Class 8 Hindi Chapter 5 Madhuban Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 8 Hindi Solutions Sulabhbharati Chapter 5 मधुबन Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Std 8 Hindi Chapter 5 Madhuban Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Hindi Sulabhbharti Class 8 Solutions Chapter 5 मधुबन Textbook Questions and Answers
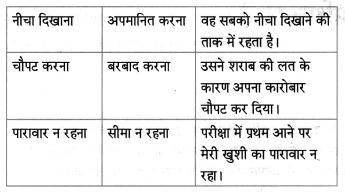
कारण लिखिए।
Question 1.
डॉक्टर साहब का मध्य प्रदेश से उत्तर प्रदेश आने के लिए प्रेरित होने का कारण:
Answer:
क्योंकि वे हिंदी से बहुत प्रेम करते थे और उन दिनों नागपुर विश्व विद्यालय में हिंदी नहीं थी।
Question 2.
रामकुमार वर्मा जी ने प्रयाग विश्व विद्यालय में प्रवेश ले लिया।
Answer:
क्योंकि वे उच्च शिक्षा पाना चाहते थे।
![]()
कृति पूर्ण कीजिए।
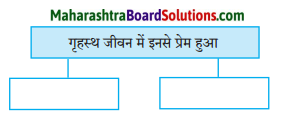
Answer:
कारण लिखिए।
Question 1.
डॉक्टर साहब का राजनीति से दूर रहने का कारण
Answer:
क्योंकि आज की राजनीति में स्थिरता का अभाव है।
Question 2.
डॉक्टर साहब साहित्य चिंतन विश्वास रखते हैं।
Answer:
क्योंकि वे साहित्यकार हैं।
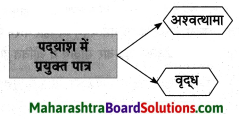
![]()
कृति पूर्ण कीजिए।

Answer:
स्वाध्याय विषयक कृतियाँ
संजाल पूर्ण कीजिए।
Answer:
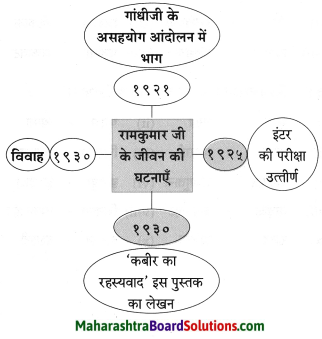
![]()
भाषाबिंदु
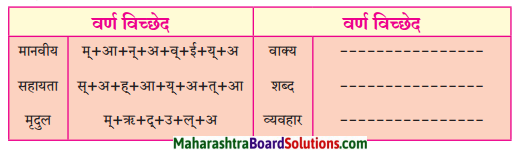
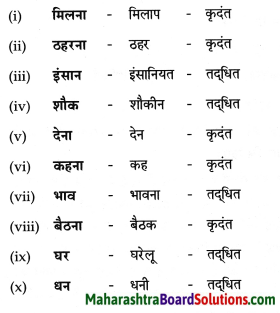
निम्न शब्दों से कृदंत/तद्धित बनाओ :
मिलना, ठहरना, इनसान, शौक, देना, कहना, भाव, बैठना, घर, धन
Answer:
उपयोजित लेखन
Question 1.
