Std 5 Marathi Lesson 13 अनुभव – १ Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 5 Marathi Solutions Sulabhbharati Chapter 13 अनुभव – १ Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
5th Std Marathi Poem Anubhav 1 Question Answer
5th Standard Marathi Digest Chapter 13 अनुभव – १ Textbook Questions and Answers
1. एका वाक्यात उत्तरे लिहा.
प्रश्न (अ)
मारियाच्या घराला कुलूप का होते?
उत्तर:
मारियाचे आईबाबा लग्नाला गेले होते, म्हणून तिच्या दाराला कुलूप होते.
![]()
प्रश्न (आ)
मारियाने दारे, खिडक्या का बंद केल्या?
उत्तर:
ढगांच्या गडगडाटासह व विजांच्या कडकडाटासह धोधो पाऊस कोसळू लागला, म्हणून मारियाने दारे, खिडक्या बंद केल्या.
प्रश्न (इ)
पानांआड लपलेले पक्षी केव्हा बाहेर आले?
उत्तर:
पाऊस कमी झाल्यावर पानांआड लपलेले पक्षी बाहेर आले.
प्रश्न (ई)
मारिया आईला का बिलगली?
उत्तर:
आईची वाट पाहत मारिया कंटाळलेली होती, म्हणून आईला पाहाताक्षणीच मारिया आईला बिलगली.
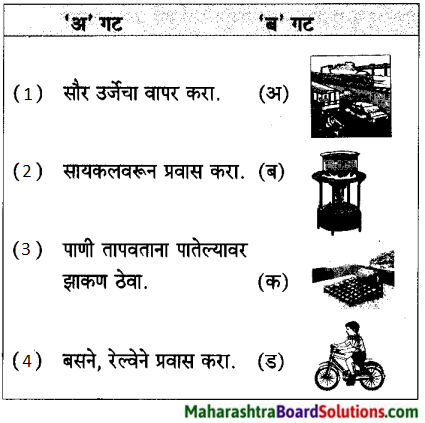
2. जोड्या जुळवा.
प्रश्न 1.
जोड्या जुळवा.
| ‘अ गट’ | ‘ब गट |
| 1. ढगांचा | (अ) खळखळाट |
| 2. विजांचा | (ब) फडफडाट |
| 3. पाण्याचा | (क) गडगडाट |
| 4. पंखांचा | (ड) कडकडाट |
उत्तर:
| ‘अ गट’ | ‘ब गट |
| 1. ढगांचा | (क) गडगडाट |
| 2. विजांचा | (ड) कडकडाट |
| 3. पाण्याचा | (अ) खळखळाट |
| 4. पंखांचा | (ब) फडफडाट |
![]()
3. वाचा. सांगा. लिहा.
प्रश्न 1.
वाचा. सांगा. लिहा.
(अ) शब्दांची पुनरावृत्ती झालेले शब्द. उदा., धाड्धाड्.
(आ) नादमय शब्द. उदा., कडकडाट, गडगडाट. यांसारखे तुम्हांला माहीत असलेले शब्द सांगा.
4. खालील शब्द वाचा व पाहून तसेच लिहा.
प्रश्न 1.
खालील शब्द वाचा व पाहून तसेच लिहा.
(अ) घड्याळ
(आ) खिडक्या
(इ) हळूहळू
(ई) गुणगुणू
(उ) रिमझिम
(ऊ) खळखळाट
उत्तर:
(अ) दार
(आ) खिडकी
5. रिकाम्या जागी विरुद्धार्थी शब्द लिहून वाक्ये पूर्ण लिहा.
प्रश्न (अ)
पाऊस सुरू झाला.
उत्तर:
पाऊस बंद झाला.
प्रश्न (आ)
मारिया सावकाश दाराकडे गेली.
उत्तर:
मारिया भरभर दाराकडे गेली.
![]()
6. खालील शब्दांचे विरुद्धार्थी शब्द लिहा.
प्रश्न 1.
खालील शब्दांचे विरुद्धार्थी शब्द लिहा.
(अ) चढणे ×
(आ) आठवणे ×
(इ) उंच ×
(ई) बाहेर ×
(उ) स्वच्छ ×
(ऊ) थांबणे ×
उत्तर:
(अ) उतरणे
(आ) विसरणे
(इ) ठेंगणे
(ई) आत
(उ) अस्वच्छ
(ऊ) चालणे
7. पावसाळ्यातील तुमचा अनुभव सांगा.
8. पावसाळ्यात तुम्ही आरोग्याविषयी कोणती काळजी घ्याल?
9. खाली दोन प्रकारचे शब्दसमूह दिलेले आहेत, ते वाचा. कोणत्या शब्दसमूहांचा अर्थ कळतो व कोणत्या शब्दांवरून कळतो ते समजून घ्या.
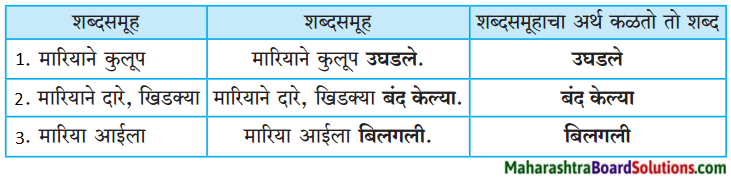
मागील तक्त्यातील दुसऱ्या शब्दसमूहांत कोणती क्रिया झाली हे दाखवणारे शब्द दिले आहेत. उदा., उघडले, बंद केल्या, बिलगली. क्रिया सांगणाऱ्या या शब्दांमुळे वाक्यांचा अर्थ कळतो. या शब्दांना क्रियापद म्हणतात.
10. खालील शब्दसमूह वाचून त्यातील क्रियापदे ओळखा.
प्रश्न 1.
खालील शब्दसमूह वाचून त्यातील क्रियापदे ओळखा.
(अ) पक्षी बाहेर आले.
(आ) मारियाने आकाशाकडे पाहिले.
(इ) दारावरची बेल वाजली.
(ई) मारिया पळत दाराकडे गेली.
(उ) तिने गणवेश बदलला.
उत्तर:
(अ) आले
(आ) पाहिले
(इ) वाजली
(ई) गेली
(उ) बदलला
![]()
11. क्रियापदे घालून वाक्ये पूर्ण करा.
प्रश्न 1.
क्रियापदे घालून वाक्ये पूर्ण करा.
(अ) मारिया घरी ……………..
(आ) मारिया कविता गुणगुणू …………………..
(इ) मी चेंडू ……………………
(ई) ताई पुस्तक ………………….
(उ) मारियाने दार ………………..
उत्तरः
(अ) आली
(आ) लागली
(इ) टाकला
(ई) वाचते
(उ) उघडले
12. खालील शब्द वाचा, त्या शब्दांत आलेली ‘र’ ची रूपे शोधा. शिक्षकांच्या मदतीने समजून घ्या.
प्रश्न 1.
खालील शब्द वाचा, त्या शब्दांत आलेली ‘र’ ची रूपे शोधा. शिक्षकांच्या मदतीने समजून घ्या.
उत्तरः
(अ) सूर्य = स + ऊ + र्रय
(आ) पर्वत = प + र् + व + त
(इ) चंद्र- च + न + द + र् – (र)
(ई) समुद्र = स + म + उ + द् + र्
(उ) कैऱ्या = क + अ + र् + य + आ
(ऊ) पऱ्या = प + र् + या
(ए) प्राणी = प + र् + आ + ण + ई (र)
(ऐ) प्रकाश = प + र् + क + आ + श
(ओ) महाराष्ट्र = म + ह + आ + र + आ + ष + ट् + र् (र)
(औ) ट्रक = ट + र् + क
उपक्रम:
पावसाबरोबर आलेले शब्द वाचा. त्या शब्दांचा उपयोग करून वाक्ये सांगा.
उदा., पावसाची बुरबुर सुरू झाली.

Marathi Sulabhbharati Class 5 Solutions Chapter 13 अनुभव – १ Additional Important Questions and Answers
1. एका वाक्यात उत्तरे लिहा.
प्रश्न 1.
उन्हाने ग्रासल्यावर सगळेजण आतुरतेने कशाची वाट पाहतात?
उत्तर:
उन्होने ग्रासल्यावर सगळेजण पावसाची आतुरतेने वाट पाहतात.
![]()
प्रश्न 2.
मारियाने दुपारी शाळेतून घरी आल्यावर काय केले?
उत्तर:
मारियाने दुपारी शाळेतून आल्यावर खिडक्या उघडल्या, गणवेश बदलला व हातपाय धुतले.
प्रश्न 3.
मारियाचे आई, बाबा कुठे गेले होते?
उत्तर:
मारियाचे आई, बाबा लग्नाला गेले होते.
प्रश्न 4.
खुर्चीत बसल्या बसल्या मारियाला काय आठवू लागले?
उत्तर:
खुर्चीत बसल्या बसल्या मारियाला पावसाच्या कविता आठवू लागल्या.
प्रश्न 5.
पानांआड बसलेले पक्षी बाहेर येऊन काय करू लागले?
उत्तर:
पानांआड बसलेले पक्षी बाहेर येऊन पंखांची फडफड करू लागले.
प्रश्न 6.
सगळीकडे कसे वातावरण होते?
उत्तरः
सगळीकडे स्वच्छ, सुंदर वातावरण होते.
प्रश्न 7.
आईने कुणाला जवळ घेतले?
उत्तर:
आईने मारियाला जवळ घेतले.
![]()
प्रश्न 8.
मारियाचे लक्ष कुठे गेले?
उत्तर:
मारियाचे लक्ष घड्याळाकडे गेले.
प्रश्न 9.
कुणाला पाहून मारियाला आनंद झाला?
उत्तर:
आईला पाहून मारियाला आनंद झाला.
थोडक्यात उत्तरे लिहा.
प्रश्न 1.
पाऊस पडण्याआधी वातावरणात कोणते बदल होतात?
उत्तर:
थंडगार वारा वाहू लागतो, आभाळात काळ्या ढगांची गर्दी होते, ढगांचा गडगडाट व विजांचा कडकडाट सुरू होतो, पाऊस पडण्याआधी वातावरणात हे बदल होतात.
प्रश्न 2.
तुम्ही कधी तुमच्या घराच्या खिडकीतून पावसाळ्यातील वातावरणाचा अनुभव घेतला आहे का?
उत्तर:
हो, आम्ही पहिल्या पावसाची चातकासारखी वाट पाहत असतो; त्यावेळी मातीचा धुरळा उडतो. वातावरणात थंडपणा येतो. लहान लहान पाखरे हवेत फिरू लागतात. काळ्या ढगांची गर्दी होते. गडगडाट व वीजांसह पावसाचे आगमन होते. मातीचा सुवास मन प्रसन्न करतो.
प्रश्न 3.
पावसाळ्यात तुम्ही आरोग्याविषयी कोणती काळजी घेता?
उत्तर:
1. पावसाळ्यात आम्ही पाणी उकळून पितो.
2. पावसाळ्यात पावसात भिजू नये यासाठी छत्री किंवा रेनकोटचा वापर करतो.
3. पावसाळ्यात शक्यतोवर बाहेर अन्नपदार्थ खाणे टाळतो.
प्रश्न 4.
पावसाबरोबर आलेले शब्द वाचा. त्या शब्दांचा उपयोग करून वाक्ये सांगा.
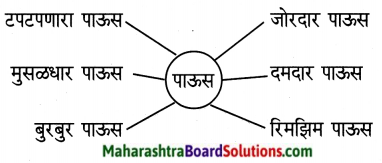
उत्तर:
- पानावर टपटपणाऱ्या पावसाचा आवाज येत होता.
- काल रात्रीपासूनच मुसळधार पावसाला सुरुवात झाली.
- पावसाची बुरबुर सुरू झाली.
- जोरदार पावसाने शेतकरीवर्ग खूश झाला.
- तलाव क्षेत्रात दमदार पाऊस झाला.
- दिवसभर रिमझिम पाऊस पडत होता.
![]()
व्याकरण व भाषाभ्यास:
अधोरेखित शब्दांचे विरुद्धार्थी शब्द लिहून वाक्य पुन्हा लिहा.
प्रश्न 1.
राम स्वच्छ कपडे घालतो.
उत्तर:
राम घाणेरडे कपडे घालतो.
प्रश्न 2.
गणपत झाडावर चढला.
उत्तर:
गणपत झाडावरून उतरला.
प्रश्न 3.
शिक्षकांनी प्रश्न विचारले.
उत्तर:
शिक्षकांनी उत्तर विचारले.
प्रश्न 4.
मुले अंधारात खेळत होती.
उत्तर:
मुले उजेडात खेळत होती.
प्रश्न 5.
पूर्वी लोकांनी गरिबीत दिवस काढले.
उत्तर:
पूर्वी लोकांनी श्रीमंतीत दिवस काढले.
![]()
शब्द शुद्ध करून लिहा.
प्रश्न 1.
शब्द शुद्ध करून लिहा.
- दूपार
- कुलुप
- पाणि
- सवच्छ
- गरदी
- उशिर
- सूंदर
- उन
- वीज
- पशी
उत्तर:
- दुपार
- कुलूप
- पाणी
- स्वच्छ
- गर्दी
- उशीर
- सुंदर
- ऊन
- विज
- पक्षी
प्रश्न 2.
वचन बदला.
- घर
- कुलूप
- दारे
- झाड
- पान
- पंख
- कविता
उत्तर:
- घरे
- कुलुपे
- घड्याळे
- झाडे
- पाने
- पंख
प्रश्न 3.
लिंग बदला.
- आई
- पक्षी
- मुलगी
उत्तरः
- बाबा
- पक्षिण
- मुलगा
![]()
प्रश्न 4.
समानार्थी शब्द लिहा.
- दुपार
- खिडकी
- दार
- लग्न
- उशीर
- जवळ
- आवाज
- पाऊस
- पाणी
- पंख
- पान
- ऊन
- पान
उत्तर:
- मध्यान्ह
- गवाक्ष
- दरवाजा
- विवाह
- विलंब
- निकट
- ध्वनी
- वर्षा
- जल, नीर
- पर
- पर्ण
- सूर्यप्रकाश
- पर्ण
प्रश्न 5.
विरुद्धार्थी शब्द लिहा.
- उघड
- लक्ष
- कमी
- उशीर
- ऊन
- कंटाळा
- विचार
- स्वच्छ
उत्तर:
- बंद
- दुर्लक्ष
- जास्त
- लवकर
- सावली
- उत्साह
- अविचार
- अस्वच्छ
![]()
प्रश्न 6.
क्रियापदे घालून वाक्ये पूर्ण करा.
- गणेश शाळेत ………………..
- आम्ही अभ्यास ………………..
- उदया ते सहलीला ………………..
- गाडी 5 वाजता …………………….
- पाऊस पडू …………………….
उत्तरः
- गेला
- करतो
- जातील
- येईल
- लागला
अनुभव – १ Summary in Marathi
पदयपरिचय:
‘अनुभव’ या पाठात मारिया या लहान मुलीने घेतलेला पावसाळ्याचा अनुभव वर्णन केला आहे. एकटेपणा व निसर्गाचा लहरीपणा, सौंदर्य हे सारे घटक या पाठात आले आहेत.
![]()
शब्दार्थ:
- दुपारी – मध्यान्ह (afternoon)
- कुलूप – दरवाजा बंद करण्याचे साधन (a lock)
- गणवेश – शाळेत घालण्याचा पोशाख (uniform)
- वारा – समीर (wind)
- गडगडाट – मेघगर्जना (thundering)
- उशीर – वेळाने (late)
- रिमझिम – पावसाच्या सतत पडणाऱ्या सरी (drizzling)
- लख्ख उन – (bright sunlight)
- बिलगणे – चिकटणे, खेटणे (to cling too closely)
- गुणगुणणे – हलक्या आवाजात गाणे (to huma tune)
- पंख – पर (wings)
- धो धो पाऊस – (heavy rain)
5th Standard Marathi Digest Pdf Download
- नाच रे मोरा Class 5 Marathi Question Answer
- हत्तीचे चातुर्य Class 5 Marathi Question Answer
- खेळूया शब्दांशी Class 5 Marathi Question Answer
- हि पिसे कोणाची ? Class 5 Marathi Question Answer
- डराव डराव Class 5 Marathi Question Answer
- ऐकुया खेळूया Class 5 Marathi Question Answer
- खेळत खेळत वाचुया! Class 5 Marathi Question Answer
- कोणापासून काय घ्यावे? Class 5 Marathi Question Answer
- सिंह आणि बेडूक Class 5 Marathi Question Answer
- बैलपोळा Class 5 Marathi Question Answer
- इंधनबचत Class 5 Marathi Question Answer
- बोलावे कसे? Class 5 Marathi Question Answer
- अनुभव-१ Class 5 Marathi Question Answer
- चित्रसंदेश Class 5 Marathi Question Answer
 उत्तरः
उत्तरः