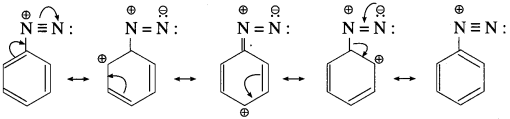
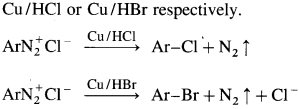
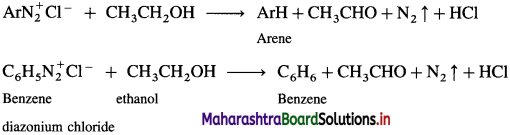
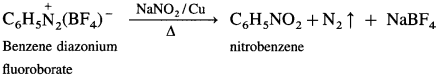
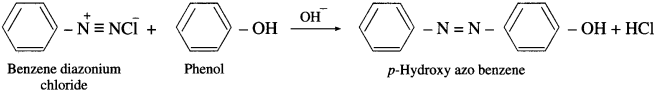
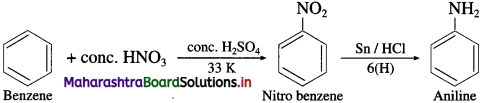
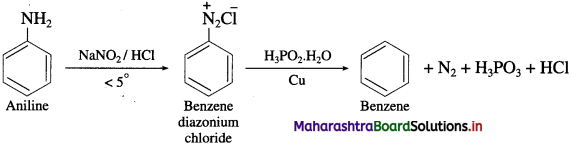
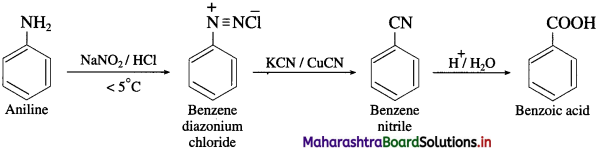
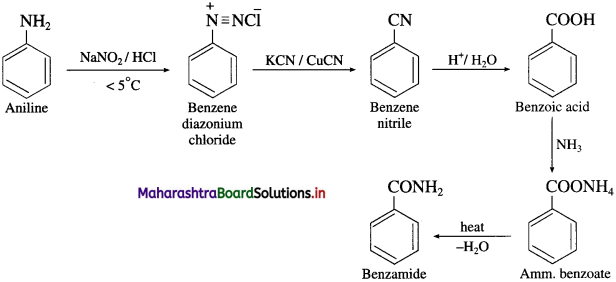
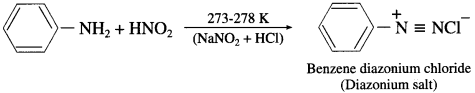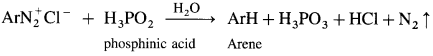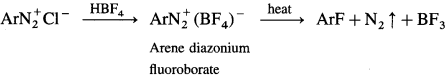Balbharti Maharashtra State Board 12th Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 5 Electrochemistry Important Questions and Answers.
Maharashtra State Board 12th Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 5 Electrochemistry
Question 1.
What is electrochemistry ?
Answer:
Electrochemistry : It is the branch of physical chemistry which involves the study of the inter-relation between chemical changes and electrical energy and also concerned with the electrical properties of electrolytic solutions such as resistance and conductance.
Question 2.
What is electric conduction?
Answer:
The transfer of electric charge or electrons from one point to another is called electric conduction which results in an electric current.
Question 3.
What are the electric conductors?
Answer:
The substances that allow the flow of electricity or electric charge transfer through them are called the electric conductors.
Question 4.
What is a flow of electricity or a transfer of electric charge?
Answer:
The flow of electricity or a transfer of electric charge through a conductor involves the transfer of electrons from one point to the other point. This takes place under the influence of applied electric potential.
Question 5.
What are the types of electric conductors? On what basis are they classified ?
Answer:
The electric conductors are classified according to the mechanism of the transfer of electrons or charge. There are two types of conductors as follows :
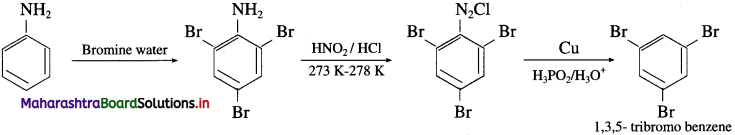
(i) Electrons (or metallic) conductors : The electric conductors through which the conduction of electricity takes place by a direct flow of electrons under the influence of applied potential are called electronic conductors.
In this case, there is no transfer of matter like atoms or ions. For example, solid and molten metals such as Al, Cu, etc.
(ii) Electrolytic conductors : The conductors in which the conduction of electricity takes place by the migration of positive ions (cations) and negative ions (anions) of the electrolyte are called electrolytic conductors. In this, the conduction involves the transfer of matter and it is accompanied with chemical changes. For example, solutions of electrolytes (strong and weak), molten salts.
![]()
Question 6.
Distinguish between electronic and electrolytic conductors.
Answer:
Electronic conductors:
- The flow of electricity takes place by direct flow of electrons through the conductor.
- The conduction does not involve the transfer of a matter.
- No chemical change is involved during conduction.
- The resistance of the conductor increases and conductivity decreases with the increase in temperature.
- The conductance of metallic conductors is very high.
- Examples are solid or molten metals, such as Al, Cu, etc.
Electrolytic conductors:
- The electron transfer takes place by the migration of ions (cations and anions) of the electrolyte.
- The conduction involves the transfer of a matter.
- Chemical changes are always involved during the passage of an electric current.
- The resistance decreases and the conductivity increases with the increase in temperature.
- The conductance of the electrolytes is comparatively low.
- Examples are aqueous solutions of acids, bases or salts.
Question 7.
What information is provided by measurement of conductivities of solutions?
Answer:
- The conducting and nonconducting properties of solutions can be identified by the measurement of their conductivities.
- The substances like sucrose and urea which do not dissociate in aqueous solutions have same conductivity as that of water. Hence they are nonelectrolytes.
- The substances like KCl, CH3COOH, NaOH, etc. dissociate in their aqueous solutions and their conductivities are higher than water. Hence they are electrolytes.
- On the basis of high or low electrical conductivity, the electrolytes can be classified as strong and weak electrolytes. The solutions of strong electrolytes have high conductivities while solutions of weak electrolytes have lower conductivities.
Question 8.
What is Ohm’s law?
Answer:
Ohm’s law : According to Ohm’s law, the electrical resistance R of a conductor is equal to the electric potential difference, V divided by the electric current, I.
R = \(\frac{V}{I}\) ohm
Question 9.
What are SI units of
(a) electrical resistance
(b) potential and
(c) electric current?
Answer:
(a) The SI unit of electrical resistance is Ohm denoted by Ω (omega).
(b) The SI unit of potential is volt denoted by V.
(c) The SI unit of electric current is ampere denoted by A.
Question 10.
How is electrical conductance of a solution denoted ? What are its units ?
Answer:
The electrical conductance of a solution is denoted by G and it is the reciprocal of resistance, R.
G = \(\frac{1}{R}\)
The unit of G is siemens denoted by S or Ω-1.
Hence we can write, S = Ω-1 = AV-1 = CV-1S-1 where A is ampere and C is coulomb.
![]()
Question 11.
What is electrical conductance? What are its units ?
Answer:
The reciprocal of the electrical resistance of a solution is called the conductance. It is represented by G.
∴ Conductance (G) = \(\frac{1}{\text { Resistance }}=\frac{1}{\mathrm{R}}\)
The conductance has units of reciprocal of ohm (Ω-1, ohm-1 or mho). In SI units, conductance has units as Siemens, (S). (1 S = 1 Ω-1 = 1 ohm-1 = 1 mho = AV-1 = CV-1 S, where C represents electric charge in coulomb, and A represents current strength)
Question 12.
What is specific conductance or conductivity?
Answer:
The reciprocal of specific resistance or resistivity is called specific conductance or conductivity.
If ρ is the resistivity then,
conductivity = \(\frac{1}{\text { resistivity }}=\frac{1}{\rho}\)
Conductivity is denoted by κ (kappa), where κ = \(\frac{1}{\rho}\)
It is the conductance of a conductor that is 1 m in length and 1 m2 in cross section area in SI units. (In C.G.S. units, it is the resistance of a conductor that is 1 cm in length and 1 cm2 in cross section area.) It is the conductance of a conductor of volume 1 m3 (or in C.G.S. units, the volume of 1 cm3).
Question 13.
What are the units of specific conductance or conductivity?
Answer:
If ρ is a resistivity and κ is conductivity or specific conductance, then
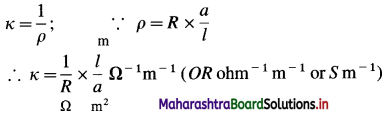
(where S is Siemens)
(In C.G.S. system, the units of κ are Ω-1 cm-1 or S cm-1 which are commonly used.)
Question 14.
Define molar conductivity. What is the significance of it ?
Answer:
Molar conductivity: It is defined as a conductance of a volume of the solution containing ions from one mole of an electrolyte when placed between two parallel plate electrodes 1 cm apart and of large area, sufficient to accommodate the whole solution between them, at constant temperature. It is denoted by ∧m.
Thus, the significance of molar conductivity is the conductance due to ions from one mole of an electrolyte.
Question 15.
Obtain a relation between conductivity (κ) and molar conductivity (∧m).
Answer:
Conductivity or specific conductance (κ) is the conductance of 1 cm3 of the solution in C.G.S. units, while molar conductivity is the conductance of a solution containing one mole of an electrolyte. Consider C molar solution, i.e., C moles of an electrolyte present in 1 litre or 1000 cm3 of the solution.
∴ C moles of an electrolyte are present in 1000 cm3 solution.
∴ 1 mole of an electrolyte is present in \(\frac{1000}{\mathrm{C}}\) cm
solution.
Now,
∴ Conductance of 1 cm3 of this solution is κ,
∴ Conductance of \(\frac{1000}{\mathrm{C}}\) cm3 of the solution is \(\frac{\kappa \times 1000}{C}\)
This represents molar conductivity, ∧m.
∴ ∧m = \(\frac{\kappa \times 1000}{C}\) cm2 mol-1 (in C.G.S units)
[In case of SI units :
Consider a solution in which C moles of an electrolyte are present in 1 m3 of solution.
Conductivity κ is the conductance of 1 m3 of solution.
∵ C moles of an electrolyte are present in 1 m3 solution.
∴ 1 mol of an electrolyte is present in \(\frac{1}{C}\) solution.
∵ Conductance of 1 m3 of this solution is κ.
∴ Conductance of \(\frac{1}{C}\) m3 of the solution is \(\frac{\kappa}{\mathrm{C}}\)
This represents molar conductivity, ∧m.
∴ ∧m = \(\frac{\kappa}{\mathrm{C}}\)Ω-1 m2 mol-1 (In SI units).]
![]()
Question 16.
What are the units of molar conductivity, ∧m?
Answer:
In SI units: Conductivity κ is expressed in Ω-1m-1 (or S m-1) and concentration of the solution is expressed in mol m-3.
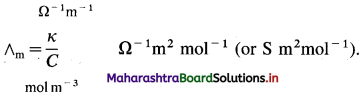
In C.G.S. units : Conductivity is expressed in Ω-1 cm-1 (or S cm-1) and concentration of the solution is expressed in mol L-1 or moles in 1000 cm3 of the solution.
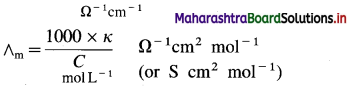
Question 17.
Explain the variation of molar conductivity with concentration for strong and weak electrolytes.
OR
How is the molar conductivity of strong electrolytes at zero concentration determined by graphical method? Why is this method not useful for weak electrolytes?
Answer:
(i) As the dilution of an electrolytic solution increases, the dissociation of the electrolyte increases, hence the total number of ions increases, therefore, the molar conductivity increases.
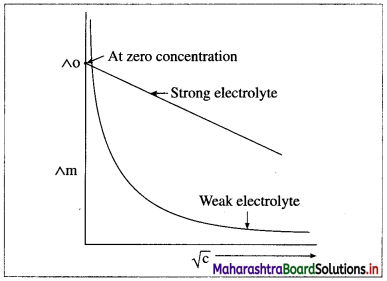
Fig. 5.5 : Variation of molar conductivity with \(\sqrt{\mathbf{c}}\)
(ii) The increase in molar conductivity with increase in dilution or decrease in concentration is different for strong and weak electrolytes.
(iii) On dilution, the molar conductivity of strong electrolytes increases rapidly and approaches to a maximum limiting value at infinite dilution or zero concentration and represented as ∧ ∞ or ∧0 or ∧0m. In case of weak electrolytes which dissociate less as compared to strong electrolytes, the molar conductivity is low and increases slowly in high concentration region, but increases rapidly at low concentration or high dilution. This is because the extent of dissociation increases with dilution rapidly.
(v) ∧0 values for strong electrolytes can be obtained by extrapolating the linear graph to zero concentration (or infinite dilution). However ∧0 for the weak electrolytes cannot be obtained by this method, since the graph increases exponentially at very high dilution and does not intersect ∧m axis at zero concentration.
Question 18.
Why has the molar conductance of an electrolyte the maximum value at infinite dilution ?
Answer:
- As the dilution of an electrolytic solution increases or concentration decreases, the dissociation of an electrolyte increases.
- At infinite dilution, the dissociation of an electrolyte is complete (100% dissociation). Hence all the ions from one mole of an electrolyte are available to carry electricity.
Therefore the molar conductance at infinite dilute (∧0) for a given electrolyte has the highest or limiting value. It is always constant for the given electrolyte at constant temperature.
Question 19.
State Kohlrausch’s law.
OR
State and explain Kohlrausch’s law of independent migration of ions.
Answer:
(A) Statement of Kohlrausch’s law : This states that at infinite dilution of the solution, each ion of an electrolyte migrates independently of its co-ions and contributes independently to the total molar conductivity of the electrolyte, irrespective of the nature of other ions present in the solution.
(B) Explanation : Both the ions, cation and anion of the electrolyte make a definite contribution to the molar conductivity of the electrolyte at infinite dilution or zero concentration (∧0).
If \(\lambda_{+}^{0}\) and \(\lambda_{-}^{0}\) are the molar ionic conductivities of cation and anion respectively at infinite dilution, then
∧0 = \(\lambda_{+}^{0}\) + \(\lambda_{-}^{0}\)
This is known as Kohlrausch’s law of independent migration of ions.
For an electrolyte, Bx Ay giving x number of cations and y number of anions,
∧0 = x\(\lambda_{+}^{0}\) + y\(\lambda_{-}^{0}\)
(C) Applications of Kohlrausch’s law :
(1) With this law, the molar conductivity of a strong electrolyte at zero concentration can be determined. For example,
\(\wedge_{0(\mathrm{KCl})}=\lambda_{\mathrm{K}^{+}}^{0}-\lambda_{\mathrm{Cl}^{-}}^{0}\)
(2) ∧0 values of weak electrolyte with those of strong electrolytes can be obtained. For example,
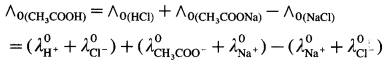
Question 20.
State Kohlrausch’s law and write mathematical expression of molar conductivity of the given solution at infinite dilution.
Answer:
Statement of Kohlrausch’s law : This states that at infinite dilution of the solution, each ion of an electrolyte migrates independently of its co-ions and contributes independently to the total molar conductivity of the electrolyte, irrespective of the nature of other ions present in the solution.
This law of independent migration of ions is represented as
∧0 = \(\lambda_{+}^{0}\) + \(\lambda_{-}^{0}\).
where ∧0 is the molar conductivity of the electrolyte at infinite dilution or zero concentration while \(\lambda_{+}^{0}\) and \(\lambda_{-}^{0}\) are the molar ionic conductivities of cation and anion respectively at infinite dilution.
![]()
Question 21.
Explain the determination of molar conductivity of a weak electrolyte at infinite dilution or zero concentration using Kohlrausch’s law.
Answer:
Molar conductivity of a weak electrolyte at infinite dilution or zero concentration cannot be measured experimentally.
Consider the molar conductivity (∧0) of a weak acid, CH3COOH at zero concentration. By Kohlrausch s law, ∧0CH3COOH = λ0CH3COOH– + λ0 H+ where λ0 CH3COO– and λ0 H+ are the molar ionic conductivities of CH3COO– and H+ ions respectively.
If ∧0CH3COONa, ∧0HCl and ∧0NaCl are the molar conductivities of CH3COONa, HCl and NaCl respectively at zero concentration, then by
Kohlrausch’s law,
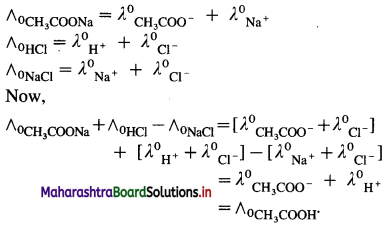
Hence, from ∧0 values of strong electrolytes, ∧0 of a weak electrolyte CH3COOH, at infinite dilution can be calculated.
Question 22.
How is the degree of dissociation related to the molar conductance of the electrolytic solution ?
Answer:
(i) At zero concentration or at infinite dilution, the molar conductivity has a maximum value denoted by ∧0.
(ii) This is due to complete dissociation of the weak electrolyte making all the ions available from one mole of the electrolyte to carry electricity at zero concentration.
(iii) If α is the degree of dissociation, then

