Std 9 Hindi Chapter 8 Veer Bhumi Par Kuch Din Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 9 Hindi Solutions Lokbharti Chapter 8 वीरभूमि पर कुछ दिन Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Hindi Lokbharti 9th Digest Chapter 8 वीरभूमि पर कुछ दिन Questions And Answers
Hindi Lokbharti 9th Std Digest Chapter 8 वीरभूमि पर कुछ दिन Textbook Questions and Answers
पठनीय
प्रश्न 1.
हिंदवी स्वराज्य निर्माता छत्रपति शिवाजी महाराज की जीवनी का अंश पढ़कर प्रेरणा प्राप्त कीजिए।

संभाषणीय
प्रश्न 1.
स्वयं देखे हुए महाराष्ट्र के दर्शनीय स्थलों के बारे में अपने मित्रों को बताइए।
उत्तर:
- स्वयं: क्या आप सब जानते हैं महाराष्ट्र की यात्रा किसी भी सैलानी को भारत के पश्चिमी भाग की खूबसूरती को जानने का मौका देती है।
- राहुल: नहीं जानता हूँ। मैं महाराष्ट्र के दर्शनीय स्थलों पर अब तक नहीं गया हूँ।
- भूषण: मैं भी कुछ नहीं जानता हूँ।
- नंदा: मैं भी जानने के लिए उत्सुक हूँ।
- स्वयः तो सुनो, मैं बताता हूँ। महाराष्ट्र भारत का तीसरा सबसे बड़ा राज्य है और यहाँ पर्यटन स्थलों के रूप में बहुत बड़ा खज़ाना है। .
कई गुफाएँ, आकर्षक हिल स्टेशन, समुद्र तट, बड़ी संख्या में वन्य जीव, भक्ति के पवित्र स्थल आदि, महाराष्ट्र में सब कुछ है। हालांकि बॉलीवुड एक ऐसी चीज़ है; जो इस राज्य को दूसरे राज्यों के मुकाबले बढ़त देता है। घूमने के शौकीनों के लिए महाराष्ट्र अपने आप में एक पूरा पर्यटन स्थल है। अपने सभी आकर्षणों के साथ महाराष्ट्र का एक ऐसा आभा मंडल है जिसे अनदेखा करना मुश्किल है। महाराष्ट्र राज्य में अजंता और एलोरा ऐसे दो विश्व विरासत स्थल हैं जो हमेशा से पर्यटकों का मन मोह लेते हैं। अगर आप तीन हज़ार साल पहले धर्म और इंसानी कल्पना को चित्रों और मूर्तियों के रूप में देखना चाहते हैं तो आपको अजंता की यात्रा जरूर करनी चाहिए।
- राहुल: बहुत खूब, और बताओ, महाराष्ट्र के दर्शनीय स्थलों के बारे में।
- स्वयं: मुंबई महाराष्ट्र की राजधानी है। यहाँ देखने लायक जगहों में गेट वे ऑफ इंडिया, हैगिंग गार्डन, महालक्ष्मी मंदिर, हाजी अली दरगाह, मरीन ड्राइव, जुहू बीच और चौपाटी शामिल हैं। मुंबई शहर बॉलीवुड का गढ़ भी है। एस्सेल वर्ल्ड देश में बच्चों द्वारा सबसे ज्यादा देखी जानेवाली जगह है।
- नंदा: मैं तो बहुत प्रसन्न हो रही हूँ क्योंकि मुझे यहीं बैठे-बैठे सारी जानकारी मिल रही है।
- स्वयं: महाबलेश्वर, लोनावाला और खंडाला की साफ हवा, शांत वातावरण, सुंदर और शांत झील और शानदार झरने आपको शहर की हलचल से दूर आनंद की अनुभूति देते हैं।
- भूषण: मैं भी अपने माता-पिता के साथ इन स्थलों की यात्रा करूँगा।
- स्वयं: हरिहरेश्वर, गणपतिपुले, जेजुरी, पंढरपुर, सिद्धिविनायक मंदिर, शिरडी आदि यहाँ के प्रसिद्ध धार्मिक स्थल हैं।
- सभी एक साथः धन्यवाद, तुमने तो अपने वक्तव्य से समूचे महाराष्ट्र की झाँकी हमारे सामने प्रस्तुत कर दी।
आसपास
प्रश्न 1.
ऐतिहासिक स्थलों के चित्रों का कोलाज तैयार कीजिए

पाठ के आँगन में…
सूचना के अनुसार कृतियाँ पूर्ण कीजिए
1. उत्तर लिखिए:
(क) ऊँट की सवारी करने के बाद लेखिका की स्थिति
(ख) ऊँट की सवारी का अनुभव रोमांचकारी और मनोरंजक था, यह दर्शाने वाला वाक्य
प्रश्न 2.
जोड़ियाँ मिलाइए:
| अ |
ब |
| 1. रेगिस्तान का जहाज |
(क) सूर्यास्त |
| 2. मखमली गददे |
(ख) ऊँट |
| 3. रंग-बिरंगी पोशाक |
(ग) होटल |
| 4. पर्यटकों की मंजिल |
(घ) रेत |
|
(ड़) पर्यटक |
उत्तरः
- ऊँट
- रेत
- पर्यटक
- सूर्यास्त
प्रश्न 3.
परिच्छेद में प्रयुक्त विलोम शब्द की जोड़ी लिखिए।
1. नर × ……………
2. बाल × ………….
उत्तर:
1. नारी
2. वृद्ध
प्रश्न 4.
‘मेरी यात्रानुभव’ पर आपके विचार लिखिए।
उत्तर:
अपने जीवन काल में मनुष्य को अनेक यात्राओं का अनुभव होता है। कुछ यात्राएँ लोग सुख व मनोरंजन के लिए करते हैं तो कुछ आवश्यकतापरक होती हैं। पिछली दिवाली की छुट्टियों में हम कुछ सहपाठी माथेरान गए थे। मुंबई के सी. एस. टी. स्टेशन से रेलगाड़ी में बैठकर हम नेरल पहुँचे। वहाँ जलपान करके हम खिलौने जैसी ‘मिनी’ रेलगाड़ी में सवार हुए। मखमल-सी मुलायम हरे वृक्ष और सघन घाटियों की शोभा देखते हुए हम माथेरान पहुँचे। माथेरान का वातावरण मोहक और स्फूर्तिदायक था। लाल-लाल मटियाले रास्ते और घनी हरियाली।
भरी दोपहर में भी वहाँ ठंडी हवा चलती है। सुबह और शाम को घूम कर हमने अनेक प्राकृतिक दृश्य देखें। प्राकृतिक दृश्य की सुंदरता अनोखी थी। इनमें से कुछ दृश्य हमें बहुत ही अच्छे लगे। ‘एको पॉइंट’ (प्रतिध्वनि बिंदु) पर हमने जोर-जोर से चिल्लाकर अपनी अनेक प्रतिध्वनि सुनी। एक दिन शाम को हमने सूर्यास्त बिंदु (सनसेट पॉईंट) पर डूबते हुए सूर्य का अद्भुत दृश्य देखा। हमने शारलोट तालाब की सुंदरता भी देखी। हमने घुड़सवारी और रिक्शा में बैठने का मज़ा भी लिया। हमने अपने कैमरों से कई तस्वीरें भी खीचीं। हम दिनभर घूमते रहे पर हमें थकान का अनुभव नहीं हुआ। माथेरान में चार दिन, चार पल की तरह बीत गए। हम वहाँ से लौट आए पर वहाँ के मनोहर दृश्य आज भी मेरी आँखों के सामने घूम रहे हैं।

