Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 8 English Solutions Chapter 2.1 Vocation Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Std 8 English Lesson 2.1 Vocation Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Class 8 English Chapter 2.1 Vocation Textbook Questions and Answers
Warming Up
1. Pick out the words that refer to ‘means of living’ and fill them in the web:
(profession / recreation / occupation /job / pastime / employment / hobby / career / entertainment /mission/ trade / business / sports / retirement / placement)
Answer:
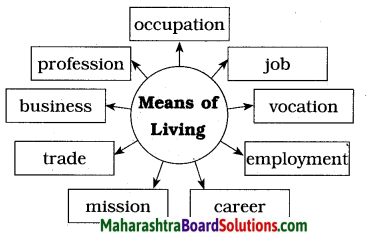
![]()
2. Using a good dictionary. find the shades of difference in the following:
2.1 Vocation Questions And Answers Question 1.
Profession
Answer:
‘Profession’ refers to a paid occupation, especially one that involves pro-longed training and a formal qualification.
Vocation Poem Class 8 Questions And Answers Maharashtra Board Question 2.
Vocation
Answer:
‘Vocation’ refers to an occupation for which a person is specially drawn or suited.
Vocation Poem Class 8 Questions And Answers Question 3.
Business
Answer:
‘Business’ refers to the activity of buying or selling goods or services; a commercial activity done by a person at his own risk.
Vocation Poem Class 8 Question 4.
Occupation
Answer:
‘Occupation’ refers to a person’s usual or principal work or business, especially as a means of earning a living.
![]()
3. When a word is formed from a sound associated with it, it is called an Onomatopoetic Word.
For example : bang, tap, tinkle. crash, whistle etc.
If an Onomatopoetic word occurs in the lines of a poem, the Figure of Speech in that line is Onomatopoeia.
Write down eight to ten Onomatopoetic words on your own.
Answer:
- buzz
- whoosh
- clang
- chirp
- clap
- howl
- hiss
- grunt
- purr
- quack
1. Which of the following words / phrases match in meaning to the underlined ones?
(a) deserted
(b) exposed to heat
(c) dirties the clothings
(d) no particular route
(e) following imaginary goals
(f) scolds and corrects
![]()
Vocation Poem Class 8 Questions And Answers State Board Question 1.
nobody takes him to task ………..
Answer:
scolds and corrects
Vocation Question Answer Class 8 Question 2.
………. if he gets baked in the sun …………..
Answer:
exposed to heat
Vocation Chapter 2.1 Question Answer Question 3.
………….chasing the shadows with my lantern ……………..
Answer:
following imaginary goals
Class 6 English Vocation Questions And Answers Question 4.
The lane is dark and lonely ……………..
Answer:
deserted
Class 6 English Vocation Question Answer Question 5.
………….. he soils his clothes with dust ………….
Answer:
dirties the clothings
Question 6.
…………. There is no road he must take ………….
Answer:
no particular route
![]()
2. Read the poem and fill in the table.
| Time of the day | Location | Poet’s Activity | Hawker’s Activities | Gardener’s Activities | Watchman’s Activities |
| Morning | |||||
| Afternoon | |||||
| Night |
Answer:
| Time of the day | Location | Poet’s Activity | Hawker’s Activities | Gardener’s Activities | Watchman’s Activities |
| Morning | In the lane | Walking to school | Selling Bangles | ||
| Afternoon | Near the poet’s house | Walking home from school | Digging the ground | ||
| Night | The poet’s home | Watching thr watchman from his bed. | Walking up and down the street.Swinging his latern. |
3. Think and answer in your own words:
Question a.
What could be the age group of the speaker in the poem?
Answer:
The speaker in the poem is a young school-going boy.
Question b.
What is the difference between a hawker and a shopkeeper?
Answer:
The difference between a hawker and a shopkeeper is that a hawker does not have a fixed shop. He goes from street to street selling his wares. A shopkeeper has a fixed shop and people who want to buy his goods must go to his shop.
![]()
Question c.
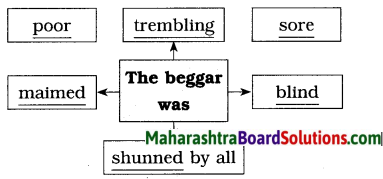
How do parents react when they see children soil their clothes in dust and heat?
Answer:
When parents see their children exposed to heat or soil their clothes in the dust, they scold them and stop them from doing it.
Question d.
Why is the street light compared to a one-red-eyed-giant?
Answer:
The street light is very tall and has a single red light at the top. Hence it is compared to a giant with one red eye.
Question e.
What exactly does the speaker in the poem crave for?
Answer:
The speaker in the poem, who is a young school-going boy, craves for complete freedom to do whatever he wants and whenever he wants. He wants freedom from authority. He wants to lead a carefree life.
![]()
Question f.
Does the poet really wish to become a hawker/gardener/watchman? Justify your response.
Answer:
The poet does not really wish to become a hawker/gardener/watchman. He is childish and sees only what he thinks is their ‘carefree’ life. He does not see the difficulties. He actually only craves for complete freedom from authority.
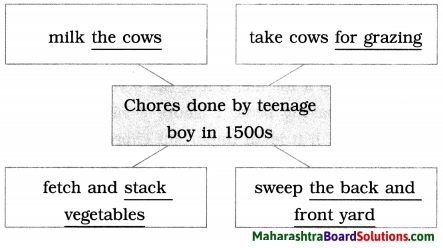
4. Say why the speaker of the poem wishes to be:
Question a.
Hawker:
Answer:
The speaker in the poem feels that there is nothing to hurry the hawker. There is no fixed road he must travel by, no place that he must go to and no time when he must get back home. The speaker feels he is lucky and hence he wishes to be a hawker. It means that the speaker wants to be free to do what he wants and go where he wants to, without any restrictions.
Question b.
Gardener:
Answer:
The speaker in the poem sees that the gardener in the nearby house is digging the ground. He does what he likes with his spade. He is free to get his clothes soiled with mud, get baked in the sun or get wet. No one scolds him. Hence the speaker wishes to be a gardener so that he is able to enjoy freedom in the open without any restrictions.
Question c.
Watchman:
Answer:
The speaker is in his bed Through the open window, he can see the watchman walking up and down the dark and lonely street with a lantern in his hand. The speaker is resentful that he has to go to bed. He thinks that the watchman never goes to bed in his life. Hence he wishes to become a watchman and walk up and down in the dark street at night, having fun chasing the shadows with his lantern
5. Pick outlines that contain Alliteration. Simile, Repetition, Onomatopoeia:
(a) Alliteration:
(i) ‘I can see through the gate the gardener digging the ground.’ Repetition of the sound of the letter ‘t’ and ‘g’.
(ii) ‘He does what he likes with his spade, he soils his clothes…’ Repetition of the sound of the letter ‘h’.
(iii) ‘nobody takes him to task’ Repetition of the sound of the letter ‘t’.
![]()
(b) Simile:
‘The street lamp stands like a giant with one red eye in its head.’ The street lamp is directly compared to a giant, using the word ‘like’.
(c) Repetition:
(i) The words ‘Bangles, crystal bangles’ are repeated to create images in our mind of the hawker.
(ii) The words ‘no’ and ‘nobody’ are repeated for emphasis.
(d) Onomatopoeia:
‘the gong sounds ten’ : the word ‘gong’ is an onomatopoeic word formed from the sound associated with it.
6. Some poets do not use uniformity in rhyming words, nor a steady rhythm. Such poems with no uniformity in rhyme, rhythm, length of lines, or stanzas are called Free Verse. Walt Whitman, Ezra Pound, T.S. Eliot, Rabindranath Tagore are some famous poets who have composed poems in Free Verse.
A quick glance at the poem Vocution’ reveals that the style used by Tagore is Free Verse.
Now turn the pages of your textbook and see if you can find other poems in Free Verse.
7. ‘occupation/profession/business would you like to take up in the future?
Prepare a fact file for the same using the following points.
- Name of the vocation / profession / business ……….
- Educational qualifications required ………..
- Work profile/description………..
- Opportunities for advancement …………..
- our personal skills/talents for the choice …………..
![]()
Answer:
- Name of the vocation/profession/business: Engineering
- Educational qualifications required: B.E/B.Tech
- Work profile/description: Setting up of projects/setting up plants/inventing new instruments and machines
- Opportunities for advancement: Excellent in a developing country like India
- Your personal skills/talents for the choice: My interest in seeing how various machines work and my talent in repairing simple instruments.
8. Read and understand the following poem paper Boats’ and write its paraphrase in your own simple language. (You may take the help of a dictionary or the internet.) The first line is done for you.
(Day after day. one after another. I sail paper boats on the stream of flowing water.)
Answer:
Paper Boats
Day after day, one after another, I sail paper boats on the stream of flowing water. I write my name and the name of my village on the boats in big black letters. I hope that someone in some strange land will find them and know who I am. I fill my little boats with ‘shiuli’ flowers and hope that these flowers which I have picked at dawn will be carried safely to land in the night.
I set my paper boats in motion and look up at the sky. The little clouds have white bulging tails behind them that look like the sails of a boat. I do not know if there is a young child like me up in the sky, who wants to play with me, and sends his boats down through the air to race with my boats.
When it is night, I bury my face in my arms and dream that my paper boats are floating in the air under the stars at midnight. The fairies who bring sleep are sailing in them, and they are filling their baskets with dreams.
![]()
Class 8 English Chapter 2.1 Vocation Additional Important Questions and Answers
Choose the correct alternative and rewrite the complete sentence:
Vocation Question Answer Question 1.
The hawker is advertising aloud for selling metal bangles/crystal bangles.
Answer:
The hawker is advertising aloud for selling crystal bangles.
Vocation Poem Class 6 Question 2.
The narrator/The gardener is scolded if he gets dirty.
Answer:
The narrator is scolded if he gets dirty.
Vocation Std 8 Questions And Answers Question 3.
The speaker in the poem is a young school-going boy/an adult going to work.
Answer:
The speaker in the poem is a young school-going boy.
Complete the following:
Question 1.
The difference between a hawker and a shopkeeper is _____.
Answer:
that a hawker does not have a fixed shop. He goes from street to street selling his wares. A shopkeeper has a fixed shop and people who want to buy his goods must go to his shop
![]()
Question 2.
When parents see their children exposed to heat or soil their clothes in the dust, they ________.
Answer:
scold them and stop them from doing it.
Question 3.
The watchman is accompanied by _______.
Answer:
his lantern and his shadow.
Question 4.
The street lamp appears to be _______.
Answer:
a giant with one red eye in its head.
Question 5.
Analysis/Appreciation Of The Poem
Answer:
- Poem and poet: ‘Vocation’ by Rabindranath Tagore
- Theme: The longing of a young boy for freedom.
- Tone: direct; full of craving
- Structure and stanzas: Stanzas of unequal length; the number and length of lines vary.
- Rhyme and Rhythm: No rhymes or rhythm; the poem is in Free Verse.
- Language and Imagery: Simple and direct; vivid images of the hawker, the j gardener and the watchman.
- Figures of Speech: Alliteration, Simile, Repetition, Onomatopoeia.
Read More: