Class 8 Hindi Chapter 3 Nakhun kyon Badhate Hain Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 8 Hindi Solutions Sulabhbharati Chapter 3 नाखून क्यों बढ़ते हैं? Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Std 8 Hindi Chapter 3 Nakhun kyon Badhate Hain Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Hindi Sulabhbharti Class 8 Solutions Chapter 3 नाखून क्यों बढ़ते हैं? Textbook Questions and Answers
स्वाध्याय विषयक कृतियाँ
प्रतीक लिखिए।
Answer:


भाषाबिंदु
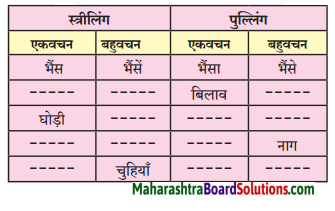
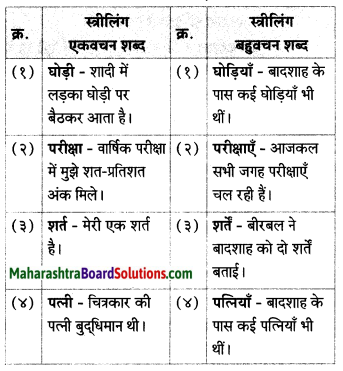
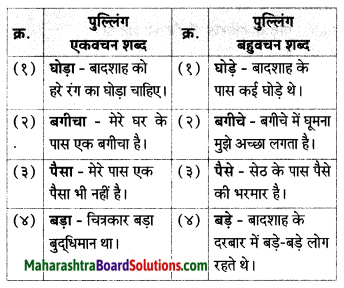
निम्न शब्दों के लिंग पहचानकर लिखिए।
(आत्मा, व्यक्ति, बादल, तार, नोट, नाखून, पुस्तक, तकिया, दही)
Answer:
पुल्लिंग: व्यक्ति, बादल, नोट, नाखून, दही, तकिया, तार
स्त्रीलिंग: आत्मा, पुस्तक, तार
कृति ग (१) आकलन कृति
प्रवाह तालिका पूर्ण कीजिए।
Answer:


Question 1.
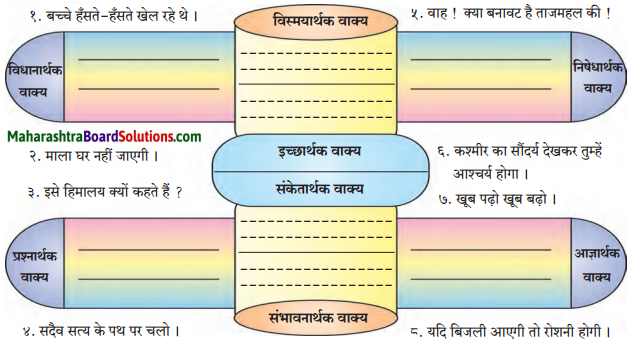
अर्थ के अनुसार वाक्य के प्रकार ढूँढ़कर लिखिए।
Answer:
(१) विधानार्थक वाक्य:
(i) उसे नाखून की जरूरत थी।
(ii) उसने धातु के हथियार बनाए।
(२) प्रश्नार्थक वाक्य:
(i) आखिर ये इतने बेहया क्यों हैं?
(ii) मनुष्य किस ओर बढ़ रहा है?
(३) निषेधार्थक वाक्य :
(i) वह मरना नहीं जानती।
(ii) मैं कुछ सोच ही नहीं सका।
(४) आज्ञार्थक वाक्य:
(i) नाखून बढ़ रहे है तो उन्हें काट दीजिए।
(५) विस्मयादिबोधक वाक्यः
(i) वाह! क्या बात है। मनुष्य मनुष्यता की ओर बढ़ रहा है।
संदेशसूचक वाक्य:
(i) मनुष्य अपनी पशुता को त्याग दे तब मरणास्त्रों का प्रयोग भी अपने आप समाप्त हो जाएगा।