लेखनीय
प्रश्न 1.
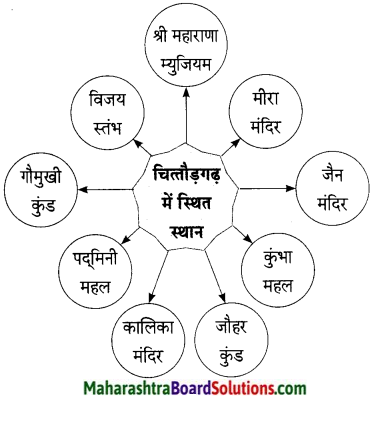
‘चित्तौड़गढ़ बोलने लगा तो…..’ अपने शब्दों में लिखिए।
उत्तर:
चित्तौड़गढ़ एक ऐतिहासिक वास्तु है । यह त्याग, बलिदान एवं वीरता की पहचान है। इसका निर्माण 7 वीं शताब्दी में मौर्य के शासन काल में किया गया था और इसका नाम भी मौर्य शासक चित्रांगदा मोरी के बाद ही रखा गया था। ऐतिहासिक दस्तावेजों के अनुसार चित्तौड़गढ़ किला 934 सालों तक मेवाड़ की राजधानी रह चुका था। इसकी स्थापना 734 में मेवाड़ के सिसोदिया वंश के शासक बाप्पा रावल ने की थी। आज भी यह किला बड़े शान से मेवाड़ की धरती पर खड़ा है। इसे देखने के बाद मेरे मन में विचार आया कि यदि चित्तौड़गढ़ बोलने लगा तो…’ चित्तौड़गढ़ बोलने लगा, तो वह अपनी सारी ऐतिहासिक गाथा हमारे सामने प्रस्तुत करेगा। वह अपनी कहानी इस प्रकार कहेगा “मैं भारत के विशालतम किलों में से एक हैं। मैं एक वर्ल्ड हेरिटेज दुर्ग भी हूँ। मैं विशेषत: मेवाड़ की राजधानी के नाम से जाना जाता हूँ।
पहले मेरे ऊपर गहलौत का शासन था और बाद में सिसोदिया का शासनकाल था। चित्तौड़ी राजपूत के सूर्यवंशी वंश ने 7 वीं शताब्दी से 1567 तक परित्याग करने तक शासन किया और १५६७ में अकबर ने मेरी घेराबंदी की थी। मैं 190 मीटर पहाड़ी की ऊँचाई पर बना हुआ हूँ और 391.9 एकड़ के क्षेत्र में फैला हुआ हूँ। मुझसे जुड़ी बहुत-सी ऐतिहासिक घटनाएँ हैं। आज मैं पर्यटकों के आकर्षण का केंद्र बना हुआ हूँ। 15 से १६ वीं शताब्दी के बाद मुझे तीन बार लुटा गया था। 1303 में अलाउद्दीन खिलजी ने राणा रतन सिंह को पराजित किया था। 1535 में गुजरात के सुल्तान बहादुर शाह ने विक्रमजीत सिंह को पराजित किया था और १५६७ में अकबर ने महाराणा उदय सिंह द्वितीय को पराजित किया था। लेकिन तीनों समय राजपूत सैनिकों ने जी-जान से लड़ाई की थीं।
उन्होंने महल को एवं राज्य को बचाने की हर संभव कोशिश की थी लेकिन हर बार उन्हें हार का ही सामना करना पड़ रहा था। सैनिकों के पराजित होने के बाद राजपूत सैनिकों की तकरीबन 13,000 से भी ज्यादा महिलाओं और बच्चों ने जौहर कर लिया था और अपने प्राणों का बलिदान दे दिया था। सबसे पहले जौहर राणा रतन सिंह की पत्नी रानी पद्मिनी ने किया था। उनके पति 1303 के युद्ध में मारे गए थे और बाद में 1537 में रानी कर्णावती ने भी जौहर किया था। जी हाँ, मैं इन सभी महिलाओं के जौहर का साक्षी हूँ। इसीलिए मैं राष्ट्रप्रेम, हिम्मत, मध्यकालीन वीरता और मेवाड़ के सिसोदिया और बच्चों का राज्य के प्रति बलिदान देने का सर्वोत्कृष्ट उदाहरण हूँ।
उस समय राजपूत शासक, सैनिक, महिलाएँ और स्थानिक लोग मुगल सेना के समक्ष समस्त समर्पण करने के बजाय लड़ते – लड़ते प्राणों की आहुति देना ठीक समझते थे। २०१३ में कोलंबिया के फ्लोम पेन्ह (Phonm Penh) में वर्ल्ड हेरिटेज कमिटी के ३७ वें सेशन में मेरे साथ ही राजस्थान के पाँच और किलो को यूनेस्को वर्ल्ड हेरिटेज साईट में शामिल किया गया था।”
अंत में मैं इतना ही कहूँगा
“अमर त्याग और बलिदान की कहानी हूँ मैं,…
स्वत्व व सतीत्व की रक्षा का आदर्श हूँ मैं।
आज भी शत्रु को परास्त करने का जज्बा रखता हूँ मैं।
भारतीय संस्कृति का धनी हूँ मैं।”
मौलिक सृजन
प्रश्न 1.
ऐतिहासिक स्थलों की सुरक्षा एवं उनका संवर्धन करना हमारा कर्तव्य है, इसके आधार पर चर्चा कीजिए और दिए गए मुद्दों से सूचना फलक तैयार कीजिए।
उत्तर:
बहुत बड़े और बहुत पुराने देशों की कुछ पुरानी और बड़ी समस्याएँ भी होती हैं। हमारी एक बहुत बड़ी समस्या प्राचीन ऐतिहासिक स्थलों को सुरक्षित रखने की भी है । पूरे देश में ऐसी अनगिनत प्राचीन और ऐतिहासिक महत्त्व की इमारतें हैं जिनकी देखभाल ठीक से नहीं हो रही हैं। पिछले एक दशक से भारत में बदलाव की जो हवा चल रही है। उसके अंतर्गत अब यह माना जा रहा है कि देश की धरोहर के संरक्षण की ज़िम्मेदारी केवल सरकार की ही नहीं है। सार्वजनिक क्षेत्र की दो बड़ी कंपनियों ने भी इस ज़िम्मेदारी को स्वीकार किया है। ‘सेल’ ने दिल्ली के लोदी गार्डन की इमारतों की मरम्मत तथा साज सज्जा के लिए बनाई गई एक योजना में 10 करोड़ रुपए लगाए हैं।
इंडियन ऑयल कॉरपोरेशन ने कान्हेरी की गुफाओं तथा कोणार्क मंदिर के – रिनोवेशन’ के लिए २५ करोड़ रुपए खर्च करने का निर्णय लिया है। इन दोनों प्रयासों से उत्साहित होकर भारत सरकार का संस्कृति मंत्रालय अब व्यापक स्तर पर बड़े औद्योगिक घरानों तथा व्यापार संगठनों को इस काम में शामिल करना चाहता है। अभी हाल में ही मंत्रालय ने ‘रिलायंस’, ‘हीरो होंडा’, ‘सैमसंग’, ‘एमआरएफ’, ‘एवीवा’, ‘विप्रो’, ‘एलजी’, जैसी कंपनियों को एक पत्र लिखकर ऐतिहासिक स्थलों को सुरक्षा एवं उनका संवर्धन देने की अपील की है। यह निश्चित रूप से एक सार्थक प्रयास है और आशा की जाती है कि बड़े औद्योगिक और व्यापारी घराने अपनी ‘पब्लिक इमेज’ बनाने के लिए इस दिशा में आगे बढ़ेंगे।
ऐतिहासिक धरोहर के संरक्षण के लिए सरकार एक बड़ी व्यापक और कारगर नीति बनाएँ। छोटे शहरों में ऐसी तमाम इमारतें हैं जो उपेक्षित पड़ी हैं। इन इमारतों पर अवैध कब्जे हैं तथा कुछ लोगों ने उन्हें अपनी निजी संपत्ति के तौर पर इस्तेमाल करना शुरू कर दिया है। ऐसी इमारतों की एक बड़ी सूची बनाना ज़रूरी है ताकि यह पता चल सके कि वे कहाँ है, किस स्थिति में हैं और उनका संरक्षण कैसे किया जा सकता है। ऐतिहासिक धरोहर के संरक्षण में आम आदमी की भागीदारी बहुत आवश्यक है। ऐतिहासिक स्थलों और सैर करने जाने वाले पर्यटक वहाँ पर कूड़ा, कचरा व प्लास्टिक आदि फेंककर प्रदूषण फैलाते हैं। यह बहुत ही चिंता का विषय है। ऐतिहासिक स्थलों की हिफाजत करना सभी का कर्तव्य हैं। उन्हें साफ़-सुथरा रखने के लिए सभी लोगों को अपनी ओर से प्रयास करना चाहिए। हमें अपने देश के ऐतिहासिक स्थलों के प्रति आस्था का भाव रखना चाहिए।

विषय से…..
प्रश्न 1.
राष्ट्र का गौरव बनाए रखने के लिए पूर्व प्रधानमंत्रियों द्वारा किए सराहनीय कार्यों की सूची बनाइए। नौवीं कक्षा पाठ-२ इतिहास और राजनीति शास्त्र
1. सूचना के अनुसार कृतियाँ कीजिए।
प्रश्न (क)
संजाल
उत्तर:
प्रश्न (ख)
संजरा पूणच कीतजए:
उत्तर:
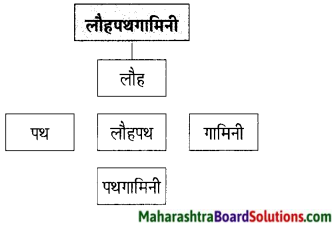
2. दिए गए शब्दों के वर्गों का उपयोग करके चार पाँच अर्थपूर्ण शब्द तैयार कीजिए।
प्रश्न 1.
दिए गए शब्दों के वर्गों का उपयोग करके चार पाँच अर्थपूर्ण शब्द तैयार कीजिए।
उत्तर:
उत्तर लिखिए।
प्रश्न 1.
स्वयं पढ़े हुए यात्रा वर्णन:
उत्तर:
1. कितनी नावों में कितनी बार: अज्ञेय
2. स्मरण यात्रा: काका कालेलकर

केवल एक शब्द में उत्तर लिखिए।
प्रश्न (त)
वीर जवानों का वह देश जो धरती का गहना:
उत्तरः
भारत देश
प्रश्न (थ)
महाराणा प्रताप के घोड़े का नाम:
उत्तरः
चेतक
स्वमत अभिव्यक्ति:
प्रश्न 1.
मैं पाठशाला जा रहा था। रास्ते में एक युवक अपनी मोटरसाइकिल आधी-टेढ़ी चलाते, कलाबाजियाँ दिखाते हुए तथा जोर-जोर से हॉर्न बजाकर लोगों को परेशान कर रहा था। उसे देखकर मेरे मन में विचार आए।
उत्तरः
स्टंट दिखाने के लिए वे रत्तीभर भी कसर नहीं छोड़ते हैं। जब मौका मिले, तब शुरू हो जाते हैं। अपनी खोखली कलाबाजियों से लोगों पर क्या गुजरती होगी, इसका तनिक भी असर उन पर नहीं पड़ता है। आखिर वे अपनी मस्ती एवं धुन में मशगूल जो होते हैं । आज के युवक फैशन एवं अपनी कलाबाजियाँ दिखाने के लिए अपनी मोटरसाइकिल आधी-टेढ़ी चलाते हैं तथा जोरजोर से हॉर्न बजाकर लोगों को परेशान करते हैं। यह तो उनके लिए एक खेल हो जाता है, पर रास्ते पर चलते समय लोगों को जिन तकलीफों का सामना करना पड़ता हैं, उनसे तो वे युवक अनभिज्ञ होते हैं। वे तो बस फैशन एवं स्टंट दिखाने के आदी हो गए हैं।
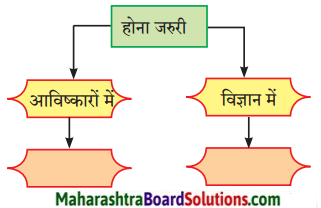
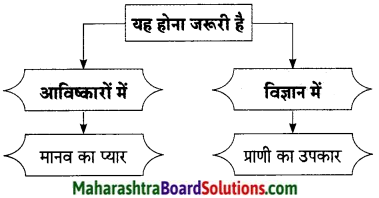
आधुनिक युग में ध्वनि-प्रदूषण समय की एक बड़ी समस्या बन गई है। पिछले कुछ वर्षों से इस समस्या ने लोगों का ध्यान आकृष्ट किया है। इस समस्या के पीछे औद्योगीकरण, यातायात के आधुनिक साधनों तथा बढ़ती मानवीय गतिविधियों का बहुत बड़ा हाथ है। मोटरसाइकिल, ट्रेन, वायुयान आदि वातावरण में तरह-तरह की ध्वनियाँ छोड़ते हैं। ये ध्वनियाँ हमारे कानों से टकराकर हमारे चित्त को अशांत कर देती हैं, जिससे मानसिक तनाव बहरापन आदि स्वास्थ्य संबंधी समस्याएँ उत्पन्न होती हैं। सभी को सड़क यातायात नियमों की अच्छे से जानकारी होनी चाहिए, खासतौर पर युवा लोगों को जो महत्त्वपूर्ण सड़क दुर्घटना के खतरे पर रहते हैं। युवकों के बीच जागरुकता उत्पन्न करने के कई सारे तरीके हैं।
जैसे-सेमिनार, कार्यशाला, पाठ्यक्रम में मूल सड़क-सुरक्षा पाठ जोड़ने के द्वारा विद्यार्थी शिक्षा, रुको, देखो, सुनो, सोचो और फिर पार करो अर्थात् ग्रीन क्रॉस कोड के बारे में लोगों को जागरुक करना यातायात लाईटों को सीखना, रोड चिहनों को समझना, सड़क के हालात के अनुसार रक्षात्मक चालन आदि। सरकार द्वारा भी इसके लिए सख्त कानून बनाना चाहिए । जैसे हॉर्न पर प्रतिबंध लगाना। मोटरसाइकिल चलाते समय हेलमेट का प्रयोग करना आदि। अंत में सिर्फ इतना ही कहना चाहता हूँ
“हे युवक, तू पहचान ले, अपनी अस्मिता को
न बिखरने दे अपनी क्षमता को
छोड़ दे व्यर्थ कि कलाबाजियाँ
स्वीकार कर अब सड़क-नीतियाँ।”

निबंध लेखन:
प्रश्न 1.
‘हमारी सैर’ पर निबंध लिखिए।
उत्तर:
कवि हरिवंशराय बच्चन कहते हैं:
“साँस चलती है –
तुझे चलना पड़ेगा ही मुसाफिर!”
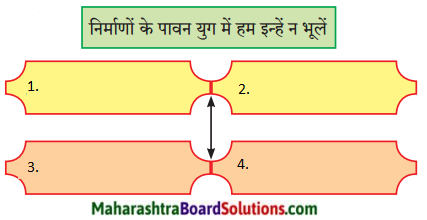
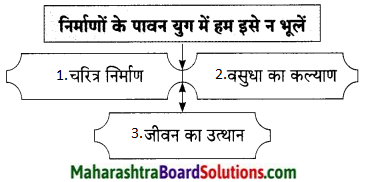
सचमुच, सैर या यात्रा करना व्यक्ति का पसंदीदा शौक होता है। सैर पर जाना सभी को अच्छा लगता है। सैर शिक्षा का एक सफल साधन है। शिक्षा का वास्तविक उद्देश्य चरित्र निर्माण होता है। जब हम सैर पर निकलते हैं, हमें अपनी चीजें संभालनी पड़ती हैं। यात्रा में हमें अपना टिकट खरीदना पड़ता है और ठीक समय पर गाड़ी पकड़नी पड़ती है। धनी व्यक्ति अपने नौकर से यह सब करा लेते हैं, किंतु भारत में अधिकांश व्यक्ति स्वयं ही यह कार्य करते हैं। छुट्टी में हम सब घूमने जाते हैं। हम हर बार नाना-नानी के घर पर जाते हैं। लेकिन इस बार हम हरिद्वार को तीर्थ यात्रा पर गए थे। यह यात्रा हमने ट्रेन से की। हमने वहाँ पर खूब मस्ती की। मेरे परिवार में पापा-मम्मी, दादा-दादी और बड़ी दीदी हैं। हरिद्वार में हमारे गुरुजी का आश्रम है। हरिद्वार में हम सबने गंगाजी में स्नान कर आरती का आनंद लिया।
हरिद्वार बहुत ही सुंदर स्थल है। सबसे पहले हम गुरुजी के आश्रम गए। फिर हमने मंदिरों के दर्शन किए । वहाँ ‘हरि की पौड़ी के सामने मनसा देवी का मंदिर है। दूसरी तरफ पहाडी पर चंडी देवी का मंदिर है। हरिद्वार में बहुत सुंदर मंदिर बने हैं। दर्शनों के बाद हम हरिद्वार से कुछ ही दूरी पर ऋषिकेश गए। वहाँ राम व लक्ष्मण झूला नामक पुल है। यह पुल गंगा नदी पर बने हैं। पहाड़ों के बीच बहती गंगा नदी का दर्शन बड़ा मनोरम प्रतीत होता है। यहाँ से खूब बड़े-बड़े पहाड़ दिखते हैं। हरिद्वार में पवित्र गंगा नदी पर हमने मस्ती की।
मुझे वहाँ नईनई जानकारी मिली। हरिद्वार में दूर-दूर से श्रद्धालु दर्शन के लिए आते हैं। यहाँ पर 12 साल में कुंभ का मेला लगता है। कुंभ के मेले में बहुत से साधु-संत आते हैं। हरिद्वार से लगभग कुछ ही दूरी पर बद्रीनाथ, केदारनाथ, गंगोत्री, यमुनोत्री के पवित्र धाम भी हैं। हमारी यात्रा बहुत ही रोमांचक व यादगार रही। हमने घूमने का मजा भी लिया और हमारी तीर्थ यात्रा भी हो गई। यहाँ हमें प्रकृति की सुंदरता देखने को मिली। अब अगली गर्मियों में हम चारधाम की सैर करेंगे।
पाठ से आगे:
ऐतिहासिक वस्तु संग्रहालय देखने का आयोजन करते हुए संक्षिप्त टिप्पणी लिखिए।
भाषा बिंदु
प्रश्न 1.
सन्दि पढिए और समझिए
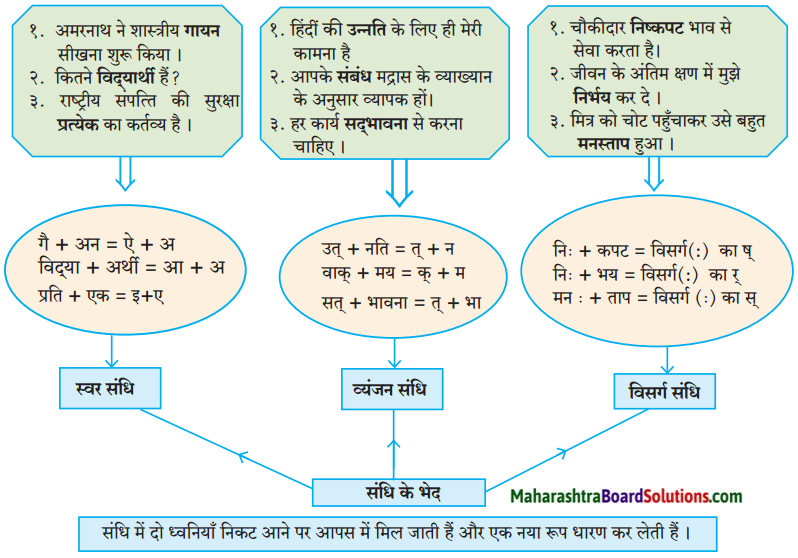
प्रश्न 2.
निम्न संधि का विग्रह कर उसके प्रकार बताइए।
- थोड़ी ही देर में हॉटेल के स्वागत में आसीन थे।
- हमारी मंजिल भी सूर्यास्त केंद्र बिंदु।
- सब कुछ इतना सुंदर सजीव और मनोहर था।
- रेखांकित प्रत्येक लोकोक्ति को सोदाहरण लिखो।
- उपर्युक्त वाङ्मय दुष्कर एवं अत्यधिक दुर्लभ है।
- भारतीय कलाकारों का सम्मान तथा उन्हें नमन करने का मन करता है।
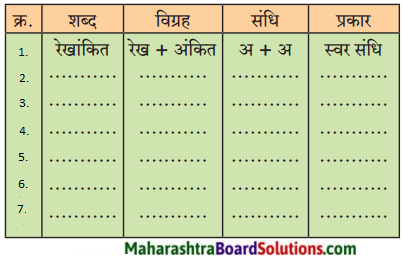
उत्तर:
| शब्द |
विग्रह |
संधि |
प्रकार |
| 1. रेखांकित |
रेख + अंकित |
अ + अ |
स्वर संधि |
| 2. स्वागत |
सु + आगत |
उ+ आ |
स्वर संधि |
| 3. सूर्यास्त |
सूर्य + अस्त |
अ + अ |
स्वर संधि |
| 4. मनोहर |
मन: + हर |
अ:+ ह |
विसर्ग संधि |
| 5. वाङ्मय |
वाक् + मय |
क् + म |
व्यंजन संधि |
| 6. सम्मान |
सत् + मान |
म् + म |
व्यंजन संधि |

Hindi Lokbharti 9th Answers Chapter 8 वीरभूमि पर कुछ दिन Additional Important Questions and Answers
(क) परिच्छेद पढ़कर दी गई सूचना के अनुसार कृतियाँ कीजिए।
कृति (1) आकलन कृति
कृति पूर्ण कीजिए।
प्रश्न 1.
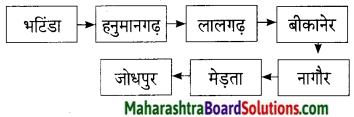
इन स्थानों से आगे बढ़ते हुए लेखिका जोधपुर पहुँची –
उत्तर:
समझकर लिखिए।
प्रश्न 1.
मेड़ता पहुँचते ही लेखिका को ऐसा क्यों लगा कि वह पंजाब के आसपास आ गई है?
उत्तर:
क्योंकि कुछ खेत, हरियाली और पशुधन भी दिखाई देने लगे।
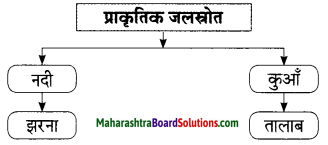
संजाल पूर्ण कीजिए।
प्रश्न 1.
संजाल पूर्ण कीजिए।
उत्तर:
कृति (2) आकलन कृति
प्रश्न 1.
सत्य या असत्य पहचानकर लिखिए।
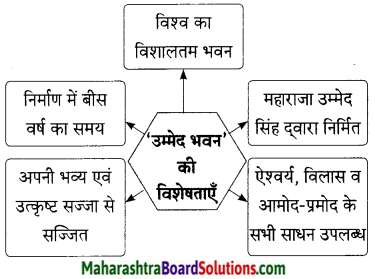
1. महल के आधे भाग में शाही परिवार रहता है।
2. उम्मेद भवन देखने के बाद लेखिका मंडोर गार्डन की ओर बढ़ी।
उत्तर:
1. असत्य
2. सत्य

प्रश्न 2.
प्रस्तुत गद्यांश के आधार पर ऐसे प्रश्न तैयार कीजिए जिनके उत्तर निम्नलिखित शब्द हो
1. द्वार पाल
2. म्यूजियम
उत्तर:
1. महल के प्रवेश द्वार पर किसे नियुक्त किया गया था?
2. भूतल पर क्या था?
प्रश्न 3.
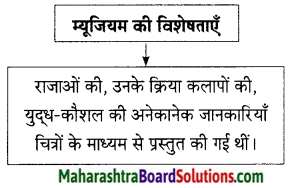
आकृति पूर्ण कीजिए।
उत्तर:
कारण लिखिए।
प्रश्न 1.
लेखिका की दृष्टि किसी भी चित्र पर चिपक-सी जाती थी।
उत्तर:
लेखिका की दृष्टि किसी भी चित्र पर चिपक-सी जाती थी क्योंकि सभी चित्र सुंदर, सजीव, भव्य और मनोहर थे।
कृति (3) शब्द संपदा
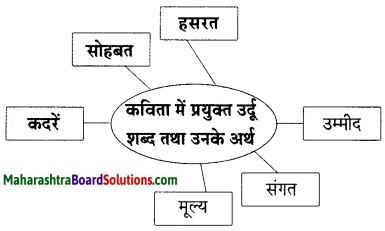
प्रश्न 1.
समानार्थी शब्द लिखिए।
- भवन
- राजा
- परिवार
- युद्ध
उत्तर:
- प्रासाद, महल
- नृप
- कुटुंब
- संग्राम

प्रश्न 2.
नीचे दिए हुए शब्दों के विरुद्धार्थी शब्द गद्यांश से ढूँढ़कर लिखिए।
- निर्जीव × ……………….
- दूर × ………………….
- असमय × …………….
- जमा × ………………..
उत्तर:
- सजीव
- पास
- समय
- खर्च
प्रश्न 3.
निम्नलिखित शब्द मानक वर्तनी के अनुसार लिखिए।
- सज्जासे
- मॉडलभी
- गन्तव्य
- प्रदरशित
उत्तर:
- सज्जा से
- मॉडल भी
- गंतव्य
- प्रदर्शित
शुद्ध शब्द पहचानकर लिखिए।
प्रश्न 1.
जानकारीयाँ, जानकारियाँ, जानरकारियाँ
उत्तरः
जानकारियाँ
शब्द समूह के लिए एक शब्द लिखिए।
प्रश्न 1.
1. द्वार पर नियुक्त व्यक्ति –
2. अलग-अलग स्थलों की सैर करने वाला –
उत्तर:
1. द्वारपाल
2. पर्यटक
प्रश्न 2.
निम्नलिखित शब्दों में से मूल शब्द व प्रत्यय अलग करके लिखिए।
उत्तर:
| शब्द |
मूल शब्द |
प्रत्यय |
| 1. सज्जित |
सज्जा |
इत |
| 2. विशालतम |
विशाल |
तम |
प्रश्न 3.
लिंग बदलिए।
महाराजा
उत्तरः
महारानी

प्रश्न 4.
वचन बदलिए।
1. जानकारियाँ
2. कमरा
उत्तर:
1. जानकारी
2. कमरे
(ख) गद्यांश पढ़कर दी गई सूचना के अनुसार कृतियाँ कीजिए।
कृति (1) आकलन कृति
प्रश्न 1.
आकृति पूर्ण कीजिए।
उत्तर:
प्रश्न 2.
समझकर लिखिए।
1. प्रहरी जान पड़ती है
2. मार्ग के दोनों ओर निर्माण हुआ है
उत्तर:
1. तीन तलोंवाली एक इमारत
2. जलाशयों का
प्रश्न 3.
कारण लिखिए।
लोकगीत गायक अपने-अपने वाद्यों पर गीत की धुन छेड़ते हैं।
उत्तरः
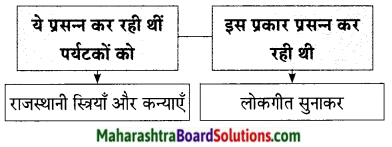
लोकगीत गायक अपने-अपने वाद्यों पर गीत की धुन छेड़ते हैं क्योंकि वे शायद वहाँ आने वाले पर्यटकों को प्रसन्न कर उनसे कुछ दक्षिणा पाना चाहते हैं।
कृति (2) आकलन कृति
प्रश्न 1.
सहसंबंध लिखिए। जैसे – विशाल – मूर्तियाँ
- ऊँची: …………..
- चमकती: …………
- रेगिस्तानी: ……….
- मनोरम: ……………
उत्तरः
- पहाड़ी
- चाँदनी
- धूप
- दृश्य

प्रश्न 2.
कृति पूर्ण कीजिए।
उत्तरः
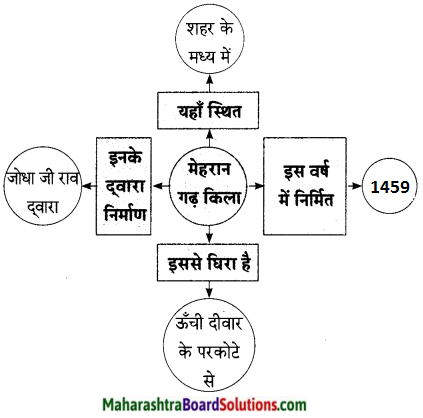
प्रश्न 3.
समझकर लिखिए।
उत्तरः
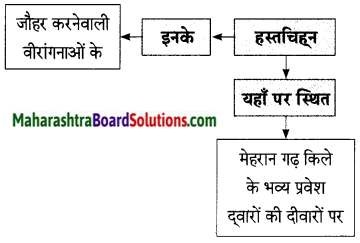
उत्तर लिखिए।
प्रश्न 1.
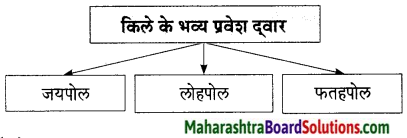
दुर्ग के अंदर मौजूद विशाल भवनों के नाम बताइए।
उत्तरः
मोतीमहल, फूलमहल, शीशमहल, दौलतखाना, फतहमहल, रानी सागर।
सत्य या असत्य पहचानकर लिखिए।
प्रश्न 1.
1. दुर्ग के अंदर भवनों में कहीं बैठकखाना, तो कहीं दीवाने खास,दीवाने आम हैं।
2. जयपोल तक आते-आते ही शहर ऊपर रह जाता है।
उत्तर:
1. सत्य
2. असत्य

