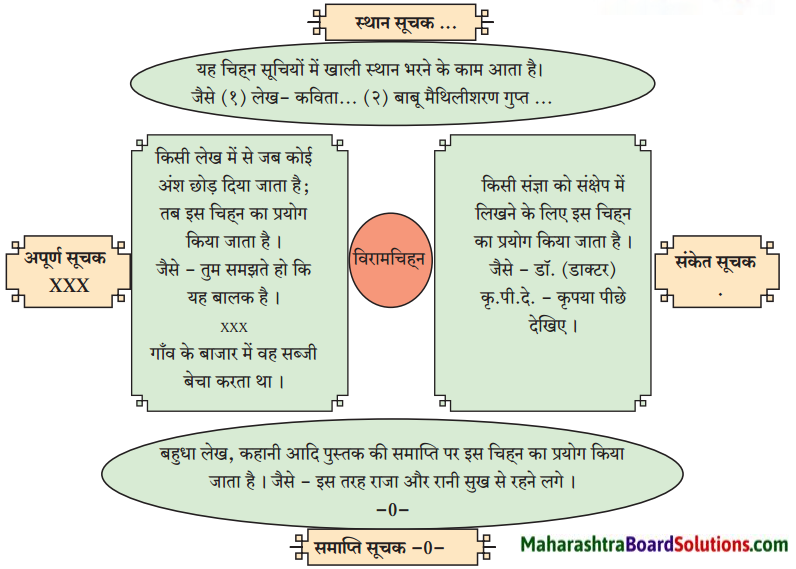
Std 9 Hindi Chapter 3 Inaam Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 9 Hindi Solutions Lokbharti Chapter 3 इनाम Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Hindi Lokbharti 9th Digest Chapter 3 इनाम Questions And Answers
Hindi Lokbharti 9th Std Digest Chapter 3 इनाम Textbook Questions and Answers
मौलिक सृजन :
प्रश्न 1.
“प्राकृतिक संसाधन मानव के लिए वरदान।’ इस विषय पर स्वमत लिखिए।
उत्तरः
सच ही कहा गया है कि प्राकृतिक संसाधन मानव के लिए वरदान होता है। सूर्य की रोशनी, हवा, मिट्टी, पानी, लकड़ी, तेल, कोयला, जीवश्म, ईधन, खनिज, वनस्पति और अन्य पदार्थ प्राकृतिक संसाधन होते हैं क्योंकि ये सन्न प्रकृति द्वारा इसान को उपहार के रूप में मिले हैं। ये प्रकृति में प्राकृतिक रूप में पाए जाते हैं। इन्हें मनुष्य द्वारा निर्मित नहीं किया जा सकता। मानव सभ्यता, शहरीकरण, तकनीकीकरण, औद्योगिकीकरण के लिए इन संसाधनों का इस्तेमाल करता है।
इंसान की मूलभूत आवश्यकताओं को पूरा करने का कार्य प्राकृतिक संसाधन करते हैं। इनके कारण ही आज मनुष्य प्रगति कर सका है। इंसान के जीवन को खुशहाल एवं समृद्ध करने में प्राकृतिक संसाधन सहायता करते हैं। इनके कारण ही इस धरती पर जीवन संभव हुआ है। अत: प्राकृतिक संसाधन मानव के लिए वरदान हैं।
![]()
आसपास :
प्रश्न 1.
आपके गाँव-शहर को जहाँ से बिजली आपूर्ति होती है, उस केंद्र के बारे में जानकारी प्राप्त करके टिप्पणी तैयार कीजिए।
संभाषणीय :
प्रश्न 1.
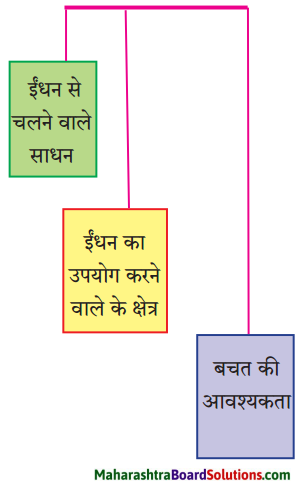
‘ईधन की बचत, समय की माँग है।’ इस विषय पर अपना मत व्यक्त कीजिए।
उत्तरः
सचमुच आज के इस तकनीकी युग में ईधन की बचत समय की माँग हो गई है। यदि हमने आने वाले समय में ईंधन की बचत नहीं की तो हमें बहुत बड़ी समस्या का सामना करना पड़ेगा। हमारे देश में ईंधन की सौमित मात्रा ही उपलब्ध है। अत: मानव का दायित्व है कि वह उसकी बचत करे। ईंधन की बचत करने के लिए हमें पब्लिक बस या रेल से सफर करना चाहिए। अपनी गाड़ियों को व्यर्थ में चालू करके नहीं छोड़ना चाहिए। हमें छोटी दूरी के लिए साइकिल का इस्तेमाल करना चाहिए। अगर हम ईंधन की बचत करेंगे; तो वह आगे आने वाले पीढ़ी को उपलब्ध हो सकेगा। ईधन की बचत करने से हम पर्यावरण को भी दूषित होने से बचा सकते हैं।
![]()
लेखनीय :
प्रश्न 1.
समुद्री लहरों से विद्युत निर्मिति के बारे में टिप्पणी तैयार कीजिए। संदर्भ यू ट्यूब से लीजिए।
उत्तरः
समुद्री लहरों से विद्युत की निर्मिति की जाती है। इसे ‘जलविद्युत ऊर्जा’ कहते हैं। समुद्र की लहरें ऊर्जा का एक प्रमुख स्रोत है। भारत एक उष्ण कटिबंधीय देश है। इसी कारण सतह के पानी व गहरे समुद्र के बीच तापमान में लगातार भिन्नता रहती है। इसका फायदा ऊर्जा निर्माण करने के लिए किया जाता है। समुद्री धाराओं में बड़े पैमाने पर फ्लोटिंग विलवणीकरण संयंत्र का कार्यान्वयन किया जा रहा है जिस कारण जलविद्युत ऊर्जा की निर्मिती हो रही है।
पठनीय :
प्रश्न 1.
दैनंदिन जीवन में उपयोग में लाए जाने वाले विविध उपकरणों के आविष्कारकों और उनके कार्यो की जानकारी प्राप्त करके पढ़िए ।
![]()
पाठ के आँगन में :
1. सूचना के अनुसार कृतियाँ पूर्ण कीजिए :
प्रश्न क.
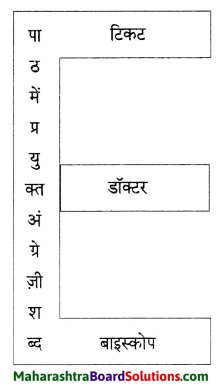
पाठ में आए और हिंदी में प्रयुक्त होने वाले पाँच-पाँच विदेशी एवं संकर शब्दों की सूची।
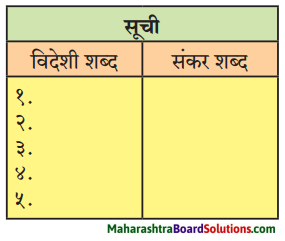
उत्तर:
| विदेशी शब्द | संकर शब्द |
| 1. रेफ्रीजरेटर | मोहल्लेदार |
| 2. टेलीफोन | छायादार |
| 3. एक्सपर्ट | लाठीचार्ज |
| 4. क्यूब | वर्षगाँठ |
| 5. आइसक्रीम | रेलगाडी |
![]()
प्रश्न ख.
वाक्य में कि, की के स्थान को स्पष्ट कीजिए।
‘माँ ने कहा कि बच्चों ने आम की आईसक्रीम तैयार की।’
उत्तर:
कि – समुच्चयबोधक अव्यय
की – संबंधकारक
की – क्रिया
प्रश्न ग.
रेफ्रीजरेटर आने के पूर्व घरवालों के विचार।
उत्तर:
प्रश्न घ.
रेफ्रीजरेटर आने के बाद घर की स्थिति।
उत्तरः
कृति ग (1) का आकलन देखिए।
पाठ से आगे :
प्रश्न 1.
प्रशंसापत्र/पुरस्कार/इनाम के प्रसंग का कक्षा में वर्णन कीजिए।
![]()
भाषा बिंदु :
प्रश्न 1.
दिए गए आकृति के अनुसार रचना की दृष्टि से सरल, संयुक्त, मिश्र अन्य वाक्य पाठ से खोजकर तालिका पूर्ण कीजिए।
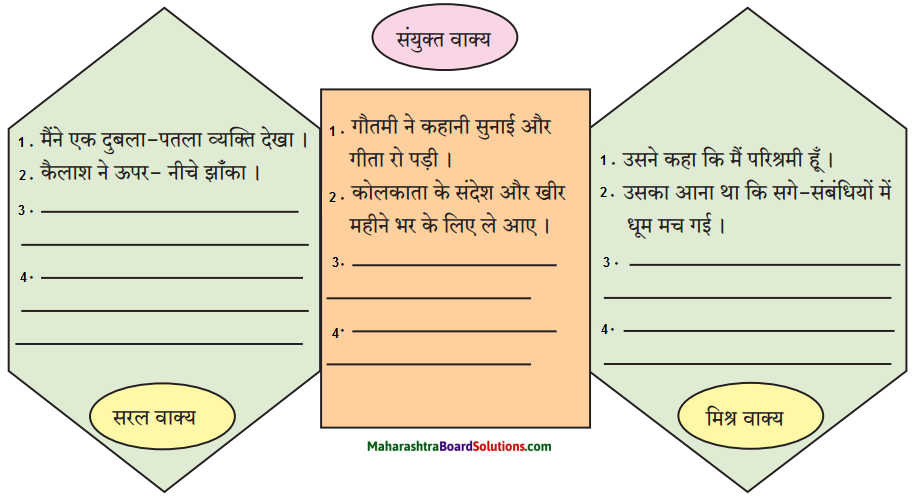
उत्तरः
छात्र स्वयं पाठ में से सरल, संयुक्त एवं मिश्र वाक्य ढूँढ़कर लिखेंगे।
![]()
Hindi Lokbharti 9th Answers Chapter 3 इनाम Additional Important Questions and Answers
(क) परिच्छेद पढ़कर सूचना के अनुसार कृतियाँ कीजिए।
कृति (1) आकलन कृति
प्रश्न 1.
आकृति पूर्ण कीजिए।
उत्तरः
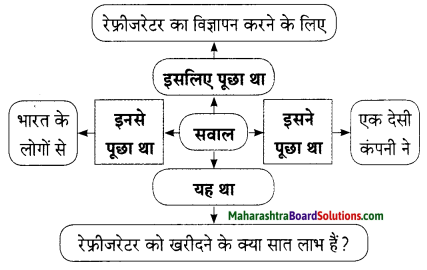
प्रश्न 2.
समझकर लिखिए।
उत्तरः

कृति (2) आकलन कृति
प्रश्न 1.
आकृति पूर्ण कीजिए।
उत्तरः
प्रश्न 2.
किसने, किससे कहा?
i. “तुम तो खयाली पुलाव पका रहे हो।”
उत्तर:
लेखक ने अपनी पत्नी से कहा।
ii. “हमारे टेलीफोन तो तुम ही हो।”
उत्तरः
लेखक की पत्नी ने लेखक से कहा।
प्रश्न 3.
सत्य-असत्य लिखिए।
i. लेखक की पत्नी के अनुसार जिसका उत्तर सबसे अच्छा होगा, उसे इनाम मिलेगा।
ii. रेफ्रीजरेटर के लिए घरेलू पावर की जरूरत होती है।
उत्तर:
i. असत्य
ii. सत्य
![]()
कृति (3) शब्द संपदा
प्रश्न 1.
समानार्थी शब्द लिखिए।
i. प्रतियोगिता
ii. जुगाड़
iii. पत्नी
iv. रात
उत्तर :
i. स्पर्धा
ii. व्यवस्था
iii. भार्या
iv. निशा
प्रश्न 2.
विरुद्धार्थी शब्द लिखिए।
i. दिन × …
ii. देसी × …..
उत्तरः
i. रात
ii. विदेशी
![]()
प्रश्न 3.
वचन बदलिए।
i. लॉटरी
ii. दाम
उत्तर:
i. लॉटरियाँ
ii. दाम
प्रश्न 4.
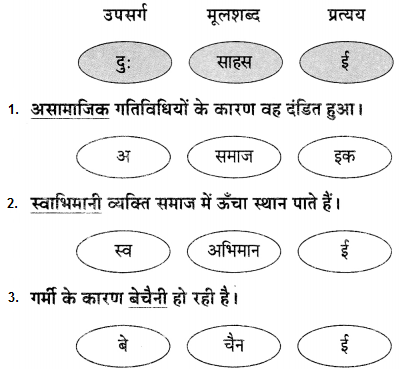
निम्नलिखित शब्दों में प्रयुक्त प्रत्यय पहचानिए।
i. प्रतियोगिता
ii. विदेशी
उत्तर:
i. ‘ता’ प्रत्यय
ii. ‘ई’ प्रत्यय
प्रश्न 5.
निम्नलिखित शब्दों में उचित प्रत्यय लगाकर नए शब्द तैयार कीजिए।
i. अच्छा
ii. भारत
उत्तर:
i. अच्छा + आई – अच्छाई
ii. भारत + ईय – भारतीय
प्रश्न 6.
‘कल्पना में खोए रहना।’ इस अर्थ का गद्यांश में प्रयुक्तं मुहावरा है।
उत्तरः
खयाली पुलाव पकाना।
![]()
कृति (4) स्वमत अभिव्यक्ति
प्रश्न 1.
क्या खयाली पुलाव पकाना अच्छी बात होती है ? इस पर आधारित अपने विचार लिखिए।
उत्तरः
‘खयाली पुलाव पकाना’ यानी कल्पना में खोए रहना। कल्पना में खोए रहना उचित बात नहीं होती है। कल्पना के सहारे जीने से किसी भी प्रकार का लाभ नहीं होता है। इंसान को कल्पना जरूर करनी चाहिए पर उस कल्पना को यथार्थ में लाने का निश्चय भी करना चाहिए। सिर्फ कल्पना करके खयाली पुलाव पकाना यानी कि जीवन की सच्चाई से दूर भागना होता है। अत: स्पष्ट है कि खयाली पुलाव पकाना अच्छी बात नहीं होती है।
(ख) परिच्छेद पढ़कर दी गई सूचना के अनुसार कृतियाँ कीजिए।
कृति (1) आकलन कृति
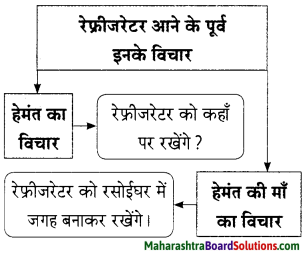
प्रश्न 1.
समझकर लिखिए।
उत्तर:
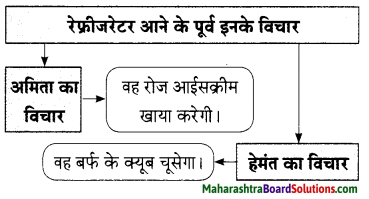
प्रश्न 2.
सही पर्याय चुनकर लिखिए।
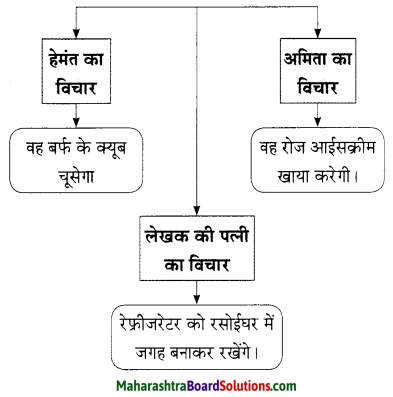
अमिता खिलखिलाई क्योंकि ……………………।
(क) वह रेफ्रीजरेटर में बर्फ जमाएगी।
(ख) वह रेफ्रीजरेटर में रोजाना आइसक्रीम जमाएगी।
(ग) वह रेफ्रीजरेटर से रोजाना ठंडा पानी पीएगी।
उत्तर:
अमिता खिलखिलाई क्योंकि वह रेफ्रीजरेटर में रोजाना आइसक्रीम जमाएगी।
![]()
कृति (2) आकलन कृति
प्रश्न 1.
