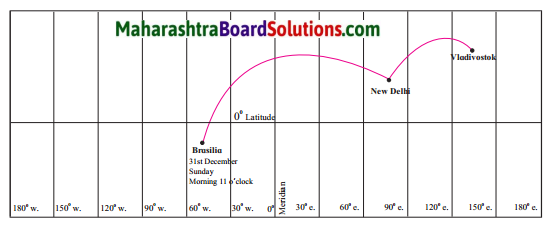
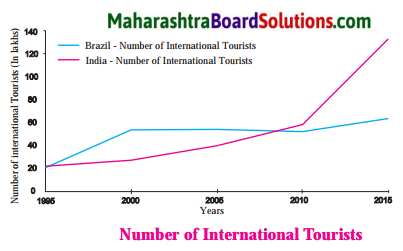
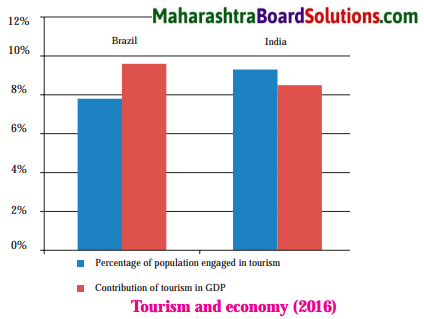
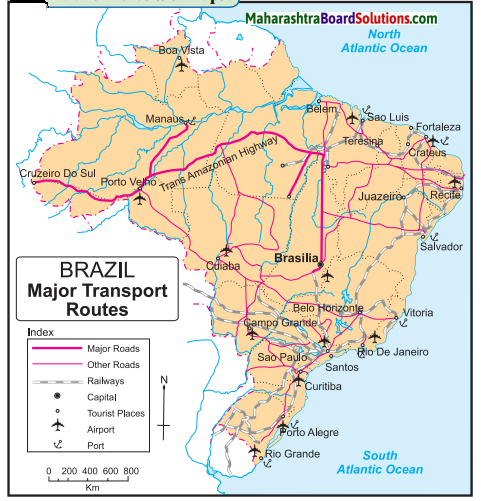
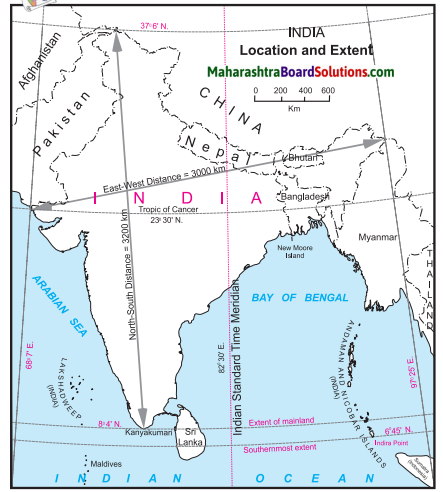
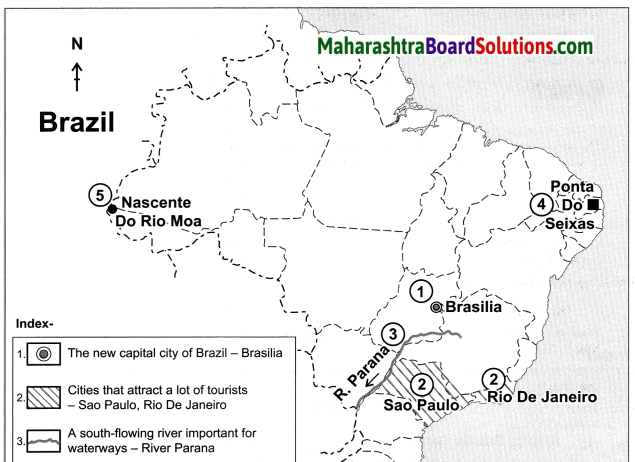
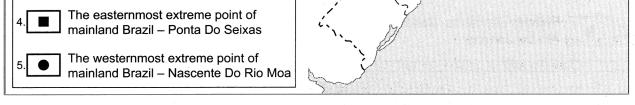
Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 10 Geography Solutions Chapter 5 Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Std 10 Geography Chapter 5 Question Answer Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Maharashtra Board
Class 10 Geography Chapter 5 Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Geography Class 10 Chapter 5 Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Question 1.
On the basis of the information given in the chapter, figures and maps, complete the table below:
| S.No |
Type of forest |
Characteristics |
Regions in India |
Regions in Brazil |
| 1 |
Tropical Forests |
Broad-leaved evergreen trees. |
|
|
| 2 |
Semi arid thorny vegetation |
1.
2. |
|
|
| 3 |
Savannah |
Scanty bushes and shrub like trees and rain resistant grass. |
|
|
| 4 |
Tropical
semi-deciduous |
Mixed type vegetation. |
|
|
| 5 |
Grasslands |
Grassland region like the Pampas of Argentina. |
|
|
Answer:
| S. No. |
Type of forest |
Characteristics |
Regions in India |
Regions in Brazil |
| (1) |
Tropical Forests |
Broad-leaved evergreen trees. |
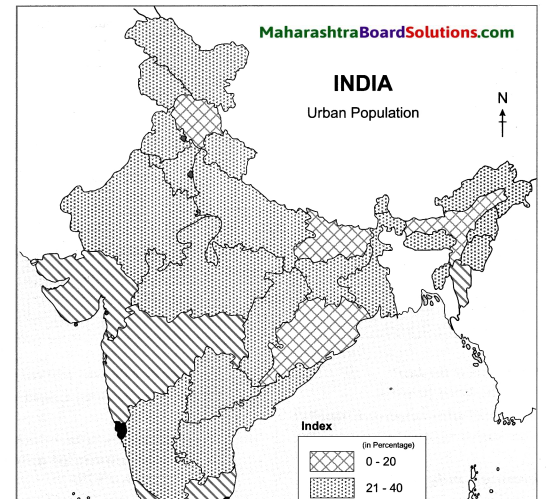
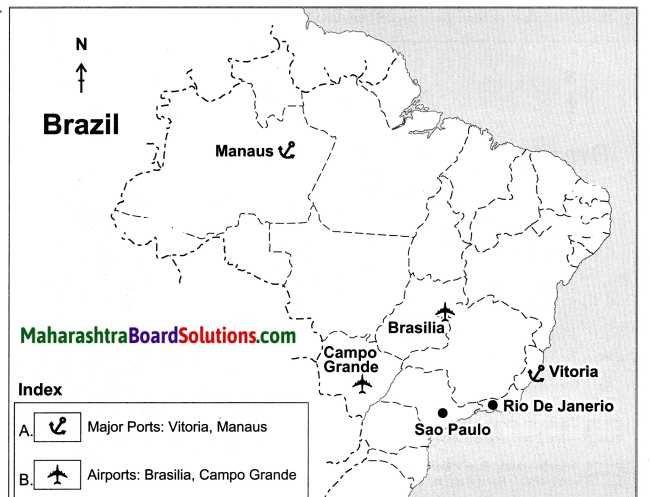
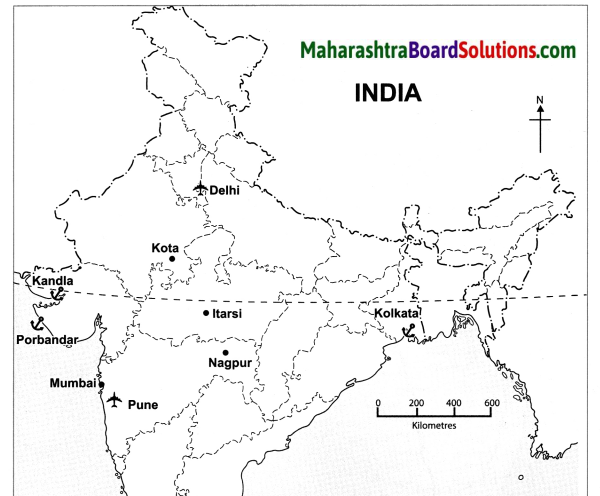
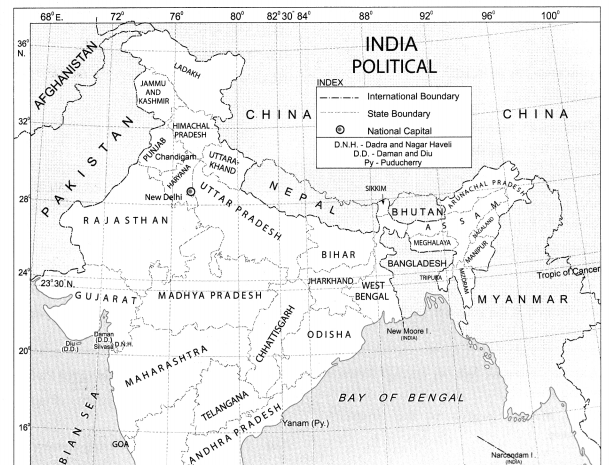
Andaman and Nicobar Islands, the Western Ghats. Some parts of North East India. |
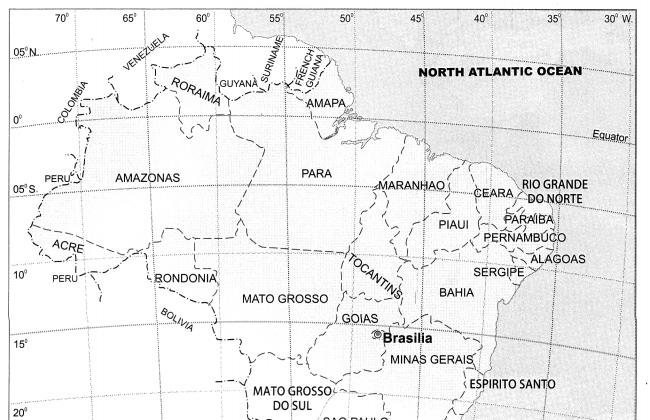
Amazon Basin, Guyana Highlands. |
| (2) |
Semi arid thorny vegetation |
(a) Thorny and shrub type vegetation.
(b) Leaves are small in size. Leaves are modified into thorns to minimise evaporation. |
Gujarat, Rajasthan, Parts of Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh. |
North-Eastern part of Brazil. |
| (3) |
Savannah |
Scanty bushes and shrub like trees and rain resistant grass. |
|
Brazilian Highland. |
| (4) |
Tropical
semi-deciduous |
Mixed type vegetation. |
Central India and South India. |
Parana Basin and South Eastern part of Brazil. |
| (5) |
Grasslands |
Grassland region like the Pampas of Argentina. |
Foothills of Shiwalik hills and Assam. |
Southern Brazil. |

2. Identify the odd man out:
Question a.
Forest type of Brazil ______.
(a) Thorny bush type vegetation
(b) Evergreen forests
(c) The Himalayan Forests
(d) Deciduous forests
Answer:
(c) The Himalayan Forests
Question b.
With reference to India
(a) Mangrove forests
(b) Mediterranean forests
(c) Thorny bush-type vegetation
(d) Equatorial forests
Answer:
(b) Mediterranean forests
Question c.
With reference to Fauna of Brazil.
(a) Anaconda
(b) Tamairin
(c) Red Panda
(d) Lion
Answer:
(c) Red Panda
Question d.
With reference to flora in India.
(a Deodar
(b) Anjan
(c) Orchid
(d) Banyan
Answer:
(c) Orchid

3. Match the Column:
| Column ‘A’ |
Column ‘B’ |
| Evergreen Forests |
(a) Sundari trees |
| Deciduous forests |
(b) Pine |
| Coastal forests |
(c) Pau Brasil |
| Himalayan forests |
(d) Khejari |
| Thorny and bush type vegetation |
(e) Teak |
|
(f) Orchid |
Answer:
1 – c
2 – e
3 – a
4 – b
5 – d
4. Answer in short:
Question a.
Differentiate between the forest types of Brazil and India.
Answer:
| Forest type of Brazil |
Forest type of India |
| 1. The northern part of Brazil lies in the equatorial region. It receives ample sunshine and heavy rainfall. So dense evergreen forests are seen here. |
1. The location of India is far away from the Equator. Heavy rainfall occurs only in the Western Ghats and North Eastern hilly areas. So evergreen forests are seen in these regions. |
| 2. The Highland region of Brazil receives low rainfall. So tropical grasslands are seen in this region. |
2. The Peninsula region of India receives rainfall between 1000 mm to 2000 mm, so they are covered by deciduous forests. |
| 3. As there are no tall and long extending mountains in Brazil, Himalayan type forests are not found here. |
3. Owing to presence of Himalayas, Himalayan type forests are found in North and North-East of India that are classified on the basis of altitude. |
| 4. Thorny shrubs are found to the North Eastern part of Brazilian Highlands which is also considered to be a Drought Quadrilateral. |
4. Thorny shrubs are found in India receiving less than 500 mm of rainfall. It is majorly found in Gujarat, Rajasthan and rain shadow regions of the Western Ghats. |
Question b.
Correlate wildlife and natural vegetation in India and Brazil.
Answer:
(i) Depending upon favourable geographical conditions, we find a variety of natural vegetation in India and Brazil. Also depending upon the vegetation we find a variety of wildlife in different regions.
(ii) Grasslands of Brazil like the Savannah and the deciduous forest of India have a large number of herbivores and carnivores.
(iii) The dense evergreen forests of India in the west, north east India and the Amazon Basin of Brazil are a home to a large variety of birds, insects, reptiles along with the herbivores and the carnivores.
(iv) Coastal forests and swampy areas of Pantanal and Sunderbans have mangroves, a variety of birds, fishes and reptiles like crocodiles, alligators and the anacondas in Brazil.
(v) Vegetation provides food and shelter to wildlife but if vegetation is limited like in the Thar desert or the Caatinga it will also limit the variety of animals species.
Question c.
What environmental issues are faced by Brazil and India?
Answer:
- Degradation of environment is happening in Brazil due to illegal smuggling of wild animals, slash and burn agriculture (roca), deforestation, pollution, etc.
- Due to these problems, many endemic species are on the verge of extinction.
- India too faces environmental issues such as poaching, pollution and the fast spreading deforestation.
- Many species of wildlife are on the verge of extinction in India.
Question d.
What are the major causes of degradation of forest in Brazil and India?
Answer:
(i) Forests are being cut down as more area is required to expand the cities. Hence rapid urbanisation is one of the reasons for degradation of forest.
(ii) To ensure continuous food supply to meet the needs of the ever increasing population, more and more area needs to be brought under agriculture. For the expansion of agricultural land, forest areas are being cut down.
(iii) In both India and Brazil, forests are being cut down for firewood and for other domestic needs.
(iv) Slash and Burn agriculture which is also known as Roca in Brazil and Jhum in India is responsible for deforestation.
(v) Apart from all the above reasons, forest fire, pollution, overgrazing, etc. are also responsible for the degradation of forests.

Question e.
Why does the deciduous type vegetation occupy most of India?
Answer:
- Vegetation in a region is affected by the climate and rainfall of the region.
- In dia lies in the tropical zone and it has a monsoon type climate throughout the year.
- Also, a major portion of India receives seasonal rainfall between 1000-2000 mm.
- Deciduous forests thrive well in this condition and these forests shed their leaves during the hot and dry summer so that water is not lost due to evaporation.
- Teak, bamboo, banyan, peepal, etc. are the trees found in deciduous forest of India.
5. Give geographical reasons:
Question a.
The northern part of Brazil is covered with dense forests.
Answer:
- The northern part of Brazil lies in the equatorial region.
- It receives ample sunlight and about 2000 mm of rainfall throughout the year.
- In this region, the growth of vegetation is very rapid.
- So, the northern part of Brazil is covered with dense and evergreen forests.
Question b.
Vegetation is scarce in the high altitude of the Himalayas.
Answer:
- As the altitude increases, the temperature decreases.
- The climate is very cold in the high altitudes. In Jammu and Kashmir and parts of Himalayas temperature drops to -40fiC.
- Also this region is snow-covered for most part of the year.
- Very few species of plants can survive in such extreme conditions. Only seasonally flowering trees are found at higher altitudes.
- Hence, vegetation is scarce in the high altitude of the Himalayas.
Question c.
A wide variety of insect species is found in Brazil.
Answer:
- Insects are mostly found in forests, grasslands and swampy lands.
- Many insects eat leaves, grass and nectar from the plant.
- The evergreen rainforests are seen in the northern parts of Brazil. The grasslands are found in the central parts and Paraguay-Parana river basin. Similarly, swampy lands are found in Pantanal region in Brazil. .
- Therefore, a wide variety of insect’s species is found in Brazil.
Question d.
Wild life in India is decreasing day by day.
Answer:
(i) Wildlife in India is decreasing day by day because of rapidly occurring deforestation, poaching, pollution.
(ii) Expansion of cities to accommodate the growing population is leading to cutting down of the valuable forest which leads to the loss of the habitat of wildlife.
(iii) Also the problem of pollution has become severe due to urbanisation. Various types of pollution have threatened the lives of many of the species.
(iv) Poaching of wildlife species have also led to the loss of wildlife in India.
(v) Agricultural practices like shifting cultivation has also reduced the forest cover leading to loss of wildlife habitat.
Question e.
Like India, there is a need for conservation of forests in Brazil too.
Answer:
(i) Like India, Brazil is facing the problem of degradation of environment due to deforestation, pollution, slash and burn agriculture, illegal smuggling of wild animals, etc.
(ii) Trees are being cut down to obtain wood, leading to large scale deforestation in both countries.
(iii) Also the problem of pollution has become severe due to urbanisation. Various types of pollution have threatened the lives of many of the species.
(iv) Agricultural practices like slash and burn agriculture (roca) has reduced the forest cover in Brazil.
(v) Like India, the problem of illegal smuggling of animals has affected Brazil too.
(vi) Hence there is a need for conservation of forests in both Brazil and India.
Class 10 Geography Chapter 5 Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Intext Questions and Answers
Observe the images given below and discuss on the basis of the following points and answer the following questions:

Question 1.
Can you tell the names of the plants/trees shown in the image?
Answer:
Coffee, cactus, rubber.
Question 2.
Where have you seen these plants before?
Answer:
Brazil.
Question 3.
Name the fauna shown in the image.
Answer:
Rufous bellied thrush, leopard, green anaconda.
Question 4.
Where have you seen them before?
Answer:
On the internet and in movies.

Question 5.
In which country do you find a greater diversity of vegetation? What is the reason behind it?
Answer:
Brazil has a greater diversity of vegetation because of the variation in climatic conditions.
Colours Of Both
Question 1.
In which country do equatorial forests occupy a greater area? What could be the reason behind it?
Answer:
Equatorial forests occupy a greater area in Brazil. This is because the Equator passes through northern part of Brazil. Hence, the climate is generally hot throughout the year. Moreover, this region receives heavy rainfall throughout the year.
Question 2.
Which type of forests found in India are not found in Brazil?
Answer:
Himalayan forests are found in India and not in Brazil.
Question 3.
Which type of forests found in Brazil are found in India too?
Answer:
Evergreen forests, deciduous forests, and thorny shrub type vegetation are found in both Brazil and India.
Question 4.
In which country a greater diversity of vegetation is found? What is the reason behind it?
Answer:
Brazil has a greater diversity of vegetation because of the equatorial climate, ample sunlight, heavy rainfall, and vast forest expanse.
Question 5.
Considering the climate and vegetation types, in which country will forest-based occupations flourish?
Answer:
Forest-based occupations will flourish more in Brazil.
Activity
Question 1.
Correlate geographical conditions and the flora and fauna there? (India)
Answer:
Depending upon favourable geographical conditions, we find a variety of flora and fauna in India.
(i) In the snow-capped regions of Himalayas where precipitation occurs in the form of snow, we find alpine vegetation. Animals like snow leopards and yaks are found who can sustain the extreme cold of the Himalayas.
(ii) The evergreen forest in the Western Ghats have hot and humid conditions with a temperature of 28°C and annual rainfall more than 2000mm. In such are as animals like lions, tigers, elephants, and a variety of birds are seen.
(iii) The coastal forest are home to many turtles, crocodiles, and gavials, etc. One-horned rhinoceroses are found in the swampy, marshy lands of Assam. Mangrove vegetation is found in the saline waters.
(iv) In areas where the climate is hot and dry and the rainfall is low, thorny scrub vegetation is found. Animals like wild ass and camels are common here.
(v) In the regions of medium rainfall. We find deciduous forest, wide variety of animals and birds.
Question 2.
Do you know some other animals too ?
Answer:
Four-horned antelope, black buck, Tibetan yak, giant squirrel (shekaru).
Use your Brain:
Question 1.
Find out in which parts of India agricultural practices like the ‘Roca’ is found? By what names are they called?
Answer:
| Slash and Burn Farming in India |
| Name |
Regions |
| Jhumming |
Assam, Meghalaya, Mizoram and Nagaland |
| Pamlou |
Manipur |
| Dipa |
Bastar (Chhattisgarh) and Andaman & Nicobar Islands |
| Bewar or Dahiya |
Madhya Pradesh |
| Podu or Penda |
Andhra Pradesh |
| Pama Dabi or Koman or Bringa |
Odisha |
| Kumara |
Western Ghats |
| Valre or Waltre |
South Eastern Rajasthan |
| Khi |
Himalayan belt |
| Kuruwa |
Jharkhand |

