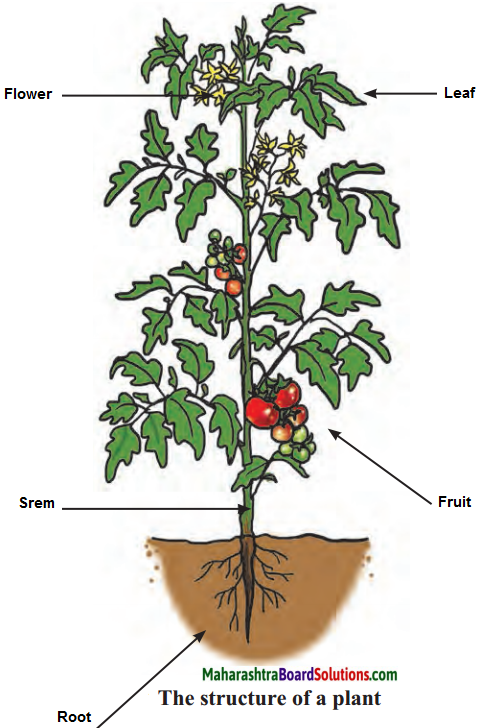
Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 6 Science Solutions Chapter 8 Our Skeletal System and the Skin Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Std 6 Science Chapter 8 Our Skeletal System and the Skin Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Class 6 Science Chapter 8 Our Skeletal System and the Skin Question Answer Maharashtra Board
1. Fill in the blanks with the proper word.
Question a.
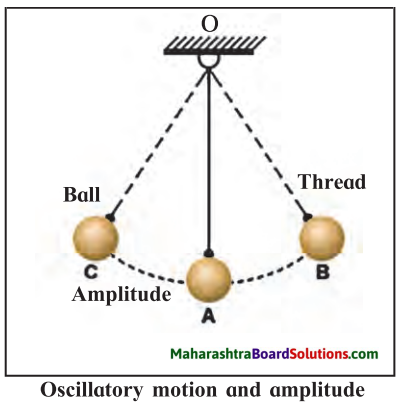
The place where two or more bones are connected is called a …………… .
Answer:
joint
Question b.
Cells of epidermis contain a pigment called ………… .
Answer:
melanin
Question c.
…………… and ……………. are the two layers of the human skin.
Answer:
epidermis, dermis
![]()
Question d.
The human skeletal, system is divided into ………….. parts.
Answer:
two
2. Match the pairs.
Question a.
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| 1. Ball and socket joint | a. Knee |
| 2. Hinge joint | b. Wrist |
| 3. Gliding joint | c. Shoulder |
Answer:
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| 1. Ball and socket joint | c. Shoulder |
| 2. Hinge joint | a. Knee |
| 3. Gliding joint | b. Wrist |
3. Right or wrong? If wrong, write the correct sentence.
Question a.
Bones are soft.
Answer:
Wrong: Bones are hard.
![]()
Question b.
The human skeleton protects the internal organs.
Answer:
Right
4. Put a [✓] mark at the proper places.
Question a.
The system which gives our body. a definite shape to
(a) Excretory system [ ]
(b) Respiratory system [ ]
(c) Skeletal system [ ]
(d) Circulatory system [ ]
Answer:
(c) Skeletal system [✓]
![]()
Question b.
The ………… joint is seen in fingers and toes.
(a) Hinge joint [ ]
(b) Ball and socket joint [ ]
(c) Immovable joint [ ]
(d) Gliding joint [ ]
Answer:
(a) Hinge joint [✓]
5. Answer the following questions in your words.
Question a.
What are the functions of your skin?
Answer:
The functions of the skin are :
- Protects the internal parts of the body like muscles, bones, organ systems etc.
- Help to preserve the moisture in the body.
- Synthesizing Vitamin D.
- Regulates body temperature by releasing sweat.
- Gives protection from heat and cold.
- Functions as the sensory organ of touch
![]()
Question b.
What should you do to keep the bones strong and healthy?