कृति पूर्ण कीजिए।
उत्तर:
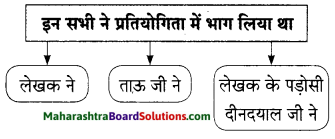
प्रश्न 2.
सहसंबंध लिखिए।
पहले आने वालों के लिए : शिंकजी :: शौकीनों के लिए :
उत्तरः
चाय
प्रश्न 3.
समझकर लिखिए।
उत्तर:
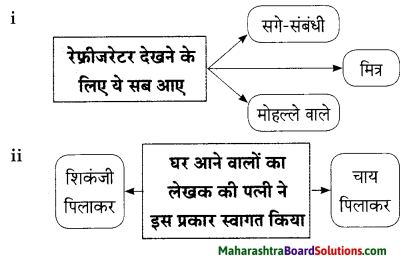
कृति (3) शब्द संपदा
प्रश्न 1.
वचन बदलिए।
- ताली
- बोतलें
- पत्नी
- बहू
उतर:
- तालियाँ
- बोतल
- पत्नियाँ
- बहुएँ
![]()
प्रश्न 2.
लिंग बदलिए।
i. पड़ोसी
ii. बहू
उत्तर:
i. पड़ोसन
ii. बेटा
प्रश्न 3.
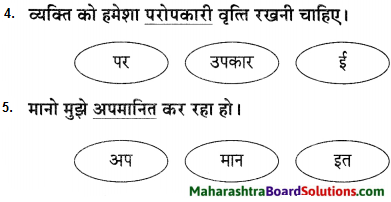
निम्नलिखित शब्दों में उचित उपसर्ग लगाकर नए शब्द तैयार कीजिए।
i. शक
ii. नम
उत्तर:
i. बे + शक – बेशक
ii. वि + नम् = विनम्
प्रश्न 4.
प्रत्यय पहचानिए।
i. खिलखिलाई
ii. रोजाना
iii. भाग्यवान
उत्तर:
i. आई
ii. आना
iii. वान
प्रश्न 5.
समानार्थी शब्द लिखिए।
i. किस्मत
ii. शक
उत्तर:
i. भाग्य
ii. संशय
![]()
प्रश्न 6.
मानक वर्तनी के अनुसार शब्द लिखिए।
i. परबंध
ii. ठण्डा
उत्तर:
i. प्रबंध
ii. ठंडा
कृति (4) स्वमत अभिव्यक्ति
प्रश्न 1.
‘यदि रेफ्रीजरेटर न होते …..’ अपने विचार लिखिए।
उत्तरः
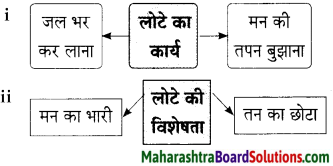
रेफ्रीजरेटर खाद्य पदार्थों को ठंडा बनाए रखता है एवं उन्हें खराब होने से बचाता है। यदि रेफ्रीजरेटर नहीं होते, तो खाद्य पदार्थों को ठंडा बनाए रखने में समस्या निर्माण हो जाती और फिर वे खराब हो जाते। रेफ्रीजरेटर के न होने से इंसान को ठंडा पानी भी पीने के लिए उपलब्ध नहीं होता। आज बाजार में आइसक्रीम के जो फैमिली पैक मिल रहे हैं। वे उपलब्ध नहीं होते। रेफ्रीजरेटर के न होने से आइसक्रीम भी तैयार नहीं हो सकती थी। गर्मियों के दिनों में इंसान की हालत बिगड़ जाती। शरबत व फलों के जूस बहुत दिनों तक नहीं रहते। इस प्रकार रेफ्रीजरेटर नहीं होते, तो इंसानों को बहुत तकलीफ होती थी।
(ग) परिच्छेद पढ़कर सूचना के अनुसार कृतियाँ कीजिए।
कृति (1) आकलन कृति
प्रश्न 1.
समझकर लिखिए।
उत्तरः
प्रश्न 2.
सत्य-असत्य लिखिए।
i. हेमंत के अनुसार देवी की मानता का आशीर्वाद था रेफ्रीजरेटर।
ii. अरुण का रिश्तेदार रेफ्रीजरेटर कंपनी में नौकरी करता है।
उत्तर:
i. असत्य
ii. सत्य
![]()
कृति (2) आकलन कृति
प्रश्न 1.
किसने, किससे कहा?
i. “मैंने फिर दुबारा दिमाग पर जोर नहीं डाला।”
उत्तरः
कुढ़मगज ने लेखक से कहा।
ii. “हमें भी बता दें।”
उत्तर:
पड़ोस की एक महिला ने लेखक से कहा।
प्रश्न 2.
समझकर लिखिए।
उत्तरः
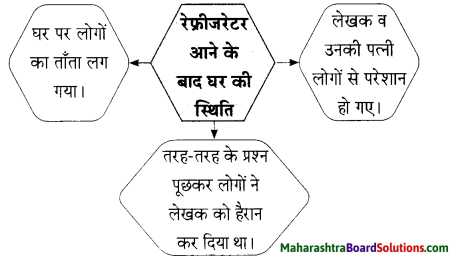
कृति (3) शब्द संपदा
प्रश्न 1.
निम्नलिखित शब्दों के भिन्नार्थक शब्द लिखिए।
i. अरुण
ii. तिरछा
उत्तर:
i. लाल, सूर्य
ii. टेढा, वक्र, बाँका
![]()
प्रश्न 2.
समानार्थी शब्द लिखिए।
- बिजली
- बेटा
- हाथी
उत्तर:
- विदयुत
- पुत्र
- गज, हस्ती
प्रश्न 3.
प्रत्यय पहचानिए।
i. रिश्तेदार
ii. पूलकर
उत्तर:
i. ‘दार’ प्रत्यय
ii. ‘कर’ प्रत्यय
![]()
प्रश्न 4.
‘अनु’ उपसर्ग से निर्मित दो शब्द लिखिए।
उत्तर:
i. अनुबंध
ii. अनुचित
प्रश्न 5.
निम्नलिखित मुहावरे का अर्थ लिखकर उसका वाक्य में प्रयोग कीजिए।
i. जली-कटी सुनाना
उत्तर:
अर्थ : खरी-खोटी सुनाना।
वाक्यः रामू से गलती क्या हो गई, सभी उसे जली-कटी सुनाने लगे।
प्रश्न 6.
निम्नलिखित शब्द मानक वर्तनी के अनुसार लिखिए।
- शककी
- इन्क
- मुफ्त
- काण्टा
उत्तर:
- शक्की
- इंक
- मुफ्त
- काँटा
![]()
कृति (4) स्वमत अभिव्यक्ति
प्रश्न 1.
‘पड़ोसियों की आदत होती है, निंदा करने की!’ क्या आप इस कथन से सहमत हैं? अपने विचार लिखिए।
उत्तर:
संकट की घड़ी में पड़ोसी अपने रिश्तेदारों की अपेक्षा तुरंत सहायता के लिए उपस्थित हो जाते हैं। भले ही यह बात सच हो लेकिन अपने पास में रहने वालों की निंदा करने से भी वे कभी बाज नहीं आते। आप कितनी भी अच्छी तरह से उनके साथ रहें या उनके साथ अच्छा व्यवहार करें; फिर भी वे आपकी निंदा करना नहीं छोड़ेंगे। निंदा करना उनकी आदत होती है।
अपने पड़ोस में रहने वाले किसी व्यक्ति ने नई गाड़ी खरीदी हो या कुछ अन्य नई वस्तु घर पर लाई हो; तो वे जल-भूनकर राख हो जाते हैं और उस व्यक्ति के बारे में भला-बुरा कहने लगते हैं। इसलिए उपर्युक्त वाक्य से मैं सहमत हूँ। (विद्यार्थी अपने व्यक्तिगत विचार स्वतंत्र रूप से भी लिख सकते हैं।)
(घ) परिच्छेद पढ़कर दी गई सूचना के अनुसार कृतियाँ कीजिए।
कृति (1) आकलन कृति
प्रश्न 1.
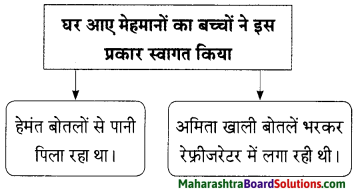
कृति पूर्ण कीजिए।
उत्तर:
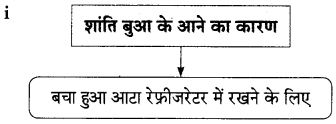

प्रश्न 2.
सहसंबंध लिखिए।
i. शांति बुआ : आटा :: लाला दीनदयाल : ……………
उत्तर:
मिठाई का बोइया
![]()
कृति घ (2): आकलन कृति
प्रश्न 1.
समझकर लिखिए।
उत्तर:
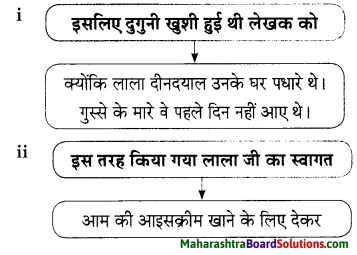
प्रश्न 2.
सही पर्याय चुनकर लिखिए।
i. लाला जी ने आइस्क्रीम नहीं खाई क्योंकि ………….।
(क) उन्हें सर्दी हो जाती है।
(ख) उन्हें बुखार चढ़ जाता है।
(ग) उनके दाँत चीसने लगते हैं।
उत्तर:
(ग) उनके दाँत चीसने लगते हैं।
ii. पत्नी का दिल बाग-बाग हो गया क्योंकि ………….।
(क) शांति बुआ आटे का कटोरा रेफ्रीजरेटर में रखना चाहती थी।
(ख) शांति बुआ बिना बुलाए लेखक के घर आई थी।
(ग) शांति बुआ रेफ्रीजरेटर का ठंडा पानी पीना चाहती थी।
उत्तर:
(क) शांति बुआ आटे का कटोरा रेफ्रीजरेटर में रखना चाहती थी।
कृति (3) शब्द संपदा
प्रश्न 1.
निम्नलिखित शब्दों के अर्थ गद्यांश से ढूँढकर लिखिए।
- प्रसन्नता
- संध्या
- दया
उत्तर:
- खुशी
- शाम
- कृपा
![]()
प्रश्न 2.
लिंग बदलिए।
i. भगवान
ii. लाला
उत्तर:
i. भगवती
ii. ललाइन
प्रश्न 3.
बचन बदलिए।
i. चिंता
ii. तश्तरी
उत्तर:
i. चिंताएँ
ii. तश्तरियाँ
प्रश्न 4.
प्रत्यय पहचानिए।
i. जल्दबाज
उत्तर:
‘बाज’ प्रत्यय
प्रश्न 5.
उपसर्ग लगाकर नए शब्द लिखिए।
i. कृपा
ii. दुआ
उत्तर:
i. अवकृपा
ii. बदुआ
![]()
प्रश्न 6.
मुहावरे का अर्थ लिखकर उसका वाक्य में प्रयोग कीजिए।
i. मिसरी घोलकर बोलना
उत्तरः
अर्थः मीठी-मीठी बातें करना।
वाक्यः रामलाल अपने स्वार्थ हेतु सभी से मिसरी घोलकर बोलते हैं।
(छ) परिच्छेद पड़कर दी गई सूचना के अनुसार कृतियाँ कीजिए।
कृति (1) आकलन कृति
प्रश्न 1.
आकृति पूर्ण कीजिए।
उत्तरः
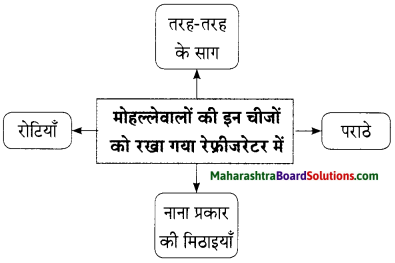
प्रश्न 2.
सहसंबंध लिखिए।
i. लखनऊ : चमनलाल :: कोलकाता : ….
उत्तर:
बनर्जी
कृति (2) आकलन कृति
प्रश्न 1.
गद्यांश के आधार पर ऐसे प्रश्न तैयार कीजिए कि जिनके उत्तर निम्न शब्द हो।
i. सिंधी आलू
ii. स्कूल
उत्तर:
i. कैलाश को क्या अच्छे लगते हैं?
ii. हेमंत-अमिता कहाँ गए थे?
![]()
प्रश्न 2.
सत्य-असत्य लिखिए।
i. सिल्वर क्रीम बनर्जी बाबू ने खाई।
ii. सिंधी आलू लेखक की पत्नी ने बनवाए थे।
उत्तर:
i. असत्य
ii. असत्य
कृति (3) शब्द संपदा
प्रश्न 1.
लिंग बदलिए।
i. भाभी
ii. पत्ति
उत्तर:
i. भैया
ii. पत्नी
प्रश्न 2.
प्रत्यय पहचानिए।
i. मूर्खता
ii. बिगड़कर
उत्तर:
i. ‘ता’ प्रत्यय
ii. ‘कर’ प्रत्यय
प्रश्न 3.
विलोम शब्द लिखिए।
i. वास्तव × ……….
ii. फायदा × …………
उत्तरः
i. काल्पनिक
ii. नुकसान
![]()
प्रश्न 4.
समानार्थी शब्द लिखिए।
- स्कूल
- निराश
- आँख
- लाचारी
उत्तर:
- विद्यालय
- उदास
- नयन
- बेबसी
प्रश्न 5.
गोश में ‘महत्त्वहीन’ इस अर्थ से संबंधित कहावत है।
उत्तरः
ऐरा-गैरा नत्थू खैरा
कृति (4) स्वमत अभिव्यक्ति
प्रश्न 1.
‘आधुनिक युग में समाचार उड़ती बीमारी से भी तेज फैलते हैं।’ अपने विचार लिखिए।
उत्तर:
आधुनिक युग विज्ञान व तकनीकी का युग है। आज मानव सभ्यता प्रगति की ओर अग्रसर है। इस युग में संचार माध्यमों का अत्यधिक प्रचार-प्रसार हुआ है। संचार माध्यमों ने विश्व की दूरियों को समेटकर बहुत छोटा कर दिया है। जितनी जल्दी से कोई भी संक्रामक बीमारी नहीं फैल सकती है; उतनी जल्दी से समाचार देश के कोने-कोने में फैलते हैं। दूरदर्शन के विविध चैनल, समाचार पत्र, मोबाइल फोन, एस. एम. एस., ट्विटर, ई-मेल आदि के जरिए समाचार तुरंत पलभर में संपूर्ण देश में फैल जाते हैं। आज हम अपने देश में बैठे हुए भी दूसरे देशों में होने वाली घटनाओं से तुरंत अवगत हो जाते हैं।
![]()
(च) परिच्छेद पढ़कर सूचना के अनुसार कृतियाँ कीजिए।
कृति (1) आकलन कृति
प्रश्न 1.
जोड़ियाँ मिलाइए।
| (अ) | (ब) |
| 1. रमा | (क) मिठाई |
| 2. रामानुज | (ख) पराठे |
| 3. शांति बुआ | (ग) साग |
| 4. चक्रवर्ती | (घ) पनीर |
उत्तरः
| (अ) | (ब) |
| 1. रमा | (ख) पराठे |
| 2. रामानुज | (क) मिठाई |
| 3. शांति बुआ | (घ) पनीर |
| 4. चक्रवर्ती | (ग) साग |
कृति (2) आकलन कृति
प्रश्न 1.