अपने विद्यालय में आयोजित विज्ञान-प्रदर्शनी के उद्घाटन समारोह का प्रमुख मुद्दों सहित वृत्तांत लेखन कीजिए।
Answer:
दिनांक २९ फरवरी, २०१८, मुंबई : इस दिन समीक्षा विद्यालय मुंबई में विज्ञान-प्रदर्शनी का आयोजन किया गया था। इस अवसर पर प्रमुख अतिथि के रूप में सुप्रसिद्ध वैज्ञानिक श्रीमान रघुनाथ माशेलकर जी उपस्थित थे। सुबह ९.०० बजे कार्यक्रम का आयोजन किया गया था। विद्यालय के विद्यार्थी प्रमुख कुमार अजय ने पुष्पगुच्छ देकर मुख्य अतिथि महोदय जी का स्वागत किया। स्कूल प्राचार्य श्रीमती विद्या जी ने विज्ञान-प्रदर्शनी के अवसर पर सभी को उद्बोधित करते हुए कहा कि विज्ञान के बिना मानव जीवन शून्य है। अतिथि महोदय जी ने भी अपने वक्तव्य में विज्ञान का महत्त्व बताया।
उन्होंने छात्रों को विज्ञान के प्रति प्रेरित एवं आकर्षित होकर वैज्ञानिक उपलब्धियाँ पाने के लिए अग्रसर होना है, इस तथ्य से अवगत कराया। विद्यालय की छात्राओं ने विज्ञान पर आधारित नाटिका प्रस्तुत कर सभी को मंत्रमुग्ध कर दिया। कक्षा आठवीं के छात्राओं ने विज्ञान प्रश्नोत्तरी व संगोष्ठी आयोजित कर सभी को विज्ञान के प्रति आकर्षित कर किया। अंत में विद्यालय के उप प्राचार्य जी ने इस अवसर पर उपस्थित सभी को हार्दिक बधाई देते हुए धन्यवाद ज्ञापन किया। इस प्रकार सुबह १२ बजे कार्यक्रम का समापन हुआ।
Question 2.
‘कहानियों एवं कविताओं द्वारा मनोरंजन तथा ज्ञान प्राप्ति होती है।’ अपना मत लिखिए।
Answer:
कहानी एवं कविता समाज का प्रतिबिंब होती है। समाज में घटित घटनाओं का प्रतिबिंब हमें कविता या कहानी के रूप में दिखाई देता है। कहानी मनोरंजन एवं ज्ञान का महत्त्वपूर्ण साधन है। कहानी के द्वारा मनोरंजन अवश्य होता है और साथ ही सीख भी मिलती है। कहानी द्वारा प्राप्त सीख का हम जीवन में पालन कर सकते हैं।
इसके द्वारा हम जीवन में आने वाली विपरीत परिस्थितियों का सामना कर सकते हैं। कविता हृदय का आविष्कार होती है। वह हमारा मनोरंजन भी करती है और हमें प्रेरणा भी देती है। कविता से प्राप्त प्रेरणा हमारे ज्ञान को समृद्ध करती है। अत: कहानियों एवं कविताओं द्वारा मनोरंजन तथा ज्ञान प्राप्ति होती हैं।
![]()
स्वयं अध्ययन
अंतरजाल से डॉ. रामकुमार वर्मा जी से संबंधित अन्य साहित्यिक जानकारियाँ प्राप्त करो।
Hindi Sulabhbharti Class 8 Solutions Chapter 5 मधुबन Additional Important Questions and Answers
निम्नलिखित गद्यांश पढ़कर दी गई सूचनाओं के अनुसार कृतियाँ कीजिए।

Answer:

कारण लिखिए।
Question 1.
लेखक पूरी रफ्तार से चला जा रहा था
Answer:
क्योंकि उसे १० बजे डॉक्टर रामकुमार वर्मा को मिलना था।
संजाल पूर्ण कीजिए।
Question 1.
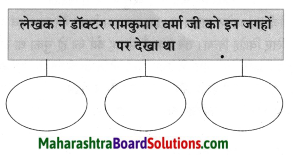
Answer:

![]()
उपर्युक्त गद्यांश से ऐसे दो प्रश्न तैयार कीजिए जिनके उत्तर निम्नलिखित शब्द हों –
Question 1.
नौकर
Answer:
लेखक को ड्राइंग रूम में किसने बिठाया?
Question 2.
मधुबन
Answer:
डॉक्टर रामकुमार वर्मा जी के निवास स्थान का नाम क्या था?
उचित जोड़ियाँ मिलाइए।
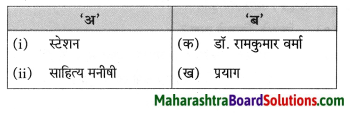
Answer:
i – ख
ii – क
मानक वर्तनी के अनुसार शब्द शुद्ध कीजिए।
- प्रेरणायें
- सम्बधित
Answer:
- प्रेरणाएँ
- संबंधित
लिंग बदलिए।
- साहब
- नौकर
Answer:
- साहिबा
- नौकरानी
![]()
विलोम शब्द लिखिए।
- सुबह x
- समय x
- नौकर x
- निकट x
Answer:
- सुबह x शाम
- समय x असमय
- नौकर x मालिक
- निकट x दूर
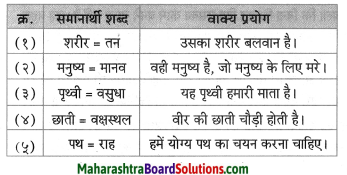
नीचे दिए हुए शब्दों के पर्यायवाची शब्द लिखिए।
- अवसर
- स्थान
Answer:
- मौका
- जगह
वचन बदलिए।
- घंटी
- दरवाजा
Answer:
- घंटियाँ
- दरवाजे
![]()
Question 1.
‘जीवन में घटित प्रसंगों से हमें महत्वपूर्ण प्रेरणाएँ मिलती है’। अपने विचार लिखिए।
Answer:
जी हाँ, मैं इस कथन से पूरी तरह सहमत हूँ। जीवन में विभिन्न प्रसंग घटित होते रहते हैं। आए दिन कुछ-न-कुछ होता ही रहता है। प्रसंगों के बिना मानव जीवन व्यर्थ ही साबित होगा। जीवन में आने वाले प्रसंग हमें भविष्य के लिए प्रेरणा देते हैं। कुछ प्रसंग ऐसे होते हैं, जो हमारे हृदय पर अमिट संस्कार एवं अपनी छाप छोड़ जाते हैं।
उन्हें भूल पाना व्यक्ति के लिए कठिन होता है। कुछ प्रसंग सुखद होते है, तो कुछ दुखद। फिर भी उनकी अपनी एक अनूठी कहानी होती है। जीवन की राह पर आगे बढ़ते हुए हम परिस्थिती के अनुरूप उन प्रसंगों को याद करते रहते हैं और उनसे नई सीख लेते रहते हैं।
निम्नलिखित गद्यांश पढ़कर दी गई सूचनाओं के अनुसार कृतियाँ कीजिए।
किसने, किससे कहा?
Question 1.
“काव्य रचना की प्रेरणा आपको कहाँ से मिली?”
Answer:
लेखक ने डॉक्टर ने रामकुमार वर्मा जी से पूछा।
Question 2.
यह मेरी कविता का मंगलाचरण था ।
Answer:
डॉक्टर रामकुमार वर्मा जी ने लेखक से कहा।
गलत वाक्य सही करके लिखिए ।
Question 1.
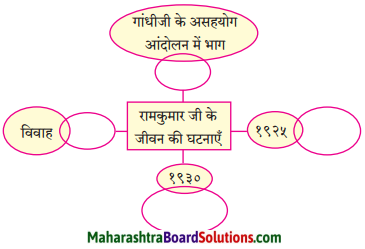
१९३१ में पंडित नेहरू जी ने असहयोग आंदोलन शुरू किया था।
Answer:
१९२१ में महात्मा गांधी जी ने असहयोग आंदोलन शुरू किया था।
Question 2.
डॉक्टर रामकुमार वर्मा जी ने अहिंसा के लिए विद्रोह किया था।
Answer:
डॉक्टर रामकुमार वर्मा जी ने सत्य एवं देश के लिए विद्रोह किया था।
![]()
उत्तर लिखिए।
Question 1.

Answer:

उचित घटनाक्रम लगाकर वाक्य फिर से लिखिए।
Question 1.
रामकुमार वर्मा राष्ट्रीय ध्वज लेकर प्रभात फेरी भी किया करते थे।
Answer:
नरसिंहपुर में मौलाना शौकत अली साहब ने भाषण किया।
Question 2.
रामकुमार वर्मा घर से निकल पड़े।
Answer:
सभी लोग सकते में आ गए।
Question 3.
सभी लोग सकते में आ गए।
Answer:
रामकुमार वर्मा घर से निकल पड़े।
Question 4.