कृति (3) शब्द संपदा
प्रश्न 1.
नीचे दिए गए शब्दों के समानार्थी शब्द पहेली में से ढूँढ़कर लिखिए।
नरेश, द्वार, मूर्ति, भव्य, देवता

उत्तरः
राजा, दरवाजा, प्रतिमा, विशाल, ईश्वर
प्रश्न 2.
विरुद्धार्थी शब्द लिखिए।
- ऊपर × …………
- समीप × ……….
- विजय × ………
- शहर × ………..
उत्तर:
- नीचे
- दूर
- पराजय
- गाँव
प्रश्न 3.
लिंग बदलिए।
- वीर
- रानी
- भगवान
- देवता
उत्तरः
- वीरांगना
- राजा
- भगवती
- देवी
प्रश्न 4.
वचन बदलिए।
1. मूर्ति
2. वीरांगना
उत्तर:
1. मूर्तियाँ
2. वीरांगनाएँ
प्रश्न 5.
गद्यांश में प्रयुक्त प्रत्यय युक्त शब्द ढूंढकर लिखिए।
उत्तर:
दौलतखाना, बैठकखाना, देवता, दर्शनीय

शब्द समूह के लिए एक शब्द लिखिए।
प्रश्न 1.
जो स्थल देखने लायक हो –
उत्तरः
दर्शनीय
प्रश्न 2.
गद्यांश में प्रयुक्त उपसर्ग युक्त शब्द ढूंढकर लिखिए।
उत्तरः
विभिन्न
कृति (4) स्वमत अभिव्यक्ति
प्रश्न 1.
‘ऐतिहासिक स्थलों की यात्रा करना एक सुखद अनुभूति के समान होता है।’ इस विषय पर अपने विचार लिखिए।
उत्तरः
भारत एक प्राचीन देश है। प्राचीनता के साथ इसका गौरवशाली इतिहास है। भारत के इतिहास की अनेक हैरतअंगेज़ घटनाएँ हैं, जिनका वर्णन भारत के ऐतिहासिक स्थल आज भी कर रहे हैं। भारत में ऐतिहासिक स्थलों की कमी नहीं है। इन दर्शनीय स्थलों को देखने के लिए हमारे देश के ही नहीं, बल्कि विदेशी पर्यटक भी प्रतिवर्ष आते हैं। इन ऐतिहासिक स्थलों की गाथाएँ सुनकर देश-विदेश के पर्यटक आज भी रोमांच का अनुभव करते हैं। भारत के लगभग सभी ऐतिहासिक स्थल वीरता, देशभक्ति, मानवता, प्रेम एवं त्याग आदि की कहानी कहते हैं।
इनमें ज्यादातर स्थल दर्शनीय हैं। भारत के अनेक ऐतिहासिक स्थलों से मैं प्रभावित हुआ हूँ। ताजमहल की सुंदरता मुझे बार-बार अपनी ओर आकर्षित करती है। वास्तुशिल्प के दृष्टिकोण से ताजमहल इतिहास का सुंदर नमूना है। पत्थरों का कलात्मक निर्माण, वास्तुकला और शिल्पकला की दृष्टि से साँची का स्तूप बहुत अनुपम है। अद्भुत और भव्य मंदिर को प्राचीन वास्तुकला का चमत्कार भी कहा जा सकता है। विजय मंदिर एक ऐतिहासिक मंदिर है। इस मंदिर को भारत का दूसरा सूर्य मंदिर भी कहते हैं। ऐतिहासिक स्थल की सैर करने से हमें अनेक प्रकार की जानकारियाँ प्राप्त होती हैं। यहाँ आकर लोग शांति की भाषा सुन और समझ पाते हैं।
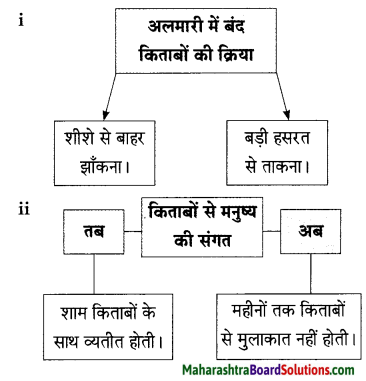
(ग) गद्यांश पड़कर दी गई सूचना के अनुसार कृतियाँ कीजिए।
कृति (1) आकलन कृति
प्रश्न 1.
आकृति पूर्ण कीजिए।
उत्तरः

प्रश्न 2.
कृति पूर्ण कीजिए।
उत्तरः
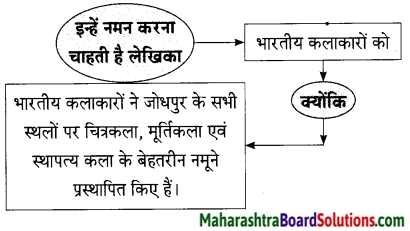
समझकर लिखिए।
प्रश्न 1.
‘जसवंत थंडा स्मारक देखते-देखते शाम हो गई थी, इसके लिए गद्यांश में प्रयुक्त वाक्य है
उत्तरः
अब सूर्य भी अपनी किरणों को समेट अस्ताचलगामी हो गया था।

कृति (2) आकलन कृति
प्रश्न 1.
निम्नलिखित वाक्यों का घटनाक्रमानुसार लेखन कीजिए।
- लेखिका पटवा की हवेलियाँ देखने के लिए गई।
- अगली प्रात: को लेखिका जैसलमेर स्टेशन पर उतरी।
- लेखिका होटल के स्वागत कक्ष में आसीन थी।
- लेखिका होटल की वैन में बैठ गई।
उत्तर:
- अगली प्रात: को लेखिका जैसलमेर स्टेशन पर उतरी।
- लेखिका होटल की वैन में बैठ गई।
- लेखिका होटल के स्वागत कक्ष में आसीन थी।
- लेखिका पटवा की हवेलियाँ देखने के लिए गई।
सत्य या असत्य पहचानकर लिखिए।
प्रश्न 1.
1. लेखिका स्वयं अपना सामान होटल के कक्ष में लेकर गई।
2. जैसलेमर से जोधपुर रात्रि की गाड़ी थी।
उत्तरः
1. असत्य
2. असत्य
प्रस्तुत गद्यांश पढ़कर ऐसे प्रश्न तैयार कीजिए जिनके उत्तर निम्न शब्द हों।
प्रश्न 1.
1. शिल्पकार
2. बारह
उत्तर:
1. धन्य कौन है?
2. एक हवेली के निर्माण में कितने वर्ष का समय लगा?

सहसंबंध लिखिए।
प्रश्न 1.
1. खूबसूरत : पत्थर :: पारदर्शक : ……..
2. पाँच : हवेलियाँ :: कलात्मक : ………
उत्तर:
1. झरोखे
2. वास्तुशिल्प
प्रश्न 2.
समझकर लिखिए।
उत्तर:
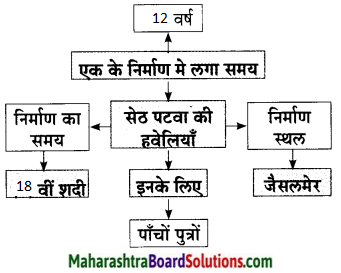
प्रश्न 3.
कृति पूर्ण कीजिए।
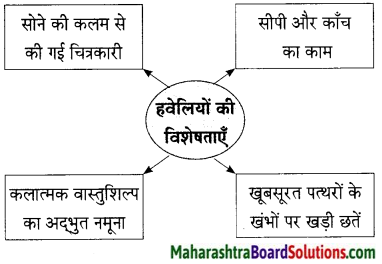
उत्तर:
कृति (3) शब्द संपदा
प्रश्न 1.
गद्यांश में इन शब्दों के अर्थ हैं
- दिनकर
- प्रसिद्ध
- तुरंत
- सिर
उत्तर:
- सूर्य
- विख्यात
- शीघ्र
- मस्तिष्क
प्रश्न 2.
विरुद्धार्थी शब्द लिखिए।
1. व्यवस्था × …………….
2. खूबसूरत × ……………
उत्तरः
1. अव्यवस्था
2. बदसूरत
प्रश्न 3.
निम्नलिखित शब्दों के कोई भी चार अनेकार्थी शब्द लिखिए।
1. काम
2. और
उत्तर:
1. इच्छा, कार्य, कामदेव, रोज़गार
2. दूसरा, तथा, खोजक शब्द, अधिक

निम्नलिखित अनेक शब्दों के लिए एक शब्द लिखिए।
प्रश्न 1.
जिसकी आने की तिथि निश्चित न हो-
उत्तरः
अतिथि
प्रश्न 2.
निम्नलिखित शब्दों में से मूल शब्द व प्रत्यय अलग करके लिखिए।
-
- भारतीय
- प्रसन्नता
- शिल्पकार
- व्यापारी
उत्तरः
| शब्द |
मूल शब्द |
प्रत्यय |
| 1. भारतीय |
भारत |
ईय |
| 2. प्रसन्नता |
प्रसन्न |
ता |
| 3. शिल्पकार |
शिल्प |
कार |
| 4. व्यापारी |
व्यापार |
ई |
लिंग बदलिए।
प्रश्न 1.
1. मालिक
2. पुत्र
उत्तर:
1. मालकिन
2. पुत्री
वचन बदलिए।
प्रश्न 1.
1. स्मृति
2. हवेलियाँ
उत्तरः
1. स्मृतियाँ
2. हवेली