घटनाक्रमानुसार वाक्य लिखिए।
- अब लेखक के घर के पास भी कोई नहीं फटकता है।
- लेखक ने पनीर फेंक दिया था।
- लेखक की पत्नी ने पराठे साधु को दिए थे।
- लेखक ने मिठाई घर पर पधारे अपने मित्रों को दे दी।
उत्तर:
- लेखक ने पनीर फेंक दिया था।
- लेखक ने मिठाई घर पर पधारे अपने मित्रों को दे दी।
- लेखक की पत्नी ने पराठे साधु को दिए थे।
- अब लेखक के घर के पास भी कोई नहीं फटकता है।
![]()
प्रश्न 2.
आकृति पूर्ण कीजिए।
उत्तरः
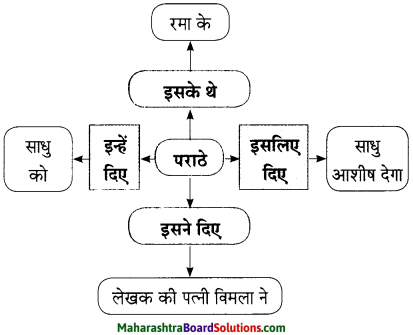
कृति (3) शब्द संपदा
प्रश्न 1.
निम्नलिखित शब्दों के अर्थ गद्यांश से ढूँड़कर लिखिए।
- आशीर्वाद
- वर्षा
- परेशान
- वस्तु
उत्तर:
- आशीष
- बारिश
- तंग
- चीज
![]()
प्रश्न 2.
बिलोम लिखिए।
i. कल x ………….
ii. विश्वास x …………
उत्तर:
i. आज
ii. अविश्वास
प्रश्न 3.
वचन बदलिए।
i. बीमारी
i. शंका
उत्तर:
i. बीमारियाँ
ii. शंकाएँ
![]()
प्रश्न 4.
प्रत्यय पहचानिए।
i. बीमारी
ii. लाचारी
उत्तर:
i. ‘ई’ प्रत्यय
ii. ‘ई’ प्रत्यय
प्रश्न 5.
लिंग बदलिए।
- साधु
- चाचा
- बुआ
उत्तर:
- साध्वी
- चाची
- फूफा
कृति (4) स्वमत अभिव्यक्ति
प्रश्न 1.
‘जैसे के साथ तैसा व्यवहार करना चाहिए।’ इस पर आधारित अपने विचार लिखिए।
उत्तर:
‘जैसे के साथ तैसा’ यह एक कहावत है। इसका अर्थ है कि जो व्यक्ति आपके साथ जिस प्रकार का व्यवहार करता हो, ठीक उसी प्रकार आपको भी उसके साथ व्यवहार करना चाहिए। यदि कोई व्यक्ति आपसे आत्मीयता एवं सादगी से पेश आता है, तो आपको भी उसके साथ आत्मीयता एवं सादगी से पेश आना चाहिए। यदि कोई आपको सभी के सामने भला बुरा कहे और आपका अपमान करें, तो आपको भी उसके साथ उसी प्रकार का व्यवहार करना चाहिए और सभी के समक्ष उसे खरी-खोटी सुनानी चाहिए। जब आप ऐसा करेंगे; तब वह व्यक्ति दुबारा आपके साथ दुर्व्यवहार करने की नहीं सोचेगा। कभी-कभी हमें दूसरों की अक्ल ठिकाने लाने के लिए उनके साथ वैसा ही व्यवहार करना पड़ता है।
भाषाई कौशल पर आधारित पाठगत कृतियाँ
प्रश्न 1.
अव्ययों का अपने बाक्यों में प्रयोग कीजिए।
i. कि
ii. अब
उत्तर:
i. मैंने कहा कि तुम अपना काम करो।
ii. अब तो मुझे चलना चाहिए।
![]()
प्रश्न 2.
काल परिवर्तन कीजिए।
- भारत में धूम मच गई है। (अपूर्ण भूतकाल)
- तुम तो खयाली पुलाव पका रहे हो। (सामान्य भूतकाल)
- तुम्हारे पराठे दे दिए। (सामान्य भविष्यकाल)
- अब मेरे घर के पास भी कोई नहीं फटक रहा था। (अपूर्ण वर्तमानकाल)
- चिंता ने चेतन की चिता सजा दी। (पूर्ण वर्तमानकाल)
- मैं जगह कर लूँगा। (पूर्ण भूतकाल)
- साधु आशीष देकर चला गया। (संयुक्त वाक्य)
- सबेरे एक साधु आ गए। (मिश्र वाक्य)
उत्तर:
- भारत में धूम मच रही थी।
- तुमने तो खयाली पुलाव पकाया।
- तुम्हारे पराठे दे दूंगा।
- अब मेरे घर के पास भी कोई नहीं फटक रहा है।
- चिंता ने चेतन की चिता सजा दी है।
- मैंने जगह कर ली थी।
- साधु ने आशीष दिया और चला गया।
- जैसे ही सबेरा हुआ वैसे ही एक साधु आ गए।
प्रश्न 3.
निम्नलिखित वाक्यों के रचना की दृष्टि से भेद लिखिए।
- जैसे ही एक जाता था; वैसे ही दो आते थे।
- यह सब लॉटरी का प्रताप था।
- “सुना है तुम्हारा रेफ्रीजरेटर आ गया है?”