नरसिंहपुर में मौलाना शौकत अली साहब ने भाषण किया।
Answer:
रामकुमार वर्मा राष्ट्रीय ध्वज लेकर प्रभात फेरी भी किया करते
![]()
कारण लिखिए।
Question 1.
रामकुमार वर्मा घर से निकल पड़े।
Answer:
क्योंकि उन्होंने गांधीजी का आदेश माना था।
Question 2.
सभी लोग सकते में आ गए।
Answer:
क्योंकि डिप्टी कलेक्टर का बेटा रामकुमार वर्मा स्कूल छोड़कर विद्रोह करने की बात कर रहा था।
कृति ख (३) शब्द संपदा (१)
विलोम शब्द लिखिए।
- तेज x
- गुलाम x
Answer:
- तेज x धौरे
- गुलाम x आजाद
अनेक शब्दों के लिए एक शब्द लिखिए।
- परिवार से संबंधित
- समाज से संबंधित
- राष्ट्र से संबंधित
- सहयोग न करना
Answer:
- पारिवारिक
- सामाजिक
- राष्ट्रीय
- असहयोग
![]()
निम्नलिखित शब्दों के अर्थ गद्यांश में से ढूँढकर लिखिए।
- कविता
- शहर
Answer:
- काव्य
- नगर
Question 1.
‘असहयोग’ शब्द से उपसर्ग अलग कीजिए और संबंधित उपसर्ग से अन्य दो शब्द बनाइए।
Answer:
उपसर्ग : अ अन्य दो शब्द : असाधारण, अनंत
निम्नलिखित शब्द से प्रत्यय अलग कीजिए।
- नौकरी
- राष्ट्रीय
Answer:
- प्रत्यय : ई
- प्रत्यय : ईय
![]()
स्वमत अभिव्यक्ति
Question 1.
‘देशप्रेम महान होता है।’ कथन के संदर्भ में अपने विचार लिखिए।
Answer:
हर व्यक्ति अपनी जन्मभूमि से जुड़ा हुआ होता है। उसके पास देशप्रेम की भावना होती है। देशप्रेम की भावना इंसान के हृदय को देशभक्ति से ओत-प्रोत रखती है। भारत का इतिहास देशभक्तों के त्याग व बलिदान की गाथाओं से भरा पड़ा है। जो व्यक्ति देश से प्रेम करता है; उसे समाज में सम्मान मिलता है।
जो व्यक्ति देश का नाम रोशन करने के लिए अपने-अपने क्षेत्र में उल्लेखनीय कार्य करता है; वह व्यक्ति ‘देशप्रेमी’ कहलाता है। अत: हमें भी देश की उन्नति के लिए देशप्रेम को अपनाना चाहिए। देशप्रेम मानव को पशुत्व की श्रेणी से ऊपर उठाकर देवत्व की श्रेणी में ले जाता है। अत: देशप्रेम करना व देशप्रेमी होना स्वयं में महानतापूर्ण कार्य है।
निम्नलिखित गद्यांश पढ़कर दी गई सूचनाओं के अनुसार कृतियाँ कीजिए।
कृति ग (१) आकलन कृति (१)
समझकर लिखिए।
- गद्यांश में प्रयुक्त दो प्रांतों के नाम –
- मनुष्य की प्राकृतिक प्रवृत्ति –
Answer:
- मध्य प्रदेश व उत्तर प्रदेश
- प्रेम
![]()
कारण लिखिए
Question 1.
डॉक्टर साहब का मध्य प्रदेश से उत्तर प्रदेश आने के लिए प्रेरित होने का कारण:
Answer:
क्योंकि वे हिंदी से बहुत प्रेम करते थे और उन दिनों नागपुर विश्व विद्यालय में हिंदी नहीं थी।
Question 2.
रामकुमार वर्मा जी ने प्रयाग विश्व विद्यालय में प्रवेश ले लिया।
Answer:
क्योंकि वे उच्च शिक्षा पाना चाहते थे।
कृति ग (२) आकलन कृति (१)
सही विकल्प चुनकर वाक्य फिर से लिखिए।
Question 1.
…….” मनुष्य की प्राकृतिक प्रवृत्ति है। (करूणा, अहिंसा, प्रेम)
Answer:
प्रेम मनुष्य की प्राकृतिक प्रवृत्ति है।
Question 2.
रामकुमार वर्मा जी को बचपन से ……. का शौक था। (अभिनय, चित्रकला, नाटक)
Answer:
रामकुमार वर्मा जी को बचपन से अभिनय का शौक था।
![]()
उचित जोड़ियाँ मिलाइए।
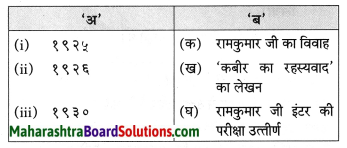
Answer:
i – ग
ii – क
iii – ख
कृति ग (३) शब्द संपदा
निम्नलिखित शब्दों में उचित प्रत्यय लगाइए।
- नागपुर
- नाटक
Answer:
- नागपुरी
- नाटकीय
लिंग बदलिए।
- कवि
- लेखक
Answer:
- कवयित्री
- लेखिका
![]()
वचन बदलिए।
- प्रवृत्ति
- श्रेणी
Answer:
- प्रवृत्तियाँ
- श्रेणियाँ
Question 1.
गद्यांश में से विलोम शब्द की जोड़ी लिखिए।
Answer:
लौकिक – परलौकिक
कृति ग (४) स्वमत अभिव्यक्ति
‘Question 1.
प्रेम मनुष्य की स्वाभाविक प्रवृत्ति है।’ कथन के संदर्भ में अपने विचार लिखिए।
Answer:
प्रेम एक एहसास है। प्रेम अनेक भावनाओं का मिश्रण है। प्रेम मनुष्य का जीवन संवारता है। जिसके हृदय में प्रेम का निवास होता है; वह व्यक्ति समाज में पूजनीय होता है। प्रेम से ही पारस्परिक संबंध अधिक मजबूत बनते हैं। प्रेम के बिना व्यक्ति का जीवन नौरस बन जाता है। व्यक्ति को जीवन जीने के लिए प्रेम की आवश्यकता होती है।
जिस प्रकार जन्म लेने के पश्चात नवजात शिशु को अपनी माँ के स्नेह की आवश्यकता होती है; उसी प्रकार प्रत्येक व्यक्ति को जिंदगी की राह पर प्रेम की जरूरत होती है। अत: प्रेम मनुष्य की प्राकृतिक शक्ति होती है।
![]()
निम्नलिखित गद्यांश पढ़कर दी गई सूचनाओं के अनुसार कृतियाँ कीजिए।
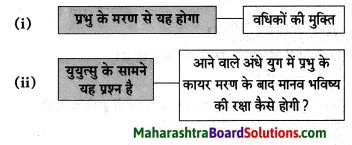
कृति घ (१) आकलन कृति (१) कारण लिखिए।
Question 1.
डॉक्टर साहब का राजनीति से दूर रहने का कारण
Answer:
क्योंकि आज की राजनीति में स्थिरता का अभाव है।
Question 2.
डॉक्टर साहब साहित्य चिंतन विश्वास रखते हैं।
Answer:
क्योंकि वे साहित्यकार हैं।
उपर्युक्त गद्यांश से ऐसे दो प्रश्न तैयार कीजिए जिनके उत्तर निम्नलिखित शब्द हों
- राजनीति
- ग्यारह
Answer:
- किसमें स्थिरता का अभाव है?
- डॉक्टर साहब को कितने बजे एक कार्य से जाना था?
Question 1.
डॉक्टर रामकुमार वर्मा जी ने अहिंसा के लिए विद्रोह किया था।
Answer:
डॉक्टर रामकुमार वर्मा जी ने सत्य एवं देश के लिए विद्रोह किया था।
![]()
समझकर लिखिए।
Question 1.
इसकी भाँति आशीर्वाद दिया डॉक्टर साहब ने लेखक को
Answer:
कुशल अभिभावक की भांति
Question 2.
डा. रामकुमार वर्मा जी को इसमें कोई रुचि नही है
Answer:
राजनीति में
कृति घ (३) शब्द संपदा
Question 1.
निम्नलिखित गद्यांश से उपसर्गयुक्त व प्रत्यययुक्त शब्द ढूँढकर लिखिए
Answer:
उपसर्गयुक्त शब्द: अभिभावक : उपसर्ग : अभि
प्रत्यययुक्त शब्द: स्थिरता : प्रत्यय : ता
![]()
विलोम शब्द लिखिए।
- रूचि x
- विश्वास x
Answer:
- रूचि x अरूचि
- विश्वास x अविश्वास
समानार्थी शब्द लिखिए।
- डॉक्टर
- अभाव
Answer:
- चिकित्सक
- कमी
![]()
वचन बदलिए।
- घड़ी
- स्थिति
Answer:
- घड़ियाँ
- स्थितियाँ
कृति ग (४) स्वमत अभिव्यक्ति
Question 1.
आज की राजनीति में स्थिरता का अभाव है।’ अपने विचार लिखिए।
Answer:
आज की राजनीति में वाकई स्थिरता का अभाव है। हमारा देश एक लोकतांत्रिक देश है। इस देश में कई राजनीति पक्ष हैं। कई पक्षों का आपस में गठबंधन है। फिर भी वह गठबंधन अस्थाई है। अवसर मिलते ही एक पक्ष तुरंत दूसरे पक्ष के साथ मेल-मिलाप कर लेता है। भले ही कोई पक्ष बहुमत प्राप्त कर ले और अपनी सरकार स्थापित कर लें।
फिर भी पाँच वर्ष के बाद वह फिर से सत्ता में आएगी, इसका आश्वासन कोई भी नहीं दे सकता है। आखिर समय के साथ लोगों के विचारों में भी परिवर्तन होता है। अत: स्पष्ट है कि आज की राजनीति में स्थिरता का सदैव अभाव है।
निम्नलिखित शब्दों के कृदंत रूप लिखिए।
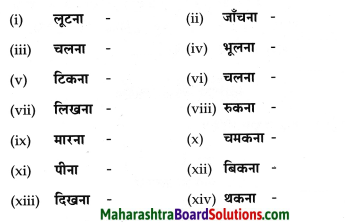
Answer:
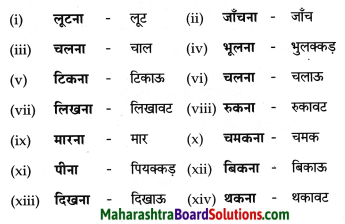
![]()
निम्नलिखित शब्दों के तद्धित रूप लिखिए।
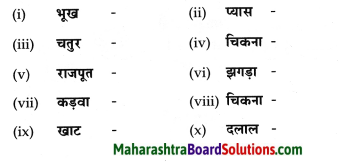
Answer:
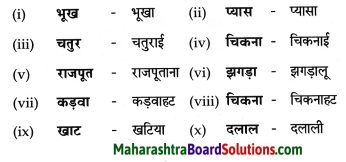
![]()
Hindi Sulabhbharti Class 8 Solutions पहली इकाई
- हे मातृभूमि! Question Answer
- वारिस कौन? Question Answer
- नाखून क्यों बढ़ते हैं? Question Answer
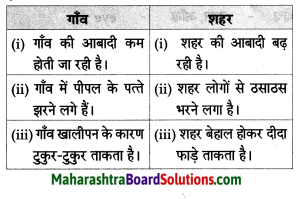
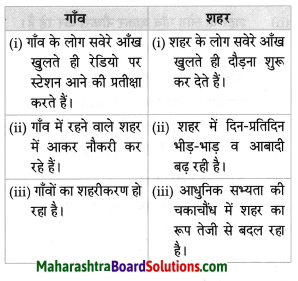
- गाँव-शहर Question Answer
- मधुबन Question Answer
- जरा प्यार से बोलना सीख लीज Question Answer
- मेरे रजा साहब Question Answer
- पूर्ण विश्राम Question Answer
- अनमोल वाणी Question Answer