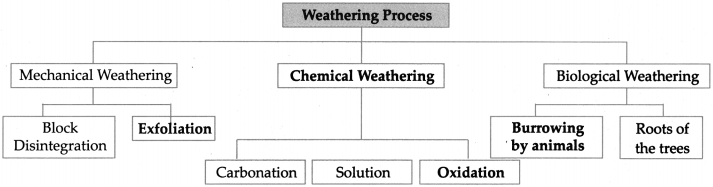
Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 9 Geography Solutions Chapter 4 Exogenetic Movements Part 2, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Exogenetic Movements Part 2 Class 9 Questions And Answers Maharashtra Board
Class 9 Geography Chapter 4 Exogenetic Movements Part 2 Questions And Answers Maharashtra Board
Geography Class 9 Chapter 4 Question Answer Maharashtra Board
1. Rewrite the correct statement:
Question 1.
The temperature range helps the wind in its work.
Answer:
Correct.

Question 2.
River’s work is more prominent than other agents of erosion in desert regions.
Answer:
Incorrect. Work of wind is more prominent in desert regions than other agents of erosion.
Question 3.
The work of groundwater is effective in the area with soft rocks.
Answer:
Correct.
2. Correct and rewrite the incorrect statements:
Question 1.
The ice on the lateral side of the glacier moves faster than the ice at the base.
Answer:
Incorrect. The ice on the base of the glacier moves faster than the ice on the lateral side.
Question 2.
The depositional work by rivers happens because of gentle slope, reduced speed and transported sediments.
Answer:
Correct.
Question 3.
A river flows at a faster speed than the glacier.
Answer:
Correct.
Question 4.
The speed of the glacier is more on both the banks than in the middle.
Answer:
Correct.
3. Identify the wrong pair
Question 1.
Deposition – V-shaped valley
Answer:
Wrong pair.
Correct pair is – Erosion – V-shaped valley

Question 2.
Transport – Ripple Marks
Answer:
Transport – Ripple Marks
Question 3.
Erosion – Mushroom Rocks
Answer:
Erosion – Mushroom Rocks
4. Identify and name the landforms in the following diagrams :
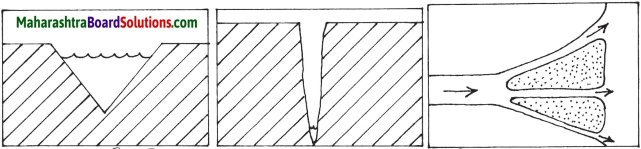
Answer:
(i) V-shaped valley
(ii) Gorge (Canyon)
(iii) Delta
5. Complete the following table by classifying the landforms according to their agents of erosion.
(waterfall, delta, cirque, arête, barchans, moraine, pothole, mushroom rock, sinkholes, beach, pillars, lagoons)
Rivers Wind Glacier Sea Waves Groundwater
Answer:
| Rivers |
Wind |
Glacier |
Sea waves |
Ground Water |
| Waterfall |
Barchans |
Cirque |
Beach |
Sinkholes |
| Delta |
Mushroom rock |
Aretes |
Lagoons |
Pillars |
| Pothole |
|
Moraine |
|
|
6. Answer the following questions in brief.
Question 1.
List the landforms that are a result of the erosional work of the rivers.
Answer:
Gorges (canyons), V-shaped valleys and waterfalls are the result of the erosional work of the rivers.
(i) ‘V’ Shaped Valley:
- A ‘V shaped valley is formed due to the erosional work of a river.
- Over a period of time, the amount of load in the flow starts increasing.
- More and more energy of the river gets consumed in transporting the material.
- As a result, there is less erosion of the bed. The erosion along the banks and the slopes of the valley increases.
- Hence, the slopes recedes and the valley with near-vertical sides becomes wider, resembling the letter ‘V’.
(ii) Gorge:
- A gorge is found in the upper course of the river.
- It is a deep and narrow valley with steep sides.
- In mountainous areas, the river flows with great speed. Therefore, the bed of the river gets eroded more than its banks, giving rise to a gorge that has a steep banks and a narrow bed.
(iii) Waterfall:
- Waterfalls are formed as a result of the erosional work of a river.
- Water flowing over a hilly region cascades down a cliff, forming a waterfall.
- In the areas, where the hard and soft rocks are next to each other, the soft rocks are eroded faster than the hard ones. A difference in the height along the river bed leads to the formation of a waterfall.

Question 2.
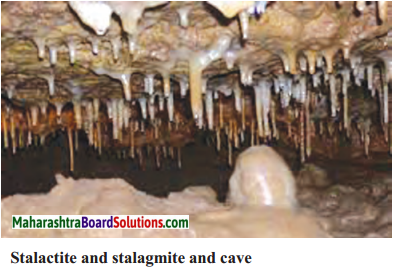
Which agent is responsible for the formation of stalactites and stalagmites and where are they formed?
Answer:
- The work of groundwater is responsible for the formation of stalactites and stalagmites.
- In areas of limestone, the alkaline water seeps through the roof of the limestone caves.
- When this water evaporates, minerals get deposited at the bottom and at the top of the limestone caves.
- This leads to formation of stalactites and stalagmites.
Question 3.
List the landforms that are produced by the depositional work of the sea waves
Answer:
The landforms like beaches, sand bar, lagoons are formed due to depositional work of the sea waves.
(i) Beach:
- Large amount of sediments come from the landward side in areas between two adjoining headlands.
- Moreover, as these areas are shallow, the velocity of the waves decreases.
- As a result, the sediments that come from the land, as well as those coming from the deep sea, get deposited in this area.
- Predominantly fine sand gets settled along the coast.
- Such sandy deposits along the coasts are called beaches.
(ii) Lagoon:
- The brackish water separated from the seawater by sand bars and lying in the areas between the coast and bars is called a lagoon.
- As the waters are separated from the open sea, large waves are not generated.
- These lagoons run parallel to the sea coast.
(iii) Sand bars:
- Sand gets deposited along the sides of the headlands.
- The deposition extends parallel to the coast from one headland to the next.
- Over a period of time, these deposits extend over long distances forming bars that protrude into the water at some distance away from the beach.
- These are known as ‘sand bars’, Sometimes, the eroded material from the’ beach, gives rise to the sand bars.

Question 4.
Name the types of moraines.
Answer:
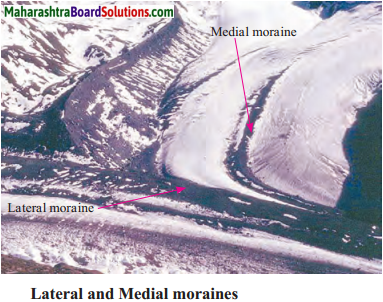
The glaciers carry sediments with them. These sediments are called moraines. Depending ond the location of the deposits, moraines can be divided into 4 types: ground moraines, lateral moraines, medial moraines and terminal moraines.
- The material deposited at the base of a glacier is called ground moraine.
- The material deposited along the banks of a glacier is called Lateral moraine.
- After the confluence of two glaciers, the moraine deposited in the central part of the glacier is known as medial moraine. It is formed out of . the side moraine of the inner banks of the two glaciers.
- At the end where a glacier turns into a stream, huge quantity of moraine is deposited. The stream of water is unable to carry the moraine further. As the deposited moraine is at the terminal part of a glacier, it is called terminal moraine.
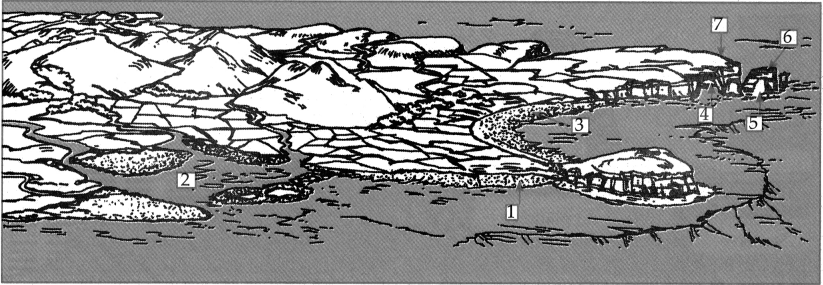
7. Observe the following picture carefully. Identify the landforms formed by different agents of erosion. Number them with a pencil here and write their names in the sequence in your notebook.

(i)

Answer:
Depositional work of river

(ii)

Answer:
Depositional work of river
(iii)

Answer:
Erosional work of river
(iv)

Answer:
Depositional work of river
(2) Some pictures of the landforms formed by glaciers3 are given below. Write the function because of which they have been formed.

(i)
Answer:
Erosional work of glacier
(ii)

Answer:
Erosional work of glacier
(iii)
Answer:
Depositional work of glacier
(iv)

Answer:
Depositional work of glacier

(v)

Answer:
Erosional work of glacier
(vi)

Answer:
Erosional work of glacier
(vii)

Answer:
Depositional work of glacier
(3) Some pictures of the Iandforms produced by the work of the winds are given below. See the pictures and write in the box whether they have been formed by erosion or deposition.
(i)

Answer:
Erosional work of wind

(ii)

Answer:
Depositional work of wind
(iii)

Answer:
Depositional work of wind
(iv)

Answer:
Depositional work of wind
(v)

Answer:
Erosional work of wind

(vi)

Answer:
Erosional work of wind
(4) Some pictures of the landforms produced by the work of the sea waves are given below. See the pictures and write in the box whether they have been formed by erosion or deposition.
With the help of internet, obtain information regarding the places along the Konkan coast where you will find the landforms formed by sea waves.
(i)

Answer:
Erosional work of sea waves.
(ii)

Answer:
Depositional work of sea waves

(iii)

Answer:
Erosional work of sea waves.
(iv)

Answer:
Erosional work of sea waves.
(v)

Answer:
Erosional work of sea waves.
(vi)

Answer:
Depositional work of sea waves.

(vii)

Answer:
Depositional work of sea waves.
(5) See the pictures of the landforms produced by the work of groundwater. Write in the box below them whether they are formed through the work of erosion or deposition.
(i)

Answer:
Erosional work of ground water
(ii)
Answer:
Depositional work of ground water
Class 9 Geography Chapter 4 Exogenetic Movements Part 2 Intext Questions and Answers
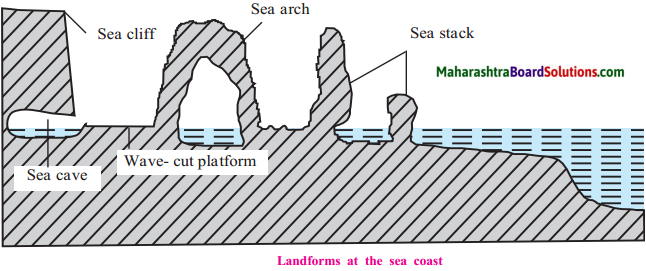
Draw a diagram showing landforms at the sea coast:
Answer:

Can You Tell?
Question 1.
How will you differentiate between a rill, gully, stream and a river?
Answer:
The smallest natural flow of rain water is a rill. Many rills come together to form a gully. Many gullies come together and form a stream. Many streams come together and form a river. Thus we can see that rills, gullies, streams nad rivers are the various forms of flowing water in increasing order of their size.
Question 2.
What is a river?
Answer:
Running water flows naturally in a direction according to gravity along the slope, making its own way. This is called a flow of water when many such flows of water come together a river is formed.
Question 3.
Where can you see the work by glaciers in India?
Answer:
Glaciers can be seen in the Himalayan region in India.
Question 4.
In which natural region can you see the work of glaciers at the sea level?
Answer:
We can see the work of glacier at sea level in the Polar regions (Antarctica).
Question 5.
Where will you find the landforms formed by sea waves along the Konkan coast?
Answer:
Along the Konkan coast, landforms formed by sea waves can be found at Harihareshwar, Bhagwatibandar, Shrivardhan, Ratnagiri and Sindhudurg.
Think about it.
Question 1.
There are many creeks found in the coastal areas of Konkan but no delta, why?
Answer:
The Konkan coast has an indented (broken) coastline. Hence many creeks are found here. Many small seasonal rivers originate in the steep western side of the Western Ghats. As the rivers flow through the steep slopes their velocity increases. So, there is very little erosion done by them. Due to the narrow width of the Konkan coast, the rivers cover a short distance and drain in the Arabian sea. Thus they do not form estuaries rather than deltas.

Question 2.
Can you see a glacier moving just as you can observe the movement of river water?
Answer:
No
Question 3.
Ramu has to dig a well in his farm. But he is in a dilemma as to which season should he dig it so that there is water supply for a longer time. What will you suggest to Ramu?
Answer:
Ramu should dig a well during the summer season. A deep well can be dug during the summer season. This will ensure water supply not only during the monsoon and winter season but also during the next summer season.
Question 4.
Which agent has more kinetic energy of all-wind, river or glacier?
Answer:
Glacier is the agent of erosion which has the most kinetic energy of all. The glacier is a mixture of heavy soil and rock particles which are flowing. Thus it has both weight and movement.
Find out.
Question 1.
Is there any lake found near the meanders of the river? Obtain information about them.
Answer:
- Ox-Bow lakes are usually found near the meanders of a river.
- Wherever the river changes its direction, erosion takes place along the outer banks.
- If these conditions occur again and again, the river develops a zigzag path.
- Such a zigzag path is called a meandering path (course) and each loop along the path is called meander.
- When the turns in the course become acute, the limbs of a turn come very close.
- During flood, as the force of water increases, the river skips the meandering path and follows a straight path.
- The abandoned portion of the loop develops into a lake that is called an ‘ox-bow’ lake.
Question 2.
Where will you find mushroom rocks in the Deccan Plateau?
Answer:
Mushroom rocks can be found in the Hyderabad.
Question 3.
Can you find the work of wind near coastal areas? What landforms will be formed there?
Answer:
Yes, Ripple marks and sand mounds can be seen on the sand in the coastal regions.

Question 4.
Where are limestone caves, stalactites and stalagmites found in Maharashtra?
Answer:
Limestone caves, stalactites and stalagmites are found in Kanhur caves in the Ahmednagar district of Maharashtra.
Question 5.
Why are the landforms formed in limestone called Karst?
Answer:
A karst is an area of land formation created by eroding and dissolving portions of limestone or other soluble rock layers above or below the ground. According to the prevalent interpretation, the term is derived from the German name for the Karst region, a limestone plateau above the city of Trieste in the northern Adriatic.
Class 9 Geography Chapter 4 Exogenetic Movements Part 2 Additional Important Questions and Answers
Complete the statements by choosing the correct options.
Question 1.
The sediments are deposited at the foothills of the mountains in a triangular area forming an/a ………….. .
(a) alluvial fan
(b) yardang
(c) delta
(d) V-shaped valley
Answer:
(a) alluvial fan
Question 2.
The sediments carried by the glacier2 are called ………….. .
(a) sediments
(b) silt
(c) moraines
(d) alluvium
Answer:
(c) moraines
Question 3.
The erosional, transportation and depositional work of wind is more prominent in ………….. .
(a) polar regions
(b) deserts
(c) temperate regions
(d) grasslands
Answer:
(b) deserts
Question 4.
When many flows of water come together a …………… is formed.
(a) gorge
(b) river
(c) glacier
(d) canyon
Answer:
(b) river

Question 5.
The water which percolates through the porous rocks on the non-porous layer of rock is termed as ………….. .
(a) glacier
(b) flood leeves
(c) ground water
(d) surface water
Answer:
(c) ground water
Question 6.
…………… is formed due to depositional work of river.
(a) Delta
(b) Gorge
(c) V-shaped valley
(d) Canyon
Answer:
(a) Delta
Question 7.
In regions, where the temperatures are generally below freezing points, precipitation is in the form of ………….. .
(a) rainfall
(b) hail
(c) snowfall
(d) frost
Answer:
(c) snowfall
Question 8.
The erosional work of glacier forms ………….. .
(a) drumlins
(b) eskers
(c) cirques
(d) yardangs
Answer:
(c) cirques
Question 9.
The Jacobshavn Glacier in …………… is one of the fastest moving glaciers in the world.
(a) Finland
(b) Greenland
(c) Antarctica
(d) Himalayas
Answer:
(b) Greenland

Question 10.
The depositional work of ground water forms ………….. .
(a) limestone caves
(b) lagoons
(c) ripple marks
(d) seifs
Answer:
(a) limestone caves
Question 11.
Stalactites grow ………….. .
(a) downwards
(b) upwards
(c) sidewards
(d) fast
Answer:
(a) downwards
Question 12.
The ground water levels sink down in …………… season.
(a) summer
(b) winter
(c) rainy
(d) spring
Answer:
(a) summer
Question 13.
…………… is formed as a result of the depositional work of the sea waves.
(a) Sea cliff
(b) Lagoon
(c) Wave-cut platform
(d) Sea cave
Answer:
(b) Lagoon
Question 14.
The landforms developed in limestone areas are also called as …………… landforms.
(a) lime
(b) sinkhole
(c) krast
(d) coastal
Answer:
(c) krast

Match the Columns:
(1) River
| Column A’ |
Column B’ |
| (1) |
Erosion |
(a) |
Ox-bow lake |
| (2) |
Deposition |
(b) |
Meanders |
|
|
(c) |
Yardangs |
Answer:
(1 – b),
(2-a)
(2) Glacier
| Column ‘A’ |
Column ‘B’ |
| (1) |
Erosion |
(a) |
Seif |
| (2) |
Deposition |
(b) |
Eskers |
|
|
(c) |
Cirque |
Answer:
(1 – c),
(2 – b)
(3) Wind
| Column ‘A’ |
Column B’ |
| (1) |
Erosion |
(a) |
Sand dunes |
| (2) |
Deposition |
(b) |
Mushroom Rock |
|
|
(c) |
Lagoon |
Answer:
(1 – b),
(2 – a)