- मुझसे नहीं खाई जाएगी।
उत्तर :
- मिश्र वाक्य
- साधारण वाक्य
- प्रश्नार्थक वाक्य
- निषेधार्थक वाक्य
प्रश्न 4.
रेखांकित शब्दों के भेद पहचानिए।
i. मैं बर्फ के क्यूब चूसूंगा।
ii. कुछ शौकीनों के लिए चाय बनी।
उत्तर:
i. मैं – सर्वनाम; बर्फ – द्रव्यवाचक संज्ञा
ii. कुछ – अनिश्चित संख्यावाचक विशेषण;
बनी – सकर्मक क्रिया
![]()
प्रश्न 5.
अव्यय पहचानिए।
i. जरा इधर तो सुन।
ii. कटोरा ले लिया गया और रेफ्रीजरेटर में रख दिया गया।
उत्तर:
i. इधर – क्रियाविशेषण अव्यय
ii. और – समुच्चयबोधक अव्यय
इनाम Summary in Hindi
लेखक-परिचय :
जीवन-परिचय : अरुण जी का जन्म 3 जनवरी 1928 को मेरठ, उत्तर प्रदेश में हुआ था। आधुनिक हिंदी लेखकों में इनका महत्त्वपूर्ण स्थान है। हिंदी साहित्य में आधुनिक कहानीकार एवं उपन्यासकार के रूप में श्रीमान अरुण जी का नाम उल्लेखनीय है। कहानियाँ एवं उपन्यास लिखना आपका शौक है। आपके समग्र साहित्य की 14 पुस्तकों का संकलन प्रकाशित हो चुका है। आपकी कलम ने साहित्य के विविध विधाओं को अनुग्रहित किया है।
प्रमुख कृतियाँ : एकांकी संकलन – ‘मेरे नवरस’; कहानी संग्रह – ‘बृहद हास्य संकलन’।
गद्य-परिचय :
हास्य-व्यंग्यात्मक निबंध : ‘हास्य-व्यंग्य’ का अर्थ ही है उपहास करना। अत: इस प्रकार के निबंध में उपहास को प्रधानता दी जाती है। इसमें किसी विषय का तार्किक एवं बौद्धिक विवेचनापूर्ण लेखन किया जाता है।
प्रस्तावना : प्रस्तुत कहानी ‘इनाम’ के माध्यम से लेखक अरुण जी ने रेफ्रीजरेटर को माध्यम बनाकर लोगों के आचरण एवं व्यवहार पर करारा व्यंग्य किया है।
![]()
सारांश :
प्रस्तुत पाठ एक हास्य-व्यंग्यात्मक निबंध है। भारतीय समाज में तरह-तरह की विसंगतियाँ पाई जाती हैं। इस पाठ के द्वारा लेखक ने रेफ्रीजरेटर का आधार लेकर समाज में पाई जाने वाली विसंगतियों पर हास्य के माध्यम से करारा व्यंग्य किया है। एक भारतीय कंपनी रेफ्रीजरेटर की प्रसिद्धि के लिए विदेशी विज्ञापन पद्धति का सहारा लेती है। इसके लिए प्रतियोगिता का आयोजन करती है। लेखक भी इसमें सम्मिलित होते हैं और वे जीत जाते हैं। इसी कारण उन्हें एक रेफ्रीजरेटर मुफ़्त में मिल जाता है।
मुफ़्त में मिले रेफ्रीजरेटर को देखने के लिए उनके घर में पास-पड़ोस एवं सगे-संबंधियों का तांता लग जाता है। घर आए लोगों की आव-भगत एवं उन्हें रेफ्रीजरेटर का ठंडा पानी पिलाते-पिलाते लेखक का परिवार तंग आ जाता है। इतना ही नहीं, आस-पास रहने वाले लोग उनके फ्रीज में ढेर सारी चीजें रखते हैं। अंत में लेखक को एक तरकीब सूझती है और वे लोगों द्वारा रखी गई चीज़ों का इस्तेमाल करना शुरू कर देते हैं। इस कारण अब लोग उनकी फ्रीज में अपनी चीजें रखना बंद कर देते हैं।
शब्दार्थ :
- जुगाड़ – व्यवस्था, प्रबंध
- दरख्वास्त – अर्ज, अरजी
- भंभड़ – शोरशराबा
- अमानत – धरोहर
- प्रतियोगिता – स्पर्धा
- प्रतियोगी – प्रतिस्पर्धी
- बिजली – विद्युत
- लाचारी – बेबसी
मुहावरे :
- जली-कटी सुनाना – खरी-खोटी सुनाना।
- मिसरी घोलकर बोलना – मीठी-मीठी बातें करना।
- खयाली पुलाव पकाना – कल्पना में खोए रहना, स्वप्नरंजन करना।
कहावत :
ऐरे गैरे नत्थू खैरे – महत्त्वहीन
Hindi Lokbharti 9th Std Digest दूसरी इकाई
- कह कविराय Question Answer
- जंगल (पूरक पठन) Question Answer
- इनाम Question Answer
- सिंधु का जल Question Answer
- अतीत के पत्र Question Answer
- निसर्ग वैभव (पूरक पठन) Question Answer
- शिष्टाचार Question Answer
- उड़ान Question Answer
- मेरे पिता जी (पूरक पठन) Question Answer
- अपराजेय Question Answer
- स्वतंत्रता गान Question Answer