Balbharti Maharashtra State Board 12th Biology Important Questions Chapter 7 Plant Growth and Mineral Nutrition Important Questions and Answers.
Maharashtra State Board 12th Biology Important Questions Chapter 7 Plant Growth and Mineral Nutrition
Multiple choice questions
Question 1.
For the following, which is the aspect of growth? Example – Increase in length, size and number of cells.
(a) Quantitative
(b) Qualitative
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) Three dimensional
Answer:
(a) Quantitative
Question 2.
In vascular plants, growth takes place due to ………………..
(a) conducting tissues
(b) embryo
(c) meristems
(d) stem cell
Answer:
(c) meristems

Question 3.
What is growth?
(a) Temporary, irreversible increase in an organism.
(b) Permanent, reversible increase in an organism.
(c) Permanent, irreversible decrease in an organism.
(d) Permanent, irreversible increase in an organism.
Answer:
(d) Permanent, irreversible, increase in an organism
Question 4.
Based on location, plants have these three types of meristems.
(a) Basal, Intercalary and Lateral
(b) Apical, Basal and Lateral
(c) Apical, Interfascicular and Lateral
(d) Apical, Intercalary, Lateral
Answer:
(d) Apical, Intercalary, Lateral
Question 5.
Meristem cells are ………………..
(a) thin walled, vacuolated with prominent nucleus
(b) thick walled, non-vacuolated without nucleus
(c) thin walled, non-vacuolated with prominent nucleus
(d) thick walled, vacuolated with prominent nucleus
Answer:
(c) thin walled, non-vacuolated with prominent nucleus
Question 6.
Select correct sequence of phases of growth.
(a) Phase of formation, phase of elongation, phase of maturation
(b) Phase of cell division, phase of enlargement, phase of elongation
(c) Phase of formation, phase of maturation, phase of elongation
(d) Phase of enlargement, phase of cell division, phase of maturation
Answer:
(a) Phase of formation, phase of elongation, phase of maturation
Question 7.
In which phase of growth, growth rate is at accelerated pace?
(a) Lag phase
(b) Log phase
(c) Steady phase
(d) Stationary phase
Answer:
(b) Log phase
Question 8.
Water is essential for growth because it is necessary ………………..
(a) for turgidity
(b) as nutrient
(c) as raw material
(d) for gravity
Answer:
(a) for turgidity
Question 9.
Which equipment is suitable for measuring linear growth of shoot?
(a) Horizontal microscope
(b) Spectroscope
(c) Crescograph
(d) Auxanometer
Answer:
(d) Auxanometer
Question 10.
Which is correct expression of absolute growth rate (AGR)?
(a) AGR = \(\frac { dn }{ dt }\)
(b) AGR = \(\frac { dt }{ dn}\)
(c) AGR = \(\frac { RGR }{ n }\)
(d) AGR = \(\frac { n }{ RGR }\)
Answer:
(a) AGR = \(\frac { dn }{ dt }\)
Question 11.
Arithmetic growth in plants shows ……………….. graph.
(a) Sigmoid
(b) J-shaped
(c) linear
(d) elliptical
Answer:
(c) linear
Question 12.
What is grand period of growth?
(a) The total time required for all phases to occur
(b) The total time required for exponential phase
(c) The total time required for Lag and Log phase together
(d) The toted time required for stationary phase
Answer:
(a) The total time required for all phases to occur
Question 13.
Which tissue is formed by process of de-differentiation?
(a) Intrafascicular cambium
(b) Secondary phloem
(c) Interfascicular cambium
(d) Secondary xylem
Answer:
(c) Interfascicular cambium
Question 14.
The example of environmental plasticity- heterophylly observed is ………………..
(a) Cotton
(b) Coriander
(c) Larkspur
(d) Buttercup
Answer:
(d) Buttercup
Question 15.
Synthesis of IAA takes place from amino acid ………………..
(a) Methionine
(b) Tryptophan
(c) Valine
(d) Aspartic acid
Answer:
(b) Tryptophan
Question 16.
Find the odd one out.
(a) IAA
(b) 2, 4-D
(c) NAA
(d) IBA
Answer:
(a) IAA
Question 17.
The selective herbicide is ………………..
(a) IBA
(b) GA3
(c) 2, 4 D
(d) NAA
Answer:
(c) 2, 4 D
Question 18.
This hormone promotes rooting in artificial method of cutting ………………..
(a) Gibberellin
(b) Auxin
(c) Cytokinin
(d) Dormin
Answer:
(b) Auxin
Question 19.
Chemically the peculiar structure of gibberellins is ……………….. ring.
la) pyrole ring
(b) purine ring
(c) gibbeane ring
(d) pyrimidine
Answer:
(c) gibbeane ring
Question 20.
First natural cytokinin was obtained from ……………….. by Letham.
(a) Maize grains
(b) Coconut milk
(c) Rice seedling
(d) Tomato
Answer:
(a) Maize grains
Question 21.
A low ratio of cytokinin to auxin induces ……………….. in plants.
(a) rooting
(b) shooting
(c) bud formation
(d) flowering
Answer:
(a) rooting
Question 22.
Apical dominance : Auxin : : Fruit ripening : ?
(a) Gibberellin
(b) Cytokinin
(c) Ethylene
(d) Abscissic acid
Answer:
(c) Ethylene
Question 23.
Which hormone is known as stress hormone ?
(a) Auxin
(b) Gibberellin
(c) Ethylene
(d) Abscissic acid
Answer:
(d) Abscissic acid
Question 24.
Abscissic acid is synthesised from ………………..
(a) Methionine
(b) Malic acid
(c) Mevalonic acid
(d) Mucin
Answer:
(c) Mevalonic acid
Question 25.
Photoperiodic response is because of pigment ………………..
(a) Cytochrome
(b) Phytochrome
(c) Anthocyanin
(d) Phycobilin
Answer:
(b) Phytochrome
Question 26.
The favourable temperature for vernalization is ………………..
(a) 1 to 6 °C
(b) 11 to 16 °C
(c) 10 to 16 °C
(d) – 1 to 1 °C
Answer:
(a) 1 to 6 °C
Question 27.
Identify the group of non-mineral elements needed by plants.
(a) PO4, CO3, SO4
(b) C, H, O
(c) N, P K
(d) C, H, N
Answer:
(b) C, H, O

Question 28.
The deficiency symptoms of these minerals are visible in young leaves ………………..
(a) Ca, CO
(b) S, P
(c) Ca, S
(d) Zn, Mg
Answer:
(c) Ca, S
Question 29.
The symptom chlorosis is observed as ………………..
(a) yellowing of leaf
(b) premature leaf fall
(c) malformation of leaf
(d) localized death of tissue
Answer:
(a) yellowing of leaf
Question 30.
…………….. is constituent of chlorophyll.
(a) Mn
(b) Mg
(c) Mo
(d) Fe
Answer:
(b) Mg
Question 31.
This is essential for O2 evolution in photosynthesis and for proper solute concentration
(a) Ca
(b) Cu
(c) Cl
(d) Co
Answer:
(c) Cl
Question 32.
For active absorption of mineral uptake, energy is supplied by ………………..
(a) respiration
(b) chemosynthesis
(c) photosynthesis
(d) transpiration
Answer:
(a) respiration
Question 33.
Cyanobacteria fix nitrogen in specialised cells called ………………..
(a) Velamen
(b) Haustoria
(c) Heteocysts
(d) Hormogonia
Answer:
(c) Heteocysts
Question 34.
In root nodule, symbiotic nitrogen fixer organism is ………………..
(a) Rhizopus
(b) Pseudomonas
(c) Rhizobium
(d) Nitrosomonas
Answer:
(c) Rhizobium
Question 35.
In plant body, amides are transported through ………………..
(a) sieve tubes
(b) xylem vessels
(c) phloem parenchyma
(d) plasmodesmata
Answer:
(b) xylem vessels
Question 36.
Building blocks of proteins are ………………..
(a) amides
(b) amino acids
(c) carboxylic acid
(d) nitrates
Answer:
(b) amino acids
Question 37.
Flowering plants Aster, Dahlia and Chrysanthemum are ………………..
(a) SDP
(b) LDP
(c) DNP
(d) SDP or LDP
Answer:
(a) SDP
Question 38.
Experimental material of Garner and Allard for discovery of photoperiodism was ………………..
(a) Cucumber and Tomato
(b) Dahlia and Aster
(c) Soybean and Tobacco
(d) Cabbage and Spinach
Answer:
(c) Soybean and Tobacco
Question 39.
Which of the following is used for the production of long seedless grapes ?
(a) Auxin
(b) Cytokinin
(c) Ethylene
(d) Gibberellin
Answer:
(d) Gibberellin
Question 40.
In vernalization, the cold stimulus is perceived by ………………..
(a) axillary bud
(b) floral bud
(c) leaves
(d) apical bud (shoot apex)
Answer:
(d) apical bud (shoot apex)
Question 41.
Xanthium is ………………..
(a) SDP
(b) LDP
(c) DNP
(d) not a flowering plant
Answer:
(a) SDP
Question 42.
Growth starts slowly during the ………………..
(a) lag phase
(b) exponential phase
(c) maturation phase
(d) stationary phase
Answer:
(a) lag phase
Question 43.
Cytokinins induce the formation of ………………..
(a) shoot apex
(b) intrafascicular cambium
(c) cork cambium
(d) interfascicular cambium
Answer:
(d) interfascicular cambium
Question 44.
Bakane disease in rice is associated with the discovery of ………………..
(a) cytokinins
(b) gibberellins
(c) auxins
(d) ethylene
Answer:
(b) gibberellins
Question 45.
ABA is also known as ………………..
(a) antitoxin
(b) antivirulent
(c) antioxidant
(d) antigibber ellin
Answer:
(d) antigibberellin
Question 46.
Gibberellins were first discovered from ………………..
(a) bacteria
(b) fungi
(c) algae
(d) gymnosperms
Answer:
(b) fungi
Question 47.
Which of the following is trace element?
(a) Mg
(b) Nitrogen
(c) Sulphur
(d) Mn
Answer:
(d) Mn

Question 48.
Which of the following is a macronutrient?
(a) Ca
(b) Mn
(c) Zn
(d) Mo
Answer:
(a) Ca
Question 49.
Nitrogen is an important constituent of ………………..
(a) carbohydrates
(b) sugars
(c) proteins
(d) polyphosphates
Answer:
(c) proteins
Question 50.
Deficiency of phosphorus causes ………………..
(a) stunted growth
(b) inward rolling of leaf margin
(c) brittle cell walls
(d) necrotic spots
Answer:
(a) stunted growth
Question 51.
Which of the following is not an essential element for plant?
(a) Sulphur
(b) Boron
(c) Iron
(d) Cadmium
Answer:
(d) Cadmium
Question 52.
…………….. is a constituent of middle lamella.
(a) Mg
(b) K
(c) Ca
(d) P
Answer:
(c) Ca
Match the columns
Question 1.
| Column A (Phase of growth) |
Column B (Condition) |
| (1) Lag phase |
(a) Growth rate faster |
| (2) Log phase |
(b) Growth rate steady state |
| (3) Stationary phase |
(c) Growth rate slow |
Answer:
| Column A (Phase of growth) |
Column B (Condition) |
| (1) Lag phase |
(c) Growth rate slow |
| (2) Log phase |
(a) Growth rate faster |
| (3) Stationary phase |
(b) Growth rate steady state |
Question 2.
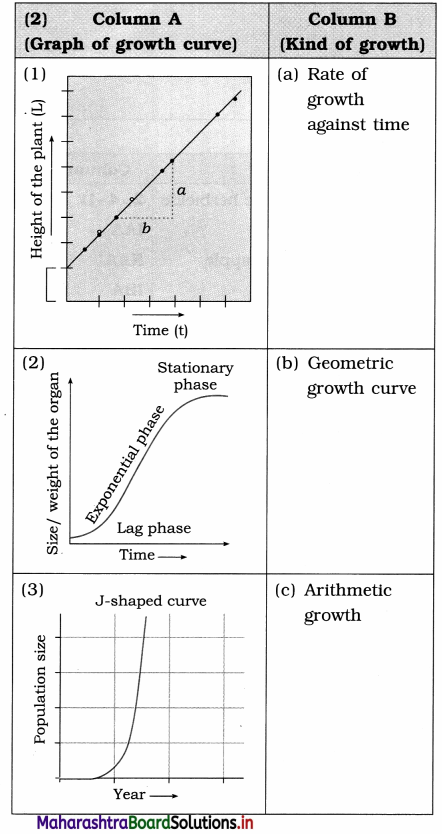
Answer:
(1) -(c) Arithmetic growth
(2) – (a) Rate of growth against time
(3) -(b) Geometric growth curve
Question 3.
| Column A |
Column B |
| (1) Use of measuring scale |
(a) Record of primary growth |
| (2) Crescograph |
(b) Increase in height of plant |
| (3) Auxanometer |
(c) Measure growth in field |
| (4) Horizontal microscope |
(d) Measurement of linear growth of shoot |
Answer:
| Column A |
Column B |
| (1) Use of measuring scale |
(b) Increase in height of plant |
| (2) Crescograph |
(a) Record of primary growth |
| (3) Auxanometer |
(d) Measurement of linear growth of shoot |
| (4) Horizontal microscope |
(c) Measure growth in field |
Question 4.
| Column A |
Column B |
| (1) Auxin |
(a) Bolting in rosette plants |
| (2) Cytokinin |
(b) Stimulate flowering in SDP |
| (3) Gibberellins |
(c) Promotion of growth of lateral buds |
| (4) Abscissic acid |
(d) Apical dominance |
Answer:
| Column A |
Column B |
| (1) Auxin |
(d) Apical dominance |
| (2) Cytokinin |
(c) Promotion of growth of lateral buds |
| (3) Gibberellins |
(a) Bolting in rosette plants |
| (4) Abscissic acid |
(b) Stimulate flowering in SDP |
Question 5.
| Column A |
Column B (Symptoms observed) |
| (1) Deficiency of Cu |
(a) Malformed leaves |
| (2) Deficiency of Bo |
(b) Leaves with yellow edges |
| (3) Deficiency of Zn |
(c) Brown heart disease |
| (4) Deficiency of K |
(d) Die back of shoot |
Answer:
| Column A |
Column B (Symptoms observed) |
| (1) Deficiency of Cu |
(d) Die back of shoot |
| (2) Deficiency of Bo |
(c) Brown heart disease |
| (3) Deficiency of Zn |
(a) Malformed leaves |
| (4) Deficiency of K |
(b) Leaves with yellow edges |
Question 6.
| Column A |
Column B (Organisms) |
| 1. Symbiotic nitrogen fixation |
a. Nitrobacter |
| 2. Denitrification |
b. Cyanobacteria |
| 3. Free living nitrogen fixers |
c. Rhizobium |
| 4. Nitrification |
d. Paracoccus |
Answer:
| Column A |
Column B (Organisms) |
| 1. Symbiotic nitrogen fixation |
c. Rhizobium |
| 2. Denitrification |
d. Paracoccus |
| 3. Free living nitrogen fixers |
b. Cyanobacteria |
| 4. Nitrification |
a. Nitrobacter |
Classify the following to form Column B as per the category given in Column A.
Question 1.
Classify the given plant growth regulators as per their specific control of event in plant life cycle in Column A and complete Column B.
(IAA, GA, Cytokinin, Abscissic acid)
| Column A |
Column B |
| (1) Shedding of leaves |
————- |
| (2) Induce flowering in LDP |
———— |
| (3) Apical dominance |
————- |
| (4) Induce RNA synthesis |
————- |
Answer:
| Column A |
Column B |
| (1) Shedding of leaves |
Abscissic acid |
| (2) Induce flowering in LDP |
GA |
| (3) Apical dominance |
IAA |
| (4) Induce RNA synthesis |
Cytokinin |

Question 2.
Classify the given specific effects of different types of auxins in Column A and complete Column B with the examples.
(IAA, NAA, 2, 4-D, IBA, 2, 4, 5-T)
| Column A |
Column B |
| (1) Selective synthetic herbicide |
————- |
| (2) Seedless fruits |
———— |
| (3) Flowering in pineapple |
————- |
| (4) Synthetic auxin |
————- |
| (5) Agent orange |
———— |
Answer:
| Column A |
Column B |
| (1) Selective synthetic herbicide |
2, 4-D |
| (2) Seedless fruits |
IAA |
| (3) Flowering in pineapple |
NAA |
| (4) Synthetic auxin |
IBA |
| (5) Agent orange |
2, 4, 5 – T |
Question 3.
Classify the given plant hormones as their specific effect observed in plants in Column A and complete Column B.
(ABA, GA, Ethylene, Kinetin)
| Column A |
Column B |
| (1) Bolting of rosette plants |
————- |
| (2) Epinasty |
———— |
| (3) Closure of stomata |
————- |
| (4) Proliferation of callus |
————- |
Answer:
| Column A |
Column B |
| (1) Bolting of rosette plants |
GA |
| (2) Epinasty |
Ethylene |
| (3) Closure of stomata |
ABA |
| (4) Proliferation of callus |
Kinetin |
Question 4.
Classify the given disease to their cause given in Column B.
(Ethylene, GA, Deficiency of BO, Deficiency of Cu)
| Column A |
Column B |
| (1) Brown heart disease |
————- |
| (2) Bakane disease of Rice |
———— |
| (3) Die back of shoot |
————- |
| (4) Degreening of Banana |
————- |
Answer:
| Column A |
Column B |
| (1) Brown heart disease |
Deficiency of BO |
| (2) Bakane disease of Rice |
GA |
| (3) Die back of shoot |
Deficiency of Cu |
| (4) Degreening of Banana |
Ethylene |
Question 5.
Classify the given organisms related to Nitrogen cycle in Column B.
[Nitrobacter, Rhizobium, Pseudomonas, Nitrosococcus)
| Column A |
Column B |
| (1) Symbiont in root nodule |
————- |
| (2) Conversion of nitrite to nitrate |
———— |
| (3) Denitrification process |
————- |
| (4) Conversion of ammonia to nitrite |
————- |
Answer:
| Column A |
Column B |
| (1) Symbiont in root nodule |
Rhizobium |
| (2) Conversion of nitrite to nitrate |
Nitrobacter |
| (3) Denitrification process |
Pseudomonas |
| (4) Conversion of ammonia to nitrite |
Nitrosococcus |
Very short answer questions
Question 1.
Enlist the types of meristems that we observe in plants.
Answer:
In plants, there are apical, intercalary and lateral meristems.
Question 2.
Give characteristic features of meristematic cells.
Answer:
Meristematic cells are thin walled, non- vacuolated with prominent nuclei having granular cytoplasm and are capable of cell division.
Question 3.
What is the role of oxygen in growth?
Answer:
Oxygen is required for respiration of cells and release of energy for the process of growth.
Question 4.
What is the role of water for growth?
Answer:
Water maintains turgidity of the cell and is chief component of protoplasm as well as it is a medium for various biochemical reactions.
Question 5.
Mention the mathematical formula for rate of absolute growth.
Answer:
Absolute Growth Rate = AGR = \(\frac { dn }{ dt }\) where dn is cell number and dt is time interval.
Question 6.
What is exponential phase of growth curve?
Answer:
In exponential phase or log phase, growth rate is faster. It accelerates and reaches its maximum.
Question 7.
Is there any relation between phases of growth and regions of growth curve?
Answer:
Yes, there is relation between the two as initially growth is slow, which accelerates and ultimately it slows down and becomes steady which is observed in growth curve.
Question 8.
Which plant organ does show both arithmetic and geometric growth?
Answer:
Embryo that develops from zygote inside the seed shows initially the growth which is geometric and later on arithmetic.

Question 9.
Describe the example of plasticity related to internal stimuli.
Answer:
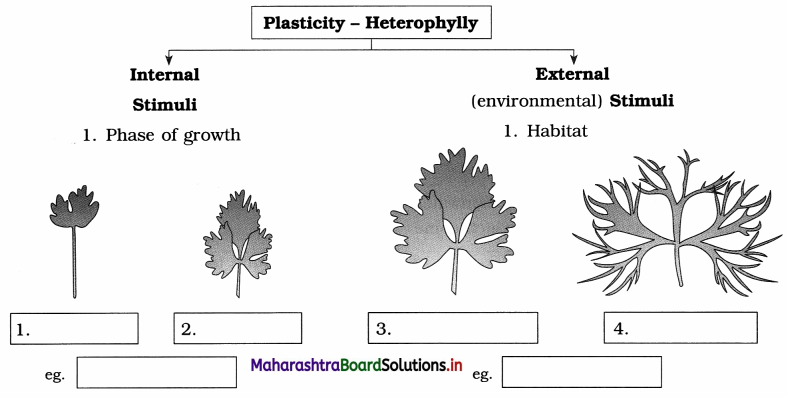
In plants like cotton, coriander and larkspur heterophylly is observed where leaves in juvenile stage and adult stage show different forms.
Question 10.
What is the role of growth hormones in plants?
Answer:
Growth hormones inhibit, promote or modify the growth in plants.
Question 11.
What is the peculiarity of growth hormones ?
Answer:
Growth hormones are needed in very small amount to evoke the response and they act at a site away from their place of production.
Question 12.
Which is the first hormone to be discovered in plants?
Answer:
Auxin IAA i.e. Indole acetic acid is the first hormone to be discovered in plants.
Question 13.
Give the full form of 2, 4 – D.
Answer:
It is synthetic auxin 2, 4-dichlorophenoxy acetic acid.
Question 14.
What is the effect of NAA and 2, 4-D foliar spray?
Answer:
Foliar spray of synthetic hormones induce flowering in plants litchi and pineapple and prevent premature fruit drop in apples, pear and oranges.
Question 15.
How cytokinins control apical dominance ?
Answer:
Cytokinins promote growth of lateral buds by cell division and thus control apical dominance.
Question 16.
What was the discovery of Richmond and Lang?
Answer:
Richmond and Lang discovered that cytokinins delay the process of ageing and senescence, abscission in plant organs.
Question 17.
What is ‘epinasty’?
Answer:
It is an effect of ethylene where it causes drooping of leaves and flowers.
Question 18.
Why is auxin called a growth regulator?
Answer:
Auxin is synthesized at meristematic region of plants and it controls cell enlargement, cell elongation and stimulates growth of stem and root, apical dominance. Hence it is growth promoting hormone.
Question 19.
What is effect of gibberellin application on apple?
Answer:
Gibberellin causes parthenocarpy in apple.
Question 20.
How can we overcome apical dominance?
Answer:
By application of cytokinin we can overcome apical dominance effect.
Question 21.
Which is standard bioassay method for auxins?
Answer:
Avena curvature test/Avena coleoptile test is a standard bioassay method for auxins.
Question 22.
ABA is called as stress hormone why?
Answer:
Answer: ABA induces dormancy in seeds by inhibiting growth. Thus plants can tide over adverse environmental conditions. Hence it is called as stress hormone.
Question 23.
What was the plant material for study of photoperiodism by Garner and Allard?
Answer:
The flowering response of Soybean and Maryland mammoth variety of tobacco was studied by Garner and Allard.
Question 24.
What is photomorphogenesis?
Answer:
Control of morphogenesis by light and phytochrome pigment is called photomorphogenesis.
Question 25.
What is critical concentration of minerals ?
Answer:
The concentration of the essential elements below which plant growth is retarded is termed as critical concentration.
Question 26.
What is a role of Sulphur in plants?
Answer:
Sulphur is constituent of amino acids, proteins, vitamins (mainly thaimine, biotin CoA) and Ferredoxin.
Question 27.
What is a role of nitrogen in plants?
Answer:
Nitrogen is constituent of amino acids, proteins, nucleic acid, vitamins, hormones, coenzymes, ATP and chlorophyll molecule.
Question 28.
Which is the process by which mainly we get nitrogen in human tissues?
Answer:
Industrial nitrogen fixation by Haber – Bosch Nitrate process is responsible for nitrogen found in human tissues.
Question 29.
Give equation of Haber – Bosch process.
Answer:


Question 30.
What is nitrogen assimilation?
Answer:
Nitrogen present in the soil as nitrates, nitrites and ammonia is absorbed by plants and converted into nitrogenous organic compounds is nitrogen assimilation.
Give definitions of the following
Question 1.
Growth
Answer:
Growth can be defined as permanent, irreversible increase in the bulk of an organism with change in form.
Question 2.
Efficiency index
Answer:
The increased growth per unit time is called efficiency index.
Question 3.
Absolute growth rate (AGR)
Answer:
The measurement and comparison of total growth per unit time is called absolute growth rate.
Question 4.
Relative growth rate (RGR)
Answer:
The growth of a particular system per unit time expressed on a common basis or alternately it is the ratio of growth in the given time per initial growth.
Question 5.
Differentiation
Answer:
A permanent change in structure and function of cells that leads to their maturation is called differentiation.
Question 6.
Redifferentiation
Answer:
When cells produced from de-differentiation lose their capacity to divide and mature for specific function it is known as re-differentiation.
Question 7.
Development
Answer:
The progressive changes in shape, form and degree of complexity which includes growth, maturation and morphogenesis is referred as development.
Question 8.
Growth Hormone or Growth regulators
Answer:
The internal factors that influence growth by inhibiting, promoting or modifying it are called growth hormones or regulators.
Question 9.
Apical dominance
Answer:
In higher plants growing apical bud inhibits the growth of lateral buds. This is known as apical dominance.
Question 10.
Critical photoperiod
Answer:
That length of photoperiod above or below which the plant shows flowering is critical photoperiod.
Question 11.
Photomorphogenesis
Answer:
The control of morphogenesis of plants by light and phytochrome is photomorphogenesis.
Question 12.
Symptom or hunger sign
Answer:
Any visible deviation from the normal structure and function of the plant is called symptom or hunger sign.
Question 13.
Active absorption of minerals
Answer:
Uptake of mineral ions against concentration gradient, with expenditure of energy (ATP) is called active absorption.
Question 14.
Nitrogen fixation
Answer:
Free nitrogen of air N2 is converted to nitrogenous salts so that it is made available to plants is called nitrogen fixation.
Question 15.
Nitrification
Answer:
Soil microbes, mainly : chemoautotrophs convert ammonia into j nitrate, the form of nitrogen which can be used by plants, this process is nitrification.
Question 16.
Amidation
Answer:
Ammonia may be absorbed by amino acids to produce amides. This process is called amidation.
Name the following
Question 1.
Instrument developed by Indian physiologist to measure growth.
Answer:
Crescograph developed by Sir J.C. Bose.
Question 2.
Instrument to measure linear growth of shoot.
Answer:
Auxanometer.
Question 3.
Type of growth curve for geometric growth.
Answer:
J-shaped or exponential growth curve.
Question 4.
The process by which cork cambium is formed.
Answer:
Dedifferentiation.