प्रश्न 2.
तालिका पूर्ण कीजिए।
(स्मारक, विख्यात, मूर्तिकला, हमें, हो गई, चल पड़े, हमारा, अद्भुत)
उत्तरः
| संज्ञा |
सर्वनाम |
विशेषण |
क्रिया |
| स्मारक |
हमें |
विख्यात |
हो गई |
| मूर्तिकला |
हमारा |
अद्भुत |
चल पडे |
कृति (4) स्वमत अभिव्यक्ति
प्रश्न 1.
‘ऐतिहासिक कलात्मक वास्तुशिल्प के प्रति हमारे मन में आकर्षण होना चाहिए।’ अपने विचार लिखिए।
उत्तरः
ऐतिहासिक कलात्मक वास्तुशिल्प हमारी ऐतिहासिक परंपरा एवं पुरातन कला के निदर्शक होते है। पुराने समय में भारतीय शिल्पकारों ने अपनी संस्कृति एवं कला को वास्तुशिल्प के माध्यम से समूचे संसार के सामने रखा। ये बहुत बड़ी बात है। इस कारण सम्पूर्ण संसार को भारतीय संस्कृति के बारे में जानकारी मिली।
आज हमारे देश में जगह-जगह ऐतिहासिक कलात्मक वास्तुशिल्प मौजूद हैं। देश-विदेश के पर्यटक भारत आकर यहाँ की ऐतिहासिक कला एवं संस्कृति का आस्वाद लेते हैं। ये ऐतिहासिक कलात्मक वास्तुशिल्प हमारे देश की धरोहर हैं। उनके प्रति आदर एवं सम्मान की भावना रखना हमारा परम कर्तव्य है। अत: ऐतिहासिक कलात्मक वास्तुशिल्प के प्रति हमारे मन में आकर्षण होना चाहिए।
(घ) गद्यांश पढ़कर सूचना के अनुसार कृतियाँ कीजिए।
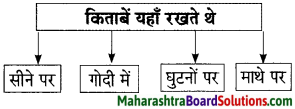
कृति (1) आकलन कृति
प्रश्न 1.
उत्तर लिखिए।
1. रेगिस्तानी जहाज पर सवार लेखिका की स्थिति
2. उँट की सवारी का अनुभव रोमांचकारी और मनोरंजक था, यह दर्शानेवाला वाक्य
उत्तर:
1. लेखिका को डर भी लग रहा था, प्रसन्नता भी हो रही थी, उत्सुकता भी थी।
2. ऊँटों की कतारें ही कतारें, सभी पर नर-नारी और बाल वृद्ध सवार थे, शायद सभी की हृदय गति वैसे ही धड़क रही थी, जैसी हमारी।
कृति (2)आकलन कृति
प्रश्न 1.
समझकर लिखिए।
1. इसे कहा गया है रेगिस्तानी जहाज –
2. विक्रेता इन वस्तुओं को बेच रहे थे –
उत्तर:
1. ऊँट
2. खिलौने, दूरबीन, चिप्स, कुरकुरे, खाखड़ा, चाट – पकोड़े

प्रश्न 2.
समझकर लिखिए।
जैसे – चमकता: सूर्य
1. अस्ता चलगामी: …..
2. राजस्थानी: …..
उत्तर:
1. भास्कर
2. कन्याएँ
प्रश्न 3.
कृति पूर्ण कीजिए।
उत्तर:
कृति (3) शब्द संपदा
निम्नलिखित शब्द मानक वर्तनी के अनुसार लिखिए।
प्रश्न 1.
- गन्तव्य
- यहां
- प्रयटक
- सूरयास्त
उत्तरः
- गंतव्य
- यहाँ
- पर्यटक
- सूर्यास्त
प्रश्न 2.
समानार्थी शब्द लिखिए।
- ग्राम
- भय
- प्रतीक्षा
- भास्कर
उत्तर:
- गाँव
- डर
- इंतजार
- सूर्य
प्रश्न 3.
शब्द समूह के लिए एक शब्द लिखिए।
1. जहाँ पहुँचना है, वह स्थान
2. जहाँ आसमान ने भूमि को स्पर्श किया है, वह स्थान
उत्तरः
1. गंतव्य
2. क्षितिज

प्रश्न 4.
गद्यांश में प्रयुक्त प्रत्यय युक्त शब्द पहचानकर लिखिए।
- रेगिस्तानी
- चमकता
- राजस्थानी
उत्तर:
- रेगिस्तान + ई
- चमक + ता
- राजस्थान + ई
लिंग बदलिए।
प्रश्न 1.
ऊँट
उत्तरः
ऊँटनी
वचन बदलिए।
प्रश्न 1.
- खिलौने
- याद
- नारी
- कतार
उत्तर:
- खिलौना
- यादें
- नारियाँ
- कतारें
कृति (4) स्वमत अभिव्यक्ति
प्रश्न 1.
ऊँट को ‘रेगिस्तान का जहाज’ कहा जाता है। इस विषय पर अपने विचार लिखिए।
उत्तरः
रेगिस्तान में जब रेतीली हवाएँ चलती हैं, तब ऊँट अपने नथुनों को बंद कर लेता है। जिससे रेत उसकी नाक में नहीं जा पाती। ऊँट के घुटने और गरदन में कठोरता होती है; जो उसे उठतेबैठते समय रगड़ से बचाती है। यह रेगिस्तान में आसानी से चल एवं दौड़ सकता है। यह अपने शरीर के उभार में अधिक मात्रा में पानी एकत्र कर सकता है। यह गाड़ी खींचने एवं बोझा उठाने के काम आता है। ऊँट का उपयोग कृषि कार्य एवं पानी खींचने में भी किया जाता है। इसलिए ऊँट रेगिस्तान के लिए सर्वाधिक उपयुक्त वाहन है।

(ङ) गद्यांश पढ़कर दी गई सूचना के अनुसार कृतियाँ कीजिए।
कृति (1) आकलन कृति
प्रश्न 1.
कारण लिखिए।
दर्शक भाव विभोर हो गए थे-
उत्तरः
दर्शक भाव विभोर हो गए क्योंकि राजस्थान के जाने-माने कलाकारों ने वहाँ की लोक-संस्कृति को नृत्य-नाटिका और गायन के माध्यम से अद्भुत प्रस्तुति दी थी।
समझकर लिखिए।
प्रश्न 1.
1. इस दिन पहुँची लेखिका चित्तौड़गढ़ –
2. ‘भोजन का लुत्फ सभी ने उठाया।’
(यह भाव व्यक्त करने वाला वाक्य है)
उत्तर:
1. 24 दिसंबर के सायंकाल।
2. सेल्फ सर्विस-जैसा रुचे, जितना रुचे, लीजिए, खाइए, आनंद उठाइए की तर्ज पर सब भोजन कर रहे थे।
कृति (2) आकलन कृति
प्रश्न 1.
कृति पूर्ण कीजिए।
- गद्यांश में प्रयुक्त स्वाभिमानी देशभक्त –
- गद्यांश में प्रयुक्त कृष्ण भक्त –
- गद्यांश में प्रयुक्त एक घोड़ा –
उत्तर:
- महाराणा प्रताप, भामाशाह
- मीरा
- चेतक

समझकर लिखिए।
प्रश्न 1.
गद्यांश में महाराणा प्रताप की विशेषता बताने वाले शब्द।
उत्तर:
वीर, साहसी, स्वाभिमानी, देशभक्त
सत्य या असत्य पहचानकर लिखिए।
प्रश्न 1.
1. भामाशाह स्वामिभक्त थे।
2. प्रतिकूल परिस्थितियों में भी महाराणा प्रताप ने हार नहीं मानी।
उत्तर:
1. सत्य
2. सत्य
कृति (3) शब्द संपदा
प्रश्न 1.
परिच्छेद में प्रयुक्त विलोम शब्द की जोड़ी लिखिए।
उत्तरः
देश – विदेश
प्रश्न 2.
इनके लिए गद्यांश में समानार्थी शब्द है।
- आग
- हर्ष
- निशा
- पृथ्वी
उत्तर:
- अग्नि
- आनंद
- रात्रि
- धरती
निम्नलिखित शब्द के अनेकार्थी शब्द लिखिए।
प्रश्न 1.
कृष्ण
उत्तर:
काला, भगवान श्री कृष्ण।
शब्द समूह के लिए एक शब्द लिखिए।
प्रश्न 1.
1. संस्कृति से संबंधित
2. स्थान, जहाँ दो या तीन नदियाँ आकर आपस में मिलती हैं
उत्तर:
1. सांस्कृतिक
2. संगम
लिंग बदलिए।
प्रश्न 1.
1. सम्राट
2. वीर
उत्तर:
1. सम्राज्ञी
2. वीरांगना