Answer the following questions on the basis of map given:
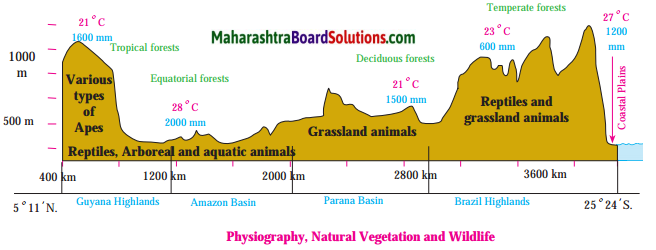
Question 1.
How many mm of rainfall does Tropical forests have?
Answer:
Tropical forests receives rainfall of 1600 mm.
Question 2.
How much rainfall does equatorial forests receive?
Answer:
Equatorial forests receive 2000 mm of rainfall.
Question 3.
Name the types of forests shown in figure.
Answer:
Tropical forests, Equatorial forests, Deciduous forests and Temperate forests are shown in the above figure.
Question 4.
Where are tropical and equatorial forests found in Brazil?
Answer:Tropical and equatorial forests are found in Guyana Highlands and Amazon basin respectively.
Question 5.
Where are deciduous forests and temperate forests found in Brazil?
Answer:
Deciduous forests and Temperate forests are found in Parana Basin and Brazilian Highlands respectively.
Question 6.
What kind of wildlife is seen in Brazilian Highlands?
Answer:
Reptiles and grassland animals are seen in Brazilian Highlands.
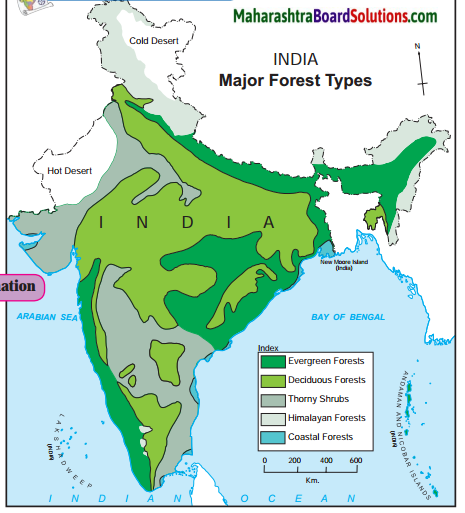
Question 1.
Which forests are found in western snow¬capped regions?
Answer:
Himalayan Forests are found in western snow-capped regions.
Question 2.
On which coast do you mainly find the coastal vegetation?
Answer:
The coastal vegetation is mainly found along the Eastern Coast.
Question 3.
Which type of forests occupy maximum area in India ? Why?
Answer:
Deciduous forests are found in the regions receiving rainfall between 1000 mm to 2000 mm Since most of India has rainfall in that range, deciduous forests dominate the Indian subcontinent.
Question 4.
Where do you find thorny and shrub vegetation in India and why?
Answer:
Semi arid areas of Gujarat, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Uttar Pradesh Maharashtra, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu and Haryana are the places where thorny and shrub vegetation are found. The thorny forests are found in these regions as the rainfall is less than 500 mm.
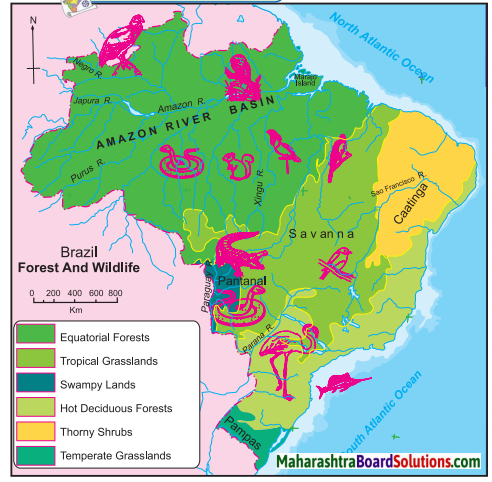