Question 2.
पाठ में आए दस पुल्लिंग व स्त्रीलिंग शब्द लिखिए।
Answer:
पुल्लिंग: प्रश्न, पिता, नाखून, शरीर, हथियार, नागरिक, आदर्श, संयम, तप, त्याग
स्त्रीलिंग: लड़की, पशुता, मनुष्यता, सहायता, इच्छा, श्रद्धा, संवेदना, पूँछ, घृणा, महिमा
उपयोजित लेखन
किसी मराठी विज्ञापन का हिंदी में अनुवाद कीजिए।
Answer:



लेखनीय
‘सुरक्षा हेतु शस्त्रों की भरमार’ विषय के पक्ष-विपक्ष में अपने विचार लिखिए।
Answer:
पक्षधर विचार:
(i) क्षत्रिय कुल के लोग शस्त्रों का पूजन करते हैं।
(ii) पुलिस विभाग द्वारा भी शस्त्रों का पूजन किया जाता है।
(iii) शस्त्र विपरीत परिस्थितियों में दूसरों के जीवन की रक्षा करते हैं।
(iv) शस्त्र शक्ति का प्रतीक होते हैं।
विपक्षी विचार:
(i) शस्त्र विनाश का प्रतीक होते हैं।
(ii) शस्त्र हिंसा का निर्माण करते हैं।
(iii) शस्त्र-निर्माण पर कई देश ढेर सारे रुपये खर्च करते हैं।
(iv) शस्त्र-निर्माण की होड़ देशों को अंधा बना देती है।

स्वयं अध्ययन
शरीर के विभिन्न अंगों से संबंधित मुहावरों की अर्थ सहित सूची बनाइए।
Answer:




उत्तर लिखिए।
Question 1.
मनुष्य को नाखून की जरूरत तब थी:
Answer:
मनुष्य को नाखून की जरुरत तब थी जब वह वनमानुष जैसा जंगली था।
Question 2.
मनुष्य का स्वधर्म यह हैं
Answer:
अपने को संयत रखना।
Hindi Sulabhbharti Class 8 Solutions Chapter 3 नाखून क्यों बढ़ते हैं? Additional Important Questions and Answers
निम्नलिखित गद्यांश पढ़कर दी गई सूचनाओं के अनुसार कृतियाँ कीजिए।
कृति क (१) आकलन कृति
उत्तर लिखिए।
Question 1.
इसे कहा गया है दयनीय जीव
Answer:
पिता को
Question 2.
इसकी पशुता का प्रयोग गद्यांश में हुआ है
Answer:
मनुष्य की

कृति पूर्ण कीजिए।

Answer:

कृति क (२) आकलन कृति
उपर्युक्त गद्यांश से ऐसे दो प्रश्न तैयार कीजिए जिनके उत्तर निम्नलिखित शब्द हों
Question 1.
हथियार
Answer:
मनुष्य ने हड्डियों के क्या बनाए?
Question 2.
नाखून
Answer:
पहले मनुष्य के अस्त्र क्या थे?

परिणाम लिखिए।
Question 1.
मनुष्य का धीरे-धीरे आगे बढ़ने का परिणाम
Answer:
उसने धातु के हथियार बनाए।
कारण लिखिए
Question 1.
मनुष्य नाखूनों को काट देता है।
Answer:
क्योंकि हर तीसरे दिन उसके नाखून बढ़ जाते हैं
कृति क (३) शब्द संपदा
Question 1.
गद्यांश में आए शब्द-युग्म ढूंढकर लिखिए।
Answer:
कभी-कभी
धीरे-धीरे
लिंग बदलिए।
- पिता
- आदमी
Answer:
- माता
- औरत

नीचे दिए हुए शब्दों के पर्यायवाची शब्द लिखिए।
- हथियार
- पाशवी
Answer:
- शस्त्र
- पशुवत, दानवी
निम्नलिखित शब्दों में उचित प्रत्यय लगाइए।
- इतिहास
- मनुष्य
Answer:
- ऐतिहासिक
- मनुष्यता
कृति क (४) स्वमत अभिव्यक्ति
Question 1.
‘मनुष्य की पशुता को जितनी बार काट दो, वह मरना नहीं जानती।’ कथन के संदर्भ में अपने विचार लिखिए।
Answer:
जी हाँ, मनुष्य की पशुता को जितनी बार काट दो, वह मरना नहीं जानती। मनुष्य का स्वभाव इतना विचित्र है कि उसमें अच्छाई भी है और बुराई भी; उसमें मानवता भी है और पशुता भी। अक्सर देखा जाता है कि बुरा काम करने वाले लोगों को कानून के द्वारा दंडित किया जाता है। फिर भी सजा काटने के बाद वे बुरा काम करते ही रहते हैं। जो व्यक्ति दूसरों का बुरा चाहता हैं; वह कभी सुधरता नहीं। उसे आप लाख समझाओ, फिर भी वह समझने के लिए तैयार नहीं होता है। वह मौका मिलते ही साँप की भाँति डंसने के लिए तैयार हो जाता है। इस प्रकार मनुष्य की पशुता को जितनी बार भी काटो, वह मरना नहीं जानती।

गद्यांश पढ़कर दी गई सूचनाओं के अनुसार कृतियाँ कीजिए।
कृति ख (१) आकलन कृति
गद्यांश के आधार पर वाक्य पूर्ण कीजिए।
Question 1.
मनुष्य को तब अपनी वास्तविक प्रवृत्ति पहचानने में बहुत सहायता मिलती हैं.
Answer:
जब वह अपने शरीर की मन की और वाक की अनायास घटने वाली वृत्तियों के विषय में सोचने लगता है।
निम्नलिखित गलत वाक्य सही करके लिखिए।
Question 1.
मनुष्य की नाखून काटने की जो प्रवृत्ति है, वह उसकी पशुता की निशानी है।
Answer:
मनुष्य की नाखून काटने की जो प्रवृत्ति है, वह उसकी मनुष्यता की निशानी है।
Question 2.
हमारी परंपरा महिमामयी और संस्कृति उज्ज्वल हैं।
Answer:
हमारी परंपरा महिमामयी और संस्कार उज्ज्वल हैं।
कृति ख (२) आकलन कृति
कृति पूर्ण कीजिए।

Answer:


कारण लिखिए।
Question 1.
हमारी परंपरा महिमामयी और संस्कार उज्ज्वल है।
Answer:
हमारी परंपरा, महिमामयी और संस्कार उज्ज्वल है क्योंकि अपने आप पर, अपने आप द्वारा लगाया हुआ बंधन हमारी संस्कृति की बहुत बड़ी विशेषता है।
कृति ख (३) शब्द संपदा
उचित प्रत्यय जोड़कर नए शब्द बनाइए।
- अर्थ
- नागरिक
Answer:
- आर्थिक
- नागरिकता
अनेक शब्दों के लिए एक शब्द लिखिए।
- मनुष्य होने की अवस्था
- उत्तम या सुधरी हुई स्थिती
Answer:
- मनुष्यता
- संस्कृति
विलोम शब्द लिखिए।
- अर्थ x
- बंधन x
Answer:
- अर्थ x अनर्थ
- बंधन x मुक्ति

कृति ख (४) स्वमत अभिव्यक्ति
‘Question 1.
आज का मनुष्य पशुता की ओर बढ़ रहा है या मनुष्यता की ओर?’ कथन के संदर्भ में अपने विचार लिखिए।
Answer:
आज का युग विज्ञान व तकनीकी का युग है। सर्वत्र मशीनों का बोलबाला है। मनुष्य ने स्वयं की प्रगति के लिए आधुनिक सभ्यता को अपना लिया है। समाज से मानवीय मूल्य कहीं गायब होते हुए दिखाई दे रहे हैं। आज हमारे समाज में हिंसा व भ्रष्टाचार जैसी कई समस्याएँ है। इनके कारण इंसान अपनी अच्छाइयों को त्याग बुराई के मार्ग पर चलता दिखाई दे रहा है। आज किसी के पास भी इतना समय नहीं है कि वह अपने ही रिश्तेदारों के साथ आराम से बैठकर बातचीत कर सकें। सभी पैसे के पीछे भाग रहे हैं। स्वार्थ की भावना ने मानव को दानव बना दिया है। अत: आज मनुष्यता की अपेक्षा पशुता ही अधिक दिखाई दे रही है।

निम्नलिखित कथन सत्व है या असत्य लिखिए।
Question 1.
मनुष्य झगड़े-टंटे को अपना आदर्श नहीं मानता है।
Answer:
सत्य
Question 2.
वचन, मन एवं शरीर से किए गए असत्याचरण को सही मानता है।
Answer:
असत्य

कृति ग (२) आकलन कृति (१) समझकर लिखिए।
Question 1.
प्राणिशास्त्रियों का अनुमान
Answer:
मनुष्य का अनावश्यक अंग उसी प्रकार झड़ जाएगा जिस प्रकार उसकी पूँछ झड़ गई है।
Question 2.
वह है मनुष्य के भीतर की पशुता की निशानी –
Answer:
नाखून का बढ़ना।
सही विकल्प चुनकर वाक्य फिर से लिखिए।
Question 1.
शायद उस दिन वह …….. का प्रयोग भी बंद कर देगा। (अस्त्री, शस्त्रों, मरणास्त्रों)
Answer:
शायद उस दिन वह मरणास्त्रों का प्रयोग भी बंद कर देगा।
Question 2.
नाखून को बढ़ने नहीं देना मनुष्य की अपनी ……… है। (इच्छा, वासना, जिज्ञासा)
Answer:
नाखून को बढ़ने नहीं देना मनुष्य को अपनी इच्छा है।

कृति ग (३) शब्द संपदा
निम्नलिखित शब्दों में उचित प्रत्यय लगाइए।
- भीतर
- झगड़ा
- प्रयोग
- इच्छा
Answer:
- भीतरी
- झगड़ालू
- प्रायोगिक
- ऐच्छिक
वचन बदलिए।
- निशानी
- संवेदना
Answer:
- निशानियाँ
- संवेदनाएँ
निम्नलिखित शब्दों में से उपसर्ग अलग करके लिखिए।
- अनावश्यक
- संवेदना
Answer:
- उपसर्ग : अन्
- उपसर्ग : सम्

कृति ग (४) स्वमत अभिव्यक्ति
‘Question 1.
किसी में बुरी आदतें आ जाए, तो उन्हें त्याग देना चाहिए।’ कथन के संदर्भ में अपने विचार लिखिए।
Answer:
मनुष्य वही कहलाता है जिसके पास मनुष्यता होती है और जिसके पास मनुष्यता होती है उसके पास अच्छाइयाँ जरूर होती है। लेकिन सभी अच्छाइयों को नहीं अपनाते हैं। किसी-किसी के स्वभाव में कुछ बुराइयाँ भी होती हैं। कई लोग बुरी आदतों के शिकार होते हैं। बुरी आदतों के कारण व्यक्ति पतन की ओर बढ़ता है। वह स्वयं तो डूब जाता है पर अपने साथ दूसरों का भी बुरा कर देता है। अत: व्यक्ति को बुरी आदतों का त्याग कर देना चाहिए। इसमें ही उसकी भलाई है। आखिर मनुष्य को अच्छे व्यवहार से ही एक-दूसरे के साथ प्रगाढ़ संबंध प्रस्थापित करने चाहिए।
निम्नलिखित गद्यांश पढ़कर दी गई सूचनाओं के अनुसार कृतियाँ कीजिए।
कृति घ(१) आकलन कृति

Answer:


समझकर लिखिए।
- पशुत्व का द्योतक
- मनुष्य का स्वधर्म यह हैं
Answer:
- अपने को संयत रखना।
- दूसरे के मनोभावों का आदर करना।
कृति घ (२) आकलन कृति
उपर्युक्त गद्यांश से ऐसे दो प्रश्न तैयार कीजिए जिनके उत्तर निम्नलिखित शब्द हों
- मनुष्य
- स्वधर्म
Answer:
- नाखून को कौन बढ़ने नहीं देगा?
- दूसरे के मनोभावों का आदर करना मनुष्य का क्या है?
कृति पूर्ण कीजिए।
Question 1.
मनुष्य की सहजात वृत्ति का परिणाम
Answer:
नाखूनों का बढ़ना
Question 2.
इनसे सूचित होती है मनुष्य की महिमा
Answer:
अभ्यास व तप से प्राप्त वस्तुओं से

कृति घ (३) शब्द संपदा
विलोम शब्द लिखिए।
- मंगल
- सफलता
- जीवन
- मैत्री
- आदर
Answer:
- अमंगल
- असफलता
- मरण
- दुश्मनी
- अनादर
समानार्थी शब्द लिखिए।
- महिमा
- आदर
- त्याग
- सफलता
- चरितार्थता
Answer:
- गौरव
- सम्मान
- बलिदान
- विजय
- सार्थकता

Question 1.
‘स्वनिर्धारित’ इस शब्द में से उपसर्ग पहचानकर संबंधित उपसर्ग से दो नए शब्द बनाइए।
Answer:
स्वनिर्धारित: उपसर्ग : स्व
नए शब्द: स्वदेश, स्वभाषा
कृति घ (४) स्वमत अभिव्यक्ति
Question 1.
‘प्रेम व त्याग सर्वश्रेष्ठ मानवीय मूल्य है।’ अपने विचार लिखिए।
Answer:
सभी धर्मों का सार प्रेम है। एक-दूसरे के प्रति प्रेम की भावना रखना एवं एक-दूसरे पर प्रेम न्योछावर कर देना, यह मनुष्य का सबसे बड़ा गुण है। त्याग यानी नि:स्वार्थ भाव से दूसरों के लिए अपना सर्वस्व अर्पण करना। मदर टेरेसा ने दीन-दुखियों को प्रेम से अपनाकर उनके लिए अपने सर्वस्व का त्याग किया और उनकी सेवा की। इसलिए संसार ने ‘मदर’ कहा। राष्ट्रपिता बापूजी ने भी प्रेम व त्याग इन मूल्यों को अपनाकर मानवता का कार्य किया। देश को आजादी दिलाने के लिए कई वीरों ने अपने घर-परिवार का त्याग कर दिया था। उनके अथक प्रयासों से ही देश आजाद हुआ। अत: प्रेम व त्याग सर्वश्रेष्ठ मानवीय हैं।
निम्नलिखित वाक्यों के अर्थ के अनुसार प्रकार पहचानकर लिखिए।
Question 1.
हमारी परंपरा महिमामयी और संस्कार उज्ज्वल हैं।
Answer:
विधानार्थक वाक्य
Question 2.
मनुष्य की चरितार्थता प्रेम में नहीं है।
Answer:
निषेधार्थक वाक्य
Question 3.
क्या मनुष्य में पशुता भरी हुई है?
Answer:
प्रश्नार्थक वाक्य

Question 4.
तुम अस्त्रों का प्रयोग त्याग दो।
Answer:
आज्ञार्थक वाक्य
Question 5.
काश! मेरे पास भी त्याग व तप जैसे गुण होते।
Answer:
विस्मयादिबोधक वाक्य
Question 6.
ध्यान रहे कि सत्याचरण में शक्ति होती है।
Answer:
संदेशवाचक वाक्य
रचनात्मक कौशल पर आधारित कृतियाँ
मौलिक सृजन
Question 1.
सद्गुणों और दुर्गुणों में अंतर लिखिए।
Answer:


Hindi Sulabhbharti Class 8 Solutions पहली इकाई

![]()