Question 5.
Ability of plant to form different kinds of structures.
Answer:
Plasticity.
Question 6.
Condition where plant exhibits different types of leaves on same plant.
Answer:
Heterophylly.
Question 7.
Growth promoter hormones.
Answer:
Auxins, gibberellins and cytokinins.
Question 8.
Growth inhibitors of plants.
Answer:
Ethylene and abscissic acid.
Question 9.
First hormone that is discovered in plant and its precursor.
Answer:
Amino acid tryptophan is precursor of Indole acetic acid (IAA).
Question 10.
A synthetic hormone that acts as selective herbicide.
Answer:
2, 4 – D (dichlorophenoxy acetic acid).
Question 11.
A plant hormone discovered from fungus.
Answer:
Gibberellic acid (GA).
Question 12.
A plant hormone also present in fish (Herring) sperm DNA.
Answer:
Kinetin (cytokinin).
Question 13.
A plant hormone also present in urine of person suffering from Pellagra.
Answer:
Auxin.
Question 14.
Most widely used source of ethylene for fruit ripening.
Answer:
Ethephon – 2 chloroethyl phosphoric acid.
Question 15.
A precursor from which GA and ABA are synthesized.
Answer:
Mevalonic acid.
Question 16.
Plant antitranspirant.
Answer:
Abscissic acid.
Question 17.
Chemical stimulant of low temperature effect on flowering of plants.
Answer:
Vernalin.
Question 18.
Methods of synthesis of amino acids.
Answer:
Reductive animation and Transamination.
Question 19.
Common amides present in plants.
Answer:
Asparagine and Glutamine.
Question 20.
Nitrogen fixing prokaryotic organisms.
Answer:
Diazotrophs or Nitrogen fixers.
Question 21.
Special structures of cyanobacteria where N2 fixation occurs.
Answer:
Heterocysts.
Question 22.
A synthetic cytokinin hormone.
Answer:
6 – benzyl adenine.
Give Functions/Significance/Importance of the following
Question 1.
Meristems
Answer:
In plants meristems are situated at specific regions where growth takes place by constant and continuous addition of new cells. Meristems have capacity to divide (Mitotic divisions).
Question 2.
Synthetic auxin 2, 4-D
Answer:
It is selective herbicide which kills dicot weeds and foliar spray of 2, 4-D induces flowering in litchi and pineapple, prevents premature fruit drop in apples, pear, oranges.
Question 3.
Coconut milk
Answer:
Coconut milk contains natural cytokinin substance kinetin which is used as nutritional supplement for callus tissue culture where proliferation is noticed due to promotion of cell division.
Question 4.
Ethylene/Ethephon
Answer:
It is used for fruit ripening and as it causes degreening effect by increasing activity of chlorophyllase enzyme for banana and citrus fruits.
Question 5.
Abscissic acid/ABA
Answer:
It is natural growth inhibiting substance in plants and it acts as plant anti Iranspirant causing closure of stomata. It is stress hormone that induces plant to bear the adverse environmental conditions like drought.
Question 6.
Phytochrome
Answer:
It is a proteinaceous pigment present in leaves which perceives stimulus of light for flowering. As it is interconvertible in two forms, it promotes flowering in SDP and inhibits flowering in LDE.

Question 7.
Vernalization
Answer:
It is response of flowering to low temperature treatment which helps in cultivation of crops in regions where they do not occur naturally and also crops can be produced earlier.
Question 8.
Nitrogen cycle
Answer:
Nitrogen is essential macronutrient for plant growth, it is constituent of amino acids, proteins, nucleic acids, vitamins, hormones, ATP coenzymes, chlorophyll molecule. It is limiting nutrient for plant productivity and agricultural ecosystem. Through food chain it moves to consumers, i.e. animals and decomposers.
Distinguish between the following
Question 1.
Phase of cell division and Phase of cell enlargement
Answer:
| Phase of cell division |
Phase of cell enlargement |
| 1. In this phase cells of meristems divide by mitotic division. |
1. In this phase newly formed cells become vacuolated and turgid, osmotically active. |
| 2. Rate of growth at slow pace. |
2. Rate of growth at accelerated pace. |
| 3. This is described as lag phase. |
3. This is described as log phase. |
| 4. There is no synthesis of any new material. |
4. Synthesis of new wall materials and other materials takes place. |
Question 2.
Long day plants and Short day plants
Answer:
| Long day plants |
Short day plants |
| 1. Plants that flower only when they are exposed to light period longer than their critical photoperiod are called long day plants (LDP). |
1. Plants that flower only when they are exposed to light period shorter than the critical photoperiod are called short day plants (SDP). |
| 2. The plants usually flower in summer. |
2. The plants usually flower in winter or late summer. |
| 3. These plants require short night period for flowering. Hence, they are also known as short night plants. |
3. These plants require long night period for flowering. Hence, they are also known as long night plants. |
| 4. Plants such as Pea, Radish, Sugar, Beet, Cabbage, Spinach, Wheat, poppy are LDP |
4. Plants such as Dahlia, Aster, Tobacco, Chrysanthemum, Soybean (Glycine max) Cocklebur (Xanthium) are SDP |
Question 3.
Passive absorption of Minerals and Active absorption of minerals
Answer:
| Passive absorption of minerals |
Active absorption of minerals |
| 1. The movement of mineral ions into root cells due to diffusion, without expenditure of energy is called passive absorption. |
1. The uptake of mineral ions by root cells that requires expenditure of ATP energy is known as active absorption. |
| 2. The movement is according to concentration gradient. |
2. The movement of mineral ions is against concentration gradient. |
| 3. It takes place by direct ion exchange, diffusion, indirect ion exchange – mass flow and Donnan equilibrium. |
3. It takes place by mineral ion accumulation in root hair and carrier concept. |
Given reasons
Question 1.
Water is essential for growth in plants.
Answer:
- Meristematic cells divide and form new cells.
- Absorption of water is necessary for maintaining turgidity in the newly formed cells.
- Turgidity results in enlargement of cells in phase of cell elongation.
- Water is essential component of protoplasm of cells.
- biochemical reactions. Therefore it is essential for growth in plants.
Question 2.
2, 4-D is used as herbicide.
Answer:
- 2, 4-D is a synthetic auxin which kills dicot weeds.
- Our most of the food crops are cereals, i.e. monocot plants.
- Weeds are unwanted plants which otherwise lower the productivity hence to kill them. Selective herbicide is used.
Question 3.
In morphogenesis of plants cytokinin auxin ratio is important.
Answer:
- Auxins and cytokinins are growth promoting substances which stimulate cell division and cell enlargement.
- A high cytokinin promotes shooting in plants.
- A low ratio of cytokinin to auxin induces root development.
- A high ratio of cytokinin to auxin induces growth of buds and shoot development.
- Thus cytokinin and auxin ratio and their interactions control morphogenesis in plants.
Question 4.
ABA is described as an antitranspirant.
Answer:
- ABA is a growth inhibiting hormone.
- ABA is responsible for causing efflux of K+ ions from guard cells of stomata.
- As a result of this, osmotic changes occur and guard cells become flaccid resulting in closure of stomata.
- Transpiration mainly occurs through open stomata and due to closure the activity is checked. Hence it is described as antitranspirant.
Question 5.
Some deficiency symptoms of mineral are visible in young leaves while some appear in older leaves.
Answer:
- When mineral element is present below a certain critical concentration it is said to be deficient.
- Symptoms are indicated in the form of certain morphological changes on the mobility of element.
- These symptoms depend on the mobility of element inside the plant body.
- When the element is relatively immobile like S, Ca then the symptoms appear first in young leaves.
- When the elements are actively mobilised inside plant body, they are transported to young tissues then the symptoms are visible in older, i.e. senescent leaves e.g. N, Mg, K.
Question 6.
In Donnan equilibrium of passive absorption of minerals concentration of cations increases inside the cell.
Answer:
- Minerals exist in soil in the form of charged particles.
- Certain negatively charged (anions) get accumulated on the inner side of cell membrane after their entry inside cell.
- These anions cannot diffuse out through semipermeable cell membrane.
- Thus additional mobile cautions are needed inside the cell to balance these fixed anions.
- Hence, the concentration of cations increases inside the cell.
Question 7.
A sudden drop in active absorption of minerals is noticed if roots are deprived of oxygen supply.
Answer:
- Absorption of mineral ions from soil against concentration gradient is known as active absorption.
- It requires energy (ATP) for absorption by absorbing root cell.
- The source of energy is respiration of cells for supply of ATE
- When the roots are deprived of oxygen, their respiration process is affected and thus energy is not supplied in required amount. Hence, a sudden drop in absorption of minerals is noticed.
Question 8.
Nitrogen is a limiting nutrient in the agricultural system.
Answer:
- Nitrogen is a major nutrient for plant growth.
- Proper carbon/nitrogen ratio in soil is necessary for plant growth.
- It is component of proteins in the form of amino acids.
- Proteins are synthesised from photosynthetic products sugars.
- Nitrogen exists in atmosphere but it is inert, non-reactive.
- Plants need nitrogen in a reactive form usually nitrate in soil.
- This supply need to be maintained through biological and physical nitrogen fixation.
- Otherwise productivity is affected hence it is limiting nutrient in the agricultural ecosystem.
Question 9.
Cucumber and sunflower are regarded as photoneutral plants.
Answer:
- In cucumber and sunflower, the flower is not controlled by light period.
- Both these plants flower in all light periods.
- Cucumber and sunflower, therefore, are regarded as photoneutral plants.
Write short notes on the following
Question 1.
Meristems
Answer:
- In vascular plants, growth is indeterminate and occurs at specific regions where meristems are located.
- Meristems are of three types based on their location – apical, intercalary and lateral.
- Meristems are thin walled cells with prominent nucleus with granular cytoplasm, non-vacuolated.
- Mitotic divisions take place in meristematic cells.
Question 2.
Phase of cell formation
Answer:
- Formative phase is the first phase of growth.
- During this phase, the meristematic cells undergo mitosis to form new cells.
- During formative phase, the rate of growth is slow.
- The phase of cell formation is also called lag phase.
- This phase is also known as phases of cell division.
Question 3.
Development
Answer:
- Development is progressive changes taking place in shape, form and degree of complexity in an organism.
- In plants, it includes all the changes taking place in sequence from seed germination to senescence or death of plant.
- Development is an orderly process.
- It includes growth, morphogenesis, maturation and senescence.
Question 4.
Plasticity
Answer:
- Plasticity is the capacity of plant being molded or formed.
- It is ability of plant to develop different kinds of structures in response to environmental factors or stimuli.
- Different kinds of structures can be developed in plants due to internal stimuli in different phases, i.e. juvenile and adult.
- Heterophylly is shown in plant in different phases or in different environmental conditions.
- In coriander and cotton plants, two different kinds of leaves are observed in young (juvenile) and mature (adult) plant.
- In buttercup, two different kinds of leaves are observed in terrestrial (on land) and aquatic (in water) habitat.
Question 5.
Phytohormones/Plant Growth Regulators
Answer:
- Phytohormones or plant growth regulators are internal factor that influence growth.
- They inhibit, promote or modify the plant growth.
- Plant hormones are organic substances produced naturally in plants and required in small amount.
- Their place of production and site of the activity are different.
- Auxins, gibberellins, cytokinins are growth promoters and ethylene, abscissic acid are growth inhibitors.
Question 6.
Phytochrome
Answer:
- These are proteinaceous pigments present
- Phytochrome exists in two interconvertible forms. Pr and Pfr.
- Phytochromes are located in cell membranes of chlorophyllous cells.
- When Pfr absorbs red light it is converted to Pr.
- Pfr is accumulated in plants during daytime and inhibits flowering in SDP but initiates flowering in LDP
Question 7.
Venralization
Answer:
- Effect of temperature on flowering of plants is known as vernalization.
- For inducing early flowering pretreatment of seeds or seedlings is done at 1 to 6 °C for about a months duration.
- Shoot apical meristem is believed to be site of vernalization stimulus.
- Vernalization stimulus is in a form of chemical named vernalin.
- Vernalization is effective in ereals (wheat) and crucifers.

Question 8.
Apical dominance
Answer:
- The presence of apical bud inhibits the growth of lateral buds. This phenomenon in which the apical (terminal) bud is active and lateral buds remain inactive is called apical dominance.
- It is believed that apical dominance is controlled by an auxin which is synthesized in the apical bud.
- From the apical bud, the auxin migrates to the lateral buds and inhibits their growth.
- When apical bud is removed, the lateral buds grow and form branches.
- For producing more branches therefore, the apical buds are removed.
- Cytokinins reverse apical dominance effect by promoting growth of lateral buds by cell division.
Question 9.
Toxicity of micronutrients or mineral toxicity
Answer:
- Micronutrients are required in minute quantities by plants.
- Their moderate decrease causes deficiency symptoms while their moderate increase causes toxicity.
- The reduction in dry weight of a tissue by 10% by any mineral is known as toxicity.
- It is not easy to identify toxicity symptoms.
- Most of the time, the excess of an element inhibits the uptake of another element resulting in causing the deficiency symptom of that element.
- Manganese inhibits calcium translocation towards apex of stem and exhibits symptoms of chlorosis with grey spots appearing on leaves.
- This is because manganese competes with iron and magnesium for uptake.
- Therefore what we see as symptoms of manganese toxicity, may be the deficiency symptoms of Fe, Mg and Ca.
Question 10.
Day neutral plants (DNP)
Answer:
- Day neutral plants are those in which flowering is not affected by the duration of the light period.
- Day neutral plants flower in all photoperiods.
- Day neutral plants are also known as photoneutral or intermediate plants.
- Plants such as cucumber, shoe-flower, sunflower, tomato, maize, balsam, etc. are day neutral plants.
Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What is de-differentiation?
Answer:
- The differentiated cells which are formed may again gain the capacity to divide as per need.
- Permanent cells (mature cells) undergo de-differentiation and become meristematic.
- This acquired feature of living permanent cells is known as de-differentiation.
- e.g. Formation of interfascicular cambium and cork cambium from parenchyma cells of medullary rays and outer cortical cells respectively.
Question 2.
Discuss about natural Auxin.
Answer:
- F.W. Went named the growth promoting substance as Auxin.
- Auxin was also isolated from urine of patient of pellagra.
- Indole 3 acetic acid was first hormone discovered in plants.
- IAA is most common and natural hormone synthesized at growing tips and responsible for cell elongation.
- It is synthesized from tryptophan and shows polar transport – Basipetal transport.
Question 3.
Discuss about discovery of Gibberellins.
Answer:
- Gibberellins are growth promoting hormones and were isolated form fungus Gibberella Jujikuroi by Kurasawa.
- Rice plants when infected with this fungus show stem elongation i.e. Bakane disease.
- Yabuta and Sumuki isolated gibberellins in crystalline form, from fungal culture and named it gibberellins.
- Gibberellins are synthesized from mevalonic acid at young leaves, seeds, root and stem tips and show non-polar transport.
Question 4.
Discuss about discovery of cytokinin.
Answer:
- Cytokinins are growth promoting hormones that stimulate cell division.
- Skoog and Miller discovered first cytokinin when they were investigating nutritional requirements of tobacco callus culture.
- It was observed that the callus proliferated when there was addition of coconut milk as supplement.
- The degraded sample of herring (fish) sperm DNA also showed similar growth of tobacco callus. They named the substance as kinetin.
Question 5.
Discuss about discovery of abscissic acid.
Answer:
- Abscissic acid (ABA) is a natural growth inhibiting hormone.
- It was observed by Carns and Addicott that shedding of cotton balls occur due to chemical substance abscission I and II.
- From the buds of Acer, Wareing isolated substance that causes bud dormancy and named it as dormin.
- These two chemical substances were identical and now known as abscissic acid.
- ABA is synthesized in leaves, fruits and seeds from mevalonic acid.
Question 6.
What is day neutral plant (DNP)? Give any two examples.
Answer:
- The plants which do not require specific duration of light period or dark period flowering are day neutral plants (DNP).
- They flower throughout the year, as they do not need specific photoperiod.
- The flowering in these plants is independent of photoperiod.
- Examples – cucumber, tomato, cotton, sunflower, maize and balsam.
Question 7.
Discuss about discovery of phytochromes.
Answer:
- Phytochromes are proteinaceous pigments present in cell membrane of green cells.
- Phytochromes receive photoperiodic stimulus and induce flowering in plants in response to light duration.
- Hendrick and Borthwick observed that in SD plants flowering is inhibited if dark period is interrupted by flash of red light (660 nm).
- If flash of far red light (730 nm) is given then again flowering is observed in SD plants.
- Pigment system of plant receives photoperiodic stimulus and these pigments exist in two interconvertible forms Pfr and Pr
Question 8.
What is mineral nutrition of plants?
Answer:
- Plants require inorganic materials for the synthesis of food.
- These elements are obtained by plants in the form of minerals mainly form soil.
- Chemical analysis of plant ash reveals that about 40 different minerals are needed by plants which are taken from surroundings, (air, soil and water)
- These minerals are absorbed in dissolved form, i.e. ionic form through root system mainly root hairs.
- Some minerals are required in large amounts (major) while some are needed only in traces or small amounts (minor).
Question 9.
What are symptoms of mineral deficiency in plants?
Answer:
Any visible deviation from the normal structure and function of plants due to lack or unavailability of particular element below its critical concentration is deficiency symptom of that mineral element.
The common symptoms observed in plants are as follows:
- Stunting : Retarded growth and thus stem appears short and condensed.
- Chlorosis : This is loss or lack of chlorophyll that result in yellowing of leaf.
- Necrosis : It is localized death of tissue. Mottling : This is appearance of green or non-green patches or spots on leaves. Abscission : This is premature fall of leaves, buds, fruits and flowers.
Question 10.
Enlist the role of following minerals and the symptoms caused due to their deficiency : (a) Calcium (b) Boron and (c) Chlorine.
Answer:
(a) Calcium:
Role : Involved in selective permeability of cell membranes, activator of certain enzymes, required as calcium pectate in middle lamella of cell wall at root and stem apex (for cell division).
Deficiency symptom : stunted growth.
(b) Boron:
Role : Required for uptake and utilization of Calcium (Ca2+), pollen germination, cell differentiation, carbohydrate translocation. Deficiency symptom : Brown heart disease
(c) Chlorine:
Role : Na+ and K+ help to determine solute concentration and anion – cation balance in cells, necessary for oxygen evolution in photosynthesis.
Deficiency symptom : Poor growth of plant.
Question 11.
What is Donnan Equilibrium?
Answer:
- Donnan equilibrium is a process of passive absorption of minerals in plants which is without any expenditure of energy.
- It is assumed that certain anions after their entry by diffusion into the cell get fixed on inner side of cell membrane.
- Additional mobile cations are needed to balance this fixed anions as they cannot diffuse outside.
- Concentration of cations thus increases due to accumulation.
- This passive absorption of anions or cations from exterior against their concentration gradients so as to neutralize the effect of cations or anion is known as Donnan equilibrium.
Question 12.
Explain physical nitrogen fixation.
Answer:
- Conversion of free nitrogen of air into nitrogenous compounds that are made available to plants for uptake is known as : nitrogen fixation.
- Physical nitrogen fixation occurs in step- : wise manner and it takes place in atmosphere j and soil.
- Under the influence of electric discharge, lightning and thunder, atmospheric nitrogen combines with oxygen to form nitric oxide.
- Nitric oxide is then oxidized to nitrogen peroxide in presence of oxygen.
- Nitrogen peroxide combines with rainwater to form nitrous and nitric acid which come on ground as acid rains.
- On ground, alkali radicals (mainly of Ca, K) react with nitric acid to produce nitrites and nitrates which are absorbable forms for plants.

Question 13.
Give equations of physical nitrogen fixation.
Answer:
(1) Physical nitrogen fixation occurs in stepwise manner in atmosphere and on land (soil)

Question 14.
Give the equations of amino acid synthesis.
Answer:
1. Macromolecule proteins are made up of building blocks of amino acids.
2. Amino acids are synthesized by two methods – Reductive animation and transamination.
3. Reductive amination – Ammonia reacts with alpha keto glutaric acid to form glutamic acid.
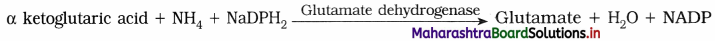
4. Transamination – Amino group of one amino acid is transferred to other carboxylic acid at keto position.
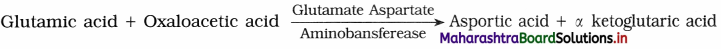
Question 15.
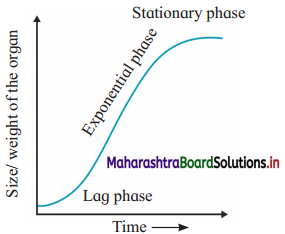
Explain lag phase, log phase and steady phase of growth.
Answer:
1. In plants, growth curve is always sigmoid, i.e. S-shaped. This is because growth starts slowly during formative phase, becomes rapid during elongation phase and finally slows down to a steady state during the maturation phase.
2. The standard growth curve shows three phases, viz. lag phase, log phase and stationary phase.
(i) Lag phase or initial growth phase : This is the initial phase of growth. During this phase of growth, the rate of growth is slow. It corresponds to formative phase of growth where new cells are formed due to cell division.
(ii) Log phase or exponential phase : This is the second phase of growth. During this phase, the growth is rapid and maximum. It corresponds to the phase of cell elongation.
(iii) Stationary phase or steady phase : The stationary phase is the third and last phase of growth. In this phase, growth slows down and becomes steady. The cells undergo differentiation during stationary phase.
Chart based or Table based questions
Question 1.
Complete the chart of plasticity.
Answer:

Question 2.
Complete the flow chart of development.
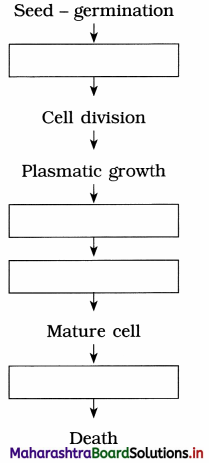
Answer:
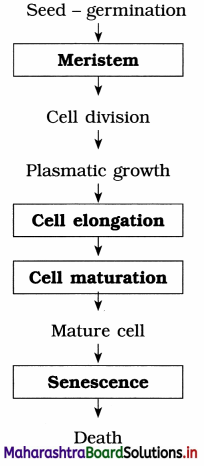
Question 3.
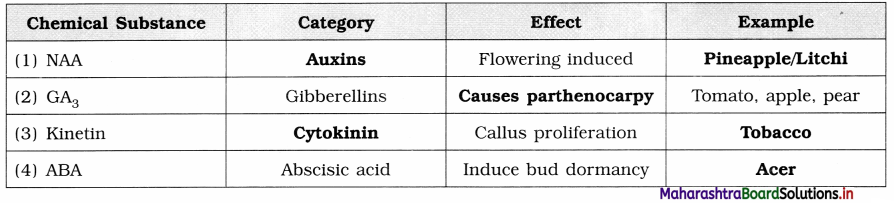
Complete the table of growth hormones.
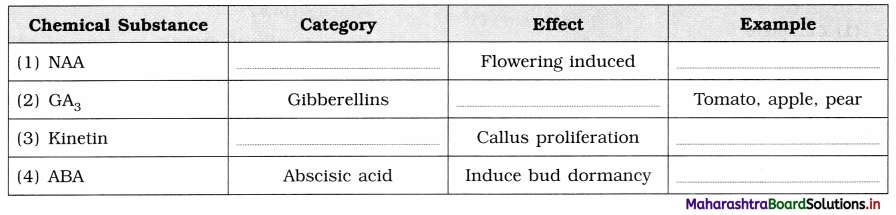
Answer:
Question 4.
Complete the table of mineral nutrition of plants.
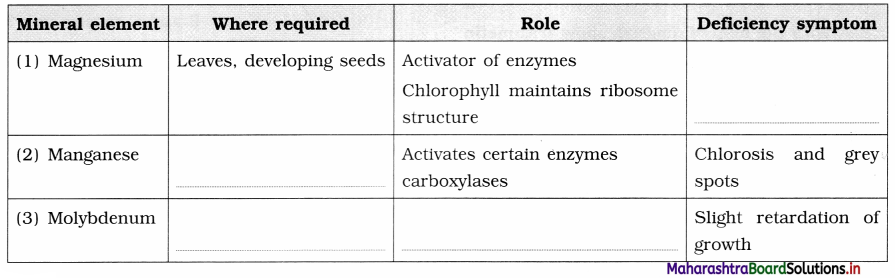
Answer:
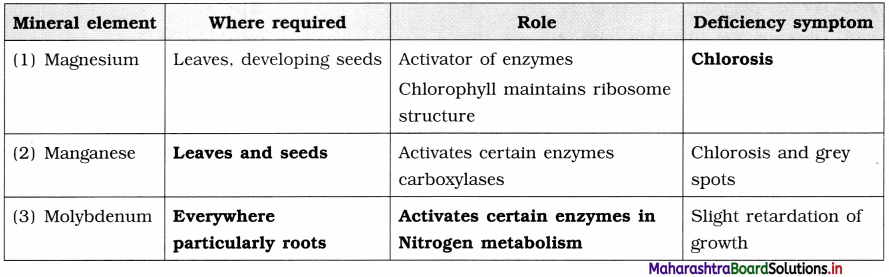
Diagram based questions
Question 1.
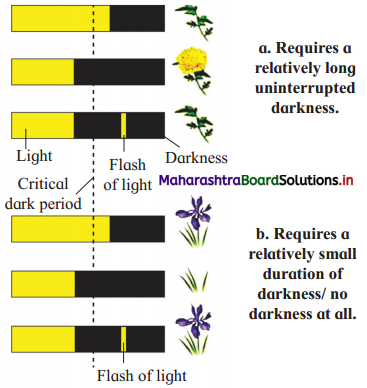
Draw diagram of photoperiodic response of SDP and LDP.
Answer:
Question 2.
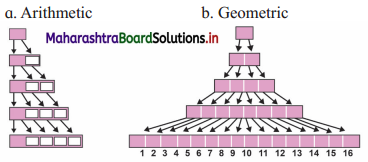
With the help of diagram show arithmetic growth and geometric growth.
Answer:
Question 3.
Draw the sigmoid growth curve.
Answer:
Question 4.
Observe the diagram and answer the questions related to it.
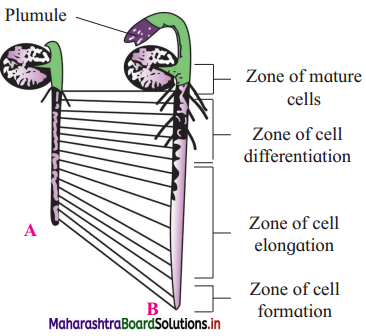
- From which cells newly formed cells are added? How?
- How is rate of growth in zone of cell elongation?
- What is peculiarity of zone of differentiation? How is rate of growth in this region?
Answer:
- Meristematlc cells add new cells by mitotic division.
- Rate of growth is at accelerated pace.
- The rate of growth is at steady state and cells become specialised to perform specific function become mature.
Question 5.
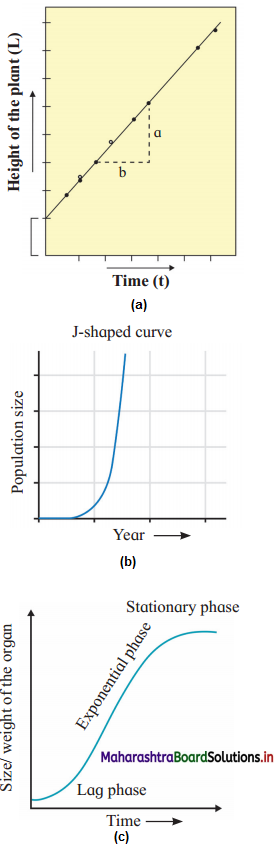
Observe the adjacent graph indicating growth. What is correct labelling of A, B and C respectively?
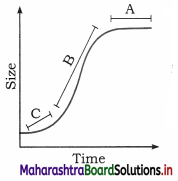
Answer:
A. Stationary Phase
B. Exponential Phase
C. Lag Phase

Question 6.
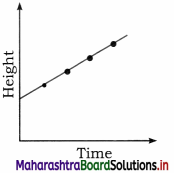
(1) Observe the above graph indicating increase in height of plants. Which type of growth indicates this pattern of graph?
(2) Give its mathematical expression.
Answer:
(1) Arithmetic growth
(2) Lt = Lo + rt where
Lt = Length at time t,
Lo = Length at time zero r = growth rate,
t = time of growth
Question 7.
Observe the figure given below of two different leaves ‘A’ and ‘B’ Which leaf shows much higher relative growth rate ?
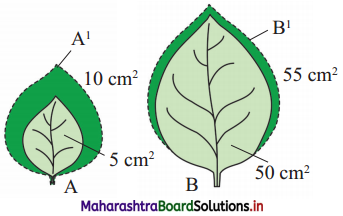
Answer:
Relative Growth Rate (RGR) = Growth per unit time as % of intial size.
RGR = \(\frac { Growth per unit time }{ intial size }\) × 100
Leaf A = 10 – 5 = 5, \(\frac { 5 }{ 5 }\) × 100 = 100%
Leaf B = 55 – 50 = 5, \(\frac { 5 }{ 50 }\) × 100 = 10%
Hence fig. A shows more relative growth.
Question 8.
Observe the diagrams A and ‘B’ showing growth in two leaves. Which diagram shows more relative growth?
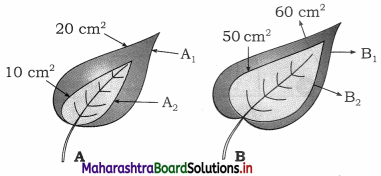
Answer:
Relative Growth Rate (RGR)
= Growth per unit time as % of intial size.
RGR = \(\frac { Growth per unit time }{ intial size }\) × 100
Leaf A = 20 – 10 = 10, \(\frac { 10 }{ 10 }\) × 100 = 100%
Leaf B = 60 – 50 = 10, \(\frac { 10 }{ 50 }\) × 100 = 20%
Hence Diagram A shows more relative growth.
Question 9.
Identify the type of growth curves observed in plants.
Answer:
Constant linear growth curve for the arithmetic growth.
Exponential (J shaped) growth curve for the geometric growth.
Sigmoid growth curve related to distinct phases of growth.
Question 10.
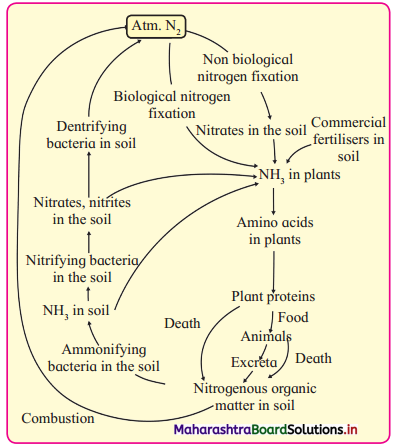
Fill in the blanks in the given nitrogen cycle.
Answer:
Long answer questions
Question 1.
What is hydroponics? How is it useful in identifying the role of nutrients?
Answer:
- Growing plants in aqueous (soilless) medium is known as hydroponics. [Greek word hudor = water and ponos = work]
- It is technique of growing plants by supplying all necessary nutrients in the water supply given to plant.
- A nutrient medium is prepared by dissolving necessary salts of micronutrients and macronutricnts In desired quantity and roots of plants are suspended in this liquid with appropriate support.
- Hydroponics is of great use in studying the deficiency symptoms of different mineral nutrients.
- The plants uptake mineral nutrients in the form of dissolved ions with the help of root hairs from the surrounding medium or nutrient solution supplied.
- While preparing the required nutrient medium particular nutrient can be totally avoided and then the effect of lack of that nntr’cnt can be studied in variation of plant growth.
- Any visible change noticed from normal structure and function of the plant is the symptom or hunger sign considered.
- For e.g. Yellowing of leaf is observed due to loss of chlorophyll pigments or Chlorosis is noticed if Magnesium is lacking as it is a structural component of chlorophyll pigment.
Question 2.
Explain the active absorption of minerals.
Answer:
- Plants absorb minerals from the soil with their root system.
- Minerals are absorbed from the soil in the form of charged particles, positively charged cations and negatively charged anions.
- The absorption of minerals against the concentration gradient which requires expenditure of metabolic energy is called active absorption.
- The ATP energy derived from respiration in root cells is utilized for active absorption.
- Ions get accumulated in the root hair against the concentration gradient.
- These ions pass into cortical cells and finally reach xylem of roots.
- Along with the water these minerals are carried to other parts of plant.
Question 3.
What is growth? What are its characteristics ?
Answer:
Growth : Growth is a “vital process which brings about an irreversible increase in an organism or its part with respect to its size, weight, form and volume.”
Characteristics of growth:
- Growth is a permanent increase in size, weight, shape, volume and dry weight of a plant.
- The change occurring due to growth is permanent and irreversible.
- Growth is an intrinsic process caused due to internal activities.
- Growth occurs by cell division and cell elongation followed by cell maturation which lead to the formation of different types of tissues.
- Growth in plants is mostly localized, i.e. restricted to some regions of plants possessing meristematic tissues or meris terns.
- Growth has a qualitative aspect where development takes place in an orderly manner and differentiation leads to higher and more complex state.

Question 4.
Describe the phases of growth.
Answer:
There are three phases of growth, viz, formation phase, elongation phase and maturation phase.
(1) Formative phase (Phase of cell division) : This is the first phase of growth. In this phase, the meristematic cells undergo mitosis to produce new cells. Owing to the formation of new cells, there occurs a slight increase in the size of the organ.
(2) Elongation phase (Phase of cell enlargement) : This is the second phase of growth. In this phase, the new cells that are formed, undergo enlargement as a result of which the size and volume of the cells increase. Enlargement of cells occur mostly in linear direction as a result of which the elongation of the root and stem takes place. The enlargement of cells causes a considerable increase in size and weight of an organ and a plant as a whole.
(3) Maturation phase (Phase of cell maturation and differentiation) : Maturation phase is the third and last phase of growth. In this phase, the elongated cells undergo maturation and differentiation to form various types of plant tissues like parenchyma, sclerenchyma, xylem and phloem.
Question 5.
Explain the various conditions of growth that are essential.
Answer:
- For a proper growth of plant various environmental and physiological conditions are necessary.
- Carbon/Nitrogen ratio in soil is having effect on growth as both carbon and nitrogen are structural elements in carbohydrates, proteins and other biomolecules.
- Water is essential component of protoplasm and required for turgidity of cells during cell enlargement phase. It is a medium in which various biochemical reactions ocfcur.
- Nutrients are necessary for proper growth. Macronutrients and micronutrients have their specific role.
- Temperature of 25 – 35 °C is optimum for growth.
- Light is essential for seed germination and photosynthesis.
- Oxygen is necessary for respiration and supply of energy.
- Gravitational force decides direction of growth for root system and shoot system.
- Growth hormones are organic compounds that are involved in various physiological aspects and control of growth.
Question 6.
What are plant growth regulators? Give the characteristics of plant growth regulators.
Answer:
Plant growth regulators : Plant growth regulators or phytohormones or plant hormones as they are also called are organic compounds synthesised by the plants which promote, inhibit or control the growth and other physiological processes.
Characteristics of plant growth regulators:
- Plant growth regulators are organic compounds other than nutrients.
- They are synthesised at the apices of root, stem and leaves from where they are transported to other parts of plants where they produce their effects.
- They are required in minute quantities.
- A single plant growth regulator can control or regulate the various aspects of growth.
Question 7.
Enlist the five main types of growth regulators and state the role of abscissic acid in plants.
Answer:
Five main types of growth regulators:
- Auxins
- Gibberellins
- Cytokinins
- Ethylene and
- Abscissic acid.
Role of abscissic acid (ABA) in plants:
- Abscissic acid influences abscission and dormancy.
- ABA accelerates senescence of leaves, flowers and fruits.
- It is a stress hormone as it is produced during drought and other unfavourable climatic conditions.
- ABA induces dormancy in seeds, buds and tubers.
- It acts as growth inhibitor as it retards growth.
- ABA plays an important role in closing of stomata to check transpiration.
- It inhibits and delays cell division and suppresses cambial activity by inhibiting mitosis in vascular cambium.
- ABA inhibits flowering in LDP and stimulates flowering in short day plants (SDP).
Question 8.
Write an account of auxins as growth regulators.
Answer:
- Auxins are plant growth regulators produced naturally by plants.
- They are weak organic acids capable of promoting cell elongation during the growth of stem and root.
- Auxins are synthesized in shoot and root apices besides young leaf primordia.
- Auxins may be natural or synthetic.
- Naturally occurring auxins are indole-3- acetic acid (IAA) and its derivatives.
- NAA, 2, 4-D and 2,4, 5-T are synthetic auxins.
- Auxins in higher concentration promote the growth of stem.
- Auxins play an important role in initiation and promotion of cell division.
- Auxins help in the formation of adventitious roots from cuttings when applied in lower concentration.
- Auxins play an important role in apical dominance.
- Auxin prevents abscission by preventing the action of hydrolytic enzymes in abscission layer.
- Auxins are used to produce parthenocarpic fruits in plants like orange, apple, tomato and grapes.
Question 9.
Give an account of physiological effects and application of auxin with examples.
Answer:
- Auxins are growth promoting substances synthesized at meristematic regions of plants.
- The primary effect of auxin is cell enlargement and it stimulates growth of stem and root.
- Apical dominance – The phenomenon where growing apical bud inhibits the growth of lateral bud is apical dominance which is controlled by auxin synthesized at apical bud.
- Owing to activity of inducing multiplication of cells it is used in plant tissue culture to produce callus.
- Auxin stimulates formation of lateral and adventitious roots hence used for rooting propagation of cuttings.
- 2, 4-D is a synthetic herbicide which kills dicot weeds.
- Induced parthenocarpy in fruits-oranges, banana, grapes, lemons is by application of auxin.
- Foliar spray of NAA and 2, 4-D induces flowering in litchi and pineapple.
- Premature fruit drop of apples, pear and oranges is prevented.
- Auxins break seed dormancy and promote germination.
- Auxins promote early differentiation of xylem and phloem, cell elongation, increase rate of respiration, prevent formation of abscission layer.
Question 10.
Explain the application of gibberellins.
Answer:
- Gibberellins are growth promoting hormone and it is present in root tips, stem tips and seeds.
- Gibberellins break dormancy of bud, dormancy of seed.
- They promote seed germination in cereals by activating or synthesising enzyme amylase to produce sugar.
- Gibberellins induce elongation of the cells in stem hence increase in internode length is noticed.
- In rosette plants like cabbage it causes ‘bolting’ that is increase in internode length before flowering.
- Gibberellins are more effective in inducing parthenocarpy than auxins in plants like tomato, apple and pear.
- It is also used to increase fruit size and length of bunches in grapes.
- By its application genetically dwarf plants can be converted to phenotypically tall e.g. Maize.
- It overcomes requirement of vernalization, delays senescence and prevents abscission.
- Application of gibberellins causes production of male flowers on female plants.
Question 11.
Describe about the physiological effects and applications of cytokinin.
Answer:
- Cytokinins are growth promoting hormone that promotes cell division. Kinetin, zeatin are examples of cytokinin.
- They promote cell division as well as cell enlargement.
- High cytokinin promotes shoot development.
- Growth of lateral buds is promoted by cytokinins. Thus it controls apical dominance.
- Process of ageing and senescence, abscission of plant organs is delayed by their application.
- It promotes formation of interfascicular cambium.
- It has a role in breaking seed dormancy and promotes seed germination.
- Cytokinins induce RNA synthesis.
- Cytokinin and auxin ratio and their interactions control morphogenesis and cell differentiation.
Question 12.
Discuss about physiological effects and applications of ethylene.
Answer:
- Ethylene is a gaseous growth inhibitor hormone.
- It promotes ripening of fruits like bananas, apples and mangoes. The commercial application of ethephon is done.
- It initiates growth of lateral roots.
- Dormancy of buds and seeds is broken by its application.
- It accelerates formation of abscission layer and thus abscission of leaves, flowers and fruits is observed.
- Ethylene is responsible for checking growth of lateral buds thus causes apical dominance and retards flowering.
- Process of senescence of plant organs is enhanced.
- Epinasty, i.e. drooping of leaves and flowers results due to its application in some plants.
- It increases activity of chlorophyllase enzyme causing degreening effect in banana and Citrus fruits.
Question 13.
Discuss about experiment of Hendricks and Borthwick for discovery of phytochromes.
Answer:
- Phytochrome pigments receive photoperiodic stimulus and control flowering in plants.
- Hendricks and Borthwick observed that in SDP flowering is inhibited if continuous dark period is interrupted even by a short duration or flash of red light of wavelength 660 nm.
- If this interruption is again exposed to flash of far red light of wavelength 730 nm, then these plants flower.
- From this they concluded that some pigment system in plant receives the photoperiodic stimulus.
- These pigment proteins are called phytochromes and it exists in two interconvertible forms – Pr and Pfr.
- These pigments are located in cell membranes of green cells.
- Pfr is biologically active form and during daytime it gets accumulated in the plant.

Question 14.
Give schematic representation of nitrogen cycle and enlist important steps of this cycle.
Answer:
- Atmospheric nitrogen is a source of nitrogen cycle.
- The important steps of the cycle are Nitrogen fixation, Nitrification, Ammonification, Nitrogen assimilation by plants. Amino acid synthesis and amidation, Denitrification and sedimentation.
- Amino acid are building blocks of proteins. Amides are amino acid with two amino groups.
- Schematic representation of Nitrogen
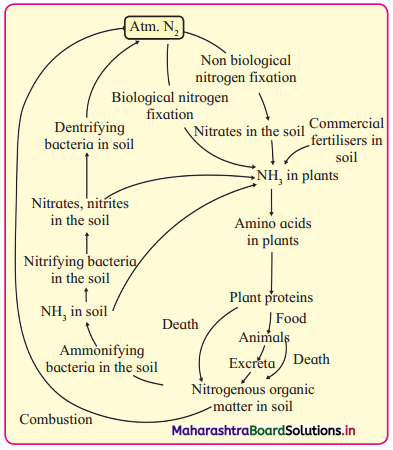
Question 15.
What is nitrogen cycle? Describe it briefly.
Answer:
- The cyclic movement of nitrogen between the atmosphere, biosphere and geosphere in different forms is called nitrogen cycle.
- Nitrogen cycle is one of the most important biogeochemical cycles.
- The nitrogen cycle involves many processes such as cycling of nitrogen through the biosphere, atmosphere and geosphere, nitrogen fixation, nitrogen uptake, formation of biomass, ammonification, nitrification and denitrification, etc.
- Bacteria such as Nitrosomonas, Nitrosococcus and Nitrobacter are the nitrifying bacteria which play an important role in nitrification.
- Denitrification is carried out by the bacteria Pseudomonas denitrifficans. From this it is obvious that bacteria play a major role in nitrogen cycle.
- Nitrogen fixation occurs by physical, industrial and biological methods. Prokaryotic organism play an important role in biological nitrogen fixation.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()























 Answer:
Answer: