Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 9 English Solutions Kumarbharati Chapter 3.2 Reading Works of Art Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Class 9 English Chapter 3.2 Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Reading Works of Art 9th Std Question Answer
Warming Up:
Question 1.
Complete the following idioms using the appropriate colour term. (blue, black, green, red)
- give someone a ……….. look (a look of anger. dislike, etc.)
- the ……….. sheep (of the family a person who brings disgrace to the family)
- a …………. list (a list of defaulters)
- a ………….. belt (area of fields, woods. etc. around a city)
- to have ……………. fingers (be good at gardening)
- be ………….. with envy (feel very jealous)
- give someone/get the signal (give/get pemilssion to do something)
- a bolt from the ………….. (a sudden shock. surprise)
- out of the ………….. (suddenly. unexpectedly)
- once in a ……………. moon (very rarely)
- vanish into the …………… (leave without any trace)
- ………….. blood (royal blood. aristocratic origin)
- …………. eyed boy (favourite person)
- catch someone …………. handed (catch someone in the act of doing something wrong)
- roll out the ……………. carpet (give a special welcome)
- a …………….. herring (something that diverts attention from the main issue)
- see …………… (become angry)
Answer:
- give someone a black look.
- out of the blue
- the black sheep (of the family)
- once in a blue moon
- a black list
- vanish into the blue
- a green belt
- blue blood
- to have green fingers
- a blue-eyed boy
- be green with envy
- catch someone red-handed
- give someone/get the green signal
- roll out the red carpet
- a bolt from the blue
- a red herring
- see red
![]()
Question 2.
What are you reminded of when you think of the following colours.
- purple
- orange
- yellow
- pink
- white

Answer:
- purple – royalty
- orange – fire
- yellow – the sun
- pink – sweetness
- white – purity
English Workshop:
1. Spot the error in the spelling of these words with reference to the passage and rewrite them correctly.
Question 1.
Spot the error in the spelling of these words with reference to the passage and rewrite them correctly.
- renouned
- geomatric
- feetures
- figars
- circals
- acheiving
Answer:
- renowned
- geometric
- features
- figures
- circles
- achieving
![]()
2. Complete the following with reference to the passage:
Question 1.
Complete the following with reference to the passage:

Answer:
3. Complete the following diagram
Question 1.
Complete the following diagram.
Answer:
4. Complete the following with reference to the passage:
Question 1.
Complete the following with reference to the passage:
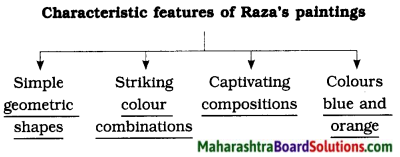
(a) Raza’s paintings do not depict ………….. .
(b) Raza’s paintings are done in the ……….. style.
(c) Raza’s paintings are not inspired by …………… .
(d) Raza’s paintings present images from his own …………. .
(e) Raza’s paintings radiate ……………… .
(f) The ……………. became the core of Raza’s paintings.
(g) For an artist like Raza. his work, or paintings are an effective ……………… .
Answer:
(a) Raza’s paintings do not depict lifelike human figures or copies of scenes from his environment.
(b) Raza’s paintings are done in the abstract style.
(c) Raza’s paintings are not inspired by any external factor.
(d) Raza’s paintings present images from his own inner mind.
(e) Raza’s paintings radiate peace and life at the same time.