Question 1.
Name the species shown on the map.
Answer:
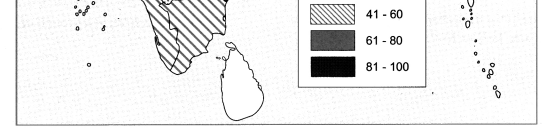
Some of the major species shown on the map are condor, golden lion tamarin, anaconda, crocodile, sword fish, flamingoes, macaw, parrots, rufous bellied thrush.
Question 2.
In which regions are these animals found? Why are their habitats found in these forests?
Answer:
- The dense equatorial forest region is home to golden lion tamarin, condor, anaconda, etc. This is because these forest lie near the Amazon River and receive rainfall throughout the year.
- Swampy lands of Pantanal is home to anacondas and crocodiles because these conditions are favourable for their habitation.
- Sword fish thrives near the South Atlantic Coast due to the extensive continental shelf.
Question 3.
Classify the forest regions in Brazil with reference to their extent.
Answer:
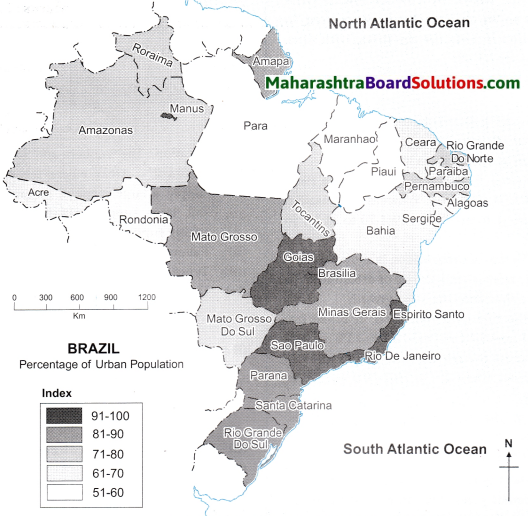
- Equatorial forests are found in the northern part of Brazil and it covers an extensive area.
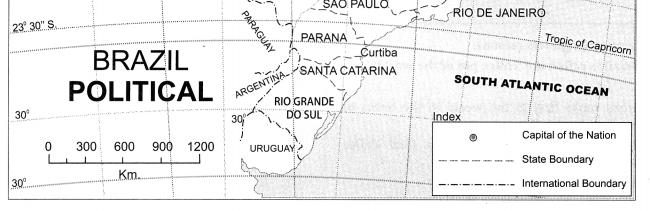
- Tropical Grasslands (Savanna) is the next major forest type occupying central part of Brazil.
- Hot deciduous forests occupy the southern Brazil whereas swampy lands of Pantanal occupy a small part of Brazil in the south west.
- Thorny shrubs occupy the north western part of Brazil owing to low rainfall whereas Temperate Grasslands (Pampas) occupy south Brazil.
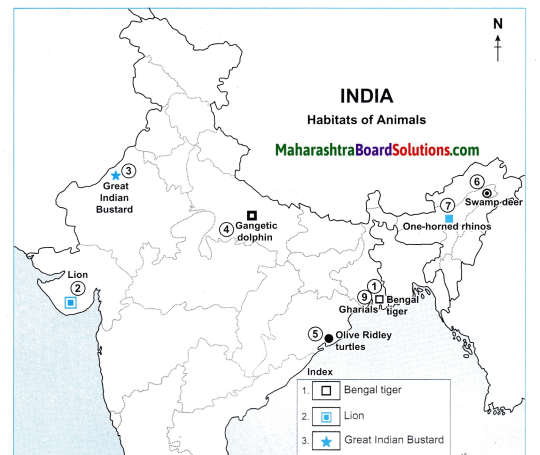
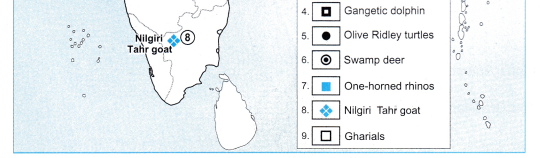
Mark the following on the map of India with the given information:
Question 1.
- Bengal Tiger
- Lion
- Great Indian Bustard
- Gangetic Dolphin
- Olive Ridley turtles
- Swamp deers
- One-horned rhinos
- Nilgiri Tahr goat
- Gharials
Answer:
Class 10 Geography Chapter 5 Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Additional Important Questions and Answers
Choose the correct option and rewrite the statements:
Question 1.
In Brazil, _____ varies due to physiography.
(a) soil
(b) rainfall
(c) agriculture
(d) mineral availability
Answer:
(b) rainfall
Question 2.
In most parts of the _____ region, it rains throughout the year.
(a) temperate
(b) tropical
(c) grasslands
(d) equatorial
Answer:
(d) equatorial
Question 3.
As one moves away from the Equator, _______ decreases.
(a) altitude
(b) forest
(c) rainfall
(d) snowfall
Answer:
(c) rainfall

Question 4.
The _______ forests are found where there is rainfall throughout the year.
(a) tropical
(b) thorny
(c) evergreen
(d) temperate
Answer:
(c) evergreen
Question 5.
Brazil has the/a ______ number of vegetation species in the world.
(a) moderate
(b) largest
(c) low
(d) smallest
Answer:
(b) largest
Question 6.
The rainforests are rightly called the _______.
(a) lungs of the world’
(b) ’limbs of the world’
(c) ’heart of the world’
(d) ’veins of the world’
Answer:
(a) lungs of the world’
Question 7.
Highest biodiversity is found in _____ forests.
(a) thorny
(b) deciduous
(c) evergreen
(d) coastal
Answer:
(c) evergreen
Question 8.
In regions receiving rainfall between 1000 mm to 2000 mm in India, ______ forests are found.
(a) thorny
(b) evergreen
(c) deciduous
(d) tropical
Answer:
(c) deciduous
Question 9.
In regions receiving less than 500 mm of rainfall that experience dry summers for a long time in India, ______ and shrub like vegetation are found.
(a) equatorial
(b) evergreen
(c) grasslands
(d) thorny
Answer:
(d) thorny
Question 10.
In _____ areas, coastal type of vegetation is found.
(a) peninsular
(b) mountainous
(c) rocky
(d) swampy
Answer:
(d) swampy
Question 11.
Coastal type of vegetation is called ____ in India.
(a) Bangar
(b) Sunderbans
(c) Pantanal
(d) Terai
Answer:
(b) Sunderbans

Question 12.
The wood found in Sunderbans is _____ light and durable.
(a) dry
(b) fragile
(c) oily
(d) soft
Answer:
(c) oily
Question 13.
In areas located in the ____ altitude of Himalayas, seasonly flowering trees are found.
(a) highest
(b) lowest
(c) plains
(d) medium
Answer:
(a) highest
Question 14.
In regions with medium altitude of Himalayas, ______ trees are found.
(a) rubber
(b) evergreen
(c) rose wood
(d) coniferous
Answer:
(d) coniferous
Question 15.
At foothills of the Himalayas _____ forests are found.
(a) mixed
(b) teak –
(c) coniferous
(d) pine
Answer:
(a) mixed
Question 16.
The proportion of ________ trees is higher at the foothills of the Himalayas.
(a) sal
(b) deodar
(c) rosewood
(d) pine
Answer:
(a) sal
Question 17.
Teak is mainly found in the _______ type of forest.
(a) Coastal
(b) Thorny and bush
(c) Coniferous
(d) Deciduous
Answer:
(d) Deciduous
Question 18.
A greater diversity of wildlife is found in ________ than any other country in the
world.
(a) India
(b) Russia
(c) Australia
(d) Brazil
Answer:
(d) Brazil
Question 19.
In the swampy areas of Pantanal, _______ are found.
(a) cobras
(b) vipers
(c) huge anacondas
(d) Indian pythons
Answer:
(c) huge anacondas
Question 20.
Among fish varieties, ______ is found in seas of Brazil
(a) mackerel
(b) king fish
(c) sword fish
(d) pink dolphins
Answer:
(c) sword fish
Question 21.
In Brazilian rivers, pink dolphins and ______ are found.
(a) gold fish
(b) piranhas
(c) king fish
(d) mackrels
Answer:
(b) piranhas

Question 22.
One of the major bird species found in Brazil includes _______.
(a) ostrich
(b) flamingoes
(c) kiwi
(d) duck
Answer:
(b) flamingoes
Question 23.
Slash and bum agriculture is also called ______ in Brazil.
(a) kumri
(b) roka (roca)
(c) dry farming
(d) bewar
Answer:
(b) roka (roca)
Question 24.
Hot and humid forests are a home for _______
(a) tiger
(b) elephants
(c) dogs
(d) leopard
Answer:
(b) elephants
Question 25.
One horned rhinoceroses are found in swampy and marshy lands of ______.
(a) Assam
(b) Madhya Pradesh
(c) Telangana
(d) Tamil Nadu
Answer:
(a) Assam
Question 26.
Indian bisons, deers, monkeys are found in the _____ region.
(a) Himalayan
(b) Western Ghats
(c) Peninsular
(d) Deccan
Answer:
(c) Peninsular
Question 27.
The only country where both lions and tigers are found is ______.
(a) Brazil
(b) India
(c) Australia
(d) America
Answer:
(b) India
Question 28.
______ which are huge in size fly high in the Brazilian sky.
(a) Macaws
(b) Kingfishers
(c) Condors
(d) Pheasants
Answer:
(c) Condors
Match the Column:
Question 1.
| Column ’A’ |
Column ‘B’ |
| 1. Evergreen Forests |
(a) Major portion of Madhya Pradesh |
| 2. Deciduous forests |
(b) Arunachal Pradesh |
| 3. Thorny shrubs |
(c) Sundarbans |
| 4. Himalayan forests |
(d) Western Ghats |
| 5. Coastal forests |
(e) Gujarat |
|
(f) Cold desert in Jammu and Kashmir |
|
(g) Hot desert in Rajasthan |
Answer:
1 – d
2 – a
3 – e
4 – b
5 – c
Question 2.
| Column ’A’ |
Column ‘B’ |
| 1. Equatorial forests |
(a) Caatinga |
| 2. Grasslands |
(b) Pantanal |
| 3. Swampy Lands |
(c) Pampas |
| 4. Hot deciduous forests |
(d) Amazon river basin |
| 5. Thorny shrubs |
(e) Escarpment |
|
(f) Savanna |
|
(g) Parana basin |
Answer:
1 – d
2 – c
3 – b
4 – e
5 – a

Identify the odd man out:
Question 1.
With reference to Fauna in India.
(a) Anaconda
(b) Elephants
(c) Lion
(d) Tiger
Answer:
(a) Anaconda
Question 2.
With reference to Flora of Brazil.
(a) Pau Brazil
(b) Rubber
(c) Mahogany
(d) Deodar
Answer:
(d) Deodar
Question 3.
With reference to Himalayan Forests.
(a) Seasonal flowering plants
(b) Orchids
(c) Pine
(d) Mixed Forests
Answer:
(b) Orchids
Question 4.
With reference to birds found in Brazil.
(a) Condors
(b) Flamingoes
(c) Macaws
(d) Peacocks
Answer:
(d) Peacocks
Question 5.
With reference to birds found in India.
(a) Peacock
(b) Kingfisher
(c) Duck
(d) Condors.
Answer:
(d) Condors.
Question 6.
With reference to protection of wildlife, Government of India has setup.
(a) Museums
(b) Biosphere reserves
(c) National Parks
(d) Wildlife sanctuaries
Answer:
(a) Museums
Answer the following questions in one sentence:
Question 1.
Where does it rain throughout the year?
Answer:
It rains throughout the year, in most parts of the equatorial region.
Question 2.
As one moves away from the Equator, does the rainfall increase?
Answer:
No, the rainfall decreases as one moves away from the Equator.
Question 3.
Where are evergreen forests found?
Answer:
Evergreen forests are found in the area where it rains throughout the year.
Question 4.
What effect does rainfall have on vegetation?
Answer:
As the rainfall decreases, the density of the vegetation also decreases.
Question 5.
What kind of vegetation is found in places of less rainfall?
Answer:
Various types of grass, short shrubs and thorny vegetation is found in places of less rainfall.

Question 6.
Where are the largest number of vegetation species found in the world?
Answer:
Brazil has the largest number of vegetation species in the world.
Question 7.
What kind of trees are found in Brazil?
Answer:
Trees like Pau Brasil, rubber, mahogany, rosewood and a variety of orchids are found in Brazil.
Question 8.
Why are the evergreen forests called the ‘lungs of the world’?
Answer:
Evergreen forests are called the lungs of the world because they release large amount of oxygen in the environment which helps to reduce the carbon dioxide levels.
Question 9.
Describe the leaves of trees found in evergreen forests.
Answer:
The leaves of trees found in evergreen forests are broad and green.
Question 10.
What quality of wood is found in evergreen forests?
Answer:
The wood found in evergreen forests is hard, heavy and durable.
Question 11.
In which regions are deciduous forests found?
Answer:
Deciduous forests are found in the regions receiving an average amount of rainfall ranging between 1000mm to 2000mm in India.
Question 12.
Which trees are found in deciduous forests?
Answer:
Trees like teak, bamboo, banyan, peepal, etc. are found in deciduous forest.
Question 13.
Which regions experience dry summers for a long time in India?
Answer:
Regions that receive less than 500 mm of rainfall experience dry summers for a long time in India.
Question 14.
Which kind of vegetation is found in regions receiving less than 500 mm of rainfall?
Answer:
Thorny or shrub like vegetation is found in regions receiving less than 500 mm of rainfall.
Question 15.
How are the leaves of trees in the region where there is less than 500 mm of rainfall?
Answer:
The leaves of trees are small in the region where there is less than 500 mm of rainfall.
Question 16.
Where is coastal vegetation found?
Answer:
Coastal vegetation is found in swampy areas, estuaries and lagoons near coastal areas.
Question 17.
What is coastal vegetation called in India?
Answer:
Coastal vegetation is called mangroves or Sunderbans in India.
Question 18.
How is the wood of trees found in coastal vegetation?
Answer:
The wood of trees found in coastal vegetation is oily, light and durable.

Question 19.
How many types of forests are there in the Himalayas?
Answer:
There are three types of forests in the Himalayas based on their altitude.
Question 20.
Which kind of trees are found in regions of high altitude in the Himalayas?
Answer:
Seasonally flowering trees are found in regions of high altitude.
Question 21.
Which type of trees are found in regions with medium altitude in the Himalayas?
Answer:
In regions with medium altitude, coniferous trees like pine, deodar and fir are found.
Question 22.
Where are mixed forests found in India?
Answer:
Mixed forest are found at the foothills of the Himalayas.
Question 23.
Where is greater diversity in wildlife found in the world?
Answer:
A greater diversity in wildlife is found in Brazil than any other country in the world.
Question 24.
Which animal is found in the swampy areas of the Pantanal?
Answer:
Huge anacondas are found in the swampy areas of Pantanal.
Question 25.
Which are the other animals found in Brazil?
Answer:
Animals like guinea pigs, crocodiles, alligators, monkeys, pumas, leopards, etc. are found in Brazil.
Question 26.
Which is the main variety of fish found in the Brazilian sea?
Answer:
Sword fish is mainly found in the Brazilian sea.
Question 27.
Which varieties of fish are found in the rivers of Brazil?
Answer:
Piranhas are found in the rivers of Brazil.
Question 28.
What kind of birds are seen in the Brazilian sky?
Answer:
Condors, parrots, macaws, and flamingoes are found in the Brazilian skies.
Question 29.
Why is degradation of environment happening in Brazil?
Answer:
Degradation of environment is happening in Brazil due to illegal smuggling of wild animals, slash and bum agriculture (roka), deforestation, and pollution.
Question 30.
Where are elephants found in India?
Answer:
Elephants are found in hot and humid forests of India.
Question 31.
Where are one homed rhinoceroses found?
Answer:
One homed rhinoceroses are found in the swampy and marshy lands of Assam.
Question 32.
Which animals are found in the arid lands of India?
Answer:
Wild ass and camels are found in the arid lands of India.
Question 33.
Which animal is found in the snow capped regions of Himalayas?
Answer:
Snow leopards are found in the snow capped regions of the Himalayas.
Question 34.
Which animals are found in the peninsular region of India?
Answer:
Indian Bisons, deer, antelopes, and monkeys are found in the Peninsular region of India.
Question 35.
Which is the only country where both lions and tigers are found?
Answer:
India is the only country where both lions and tigers are found.
Question 36.
Where are turtles, crocodiles and gharials found in India?
Answer:
Turtles, crocodiles and gharials are found in rivers, estuaries, and coastal areas of India.

Question 37.
Which birds are found in the forests and wetlands of India?
Answer:
Birds like peacocks, Indian bustard, kingfishers, peasants, ducks, parakeet, cranes, and pigeons are found in the forests and wetlands of India.
Question 38.
What measures are taken by the Government of India for the protection of wildlife and forests of India?
Answer:
The Government of India has set up a number of national parks, wildlife sanctuaries, bird sanctuaries, and biosphere reserves for the protection of wildlife and forests in India.
Question 39.
Name some plants found in regions having less than 500 mm of rainfall in India.
Answer:
Catechu, acacia, khejri and a variety of cactus like aloevera and agave are found in regions having less than 500 mm of rainfall in India.
Name the following:
Question 1.
The region where it rains throughout the year.
Answer:
Equatorial region.
Question 2.
The forests which are found where it rains throughout the year.
Answer:
Evergreen forests.
Question 3.
Kind of vegetation found in places of less rainfall.
Answer:
Grass, short shrubs, thorny vegetation.
Question 4.
Country where the largest number of vegetation species in the world is located.
Answer:
Brazil.
Question 5.
The types of trees found in Brazil.
Answer:
Pau Brasil, rubber, mahogany, rosewood and variety of orchids.
Question 6.
Other name for rain forests.
Answer:
‘The lungs of the world.’
Question 7.
Trees found in deciduous forests.
Answer:
Teak, bamboo, banyan, peepal.
Question 8.
Type of vegetation found in regions having less than 500 mm of rainfall.
Answer:
Thorny and shrub-like.
Question 9.
Plants found in regions having less than 500 mm of rainfall.
Answer:
Catechu, acacia, khejri and varieties of cactus.
Question 10.
Kind of vegetation found in swampy areas.
Answer:
Coastal type.
Question 11.
Another name of coastal type of vegetation in India.
Answer:
Mangroves or sunderbans.

Question 12.
Kind of trees found in forests located on higher altitudes in the Himalayas.
Answer:
Seasonally flowering trees.
Question 13.
Kind of trees which have grown in forests located on medium altitudes in Himalayas. Coniferous trees like Pine, Deodar and Fir.
Answer:
Region where mixed forests are found in Himalayas.
Question 14.
Foothills of Himalayas.
Answer:
Animal found in the swampy areas of Pantanal.
Question 15.
Huge anacondas.
Answer:
Any two varieties of animals found in Brazil. Guinea pigs and crocodiles.
Question 16.
Kind of fishes found in seas of Brazil.
Answer:
Sword fish.
Question 17.
Fish varieties found in the rivers of Brazil.
Answer:
Pink dolphins and Piranhas.
Question 18.
Any two species of birds found in Brazil.
Answer:
Condors and macaws.
Question 19.
Causes for degradation of environment.
Answer:
Illegal smuggling of wild animals, roka, deforestation and pollution
Question 20.
Region where elephants are found in India.
Answer:
Hot and humid forests.
Question 21.
Animal which is found in the swampy and marshy lands of Assam.
Answer:
One horned rhinoceroses.
Question 22.
Animals which are found in arid lands of India.
Answer:
Wild ass and camels.
Question 23.
Animals which are found in the snowcapped mountain of Himalayas.
Answer:
Yaks and snow leopards.
Question 24.
Animals found in the Peninsular region of India.
Answer:
Indian bisons, deer, antelopes and monkeys.
Question 25.
Country where both lion and tigers are found.
Answer:
India.
Question 26.
Animals found in rivers, estuaries and coastal areas of India.
Answer:
Turtles, crocodiles and garials.
Question 27.
Measures taken by the Government of India to protect wildlife.
Answer:
Setting up of National parks, bird sanctuaries, wildlife sanctuaries and biosphere reserves.
Question 28.
National animal of India.
Answer:
Tiger.

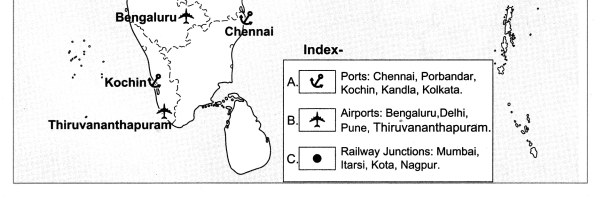
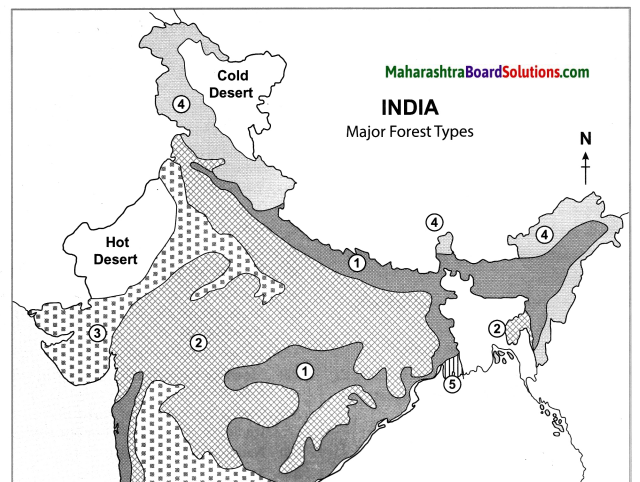
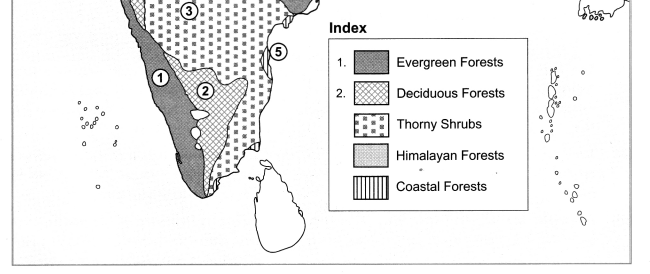
Mark the following on the map of India with the given information:
- Evergreen forests
- Deciduous forest
- Thorny shrubs
- Himalayan Forests
- Coastal Forests
Answer:
Mark the following on the map of Brazil with the given information:
- Equatorial forests
- Tropical grasslands
- Swampy lands
- Hot deciduous forest
- Caatinga
- Temperate grasslands
Answer:
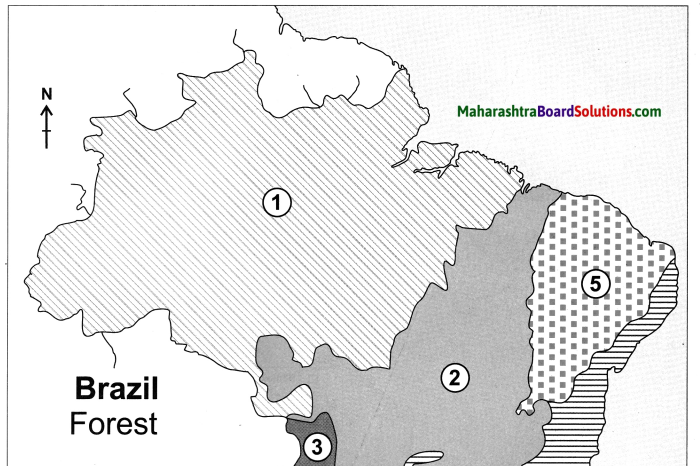
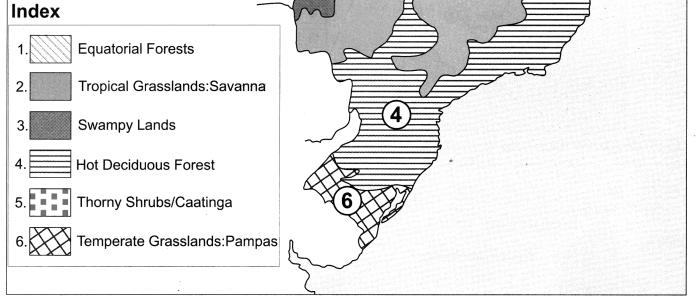
Equatorial Forests Tropical Grasslands:Savanna Swampy Lands Hot Deciduous Forest Thorny Shrubs/Caatinga Temperate Grasslands:Pampas

Question 1.
Show the habitats of tigers in India with their names on a map.
Answer:
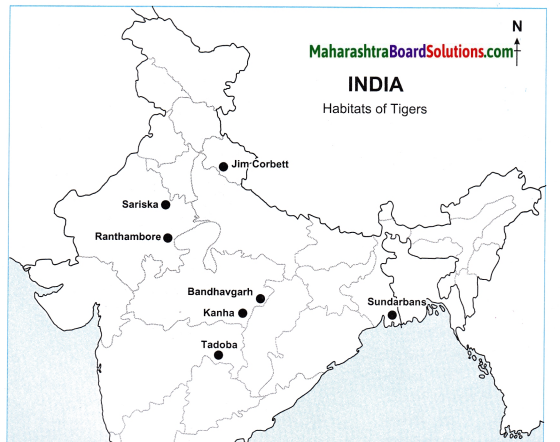
Question 2.
Why is their habitat found in these regions?
Answer:
Tiger’s habitats are found in these regions because here there are various types of forest areas with different types of herbivorous animals.
Answer the Questions Briefly:
Question 1.
Thorny and shrub-like vegetation is found in regions where there is less or no rainfall.
Answer:
- The regions where there is less or no rainfall have a hot and dry climate.
- The soils in these regions are also rocky and dry.
- Water evaporation in leaves is more since the surface area of exposure is more than that of thorns
- Hence, thorny and shrub-like vegetation is found in regions where there is less or no rainfall to conserve water.
Question 2.
The evergreen rainforests in Brazil are rightly called the ‘Lungs of the world’.
Answer:
- The northern Part of Brazil has dense evergreen forests. .
- These forests release a large amount of oxygen in the environment.
- This helps to reduce carbon dioxide levels.
- Therefore, these rainforests are rightly called the Tungs of the world’.
Question 3.
The largest variety of flora is found in Brazil.
Answer:
- The flora of any region depends upon the amount of rainfall and its physiography.
- Brazil has equatorial forests in high rainfall areas, tropical grasslands and deciduous forests in moderate rainfall areas.
- Western part of Brazil has swampy lands, whereas low rainfall regions have thorny shrubs.
- Temperate grasslands are found in temperate regions.
- Thus, the largest variety of flora is found in Brazil.
Question 4.
Suggest measures for the conservation of wildlife and forest in India?
Answer:
Measures for the conservation of wildlife and forest in India are as follows:
- Restricting wildlife trading and hunting.
- Declaring more national parks and sanctuaries.
- Giving more importance to the protection of endangered animals.
- Controlling felling of trees.
- Implementing afforestation and social forestry programmes.

Write short notes on:
Question 1.
Brazilian Vegetation:
Answer:
(i) In Brazil, rainfall varies due to physiography. In most parts of the Equatorial region, it rains throughout the year.
(ii) As one moves away from the equator, the number of rainy days as well as amount of rainfall reduces.
(iii) This affects the life cycle of the vegetation too.
(iv) Evergreen forests are found in the areas where it rains throughout the year.
(v) In regions which receive rainfall only during certain seasons, the density of the vegetation reduces.
(vi) Instead of forests, various types of grass, short shrubs,,thorny vegetation, etc. are found.
(vii) Brazil has the largest number of vegetation species in the world.
(viii) This includes evergreen vegetation, semi-evergreen, arid, etc.
(ix) One finds trees like Pau Brasil, rubber, mahogany, rosewood and a variety of orchids.
Question 2.
wildlife of Brazil:
Answer:
(i) A greater diversity in wildlife is found in Brazil compared to any other country in the world.
(ii) In the swampy areas of the Pantanal, huge anacondas are found.
Animals, such as guinea pigs, crocodiles,
alligators, monkeys, pumas, leopards, etc. are found.
(iv) Among the fish varieties, mainly swordfish are found in the seas, while pink dolphins and piranhas are found in the rivers .
(v) Condors which are huge in size and fly high in the sky, various types of parrots, macaws, and flamingoes are the major birds found here.
(vi) Millions of insect varieties are also found here.
Question 3.
The wildlife of India:
Answer:
(i) India is also a mega-diverse country in terms of wildlife. There are many species of wildlife in Irdia.
(ii) Elephants are found in hot and humid forests. One-horned rhinoceroses are found in swampy and marshy lands of Assam.
(iii) Wild ass and camels are found in arid lands. Snow leopards and yaks are found in the snow-capped regions of the Himalayas.
(iv) Indian Bisons, deer, antelopes, and monkeys are found in the Peninsular region.
(v) India is the only country in the world where both tigers and lions are found.
(vi) Rivers, estuaries and coastal areas are homes to many turtles, crocodiles, and gavials (gharials).
(vii) The forests and wetlands are the shelters of variety of birds like peacocks, Indian bustard, kingfishers, pheasants, ducks, parakeets, cranes, and pigeons.
10th Std Geography Questions And Answers:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()