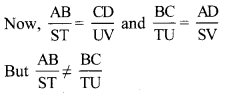Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 9 Maths Solutions covers the Problem Set 3 Geometry 9th Class Maths Part 2 Answers Solutions Chapter 3 Triangles.
9th Standard Maths 2 Problem Set 3 Chapter 3 Triangles Textbook Answers Maharashtra Board
Class 9 Maths Part 2 Problem Set 3 Chapter 3 Triangles Questions With Answers Maharashtra Board
Question 1.
Choose the correct alternative answer for the following questions.
i. If two sides of a triangle are 5 cm and 1.5 cm, the length of its third side cannot be ____.
(A) 3.7 cm
(B) 4.1 cm
(C) 3.8 cm
(D) 3.4 cm
Answer:
Sum of the lengths of two sides of a triangle > length of the third side
Here, 1.5 cm + 3.4 cm = 4.9 cm < 5 cm
∴ Third side ≠ 3.4 cm
(D) 3.4 cm
ii. In ∆PQR, if ∠R > ∠Q, then _____ .
(A) QR > PR
(B) PQ > PR
(C) 3.8 cm
(D) 3.4 cm
Answer:
(B) PQ > PR
iii. In ∆TPQ, if ∠T = 65°, ∠P = 95° , Which of the following is a true statement?
(A) PQ < TP
(B) PQ < TQ
(C) TQ < TP < PQ
(D) PQ < TP < TQ
Answer:
∠Q = 180° – (95° + 65°) = 20°
∴ ∠Q < ∠T < ∠P
∴ PT < PQ < TQ
(B) PQ < TQ
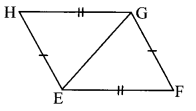
Question 2.
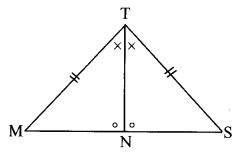
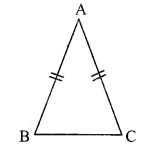
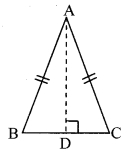
∆ABC is isosceles in which AB = AC. Seg BD and seg CE are medians. Show that BD = CE.
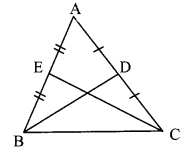
Given: In isosceles ∆ABC, AB = AC. seg BD and seg CE are the medians of ∆ABC.
To prove: BD = CE
Proof: AE = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) AB …..(i) [E is the midpoint of side AB]
AD = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) AC ….(ii) [D is the midpoint of side AC]
Also, AB = AC ……(iii) [Given]
∴ AE = AD ….(iv) [From (i), (ii) and (iii)]
In ∆ADB and ∆AEC,
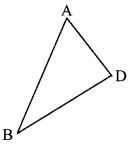
seg AB ≅ seg AC ∠BAD ≅ ∠CAE
seg AD ≅ seg AE
∴ ∆ADB ≅ ∆AEC
∴ seg BD ≅ seg CE
∴ BD = CE
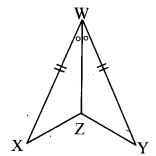
Question 3.
In ∆PQR, if PQ > PR and bisectors of ∠Q and ∠R intersect at S. Show that SQ > SR.
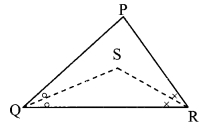
Given: In APQR, PQ > PR and bisectors of ∠Q and ∠R intersect at S.
To prove: SQ > SR
Solution:
Proof:
∠SQR = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) ∠PQR ….(i) [Ray QS bisects ∠PQR]
∠SRQ = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) ∠PRQ ….(ii) [Ray RS bisects ∠PRQ]
In ∆PQR,
PQ > PR [Given]
∴ ∠R > ∠Q [Angle opposite to greater side is greater.]
∴ \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)(∠R) > \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)(∠Q) [Multiplying both sides by \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) ]
∴ ∠SRQ > ∠SQR ….(iii) [From (i) and (ii)]
In ∆SQR,
∠SRQ > ∠SQR [From (iii)]
∴ SQ > SR [Side opposite to greater angle is greater]
Question 4.
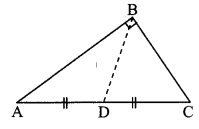
In the adjoining figure, points D and E are on side BC of ∆ABC, such that BD = CE and AD AE. Show that ∆ABD ≅ ∆ACE.
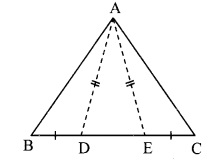
Given: Points D and E are on side BC of ∆ABC,
such that BD = CE and AD = AE.
To prove: ∆ABD ≅ ∆ACE
Proof:
In ∆ADE,
seg AD = seg AE [Given]
∴ ∠AED = ∠ADE …(i) [Isosceles triangle theorem]
Now, ∠ADE + ∠ADB = 180° …(ii) [Angles in a linear pair]
∴ ∠AED + ∠AEC = 180° ….(iii) [Angles in a linear pair]
∴ ∠ADE + ∠ADB = ∠AED + ∠AEC [From (ii) and (iii)]
∴ ∠ADE + ∠ADB = ∠ADE + ∠AEC [From (i)]
∴ ∠ADB = ∠AEC ….(iv) [Eliminating ∠ADE from both sides]
In ∆ABD and ∆ACE,
seg BD ≅ seg CE [Given]
∠ADB = ∠AEC [From (iv)]
seg AD ≅ seg AE [Given]
∴ ∆ABD ≅ ∆ACE [SAS test]
Question 5.
In the adjoining figure, point S is any point on side QR of ∆PQR. Prove that: PQ + QR + RP > 2PS
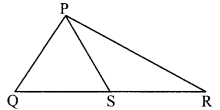
Proof:
In ∆PQS,
PQ + QS > PS …..(i) [Sum of any two sides of a triangle is greater than the third side]
Similarly, in ∆PSR,
PR + SR > PS …(ii) [Sum of any two sides of a triangle is greater than the third side]
∴ PQ + QS + PR + SR > PS + PS
∴ PQ + QS + SR + PR > 2PS
∴ PQ + QR + PR > 2PS [Q-S-R]
Question 6.
In the adjoining figure, bisector of ∠B AC intersects side BC at point D. Prove that AB > BD.
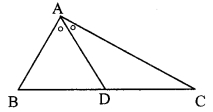
Given: Bisector of ∠BAC intersects side BC at point D.
To prove: AB > BD
Solution:
Proof:
∠BAD ≅ ∠DAC ….(i) [Seg AD bisects ∠BAC]
∠ADB is the exterior angle of ∆ADC.
∴ ∠ADB > ∠DAC ….(ii) [Property of exterior angle]
∴ ∠ADB > ∠BAD ….(iii) [From (i) and (ii)]
In AABD,
∠ADB > ∠BAD [From (iii)]
∴ AB > BD [Side opposite to greater angle is greater]
Question 7.
In the adjoining figure, seg PT is the bisector of ∠QPR. A line through R intersects ray QP at point S. Prove that PS = PR.
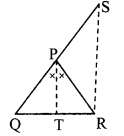
Given: Seg PT is the bisector of ∠QPR.
To prove: PS = PR
Construction: Draw seg SR || seg PT.
Solution:
Proof:
seg PT is the bisector of ∠QPR. [Given]
∴ ∠QPT = ∠RPT ….(i)
seg PT || seg SR [Construction]
and seg QS is their transversal.
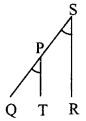
∴ ∠QPT = ∠PSR …(ii) [Corresponding angles]
seg PT || seg SR [Construction]
and seg PR is their transversal.
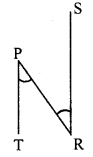
∴ ∠RPT = ∠PRS …..(iii) [Alternate angles]
∴ ∠PRS = ∠PSR …(iv) [From (i), (ii) and (iii)]
In ∆PSR,
∠PRS = ∠PSR [From (iv)]
∴ PS = PR [Converse of isosceles triangle theorem]
Question 8.
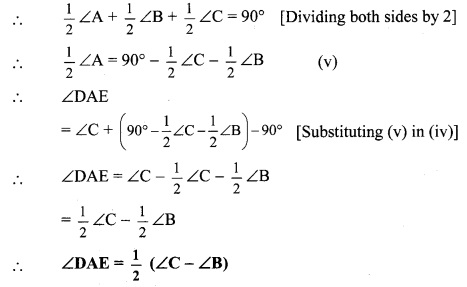
In the adjoining figure, seg AD ⊥ seg BC. Seg AE is the bisector of ∠CAB and B – E – C. Prove that ∠DAE = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) (∠c – ∠B).
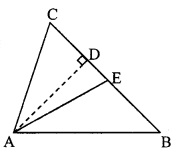
Given: seg AD ⊥ seg BC
seg AE is the bisector of ∠CAB.
To prove: ∠DAE = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) (∠C – ∠B) [∵ AD ⊥ BC]
∴ ∠DAE = 180° – 90° – ∠AED
∴ ∠DAE = 90° – ∠AED ….(ii)
Proof:
∴ ∠CAE = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)∠A ….(i) [seg AE is the bisector of ∠CAB]
In ∆DAE,
∠DAE + ∠ADE + ∠AED = 180° [Sum of the measures of the angles of a triangle is 180°]
∴ ∠DAE + 90° + ∠AED = 180° [∵ AD ⊥ BC]
∴ ∠DAE = 180° – 90° – ∠AED
∴ ∠DAE = 90° – ∠AED ….(ii)
In ∆ACE,
∴ ∠ACE + ∠CAE + ∠AEC = 180° [Sum of the measures of the angles of a triangle is 180°]
∠C + -∠A + ∠AED = 180° [From (i) and C-D-E]
∴ ∠AED = 180° – ∠C – \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)∠A ……(iii)
∴ ∠DAE = 90° – 180°- ∠C+ \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) ∠A [Substituting (iii) in (ii)]
∴ ∠DAE = ∠C + \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)∠A – 90° …..(iv)
In ∆ABC,
∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 180°
Maharashtra Board Class 9 Maths Chapter 3 Triangles Problem Set 3 Intext Questions and Activities
Question 1.
Draw a triangle of any measure on a thick paper. Take a point T on ray QR as shown in the figure given below. Cut two pieces of thick paper which will exactly fit the comers of ∠P and ∠Q. See that the same two jpieces fit exactly at the comer of ∠PRT as shown in the figure. (Textbook pg. no. 24)
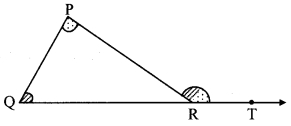
Question 2.
Check the congruence of triangles.
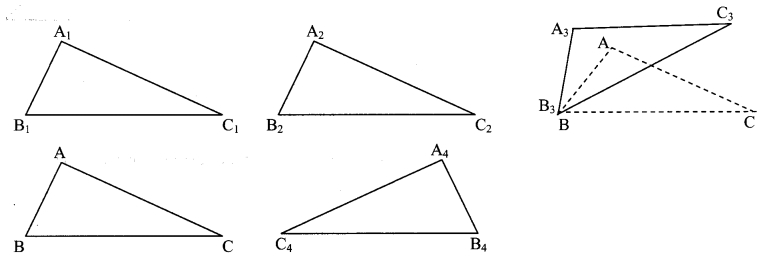
Draw ∆ABC of any measure on a card-sheet and cut it out. Place it on a card-sheet. Make a copy of it by drawing its border. Name it as ∆A1B1C1. Now slide the ∆ABC which is the cut out of a triangle to some distance and make one more copy of it. Name it ∆A2B2C2. Then rotate the cut out of triangle ABC a little, as shown in the figure, and make another copy of it. Name the copy as ∆A3B3C3 . Then flip the triangle ABC, place it on another card-sheet and make a new copy of it. Name this copy as ∆A4B4C4 . Have you noticed that each of ∆A1B1C1, ∆A2B2C2, ∆A3B3C3 and ∆A4B4C4 is congruent with ∆ABC ? Because each of them fits exactly with ∆ABC. Let us verify for ∆A3B3C3. If we place ∠A upon ∠A3, ∠B upon ∠B3 and ∠C upon ∠C3, then only they will fit each other and we can say that ∆ABC = ∆A3B3C3. We also have AB = A3B3, BC = B3C3, CA = C3A3 . Note that, while examining the congruence of two triangles, we have to write their angles and sides in a specific order, that is with a specific one-to-one correspondence. If ∆ABC ≅ ∆PQR, then we get the following six equations:
∠A = ∠P, ∠B = ∠Q, ∠C = ∠R ……..(i)
and AB = PQ, BC = QR, CA = RP …….(ii)
This means, with a one-to-one correspondence between the angles and the sides of two triangles, we get hree pairs of congruent angles and three pairs of congruent sides. (Textbook pg. no. 29)
Question 3.
Every student in the group should draw a right angled triangle, one of the angles measuring 30°. The choice of lengths of sides should be their own. Each one should measure the length of the hypotenuse and the length of the side opposite to 30° angle.
One of the students in the group should fill in the following table.
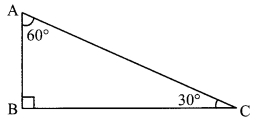
Did you notice any property of sides of right angled triangle with one of the angles measuring 30°? (Textbook pg. no. 34)
Answer:
We observe that the length of the side opposite to 30° is half the length of the hypotenuse.
Question 4.
The measures of angles of a set square in your compass box are 30°, 60° and 90°. Verify the property of the sides of the set square. (Textbook pg. no. 34)
[Students should attempt the above activity on their own.]
Question 5.
Draw a triangle ABC. Draw medians AD, BE and CF of the triangle. Let their point of concurrence be G, which is called the centroid of the triangle. Compare the lengths of AG and GD with a divider. Verify that the length of AG is twice the length of GD. Similarly, verify that the length of BG is twice the length of GE and the length of CG is twice the length of GF. Name the property of medians of a triangle observed here. (Textbook pg. no. 37)
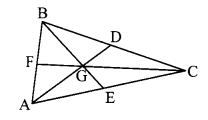
Answer:
The point of concurrence of medians of the triangle divides each median in the ratio 2 : 1.
Question 6.
Draw a triangle ABC on a cardboard. Draw its medians and denote their point of concurrence as G. Cut out the triangle. Now take a pencil. Try to balance the triangle on the flat tip of the pencil. The triangle is balanced only when the point G is on the flat tip of the pencil. This activity shows an important property of the centroid (point of concurrence of the medians) of the triangle. Point it out. (Textbook pg. no. 37)
Answer:
The centroid of the triangle is the triangle’s centre of gravity. Hence, the triangle in the experiment remains balanced.
Question 7.
Take a photograph on a mobile or a computer. Recall what you do to reduce it or to enlarge it. Also recall what you do to see a part of the photograph in detail. (Textbook pg. no, 45 )
Question 8.
On a card-sheet, draw a triangle of sides 4 cm, 3 cm and 2 cm. Cut it out. Make 13 more copies of the triangle and cut them out from the card sheet. Note that all these triangular pieces are congruent. Arrange them as shown in the following figure and make three triangles out of them.
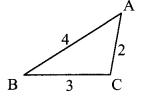
Number of triangle: 1

Number of triangles: 4
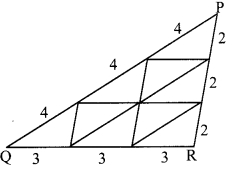
Number of triangles: 9
∆ABC and ∆DEF are similar in the correspondence ABC ↔ DEF.
∠A ≅ ∠D, ∠B ≅ ∠E, ∠C ≅ ∠F
and \(\frac{\mathrm{AB}}{\mathrm{DE}}=\frac{4}{8}=\frac{1}{2} ; \frac{\mathrm{BC}}{\mathrm{EF}}=\frac{3}{6}=\frac{1}{2} ; \frac{\mathrm{AC}}{\mathrm{DF}}=\frac{2}{4}=\frac{1}{2}\) …the corresponding sides are in proportion.
Similarly, consider ∆DEF and ∆PQR. Are their angles congruent and sides proportional in the correspondence DEF ↔ PQR? (Textbook pg. no. 45)
Answer:
Yes.
∠D ≅ ∠P, ∠E ≅ ∠Q, ∠F ≅ ∠R
\(\frac{\mathrm{DE}}{\mathrm{PQ}}=\frac{8}{12}=\frac{2}{3} ; \frac{\mathrm{EF}}{\mathrm{QR}}=\frac{6}{9}=\frac{2}{3} ; \frac{\mathrm{DF}}{\mathrm{PR}}=\frac{4}{6}=\frac{2}{3}\)
Question 9.
Draw a triangle ∆A1B1C1 on a card-sheet and cut it out. Measure ∠A1, ∠B1, ∠C1 Draw two more triangles AA2B2C2 and AA3B3C3 such that
∠A1 = ∠A2 = ∠A3, ∠B1 = ∠B2 = ∠B3, ∠C1 = ∠c2 = ∠c3
and B1C1 > B2C2 > B3C3. Now cut these two triangles also. Measure the lengths of the three triangles. Arrange the triangles in two ways as shown in the figure.
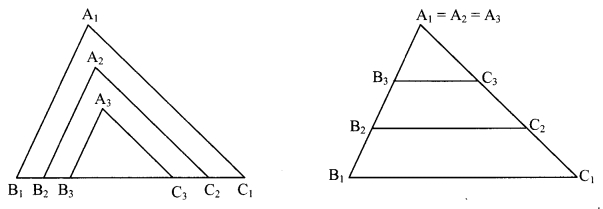
Check the ratios \(\frac{A_{1} B_{1}}{A_{2} B_{2}}, \frac{B_{1} C_{1}}{B_{2} C_{2}}, \frac{A_{1} C_{1}}{A_{2} C_{2}}\). You will notice that the ratios are equal.
Similarly, see whether the ratios \(\frac{A_{1} C_{1}}{A_{3} C_{3}}, \frac{B_{1} C_{1}}{B_{3} C_{3}}, \frac{A_{1} B_{1}}{A_{3} B_{3}}\) are equal. What do you observe? (Texthook pg. no. 46)
Answer:
From the activity we observe that, when corresponding angles of two triangles are equal, the ratios of their corresponding sides are also equal i.e., their corresponding sides are in the same proportion.
Question 10.
Prepare a map of road surrounding your school or home, upto a distance of about 500 metre. How will you measure the distance between two spots on a road? While walking, count how many steps cover a distance of about two metre. Suppose, your three steps cover a distance of 2 metre. Considering this proportion 90 steps means 60 metre. In this way you can judge the distances between different spots on roads and also the lengths of roads. You have to judge the measures of angles also where two roads meet each other. Choosing a proper scale for lengths of roads, prepare a map. Try to show shops, buildings, bus stops, rickshaw stand etc. in the map. (Textbook pg. no. 48)
Class 9 Maths Digest