![]()
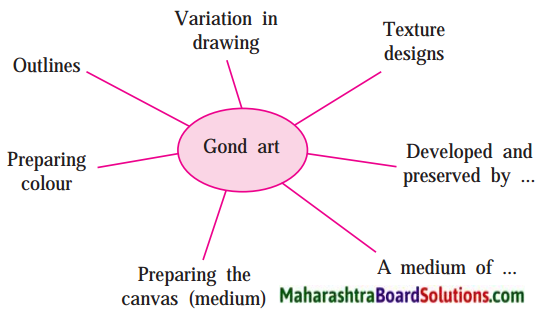
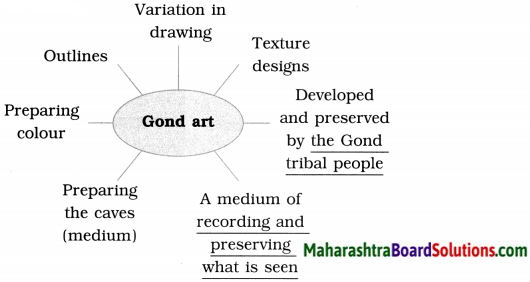
5. Write about the important features of Gond art with reference to the passage.
Question 1.
Write about the important features of Gond art with reference to the passage.
Answer:
Gond art involves natural techniques of preparing colours and the use of several mediums. They are transferred from generation to generation in a smoothly flowing process. It is a medium of j recording and preserving what is seen.
6. Why does the author think that the roots of folk art lies in women’s chores?
Question 1.
Why does the author think that the roots of folk art lies in women’s chores?
Answer:
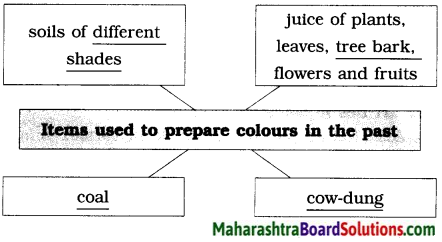
Natural colours available in various things around the house are used in Gond art. The pictures drawn are lively and attractive and depict simple things. The different colours, various textures and patterns were used year after year. The pictures were drawn on the walls of the home earlier. All this makes the author think that the roots of folk art lies in women’s chores.
7. From the passage, list the words related to:
Question 1.
From the passage, list the words related to:
(a) Geometry
(b) colours
(c) designs
Answer:
(b) colours – blue, orange, colour combinations.
(c) designs – abstract, scenes, geometric.
![]()
8. These two passages are examples of a short introduction to works of art a short review. They cover the following points:
Question 1.
These two passages are examples of a short introduction to works of art a short review. They cover the following points:
- The creator
- The theme or subject matter
- Type of ail
- Individual style tÐ1tjf
- Presentation techniques SIlO 3DF
- Its effect on viewers
- Message or interpretation
Compare the points with those you used for a book review and the review of a play. Present the comparison in the form of a chart.

Answer:
| Book Review | Review of a Play | Review of a Painting |
| 1. Title of the book | Name of the play/skit | The name of the artist |
| 2. Author / Authors | Important characters | The theme or subject matter |
| 3. Genre/category of the book | Any famous actors/actresses | Type of art |
| 4. Target group written for | Theme | Individual style |
| 5. Setting and time of the story | Climax | Presentation techniques |
| 6. Central idea of the story | Ending | Its effect on viewers |
| 7. Important characters | Use of lights and special effects if any | Medium – e.g. oil on canvas |
| 8. Style of writing | Use of background music and sound effects if any | Message / Interpretation |
| 9. Some special features | The costumes, make up, etc. of the characters | Colour composition |
| 10. Publisher, year of publication | How well the actors present the play and behave on the stage? | Texture / Strokes |
| 11. Your own opinion | Your own opinion about the play. | Your opinion |
![]()
9. Using the Information given in the passage, write a short note on the following in your mother tongue:
Question 1.
Using the Information given in the passage, write a short note on the following in your mother tongue:
(a) The paintings of Raza
(b) Gond art.
(Students may attempt this In their notebook.)
10. Gather Information on any of the following by talking to your elders, family members and from other sources in your mother tongue and write a short note on it in English.
Question 10.
Gather Information on any of the following by talking to your elders, family members and from other sources in your mother tongue and write a short note on it in English.
Answer:
- a special type of embroidery
- a special dish that is prepared on a special occasion at home.
- something that you use to decorate your home on special occasions.
11. Read the following from the Language Study pages:
Question 1.