निम्नलिखित शब्दों के उचित प्रत्यय लगाकर नए शब्द तैयार कीजिए।
प्रश्न 1.
- परिवार
- स्वाभिमान
- साहस
उत्तर:
- पारिवारिक
- स्वाभिमानी
- साहसी
निम्नलिखित वाक्य शुद्ध करके फिर से लिखिए।
प्रश्न 1.
1. इन सब स्मृति की साथ होटल वापस आए।
2. लेखिका जीप में सवार हुआ।
उत्तरः
1. इन सब स्मृतियों के साथ होटल वापस आए।
2. लेखिका जीप पर सवार हुई।
विराम चिह्न का प्रयोग कीजिए।
प्रश्न 1.
कितने साहसी वीर और स्वाभिमानी देशभक्त थे महाराणा प्रताप
उत्तर:
कितने साहसी, वीर और स्वाभिमानी देशभक्त थे, महाराणा प्रताप।
कृति (4) स्वमत अभिव्यक्ति
प्रश्न 1.
‘राजस्थानी संस्कृति की अपनी विशेषता है।’ इस विषय पर अपने विचार लिखिए।
उत्तर:
राजस्थान का विशिष्ट नृत्य घूमर है । विविध उत्सवों के अवसर पर केवल महिलाओं द्वारा यह नृत्य किया जाता है। घेर नृत्य, पनिहारी नृत्य व कच्ची घोड़ी (जिसमें पुरुष नर्तक बनावटी घोड़ी पर बैठे होते हैं) भी लोकप्रिय है। राजस्थान में मुश्किल से कोई महीना ऐसा जाता होगा, जिसमें धार्मिक उत्सव न हो। सबसे उल्लेखनीय व विशिष्ट उत्सव गणगौर है, जिसमें महादेव व पार्वती की मिट्टी की मूर्तियों की पूजा 15 दिन तक सभी जातियों की स्त्रियों के द्वारा की जाती है और बाद में उन्हें जल में विसर्जित कर दिया जाता है।
विसर्जन की शोभायात्रा में पुरोहित व अधिकारी भी शामिल होते हैं व बाजे-गाजे के साथ शोभा यात्रा निकलती है। हिन्दू और मुसलमान, दोनों एकदूसरे के त्योहारों में शामिल होते हैं। इन अवसरों पर उत्साह व उल्लास का बोलबाला रहता है। अमलाना, अरबी का साग, आटे का मालपुवा, आम और चने का अचार, आम की लौजी, आलू पेठे का साग, कांजी वड़ा व तरला दलाल ये राजस्थान के खास व्यंजन हैं।

(च) गद्यांश पढ़कर दी गई सूचना के अनुसार कृतियाँ कीजिए।
कृति (1) आकलन कृति
प्रश्न 1.
समझकर लिखिए।
इन गुणों से परिपूर्ण हैं चित्तौड़ के बाशिंदे
उत्तरः
सहजता, सरलता, भाईचारा
प्रश्न 2.
गद्यांश में प्रयुक्त राजस्थान की प्रसिद्ध रानी
उत्तरः
रानी पद्मिनी
प्रश्न 3.
इसका प्रतीक है ‘विजय स्तंभ’
उत्तरः
मालवा के सुल्तान और गुजरात के सुल्तान के संयुक्त आक्रमण की साहसिक विजय गाथा का प्रतीक है।
कृति (2) आकलन कृति
प्रश्न 1.
कृति पूर्ण कीजिए।
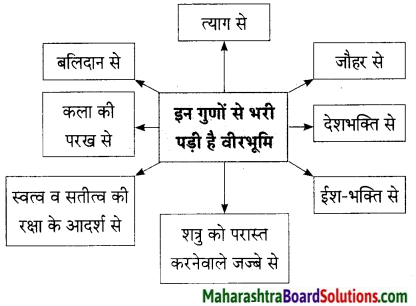
उत्तरः
प्रश्न 2.
सत्य या असत्य पहचानकर लिखिए।
1. गढ़ों में गढ़ चित्तौड़गढ बाकी सब गलैया।
2. पूर्व की ओर बना रामपोल ही किले का मुख्य प्रवेश द्वार है।
उत्तर:
1. सत्य
2. असत्य

कृति (3) शब्द संपदा
प्रश्न 1.
समानार्थी शब्द लिखिए।
- दुर्ग
- प्रतिमा
- मंदिर
- बाशिंदा
उत्तर:
- किला
- मूर्ति
- देवालय
- निवासी
प्रश्न 2.
विलोम शब्द लिखिए।
1. शत्रु × ……………….
2. वीरता × …………….
उत्तर:
1. मित्र
2. कायरता
प्रश्न 3.
वचन बदलिए।
- यात्रा
- प्रतिमा
- संस्कृति
- रानी
उत्तर:
- यात्राएँ
- प्रतिमाएँ
- संस्कृतियाँ
- रानियाँ
प्रश्न 4.
निम्नलिखित शब्दों में उचित प्रत्यय लगाकर नए शब्द तैयार कीजिए।
- विजय
- निर्मित
- वीर
- दर्शन
- सहज
- सरल
उत्तर:
- विजयी
- निर्मिती
- वीरता
- दर्शनीय
- सहजता
- सरलता

कृति (4) स्वमत अभिव्यक्ति
प्रश्न 1.
‘राजस्थान त्याग व बलिदान की भूमि है।’ इस विषय पर अपने विचार लिखिए।
उत्तर:
राजस्थान त्याग व बलिदान की भूमि है। इस विचार से मैं पूर्णत:
सहमत हूँ। राजस्थान की रक्षा करने के लिए कई वीरों ने अपने प्राणों का बलिदान दिया हैं। सिर्फ वीर ही नहीं बल्कि कई स्त्रियों ने अपने प्राणों की कुरबानी दे दी है। इतना ही नहीं, अपनी भूमि की रक्षा करने के लिए एवं अपनी देशभक्ति निभाने के लिए पन्ना धाय ने कुँवर के प्राणों की रक्षा हेतु अपने पुत्र की बलि दे दी थी। वीर महाराणा प्रताप अपनी भूमि की रक्षा हेतु प्रतिकूल परिस्थितियों में जंगल में रहे। इतना ही नहीं, दुश्मनों के हाथों से अपनी प्रतिष्ठा एवं लाज रखने हेतु कई स्त्रियों ने आत्मदहन भी किया था। रानी पद्मिनी के जौहर को हम भारतवासी कैसे भूल सकते हैं।
भाषाई कौशल पर आधारित पाठगत कृतियाँ
भाषा बिंदु –
प्रश्न 1.
अव्यय पहचानकर लिखिए।
- सामान वहाँ रखकर थोड़ा तरोताजा हुए।
- हम ‘उम्मेद भवन’ की ओर चल पड़े।
- रानी उद्यान के बाईं ओर पहाड़ी की एक चट्टान है।
- दुर्ग के अंदर कई भव्य और विशाल भवन हैं।
- यहाँ जौहर कुंड में कई वीरांगनाओं ने अपने आप को समर्पित कर दिया था।
- इस भूमि पर त्याग भी है और बलिदान भी।
- पर्यटक भास्कर को कैमरे में बंद करने के लिए सन्नद्ध थे।
- आज ही ‘सम’ का कार्यक्रम भी था।
उत्तर:
- वहाँ – क्रियाविशेषण अव्यय
- की ओर – संबंधसूचक अव्यय
- ओर – संबंधसूचक अव्यय
- और – समुच्चयबोधक अव्यय
- यहाँ – क्रियाविशेषण अव्यय
- और – समुच्चय बोधक अव्यय
- (के) लिए – संबंधसूचक अव्यय
- आज – क्रिया विशेषण अव्यय
प्रश्न 2.
काल परिवर्तन कीजिए।
- एक भाग में शाही परिवार रहता है। (अपूर्ण भूतकाल)
- ‘भवन’ का मॉडल भी प्रदर्शित किया गया है। (अपूर्ण वर्तमानकाल)
- हम काफी ऊपर आ जाते हैं। (अपूर्ण भूतकाल)
- उन्होंने देवताओं की विशाल मूर्तियाँ बनवाई। (सामान्य भविष्यकाल)
- हम जैसलमेर स्टेशन पर उतरे। (पूर्ण वर्तमानकाल)
- इसी शहर से मीरा जैसी कृष्ण भक्त की यादें भी जुड़ी हैं। (अपूर्ण भूतकाल)
- हम ‘चित्तौड़गढ़’ पहुँच गए। (सामान्य वर्तमानकाल)
उत्तर:
- एक भाग में शाही परिवार रह रहा था।
- ‘भवन’ का मॉडल भी प्रदर्शित किया जा रहा है।
- हम काफी ऊपर आ रहे थे।
- वे देवताओं की विशाल मूर्तियाँ बनवाएँगे।
- हम जैसलमेर स्टेशन पर उतरे हैं।
- इसी शहर से मीरा जैसी कृष्ण भक्त की यादें भी जुड़ रही थीं। .
- हम ‘चित्तौड़गढ़’ पहुँच जाते हैं।

प्रश्न 3.
निम्नलिखित वाक्यों में विराम-चिह्नों का प्रयोग कीजिए।
1. इसमें ऐश्वर्य विलास और आमोद प्रमोद के सभी साधन उपलब्ध हैं
2. आज का हमारा पड़ाव जोधपुर था
उत्तर:
1. इसमें ऐश्वर्य, विलास और आमोद-प्रमोद के सभी साधन उपलब्ध हैं।
2. आज का हमारा पड़ाव ‘जोधपुर’ था।
प्रश्न 4.
निम्नलिखित वाक्य शुद्ध करके फिर से लिखिए।
- इसका निर्माण पर बीस वर्ष का समय लगा।
- अभी हम अपना दूसरे गंतव्य की ओर बढ़ना था।
- जयपोल तक आते-आते ही शहर नीचा रह जाता हैं।
- यह प्रवेश द्वार विजय की प्रतीक रूप में बनवाए गए हैं।
उत्तरः
- इसके निर्माण में बीस वर्ष का समय लगा।
- अभी हमें अपने दूसरे गंतव्य की ओर बढ़ना था।
- जयपोल तक आते-आते ही शहर नीचे रह जाता है।
- ये प्रवेश द्वार विजय के प्रतीक रूप में बनवाए गए हैं।
सर्वनाम पहचानकर लिखिए।
प्रश्न 1.
उसके परकोटे में बुर्जियाँ बनाई गई हैं।
उत्तरः
उसके – सर्वनाम
विशेषण पहचानकर लिखिए।
प्रश्न 1.
मेहरान गढ़ किला ऊँची दीवार के परकोटे से घिरा है।
उत्तरः
ऊँची – विशेषण
प्रश्न 2.
वाक्य के प्रकार पहचानकर लिखिए।
- कहीं बैठकखाना तो कहीं दीवानेखास हैं तो कहीं पेंटिंग्स एवं दरियाँ भी प्रदर्शित की गई हैं।
- चट्टानों को काटकर मूर्तियों को दर्शाया गया है।
- सभी की हृदयगति धड़क रही थी।
- ‘सम’ एक ग्राम है, जो होटल से ११-१२ कि. मी. दूर रेत की चादर पर बसा है।
- र्शनीय स्थलों में एक विशाल दुर्ग है, जिसके विषय में कहा जाता है कि गढ़ों में गढ़ चित्तौड़गढ़ बाकी सब गढ़ेया।
- इस भूमि पर त्याग भी है और बलिदान भी।
उत्तरः
- मिश्र वाक्य
- सरल वाक्य
- सरल वाक्य
- मिश्र वाक्य
- मिश्र वाक्य
- संयुक्त वाक्य

प्रश्न 3.
निम्नलिखित वाक्यों में से कारक छाँटिए और उनके भेद पहचानिए।
- वह ऊँची दीवार के परकोटे से घिरा है।
- उसके परकोटे में जगह-जगह बुर्जियाँ बनाई गई हैं।
- द्वारों की दीवारों पर जौहर करनेवाली वीरांगनाओं के हस्तचिह्न भी बने हैं।
- विक्रेता बच्चों के खिलौने बेच रहे थे।
- हम सब अपने गंतव्य पर पहुंच गए।
- रानी पद्मिनी ने जौहर कुंड में अपने प्राण समर्पित कर दिए थे।
- महाराणा प्रताप ने देश के लिए अपने प्राण अर्पण किए।
उत्तर:
- से – करण कारक
- में – अधिकरण कारक
- पर – अधिकरण कारक
- के – संबंध कारक
- पर – अधिकरण कारक
- ने – कर्ता कारक
- के – संप्रदान कारक
प्रश्न 4.
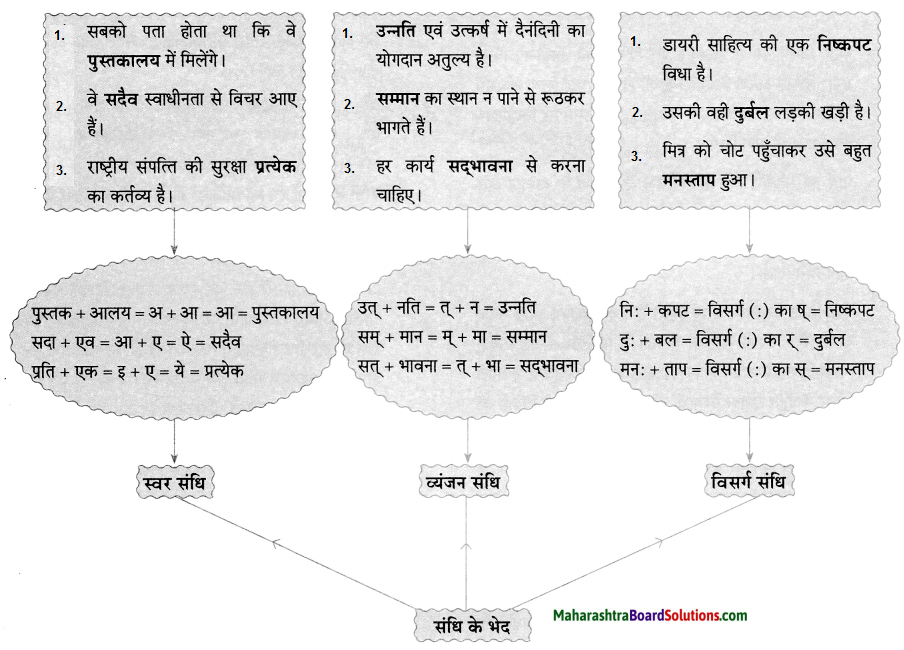
निम्नलिखित शब्दों के संधि-विच्छेद कीजिए।
- नरेश
- गायक
- जलाशय
- मनोरम
- तत्काल
- स्वागत
- मनोरंजक
उत्तर:
- नर + ईश
- गै + अक
- जल + आशय
- मनः + रम
- तत् + काल
- सु + आगत
- मनः + रंजक
प्रश्न 5.
निम्नलिखित क्रियाओं के प्रथम तथा द्वितीय प्रेरणार्थक रूप लिखिए।
1. दिखना
2. करना
उत्तर:
1. दिखाना – दिखवाना
2. कराना – करवाना

प्रश्न 6.
निम्नलिखित क्रिया शब्द के प्रथम तथा द्वितीय प्रेरणार्थक क्रिया रूप लिखिए।
उत्तर:
| मूल क्रिया |
प्रथम प्रेरणार्थक |
द्वितीय प्रेरणार्थक |
| 1. सुनना |
सुनाना |
उतारना |
| 2. उतरना |
सुनवाना |
उतरवाना |
वीरभूमि पर कुछ दिन Summary in Hindi
लेखक-परिचय:
जीवन-परिचय: रुक्मणी संगल का जन्म 1 सितंबर 1945 को बुढ़ाना (उत्तर प्रदेश) में हुआ। वह एक आधुनिक लेखिका हैं। इनके द्वारा लिखे गए यात्रा वर्णनपरक लेख प्रसिद्ध हैं। विभिन्न पत्र-पत्रिकाओं में स्वतंत्र लेखन करने का कार्य रुक्मणी जी कर रही हैं। प्रमुख कृतियाँ: ‘दिनकर के काव्य में जीवन मूल्य’ विषय पर शोध प्रबंध।
गद्य-परिचय:
यात्रा वर्णन: यात्रा वर्णन में अपने द्वारा किए गए किसी पर्यटन की अपनी अनुभूतियों, प्रकृति कला का पर्यवेक्षण, स्थान की विशेषताओं
आदि का लगावपूर्ण वर्णन किया जाता है।
प्रस्तावना: प्रस्तुत पाठ यात्रा वर्णनपरक है। इस पाठ में लेखिका ने वीरभूमि राजस्थान की यात्रा का बड़ा ही मनोहारी वर्णन किया है। वहाँ के गढ़, किले, महल एवं वहाँ की कला-संस्कृति का सुंदर वर्णन किया है।
सारांश:
रुक्मणी जी को ऐतिहासिक स्थलों की यात्रा करना बहुत अच्छा लगता है। लेखिका ने वीरभूमि राजस्थान की यात्रा का वर्णन इस पाठ में किया है। वहाँ के शाही महल एवं उनकी कलात्मकता का चित्रमय वर्णन पाठ में हुआ है। मेहरान गढ़ किला राजस्थान की कला का एक सुंदर उदाहरण है। पटवा की हवेलियाँ कलात्मक वास्तु शिल्प का अद्भुत नमूना है। चित्तौड़गढ़ के दर्शनीय स्थल सभी पर्यटकों के आकर्षक केंद्र हैं। सचमुच राजस्थान सिर्फ एक वीरभूमि ही नहीं बल्कि कला संस्कृति की अनुपम भूमि भी है।
शब्दार्थ:
- गति – वेग
- अल्पाहार – नाश्ता
- भवन – महल या प्रासाद
- आमोद-प्रमोद – मनोरंजन
- शाही – राजवंशी
- मनोहर – सुंदर
- समीप – पास
- अपभ्रंश – शब्द का बिगड़ा हुआ रूप
- आकांक्षा – इच्छा
- लौहपथगामिनी – रेल
- भाँति-भाँति – तरह-तरह की
- पंक्तिबद्ध – क्रमबद्ध, एक के बाद एक
- सन्नद्ध – एकाग्र या व्यस्त
- परकोटा – गढ़ या किले की रक्षा के लिए बनाया गया घेरा जिसके ऊपर टहलने के लिए जगह होती है।
- मनभावन – मन को आकर्षित करनेवाली
- जौहर – वीर राजपूत स्त्रियों ने दुश्मनों से अपनी लाज एवं प्रतिष्ठा बरकरार रखने के लिए अपने आप को अग्निकुंड में समर्पित कर दिया था।
- उनके इस कार्य को जौहर कहा जाता है।
- सैलाब – पानी की बाढ़

मुहावरे:
1. दृष्टिगोचर होना – दिखाई देना।
2. दस्तक देना – दरवाजा खटखटाना।
Hindi Lokbharti 9th Digest Answers Pdf पहली इकाई
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()