Answer:
To keep the bones strong and healthy:
- We should include calcium and phosphrous rich food in our diet.
- We also include vitamin D rich food in our diet.
- We get these from milk, milk products, leafy vegetables, meat and exposure to sunlight.
- We should exercise regularly.
Question c.
What are the functions of human skeletal system?
Answer:
The functions of human skeletal system are:
- Gives a definite shape to the body.
- Provides support to the body.
- Protects the delicate organs inside the body.
Question d.
Which are the various reasons due to which our bones might break?
Answer:
The bones in our body might break due to:
- Lack of calcium and phosphorous.
- Due to fracture because of an accident or a fall.
- Lack of proper nutrition.
- Due to deficiency of Vitamin D.
![]()
Question e.
What are the different types of bones? How many types are there? Give example of each.
Answer:
There are four types of bones in our body:
| Types of Bone | Example | |
| 1. Flat bones | Sternum in the chest | |
| 2. Small bones | Stirrup in each ear | |
| 3. Irregular bones | Vertebra posterior (back side) of the body | |
| 4. Long bones | Femur or thigh bone | |
Types of Bone Example
- Flat bones Sternum in the chest
- Small bones Stirrup in each ear
- Irregular bones Vertebra posterior (back side) of the body
- Long bones Femur or thigh bone
6. What will happen if?
Question a.
There are no joints in our body.
Answer:
If there are no joints in our body, we will be standing like a tree without any movement, we can move only because of joints.
Question b.
There is no melanin pigment in our body.
Answer:
We will not have protection from ultraviolet rays. Our skin will become whitish.
Question c.
Instead of 33 vertebras in our body, we had one single and straight bone.
Answer:
We cannot bend down at our will.
![]()
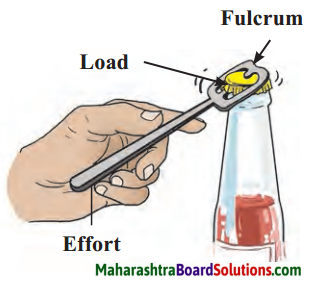
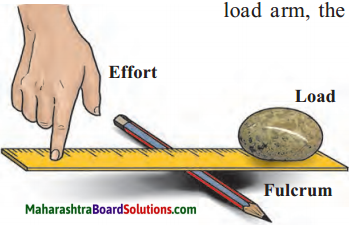
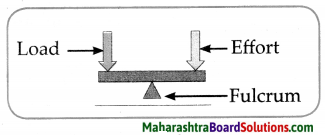
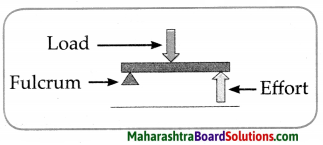
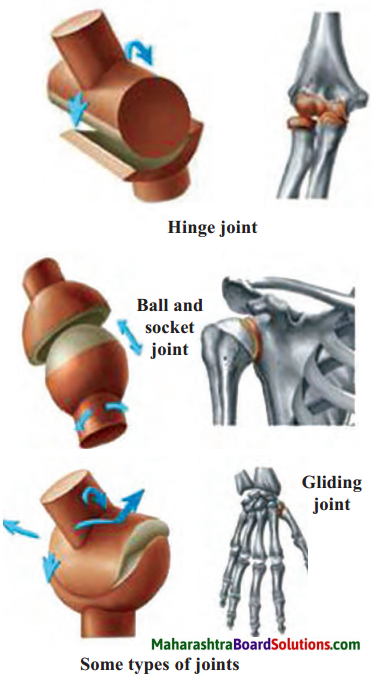
7. Draw diagrams.
Question a.
Types of joints.
Answer:
Question b.
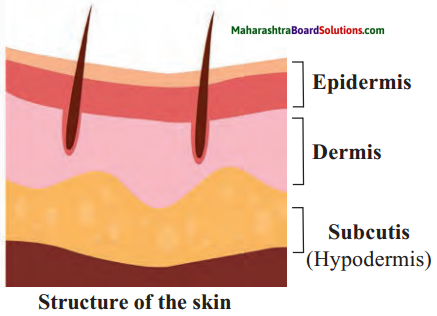
Structure of skin
Answer:
Activity:
Question 1.
Collect pictures of the different parts of the human skeletal system and paste them on chart paper. Write the functions of
each, too.
![]()
Question 2.
Collect the pictures, newspaper cuttings, etc. which show the skeletal systems of various animals and observe the differences between them.
Class 6 Science Chapter 8 Our Skeletal System and the Skin Important Questions and Answers
Choose the correct alternative:
Question 1.
The ………………….. protects the brain.
(a) skull
(b) rib cage
(c) spine
(d) none of above
Answer:
(a) skull
Question 2.
X-rays were discovered by ………………….. .
(a) Sir C.V.Raman
(b) Galileo
(c) Sir Isaac Newton
(d) Roentgen
Answer:
(d) Roentgen
![]()
Question 3.
The bones of ………………….. are immovable.
(a) hand
(b) leg
(c) spine
(d) skull
Answer:
(d) skull
Question 4.
We can move the bones of ………………….. in a 360° angle.
(a) elbow
(b) knee
(c) shoulder
(d) wrist
Answer:
(c) shoulder
Question 5.
Our body temperature usually remains constant at ………………….. °C.
(a) 32
(b) 35
(c) 37
(d) 40
Answer:
(c) 37
![]()
Question 6.
The part of the skin which maintains body temperature is ………………….. .
(a) Epidermis
(b) Dermis
(c) Subcutaneous layer
(d) Network of blood vessels and nerve fibers
Answer:
(c) Subcutaneous layer
Fill in the blanks:
Question 1.
Except for the …………….., none of the bones of the skull can move.
Answer:
lower jaw
![]()
Question 2.
The spinal cord originates from the …………… .
Answer:
brain
Question 3.
The longest and the strongest bone in the human body is …………… .
Answer:
femur
Question 4.
…………….. is the smallest bone in our body.
Answer:
stirrup
Question 5.
The vertical, flat bone in the chest is called the ……………… .
Answer:
sternum
![]()
Question 6.
The …………… joint moves in a 180° angle.
Answer:
hinge
Match the columns:
Question 1.
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| 1. Skull | a. 25 bones |
| 2. Rib cage | b. 6 bones |
| 3. Spine | c. 22 bones |
| 4. Both ears | d. 33 bones |
Answer:
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| 1. Skull | c. 22 bones |
| 2. Rib cage | a. 25 bones |
| 3. Spine | d. 33 bones |
| 4. Both ears | b. 6 bones |
![]()
Question 2.
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| 1. Lower jaw | a. Movable joint |
| 2. Ears | b. Femur |
| 3. Thigh | c. Movable joint in skull |
| 4. Elbow | d. Smallest bone |
Answer:
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| 1. Lower jaw | c. Movable joint in skull |
| 2. Ears | d. Smallest bone |
| 3. Thigh | b. Femur |
| 4. Elbow | a. Movable joint |
Right or Wrong? If wrong, write the correct answers:
Question 1.
The spine is a part of the appendicular skeleton.
Answer:
Wrong: The spine is a part of the axial skeleton.
Question 2.
Ankle joints are gliding joints.
Answer:
Right
Question 3.
All the skull joints are immovable.
Answer:
Wrong: Except lower jaw, all the skull joints are immovable.
![]()
Question 4.
The skin maintains normal body temperature.
Answer:
Right
Answer in one word:
Question 1.
The part which protects the heart and lungs.
Answer:
Rib cage
Question 2.
Ali falls down and his elbow is broken.
Answer:
Fracture
Question 3.
The image which spots the broken bone.
Answer:
X-ray
Question 4.
The biotic component of our body.
Answer:
Bone cell
![]()
Question 5.
The part which protects the vertebral column.
Answer:
Spine
Question 6.
The part which connects the bone in our body.
Answer:
Ligament
Question 7.
The organ which helps us to sense whether something is hot or cold.
Answer:
Skin
Question 8.
The pigment which gives colour to the skin.
Answer:
Melanin
![]()
Can you tell?
Question 1.
What is a fracture? How will you help a friend who has met with an accident and fractured his leg?
Answer:
Fracture is a crack or break in a bone. Fracture may occur due to accident or fall from height or injury. If my friend’s leg is fractured, then. I would –
- Ask him to prevent any movement of the fractured part.
- Get immediate medical help.
- Take the x-ray image of the fractured or swollen part.
- An x-ray image shows the exact spot where the bone is broken. This will help in providing proper treatment.
Question 2.
What are the properties of bones?
Answer:
The properties of bones are:
- Bones are hard and not flexible.
- Bone cells are composed of two main constituents:
- Bone cells are biotic components.
- Calcium carbonate, calcium phosphate, minerals and salts are abiotic components.
- Calcium imparts strength to bones.
- As we grow the size and length of bones increases upto a certain limit.
![]()
Question 3.
What is human skeletal system? How is it divided?
Answer:
- All the bones together form a framework or a skeleton.
- All the bones of the body along with cartilage together form the skeletal system.
- The human skeletal system can be divided into two parts – the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton.
- The axial skeleton consists of the skull, the spine and the rib cage. These are situated symmetrically along the central axis.
- The appendicular skeleton consists of the bones of arms and legs on either side of the central axis.
Question 4.
What is a joint? What are it’s types?
Answer:
Joints are places where two or more than two bones are connected to each other.
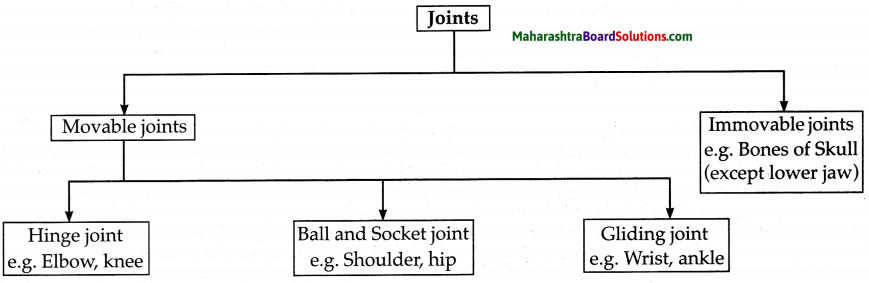
Question 5.
Describe the structure of skin.
Answer:
- Human skin is made up of two main layers- outermost layer, epidermis and layer below it called dermis.
- Below dermis there is a network of blood vessels and nerve fibers.
- Under this layer there is a subcutaneous layer, which maintains body temperature.
- The epidermis has various layers.
- There are sweat glands in the skin which secrete sweat.
![]()
Question 6.
Write a short note on melanin.
Answer:
- Melanin is a pigment present in the cells of epidermis.
- Melanin is synthesized in certain glands in the skin.
- The percentage of melanin decides the fairness or darkness of the skin.
- Melanin protects our skin and the inner parts from ultraviolet sunrays.
Use your brain power!
Question 1.
Which colour of the skin will give greater protection from sun’s rays?
Answer:
Darker colour will give greater protection.
Give scientific reasons:
Question 1.
We are able to bend down at our will.
Answer:
- 33 bones of the spine are placed straight one above the other.
- They are arranged flexibly.
- Their flexibility allows us to bend down at our will.
Question 2.
Calcium is an important mineral.
Answer:
- Calcium imparts strength to our bones.
- If we are calcium deficient, possibility of bone fracture during a fall or an accident increases.
- Hence, calcium is an important mineral.
![]()
Question 3.
Sweating helps to lower the body temperature.
Answer:
- In the hot sun, the temperature of the skin rises.
- The sweat is released.
- The heat required for the evaporation of sweat is drawn from the body itself.
- Hence, sweating lowers the body temperature.
Question 4.
Some people have jet black hair, while others have brown or reddish hair.
Answer:
- It is melanin that determines the colour of our hair.
- Jet black hair is due to pure melanin.
- Brown hair is due to sulphur in the melanin.
- Reddish hair is due to iron in the melanin.
Question 5.
Observe and discuss:
Your grandmother has wrinkles on her skin.
Answer:
- As we grow older, the proportion of fat beneath the skin reduces.
- However, previously tout skin does not shrink.
- This causes wrinkles on the face of older people.
![]()
What will happen if:
Question 1.
If skin had no sweat glands.
Answer:
Skin regulates body temperature by releasing sweat. If skin had no sweat glands then we will not be able to maintain our body temperature at a constant 37°C.
Can you recall?
Question 1.
Which organ help us to sense whether something is hot or cold, rough or smooth, etc?
Answer:
The skin functions as the sensory organ of touch.
Question 2.
What happens when we walk or play in the hot sun?
Answer:
When we walk or play in the sun, we get tired, our skin secrete sweat.
![]()
Observe the figure and label as directed.
Question 1.
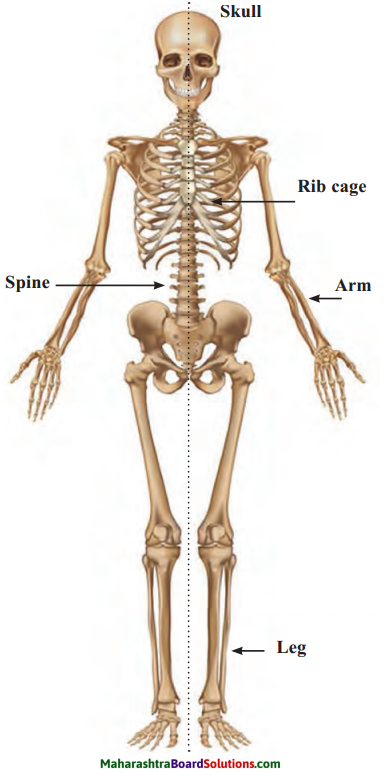
In the above figure label the parts marked a, b, c, d, e and hence show axial and appendicular
skeleton.
Answer:
(a) Skull
(b) Rib cage
(c) Spine
(d) Arm
(e) Leg
Axial skeleton: skull, the spine and rib cage
Appendicular: legs, arms
![]()
Question 2.
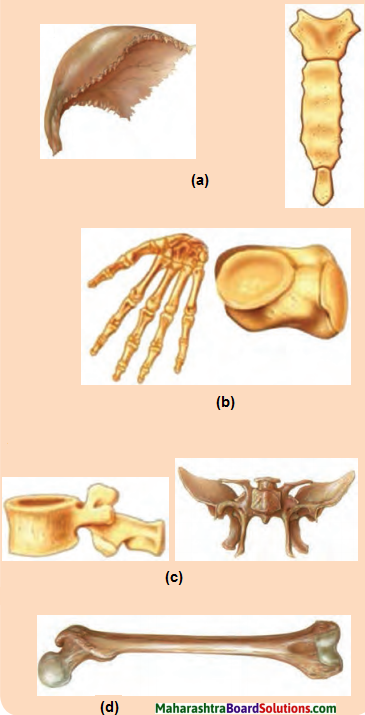
In the given figure, name the type of bones marked a, b, c, d. State where they are seen in our body.
Answer:
(a) Flat bones – rib cage and gliding joint
(b) small bones – finger
(c) Irregular bones – vertebal column
(d) Long bones – legs, arms
6th Std Science Questions And Answers:
- Natural Resources – Air, Water and Land Class 6 Questions And Answers
- The Living World Class 6 Questions And Answers
- Diversity in Living Things and their Classification Class 6 Questions And Answers
- Disaster Management Class 6 Questions And Answers
- Substances in the Surroundings – Their States and Properties Class 6 Questions And Answers
- Substances in Daily Use Class 6 Questions And Answers
- Nutrition and Diet Class 6 Questions And Answers
- Our Skeletal System and the Skin Class 6 Questions And Answers
- Motion and Types of Motion
- Force and Types of Force Class 6 Questions And Answers