This suggests that at zero concentration or infinite dilution, the electrolyte is completely (100%) dissociated.
Question 23.
Write the relation between molar conductivity and molar ionic conductivities for the following electrolytes :
(a) KBr, (b) Na2SO4, (c) AlCl3.
Answer:
(a) If ∧0 is molar conductivity of an electrolyte at infinite dilution and \(\lambda_{+}^{0}\) and \(\lambda_{-}^{0}\) are molar ionic conductivities then,
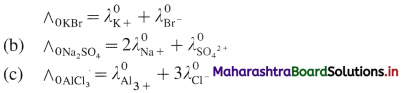
Question 24.
How is molar conductivity of an electrolytic solution measured ?
Answer:
The resistance of an electrolytic solution is measured by using a conductivity cell and Wheatstone bridge.
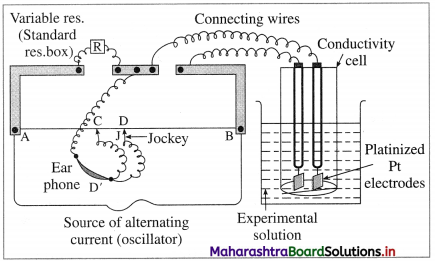
Fig. 5.6 : Measurement of conductance
The measurement of molar conductivity of a solution involves two steps as follows :
Step I : Determination of cell constant of the conductivity cell :
KCl solution (0.01 M) whose conductivity is accurately known (κ = 0.00141 Ω-1 cm-1) is taken in a beaker and the conductivity cell is dipped. The two electrodes of the cell are connected to one arm while the variable known resistance (R) is placed in another arm of Wheatstone bridge.
A current detector D’ which is a head phone or a magic eye is used. J is the sliding jockey (contact) that slides on the arm AB which is a wire of uniform cross section. A source of A.C. power (alternating power) is used to avoid electrolysis of the solution.
By sliding the jockey on wire AB, a balance point (null point) is obtained at C. Let AC and BC be the lengths of wire.
If Rsolution is the resistance of KCl solution and Rx is the known resistance then by Wheatstone’s bridge principle,
\(\frac{R_{\text {solution }}}{\mathrm{BC}}=\frac{R_{x}}{\mathrm{AC}}\)
∴ Rsolution = \(\mathrm{BC} \times \frac{R_{x}}{\mathrm{AC}}\)
Then the cell constant ‘b’ of the conductivity cell is obtained by, b = κKCl × Rsolution.
Step II : Determination of conductivity of the given solution :
KCl solution is replaced by the given electrolytic solution and its resistance (Rs) is measured by Wheatstone bridge method by similar manner by obtaining a null point at D.
The conductivity (κ) of the given solution is, cell constant b
κ = \(\frac{\text { cell constant }}{R_{\mathrm{s}}}=\frac{b}{R_{\mathrm{s}}}\)
Step III: Calculation of molar conductivity :
The molar conductivity (∧m) is given by,
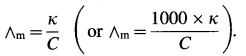
Since the concentration of the solution is known, ∧m can be calculated.
![]()
Solved Examples 5.3
Question 25.
Solve the following :
(1) The resistance of a solution is 2.5 × 103 ohm. Find the conductance of the solution.
Solution :
Given : Resistance of solution = R = 2.5 × 103 Ω
Conductance of solution = G = ?
G = \(\frac{1}{R}\)
= \(\frac{1}{2.5 \times 10^{3}}\) ohm-1 (Ω-1 or S)
= 4 × 10-3 Ω-1 (or S)
Ans. Conductance = G = 4 × 10-3 Ω-1
(2) A conductivity cell has two electrodes 20 mm apart and of cross section area 1.8 cm2. Find the cell constant.
Solution :
Given: Distance between two electrodes = l
= 20 mm
= 2 cm
Cross section area = a = 1.8 cm
Cell constant = b = ?
b = \(\frac{l}{a}=\frac{2}{1.8}\) = 1.111 cm-1
Ans. Cell constant = 1.111 cm-1
(3) The conductivity of 0.02 M AgNO3 at 25 °C is 2.428 × 10-3 Ω-1 cm-1. What is its molar conductivity ?
Solution :
Given : Concentration of solution = C = 0.02 M AgNO3
Temperature = T = 273 + 25 = 298 K
Conductivity = κ = 2.428 × 10-3 Ω-1 cm-1 (or S cm-1)
Molar conductivity = ∧m = ?
∧m = \(\frac{\kappa \times 1000}{C}\)
= \(\frac{2.428 \times 10^{-3} \times 1000}{0.02}\)
= 121.4 Ω-1 cm2 mol-1 (or 121.4 S cm2 mol-1)
Ans. Molar conductivity = ∧m
= 121.4 Ω-1 cm2 mol-1
(4) 0.05 M NaOH solution offered a resistance of 31.6 in a conductivity cell at 298 K. If the cell constant of the cell is 0.367 cm-1, calculate the molar conductivity of NaOH solution.
Solution :
Given : Concentration = C = 0.05 M NaOH
Resistance = R = 31.6 Ω
Cell constant = b = 0.367 cm-1
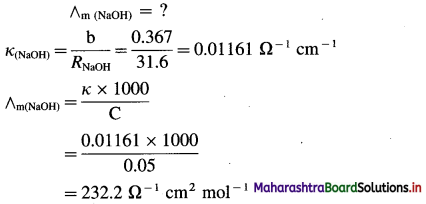
Ans. Molar conductivity = ∧m = 232.2 Ω-1 cm2 mol-1
![]()
(5) A conductivity cell filled with 0.1 M KCl gives at 25 °C a resistance of 85.5 ohms. The conductivity of 0.1 M KCl at 25° is 0.01286 ohm-1 cm-1. The same cell filled with 0.005 M HCl gives a resistance of 529 ohms. What is the molar conductivity of HCl solution at 25 °C ?
Solution :
Given : Resistance of KCl solution = RKCl = 85.5 Ω
Conductivity of KCl solution = κKCl
= 0.01286 ohm-1 cm-1
Concentration = C = 0.005 M HCl
Resistance of HCl solution = Rsoln = 529 ohms
Molar conductivity of HCl = ∧m(HCl) = ?
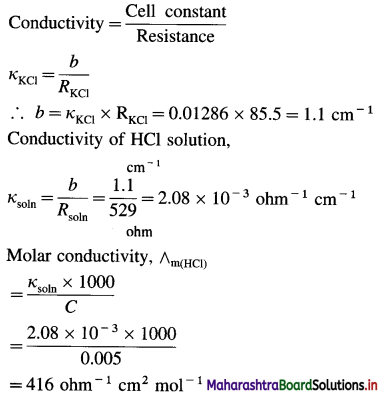
Ans. Molar conductivity of HCl solution = ∧m(HCl)
= 416 ohm-1 cm2 mol-1
(6) The molar conductivity of 0.05 M BaCl2 solution at 25 °C is 223 Ω-1 cm2 mol-1. What is its conductivity?
Solution :
Given : Molar conductivity = ∧m
= 223 Ω-1 cm2 mol-1
Concentration = C = 0.05 M BaCl2
Conductivity = κ = ?
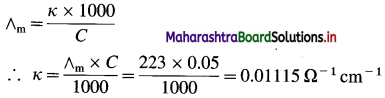
Ans. Conductivity = κ = 0.01115 Ω-1 cm-1
(7) Conductivity of a solution is 6.23 × 10-5 Ω-1 cm-1 and its resistance is 13710 Ω. If the electrodes are 0.7 cm apart, calculate the cross-sectional area of electrode.
Solution :
Given : κ = 6.23 × 10-5 Ω-1 cm-1
R = 13710 Ω
l = 0.7 cm
a = ?
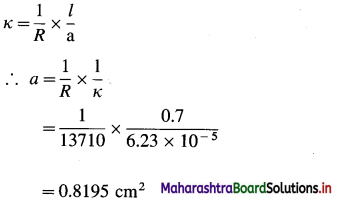
Ans. Cross sectional area of electrode = 0.8195 cm2
(8) A conductivity cell filled with 0.01 M KCl gives at 25 °C the resistance of 604 ohms. The conductivity of KCl at 25 °C is 0.00141 Ω-1 cm-1. The same cell filled with 0.001 M AgNO3 gives a resistance of 6529 ohms. Calculate the molar conductivity of 0.001 M AgNO3 solution at 25 °C.
Solution :
Given : Resistance of KCl solution = RKCl
= 604 ohm (Ω)
Conductivity of KCl solution = κKCl
= 0.00141 Ω-1 cm-1
Concentration = C = 0.001 M AgNO3
Resistance of solution = Rsol = 6529 ohm (Ω)
Molar conductivity = ∧m = ?
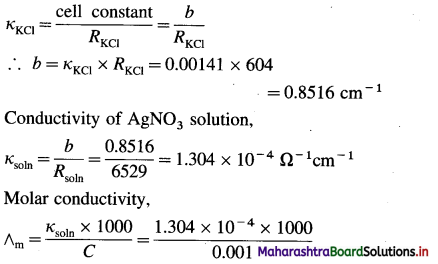
cell constant b
= 130.4 Ω-1 cm2 mol-1
Ans. Molar conductivity of AgNO3 solution = ∧m
= 130.4 Ω-1 cm2 mol-1
(9) Resistance and conductivity of a cell containing 0.001 M KCl solution at 298 K are 1500 Ω and 1.46 × 10-4 S.cm-1 respectively. What is cell constant.
Solution :
Given : Resistance of KCl solution = 1500 Ω, conductivity of KCl solution = κ = 1.46 × 10-4 S.cm-1, Cell constant = b = ?
Cell constant = Conductivity (k) × Resistance
= 1.46 × 10-4 × 1500
= 0.219 cm-1
Ans. Cell constant = 0.219 cm-1
![]()
(10) A conductivity cell filled with 0.02 M H2SO4 gives at 25 °C resistance of 122 ohms. If the molar conductivity of 0.02 H2SO4 is 618 Ω-1 cm2 mol-1, what is the cell constant?
Solution :
Given : Concentration = C = 0.02 M H2SO4
Resistance of H2SO4 solution = Rsoln = 122 Ω
Molar conductivity = ∧m = 618 Ω-1 cm2 mol-1
Cell constant = b = ?
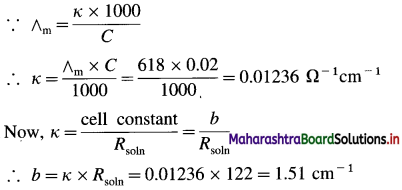
Ans. Cell constant = b = 1.51 cm-1
(11) A conductivity cell filled with 0.02 M AgNO3 gives at 25 °C resistance of 947 ohms. If the cell constant is 2.3 cm-1, what is the molar conductivity of 0.02 M AgNO3 at 25 °C?
Solution :
Given : Concentration = C = 0.02 M AgNO3
Resistance of solution = Rsoln = 947 Ω
Cell constant = b = 2.3 cm-1
Molar conductivity = ∧m = ?
Conductivity of soln = κ
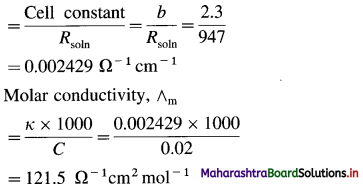
Ans. Molar conductivity = ∧m
= 121.5 Ω-1 m2 mol-1
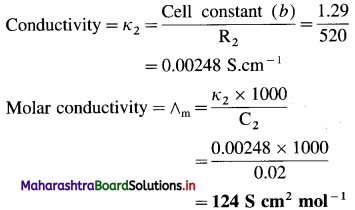
(12) Resistance of conductivity cell filled with 0.1 M KCl solution is 100 ohms. If the resistance of the same cell when filled with 0.02 M KCl solution is 520 ohms, calculate the conductivity and molar conductivity of 0.02 M KCl solution. [Given : Conductivity of 0.1 M KCl solution is 1.29 Sm-1.]
Solution:
Given : Resistance of 0.1 M KCl solution = R1 = 100 Ω
Resistance of 0.02 M KCl solution = R2 = 520 Ω
Conductivity of 0.02 M KCl solution = κ2 = ?
Molar conductivity of 0.02 M KCl solution = ∧m = ?
Conductivity of 0.1 M KCl solution = κ1
= 1.29 S m-1
Cell constant = b = κ1 × R1 = 1.29 × 100
= 129 m-1
= 1.29 cm-1
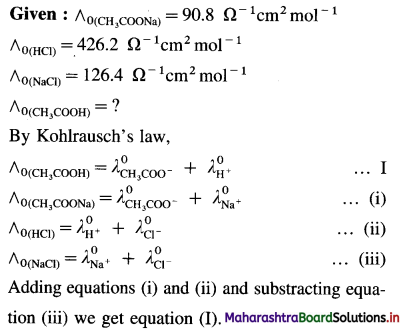
(13) The molar conductivities at zero concentration (or at infinite dilution) of CH3COONa, HCl and NaCl in Ω-1 cm2 mol-1 are 90.8,426.2 and 126.4 respectively. Calculate the molar conductivity of CH3COOH at infinite dilution.
Solution :
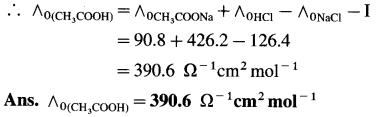
![]()
(14) The molar conductivities at zero concentrations of NH4Cl, NaOH and NaCl are respectively 149.7Ω-1 cm2 mol-1, 248.1 Ω-1 cm2 mol-1 and 126.5 Ω-1 cm2 mol-1. What is the molar conductivity of NH4OH at zero concentration ?
Solution :

(15) What is the molar conductivity of AgI at zero concentration if the ∧0 values of NaI, AgNO3 and NaNO3 are respectively 126.9 Ω-1 cm2 mol-1, 133.4 Ω-1 cm2 mol-1 and 121.5 Ω-1 cm2 mol-1 ?
Solution :
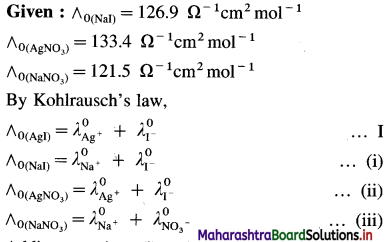
Adding equations (i) and (ii) and subtracting equation (iii) we get equation I.
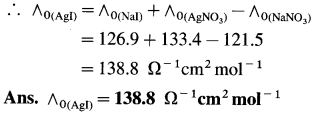
(16) Molar conductivity of KCl at infinite dilution is 150.3 S cm2 mol-1. If the molar conductivity of K+ is 73.4, calculate that of Cl–.
Solution :
Given : Molar conductivity at infinite dilution
= ∧(KCl) = 150.3 S cm2 mol-1
Molar conductivity of K+
= \(\lambda_{\mathrm{K}^{+}}^{0}\) = 73.4 S cm2 mol-1
Molar conductivity of Cl– = \(\lambda_{\mathrm{Cl}^{-}}^{0}\) = ?
By Kohlrausch’s law,
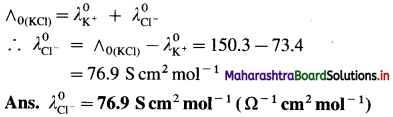
(17) Molar conductivities at infinite dilution of Mg2+ and Br– are 105.8 Ω-1 cm2 mol-1 and 78.2 Ω-1 cm2 mol-1 respectively. Calculate molar conductivity at zero concentration of MgBr2.
Solution :
Given : \(\lambda_{\mathrm{Mg}^{2+}}^{0}\) = 105.8 Ω-1 cm2 mol-1
\(\lambda_{\mathrm{Br}^{-}}^{0}\) = 78.2 Ω-1 cm2 mol-1
\(\wedge_{0\left(\mathrm{MgBr}_{2}\right)}\) = ?
By Kohlrausch’s law,
\(\wedge_{0\left(\mathrm{MgBr}_{2}\right)}\) = \(\lambda_{\mathrm{Mg}^{2+}}^{0}\) + 2\(\lambda_{\mathrm{Br}^{-}}^{0}\)
= 105.8 + 2 × 78.2 = 105.8 + 156.4
= 262.2 Ω-1 cm2 mol-1
Ans. Molar conductivity of MgBr2 at zero concentration = \(\wedge_{0\left(\mathrm{MgBr}_{2}\right)}\) = 262.2 Ω-1 cm2 mol-1
![]()
(18) The molar conductivity of 0.1 M CH3COOH at 25 °C is 15.9 Ω-1 cm2 mol-1. If the molar conductivities of CH3COO– and H+ ions in Ω-1 cm2 mol-1 at zero concentration are 40.8 and 349.6 respectively, calculate degree of dissociation of 0.1 M CH3COOH.
Solution :
Given : Concentration = C = 0.1 M CH3COOH
Molar conductivity = ∧m = 15.9 Ω-1 cm2 mol-1
\(\lambda_{\mathrm{CH}_{3} \mathrm{COO}^{-}}^{0}\) = 40.8 Ω-1 cm2 mol-1;
\(\lambda_{\mathrm{H}^{+}}^{0}\) = 349.6 Ω-1 cm2 mol-1
Degree of dissociation = α = ?
By Kohlrausch’s law,
\(\wedge_{0\left(\mathrm{CH}_{3} \mathrm{COOH}\right)}=\lambda_{\mathrm{CH}_{3} \mathrm{COO}^{-}}^{0}+\lambda_{\mathrm{H}^{+}}^{0}\)
= 40.8 + 349.6
= 390.4 Ω-1 cm2 mol-1
α = ∧m/∧0
= \(\frac{15.9}{390.4}\) = 0.0407
Ans. The degree of dissociation of CH3COOH = 0.0407
(19) The dissociation constant of a weak monoacidic base is 1.2 × 10-5 at 25 °C. The molar conductivity of the base at zero concentration is 354.8 Ω-1 cm2 mol-1 at 25°C. Calculate the percentage dissociation and molar conductivity of the weak base at 0.1 M concentration.
Solution :
Given : Dissociation constant of the base = Kb = 1.2 × 10-5
Concentration = C = 0.1 M
∧0 = 354.8 Ω-1 cm2 mol-1
Percentage dissociation = ?
∧m = ?
Ka = \(\frac{\mathrm{C} \alpha^{2}}{1-\alpha}\); For a week electrolyte, α is small,
∴ Ka = cα2;
∴ α = \(\sqrt{\frac{\mathrm{K}_{\mathrm{a}}}{\mathrm{C}}}=\left(\frac{1.2 \times 10^{-5}}{0.1}\right)^{\frac{1}{2}}\) = 1.0954 × 10-2
∴ Percentage dissociation = α × 100
= 1.0954 × 10-2 × 100 = 1.0954%
Now, α = \(\frac{\wedge_{\mathrm{m}}}{\wedge_{0}}\)
∴ ∧m = α × ∧0 = 1.954 × 10-2 × 354.8
= 6.932 Ω-1 cm2 mol-1
Ans. Percentage dissociation = 1.0954
Molar conductivity = ∧m
= 6.932 Ω-1 cm2 mol-1
Question 26.
What is an electrochemical cell? What does it consist of?
Answer:
Electrochemical cell : It consists of two electronic conductors such as metal plates dipping into an electrolytic or ionic conductor which is an aqueous electrolytic solution or a pure liquid of a molten electrolyte.
Question 27.
What are electrochemical reactions ?
Answer:
- Electrochemical reactions : The chemical reactions occurring in electrochemical cells which involve transfer of electrons from one species to other are called electrochemical reactions. They are redox reactions.
- These reactions are made of two half reactions namely oxidation at one electrode (anode) and reduction at another electrode (cathode) of the electrochemical cell.
- The net reaction is the sum of the above two half reactions.
Question 28.
Define electrode.
Answer:
Electrode : The arrangement consisting of a metal rod dipping in an aqueous solution or molten electrolyte containing ions and conduct electric current due to oxidation or reduction half reactions occurring on its surface is called an electrode.
The electrodes which take part in the reactions are called active electrodes while those which do not take part in the reactions are called inert electrodes.
![]()
Question 29.
Define : (a) Anode (b) Cathode.
Answer:
(a) Anode : An electrode of an electrochemical cell, at which oxidation half reaction occurs due to the loss of electrons from some species is called an anode.
(b) Cathode : An electrode of an electrochemical cell at which reduction half reaction occurs due to gain of electrons by some species is called a cathode.
Question 30.
What are the types of electrochemical cells ?
Answer:
There are two types of electrochemical cells as follows :
- Electrolytic cells
- Voltaic or galvanic cells.
Question 31.
Define : (1) Electrolytic cell (2) Voltaic or galvanic cell.
Answer:
(1) Electrolytic cell : An electrochemical cell in which a non-spontaneous chemical reaction is forced to occur by passing direct electric current into the solution from the external source and where electrical energy is converted into chemical energy is called an electrolytic cell. E.g. voltameter, electrolytic cell for deposition of a metal.
(2) Voltaic or galvanic cell : An electrochemical cell in which a spontaneous chemical reaction occurs producing electricity and where a chemical energy is converted into an electrical energy is called voltaic cell or galvanic cell. E.g. Daniell cell, dry cell, lead storage battery, fuel cells, etc.
Question 32.
Define electrolysis.
Answer:
Electrolysis : The process of a non-spontaneous chemical decomposition of an electrolyte by the passage of an electric current through its aqueous solution or fused mass and in which electrical energy is converted into chemical energy is called electrolysis. E.g. Electrolysis of fused NaCl.
Question 33.
Describe electrolysis of aqueous NaCl.
Answer:
(1) Construction of an electrolytic cell : It consists of a vessel containing aqueous solution of NaCl. Two inert electrodes (graphite electrodes) are dipped in it and connected to an external source of electricity like battery. The electrode connected to the negative terminal is a cathode and that connected to a positive terminal is an anode.
(2) Working of the cell :
(A) NaCl(aq) and H2O(l) dissociate as follows :
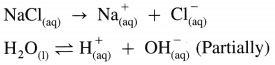
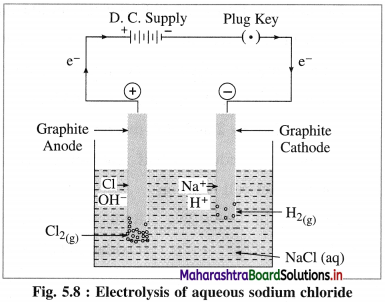
(3) Reactions in electrolytic cell :
(i) Reduction half reaction at cathode : There are Na+ and H+ ions but since H+ are more reducible than Na+, they undergo reduction liberating hydrogen and Na+ are left in the solution.
2H2O(l) + 2e– → H2(g) + \(2 \mathrm{OH}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{-}\) (reduction)
E0 = -0.83 V
(ii) Oxidation half reaction at anode : At anode there are Cl– and OH–. But Cl– ions are preferably oxidised due to less decomposition potential.

Net cell reaction : Since two electrons are gained at cathode and two electrons are released at anode for each redox step, the electrical neutrality is maintained. Hence we can write,
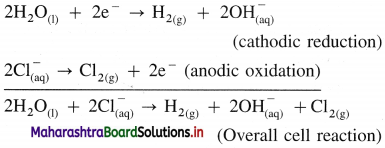
Since Na+ and OH– are left in the solution, they form NaOH(aq).
(4) Results of electrolysis :
- H2 gas is liberated at cathode.
- Cl2 gas is liberated at anode.
- NaOH is formed in the solution and it reacts basic.
![]()
Question 34.
Define and explain the following electrical units : (1) Coulomb (2) Ampere (3) Volt (4) Joule (5) Ohm.
Answer:
(1) Coulomb : It is a quantity of electricity obtained when one ampere current flows for one second.
It is the unit of quantity of electricity.
Q = I × t Coulomb (C)
where Q is the charge or quantity of electricity in coulombs.
(2) Ampere : It is a strength of an electric current obtained when one coulomb of electricity is passed through a circuit for one second.
∴ I = Q/t
(3) Volt : It is the potential difference between two points of an electric conductor required to send a current of one amphere through a resistance of one ohm.
∴ V = I × R
where V is the potential difference in volts and R is the resistance of a conductor in ohms.
(4) Joule : It is the electrical work or energy produced when one coulomb of electricity is passed through a
potential difference of one volt.
∴ Electrical work = Q × V J
where Q is electrical charge in coulombs and V is the potential difference.
(5) Ohm : It is the resistance of an electrical conductor across which when potential difference of 1 volt is applied, a current of one ampere is obtained. It has units, Ω or per siemens.
Question 35.
Explain quantitative aspects of electrolysis.
Answer:
(1) Calculation of quantity of electricity : If an electric current of strength I A is passed through the cell for t seconds, then quantity of electricity (Q) obtained is given by,
Q = I × t C (Coulomb)
(2) Calculation of moles of electrons passed : The charge carried by one mole of electrons is referred to as one faraday (F). If total charge passed is Q C, then moles of electrons passed = \(\frac{Q(\mathrm{C})}{F\left(\mathrm{C} / \mathrm{mol} \mathrm{e}^{-}\right)}\)
(3) Calculation of moles of product formed : Consider one mole of ions, \(\mathbf{M}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{n^{+}}\) which will require n moles of electrons for reduction.
\(\mathbf{M}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{n^{+}}\) + ne– → M (Reduction half reaction)
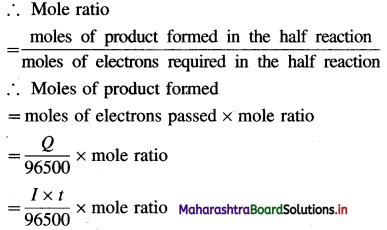
(4) Calculation of mass of product : Mass, W of product formed is given by,
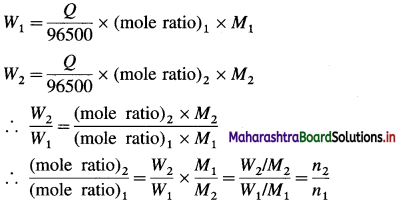
W = moles of product × molar mass of product (M)

When two electrolytic cells containing different electrolytes are connected in series so that same quantity of electricity is passed through them, then the masses W1 and W2 of products produced are given by,
Question 36.
Define Faraday.
Answer:
Faraday : It is defined as the quantity of the electric charge carried by one mole of electrons.
It has value, 1F = 96500 C/mol
Question 37.
Obtain a charge on one electron from Faraday’s value.
Answer:
- One Faraday is the electric charge on one mole of electrons (6.022 × 1023 electrons).
- 1 Faraday = 96500 (per mol of electrons).
- Hence the charge on one electron is, change on one electron = \(\frac{96500}{6.022 \times 10^{23}}\)
= 1.602 × 10-9 C.
![]()
Solved Examples 5.4-5.5
Question 38.
Solve the following :
(1) An electric current of 100 mA is passed through an electrolyte for 2 hours, 20 minutes and 20 seconds. Find the quantity of electricity passed.
Solution :
Given : Electric current = I = 100 mA
= 100 × 10-3 A
= 0.1 A
Time = t = 2 hrs + 20 min + 20 s
= 2 × 60 × 60 + 20 × 60 + 20
= 8420 s
The quantity of electricity = Q = ?
Q = I × t
= 0.1 × 8420
= 842 C
Ans. Quantity of electricity passed, Q = 842 C
(2) An electric current of 500 mA is passed for 1 hour and 30 minutes. Calculate the
(i) Quantity of electricity (or charge)
(ii) Number of Faradays of electricity
(iii) Number of electrons passed (Charge on 1 electron = 1.602 × 10-19 C)
Solution :
Given : Electric current = I = 500 mA
= 500 × 10-3 A = 0.5 A
Time = t = 1 hr + 30 min
= 1 × 60 × 60 + 30 × 60
= 5400 s
(i) The quantity of electricity = Q = ?
(ii) Number of Faradays of electricity = ?
(iii) Number of electrons passed = ?
(i) Q = I × t = 0.5(A) × 5400(s) = 2700 C
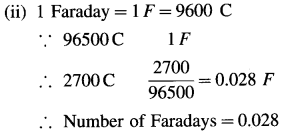
(iii) 1F is the electric charge on 6.022 × 1023 electrons.
∴ 0.028F is the charge on,
0.028 × 6.022 × 1023 = 1.686 × 1022 electrons
∴ Number of electrons passed = 1.686 × 1022
Ans. (i) The quantity of electricity = Q = 2700 C
(ii) Number of Faradays of electricity = 0.028 F
(iii) Number of electrons passed = 1.686 × 1022
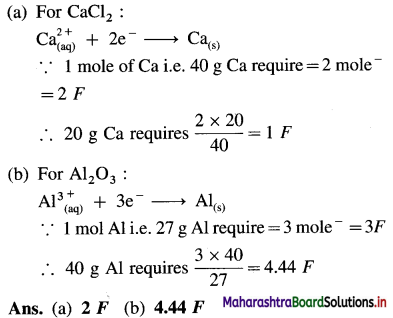
(3) How much electricity in terms of Faraday is required to produce :
(a) 20 g of Ca from molten CaCl2
(b) 40 g of Al from molten Al2O3
(Given : Molar mass of Calcium and Aluminium are 40 g mol-1 and 27 g mol-1 respectively.)
Solution :
(4) For the following conversions,
calculate
(i) number of moles of electrons
(ii) number of Faradays
(iii) Amount of electricity :
(A) 0.1 mol conversion of Zn2+ to Zn.
(B) 0.08 mol conversion of \(\mathbf{M n O}_{4}^{2-}\) to Mn2+
(C) 1.1 mol conversion of \(\mathrm{Cr}_{2} \mathbf{O}_{7}^{2-}\) to Cr3+.
Solution :
(i) Number of moles of electrons = ?
(ii) Number of Faradays = ?
(iii) Amount of electricity = Q = ?
(A) Number of moles of Zn2+ =0.1 mol
Zn2+ + 2e– → Zn
(i) ∵ 1 mol Zn2+ requires 2 mol electrons
0.1 mol Zn2+ will require
∴ 0.1 × 2 = 0.2 mol electrons
(ii) ∵ 1 mol electrons = 1 Faraday
∴ 0.2 mol electrons = 0.2 × 1
= 0.2 Faradays
(iii) ∵ 1 Faraday = 96500 C
∴ 0.2 Faraday = 96500 × 0.2 = 48250 C
Amount of electricity required =48250C
(B) Number of moles of \(\mathrm{MnO}_{4}^{-}\) = 0.08 mol
\(\mathrm{MnO}_{4}^{-}+5 \mathrm{e}^{-} \longrightarrow \mathrm{Mn}^{2+}\)
(i) ∵ 1 mol \(\mathrm{MnO}_{4}^{-}\) requires 5 mol electrons
∴ 0.08 mol \(\mathrm{MnO}_{4}^{-}\) will require
5 × 0.08 = 0.4 mol electrons
(ii) Number of Faradays = 0.4 × 1 = 0.4
(iii) Amount of electricity = Q = 0.4 × 96500
= 38600 C
(C) Number of moles of \(\mathrm{Cr}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{7}^{2-}\) = 1.1 mol
![]()
(i) ∵ 1 mol \(\mathrm{Cr}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{7}^{2-}\) requires 6 mol electrons
∴ 1.1 mol \(\mathrm{Cr}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{7}^{2-}\) will require
6 × 1.1 = 6.6 mol electrons
(ii) Number of Faradays = 1 × 6.6 = 6.6
(iii) Amount of electricity = 6.6 × 96500
= 6.369 × 105 C
Ans.
(A) (i) Number of moles of electrons = 0.2 mol
(ii) Number of Faradays = 0.2
(iii) Amount of electricity = 48250 C
(B) (i) Number of moles of electrons = 0.4 mol
(ii) Number of Faradays = 0.4
(iii) Amount of electricity = 38600 C
(C) (i) Number of moles of electrons = 6.6 mol
(ii) Number of Faradays = 6.6
(iii) Amount of electricity = 6.369 × 105 C
![]()
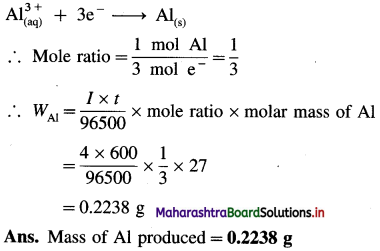
(5) What mass of aluminium is produced at the cathode during the passage of 4 ampere current through Al2(SO4)3 solution for 100 minutes? Molar mass of aluminium is 27 g mol-1.
Solution :
Given : I = 4 A; t = 100 × 60 = 600 s
F = 96500 C mol-1, M = 27 g mol-1, WAl = ?
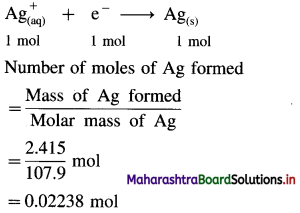
(6) How long will it take to produce 2.415 g Ag metal from its salt solution by passing a current of 3 amperes? How many moles of electrons are required ? Molar mass of Ag is 107.9 gmol-1.
Solution :
Given : Electric current = I = 3A
Mass of Ag produced = 2.415 g
Molar mass of Ag = Atomic mass of Ag
= 107.9 gmol-1
Time = t = ? Number of moles of electrons = ?
Reduction half reaction at cathode :
From the reaction,
∵ 1 mole of Ag requires 1 mole of electrons
∴ 0.02238 mole of Ag will require,
0.02238 mol electrons
∵ 1 mole of electrons carries a charge of 96500 C,
∴ 0.02238 mole of electrons will carry a charge, 0.02238 × 96500 = 2160 C
∴ Quantity of electricity passed = Q = 2160 C
Let I be the current strength and t be time of electrolysis. Then,
∵ Q = I × t
∴ t = \(\frac{Q}{I}=\frac{2160}{3}\) = 720 s = \(\frac{720}{60}\) min = 12 min.
Ans. Time of electrolysis = 12 min
Moles of electrons = 0.02238 mol
(7) What current strength in ampere will be required to produce 2.369 × 10-3 kg of Cu from CuSO4 solution in one hour? How many moles of electrons are required? Molar mass of copper is 63.5 gmol-1.
Solution :
Given : Mass of Cu produced = 2.369 × 10-3 kg
= 2.369 g
Time = t = 1 hr = 1 × 60 × 60 = 3600 s
Molar mass of Cu = 63.5 g mol-1
Strength of current = I = ?
1 Faraday = 96500 C = 1 mol electrons
1 mol Cu = Molar mass of Cu = 63.5 g
Reduction half reaction :
![]()
Moles of Cu deposited = \(\frac{2.369}{63.5}\) = 0.0373 mol Cu
From the reaction,
∵ 1 mol of Cu requires 2 mol electrons
∴ 0.0373 mol Cu will require 2 × 0.0373
= 0.0746 mol electrons
Now,
∵ 1 mol electrons = 96500 C
∴ 0.0746 mol electrons = 96500 × 0.0746 = 7199 C
∴ Quantity of electricity required = Q = 7199 C
∴ Q = I × t
∴ Current, I = \(\frac{Q}{t}=\frac{7199}{3600}\) = 2A
Ans. Current strength = I = 2A
Moles of electrons required = 0.0746 mol
(8) A current of 6 amperes is passed through AlCl3 solution for 15 minutes using Pt electrodes, when 0.504 g Al is produced. What is the molar mass of Al ?
Solution :
Given : Electric current = I = 6 A
Time = t = 15 min = 15 × 60 s = 900 s
Mass of Al produced = 0.504 g
Molar mass of Al = ?
Reduction half reaction,
\(\mathrm{Al}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{3+}+3 \mathrm{e}^{-} \longrightarrow \mathrm{Al}_{(\mathrm{aq})}\)
Quantity of electricity passed = Q = I × t
= 6 × 900 = 5400 C
Number of moles of electrons = \(\frac{Q}{F}=\frac{5400}{96500}\)
= 0.05596 mol
From half reaction,
∵ 3 moles of electrons deposit 1 mole Al
∴ 0.05596 moles of electrons will deposit,
\(\frac{0.05596}{3}\) = 0.01865 mol Al
Now,
∵ 0.01865 mole Al weighs 0.504 g
∴ 1 mole Al will weigh, \(\frac{0.504}{0.01865}\) = 27 g
Hence molar mass of Al is 27 g mol-1
Ans. Molar mass of Al = 27 g mo-1
![]()
(9) How many moles of electrons are required for the reduction of (i) 3 moles of Zn2+ to Zn,
(ii) 1 mol of Cr3+ to Cr ?
How many Faradays of electricity will be required in each case ?
Solution :
(i) Given : For reduction of 3 mol Zn2+ to Zn;
Number of moles of electrons required = ?
Reduction half reaction,
Zn2+ + 2e– → Zn
∵ 1 mole of Zn2+ requires 2 moles of electrons
∴ 3 moles of Zn2+ will require,
∵ 3 × 2 = 6 moles of electrons
∴ 1 mole of electrons = 1 F 6 moles of electrons = 6 F
(ii) Given : Reduction of 1 mol of Cr3+ to Cr :
Reduction half reaction,
Cr3+ + 3e– → Cr
Hence 1 mole of Cr3+ will require 3 moles of electrons
∵ 1 mole of electrons = 1
∴ 3 moles of electrons = 3 F
Ans. (i) 6 mol electrons and 6 Faradays.
(ii) 3 mol electrons and 3 Faradays.
(10) In an electrolysis of AgNO3 solution, 0.7 g of Ag is deposited after a certain period of time. Calculate the quantity of electricity required in coulomb. (Molar mass of Ag is 107.9 g mol-1.)
Solution :
Given : Mass of Ag deposited = 0.7 g
Molar mass of Ag = 107.9 g mol-1
Quantity of electricity = Q = ?
Reduction half reaction is,
Ag+ + e– → Ag
1 mole of Ag = 107.9 g Ag requires 1 mole of electrons
∴ 0.7 g Ag will require, \(\frac{0.7}{107.9}\) = 6.49 × 10-3 mole of electrons
∵ 1 mole of electrons carry 96500 C charge
∴ 6.49 × 10-3 mole of electrons will carry, 96500 × 6.49 × 10-3 = 626 C
Ans. Quantity of electricity required = 626 C,
(11) Calculate the amounts of Na and Chlorine gas produced during the electrolysis of fused NaCl by the passage of 1 ampere current for 25 minutes. Molar masses of Na and Chlorine gas are 23 g mol-1 and 71 g mol-1 respectively.
Solution :
Given : Electric current = I = 1 ampere
Time = t = 25 minutes = 25 × 60 s = 1500 s
Molar mass of Na = 23 g mol-1
Molar mass of Cl2 = 71 g mol-1
Mass of Na produced = ?, Mass of Cl2 produced = ?
Reactions during electrolysis :
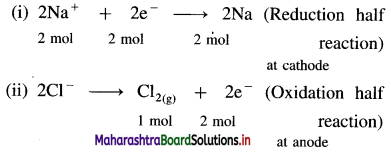
Quantity of electricity = Q = I × t = 1 × 1500
= 1500 C
Number of moles of electrons passed
= \(\frac{Q}{F}=\frac{1500}{96500}\) = 0.01554
From half reaction (i),
∵ 2 moles of electrons deposit 2 moles of Na
∴ 0.01554 moles of electrons will deposit, \(\frac{0.01554 \times 2}{2}\) = 0.01554 mol Na
Mass of Na = Moles of Na × Molar mass of Na
= 0.01554 × 23 = 0.3572 g Na
From half reaction (ii)
∵ 2 moles of electrons produce 1 mole Cl2
∴ 0.01554 moles of electrons will produce,
\(\frac{0.01554 \times 1}{2}\) = 7.77 × 10-3 × 71
∴ Mass of Cl2 gas = Moles of Cl2 × Molar mass
= 7.77 × 10-3 × 71
= 0.5518 g
Ans. Mass of Na deposited = 0.3572 g
Mass of Cl2 liberated = 0.5518 g
(12) Calculate the mass of Mg and the volume of Chlorine gas at NTP produced during the electrolysis of molten MgCl2 by the passage of 2 amperes of current for 1 hour. Molar masses of Mg and Cl2 are 24 g mol-1 and 71 g mol-1 respectively.
Solution :
Given : Electric current = I = 2A
Time = t = 1 hr = 1 × 60 × 60 s = 3600 s
Molar mass of Mg = 23 g mol-1
Molar mass of Cl2 = 71 g mol-1
Mass of Mg produced = ?
Volume of Cl2 at NTP produced = ?
Reactions during electrolysis :
(i) Mg2+ + 2e– → Mg (Reduction half reaction)
(ii) 2Cl– → Cl2(g) + 2e– (Oxidation half reaction)
Quantity of electricity passed = Q = I × t
= 2 × 3600 = 7200 C
∵ 1 Faraday = 1 mol electrons
∴ Number of moles of electrons passed
= \(\frac{Q}{F}=\frac{7200}{96500}\) = 0.07461 mol
From half reaction (i),
∵ 2 moles of electrons deposit 1 mole of Mg
∴ 0.07461 moles of electrons will deposit, \(\frac{0.07461 \times 1}{2}\) = 0.037305 mol Mg
Mass of Mg = Moles of Mg × Molar mass of Mg
= 0.037305 × 24 = 0.8953 g Mg
From half reaction (ii),
∵ 2 moles of electrons produce 1 mol Cl2 gas
∴ 0.07461 moles of electrons will produce,
\(\frac{0.07461}{2}\) = 0.037305 mol Cl2
∵ 1 mole of Cl2 occupies 22.4 dm at NTP
∴ 0.037305 mole of Cl2 will occupy,
22.4 × 0.037305 = 0.8356 dm3
∴ Volume of Cl2 gas produced
= 0.8356 dm3
= 0.8356 × 103 cm3
= 835.6 cm3
Ans. Mass of Mg produced = 0.8953 g
Volume of Cl2(g) at NTP produced = 835.6 cm3
![]()
(13) How many Faradays would be required to plate out one mole of free metal from the following cations?
(a) Mg2+ (b) Cr3+ (c) Pb2+ (d) Cu+
Solution :
(a) Reduction half reaction :
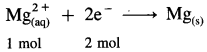
∵ 1 mol electrons = 1 Faraday
Since to deposite 1 mol Mg, two moles of electrons are required,
∴ To plate one mole Mg, 2 Faradays of electricity will be required.
(b) Reduction half reaction :
\(\mathrm{Cr}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{3+}+3 \mathrm{e}^{-} \longrightarrow \mathrm{Cr}_{(\mathrm{s})}\)
∴ 1 mol Cr will require 3 mol electrons, hence 3 Faradays of electricity are required.
(c) Reduction half reaction :
\(\mathrm{Pb}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{2+}+2 \mathrm{e}^{-} \longrightarrow \mathrm{Pb}_{(\mathrm{s})}\)
∴ 1 mol Pb will require 2 mol electrons, hence 2 Faradays are required.
(d) Reduction half reaction :
\(\mathrm{Cu}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{+}+\mathrm{e}^{-} \longrightarrow \mathrm{Cu}_{(\mathrm{s})}\)
∴ 1 mol Cu will require 1 mol electrons hence one Faraday of electricity is required.
(14) In a certain electrolysis experiment, 0.561 g of Zn is deposited in one cell containing ZnSO4 solution. Calculate the mass of Cu deposited in another cell containing CuSO4 solution in series with ZnSO4 cell. Molar masses of Zn and Cu are 65.4 g mol-1 and 63.5 g mol-1 respectively.
Solution :
Given : Mass of Zn deposited = WZn = 0.561 g
Molar mass of Zn = 65.4 g mol-1
Molar mass of Cu = 63.5 g mol-1
Mass of Cu deposited = ?
Number of moles of Zn deposited
= \(\frac{\text { Mass of Zn deposited }}{\text { Molar mass of } \mathrm{Zn}}=\frac{0.561}{65.4}\)
= 8.578 × 10-3 mol Zn
Reactions of electronics:
(i) Zn++ + 2e– → Zn (Half reaction in ZnSO4 cell)
(ii) Cu++ + 2e– → Cu (Half reaction in CuSO4 cell)
Mole ratio of Zn
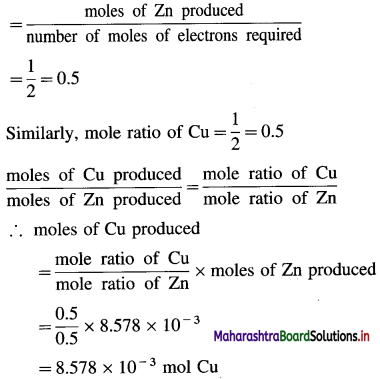
∴ Mass of Cu produced
= moles of Cu × molar mass of Cu
= 8.578 × 10-3 × 63.5
= 0.5447 g Cu
Ans. Mass of Cu deposited = 0.5447 g
(15) Two electrolytic cells, one containing AlCl3 solution and the other containing ZnSO4 solution are connected in series. The same quantity of electricity is passed through the cells. Calculate the amount of Zn deposited in ZnSO4 cell if 1.2 g of Al are deposited in AlCl3 cell. The molar masses of Al and Zn are 27 g mol-1 and 65.4 g mol-1 respectively.
Solution :
Given : Mass of Al deposited = 1.2 g
Molar mass of Al = 27 g mol-1
Molar mass of Zn = 65.4 g mol-1
Mass of zinc deposited = ωZn = ?
Reduction reactions in electrolysis :
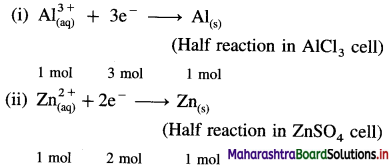
Number of moles of Al deposited = \(\frac{1.2}{27}\)
= 0.04444 mol.
From reaction (i),
∵ 1 mol Al requires 3 mol electrons
∴ 0.04444 mol Al requires 3 × 0.04444
= 0.1333 mol electrons
Hence 0.1333 moles of electrons are passed through both the cells in the series.
From reaction (ii),
∵ 2 moles of electrons deposit 1 mol Zn
∴ 0.1333 moles of electrons will deposit, \(\frac{0.1333}{2}\) = 0.06665 mol Zn
Mass of Zn deposited = 0.06665 × 65.4 = 4.36 g
Ans. Mass of Zn deposited = 4.36 g
(16) How much quantity of electricity in coulomb is required to deposit 1.346 × 10-3 kg of Ag in 3.5 minutes from AgNO3 solution ?
(Given : Molar mass of Ag is 108 × 10-3 kg mol-1)
Solution :
Given : Mass of Ag deposited = 1.346 × 10-3 kg
Molar mass of Ag = 108 × 10-3 kg mol-1
Time = t = 3.5 × 60 s
∵ 108 × 10-3 kg Ag requires 1 Faraday
1.346 × 10-3 kg Ag will require,
\(\frac{1.346 \times 10^{-3}}{108 \times 10^{-3}}\) = 0.01246 F
∵ If F = 96500 C
∴ 0.01246 F = 96500 × 0.01246 = 1202 C
Ans. Amount of electricity required = 1202 C
![]()
(17) How many electrons will have a total charge of 1 Coulomb ?
Solution :
Given : Charge = 1 Coulomb
Number of electrons = ?
1 Faraday = 96500 C per mol electrons
∵ 96500 C electric charge is present on 1 mol electrons
∴ 1C charge is present on \(\frac{1}{96500}\) mol electrons
∴ Number of electrons = \(\frac{1}{96500}\) × 6.022 × 1023
= 6.24 × 1018 electrons
Ans. 1 Coulomb charge is present on 6.24 × 1018 electrons.
(18) A constant electric current flows for 4 hours through two electrolytic cells connected in series. One contains AgNO3solution and second contains CuCl2 solution. During this time, 4 grams of Ag are deposited in the first cell.
(a) How many grams of Cu are deposited in the second cell?
(b) What is the current flowing in amperes? (Atomic mass : Cu = 63.5 gmol-1; Ag = 107.9 gmol-1)
Solution :
Given : Mass of Ag deposited = 4 g
Molar mass of Cu = 63.5 g mol-1
Molar mass of Ag = 107.9 g mol-1
Time = t = 4 hrs = 4 × 60 × 60 = 14400 s
Mass of Cu deposited = WCu = ?
Current = I = ?
(a) Number of moles of Ag deposited
\(=\frac{\text { Mass of } \mathrm{Ag}}{\text { Molar mass of } \mathrm{Ag}}=\frac{4}{107.9}\)
= 0.03707 mol of Ag
Reactions of electrolysis :
(i) Ag+ + e– → Ag (Half reaction in AgNO3 cell)
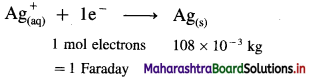
(ii) Cu2+ + 2e– → Cu (Half reaction in CuCl2 cell)
Mole ratio of Ag
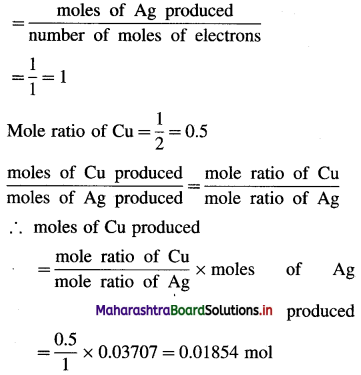
∴ Mass of Cu produced = 0.01854 × 63.5 = 1.177 g
(b) From the reaction,
∵ 1 mol Ag+ requires 1 mol electrons
∴ 0.03707 mol Ag will require 0.03707 mol electrons
∵ 1 mol electrons = 1 Faraday
∴ 0.03707 mol electrons = 0.03707 Faraday
∵ 1 Faraday = 96500 C
∴ 0.03707 Faraday
= 0.03707 × 96500 = 3577 C
∴ Quantity of electricity = Q = 3577 C.
Q = I × t
∴ I = \(\frac{\mathrm{Q}}{t}=\frac{3577}{14400}\) = 0.25 A
Ans. (a) Mass of Cu deposited = 1.177 g
(b) Current passed = 0.25 A
(19) The passage of 0.95 A current for 40 minutes deposited 0.7493 g Cu from CuSO4 solution. Calculate the molar mass of Cu.
Solution :
Given : Electric current = I = 0.95 A
Time = f = 40 min = 40 × 60 = 2400 s
Mass of Cu deposited = 0.7493 g
Molar mass of Cu = ?
Reduction half reaction,
\(\mathrm{Cu}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{2+}+2 \mathrm{e}^{-} \longrightarrow \mathrm{Cu}_{(\mathrm{s})}\)
Quantity of electricity = Q = I × t
= 0.95 × 2400
= 2280 C
Number of moles of electrons = \(\frac{2280}{96500}\)
= 0.02362 mol
∵ 2 mol electrons deposit 1 mol Cu
∴ 0.02362 mol electrons will deposit,
\(\frac{0.02362}{2}\) = 0.01181 mol Cu
Now,
0.01181 mol Cu weighs 0.7493 g
∴ 1 mol of Cu weigh, \(\frac{0.7493 \times 1}{0.01181}\) = 63.44 g
Hence molar mass of Cu 63.44 g mol-1
Ans. Molar mass of Cu = 63.44 g mol-1
(20) A quantity of 0.3 g of Cu was deposited from CuSO4 solution by passing 4A through the solution for 3.8 min. Calculate the value of Faraday constant. (Atomic mass of Cu = 63.5 g mol-1)
Solution :
Given : Mass of Cu deposited = 0.3 g
Electric current = I = 4A
Time = t = 3.8 min = 3.8 × 60 = 228 s
Value of Faraday = ?
Quantity of electricity passed = Q = I × t
= 4 × 228 = 912 C
Reduction half reaction,
\(\mathrm{Cu}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{2+}+2 \mathrm{e}^{-} \longrightarrow \mathrm{Cu}_{(\mathrm{s})}\)
Number of moles of Cu deposited 0.3
= \(\frac{0.3}{63.5}\) = 0.004724 mol
From reduction half reaction,
1 mol Cu ≡ 2 mol electrons
∴ 0.004724 mol Cu = 2 × 0.004724
= 0.009448 mol electrons
Now
∵ 0.009448 mol electrons = 912 C
∴ 1 mol electrons = \(\frac{912}{0.009448}\) = 96528 C
∵ 1 Faraday charge is equal to charge on 1 mol electrons
∴ 1 Faraday = 96528 C
Ans. 1 Faraday = 96528 C
(21) In the electrolysis of water, one of the half reactions is
2H+(aq) + 2e– → H2(g)
Calculate the volume of H2 gas collected at 25 °C and 1 atm pressure by passing 2A for 1h through the solution. R = 0.08205 L atm K-1 mol-1.
Solution :
Given : Reduction half reaction :
![]()
Temperature = T = 273 + 25 = 298 K
Pressure = P = 1 atm
Electric current = I = 2A
Time = t = 1 hr = 1 × 60 × 60 = 3600 s
R = 0.08205 L atm K-1 mol-1
Volume of H2 = VH2 = ?
Quantity of electricity passed = Q = I × t
= 2 × 3600 = 7200 C
Number of moles of electrons = \(\frac{Q}{F}\)
\(\frac{7200}{96500}\) = 0.0746 mol
From the reaction,
∵ 2 mol electrons produces 1 mol H2 gas
∴ 0.0746 mol electrons will produce \(\frac{0.0746}{2}\)
= 0.0373 mol H2.
pVH2 = nRT
![]()
= 0.912 L
Ans. Volume H2 gas = 0.912 L
![]()
(22) Calculate the current strength and number of moles of electrons required to produce 2.369 × 10-3 kg of Cu from CuSO4 solution in one hour. (Molar mass of Cu is 63.5 g/mol)
Solution :
Given : Mass of Cu deposited = 2.369 × 10-3 kg;
t = 1 hr = 3600 s
Molar mass of Cu = 63.5 g mol-1
I = ?; Number of moles of electrons = ?
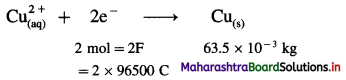
∵ For 63.5 × 10-3 kg Cu Q = 2 × 96500 C
∴ For 2.369 × 10-3 kg Cu
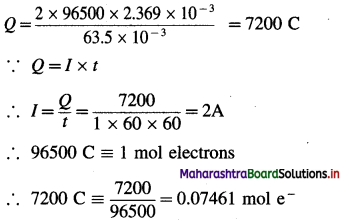
Ans. I = 2A; Number of moles of electrons = 0.07461
Question 39.
Define : Galvanic cell or voltaic cell.
Answer:
Galvanic or voltaic cell : An electrochemical cell which is used to produce electrical energy by a spontaneous chemical reaction inside it is called an electrochemical cell. In this chemical energy is converted into electrical energy.
Example : Daniell cell.
Question 40.
Define : Half cell or Electrode.
Answer:
Half cell or Electrode : It is a metal electrode dipped in the electrolytic solution and capable of establishing oxidation reduction equilibrium with one of the ions of electrolyte solution and develop electrode potential. E.g. Zn in ZnSO4 solution.
Question 41.
What are the functions of a salt bridge ?
Answer:
The functions of a salt bridge are :
- It maintains the electrical contact between the two electrode solutions of the half cells.
- It prevents the mixing of electrode solutions.
- It maintains the electrical neutrality in both the solutions of two half cells by a flow of ions.
- It eliminates the liquid junction potential.
![]()
Question 42.
What are the conventions used to write galvanic cell or cell diagram (cell formula) ?
Answer:
A galvanic cell or voltaic cell is represented by a short notation or diagram which includes electrodes, aqueous solutions of ions and other species that may or may not involve in the cell reaction.
The following conventions are used to represent the cell or write the cell notation :
(1) The metal electrodes or the inert electrodes like platinum are placed at the ends of the cell formula.
(2) The galvanic cell consists of two half cells or electrodes. The electrode on the extreme left hand side is anode where oxidation takes place and it carries negative (-) charge while extreme right hand electrode is cathode where reduction takes place and it carries positive (+) charge.
(3) The gases or insoluble substances are placed in the interior positions adjacent to the metal electrode.
(4) A single vertical line is written between two phases like solid electrode and aqueous solution containing ions.
(5) A double vertical line is drawn between two solutions of two electrodes which indicates a salt bridge connecting them electrically.
(6) The concentration of solutions or ions or pressures of gases are written in brackets along with the substances in the cell.
(7) Different ions in the same solution are separated by a comma.
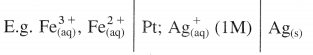
(8) Examples of electrochemical cells :
(i) Daniel cell is represented as,
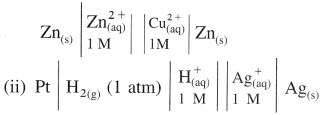
Question 43.
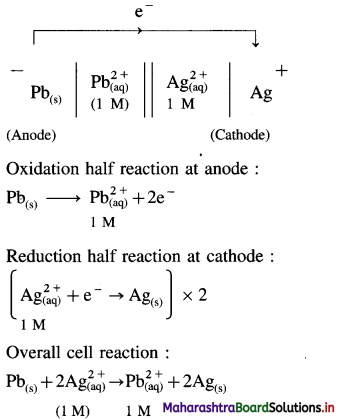
How to write cell reaction for a galvanic cell ?
Answer:
(1) A galvanic cell consists of two half cells or electrodes.
(2) Write oxidation half reaction for left hand electrode which is an anode and reduction half reaction for right hand electrode which is a cathode.
(3) Balance the number of electrons in the oxidation and reduction reactions.
(4) By adding both the reactions, overall cell reaction is obtained.
(5) For example, consider following cell :
Question 44.
Why is anode in a galvanic cell considered to be negative?
Answer:
- According to IUPAC conventions, the electrode of a galvanic cell where de-electronation or oxidation takes place releasing electrons is called anode. Zn(s) → \(\mathrm{Zn}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{2+}\) + 2e–
- The electrons released due to oxidation reaction are accumulated on the metal electrode surface charging it negatively.
Hence anode in the galvanic cell is considered to be negative.
Question 45.
Why is cathode in a galvanic cell considered to be positive electrode?
Answer:
(1) According to IUPAC conventions, the electrode of the galvanic cell where electronation or reduction takes place is called cathode. In this, the electrons from the metal electrode are removed by cations required for their reduction.
\(\mathrm{Cu}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{2+}\) + 2e– → Cu(s)
(2) Since the electrons are lost, the metal electrode acquires a positive charge.
Hence cathode in the galvanic cell is considered to be positive.
![]()
Question 46.
Give the cell reactions in the case of the following cells :
(1)
![]()
Answer:
(2)
![]()
Answer:
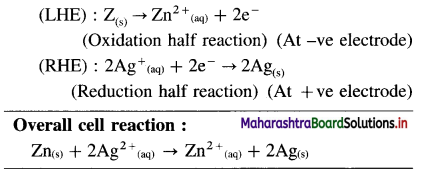
(3) Pt, H2(g) | H+(aq) || Cl–(aq) | Cl2(g), Pt
Answer:
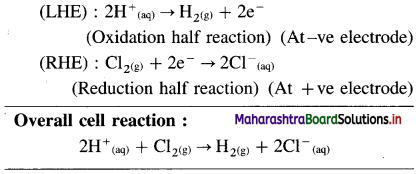
(4) Ni(s)|Ni2+ (1 M) || Al3+ (1 M) | Al(s)
Answer:

Question 47.
Represent the half cells or electrodes for the following reactions :
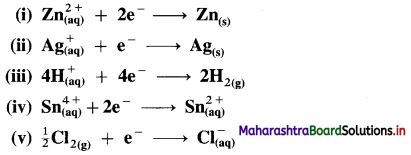
Answer:
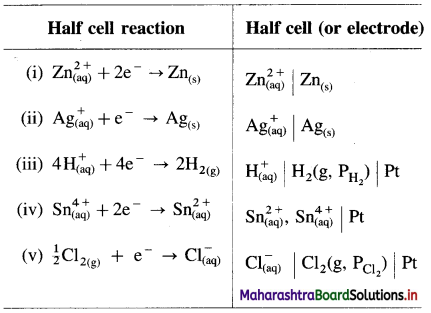
Question 48.
Formulate a cell from the following electrode reactions :
(a) Cl2(g) + 2e– → 2Cl–(aq)
(b) 2I–(aq) → I2(s) + 2e–
Answer:
(a) Cl2(g) + 2e– → 2Cl–(aq) (Reduction half reaction)
(b) 2I–(aq) → I2(s) + 2e– (Oxidation half reaction)
The galvanic cell is,
Pt |I2(s)|I–(aq) (1 M) | Cl–(aq) (1 M) | Cl2(g, PCl2)|Pt
![]()
Question 49.
Formulate a cell for each of the following reactions :
(a) \(\mathrm{Sn}_{\text {(aq) }}^{2+}\) + 2AgCl(s) → \(\mathrm{Sn}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{4+}\) + 2Ag(s) + \(2 \mathrm{Cl}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{-}\)
(b) Mg(s) + Br2(l) → \(\mathrm{Mg}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{2+}+2 \mathrm{Br}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{-}\)
Answer:
(a) \(\mathrm{Sn}_{\text {(aq) }}^{2+}\) + 2AgCl(s) → \(\mathrm{Sn}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{4+}\) + 2Ag(s) + \(2 \mathrm{Cl}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{-}\)
The overall reaction takes place into two steps :
(i) \(\mathrm{Sn}_{\text {(aq) }}^{2+}\) → Sn4+ + 2e– (Oxidation half reaction)
(ii) 2AgCl(s) + 2e– → 2Ag(s) + \(2 \mathrm{Cl}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{-}\) (Reduction half reaction)
Hence the cell is,
![]()
(b) Mg(s) + Br2(l) → \(\mathrm{Mg}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{2+}+2 \mathrm{Br}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{-}\)
The overall reaction takes place into two steps :
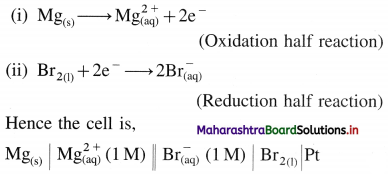
Question 50.
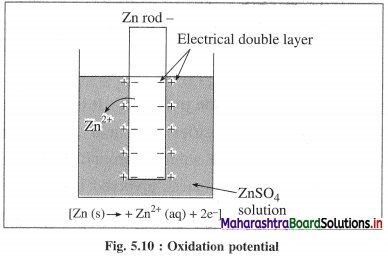
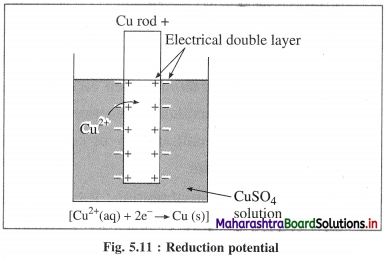
What is electrode potential?
Answer:
(1) Electrode potential : It is defined as the difference of electrical potential established due to electrode half reaction between metal electrode and the solution around it at equilibrium at constant temperature.
(2) Explanation : When a metal is immersed into a solution containing its ions there arises oxidation (or reduction) reaction involving a release of electrons (or gain of electrons). This gives rise to the formation of an electrical double layer, consisting of a charged metal surface and an ionic layer. The potential across this double layer i.e., between metal and the solution is an electrode potential.
Question 51.
Define :
(1) Oxidation potential,
(2) Reduction potential.
Answer:
(1) Oxidation potential : It is defined as the difference of electrical potential between metal electrode and the solution around it at equilibrium developed due to oxidation reaction at anode and at constant temperature.
(2) Reduction potential : It is defined as the difference of electrical potential between metal electrode and the solution around it at equilibrium developed due to reduction reaction at cathode and at constant temperature.
Question 52.
What is a standard state of a substance ?
Answer:
The standard state of a substance is that state in which the substance has unit activity or concentration at 25 °C. i.e., For solution having concentration 1 molar, gas at 1 atm, pure liquids or solids are said to be in their standard states.
![]()
Question 53.
Define the following terms :
(1) Standard electrode potential
(2) Standard oxidation potential
(3) Standard reduction potential.
Answer:
(1) Standard electrode potential : It is defined as the difference of electrical potential between metal electrode and the solution around it equilibrium when all the substances involved in the electrode reaction are in their standard states of unit activity or concentration at constant temperature.
(2) Standard oxidation potential : It is defined as the difference of electrical potential between metal electrode and the solution around it at equilibrium due to oxidation reaction, when all the substances involved in the oxidation reaction are in their standard states of unit activity or concentration at constant temperature.
(3) Standard reduction potential : It is defined as the difference of electrical potential between metal electrode and the solution around it at equilibrium due to reduction reaction, when all the substances involved in the reduction reaction are in their standard states of unit activity or concentration at constant temperature.
Question 54.
What is the standard potential of an electrode according to IUPAC convention?
Answer:
Standard reduction potential : According to IUPAC convention, the standard potential of an electrode due to reduction reaction at 298 K is taken as the standard reduction potential. In this active mass of the substance has unit value.
Question 55.
What is cell potential or emf of a cell ?
Answer:
Cell potential or emf of a cell : It is defined as the potential difference between two electrodes, responsible for an external flow of electrons from the left hand electrode at higher potential (anode), to the right hand electrode at lower potential (cathode), when connected to form an electrochemical or galvanic cell.
Since there is oxidation reaction at left hand electrode (LHE) or anode and reduction reaction at right hand electrode (RHE) or cathode, emf of the galvanic, Ecell, is given by
Ecell = (Eoxi)anode + (Ered)cathode
Since by IUPAC conventions, generally reduction potentials are used, hence, for the given cell,
(∵ Eoxi = -Ered)
∴ Ecell = (Ered)cathode – (Ered)anode
Similarly, standard emf of the cell, E0cell is given by
E0cell = (E0red)cathode – (E0red)anode
Question 56.
Explain dependence of cell potential on concentration.
OR
Explain Nernst equation for cell potential.
Answer:
Consider following general reaction taking place in the galvanic cell.
aA + bB → cC + dD
The cell voltage is given by,

where,
T → temperature
R → Gas constant
F → Faraday
n → Number of electrons in the redox cell reaction.
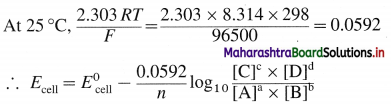
This is Nernst equation for cell potential. It is used to calculate cell potential and electrode potentials.
Question 57.
State (or write) Nernst equation for the electrode potential and explain the terms involved.
Answer:
The Nernst equation for the single electrode reduction potential for a given ionic concentration in the solution in the case, \(M_{(a q)}^{n+}\) + ne– → M(s) is given by
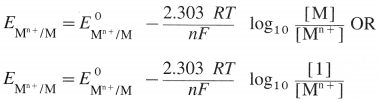
\(\mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{M}^{\mathrm{n}+} / \mathrm{M}}\) is the single electrode potential,
\(E_{\mathrm{M}^{n+} / \mathrm{M}}^{0}\) is the standard reduction electrode potential,
R is the gas constant = 8.314 JK-1 mol-1
T is the absolute temperature,
n is the number of electrons involved in the reaction,
F is Faraday (96500 C)
[Mn+] is the molar concentration of ions.
![]()
Question 58.
Obtain Nernst equation for the following cell :
![]()
Answer:
Electrode reactions and a cell reaction for the given cell are,
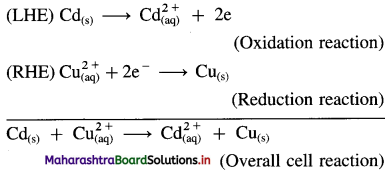
Here, n = 2
By Nernst equation, the cell potential is given by,

Question 59.
Obtain Nernst equation for the electrode potential for the electrode, \(\mathrm{Zn}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{2+} \mid \mathrm{Zn}_{(\mathrm{s})}\).
Answer:
For the electrode, \(\mathrm{Zn}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{2+} \mid \mathrm{Zn}_{(\mathrm{s})}\),
the reduction reaction is,
\(\mathrm{Zn}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{2+}+2 \mathrm{e}^{-} \longrightarrow \mathrm{Zn}_{(\mathrm{s})}\) ∴ n = 2
By Nernst equation, the reduction electrode potential is given by,
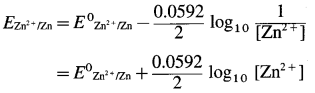
where E0zn2+/zn is the standard electrode potential of zinc electrode.
Question 60.
Obtain a relation between cell potential and Gibbs energy for the cell reaction.
Answer:
Consider a galvanic cell which involves n number of electrons in the overall cell reaction. Since one mole of electrons involve the electric charge equal to one Faraday (F) which is equal to 96500 C, the total charge involved in the reaction is,
Electric charge = n × F
If Ecell is the cell potential, then Electrical work = n × F × Ecell
According to thermodynamics, electric work is equal to decrease in Gibbs energy, -ΔG, we can write,
Electric work = n × F × Ecell = -ΔG
∴ ΔG = -nFEcell
Under standard conditions, we can write
∴ ΔG0 = -nF\(E_{\text {cell }}^{0}\)
where \(E_{\text {cell }}^{0}\) is the standard cell potential and ΔG0 is the standard Gibbs free energy change.
Question 61.
Write Nernst Equation for the following reactions :
(a) Cr(s) + 3Fe3+(aq) → Cr3+(aq) + 3Fe2+(aq)
(b) Al3+(aq) + 3e– → Al(s)
Answer:
(a) Cr(s) + 3Fe3+(aq) → Cr3+(aq) + 3Fe2+(aq)
The cell formulation is,
Cr(s)|Cr3+(aq) || Fe3+(aq), Fe2+(aq)| Pt
Hence cell potential is,
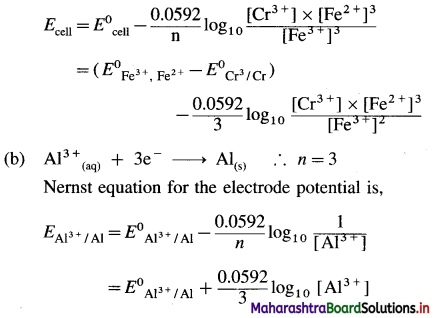
Question 62.
A single electrode potential can’t be measured but the cell potential can be measured. Explain.
Answer:
(1)
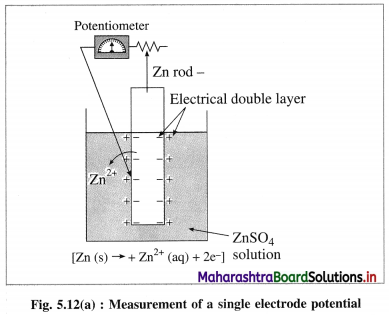
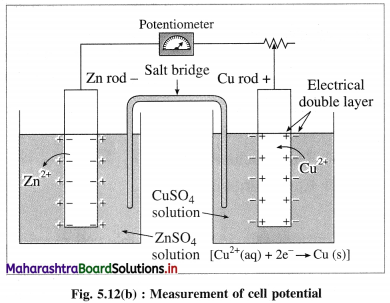
According to Nemst theory, electrode potential is the potential difference between the metal and ionic layer around it at equilibrium, i.e. the potential across the electric double layer.
(2) For measuring the single electrode potential, one part of the double layer, that is metallic layer can be connected to the potentiometer but not the ionic layer. Hence, single electrode potential can’t be measured experimentally.
(3) When an electrochemical cell is developed by combining two half cells or electrodes, they can be connected to the potentiometer and the potential difference or cell potential can be measured.
Ecell = E2 – E1
where E1 and E2 are reduction potentials of two electrodes.
(4) If one of the electrode potentials is known or arbitrarily assumed and Ecell is measured by potentiometer, then potential of another electrode can be obtained. Therefore it is necessary to choose a reference electrode with arbitrarily fixed potential and measure the potentials of other electrodes.
(5) Therefore Standard Hydrogen Electrode (SHE) is selected assuming arbitrary potential 0.0 volt. Hence potentials of all other electrodes are referred to as hydrogen scale potentials.
![]()
Question 63.
Describe the construction and working of the standard hydrogen electrode (S.H.E.). Give its advantages and disadvantages.
OR
What is the standard hydrogen electrode
OR
Primary reference electrode? Write the construction and working of it.
Answer:
A single electrode potential cannot be measured, but the cell potential can be measured experimentally. Hence, it is necessary to have a reference electrode. S.H.E. is a primary reference electrode.
(1) Construction :
(1) The standard hydrogen electrode (S.H.E.) consists of a glass tube at the end of which a piece of platinised platinum foil is attached as shown in Fig. 5.14. Around this plate there is an outer jacket of glass which has a side inlet through which pure and dry hydrogen gas is bubbled at one atmosphere pressure. The inner tube is filled with a little mercury and a copper wire is dipped into it. This provides an electrical contact with the platinum foil. The outer jacket ends into a broad opening.
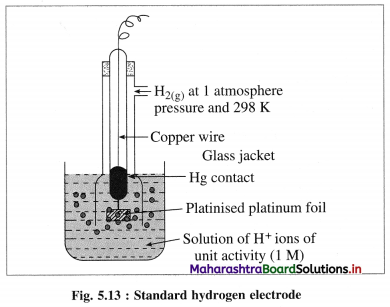
(2) The whole assembly is kept immersed in a solution containing hydrogen ions (H+) of unit activity.
(3) This electrode is arbitrarily assigned zero potential.
(4) The platinised platinum foil is used to provide an electrical contact for the electrode. This permits rapid establishment of the equilibrium between the hydrogen gas adsorbed by the metal and the hydrogen ions in solution.
(2) Representation of S.H.E. :
H+ (1 M) | H2 (g, 1 atm) | Pt
(3) Working :
Reduction : H+(aq) + e– ⇌ \(\frac {1}{2}\)H2(g) E0 = 0.00 V
H2 gas in contact with H+(aq) ions attains an equilibrium establishing a potential.
(4) Applications of SHE : A reversible galvanic cell with the experimental (indicator) electrode, Zn2+ (1M) | Zn(s) and SHE can be developed as follows :
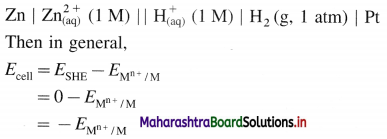
Thus the potential can be directly obtained.
(5) Disadvantages (Drawbacks or Difficulties) :
- It is difficult to construct and handle SHE.
- Pure and dry H2 gas cannot be obtained.
- Pressure of H2 gas cannot be maintained exactly at 1 atmosphere.
- The active mass or concentration of H+ from HCl cannot be maintained exactly unity.
Question 64.
How is the potential of hydrogen electrode obtained?
Answer:
Hydrogen gas electrode is represented as,
H+(aq) | H2 (g, PH2) | Pt
Electrode reduction reaction is,
2H+(aq) + 2e– → H2(g)
By Nernst equation, the reduction potential is,

If H2 gas is passed at 1 atm, then PH2 = 1 atm
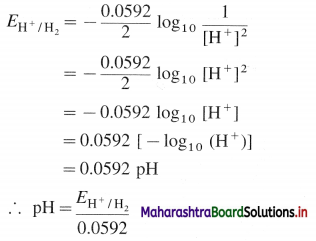
Question 65.
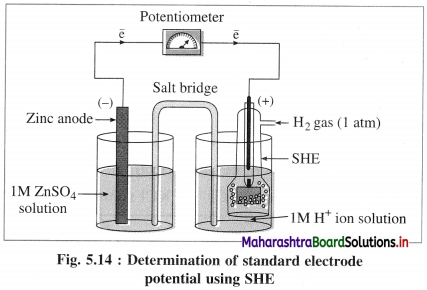
Draw the diagram for the determination of standard electrode potential with SHE.
Answer:
Consider the following cell :
Zn | Zn2+(aq) || HCl | H2(g, 1atm) | Pt
![]()
Question 66.
A voltaic cell consisting of Fe2+(aq)|Fe(s) and Bi3+(aq) | Bi(s) electrodes is constructed. When the circuit is closed, mass of Fe electrode decreases and that of Bi electrode increases.
(a) Write cell formula, (b) Which electrode is cathode and which electrode is anode ? (c) Write electrode reactions and overall cell reaction.
Answer:
(a) Since the mass of Fe electrode decreases, it undergoes oxidation and it is an anode or an oxidation electrode while as the mass of Bi electrode increases, there is a reduction of Bi3+ to Bi and it is cathode or a reduction electrode. Hence the cell formula is,
\(\mathrm{Fe}_{(\mathrm{s})}\left|\mathrm{Fe}_{\mathrm{(aq})}^{2+}(1 \mathrm{M}) \| \mathrm{Bi}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{3+}(1 \mathrm{M})\right| \mathrm{Bi}\)
(b) The left hand electrode is an anode and right hand electrode is a cathode.
(c) Reactions :
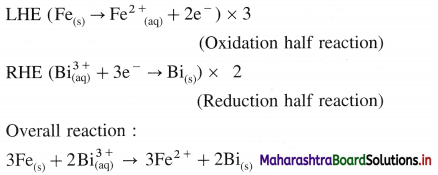
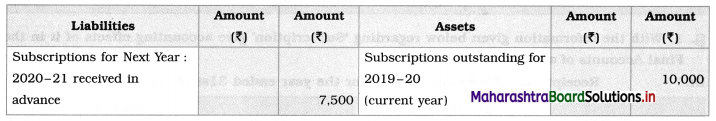
Solved Examples 5.7 – 5.9
Question 67.
Solve the following :
(1) Write the reaction and calculate the potential of the half cell,
\(\mathbf{Z n}_{(\mathbf{a q})}^{2+}\) (0.2M) | Zn. (E0Zn2+/Zn = – 0.76 V).
Solution :
Given : E0Zn2+/Zn = -0.76 V
Concentration of Zn2+ = [Zn2+] = 0.2 M
EZn2+/Zn = ?
Reduction reaction for the half cell,
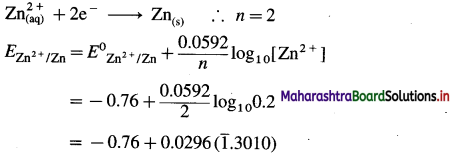
= – 0.76 + 0.0296 (-0.6990)
= -0.76 – 0.02069
= -0.78069 V
Ans. E0Zn2+/Zn = -0.78069 V
(2) Write a reaction and calculate the potential of the electrode, \(\mathrm{Cl}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{-}\) (0.05 M) | Cl2 (g, 1 atm) | Pt E0Cl2/Cl– = 1.36 V.
Solution :
Given : Reduction reaction :
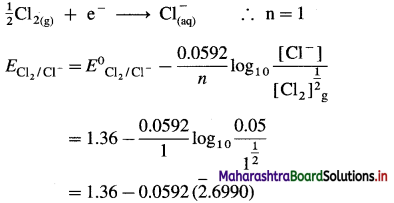
= 1.36 – 0.0592 (- 2 + 0.6990)
= 1.36 – 0.0592 (-1.3010)
= 1.36 + 0.077
= 1.437 V
Ans. Potential of the electrode = 1.437 V
(3) Calculate the potential of the electrode,
pH = 4.5 | H2 (g, 1 atm) |Pt.
Solution :
Given : pH = 4.5
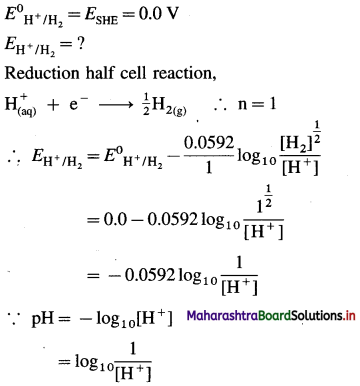
∴ EH+/H2 = -0.0592 pH
= -0.0592 × 4.5
= -0.2664 V
Ans. EH+/H2 = -0.2664 V
(4) If the standard cell potential of Daniell cell is 1.1 V, calculate standard free energy change for the cell reaction.
Solution :
Given : Daniell cell :
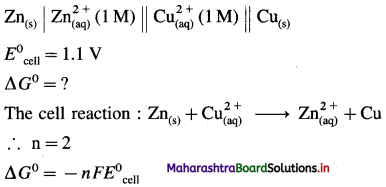
= – 2 × 96500 × 1.1
= -212300 J
= -212.3 kJ
Ans. Standard free energy change = ΔG0
= -212.3 kJ
![]()
(5) Write balanced equations for the half reactions and calculate the reduction potentials at 25 °C for the following half cells :
(a) Cl– (1.2 M) | Cl2(g, 3.6 atm) E0 = 1.36 V
(b) Fe2+ (2 M) | Fe(s) E0 = – 0.44 V
Solution :
(a) Given : Half cell,
\(\mathrm{Cl}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{-}\) (1.2 M) | Cl2(g, 3.6 atm)|Pt
E0Cl2/Cl– = 1.36 V
The reduction reaction:
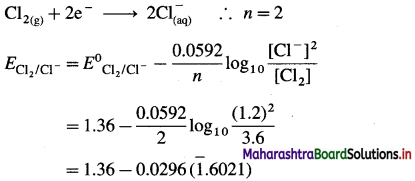
= 1.36 – 0.0296 (-0.3979)
= 1.36 + 0.01178
= 1.37178
≅ 1.372 V
(b) Given: Half cell, \(\mathrm{Fe}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{2+}\) (2M) |Fe(s)
E0 Fe2+/Fe = -0.44 V
The reduction reaction:
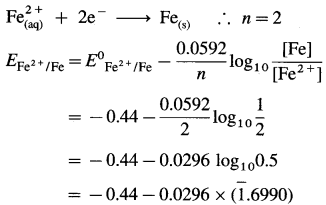
= – 0.44 – 0.0296 × (- 0.3010)
= -0.44 + 0.00891
= -0.43109 V
Ans. (a) Half reaction : Cl2(g) + 2e– → \(2 \mathrm{Cl}_{\text {(aq) }}^{-}\)
ECell = 1.372 V
(b) \(\mathrm{Fe}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{2+}\) + 2e– → Fe(s)
ECell = -0.43109 V.
(6) Using Nernst equation, calculate the potentials for the following half reactions :
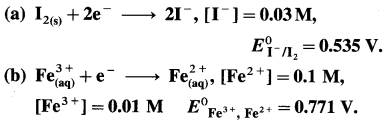
Solution :
(a) Given :
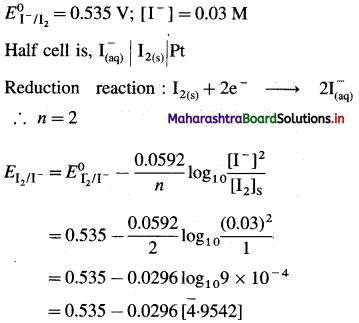
= 0.535 – 0.0296 [ – 4 + 0.9542]
= 0.535 – 0.0296 [-3.0458]
= 0.535 + 0.0902
= 0.6252 V

Ans. (a) Potential of the half cell = 0.6252 V
(b) Potential of the half cell = 0.7118 V.
(7) Write the cell reaction and calculate the standard potential of the cell,
Ni(s) | Ni2+(1 M) || Cl–(1M) | Cl2 (g, 1 atm) | Pt
E0Cl2 = 1.36 V and E0Ni = – 0.25 V.
Solution :
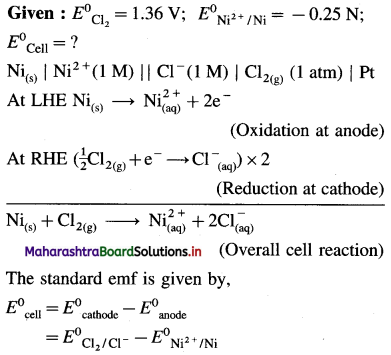
= 1.36 – (-0.25)
= 1.36+ 0.25 = 1.61V
Ans. Cell reaction : Ni(s) + Cl2(g) → \(\mathrm{Ni}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{2+}+2 \mathrm{Cl}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{-}\)
E0Cell = 1.61 V
(8) Write the cell reaction and calculate cell potential and standard free energy change for a cell reaction in the following cell :
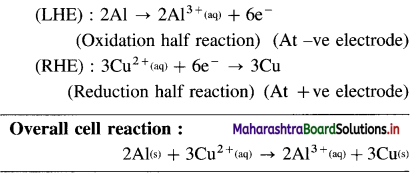
\(\mathbf{A l}_{(\mathrm{s})}\left|\mathbf{A l}_{(\mathbf{a q})}^{3+}(1 \mathbf{M}) \| \mathbf{C d}_{(\mathbf{a q})}^{2+}(1 \mathrm{M})\right| \mathbf{C} d\)
E0Al3+/Al = -1-66 V and E0cd2+/cd = -0.403 V
Solution :
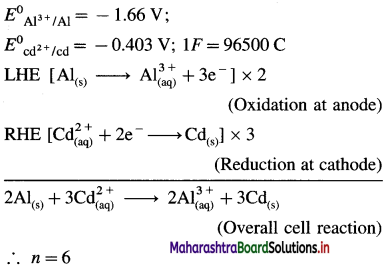
Since concentrations of ions are 1 M each, it is a standard cell, hence the cell potential is E0Cell.
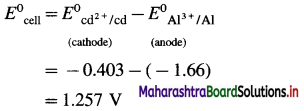
Standard free energy change ΔG0 is given by,
ΔG0= – nFE0Cell
= -6 × 96500 × 1.257
= – 727800 J
= -727.8 kJ
Ans. Cell reaction :
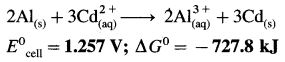
![]()
(9) Write the cell reaction and calculate cell potential and the standard free energy change for the cell reaction in the following cell :
Pt | H2 (g, 1 atm) | \(\mathbf{H}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{+}\)(1M) || \(\mathrm{Cu}_{\text {(aq) }}^{2+}\) (1M) | Cu(s).
Mention anode and cathode and direction of flow of electrons in the external circuit. (E0Cu2+/Cu = 0.337 V)
Solution :
Given : E0Cu2+/Cu = 0.337 V;
E0H+/H2 = E0SHE = 0.0V
Pt | H2(g, 1 atm) | \(\mathbf{H}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{+}\) (1M) || \(\mathrm{Cu}_{\text {(aq) }}^{2+}\) (1M) | Cu(s)
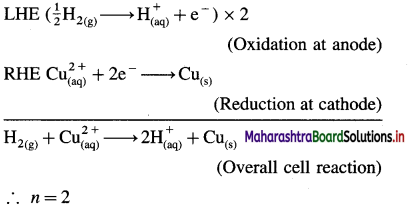
Anode : Hydrogen gas electrode (LHE)
Cathode : Copper electrode (RHE)
E0Cell = E0Cu2+/Cu – E0H+/H2
= 0.337 – (0.0)
= 0.337 V
ΔG0 = – nFE0 = -2 × 96500 × 0.337
= – 65040J
= – 65.04 kJ
Electrons in the external circuit will flow from (LHE) hydrogen gas electrode to (RHE) copper electrode.
Ans. Cell reaction : H2(g) + \(\mathrm{Cu}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{2+}\) → 2 \(\mathrm{H}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{+}\) + Cu(s)
Cell potential = E0Cell = 0.337 V
ΔG0 = -65.04 kJ
(10) Calculate the reduction potential of the electrode, Zn2+ (0.02 M) | Zn(s). E0Zn++/Zn = – 0.76 V.
Solution :
Given :E0red = E0Zn++/Zn = -0.76 V;
Concentration of \(\mathrm{Zn}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{2+}\) = [Zn2+] = 0.02 M
The reduction reaction for the electrode,
\(\mathrm{Zn}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{2+}\) +2e– → Zn(s); ∴ n = 2
The reduction potential is given by,

= – 0.76 + 0.0296 (- 1.6990)
= -0.76 – 0.0296 × 1.6990
= -0.76 – 0.0503
= -0.8103 V
Ans. Ered = EZn2+/Zn = -0.8103 V
(11) Calculate the potential of the following cell at 25 °C :
Zn | Zn2+(0.6 M) ||H+(1.2 M) | H2 (g, 1 atm) | Pt
E°Zn2+/Zn = -0.763 V
Solution :
Given : E0Zn2+/Zn = -0.763 V;
Concentrations : [Zn2+] = 0.6 M; [H+] = 1.2 M
[H2]g = 1 atm
Cell potential = Ecell = ?
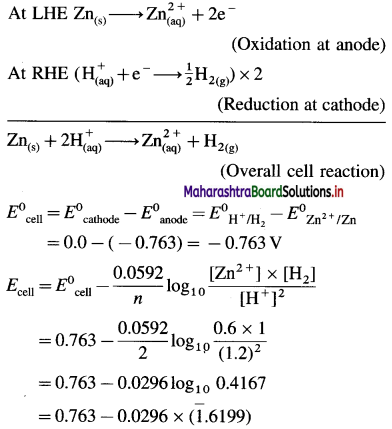
= 0.763 – 0.0296 × (- 0.3801)
= 0.763 + 0.01125
= 0.77425 V
Ans. Cell potential = E0cell = 0.77425 V
(12) The following redox reaction occurs in a galvanic cell.
2Al(s) + 3Fe2+(1 M) → 2Al3+(1 M)+ 3Fe(s)
(a) Write the cell notation.
(b) Identify anode and cathode
(c) Calculate E0cell if E0anode = – 1.66 V and E0cathode = – 0 44 V
(d) Calculate ΔG0 for the reaction.
Solution :
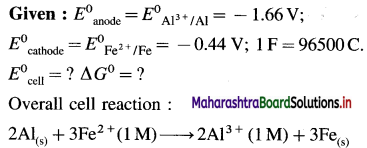
(a) In the cell reaction, Al is oxidised from zero to 3+ while Fe3+ is reduced from 3+ to zero. Hence the cell notation is,
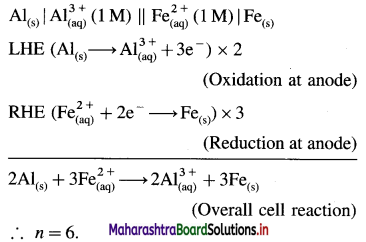
(b) Anode : Al electrode at LHE
Cathode : Fe electrode at RHE

(d) The standard free energy change ΔG0 is given by,
ΔG0 = – nFE0cell
= – 6 × 96500 × 1.22
= – 70640 J
= – 706.4 kJ
Ans. (a) Cell notation :
\(\mathrm{Al}_{(\mathrm{s})}\left|\mathrm{Al}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{3+}(1 \mathrm{M}) \| \mathrm{Fe}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{2+}(1 \mathrm{M})\right| \mathrm{Fe}_{(\mathrm{s})}\)
(b) Anode : Al; Cathode : Fe
(c) E0cell = 1.22 V
(d) ΔG0 = – 706.4 kJ
![]()
(13) Construct a cell consisting of \(\mathbf{N i}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{2+}\) | Ni(s) half cell and H+ | H2(g) | Pt half cell.
(a) Write the cell reaction
(b) Calculate emf of the cell if [Ni2+] = 0.1M,
PH2 = 1 atm [H+] = 0.05 M and
E0Ni = – 0.257 V.
Solution :

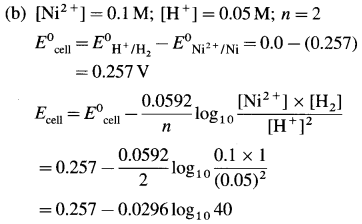
= 0.257 – 0.0296 × 1.6020
= 0.257 – 0.04742
= 0.20958
≅ 0.2096 V
Ans.

(14) Calculate the cell potential of the following cell at 25°C,
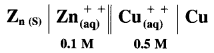
Standard reduction potentials (SRP) of Zn and Cu are -0.76 V and 0.334 V respectively.
Solution:
Given:
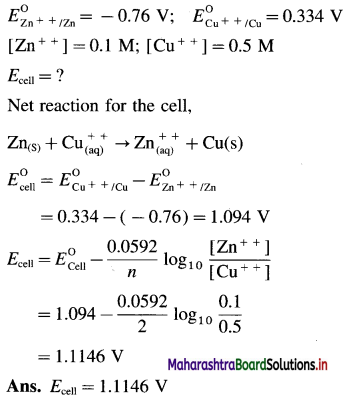
(15) Set up the cell consisting of \(\mathbf{H}_{\text {(aq) }}^{+} \mid \mathbf{H}_{2(\mathrm{~g})}\) and \(\mathbf{P b}_{(\mathbf{a q})}^{2+}\) | Pb(s) electrodes. Calculate the emf at 25 °C of the cell if [Pb2+] = 0.1 M,
[H+] = 0.5 M and hydrogen gas is at 2 atm pressure. E0pb2+/pb = – 0.126 V.
Solution :
Given : Half cells :
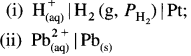
Concentrations : [H+] = 0.5 M; [Pb2+] = 0.1M;
[H2]g = PH2 = 2 atm; E0H+/H2 = ESHE = 0.0 V;
E0pb2+/pb = -0.126 V
Since E0pb2+/pb (reduction) < E0H+/H2 the Pb electrode is anode and hydrogen gas electrode is cathode.
The cell formulation :
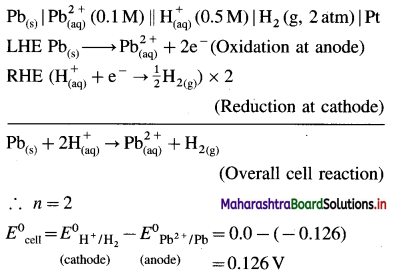
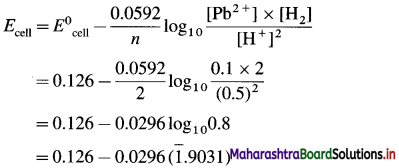
= 0.126 – 0.0296 (- 0.0969)
= 0.126 + 0.002868
= 0.128868
≅ 0.1289 V
Ans. Ecell = 0.1289 V
(16) Consider a galvanic cell that uses the half reactions,
2H+(aq) + 2e– → H(g)
Mg2+(aq) + 2e– → Mg(s)
Write balanced equation for the cell reaction. Calculate E0cell, Ecell and ΔG0 if concentrations are 1M each and PH2 = 10 atm
E0Mg2+/Mg = -2.37 V.
Solution :
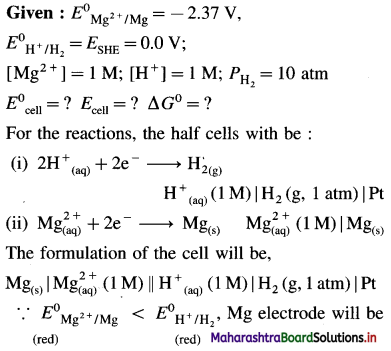
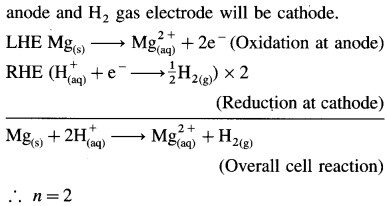
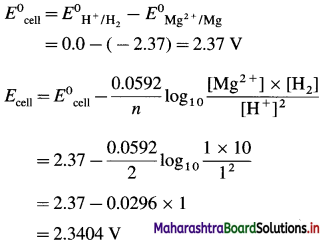
The standard free energy change ΔG0 is given by
ΔG0= – nFE0cell
= – 2 × 96500 × 2.37
= -457400 J
= – 457.4 kJ
Ans. E0cell = 2.37 V; Ecell = 2.3404 V;
ΔG0 = -457.4 kJ
![]()
(17) Calculate Ecell and ΔG for the following at 28 °C : Mg(s) + Sn2+ (0.04M) → Mg2+ (0.06M) + Sn(s)
E0cell = 2.23 V
Is the reaction spontaneous ?
Solution:
Given:
Mg(s) + Sn2+ (0.04 M) → Mg2+ (0.06 M) + Sn
[Sn2+] = 0.4 M
[Mg2+] = 0.06 M
E0cell = 2.23V
Ecell = ?
ΔG = ?
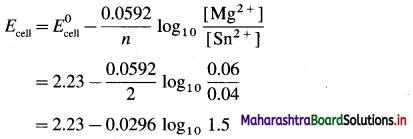
2.23 – 0.0296 × 0.1761
= 2.23 – 0.005213
= 2.224V
ΔG = – nFE
= – 2 × 96500 × 2.224
= – 4.292 × 105 J
= -429.2 kJ
Since ΔG is negative, the electrochemical reaction is spontaneous.
(18) The standard potentials for Sn2+/Sn and Fe2+/Fe half reactions are -0.136 V and -0.440 V respectively. At what relative concentrations of Sn2+ and Fe2+ will these have the same reduction potentials?
Solution :


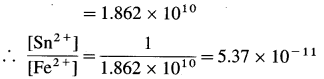
Hence when relative concentrations of Sn2+ and Fe2+ i.e., [Sn2+]/[Fe2+] = 5.37 × 10-11, both the electrodes will have same potential.
(19) Write the cell reaction and calculate the emf of the cell at 25 °C.
Cr(s) | Cr3+(0.0065 M) || Co2+(0.012 M) | Co(s)
E0Co = – 0.280 V, E0Cr = – 0.74 V
What is ΔG for the cell reaction ?
Solution :
Given :
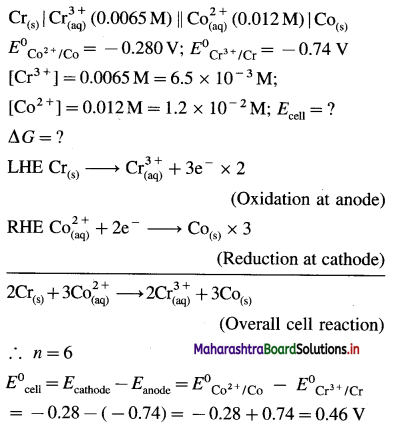
By Nernst equation,
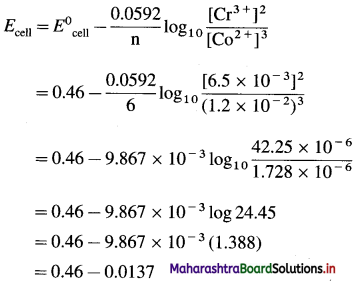
Ecell = 0.4463 V
ΔG = -nFECell
= – 6 × 96500 × 0.4463
= – 258407 J
= – 258.4 kJ
Ans. Cell reaction :
\(2 \mathrm{Cr}_{(\mathrm{s})}+3 \mathrm{Co}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{2+} \rightarrow 2 \mathrm{Cr}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{3+}+3 \mathrm{Co}_{(\mathrm{s})}\)
ECell = 0.4463 V; ΔG = – 258.4 kJ.
![]()
(20) Calculate E0Cell, ΔG0 and equilibrium constant for the reaction 2Cu+ → Cu2+ + Cu.
E0Cu+/Cu = 0.52 V and E0Cu2+,Cu+ = 0.16 V.
Solution :
Given : Cell reaction : 2Cu+(aq) → Cu2+(aq) +Cu(s)
E0Cu+/Cu = 0.52V; E0Cu2+,Cu+ = 0.16 V
1F = 96500 C
E0Cell = ? ΔG0 = ? K=?
(i) The formulation of the cell :
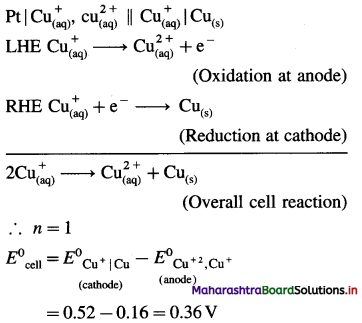
(ii) ΔG0 = – nFE0Cell = – 1 × 96500 × 0.36
= – 34740 J
= – 34.74 kJ
(iii) Electrochemical redox reactions are considered as reversible reactions. If K is the equilibrium constant for the electrochemical redox reaction, then
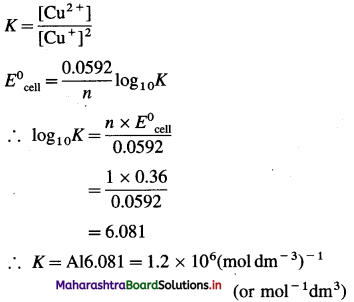
Ans. E0Cell = 0.36 V; ΔG0 = – 34.74 kJ; Equilibrium constant = K= 1.2 × 106 mol-1 dm3.
(21) Calculate the equilibrium constant for the redox reaction at 25 °C.
Sr(s) + Mg2+ → Sr2+(aq) + Mg(s),
that occurs in a galvanic cell. Write the cell formula.
E0Mg = – 2.37 V and E0Sr = – 2.89 V.
Solution :
Given :
Cell reaction : Sr(s) + Mg2+ → Sr2+(aq) + Mg(s)
E0 Mg2+/Mg = -2.37 V; E0 Sr2+/Sr = -2.89 V
Equilibrium constant K = ?
The formation of the cell :
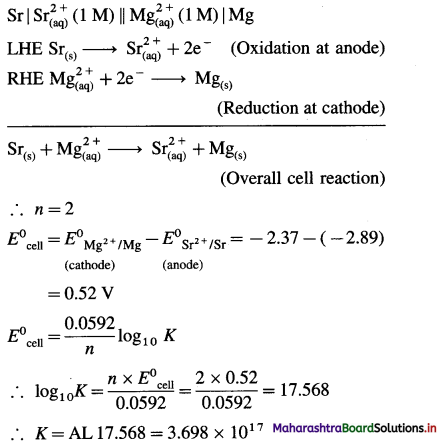
Ans. Equilibrium constant = K = 3.698 × 1017
(22) The equilibrium constant for the following reaction at 25 °C is 2.9 × 109. Calculate standard voltage of the cell.
Cl2(g) + 2Br–(aq) ⇌ Br2(l) + 2Cl–(aq)
Solution :
Given : Cell reaction : Cl2(g) + 2Br–(aq) ⇌ Br2(l) + 2Cl–(aq)
Equilibrium constant = K = 2.9 × 109 atm-1
Standard voltage of the cell = E0Cell = ?
The formulation of the cell :
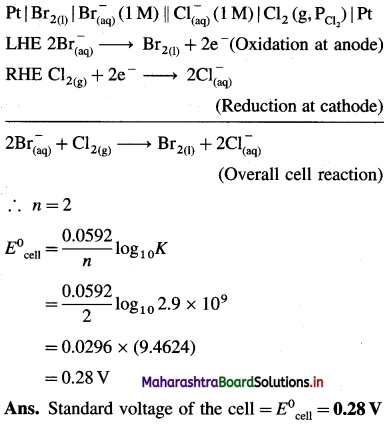
(23) Write the cell representation and calculate equilibrium constant for the following redox reaction :
Ni(s) + 2 Ag+(aq) (1M) → Ni2+(aq) (1 M) + 2Ag(s)
at 25 °C
E0Ni = – 0.25 V and E0Ag = 0.799 V
Solution :
Given : E0Ni2+/Ni = – 0.25 V; E0Ag+/Ag = 0.799 V
Equilibrium constant = K = ?

(24) Calculate the cell potential of the following galvanic cell :
Pt|H2 (g, 1 atm)|\(\mathbf{H}_{\text {(aq) }}^{+} \mathbf{p H}\) = 3.51||Calomel electrode
Ecal = 0.242 V at 25 °C.
Solution :
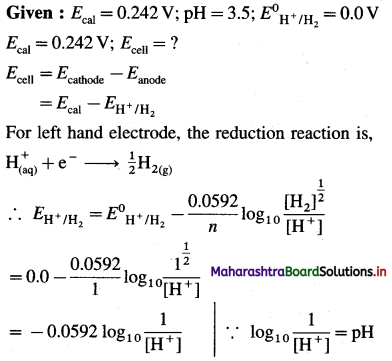
= -0.0592 × pH
= -0.0592 × 3.5
= -0.2072 V
∴ Ecell = Ecal – EH+/H2
= 0.242 – (-0.2072)
= 0.242 + 0.2072
= 0.4492 V
Ans. Ecell = 0.4492 V
![]()
Question 68.
How are the voltaic cells classified ?
Answer:
The voltaic cells are classified as primary and secondary voltaic cells.
(1) Primary voltaic cells : These are the voltaic cells in which the electrical energy or cell potentials are developed within the cells due to oxidation and reduction reactions at the reversible electrodes.
The chemicals and electrode materials consumed during the discharging can be regenerated by passing the current in opposite direction from the external source of electricity i.e., these cells can be recharged. For example, Daniell cell. There are the examples where the primary cells can’t be recharged. E.g. Dry cell.
(2) Secondary voltaic cells :
(i) These are the voltaic cells in which the electrical energy or cell potentials are not developed within the cell but electrical energy can be stored or cell potentials can be regenerated by passing electricity from the external source of electricity. Since the electrical energy obtained is second hand, these cells are called secondary cells or accumulators or storage cells.
(ii) These cells can be recharged by passing electric current in opposite direction from the external source of higher emf. Therefore the secondary cells are reversible cells. For example, lead accumulator (lead storage battery).
Question 69.
Explain the construction and working of a dry cell (or Leclanche’s cell).
OR
Write a note on dry cell.
Answer:
(A) Principle :
- Leclanche’s cell is a primary voltaic cell.
- It doesn’t contain mobile liquid electrolyte but contains moist viscose aqeuous paste of the electrolytes.
- It is an irreversible voltaic cell which can’t be recharged.
(B) Construction :
(i) It consists of a small zinc vessel which serves as an anode (negative electrode).
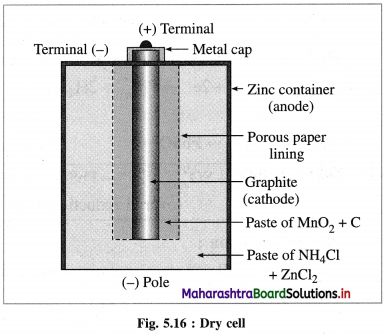
(ii) The zinc vessel contains a porous paper bag containing an inert graphite (C) electrode which serves as cathode, immersed in a paste of MnO2 and carbon black. This paper bag divides the dry cell into two compartments, namely anode and cathode compartments.
(iii) The rest of the cell is filled with a moist paste of NH4Cl and ZnCl2 which acts as an electrolyte for zinc anode.
(iv) The graphite rod is fitted with a metal cap and the cell is sealed to prevent the drying of moist paste by evaporation.
(C) The dry cell can be represented as,
– Zn|ZnCl2(aq), NH2Cl(aq), MnO2(s)|C+.
(D) Reactions in the dry cell :
(i) Oxidation at zinc anode :
Zn(s) → \(\mathrm{Zn}_{\text {(aq) }}^{2+}\) + 2e– (oxidation half reaction)
(ii) Reduction at graphite (C) cathode :
The electrons released in the oxidation reaction at anode, flow to cathode through external circuit.
Hydrogen in NH4 ion is reduced to molecular hydrogen which reduces MnO2 to Mn2O3.
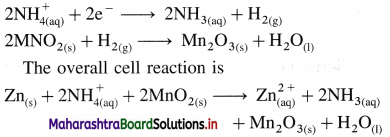
(iii) Zn2+ react with NH3 and form a complex.
\(\mathrm{Zn}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{2+}+4 \mathrm{NH}_{3(\text { aq) }} \longrightarrow\left[\mathrm{Zn}\left(\mathrm{NH}_{3}\right)_{4}\right]^{2+}{ }_{(\mathrm{aq})}\)
Since Zn2+ ions are removed, the overall cell reaction can’t be reversed.
(E) Uses of dry cell :
- Dry cell is used as a source of electric power in radios, flashlights, torches, clocks, etc.
- Since they are available in small size and portable, they can be used conveniently.
Question 70.
Describe the construction and working of lead accumulator (lead storage cell).
OR
Draw a neat labelled diagram of the lead accumulator. Explain the reactions involved in discharging and charging this cell. Represent this cell using cell conventions.
Answer:
(A) Principle :
(1) The lead accumulator is a secondary electrochemical cell since electrical energy and emf are not developed within the cell but it is previously stored by passing an electric current. Hence it is also called lead accumulator or lead storage battery.
(2) It is reversible since the electrochemical reaction can be reversed by passing an electric current in opposite direction and consumed reactants can be regenerated.
(3) Hence battery can be charged after it is discharged.
(B) Construction : In a lead accumulator, the negative terminal (anode) is made up of lead sheets packed with spongy lead, while the positive terminal (cathode) is made up of lead grids packed with PbO2.
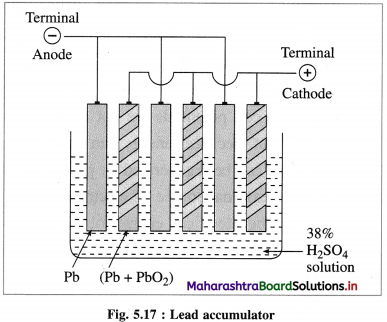
Sulphuric acid of about 38% strength (%w/w) or specific gravity 1.28 or 4.963 molar is the electrolyte in which the lead sheets and lead grids are dipped. The positive terminal and negative terminal are alternatively arranged in the electrolyte and are separately interconnected.
(C) Representation of lead accumulator :
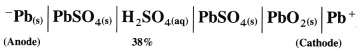
(D) Working of a lead accumulator :
(1) Discharging : When the electric current is withdrawn from lead accumulator, the following reactions take place :
Oxidation at the – ve electrode or anode :
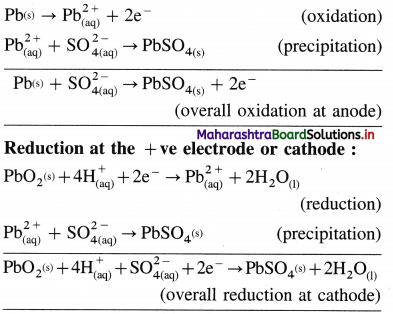
(2) Net cell reaction :
(i) Thus, the overall cell reaction during discharging is
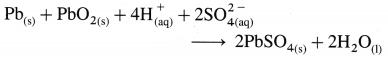
OR
Pb(s) + PbO2(s) + 2H2SO4(aq) → 2PbSO4(s) + 2H2O(l)
The cell potential or emf of the cell depends upon the concentration of sulphuric acid. During the operation, the acid is consumed and its concentration decreases and specific gravity decreases from 1.28 to 1.17. As a result, the emf of the cell decreases. The emf of a fully charged cell is about 2.0 V.
(ii) Recharging of the cell : When the discharged battery is connected to external electric source and a higher external potential is applied the cell reaction gets reversed generating H2SO4.
Reduction at the – ve electrode or cathode :
PbSO4(s) + 2e– → Pb(s) + \(\mathrm{SO}_{4(a q)}^{2-}\)
Oxidation at the + ve electrode or anode :
PbSO4(s) + 2H2(l)O → PbO2(s) + 4H+(aq) + \(\mathrm{SO}_{4(a q)}^{2-}\) + 2e–
The net reaction during charging is
2PbSO4(s) + 2H2O(l) → Pb(s) + PbO2(s) + 4H+(aq) + 2\(\mathrm{SO}_{4(a q)}^{2-}\)
OR
2PbSO4(s) + 2H2O → Pb(s) + PbO2(s) + 2H2SO4(aq)
The emf of the accumulator depends only on the concentration of H2SO4.
(E) Applications :
- It is used as a source of d.c. electric supply.
- It is used in automobile in ignition circuits and lighting the head lights by connecting 6 batteries giving 12V potential.
- It is also used in invertors.
![]()
Question 71.
In lead accumulator which electrode is coated with PbO2 ? Anode or cathode ?
Answer:
In lead accumulator, cathode is coated with PbO2.
Question 72.
Write net charging and discharging reactions for lead storage battery.
Answer:
For lead storage battery :
Net charging reaction :
2PbSO4(s) + 2H2O(l) → Pb(s) + PbO2(s) + 2H2SO4(aq)
Net discharging reaction :
Pb(s) + PbO2(s) + 2H2SO4(aq) → 2PbSO4(s) + 2H2O(l)
Question 73.
Write a note on Nickel-Cadmium (NICAD) cell.
Answer:
(1) Nickel-Cadminum (NICAD) cell is a secondary dry cell.
(2) It is rechargable, hence it is a reversible cell.
(3) It consists of a cadmium electrode in contact with an alkali and acts as anode while nickel (IV) oxide, NiO2 in contact with an alkali acts as cathode. The alkali used is moist paste of KOH.
(4) Reactions in the cell :
(i) Oxidation at cadmium anode :
Cd(s) + 2OH–(aq) → Cd(OH)2(s) + 2e–
(ii) Reduction at Ni02(s) cathode :
NiO2(s) + 2H2O(l) + 2e– → Ni(OH)2(s) + 2OH–(aq)
The overall cell reaction is the combination of above two reactions.
Cd(s) + NiO2(s) + 2H2O(l) → Cd(OH)2(s) + Ni(OH)2(s)
(5) Since the net cell reaction doesn’t involve any electrolytes but solids, the voltage is independent of the concentration of alkali electrolyte.
(6) The cell potential is about 1.4 V.
(7) This cell has longer life than other dry cells.
Question 74.
Write a note on mercury battery.
Answer:
(1) Mercury battery is a rechargeable secondary dry cell.
(2) It consists of zinc anode amalgamated with mercury.
(3) The cathode consists of a paste of Hg and carbon.
(4) The electrolyte is a paste of KOH and ZnO in a strong alkaline medium.
(5) Reactions:
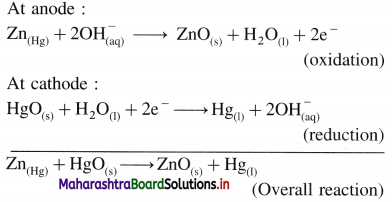
(6) The overall reaction involves only solid substances and electrolytic composition remains unchanged.
(7) Therefore mercury battery provides constant voltage (1.35 V) over a long period.
(8) It is superior to Leclanche’s cell in durability.
(9) Uses : It is used in hearing aids, electric watches, pacemakers, etc.
Question 75.
Describe the construction and working of hydrogen-oxygen (H2-O2) fuel cell.
Answer:
(A) Principle :
(i) The functioning of the fuel cell is based on the combustion reaction like,
2H2(g) + O2(g) → 2H2O(g) is exothermic redox reaction and hence it can be used to produce electricity.
(ii) The reactants of this fuel cell can be continuously supplied from outside, hence this can be used to supply electrical energy for a very long period.
(B) Construction :
(i) In fuel cell the anode and cathode are porous electrodes with suitable catalyst like finely divided platinum.
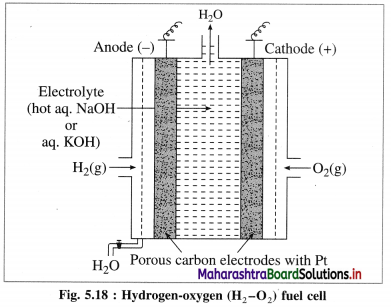
(ii) The electrolyte used is hot aqueous KOH solution in which porous anode and cathode carbon rods are immersed.
(iii) H2 is continuously bubbled through anode while O2 gas is bubbled through cathode.
(C) Working (cell reactions) :
(i) Oxidation at anode : At anode, hydrogen gas is oxidised to H2O.
2H2(g) + 4OH–(aq) → 4H2O(l) + 4e– (oxidation half reaction)
(ii) Reduction at cathode : The electrons released at anode travel to cathode through external circuit and reduce oxygen gas to OH-.
O2(g) + 2H2O(l) + 4e– → 4OH–(aq) (reduction half reaction)
(iii) Net cell reaction: Addition of both the above reactions at anode and cathode gives a net cell reaction.
2H2(g) + O2(g) → 2H2O(l) (overall cell reaction)
(D) Representation of the cell :
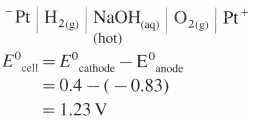
The overall cell reaction is an exothermic combustion reaction. However in this, H2 and O2 gases do not react directly but react through electrode reactions. Hence the chemical energy released in the formation of O-H bonds in H2O, is directly converted into electrical energy.
(E) Advantages :
- The fuel cell operates continuously as long as H2 and O2 gases are supplied to the electrodes.
- The cell reactions do not cause any pollution.
- The efficiency of this galvanic cell is the highest about 70% as compared to ordinary galvanic cells.
(F) Drawbacks of H2-O2 fuel cell :
- The cell requires expensive electrodes like Pt, Pd.
- In practice, voltage is less than 1.23 volt due to spontaneous reactions at the electrodes.
- H2 gas is expensive and hazardous.
(G) Applications :
- It was successfully used in spacecraft.
- It has potential applications in automobiles, power generators for domestic and industrial uses.
![]()
Question 76.
What are the applications of the fuel cells?
Answer:
- Fuel cells have been used in the space programme providing electrical energy for a long duration.
- The fuel cells have been used in automobiles on experimental basis.
- In case of H2-O2 fuel cell, used in spacecraft, the water produced is used for drinking for astronauts.
- The fuel cells using methanol as a fuel for combustion are used in electronic products such as cell phones and laptop computers.
- The fuel cells have many potential applications as power generators for domestic and industrial uses.
Question 77.
In what way fuel cell differs from ordinary galvanic cells ?
Answer:
- Fuel cell is a modified galvanic cell in which the thermal energy of combustion reactions is directly converted into electrical energy.
- In the fuel cell, the reactants are not placed within the cell like ordinary galvanic cells, but they are continuously supplied to the electrodes from outside reservoir.
- They cannot be recharged unlike ordinary galvanic cell.
Question 78.
Define electrochemical series or electromotive series.
Answer:
Electrochemical series (Electromotive series) : It is defined as the arrangement in a series of electrodes of elements (metal or non-metal in contact with their ions) with the electrode half reactions in the decreasing order of their standard reduction potentials.
Question 79.
Explain electrochemical series or electromotive series.
Answer:
The conventions used in the construction of electrochemical series (or electromotive series) are as follows :
- The (reduction) electrodes or half cells of the elements are written on the left hand side of the series and they are arranged in the decreasing order of their standard reduction potentials (E°red).
- Reduction half reactions are written for each half cell in such a way that the species with higher oxidation state and electrons are on left hand side while reduced species with lower oxidation state are on right hand side.
- The standard reduction potential of standard hydrogen electrode is 0.00 V, i.e., E0H+/H2 = 0.0 V. The electrodes and half cell reactions with positive E0red values are located above hydrogen and those with negative E0red values below hydrogen. Above hydrogen, positive E0red values increase, while below hydrogen negative E0 values increase.
- The positive E0red values indicate the tendency for reduction and the negative E0red values indicate the tendency for oxidation.
- The elements, whose electrodes are at the top of the series having high positive values for E0red are good oxidising agents.
- The elements, whose electrodes are at the bottom of the series having high negative values for E0red are good reducing agents.
Question 80.
What are the applications of electrochemical series (or electromotive series) ?
Answer:
The applications of electrochemical series (or electromotive series) are as follows :
(1) Relative strength of oxidising agents in terms of E0red values : The E0red value is a measure of the tendency of the species to be reduced i.e., to accept electrons and act as an oxidising agent. The species mentioned on left hand side of the half reactions are oxidising agents.
The substances in the upper positions in the series and hence in the upper left side of the half reactions have large positive E0red values hence are stronger oxidising agents. For example, F2, Ce4+, Au3+, etc. As we move down the series, the oxidising power decreases. Hence from the position of the elements in the electrochemical series, oxidising agents can be selected.
(2) Relative strength of reducing agents in terms of E0red values : The lower E0red value means lower tendency to accept electrons but higher tendency to lose electrons. The tendency for reverse reaction or oxidation increases as E0red becomes more negative and we move towards the lower side of the series. For example, Li, K, Al, etc. are good reducing agents.
(3) Identifying the spontaneous direction of reaction : From the standard reduction potentials, E0red, the spontaneity of a redox reaction can be determined. The difference between E0red values for any two electrodes represents cell potential E0cell, constituted by them.
If E°cell is positive then the reaction is spontaneous while if E0cell is negative the reaction is non-spontaneous. For example, E0Mg2+/Mg and E0Ag+/Ag have values -2.37 V and 0.8 V respectively. Then Mg will be a better reducing agent than Ag. Therefore Mg can reduce Ag+ to Ag.
The corresponding reactions will be:
Therefore above reaction in the forward direction will be spontaneous while in the reverse direction will be non-spontaneous since for it E0cell = -3.17V.
(4) Calculation of standard cell potential E0cell : From the electrochemical series, the standard cell potential, E0cell from the E0red values for the half reactions given can be calculated.
For example,
Question 81.
Write any four applications of electrochemical series.
Answer:
The applications of electrochemical series are as follows :
- Predicting relative strength of oxidising agents.
- Predicting relative strength of reducting agents.
- Identifying the spontaneous direction of a reaction.
- To calculate the standard cell potential E°cell.
![]()
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 82.
Select and write the most appropriate answer from the given alternatives for each subquestion :
1. The cell constant of a conductivity cell is given by
(a) l × a
(b) \(\frac{a}{l}\)
(c) \(\frac{1}{l \times a}\)
(d) \(\frac{l}{a}\)
Answer:
(d) \(\frac{l}{a}\)
2. A conductivity cell has two platinum electrodes of area 1.2 cm2 and 0.92 cm apart. Hence the cell constant is
(a) 1.104 cm-1
(b) 1.304 cm-1
(c) 0.906 cm-1
(d) 0.767 cm-1
Answer:
(d) 0.767 cm-1
3. The conductivity of 0.02 M KI solution is 4.37 × 10-4 Ω-1 cm-1. Hence its molar conductivity is
(a) 8.74 × 10-6 Ω-1 cm2 mol-1
(b) 21.85 Ω-1 cm2 mol-1
(c) 4.58 × 10-4 Ω-1 cm2 mol-1
(d) 136.5 Ω-1 cm2 mol-1
Answer:
(b) 21.85 Ω-1 cm2 mol-1
4. The specific conductance of 0.02 M HCl is 8.2 × 10-3 Ω-1 cm-1. Hence its molar conductivity is
(a) 164 Ω-1 cm2 mol-1
(b) 6.1 × 103Ω-1 cm2 mol-1
(c) 239.6 S cm2 mol-1
(d) 410 S cm2 mol-1
Answer:
(d) 410 S cm2 mol-1
![]()
5. Molar conductivity of an electrolyte is given by,
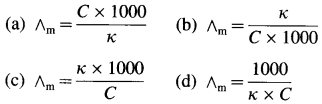
Answer:
(c) \(\wedge_{\mathrm{m}}=\frac{\kappa \times 1000}{\mathrm{C}}\)
6. The units of molar conductivity are
(a) Ω cm-2 mol-1
(b) Ω-1 cm2 mol-1
(c) Ω-1 cm-1 mol-1
(d) Ω– cm-1 mol-2
Answer:
(b) Ω-1 cm2 mol-1
7. If conductivity is expressed in Ω-1 m-1 and concentration of the electrolytic solution in mol m-3 then, the molar conductance is given by
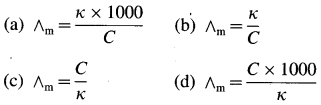
Answer:
(b) \(\wedge_{\mathrm{m}}=\frac{\kappa}{C}\)
8. Kohlrausch’s law is represented as
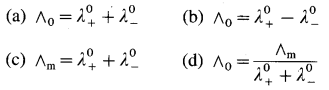
Answer:
(a) \(\wedge_{0}=\lambda_{+}^{0}+\lambda_{-}^{0}\)
9. The degree of dissociation of a weak electrolyte is given by

Answer:
(c) α = \(\frac{\wedge_{\mathrm{m}}}{\wedge_{0}}\)
10. ∧0 for CH3COOH is 390.7 Ω-1 cm2 mol-1. If ∧0 for CH3COOK, and HBr in Ω-1 cm2 mol-1 are 115 and 430.4 respectively, then ∧0 for KBr is
(a) 74.6 Ω-1 cm2 mol-1
(b) 180.6 Ω-1 cm2 mol-1
(c) 154.7 Ω-1 cm2 mol-1
(d) 706.1 Ω-1 cm2 mol-1
Answer:
(c) 154.7 Ω-1 cm2 mol-1
![]()
11. The molar conductivity of cation and anion of salt BA are 180 and 220 mhos respectively. The molar conductivity of salt BA at infinite dilution is
(a) 90 mhos · cm2 · mol-1
(b) 110 mhos · cm2 · mol-1
(c) 200 mhos · cm2 · mol-1
(d) 400 mhos · cm2 · mol-1
Answer:
(d) 400 mhos · cm2 · mol-1
12. If ∧m and ∧0 are the molar conductivities of a weak electrolyte at concentration C and at zero concentration, then the dissociation constant Ka is given by
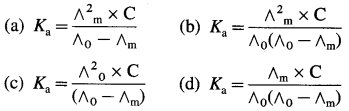
Answer:
(b) Ka = \(\frac{\wedge_{\mathrm{m}}^{2} \times \mathrm{C}}{\Lambda_{0}\left(\wedge_{0}-\wedge_{\mathrm{m}}\right)}\)
13. What is the ratio of volumes of H2 and O2 liberated during electrolysis of acidified water ?
(a) 1 : 2
(b) 2 : 1
(c) 1 : 8
(d) 8 : 1
Answer:
(b) 2 : 1
14. What weight of copper will be deposited by passing 2 Faradays of electricity through a cupric salt? (atomic mass = 63.5)
(a) 63.5 g
(b) 31.75 g
(c) 127 g
(d) 12.7 g
Answer:
(a) 63.5 g
15. The S.I. unit of cell constant for conductivity cell is
(a) m-1
(b) S·m-2
(c) cm-2
(d) S·dm2·mol-1
Answer:
(a) m-1
![]()
16. The charge of how many coulomb is required to deposit 1.0 g of sodium metal (molar mass 23.0 g mol-1) from sodium ions is
(a) 2098
(b) 96500
(c) 193000
(d) 4196
Answer:
(d) 4196
17. The amount of electricity equal to 0.05 F is
(a) 48250 C
(b) 3776 C
(c) 4825 C
(d) 4285 C
Answer:
(c) 4825 C
18. The number of electrons that have a total charge of 965 coulombs is
(a) 6.022 × 1023
(b) 6.022 × 1022
(c) 6.022 × 1021
(d) 3.011 × 1023
Answer:
(c) 6.022 × 1021
19. When 0.2 Faraday of electricity is passed through an electrolytic solution, the number of electrons involved are
(a) 96500
(b) 1.603 × 10-19
(c) 1.2046 × 1023
(d) 12 × 106
Answer:
(c) 1.2046 × 1023
20. When a charge of 0.5 Faraday is passed through AlCl3 solution, the amount of aluminium deposited at the cathode is (Atomic weight of Al = 27)
(a) 4.5
(b) 18
(c) 27
(d) 2.7
Answer:
(a) 4.5
21. The quantity of electricity required to deposit 54 g of silver from silver nitrate solution is
(a) 0.5 Coulomb
(b) 0.5 Ampere
(c) 0.5 Faraday
(d) 0.5 Volt
Answer:
(c) 0.5 Faraday
![]()
22. Passage of 5400 C of electricity through an electrolyte deposited 5.954 × 10-3 kg of the metal with atomic mass 106.4. The charge on the metal ion is
(a) + 1
(b) + 2
(c) + 3
(d) + 4
Answer:
(a) + 1
23. On calculating the strength of current in amperes if a charge of 840 C (coulomb) passes through an electrolyte in 7 minutes, it will be
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer:
(b) 2
24. On passing 1.5 F charge, the number of moles of aluminium deposited at cathode are [Molar mass of Al = 27 gram mol-3]
(a) 1.0
(b) 13.5
(c) 0.50
(d) 0.75
Answer:
(c) 0.50
25. Number of faradays of electricity required to liberate 12 g of hydrogen is
(a) 1
(b) 8
(c) 12
(d) 16
Answer:
(c) 12
26. Daniell cell is
(a) Secondary cell
(b) Irreversible cell
(c) primary irreversible cell
(d) primary reversible cell
Answer:
(d) primary reversible cell
![]()
27. In the representation of galvanic cell, the ions in the same phase are separated by a
(a) single vertical line
(b) comma
(c) double vertical lines
(d) semicolon
Answer:
(b) comma
28. In the Daniell cell, reduction occurs at the
(a) anode
(b) zinc rod
(c) negative electrode
(d) positive electrode
Answer:
(d) positive electrode
29. The standard hydrogen electrode is represented as
(a) \(\mathrm{H}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{+}\)|H2(g, 1 atm) | Pt
(b) \(\mathrm{H}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{+}\) 1M | H2(g, 1 atm) | Pt
(c) \(\mathrm{H}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{+}\) 1M|H2(g)|Pt
(d) \(\mathrm{H}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{+}\) 0.1M|H2(g, 1 atm) | Pt
Answer:
(b) \(\mathrm{H}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{+}\) 1M | H2(g, 1 atm) | Pt
30. The essential condition to set a standard hydrogen electrode is
(a) 298 K
(b) pure and dry H2 gas at 1 atm
(c) solution containing H+ at unit activity
(d) all of these
Answer:
(d) all of these
31. In hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell, the carbon rods are immersed in hot aqueous solution of
(a) KCl
(b) KOH
(c) H2SO4
(d) NH4Cl
Answer:
(b) KOH
32. The emf of cell is 1.3 volt. The positive electrode has potential of 0.5 volt. The potential of negative electrode is
(a) 0.8 V
(b) -0.8 V
(c) 1.8 V
(d) – 1.8 V
Answer:
(b) -0.8 V
33. The electrode potential of a silver electrode dipped in 0.1 M AgNO3 solution at 298 K is (E0red of Ag = 0.80 volt)
(a) 0.0741 V
(b) 0.0591 V
(c) 0.741 V
(d) 0.859 V
Answer:
(c) 0.741 V
34. Which of the following species gains electrons more easily ?
(a) Na+
(b) H+
(c) Mg+
(d) Hg+
Answer:
(b) H+
![]()
35. In Nernst equation the constant 0.0592 at 298 K represents the value of

Answer:
(d) \(\frac{2.303 R T}{F}\)
36. The concept of electrode potential is explained on the basis of
(a) Arrhenius’ theory
(b) Ostwald’s theory
(c) Nemst’s theory
(d) Faraday’s law
Answer:
(c) Nemst’s theory
37. The standard reduction potentials of metals A and B are x and y respectively. If x > y, the standard emf of the cell containing these electrodes would be
(a) 2x – y
(b) y – x
(c) x – y
(d) x + y
Answer:
(c) x – y
38. The emf of the cell,
![]()
(E0red = 0.34 V)
(a) -1.34
(b) 0.34 V
(c) -0.34 V
(d) 1.34
Answer:
(b) 0.34 V
39. The Electromotive Force of the following Cell Cu|Cu++ (1 M)||A+g (1 M)|Ag is …………….. if E0cu++ = 0.33 V and E0 Ag++/Ag = 0.79 V
(a) 0.46 V
(b) – 0.46 V
(c) 1.12 V
(d) – 112 V
Answer:
(a) 0.46 V
40. The standard cell potential of the following cell is 0.463 V Cu|Cu++ (1 M)||Ag+ (1 M)|Ag. If E0Ag = 0.8 V, what is the standard potential of Cu electrode ?
(a) 1.137 V
(b) 0.337 V
(c) 0.463 V
(d) – 0.463 V
Answer:
(b) 0.337 V
![]()
41. The metal which cannot displace hydrogen from dil. H2SO4 solution is
(a) Zn
(b) Al
(c) Fe
(d) Ag
Answer:
(d) Ag
42. In the Lead storage battery during discharging
(a) pH of the electrolyte increases
(b) pH decreases
(c) pH remain unchanged
(d) pH increases or decreases depends on the extent of discharging
Answer:
(a) pH of the electrolyte increases
43. During the discharging of a lead storage battery,
(a) H2SO4 is consumed
(b) PbSO4 is consumed
(c) Pb2+ ions are formed
(d) Pb is formed
Answer:
(a) H2SO4 is consumed
44. In lead accumulator, anode and cathode are
(a) (Pb + PbO2), Pb
(b) Pb, PbO2
(b) PbO2, Pb
(d) Pb, (Pb + PbO2)
Answer:
(d) Pb, (Pb + PbO2)
45. The efficiency of the hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell is about
(a) 20%
(b) 40%
(c) 70%
(d) 90%
Answer:
(c) 70%
46. The strongest oxidizing agent among the species In3+ (E0 = – 1.34 V), Au3+ (E0 = 1.4 V), Hg2+ (E0 = 0.86 V), Cr3+ (E0 = – 0.74 V) is
(a) Cr3+
(b) Au3+
(c) Hg2+
(d) In3+
Answer:
(b) Au3+
![]()
47. The reaction, \(2 \mathrm{Br}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{-}+\mathrm{Sn}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{2+} \longrightarrow \mathrm{Br}_{2(\mathrm{l})}+\mathrm{Sn}_{(\mathrm{s})}\)
with the standard potentials, E0Sn = -0.114 V, E0Br2 = + 1.09 V, is
(a) spontaneous in reverse direction
(b) spontaneous in forward direction
(c) at equilibrium
(d) non-spontaneous in reverse direction
Answer:
(a) spontaneous in reverse direction
48. The cell potential of the following cell is
(E0Al3+/Al = – 1.66 V)
![]()
(a) 1.66 V
(b) -1.66 V
(c) 0.5533 V
(d) 2.14 V
Answer:
(a) 1.66 V
49. The standard reduction potentials of Sn, Hg and Cr are – 1.36 V, 0.854 V and – 0.746 V respectively. The increasing order of oxidising power of the given elements is
(a) Sn < Hg < Cr
(b) Hg < Cr < Sn
(c) Sn < Cr < Hg
(d) Cr < Hg < Sn
Answer:
(c) Sn < Cr < Hg
50. If standard reduction potentials for Pb, K, Zn and Cu are -0.126 V, -2.925 V, -0.763 V and 0.337 V, the decreasing order of reducing power is
(a) Zn > Pb > K > Cu
(b) Cu > Pb > Zn > K
(c) K > Zn > Pb > Cu
(d) K > Pb > Cu > Zn
Answer:
(c) K > Zn > Pb > Cu+


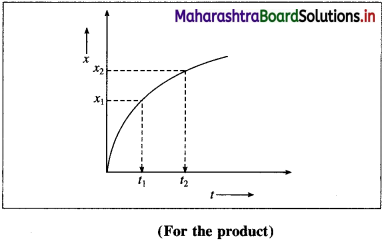








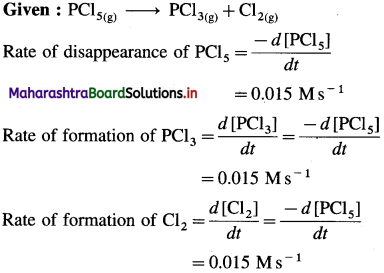

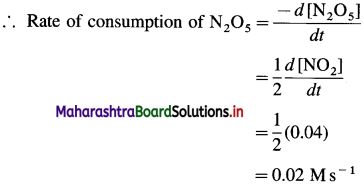


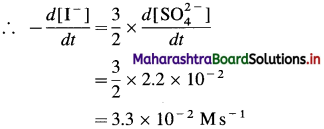




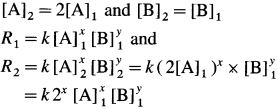

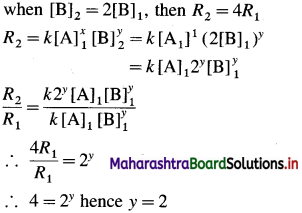

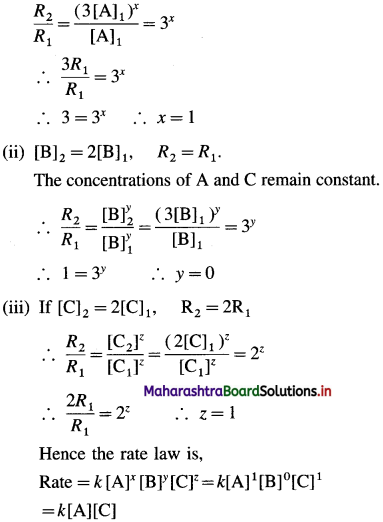
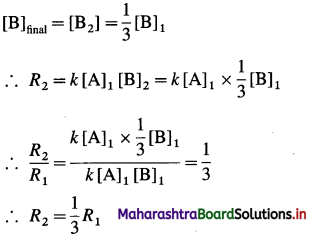










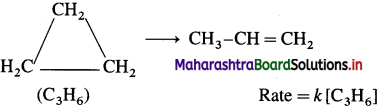










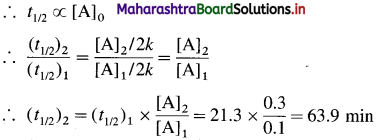
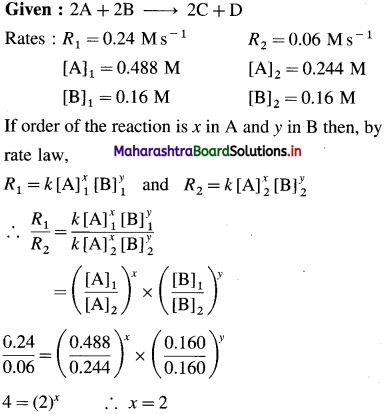
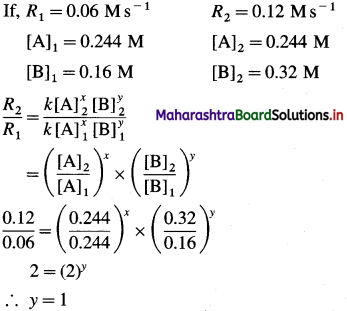
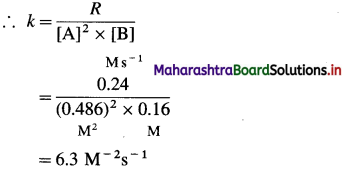





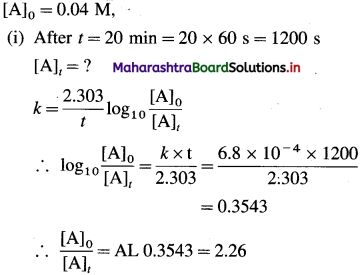


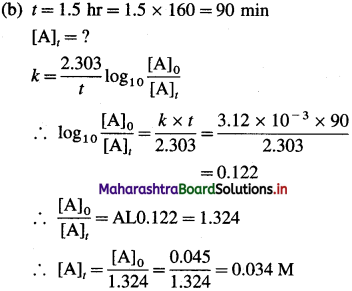











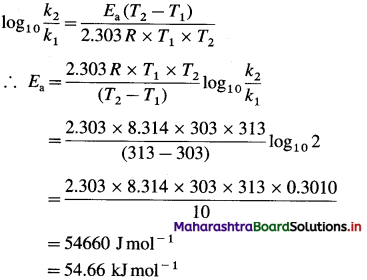

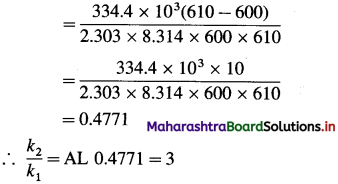

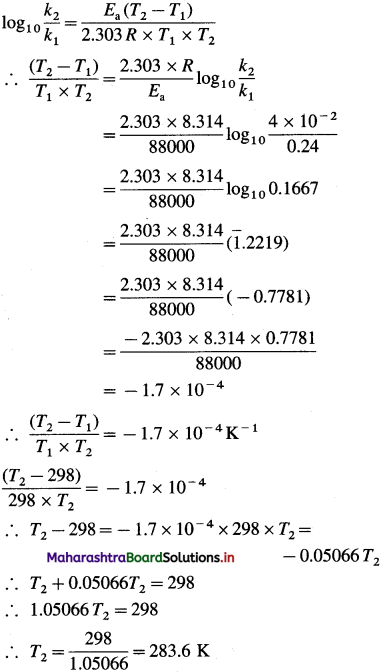

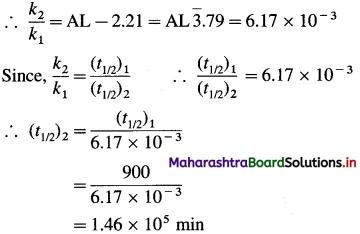



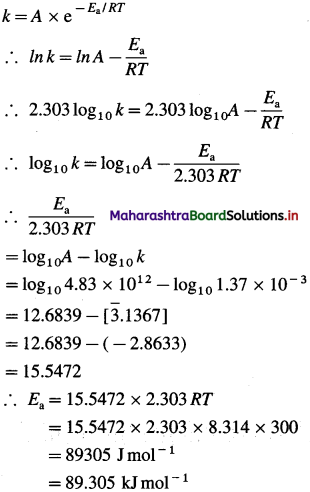


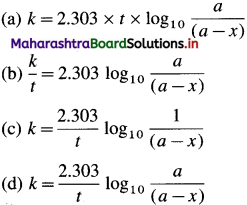






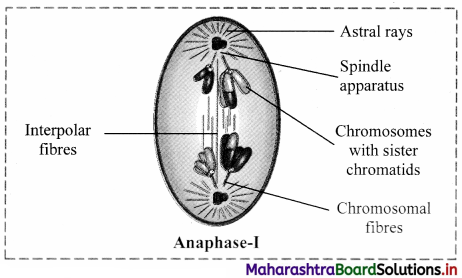
 Karyokinesis is the nuclear division which is divided into prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase.
Karyokinesis is the nuclear division which is divided into prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase.
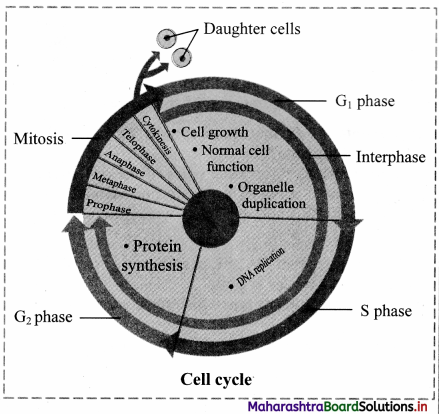
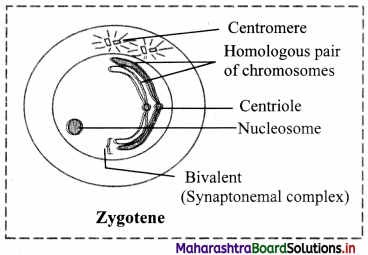
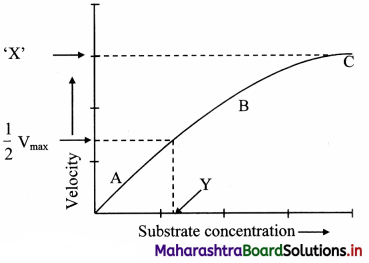





 .
.


















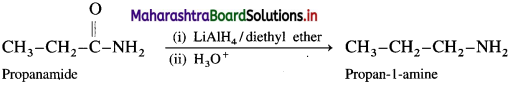













 ethyl-N-methylethanamine since compound X is tertiary amine. It reacts with one mole of CH3I to give a quaternary ammonium salt.
ethyl-N-methylethanamine since compound X is tertiary amine. It reacts with one mole of CH3I to give a quaternary ammonium salt.