलगद उतरतात दवांचे टपोरे थेंब झाड छाया देते, निवारा देते, फळे-फुले सर्व काही इतरांना देते. परोपकार हा त्याचा गुणधर्मच आहे. निर्दयी मानव जेव्हा आपल्या फायद्यासाठी या झाडाच्या मुळावर घाव घालतो तेव्हा देखील झाड बिनतक्रार ते सहन करते. झाडांची कत्तल होत असताना झाडाच्या पानांवरील दवबिंदू घरंगळत जणू वहीतील शब्दांमध्ये डोकावतात व आपली करुण कहाणी शब्दांकीत करतात याचाच अर्थ असा की, झाडांपासून कागद, वह्या बनविल्या जातात आणि मग अशा वहिच्या पानावर कोणीतरी कवी, लेखक झाडाचे दुःख नेमक्या शब्दांत लिहून काढतो. जणू झाडाच्या शरीरावर बसलेल्या घावाचे रूपांतर दवांच्या टपोऱ्या थेंबात होते असे कवीला वाटते. कवीने झाडाचा सहनशील हा गुण येथे दर्शविला आहे.
(४) प्रस्तुत कवितेतून मिळणारा संदेशः
“हिरवंगार झाडासारखं’ या कवितेत झाडांची सहनशीलता, दातृत्व, सहकार्याची वृत्ती, कठीण प्रसंगातही घट्ट पाय रोवून उभे राहण्याची वृत्ती याचे वर्णन केले आहे. आनंदी जीवन जगण्यासाठी झाडांसारखे हिरवेगार, ताजे प्रफुल्लित राहावे असा संदेश दिला आहे. झाड ‘मौनव्रत’ धारण करून तपश्चर्या करते. ते निरपेक्षपणे दुसऱ्यांना सहकार्य करते. त्याच्याकडे दातृत्वाचा गुण असल्यामुळे आपल्याकडची फुले, फळे सर्वकाही ते इतरांना देते. संकटांशी सामना करते. नकारात्मकतेची मरगळ झटकून हिरवेगार ताजेतवाने राहते. मुळावर घाव घातला तरी त्याचा सहनशीलता हा गुण ढळत नाही. पानगळीने झाड खचत नाही तर वसंतऋतू येताच ते पुन्हा बहरते. नव्या नवरीसारखे सजते. त्यामुळेच हिरव्यागार झाडासारखे अनेक गुणांना आत्मसात करून आपण आनंदाने जगावे, असा संदेश या कवितेतून मिळतो.
![]()
(५) प्रस्तुत कविता आवडण्याचे वा न आवडण्याचे कारणः
कवी जॉर्ज लोपीस यांची ‘हिरवंगार झाडासारखं’ ही कविता खूप आवडली आहे. त्याचे मुख्य कारण म्हणजे ‘जीवन जगण्याची कला शिकवणारे झाड’ हा या कवितेचा गाभा आहे. झाडांचे मानवी जीवनातील स्थान अतुलनीय आहे. झाडे हा मानवी जीवनाचा ‘श्वास’च आहेत. जॉर्ज लोपीस यांनी प्रत्येक ओळीत झाडाचा जगण्याशी संबंध जोडला आहे. झाडे आनंदी जीवनाचा आदर्शच आपल्यासमोर ठेवतात. कवितेत ठिकठिकाणी उदाहरणे देऊन कवीने ते मांडले आहे. कवितेतील प्रत्येक ओळीतून झाडाविषयी आपुलकीची, कृतज्ञतेची भावना मनात निर्माण होते. मनातील नैराश्य दूर करणारी व आशावादाची ज्योत पेटवणारी मन हिरवंगार करणारी ही कविता खरोखरच मनापर्यंत पोहोचते.
प्रस्तुत कवितेतील खालील शब्दांचा अर्थः
(i) झाड – वृक्ष
(ii) ऋषी – साधू, मुनी
(iii) व्रत – वसा
(iv) पक्षी – खग, विहंग
स्वाध्याय कृती
(३) खालील प्रश्नांची उत्तरे एका वाक्यात लिहा.
(i) झाडाच्या जीवनाचे गाणे कशात दडलेले आहे?
उत्तरः
झाडाच्या जीवनाचे गाणे पक्ष्यांच्या मंजुळ नादात दडले आहे.
काव्यसौंदर्य
(i) झाडाचे मानवी जीवनातील महत्त्वाचे स्थान या विधानाचा तुम्हाला कळलेला अर्थ स्पष्ट करा.
उत्तरः
झाडांचे मानवी जीवनातील स्थान अतुलनीय आहे. संपूर्ण पर्यावरण झाडांवर अवलंबून आहे. निसर्गाचे संतुलन राखण्यात झाडे अग्रेसर आहेत. झाडांमुळे फळे, फुले, औषधे तर मिळतांतच; पण थकलेल्या जीवाला सावली मिळते. झाडांमुळे पाऊस पडतो. झाडे मानवी जीवनातील ‘श्वास’ च आहेत. त्यावाचून आपले जीवन जगणे अशक्य आहे.
![]()
(ii) झाडापासून आनंदी जीवन जगणे शिकावे या विधानातील विचार स्पष्ट करा.
उत्तरः
झाड कोणत्याही परिस्थितीत घट्ट पाय रोवून उभे असते. वाऱ्याच्या झुळूकीबरोबर पानांच्या सळसळाटीने हसते. पक्ष्यांच्या मंजुळ गाण्याबरोबर जीवनाचे गाणे गाते. आपल्या विशाल सावलीत मुसाफिरांना कवेत घेते. पावसाळ्यात हिरवेगार ताजेतवाने होऊन न्हाऊन निघते. पानझडीनंतर नव्या नवरीसारखा नवीन वेष धारण करते. दातृत्व हा झाडाचा मोठाच गुण आहे. फळे, फुले बहरली की झाडे ती दुसऱ्यांच्या पदरात दान करते. संपूर्ण आयुष्य हिरवगार होऊन जगते. अशाच प्रकारे माणसानेही सहनशीलता, सहकार्याची वृत्ती, कठीण प्रसंगातही घट्ट पाय रोवून ठेवण्याची वृत्ती जोपासली तर त्याचेही जीवन आनंदाने भरून जाईल.
हिरवंगार झाडासारखं Summary in Marathi
हिरवंगार झाडासारखं काव्यपरिचय
‘हिरवंगार झाडासारखं’ ही कविता कवी ‘जॉर्ज लोपीस’ यांनी लिहिली आहे. या कवितेमध्ये झाडांची सहनशीलता, दातृत्व, सहकार्याची वृत्ती, कठीण प्रसंगातही घट्ट पाय रोवून उभे राहण्याची वृत्ती याचे वर्णन केले आहे. तसेच आनंदी जीवन जगण्यासाठी झाडांसारखे हिरवेगार ताजे, प्रफुल्लित राहावे असा संदेश दिला आहे.
हिरवंगार झाडासारखं Summary in English
This poem is written by George Lopis. In it, he speaks, at length, about the traits of a tree its patience, generosity, cooperation and resoluteness in difficult situations. Always be happy and evergreen like a tree. This is the message in this poem.
हिरवंगार झाडासारखं भावार्थ
झाड बसते ध्यानस्थ ऋषिसारखं मौन व्रत
धारण करून तपश्चर्या करत …
आनंदी जीवन जगण्यासाठी आपण झाडाचा आदर्श घ्यावा, असे कवी ‘जॉर्ज लोपीस’ आपल्याला पटवून देत आहेत. ते म्हणतात की, झाड अचल असते. ते एका ठिकाणी काहीही न बोलता अढळ उभे असते. ऋषीमुनी जसे तपश्चर्येला ध्यान लावून बसतात. त्याचप्रमाणे झाड देखील मौन व्रतात उभे असते. बाह्य गोष्टींच्या सर्व परिणामांना ते बिनतक्रार सहन करत असते. पक्षी येतात-जातात, झाडांच्या मुळांवरही कधी कधी घाव बसतात. पानझड होते तरी झाड स्थिर व सहनशील असते. कठीण प्रसंगातही पाय घट्ट रोवून ध्यानस्थ ऋषिसारखे शांत असते. आपणही तोच मार्ग अनुसरला पाहिजे.
पक्षी झाडांचे कुणीच नसतात
तरीही झाड त्यांचं असतं
पक्षी झाडांवर सतत येत असतात. घरटे बांधून राहतात. काम झाले की, फळे चाखून, खाऊन पुन्हा दुसरीकडे उडून जातात. झाड त्यांना निवारा देते, अन्न देते. ऊन-पावसापासून रक्षण करते; पण जेव्हा झाडावर घाव घातले जातात, ते कापले जाते तेव्हां पक्षी स्वत:चाच विचार करून झाडावरून उडून जातात. परंतु, झाड मात्र हिरवेगार असताना येणाऱ्या पक्ष्यांना कधीही अडवत नाही, आश्रय नाकारत नाही. म्हणूनच पक्षी झाडांचे कुणीही नसून झाड त्यांचे असते, असे कवी म्हणतात.
मुळावर घाव घातला तरी झाड मुकाट सहन करते
झाडांच्या पानावरून वहीच्या पानावर
अलगद उतरतात दवांचे टपोरे थेंब
झाडाचे कुणीच नसते, पण झाड मात्र सर्वांचे असते. झाड छाया देते, निवारा देते, फळे-फुले सर्व काही इतरांना देते. परोपकार हा त्याचा गुणधर्मच आहे. निर्दयी मानव जेव्हा आपल्या फायद्यासाठी या झाडाच्या मुळावर घाव घालतो तेव्हा देखील झाड बिनतक्रार ते सहन करते. झाडांची कत्तल होत असताना झाडाच्या पानांवरील दवबिंदू घरंगळत जणू वहीतील शब्दांमध्ये डोकावतात व आपली करुण कहाणी शब्दांकीत करतात याचाच अर्थ असा की, झाडांपासून कागद, वह्या बनविल्या जातात आणि मग अशा वहीच्या पानावर कोणीतरी कवी, लेखक झाडाचे दु:ख नेमक्या शब्दांत लिहून काढतो. जणू झाडाच्या शरीरावर बसलेल्या घावाचे रूपांतर दवांच्या टपोऱ्या थेंबात होते असे कवीला वाटते. कवीने झाडाचा सहनशील हा गुण येथे दर्शविला आहे.
झाडाकडे टक लावून पाहिलं तर
शरीरभर विरघळतो हिरवा रंग
रक्त होते क्षणभर हिरवेगार
आयुष्य होतं नुकत्याच खुडलेल्या फुलासारखं टवटवीत कोणतेही झाड असो ते प्रेरणादायी असते. आयुष्य होतं नुकत्याच खुडलेल्या फुलासारखं टवटवीत. पाना-फुलांनी बहरलेल्या हिरव्यागार झाडाकडे टक लावून पाहिले असता, झाडाची सहनशीलता, दुसऱ्यांना मदत करण्याची वृत्ती, त्याचे दातृत्व, कठीण प्रसंगातही घट्ट पाय रोवून उभे राहण्याची वृत्ती हे सारे गुण आपल्याला जाणवतात. तसेच कठोर क्षणी सुद्धा हे झाड आपला हिरवागार ताजेपणा कधी सोडत नाही, हे जाणून आपल्याला आनंद होतो. आपणही त्याच्यासारखे गुण स्वीकारावे असे वाटू लागते. जणू त्याचा हिरवा रंग आपल्या शरीरभर विरघळतो. तसेच क्षणभर आपले लाल रक्तही हिरवेगार झाल्यासारखे वाटते. म्हणजेच झाडांकडे पहिल्यावर त्यांच्यातला उत्साह आपल्यामध्ये भिनतो आणि आपले आयुष्य नुकत्याच खुडलेल्या फुलासारखे ताजे, टवटवीत होऊन जाते.
झाडाचे बाहु सरसावलेले असतात मुसाफिराना कवेत घेण्यासाठी
झाडाची सहकार्याची वृत्ती विलक्षण असते. परोपकाराची भावना त्यांच्या मनात सतत जागी असते. आपल्या सर्वदूर पसरलेल्या फांदयांमुळे झाड कडक उन्हात वाटसरूंना सावली देते त्यांचा थकवा दूर करते. जणू आपले बाहू पसरवून हे झाड मुसाफिरांना म्हणजे वाटसरूंना आपल्या कवेत घेते, असे वाटते.
पानझडीनंतर झाड पुन्हा नवीन वस्त्र धारण करतं
नव्या नवरीसारखं
झाडाला पालवी फुटल्यावर फुटते शरीरभर पालवी
अन झटकली जाते मरगळ
ऋतूनुसार झाडाच्या अवस्था बदलत जातात. पानझडीत म्हणजेच थंडीत, शिशिर ऋतूत झाडाची सगळी पाने गळून जातात. झाड पूर्ण रिकामे होते. तेव्हा ते एकटे असते तरी ते पुन्हा बहरते. वसंत ऋतूत झाडाला पुन्हा पालवी फुटते. कोवळी हिरवीगार पाने संपूर्ण झाडावर डोलायला लागतात. नव्या नवरीसारखे सजून झाड पुन्हा तजेलदार दिसू लागते. झाडाची ही प्रफुल्लितता पाहून, आपले मन शरीराचा सारा थकवा तसेच आलेली मरगळ झटकून टाकते. जणू आपल्या मनालाच नव्हे तर संपूर्ण शरीराला उत्साहाची पालवी फुटल्यासारखे वाटते.
पक्ष्यांच्या मंजुळ नादात झाडाचंही जीवनाचं
एक संथ गाणे दडलेले असते
कोणतेही झाड असो ते आपल्याच मस्तीत, धुंदीत जगत असते. बाहेरची परिस्थिती कशीही असो ते कधी तक्रार करत नाही. थंडी, ऊन, वारा, पाऊस यांचा सामना हसतमुखाने करत ते मौजेने जगत असते. त्याच्या आश्रयाला येणाऱ्या प्रत्येक प्राणी-पक्ष्यांना ते आनंदच देत असते. झाडावर बसणारे पक्षी आनंदाने झोके घेत मंजुळ गाणी गात असतात, किलबिलाट करत असतात. जणू त्या गाण्याचा आनंद घेत घेत हे झाड आपले जीवन मजेने, उत्साहाने जगत असते.
हसावं कसं सळसळत्या पानासारखं
मुळावं मुरावं कसं तर? झाडासारखं घट्ट पाय रोवीत
जगावं कसं तर? हिरवंगार झाडासारखं
रोजचं चिंतन करावं कसं तर झाडासारखं!
माणसाने झाडाकडून जगण्याच्या कला शिकून घेतल्या पाहिजेत, असे कवी म्हणतात. कोणतेही झाड असो ते वाऱ्याच्या झुळुकीबरोबर पानांच्या सळसळीने हसते. पक्ष्यांच्या मंजुळ गाण्याबरोबर जीवनाचे गाणे गाते, त्याचप्रमाणे आपणही सळसळत्या पानासारखं हसलं पाहिजे. झाड कोणत्याही परिस्थितीत घट्ट पाय रोवून उभे असते. त्याचप्रमाणे आपणही घट्ट पाय रोवून खंबीरपणे जीवनात मुरलं पाहिजे. तसेच येणाऱ्या संकटांचा खंबीरपणे सामना केला पाहिजे. पानगळ झाली तरी झाड खचून जात नाही. वसंतऋतू येताच कोवळी हिरवीगार पाने झाडाच्या अंगावर डोलू लागतात. जणू नव्या नवरीसारखे ते झाड सजते. त्याचप्रमाणे आयुष्यात कितीही संकटे आली तरी त्याचा सामना करून त्यातून मार्ग काढता आला पाहिजे. नव्या उमेदीने हिरव्यागार झाडासारखे प्रफुल्लित राहून जगले पाहिजे. शिवाय झाडासारखे रोजचे चिंतन करत आनंदी जीवन जगले पाहिजे,
हिरवंगार झाडासारखं शब्दार्थ
- ध्यानस्थ – चिंतनात मग्न – (absorbed in meditation)
- मौन – नि:शब्द – (state of being quiet silence)
- व्रत – स्वत:ला लावून – oath
घेतलेला विशिष्ट
धार्मिक नियम,
नेम. - धारण करणे – आचरणे – to apply
- अलगद – हळूवारपणे – softly
- विरघळणे – मिसळून जाणे – dissolve
- खुडणे – तोडणे – to pluck
- मुसाफिर – यात्री – traveller
- कवेत – मिठीत – to embrace
- पानझड – पानगळ – fall
- मरगळ – थकवा – fatigue
- नाद – आवाज – sound
- मंजुळ – गोड – sweet voice
- संथ – हळू – slow
- सळसळ – पानांचा आवाज – rustling
- मुरणे – अंगात भिनणे – absorb
- चिंतन – मनन – meditation
हिरवंगार झाडासारखं वाक्प्रचार
- मुळावर घाव घालणे – नष्ट करणे.
- मुकाट सहन करणे – बिनतक्रार स्वीकारणे.
- पाय रोवणे – तळ जमवणे, पकडून ठेवणे
- मुक्काम ठोकणे
- टक लावून पाहणे – एक सारखे बघणे; निरखणे.
SSC Marathi Textbook Class 10 Solutions भाग-४
- हिरवंगार झाडासारखं Question Answer (कविता)
- बीज पेरले गेले Question Answer
- खरा नागरिक Question Answer
- स्वप्न करू साकार Question Answer (कविता)
- व्युत्पत्ती कोश Question Answer (स्थूलवाचन)