(4)
| Column ‘A’ |
Column B’ |
| (1) |
Ground water |
(a) |
Delta region |
| (2) |
Sea waves |
(b) |
Lagoon |
|
|
(c) |
Sink holes |
Answer:
(1 – c),
(2 – b)
(5)
| Column ‘A’ |
Column B’ |
| (1) |
Stalactites & stalagmites |
(a) |
wind |
| (2) |
Sand bar |
(b) |
ground water |
|
|
(c) |
sea waves |
Answer:
(1 – b),
(2 – c)
Answer in one sentence:
Question 1.
Name the agents of erosion.
Answer:
The agents of erosion are wind, rivers, glaciers, sea waves and ground water.
Question 2.
What factors does the work of a river depend on?
Answer:
The works of river depends on the nature of rock, the slope of land, velocity of the flow and the volume of water.
Question 3.
What are the important phases of a river’s work?
Answer:
The important phases of a river’s work are erosion, transportation and deposition.
Question 4.
What factors does the work of glaciers depend on?
Answer:
The work of glacier depends on the thickness of the accumulated ice, the temperature, and the slope of the land.
Question 5.
Which landforms are created due to the processes of erosion by the river?
Answer:
Landforms like gorges, V-shaped valleys, potholes and waterfalls are created due to the processes of erosion by the river.

Question 6.
Which landforms are formed mainly due to the transportational and depositional work of a river?
Answer:
Due to the transportational and depositional work of a river, meanders, ox-bow lakes, flood levees, flood plains and delta regions are formed.
Question 7.
Which landforms are created as a result of the erosional work of a glacier?
Answer:
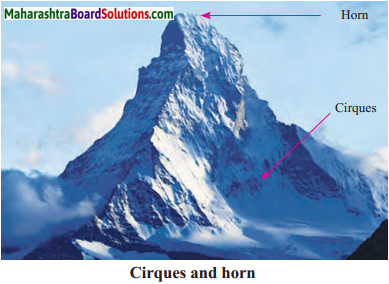
The landforms such as a cirque, arete and matterhorn, U-shaped valley, hanging valleys, etc. are created as a result of the erosional work of a glacier.
Question 8.
Name the landforms formed by the depositional work of glaciers.
Answer:
The landforms formed by the depositional work of glaciers are drumlins, eskers etc.
Question 9.
Name the types of moraine.
Answer:
Ground moraine, lateral moraine, medial moraine and terminal moraine are the different types of moraine.
Question 10.
Which landforms are created as a result of the erosional work of the wind?
Answer:
The landforms like mushroom rocks, deflation hollows, yardangs etc. are created as a result of the erosional work of the wind.
Question 11.
Which landforms are created as a result of the transportation and depositional work of the wind?
Answer:
Sand dunes, barchans, seif, ripple marks, and loess plains are created as a result of transportation and depositional work of the wind.
Question 12.
Which landforms are produced as a result of the erosional work of sea waves?
Answer:
The landforms like sea cliffs, sea caves, wave-cut platforms, sea arches and sea stacks are produced as a result of the erosional work of sea waves.

Question 13.
Mention the landforms created due to the transportation and depositional work of sea waves.
Answer:
Beaches, sand bars and lagoons are created due to the transportation and depositional work of sea waves.
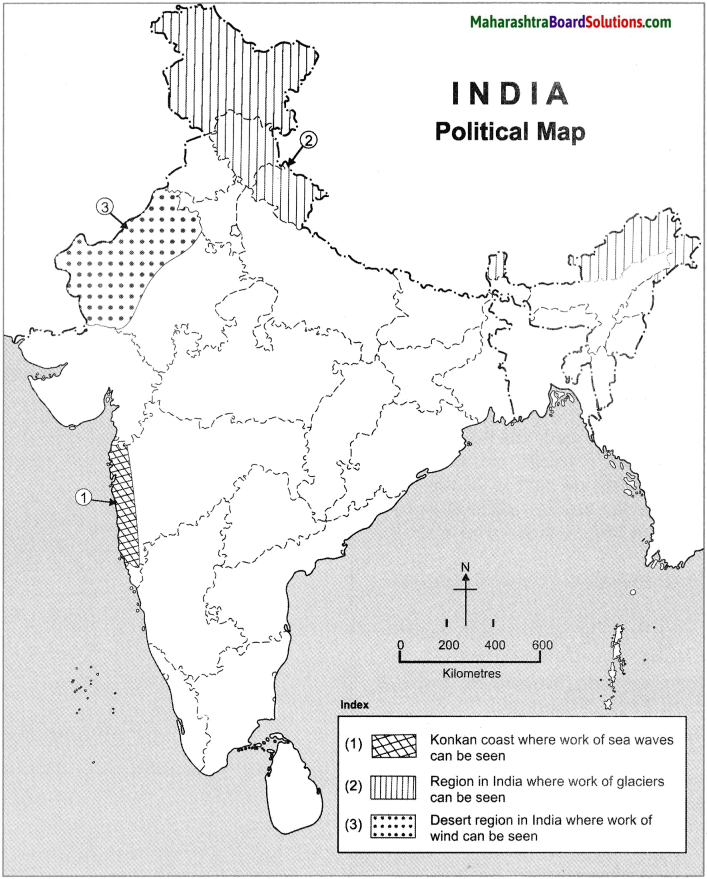
Fill the map with the given information and make a legend.
(1) Konkan Coast where work of sea waves can be seen
(2) Region in India where work of glaciers can be seen
(3) Desert region in India where work of wind can be seen
Answer:
Give geographical reasons:
Question 1.
Like the river, a glacier too carries out the work of erosion, transportation and deposition.
Answer:
- In regions, where the temperatures are generally below freezing points, precipitation is in the form of snowfall.
- Layers of snow accumulate on the earth’s surface because of snowfall.
- The heavy weight of these overlying layers makes the snow move along the slope.
- At the base of the layer, the snow starts melting because of the friction and the pressure from above. Glacier starts moving slowly along the slope.
- Thus like the river, a glacier too carries out the work of erosion, transportation and deposition.

Question 2.
Specific landforms are formed due to deposition by wind in arid and semi arid regions.
Answer:
- Sand particles that blow with the winds are of different shapes and sizes.?
- Those particles which are very fine are carried to larger distances while the larger ones get transported to shorter distances only.
- These sand particles get deposited in deserts and semi-arid climates.
- As a result, specific landforms are formed.
- Sand dunes, barchans, seifs, ripple marks, loess plains, etc. are formed by deposition by wind.
Question 3.
The work of sea waves cause different landforms.
Answer:
- In coastal areas, the sea waves carry out erosional, depositional and transportational work.
- Winds and tides cause the movements of sea water. As a result, waves come to the coast.
- Because of their hitting the rocks at the coasts, erosion of the rocks occurs.
- The landforms like wave cut platforms, sea caves, sea arches, sea cliffs, etc. are formed because of the erosional work of the waves.
- The landforms like beaches, sand bar, lagoons are formed due to depositional work of the sea waves.
Question 4.
In the desert, the work of wind is effective.
Answer:
- The work of wind is predominantly found in the hot desert and semi-arid regions.
- Hot deserts are found close to the Tropic of Cancer and Tropic of Capricorn.
- The average annual rainfall in the hot deserts is 250 mm or even less. Therefore, the vegetal cover is negligible.
- As there are no obstacles due to lack of vegetal cover, the work of wind is effective in the desert.
Question 5.
Glaciers have a low velocity.
Answer:
- In the high altitude areas and the areas of high elevation, the ice slides down the slope. Such a sliding mass of ice is called a glacier.
- As the ice moving in a glacier is in the solid state, its velocity is very low.
- The thickness of the accumulated ice, the temperature and the slope of the land are the factors that determine the velocity of the glacier.
Question 6.
The ground water level changes according to seasons.
Answer:
- The upper level of the stored ground water is called ground water level.
- It varies according to the slope of the land, porosity and compactness of the rocks and the rainfall in the region.
- Ground water level also changes according to season.
- In the rainy season, it is closer to the ground surface whereas during summer, it drops down deeper.

Identify the land forms made by waves and write their names in the given picture.
Answer:
- Wave-cut platform
- Lagoon
- Beach
- Sea cave
- Sea arch
- Sea stack
- Sea cliff
Write the name of the landforms with which the following diagrams are associated. Colour the eroded and the remaining part, if any, in the given diagrams.
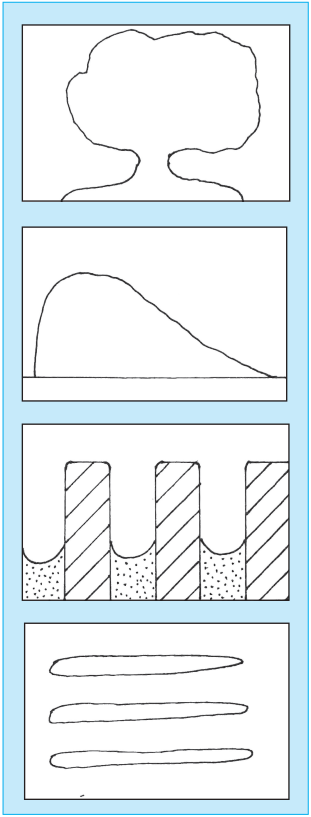
Answer:
(a) Mushroom Rock
(b) Sand Dune (Barchan)
(c) Yardangs
(d) Seif (Sand Mounds)

Identify the landforms formed by groundwater in the given diagram.
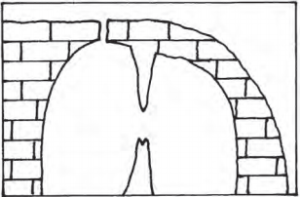
Answer:
Stalactite and Stalagmite cave.
Answer the following questions in brief:
Question 1.
List the agents responsible for new landforms. i
Answer:
The agents – running water (river), glaciers, wind, sea waves and groundwater, – do the work of erosion, transportation and deposition. Because of these agents, the earth’s surface keeps undergoing changes and new landforms are formed.
(i) Running water (river):
- The river beds, as well as the banks of a river, are eroded due to the speedy flowing stream of water. The load that a river carries also erodes the banks and the bed of the river.
- The rocks, stones, sand, etc. collide with one another and break into fragments
- Different landforms like gorge, V-shaped valley, pothole and waterfall are formed due to the erosional work of a river.
(ii) Glaciers:
- As a glacier is nothing but a solid mass of ice, its velocity is very low. Nevertheless, the mass of water in the solid form is quite high. Therefore, glaciers cause a considerable amount of erosion.
- The glaciers erode the ice-clad base of the mountain slopes and the snow-clad sides of the mountains to a large extent.
- The Cirque, Arete and horn, U-Shaped valley and hanging valley are the landforms formed by the erosional work of a glacier.
(iii) Wind:
- The wind carries sand and pebbles.
- When they strike and scratch the rocks, the elevated and basal parts of the rocks get eroded.
- Due to the erosional processes of the wind, deflation hollows, mushroom rocks and yardangs3 are formed.
(iv) Sea waves:
- The basal portions of the headlands get severely eroded due to the continuous attack of sea waves. This leads to the erosion of the rocks on a large scale.
- Rocky coasts are formed where the headlands get severely eroded.
- Landforms such as sea cliffs, sea caves, wave- cut platforms, sea arches and sea stacks are formed due to the erosional work of sea waves.

(v) Groundwater:
- Soluble minerals in the rocks dissolve in water and they move along with the ground water. This process is called erosion by ground water.
- The work of ground water is predominant in the region where rock like limestone is found on a large scale.
- Limestone dissolves in carbonic acid. Carbonic acid is formed due to the presence of carbon? dioxide in ground water. This acid dissolves carbonates like limestone. Thus, chemical weathering takes place.
- The landforms like sinkholes and caves are the result of the erosional work of groundwater.
Question 2.
List the landforms that are produced due to deposition of sediments by rivers.
Answer:
Landforms like flood levees, flood plains, deltas are formed because of deposition of sediments,
- Flood levees: When in flood, the river deposits ; the coarser material on the banks which in duecourse rises parallel to the banks of the river. These are called ‘flood levees’.
- Flood plains: The finer silt deposited away from the banks during the flood form plains on ! either side of the river. They are called ‘flood plains’.
- Delta: The continuous deposition leads to the formation of a plain in the shape of a triangle called delta. Extensive deltas have been formed ! at the mouth of rivers Ganga, Godavari, Kaveri.
Question 3.
Write in detail about the erosional and depositional work of wind.
Answer:
(i) Erosional work of winds:
- Wind carries small sand particles, small pebbles, etc. along with it.
- These particles cause erosion along rocks coming in the way due to friction.
- This leads to formation of mushroom rocks, deflation hollows, yardangs, etc.
(ii) Depositional work of winds:
- Sand particles that blow with the winds are of different shapes and sizes.
- Those particles which are very fine are carried to larger distances while the larger ones get transported to shorter distances only.
- These sand particles get deposited in deserts and semi-arid climates. As a result, specific landforms are formed.
- Sand dunes, barchans, seifs, ripple marks, loessplains, etc. are formed by deposition by wind.
Question 4.
Write in detail about the erosional and depositional work of sea waves.
Answer:
(i) Erosional work of sea waves:
- When the waves break at the coast, they bring with them water, transported stones, pebbles,sand particles, etc. This leads to the erosion of the coast.
- Because of the chemical and hydraulic action of the sea wave too, the erosion occurs. The landforms like wavecut platforms, sea caves, sea arches, sea cliffs, etc. are formed because of the erosional work of the waves.
(ii) Depositional work of sea waves:
- The eroded materials accumulate at the sea bed. Because of tides, they keep on moving towards the coast and away from the coast.
- They become fine because of attrition and hitting towards each other.
- Deposition of such materials occurs at the places where the effect of waves is less. The landforms like beaches, sand bar, lagoons are formed due to the depositional work of the sea waves.

Explain:
Question 1.
Erosional work of rivers
Answer:
- The rivers originate at a much higher altitude from the sea level.
- Here, the river flows at a great speed and therefore, its power to erode is great.
- The riverbed and the river banks get eroded because of the speedy flow of the river, sand particles, pebbles. Also, various tributaries join the main river.
- All these lead to the formation of gorges (canyons), V-shaped valleys and waterfalls.
Question 2.
Transportation and deposition by rivers
Answer:
- A river flows down the slope from a hilly region.
- At the foothills, the change in the slope causes deposition of coarse sediments.
- As these are deposited in a triangular shape, they form an alluvial fan. As the steepness of the slope decreases and the transport capacity of the river reduces, it starts flowing slowly.
- It bends (meanders) often in its way in an effort to cross even small obstacles.
- By the time the river reaches the sea, its riverbed becomes very wide and its speed becomes very slow.
- The sediments of the river get deposited in its bed and on its banks. The factors that determine the deposition of sediments are thelength of the rivers, volume of water, amountof sediments, and the slope of the river and the earth’s surface.
- Thus, landforms like flood levees, flood plains,deltas are formed because of deposition of sediments.
Question 3.
Erosion work by glaciers
Answer:
- Though the velocity of glaciers is less, the mass of the ice is more and hence the glacier erodes its own banks and its bed on a large scale.
- The erosional work of glaciers produces landforms like cirques, aretes, horns, U-shaped valleys, hanging valleys and roche moutonnees (or sheepbacks).
Question 4.
Transportation and deposition by glaciers
Answer:
- The glaciers carry sediments with them. These sediments are called moraines.
- Depending on the location of the deposits, moraines can be divided into 4 types: ground moraines, lateral moraines, medial moraines and terminal moraines.
- The depositional work of glacier produces landforms like drumlins, eskers, etc.

Question 5.
Erosional and depositional work of wind
Answer:
- Erosional work of wind: Wind carries smallsand particles, small pebbles, etc. along with I it. These particles cause erosion along rockscoming in the way due to friction.
- This leads to formation of mushroom rocks, deflation hollows, yardangs, etc.
- Depositional work of winds: Sand particles that blow with the winds are of different shapes and sizes.
- Those particles which are very fine are carried to larger distances while the larger ones get transported to shorter distances only.
- These sand particles get deposited in deserts ; and semi-arid climates. As a result, specific landforms are formed.
- Sand dunes, barchans, seifs, ripple marks, loess plains, etc. are formed by deposition by wind.
Question 6.
Erosional work of sea waves
Answer:
- When the waves break at the coast, they bring with them water, transported stones, pebbles, sand particles, etc.
- This leads to the erosion of the coast. Because of the chemical and hydraulic action of the sea wave too, the erosion occurs.
- The landforms like wave cut platforms, sea caves, sea arches, sea cliffs, etc. are formed because of the erosional work of the waves.
Question 7.
Depositional work of sea waves
Answer:
- The eroded materials accumulate at the sea bed.
- Because of tides, they keep on moving towards the coast and away from the coast.
- They become fine because of attrition and hitting towards each other. Deposition of such materials occurs at the places where the effect of waves is less.
- The landforms like beaches, sand bar, lagoons are formed due to depositional work.
Question 8.
Work of groundwater and landforms
Answer:
- The rainwater seeps below the earth’s surface through porous rocks or the cracks in the rocks.
- This water accumulates at the non-porous layer of the rock. This accumulated water is called groundwater.
- The soluble minerals in the water get dissolved and flow with the groundwater. This is the erosional work of the groundwater.
- When the groundwater evaporates or the volume of soluble minerals is more than the solubility of the groundwater, the deposition of dissolved materials starts.
- Landforms like sinkholes, limestone caves, stalactites and stalagmites are formed.
- Thus, the groundwater carries out the erosion, transportation and depositional work.

Question 9.
Groundwater table
Answer:
- The upper surface of the water accumulated below the ground is called the ground water table.
- Factors like seasons, porosity of rocks, amount of rainfall, etc. affect the level of water table.
- The water table is closer to the ground during rainy seasons while it is deeper in the summers.?
9th Std Geography Questions And Answers:
![]()
![]()
![]()

![]()