Read the following from the Language Study pages:
- adjective clause
- adverb clause
- noun clause.
Find an example of each of the following i from the passage and underline the linking words:
Answer:
1. My work is my own inner experience and Involvement with the mysteries of nature and form which is expressed In colour, line, space and light. which Is expressed in colour, line, space and light – Adjective clause
2. They originate when the artist tries to peep into his own inner mind. when the artist tries to peep into his own inner mind – adverb clause.
3. We realize that the painting is a visible form of very deep thought that the painting is a visible form of very deep thought – noun clause.
English Kumarbharati 9th Digest Chapter 3.2 Reading Works of Art Additional Important Questions and Answers
Activities based on Contextual Grammar.
Question 1.
His pictures seem to radiate peace and life. (Rewrite, beginning with ‘Peace and life’ …)
Answer:
Peace and life seem to be radiated from his pictures.
![]()
Personal Response:
Question 1.
Do you like to draw and paint? Elaborate on your answer.
Answer:
Yes, I do. I go to a drawing class regularly and my teacher says I am quite good at it. I also participate in drawing competitions and have won many prizes.
Simple Factual Activity:
Question 1.
‘Complete the following with reference to the passage: (The answers are given directly and underlined.)
Answer:
- The ‘bindu’ or point became the core of Raza’s paintings.
- For an artist like Raza, his work, or paintings, are an effective medium of communication.
- Raza was born in a small village in Madhya pradesh.
- Raza won many national & international awards.
Complex Factual Activity:
Question 1.
Name some of the awards won by Raza.
Answer:
Raza was honoured with the Padma Shri, the Padma Bhushan and the Padma Vibhushan.
![]()
Question 2.
How did the artist himself describe his work?
Answer:
Raza described his work in these words: My work is my own inner experience and involvement with the mysteries of nature and form which is expressed in colour, line, space and light.
Activity-based on Vocabulary:
Question 1.
Spot the error in the spelling of these words with reference to the passage and correct them :
- penting
- vilage
- innar
- dicided
Answer:
- painting
- village
- inner
- decided.
![]()
Activities based on Contextual Grammar.
Question 1.
Find an example of each of the following from the passage and underline the linking words :
1. adverb clause
Answer:
1. Sometimes, an artist’s thoughts appear to be too complex or even complicated when they are expressed through words. when they are expressed through words – adverb clause.
Question 2.
Join the sentences using ‘not only … but also …’ Raza had great creativity. His paintings are very expressive.
Answer:
Raza not only had great creativity but his paintings are also very expressive.
Personal Response.
Question 1.
What is your opinion about abstract art?
Answer:
I do not understand abstract art. I prefer paintings of animals and natural scenes. However, I am sure abstract art is also very great. One has to learn to understand it.
![]()
Simple Factual Activity:
Question 1.
Write if the following sentences are True or False: (The answers are given directly and underlined.)
Answer:
- The Gond language is similar to Tamil – False
- Gond art has spread mainly in North India – False
- Gond art is a tribal art – True
- Gonds have been residing in India for thousands of years – True
Activities based on Vocabulary:
Question 1.
Spot the error in the spelling of these words with reference to the passage and correct them:
- mediam
- tribel
- mithology
- erthen
Answer:
- medium
- tribal
- mythology
- earthen.
![]()
Question 2.
Write the noun forms of the following:
- developed
- preserved
- similar
- pleasant
Answer:
- developed – development
- preserved – preservation
- similar – similarity
- pleasant – pleasantness.
Activities based on Contextual Grammar.
Question 1.
Find two examples of noun clauses from the passage and underline the linking words :
Answer:
1. We learn that they have lived in India for thousands of years.
that they have lived in India for thousands of years – noun clause
2. Art is a medium of recording and preserving what is seen.
what is seen – noun clause
![]()
Question 2.
Frame a Wh question to get the underlined part as the answer:
It has been developed and preserved by the Gond tribal people.
Answer:
By whom has it been developed and preserved? OR Who has developed and preserved it?
Personal Response:
Question 1.
‘A house decorated with beautiful pictures creates a pleasant atmosphere’. Do you agree with this? Explain your answer.
Answer:
Yes, I agree with this statement. In my house, there are many paintings of beautiful scenes. When you look at these paintings of nature, you feel soothed and happy. However, I feel this is true only with those people who love art.
Simple Factual Activity:
Question 1.
Complete the web: (The answers are underlined directly.)
Answer:
Complex Factual Activity.
Question 1.
Write about the important features of Gond art with reference to the passage.
Answer:
Natural colours available in various things around the house are used in Gond art. The different colours, various textures and patterns were used year after year. The outlines may vary a little from artist to artist, but the pictures are lively and attractive. The designs include simple textures using dots, straight lines, dotted lines, curvy shapes and circles. Special attention is given to the choice of colours.
![]()
Activities based on Vocabulary.
Question 1.
Spot the error in the spelling of the following words with reference to the passage and rewrite them correctly:
- diffarent
- stright
- amasing
- decorateing
Answer:
- different
- straight
- amazing
- decorating.
Question 2.
From the passage, list the words related to:
1. colours
2. designs
Answer:
1. colours – colours, shades.
2. designs – patterns, Gond styles.
![]()
Activities based on Contextual Grammar.
Question 1.
Find an example of each of the following from the passage and underline the linking words :
1. noun clause
2. adverb clause
Answer:
1. We realize that a picture drawn this way or the other can look equally beautiful.
that a picture drawn this way or the other can look equally beautiful. – noun clause
2. Special attention is given to the choice of various colours so that the total effect is amazing and beautiful. so that the total effect is amazing and beautiful – adverb clause
Question 2.
The designs include simple textures. (Rewrite using the noun form of the underlined word.)
Answer:
There is an inclusion of simple textures in the designs.
Simple Activities.
Question 1.
Write two compound words of your own.
Answer:
lifelike, coastline
Question 2.
Make a meaningful sentence using the phrase ‘at the same time’.
Answer:
It is not possible to be at two different places at the same time.
Question 3.
Spot the error and correct the sentence: Art are a medium of recording and preserving what is seen.
Answer:
Art is a medium of recording and preserving what is seen.
![]()
Pick out the gerund from the given sentence:
Question 1.
The roots of folk arts lie in women’s chores like cleaning.
Answer:
cleaning – gerund.
Question 2.
Identify the type of sentence: What a deep thought it conveys!
Answer:
Exclamatory sentence
Question 3.
Find out two hidden words from the word ‘complicated’.
Answer:
complicated-complicate, clamp (leapt, pleat).
Question 4.
Form a present participle in which the last i letter is doubled.
Answer:
run-running
Question 5.
Arrange the following in Alphabetical order:
colour, composition, combination, captivating.
Answer:
captivating, colour, combination, composition.
![]()
Question 6.
Make a word chain of verbs starting with : the following verb:
reward →
Answer:
reward → disappear → remain notice → empathize
Medium-Level Activities.
Question 1.
He won many awards.
(Change the voice beginning ‘Many ….’)
Answer:
Many awards were won by him.
Question 2.
He studied art at Nagpur. (Use the past | perfect continuous tense of the verb.)
Answer:
He had been studying art at Nagpur.
Question 3.
Prepare a word register for ‘geometry’ with words from the lesson.
Answer:
geometry – shapes, circles, triangles, squares, rectangles, lines, dots, straight lines, dotted lines, curvy slopes, circles, point, bindu, space.
![]()
Challenging Activities.
Question 1.
Use the following word as a verb and a noun in two separate sentences : draw
Answer:
(a) The match ended in a draw. (noun)
(b) The teacher asked the children to draw a monkey. (verb)
Question 2.
We see that the outlines may vary a little. (Pick out the modal and state the function.)
Answer:
may – possibility
Maharashtra State Board Class 9 English Solutions
9th Std English Questions And Answers: